9 Administering and Monitoring the Upgrade of SOA Instances
The standard upgrade process for SOA Suite and BPM 12c provides an automated solution that will upgrade your open and closed instances. The upgrade of closed instances can be monitored and configured with the administration scripts described in the following sections:
- Understanding the Instance Upgrade Process
- Understanding Instance Upgrade Background Jobs
- Understanding the Flow Trace Changes in 12c
- Using Purge Scripts Before You Upgrade
- Using the Upgrade Administration Scripts
- Configuring the Administration Scripts
- Stopping Upgrade Sessions and Jobs
- Restarting an Incomplete Upgrade
- Monitoring Upgrade Status with SQL Queries
- Monitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control
- Resolving Instance Upgrade Errors
- Restarting a Failed Upgrade
Understanding the Instance Upgrade Process
The Upgrade Assistant framework delegates the upgrade of schemas to respective component installations (MDS, ORASDPM, OPSS, SOA, etc.) During the 12c SOA upgrade, the Upgrade Assistant can also upgrade instances.
What is being upgraded?
The SOA installation will also upgrade various components as part of upgrade process, including _MDS schema and the _SOAINFRA schema. The _SOAINFRA schema contains the following schema components:
-
Schema definitions - such as tables and indexes
-
Metadata - the data required to run the SOA server and SOA composites
Note:
The BPM metadata upgrade begins once you log into Business Process Composer 12c (12.2.1) for the first time (after a successful upgrade).
For more information on using Business Process Composer, see Developing Business Processes with Oracle Business Process Composer.
-
Instance Data - the data created by the various composites. Instances can be open or closed.
How are these components upgraded?
During the 12c schema upgrade process, it is important to understand the order in which UA performs the upgrade of these components.
The upgrade occurs in four distinct stages:
-
Upgrade Assistant will upgrade 11g schema definitions.
-
Upgrade Assistant will then upgrade 11g metadata and create background control jobs to upgrade open instances.
NOTE: This process may be time consuming as the jobs will continue to run within UA until the final database job finishes upgrading the open instances. It is important not to close the Upgrade Assistant until the final job is complete.
For example, the time required to upgrade instances depends on the following:
-
Size of prefix
_SOAINFRAschema (number of open and closed instances) -
System configuration (such as the number of CPI's (cores), memory usage, disk I/O configuration).
-
Speed of the system and size of driver tables
-
-
Once all of the open instances have been upgraded, the background jobs begin upgrading the closed instances. Note that the upgrade of closed instances continues to run in the background even after you close the Upgrade Assistant. However, if the background job is stopped, and there are still closed instances to be upgraded, then you must restart them with the administration scripts.
-
Finally, once the last job finishes upgrading the open instances, the Upgrade Assistant provides the upgrade status and lists the next steps to take in the upgrade process.
You should review the Upgrade Success screen of the Upgrade Assistant to determine your next steps based on the information provided. NOTE: If you are running in -response (silent) mode, this information will be listed in the UA
stdoutfile.-
If the Upgrade Assistant reports that there are no additional instances to be upgraded, then simply close the Upgrade Assistant UI and continue with the remaining upgrade procedures (launching the Reconfiguration Wizard for example).
-
If the Upgrade Assistant reports that there was an error during the instance upgrade, then correct the error(s) and resubmit the database job to complete the upgrade. You can also use the Report Upgrade Summary administration script (Option 1) to check the
UPGRADE ERROR COUNTsection of the report. -
You will be notified that the upgrade of the closed instances will continue in the background after you close the Upgrade Assistant. Do not close the Upgrade Assistant until UA reports it is finished and you see the following:
Oracle SOA 1. The Upgrade Assistant has successfully upgraded all open instances. You can now close the Upgrade Assistant. 2. The automated upgrade of closed instances will continue in the background after the Upgrade Assistant is exited and until the SOA server is started,at which point the upgrade will stop. You can schedule the upgrade of any remaining closed instances for a time when the SOA server is less busy. Close the Upgrade Assistant and use the instance data administration scripts to administer and monitor the overall progress of this automated upgrade. For more information see "Administering and Monitoring the Upgrade of SOA Instance Data" in Upgrading SOA Suite and Business Process Management.
-
Note:
The upgrade of closed instances will continue until all instances have been upgraded or the middle tier is started (such as the SOA managed server, for example.)
If the middle tier is started before all closed instances are upgraded, then the upgrade job will stop. You will have to use the administration scripts to manually restart the upgrade.
Understanding Instance Upgrade Background Jobs
The background jobs are created by Upgrade Assistant during the _SOAINFRA schema upgrade. These jobs run in the background and automate the upgrade of the open and closed instance data. It is important to understand how these jobs operate within the upgrade process and how you can manage them. The list below describes some important information about these jobs:
-
Jobs are created by Upgrade Assistant (UA), but they are managed through administration scripts. You can use the administration scripts to configure how and when these jobs will run, for example.
-
Jobs are automatically started after the schema upgrade process.
-
Jobs that are initiated through UA are automatically stopped when one of the following occurs:
-
The job is complete and all closed instances are migrated to 12c
-
A middle tier application is started (a managed server, for example)
-
The Stop Jobs script (Option 8) is started
-
-
If closed instances have not yet been upgraded, then the background jobs will continue to run in the background - even after the Upgrade Assistant has been closed.
-
If the job is stopped, and there are still instances to be upgraded, you can enable and schedule the jobs to run at another time using the administration scripts.
