20 Configuring Oracle Managed File Transfer in an Enterprise Deployment
The procedures explained in this chapter guide you through the process of adding Oracle Managed File Transfer to your enterprise deployment.
- About Oracle Managed File Transfer
Oracle Managed File Transfer (MFT) provides a standards-based file gateway. It features design, deployment, and monitoring of file transfers by using a web-based design-time console that includes transfer prioritization, file encryption, scheduling, and embedded FTP and sFTP servers. - Variables Used When Configuring Managed File Transfer
The procedures for installing and configuring Managed File Transfer reference use a series of variables that you can replace with the actual values used in your environment. - Support for Dynamic Clusters in Managed File Transfer
Managed File Transfer supports two different topologies: static clusters-based topology and dynamic clusters-based topology. When choosing the dynamic cluster topology, there are some differences with respect to the conventional static clusters configuration. - Synchronizing the System Clocks
Before you extend the domain to include Oracle SOA Suite, verify that the system clocks on each host computer are synchronized. - Prerequisites for Creating the Managed File Transfer Domain
Before you create the Managed File Transfer domain, ensure that your existing deployment meets the following prerequisites. - Installing the Software for an Enterprise Deployment
The procedure to install the software for an enterprise deployment is explained in this section. - Creating the Managed File Transfer Database Schemas
Before you can configure an Managed File Transfer domain, you must install the required schemas in a certified database for use with this release of Oracle Fusion Middleware. - Creating the Managed File Transfer Domain for an Enterprise Deployment
You create a separate Managed File Transfer domain by using the Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard. - Configuring Node Manager for the Managed File Transfer Domain
The Managed File Transfer domain uses a per host Node Manager, which allows the Node Manager to control multiple domains on the same host. - Creating the boot.properties File
You must create aboot.propertiesif you want to start the Administrator Server without being prompted for the Administrator Server credentials. This step is required in an enterprise deployment. When you start the Administration Server, the credentials that you enter in this file are encrypted. - Starting the Node Manager on MFTHOST1
After you manually set up the Node Manager to use a per-host Node Manager configuration, you can start the Node Manager on MFTHOST1by using thestartNodeManager.shscript. - Configuring the Node Manager Credentials and Type
By default, a per-host Node Manager configuration does not use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) for Node Manager-to-server communications. As a result, you must configure each system in the domain to use a communication type of plain, rather than SSL. In addition, you should set the Node Manager credentials so that you can connect to the Administration Server and Managed Servers in the domain. - Configuring the Domain Directories and Starting the Servers on MFTHOST1
After the domain is created and the node manager is configured, you can then configure the additional domain directories and start the Administration Server and the Managed Servers on MFTHOST1. - Propagating the Domain and Starting the Servers on MFTHOST2
After you start and validate the Administration Server and WLS_MFT1 Managed Server on MFTHOST1, you can then perform the following tasks on MFTHOST2. - Modifying the Upload and Stage Directories to an Absolute Path
- Configuring Listen Addresses When Using Dynamic Clusters
- Configuring the Web Tier for the Extended Domain
Configure the web server instances on the web tier so that the instances route requests for both public and internal URLs to the proper clusters in the extended domain. - Validating the Managed File Transfer URLs Through the Load Balancer
- Configuring and Enabling the SSH-FTP Service for Managed File Transfer
The Oracle Managed File Transfer enterprise deployment topology is based on the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for file transfer. SFTP is a separate protocol, packaged with SSH and designed to work similar to FTP, but over a secure connection. - Creating a New LDAP Authenticator and Provisioning Users for Managed File Transfer
When you configure an Oracle Fusion Middleware domain, the domain is configured by default to use the WebLogic Server authentication provider (DefaultAuthenticator). However, for an enterprise deployment, Oracle recommends that you use a dedicated, centralized LDAP-compliant authentication provider. - Enabling JDBC Persistent Stores for Oracle Managed File Transfer
Oracle recommends that you use JDBC stores, which leverage the consistency, data protection, and high availability features of an oracle database and makes resources available for all the servers in the cluster. - Enabling Automatic Service Migration for Oracle Managed File Transfer
To ensure that Oracle Managed File Transfer (MFT) is configured for high availability, you must configure the MFT Servers for service migration. - Backing Up the Configuration
It is an Oracle best practices recommendation to create a backup after you successfully extended a domain or at another logical point. Create a backup after you verify that the installation so far is successful. This is a quick backup for the express purpose of immediate restoration in case of problems in later steps.
Parent topic: Configuring the Enterprise Deployment
About Oracle Managed File Transfer
Oracle Managed File Transfer (MFT) provides a standards-based file gateway. It features design, deployment, and monitoring of file transfers by using a web-based design-time console that includes transfer prioritization, file encryption, scheduling, and embedded FTP and sFTP servers.
For more information about Oracle MFT, see Understanding Oracle Managed File Transfer in Using Oracle Managed File Transfer.
About Managed File Transfer in an Enterprise Deployment
Managed File Transfer runs in its own domain, separate from other components, such as Oracle SOA Suite, Oracle Service Bus, and Business Activity Monitoring. Typically, you create the domain and configure the Managed Servers for Managed File Transfer in a single configuration wizard session.
Managed File Transfer uses Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM), and runs the OWSM services on the same servers as the Managed File Transfer applications.
If you configure a web tier, then Managed File Transfer requires Oracle Traffic Director, which provide TCP communication load balancing for the Managed File Transfer SFTP requests.
Figure 20-1 illustrates the Managed File Transfer deployment topology.
For a description of the standard elements shown in the diagram, see Understanding the Typical Enterprise Deployment Topology Diagram.
For a description of the elements shown in the diagram, see Understanding the Primary Oracle SOA Suite Topology Diagrams.