For more information on configuring the background jobs, see: Enabling and Disabling Background Control Job (Option 6), Stopping Upgrade Sessions and Jobs, and Restarting an Incomplete Upgrade.
Understanding the Flow Trace Changes in 12c
In 12c SOA, instances are controlled using flowIDs instead of ECIDs. When the Upgrade Assistant upgrades instances from 11g SOA to 12c SOA, there are few differences between the 11g upgraded flow instances and the newly created 12c instances. These differences will not impact the functionality of the flow trace, but it is important to note the differences.
The flow trace XML examples below show the following differences:
-
The attributes ActionType and ActionName are new in 12c and are not available in 11g upgraded instances.
-
Date and lastUpdatedDate are the same for 11g Upgraded instances.
-
ElapsedTime for Entry Instance Id is 0 for 11g Upgraded instances.
Flow trace XML for 11g to 12c upgraded instances:
================================ <audit_trail ecid="9dd01e5816e19dbc:-33f3b618:140c1ee8b0f:-8000-000000000000317e" flowId="96102" flowCorrelationId="null" activeInstances="0" date="2013-09-02 00:09:52.133 PDT" lastUpdatedDate="2013-09-02 00:09:52.156 PDT" elapsedTime="23"> <entry instanceId="10093" parentInstanceId="-110092" date="2013-09-02 00:09:52.156 PDT" lastUpdatedDate="2013-09-02 00:09:52.156 PDT" elapsedTime="0" timestamp="1378105792156" state="18" subType="bpel" type="component"> ... </entry> </audit_trail>
Flow trace XML in newly created 12c instances:
====================================
<audit_trail ecid="dfcc3828-d7de-4af8-b94e-474ff830c961-0000069a" flowId="6"
flowCorrelationId="0000K7z3tBPFCCGpIwt1if1IRXgh00000M" activeInstances="0"
date="2013-10-28 05:35:12.738 PDT" lastUpdatedDate="2013-10-28 05:35:12.825
PDT" elapsedTime="87">
<entry instanceId="13" parentInstanceId="12" date="2013-10-28
05:35:12.749 PDT" lastUpdatedDate="2013-10-28 05:35:12.786 PDT"
elapsedTime="37" timestamp="1382963712749" state="18" actionType="operation"
actionName="process" subType="bpel" type="component">
...
</entry>
</audit_trail>
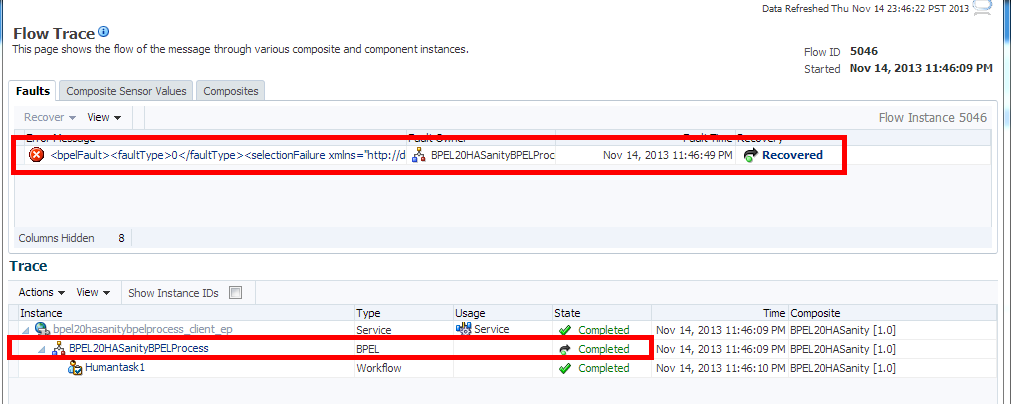
In addition, the Recovery status of the new instances created in 12c for a caught fault in BPEL shows the fault as recovered as shown in Figure 9-1:
Nonrecoverable as shown in Figure 9-2:
Note:
The information passed from the 11g faults is not enough to correctly identify the state of a fault. To handle this, all the actual faults retrieved from 11g are initially identified as nonrecoverable. Dummy faults are then created to set the proper state (BPEL_invoke_recovery, Bpel_activity_recovery). Therefore, if you see a warning or notice that the 11g faults are nonrecoverable, you can ignore the warning.Figure 9-2 Upgraded 11g Instance Flow Trace
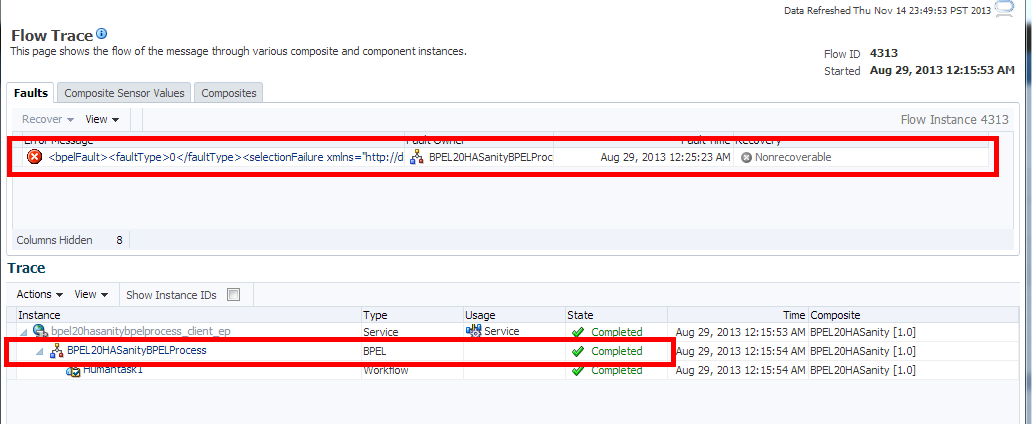
Description of "Figure 9-2 Upgraded 11g Instance Flow Trace"
Using Purge Scripts Before You Upgrade
Use the purge scripts before you start the instance upgrade to purge the closed 11g instances that you do not need in the upgraded 12c environment. The 12c purge scripts will include non-migrated closed instances. This means that post upgrade, if you schedule to run 12c Purge scripts, the scripts will purge non-migrated closed instances. Using the purge scripts to remove closed instances can help improve the overall performance of the upgrade.
Note:
When upgrading open instances only, you may see an aborted status flow. A flow will be in an aborted state if the child flow was aborted in 11g.
All composite instance associated with this ECID will remain in terminated state.
For more information on using Auto Purge or purge scripts, see Managing Database Growth.
Caution:
Do not schedule purge jobs to run while the Upgrade Assistant background jobs are running. Running the scripts while Upgrade Assistant is running can cause the purge or upgrade to fail.
If you do configure purge scripts to run while Upgrade Assistant is running, you will see: "ORA-20099: ERROR The 11g to 12c Upgrade is in progress".
If you run UA while purge scripts are running, you will see: "SQLException: ORA-00054: resource busy and acquire with NOWAIT specified or timeout expired".
Using the Upgrade Administration Scripts
The upgrade administration scripts are included as part of the Upgrade Assistant functions provided with the SOA Suite installation. These PL/SQL scripts provide additional administrative control over the upgrade of instances. Once upgraded, the instances can be viewed from Oracle Enterprise Manager Console. If more detailed information is needed about the upgrade progress, then use the administration scripts for additional reporting and configuration options.
Note:
The administration upgrade scripts provide detailed information about the upgrade. These scripts provide additional configuration, administration, and monitoring functionality for your instance upgrade. You can configure these scripts to run (or not run) based on your own requirements.
The Fusion Middleware Control Console can also be used to administer and monitor the upgrade process, but you will have more administration options using the administration scripts.
Oracle recommends that you run the Report Upgrade Summary (Option 1) script after using the Upgrade Assistant to monitor Upgrade of closed instances.
For more information about using the Fusion Middleware Control Console to monitor the progress of the upgrade, seeMonitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control.
Accessing the Upgrade Scripts Menu
There are several scripts that can be used to configure, administer and monitor your instance upgrade. These scripts can be accessed using the soa_upgrade_menu PL/SQL script.
To access the upgrade scripts menu:
-
Locate the /admin directory of the SOA home.
For example:
cd <ORACLE_HOME>/soa/common/sql/soainfra/sql/oracle/upgrade/admin
-
Use SQL* Plus to access the _SOAINFRA schema using the schema owner name and password.
For example:
sqlplus dev_soainfra/passwordwhere
devis the schema owner prefix you used when the SOAINFRA schema was created, andpasswordis your schema password.Note:
If you attempt to access the administration scripts using a user other than <prefix>_
SOAINFRA, you will encounter the following error message:ERROR at line 24: ORA-06550: line 24, column 3: PLS-00201: identifier 'CONTROL_MIGRATION.UPGRADE_STATUS_INFO' must be declared
-
Run the soa_upgrade_menu.sql script to see the upgrade administration options menu.
SQL> @soa_upgrade_menu.sql ================================================== 1: Report upgrade summary. 2: Report upgrade database sessions (Running sessions). 3: Report upgrade database background jobs (Completed jobs). 4: Report background control job parameters. 5: Change background control job execution schedule. 6: Enable/Disable background control job. . Advanced Options: . 7: Change background control job parameters. 8: Stop upgrade database background sessions and jobs. 9: Reset errored 11g instances. 10: Report Current job run log (Oracle Internal Use). . 11: EXIT. . . (NOTE: for error SP2-0309, please restart menu) . Enter option : ***********************************************************************************************
Table 9-1 describes the functionality of each script.
Parent topic: Using the Upgrade Administration Scripts
Running the Administration Scripts
The Administration Scripts Main Menu displays all of the options you have to monitor and administer the background control jobs and other administration tasks such as troubleshooting.
Caution:
The Advanced Options should only be used to troubleshoot the upgrade or to make changes to the upgrade process based on specific upgrade requirements. In most cases these scripts should only be executed by a designated system administrator or Oracle Support.
To run one of the administration scripts, enter an option number when prompted. Table 9-1 describes the functionality of each script.
Table 9-1 Menu Options for Upgrade Administration Scripts
| Option Number | Scripts Name | Use this option to... | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Report Upgrade Summary |
View the overall status of the upgrade. |
The report is divided into sub-sections and provides an overview of the overall upgrade and the current run. The In addition, it describes the following:
The report data is shown below: ============================================= Report Upgrade Summary (Please wait for report to generate) ============================================= . . METADATA : COMPLETE . OPEN FLOWS : COMPLETE . ALL FLOWS : COMPLETE . . ------------------------------------------ . Date of last upgraded and closed 11g Flows . ------------------------------------------ . DATE : NOT AVAILABLE OR ALL DATA UPGRADED . . NOTE: Closed 11g flows prior to this date . may not be visible on the EM console . until they are upgraded. . . --------------------- . UPGRADE ERROR COUNT . --------------------- . COUNT : 0 PL/SQL procedure successfully completed. Enter to continue.. . --------------------------------------------- Upgrade Start Date and Initial Instance Count --------------------------------------------- . Upgrade Start Date : 06/MAY/2014:04/50 . Initial Instance Count : 1881 . Outstanding Instances Count : 0 . ------------------------------------ CURRENT RUN STATISTICS (run#: 1) ------------------------------------ . Note: 1/ Statistics maybe from previous run . until new statistics are generated. . 2/ Statistics can take 10mins to refresh. . . STARTED: 06/MAY/2014:04/50 . ENDED: 06/MAY/2014:04/52 . START COUNT: 1881 . PROCESSED COUNT: 1881 . REMAINING COUNT: 0 . ========= End of Report ===================== Upgrade Counter (Oracle Internal Use): < 300 |
|
2 |
Report upgrade database sessions (Running sessions). |
Determine which jobs are still running. Do NOT use this information to manually kill the jobs. |
The option will return running sessions data under 'Module', 'Inst', 'Sid' and 'Serial' columns. For example: ====================================================== Report Upgrade Database Sessions (Running) ====================================================== . Module Inst Sid Serial --- -- -- ---- SOAUPGRADECONTROLMAIN 1 122 16535 SOAUPGRADEDATA_0 1 228 14557 SOAUPGRADEDATA_1 1 64 46683 SOAUPGRADEDATA_2 1 180 621 SOAUPGRADEDATA_3 1 130 61577 SOAUPGRADESUBMITJOBS 1 172 66 Monitor job completion through the database scheduler job log. CAUTION: Do not use this information to stop the sessions. Use the administration script as described in Stopping Upgrade Sessions and Jobs. |
|
3 |
Report upgrade database background jobs (Completed jobs). |
Determine which jobs have completed the upgrade. |
The database sessions that perform the instance upgrades are executed as database jobs. Once the jobs are complete, the status can be viewed with this option. The user is not expected to understand what each job does, only to ensure that the status shows success without any errors. The report displays the control job parameter values, the submitted upgrade job, current status of the job (submitted, waiting, running) and the job thread number (if applicable). For example: ====================================================== Report Upgrade Database Background Jobs (Completed) ====================================================== . . State of last 15 completed Jobs in descending order . Log_date Job_name Status ERROR ---- ---- --- ---- 21-FEB-2014 03:07:36 UPGRADE_SOA_METADATA_JOB SUCCEEDED 0 |
|
4 |
Report background control job parameters. |
View the current background control job parameters. |
This option will report the parameters that are passed to the control job which coordinates the instance upgrade. ====================================================== Report Backgrond Control Job Parameters ------------------------------------------------------ BATCH_SIZE : 10000 MAX_COUNT : 100000 JOB_MAX_RUNTIME : 240 DOP : 4 METADATA_JOB_COMPLETE : TRUE OPEN_ECIDS_COMPLETE : FALSE DATA_JOB_COMPLETE : FALSE CTL_MAX_RUNTIME : 1 FIRST_TIME : FALSE FIRST_CTL_MAX_RUNTIME : 0 FIRST_JOB_MAX_RUNTIME : 0 SQL_TRACE : FALSE METRICS : TRUE ASYNC : TRUE ----------------------- ENABLE : FALSE REPEAT INTERVAL : freq=daily; byhour=3; byminute=0; bysecond=0 |
|
5 |
Change background control job execution schedule. |
Change the repeat interval time and duration of the background control job. |
By default, the background control job interval will start at 3AM (local time) and run for 4 hours (240 minutes) every day until all of the closed instances have been upgraded (set in terms freq=daily; byhour=3; byminute=0; bysecond=0). If you want this job to run at a different time, use this option to change the repeat interval. Change Background Control Job Execution Schedule - Repeat Interval ================================================================== The repeat interval determines when the control procedure is executed by the database scheduler. Examples of repeat intervals can be found in the Oracle Database Administors Guide. Enter REPEAT INTERVAL: For more information, see Changing Background Control Job Execution Schedule (Option 5) NOTE: To change the duration of the run (default is 240 minutes), modify the |
|
6 |
Enable/Disable background control job. |
Enable or disable the background job. |
By default, the Enable/Disable background control job is disabled ( The setting will appear in the Summary Report as Enter N (No) to retain the current setting. ENABLE/DISABLE CONTROL JOB SCHEDULE =================================== Disabling the Control Schedule will stop the Control job from executing at the specified Repeat Interval. Change ENABLE Y/N: For more information, see Enabling and Disabling Background Control Job (Option 6) |
|
7 |
Change background control job parameters. |
Change the BATCH_SIZE, MAX_COUNT, JOB_MAX _RUNTIME or DOP (degree of parallel (options 1-4). Do not change the Advanced Options (options 5-14) unless instructed to do so by Oracle Support to troubleshoot an upgrade. |
For most upgrades, the default values for the background control job parameters are sufficient. However, if you need to make changes, review the parameter descriptions in Setting Control Job Parameters (Option 7). 1: Set BATCH_SIZE 2: Set MAX_COUNT 3: Set JOB_MAX_RUNTIME 4: Set DOP . Advanced Options: . (Options below for Oracle Internal Use) . (Please contact Oracle Support) . 5: Set METADATA_JOB_COMPLETE 6: Set DATA_JOB_COMPLETE 7: Set OPEN_ECIDS_COMPLETE 8: Set CTL_MAX_RUNTIME 9: Set FIRST_TIME 10: Set FIRST_CTL_MAX_RUNTIME 11: Set FIRST_JOB_MAX_RUNTIME 12: Set SQL_TRACE 13: Set METRICS 14: Set ASYNC . 15: MAIN MENU . Enter option : |
|
8 |
Stop upgrade database background sessions and jobs. |
Stop the current background database sessions or jobs. |
Use this option to gracefully stop the current background jobs or sessions as described in Stopping Upgrade Sessions and Jobs Stop Upgrade Database Background Sessions/Jobs ============================================== All upgrade sessions and jobs should stop but this may require 5 minutes to take affect. There will be a one minute wait before this procedure returns. Are you sure Y/N: Y Enter for MENU |
|
9 Reset errored 11g instances. |
Once an upgrade is run, check the upgrade_error_log and correct any reported errors. Then, use this option to resubmit those instances to process again in the next upgrade job. |
This option will enable the instances with errors to be processed again in the next upgrade job. Use this option only after you have corrected the errors reported in the upgrade_error_log. Reset errored 11g instances ======================= The 11g instances which have encountered an error will have their flow_id set to -1. This reset updates the flow_id back to null so they can be processed in the next exection of the background job. . The rows in the upgrade_error_log table will have their type column set to zero. The rows in this table are not removed so that history is not lost. . NOTE: Ensure to schedule and enable the background job. Are you sure Y/N: |
|
|
10 Report Current job run log (Oracle Internal Use). |
Generate a report for Oracle Support that shows the parameters used in the current run. |
The output of this report can be sent to Oracle Support when troubleshooting an upgrade. You can also use this report to verify that any changes made to the Control Job Parameters are correct. Example: ====================================================== Report Current RUN log (Oracle Internal Use) ====================================================== . Module Type Comment --- --- ----- CONTROL PARM batch_size => 10000 CONTROL PARM max_count => 100000 CONTROL PARM use_ctl_max_runtime => 0 CONTROL PARM use_job_max_runtime => 0 CONTROL PARM DOP => 4 CONTROL PARM metadata_job_complete => FALSE CONTROL PARM data_job_complete => FALSE CONTROL PARM open_ecids_complete => FALSE CONTROL PARM first_time => TRUE CONTROL PARM sql_trace => FALSE CONTROL PARM metrics => TRUE CONTROL PARM async => TRUE CONTROL PARM ctl_stoptime_d => NULL CONTROL PARM job_stoptime_d => NULL CONTROL INFO UPGRADE jobs submitted ASYNCRONOUS METADATA INFO UPGRADE submitting: UPGRADE_SOA_METADATA_JOB CONTROL INFO CONTROL procedure waiting for (metadata and/or open ecids) METADATA INFO UPGRADE UPGRADE_SOA_JOB will wait for UPGRADE_SOA_METADATA_J DATA INFO UPGRADE submitting: UPGRADE_SOA_JOB0 DATA INFO UPGRADE submitting: UPGRADE_SOA_JOB1 DATA INFO UPGRADE submitting: UPGRADE_SOA_JOB2 DATA INFO UPGRADE submitting: UPGRADE_SOA_JOB3 DATA INFO UPGRADE will wait if UPGRADE_SOA_JOB running |
|
|
11 Exit |
|
Close the Script Administration Menu. |
This option will close the menu. |
Parent topic: Using the Upgrade Administration Scripts
Configuring the Administration Scripts
This section describes the steps needed to configure the upgrade administration scripts.
Changing Background Control Job Execution Schedule (Option 5)
Use Option 5 to change the execution schedule of the Background Control Job.
In the example below, the start time of the job was changed from 3AM to 4AM (local time).
Change Background Control Job Execution Schedule - Repeat Interval ================================================================== The repeat interval determines when the control procedure is executed by the database scheduler. Examples of repeat intervals can be found in the Oracle Database Administors Guide. Enter REPEAT INTERVAL: freq=daily; byhour=4; BEFORE Change : freq=daily; byhour=3;byminute=0; bysecond=0 AFTER Change : freq=daily; byhour=4
Parent topic: Configuring the Administration Scripts
Enabling and Disabling Background Control Job (Option 6)
Use the Enable/Disable Background Control Job script (Option 6) to enable the start of a background control job OR to prevent the start of a scheduled control job. T
Note:
The background control job is disabled by default (ENABLE: FALSE). If you manually enable the job (ENABLE: TRUE), then you must also manually disable it.
ENABLE/DISABLE CONTROL JOB SCHEDULE =================================== Disabling the Control Schedule will stop the Control job from executing at the specified Repeat Interval. Change ENABLE Y/N:
Parent topic: Configuring the Administration Scripts
Setting Control Job Parameters (Option 7)
The Set Control Job Parameters script (option 7) can be used to configure the parameters described in Table 9-2.
Table 9-2 Background Control Job Parameters
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
BATCH_SIZE |
10000 |
Determines the number of updates (inserts, updates and deletes) that are sent to the database at one time for execution. |
|
MAX_COUNT |
100000 |
Determines the number of instances (ECIDs) that are fetched to upgrade before another MAX_COUNT worth of instances is fetched. |
|
JOB_MAX_RUNTIME |
240 minutes (4 hours) |
This is the maximum number of minutes that a background control job will run. |
|
DOP |
4 |
The number of parallel execution servers associated with a single operation is known as the degree of parallelism (DOP). Parallel execution is designed to effectively use multiple CPUs. CAUTION: Changing the degree of parallel is an advanced option. Refer to your database administration documentation for more information on setting the appropriate degree of parallelism for your deployment. |
|
SQL_TRACE |
FALSE |
NOTE: Setting $ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL> grant alter session to <soainfra>; |
To Change the Job Control Parameters:
Parent topic: Configuring the Administration Scripts
Resetting Errored 11g instances (Option 9)
If the upgrade encountered errors during the run, resolve the issue(s) and then resubmit the errored instances by resetting the error flow_id from (-1) to null. The instances will be processed in the next scheduled background control job run.
For more information, see Resolving Instance Upgrade Errors.
Reset errored 11g instances ======================= The 11g instances which have encountered an error will have their flow_id set to -1. This reset updates the flow_id back to null so they can be processed in the next exection of the background job. . The rows in the upgrade_error_log table will have their type column set to zero. The rows in this table are not removed so that history is not lost. . NOTE: Ensure to schedule and enable the background job. Are you sure Y/N:
Parent topic: Configuring the Administration Scripts
Stopping Upgrade Sessions and Jobs
You can use the administration scripts to stop a running session or job.
Note:
If you stop a running upgrade job before it has completed, you will not be able to query the remaining data or view it using Enterprise Manager Console.
The background jobs upgrade the newest instances first, so you can see how far the upgrade has progressed by looking at the timestamp of the last upgraded instance in the Upgrade Summary Report (Option 1) under the Maximum Upgrade Date for Closed 11g instances section.
There are two ways to stop the upgrade of read-only instances:
-
Once the background database control job has started, use the Stop Upgrade Database Background Sessions and Job script (Option 8) to stop ALL of the upgrade sessions and jobs that are currently running. It can take a few minutes before all of the jobs have stopped.
Stop Upgrade Database Background Sessions/Jobs ============================================== All upgrade sessions and jobs should stop but this may require 5 minutes to take affect. There will be a one minute wait before this procedure returns. Are you sure Y/N: Y Enter for MENU
Use the Report Upgrade Database Sessions (Option 2) to verify that there are no jobs running.You can restart the upgrade job, if needed, by scheduling a job to run at a user-defined time. This is the preferred method.
-
Start a middle tier application, such as the SOA Managed Server.
Once a mid-tier application such as a managed server is started, the upgrade of closed instances is stopped automatically. You can use the administration scripts to schedule the upgrade job to run at another time.
Restarting an Incomplete Upgrade
If the instance upgrade is stopped, it must be manually restarted using the administrations scripts as described below.
Monitoring Upgrade Status with SQL Queries
This section provides SQL queries that can be used to monitor and validate upgrade in addition to the Administration Scripts.
| To determine if... | Use this query | More Information |
|---|---|---|
|
A flow instance has encountered an error during upgrade (flowId is set to -1 or -2). |
Select count (*) from composite_instance where flow_id=-1; select count(*) from composite_instance where flow_id = -1; select count(*) from cube_instance where flow_id = -2 select count(*) from dlv_message where flow_id = -2; select count(*) from mediator_instance where flow_id = -2; |
Once Upgrade Assistant completes upgrading Open instances, Oracle recommends that you check for rows in UPGRADE_ERROR_LOG table within SOAINFRA schema. This table stores errored data that was not upgraded to 12c. The column ‘type' determines the type of error encountered. The different type of error that can be reported in the UPGRDAE_ERROR_LOG table:
It is important to ensure that no errored records exist in these tables. For more information, see Resetting Errored 11g instances (Option 9) |
|
All Open instances are upgraded. |
select count (*) from cube_instance where state < 5 and flow_id = -1; select count (*) from dlv_message where state in (0,1,4) and flow_id = -1 select count (*) from mediator_instance where component_state between 4 and 15 and flow_id is null; |
Run these queries post-upgrade to verify and they should return zero rows if all Open have been migrated. |
Monitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control
In addition to the administration scripts, you can also use the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control Console to view the general status of the upgrade. The administration scripts will provide you with more administrative control of the upgrade jobs, but you can monitor the following with the Fusion Middleware Control Console:
Note:
If you need to perform advanced administration tasks for the upgrade, such as modifying the schedule or interval time of the upgrade, for example, you must use the administration scripts as described in Using the Upgrade Administration Scripts.
Verifying Data Migration is Complete
In the target navigation pane of Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, expand SOA, click soa-infra (soa_server1) and verify that the Data Migration Completed link is displayed under SOA Runtime Health section as shown below:
Figure 9-3 SOA Runtime Health: Data Migration Completed
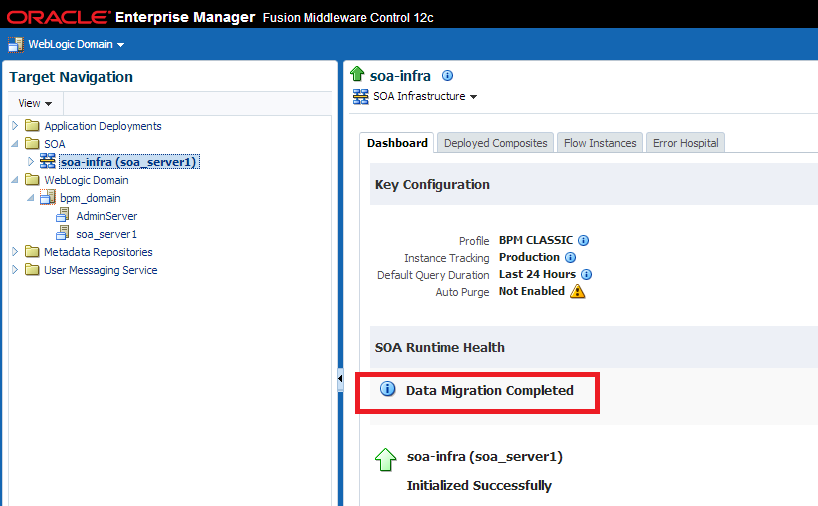
Description of "Figure 9-3 SOA Runtime Health: Data Migration Completed"
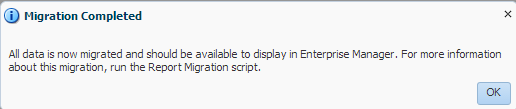
Click Data Migration Complete and verify that the following message is displayed:
Click OK to close the Migration Completed dialog box. You will see the SOA Runtime Health migration status message (Figure 9-5).
Figure 9-5 SOA Runtime Health: Migration Status Message

Description of "Figure 9-5 SOA Runtime Health: Migration Status Message"
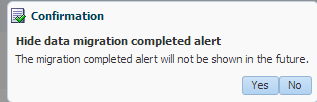
Click Close this message. The following confirmation dialog appears:
Click Yes to hide the data migration completed alert. The Close the message button will disappear from the SOA Runtime Health section.
Click No to retain the alert in the SOA Runtime Health section.
Parent topic: Monitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control
Managing an Incomplete (Stopped) Upgrade
You can use Fusion Middleware Control to manage an incomplete upgrade, which can occur in the following situations:
-
None of the open or closed instances are upgraded.
-
Some of the open instances have upgraded. For example, if you stop the background control job manually using administration script option 8 (Stop upgrade database background sessions and jobs) during the upgrade of open instances.
-
Only open instances have been upgraded.
-
Some or none of the closed instances have been upgraded.
Note:
If you start the SOA managed servers before the instance upgrade is complete, Fusion Middleware Control will show the upgrade status as Data Migration Not Complete and you will have to manually restart the upgrade as described in Restarting an Incomplete Upgrade.
If the upgrade is not yet complete, Fusion Middleware Control can provide the maximum creation date for all 11g instances that have not yet been upgraded. This is important because the maximum creation date can also help you determine why some instances might not be visible in the 12c Enterprise Manager Console. For example, if you notice that some older 11g closed instances are not be visible in the Fusion Middleware Control console, you can check the maximum creation date for all non-upgraded instances to help you determine if its because the upgrade has not reached those instances yet.
To verify the status of an incomplete (stopped) upgrade using Middleware Control do the following:
In the target navigation pane of Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, expand SOA, click soa-infra (soa_server1). In the SOA Runtime Health section of the screen you will see the current status of the upgrade. For an incomplete upgrade, the status will be Data Migration Not Complete. You can refresh this screen every 5 minutes.
Figure 9-7 SOA Runtime Health: Data Migration Not Complete

Description of "Figure 9-7 SOA Runtime Health: Data Migration Not Complete"
Click Data Migration Not Complete and the following message is displayed:
Figure 9-8 SOA Runtime Health: Migration Not Complete Status Message
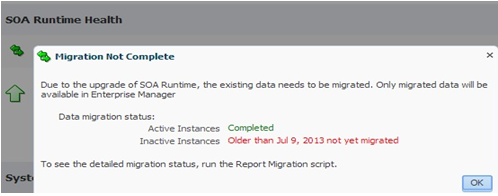
Description of "Figure 9-8 SOA Runtime Health: Migration Not Complete Status Message"
Data Migration Status:
-
Active Instances: Shows the status of upgraded open instances. In the example above, the open instances have already been upgraded (status will be Completed).
-
Inactive Instances: Shows the status of upgraded closed instances. In the example above, closed instances older than July 9, 2013 have not yet been upgraded. The upgrade is performed newest to oldest. Any instances that have not yet been upgraded will not appear in any Fusion Middleware Control reports or views. You can refresh the report every 5 minutes.
Note:
For a detailed report of the running upgrade, run the Report Upgrade Summary script (Option 1) as described in Running the Administration Scripts.
Once all the closed instances are upgraded, the link will change to Data Migration Completed as shown in Figure 9-4.
Parent topic: Monitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control
Viewing Instances that Faulted During the Upgrade
The 11g instances that incur a fault and fail during the upgrade can be seen only at the composite level post-upgrade. These instances will not be displayed at the partition level.
To view these instances, navigate to the Flow Instances tab of the deployed composite as shown in Figure 9-9:
Figure 9-9 Using the composite level to view instances that faulted during upgrade
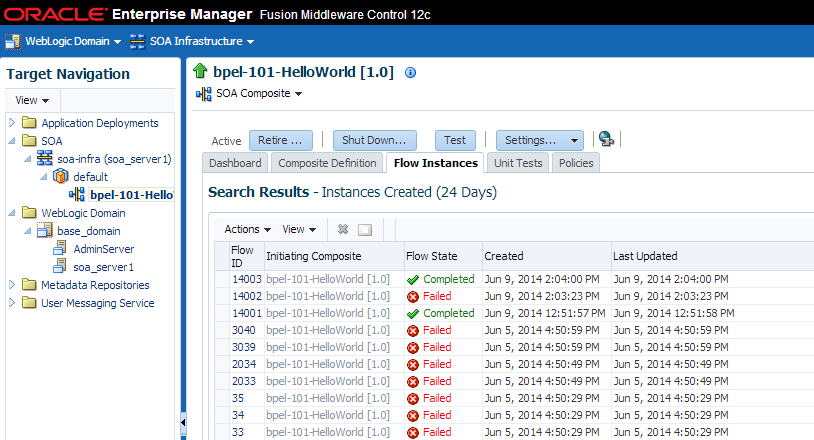
Description of "Figure 9-9 Using the composite level to view instances that faulted during upgrade"
NOTE: Use Search Options to specify a specific instance creation time or date range.
Parent topic: Monitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control
Viewing Instances Created Prior to Composite Redeployment
If a composite is redeployed with the same pre-upgrade revision, then you must navigate to the partition level (instead of composite level) to view these instances as shown in Figure 9-10.
Instances created after the upgrade, however, can be viewed in the 12c composite level.
Figure 9-10 Using the partition level to see instances created prior to upgrade
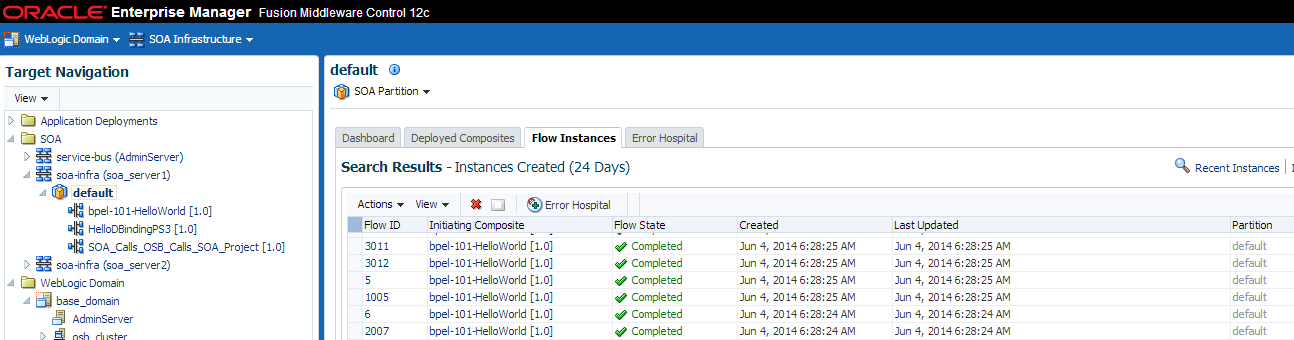
Description of "Figure 9-10 Using the partition level to see instances created prior to upgrade"
Parent topic: Monitoring Upgrade Status with Fusion Middleware Control
Resolving Instance Upgrade Errors
If the upgrade fails or the UPGRADE ERROR COUNT section of the Report Upgrade Summary report (Option 1) shows that there were errors in the current run, you must resolve the errors before resubmitting the instances to upgrade.
The upgrade_error_log can be used to diagnose the error situation and may provide guidance on how to resolve the issue. For more information on resolving common upgrade errors, see Recovering From a Failed Upgrade.
The table below describes each of the errors and possible resolutions:
| Error Type | Description | Error Message | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0 |
These errors were reported in the previous upgrade run. Type will be set to 0 after resetting the errored instances as described in Resetting Errored 11g instances (Option 9)). |
Error message giving details about error occurred based on previous error type. |
Correct the errors from the previous run and reset using Administrative Script. |
|
1 |
Error occurred during the upgrade of instances. |
The error message will have actual error thrown from the Upgrade script. It will also show a stack trace which will point out the line in the Upgrade PL/SQL script where the error has occurred. |
Debugging the root cause can be done by looking at the actual error along with the trace to get the location of the error. ECID populated in the info column will be helpful in getting the data for failed instance. |
|
2 |
Error occurred during upgrade of EDN error event store or Adapter rejected messages. |
The error message will contain the string It will contain the reason for failure along with the id of the message which failed. |
Debugging can be done by analyzing the actual reason of the error. To get the details of the adapter/edn message which has failed the id logged as part of ERROR_MSG can be used. |
|
9 |
Error occurred during the upgrade of metadata. |
It will have details of the It will have the actual error thrown from Upgrade script also with a stack trace which will point out the line in the Upgrade PL/SQL script where the error has occurred. |
Debugging can be done by looking at the actual error along with the trace to get the location of the error. Info column will give the whole |
|
12 |
Generic error occurred during the data upgrade process and not pertaining to any single instance. |
Info will only contain the string It will have the actual error thrown from Upgrade script also with a stack trace which will point out the line in the Upgrade PL/SQL script where the error has occurred. |
This error type will be reported during upgrade run when the data upgrade as a whole fails and not necessarily pertaining to any particular instance. An example of this type of error may be the TEMP table space issue. |
Restarting a Failed Upgrade
Once the errors have been resolved, use the following steps to restart the upgrade:
- Fix the error condition(s) displayed in the
upgrade_error_log. - Remove the error flags from the
upgrade_error_logas described in Resetting Errored 11g instances (Option 9). This will allow the errored instances to be resubmitted in a subsequent run. - Enable the background control job as described in Enabling and Disabling Background Control Job (Option 6). You will have to trigger another upgrade run.
- If necessary, change the repeat interval time and duration of the background control job as described in Changing Background Control Job Execution Schedule (Option 5).
- Monitor the upgrade status using the Report Summary Upgrade script (Option 1). The
UPGRADE ERROR COUNTsection of the report should show 0 errors. If errors persist, resolve the issue and repeat these steps.