Figure 20-1 Managed File Transfer Topology
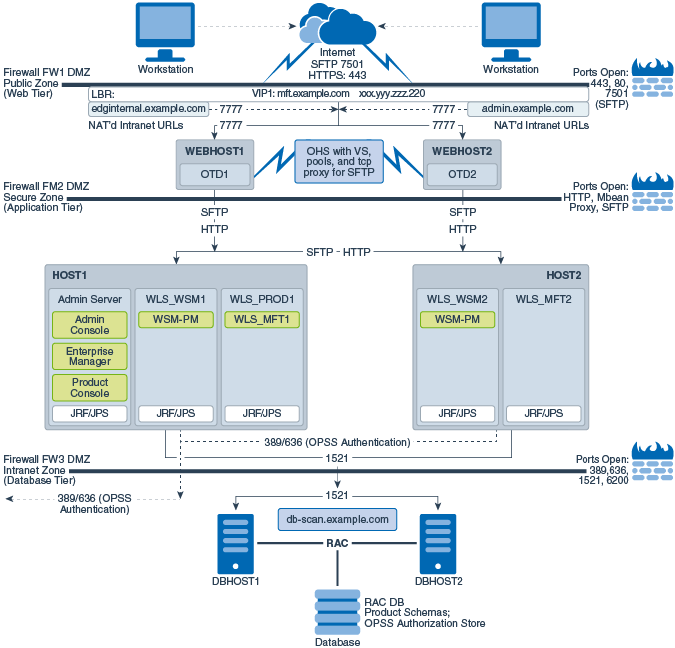
Description of "Figure 20-1 Managed File Transfer Topology"
The Managed File Transfer domain can be configured on the same host as other FMW components. For this reason, Oracle recommends that you use a per host Node Manager configuration. In this configuration, a single Node Manager can control different domains on the same machine. See Configuring a Per Host Node Manager for an Enterprise Deployment.
Parent topic: About Oracle Managed File Transfer
Characteristics of the Managed File Transfer Domain
The following table lists some of the key characteristics of the domain that you are about to create. By reviewing and understanding these characteristics, you can better understand the purpose and context of the procedures used to configure the domain.
Many of these characteristics are described in more detail in Understanding a Typical Enterprise Deployment.
| Characteristic of the Domain | More Information |
|---|---|
|
Uses a separate virtual IP (VIP) address for the Administration Server. |
Configuration of the Administration Server and Managed Servers Domain Directories |
|
Uses separate domain directories for the Administration Server and the Managed Servers in the domain. |
Configuration of the Administration Server and Managed Servers Domain Directories |
|
Uses Oracle Web Services Manager, which is deployed to the same servers as Managed File Transfer |
|
|
Requires Oracle Traffic Director for routing SFTP requests from the web tier. |
|
|
Uses a single Configuration Wizard session to configure the Infrastructure and Managed File Transfer software on the Managed File Transfer Managed Servers. The domain is later extended to include Oracle Traffic Director. |
Creating the Managed File Transfer Domain for an Enterprise Deployment |
|
Uses a per host Node Manager configuration. |
About the Node Manager Configuration in a Typical Enterprise Deployment |
|
Requires a separately installed LDAP-based authentication provider. |
Understanding OPSS and Requests to the Authentication and Authorization Stores |
Parent topic: About Oracle Managed File Transfer
Variables Used When Configuring Managed File Transfer
The procedures for installing and configuring Managed File Transfer reference use a series of variables that you can replace with the actual values used in your environment.
The following directory location variables are used in these procedures:
-
WEB_ORACLE_HOME
-
ASERVER_HOME
-
MSERVER_HOME
-
WEB_DOMAIN_HOME
-
JAVA_HOME
-
NM_HOME
See File System and Directory Variables Used in This Guide.
In addition, you reference the following virtual IP (VIP) address that are defined in Reserving the Required IP Addresses for an Enterprise Deployment:
-
ADMINVHN
Actions in this chapter are performed on the following host computers:
-
APPHOST1
-
APPHOST2
-
WEBHOST1
-
WEBHOST2
Note:
Note that for this chapter, APPHOST1 and APPHOST2 provide a more generic variable for the application tier hosts. This is because, depending upon the domain you are creating, the host name variable varies.
For example, if you are configuring Oracle Traffic Director for an Oracle SOA Suite domain, APPHOST1 is the same as SOAHOST1. However, if you are configuring Oracle Traffic Director for an Oracle Managed File Transfer domain, which is typically configured in its own domain, then APPHOST1 is the same as MFTHOST1.
Support for Dynamic Clusters in Managed File Transfer
Managed File Transfer supports two different topologies: static clusters-based topology and dynamic clusters-based topology. When choosing the dynamic cluster topology, there are some differences with respect to the conventional static clusters configuration.
Static clusters, also called configured clusters, are conventional clusters where you manually configure and add each server instance. A dynamic cluster includes a new "server-template" object that is used to define a centralized configuration for all generated (dynamic) server instances. When you create a dynamic cluster, the dynamic servers are preconfigured and automatically generated for you. This feature enables you to scale up the number of server instances in the dynamic cluster when you need additional server capacity. You can simply start the dynamic servers without having to first manually configure and add them to the cluster.
-
The Configuration Wizard process may differ for each case. For example, you should define server templates for dynamic clusters instead of servers.
-
For dynamic clusters, you should perform the server-specific configurations such as setting the listen address, configuring the upload and staging directories, or configuring the keystores in the server template instead of in the server.
-
Service migration is configured in a different way for dynamic clusters. Dynamic clusters do not use migratable targets, instead the JMS resources are targeted to the cluster. Specific procedure for configuring service migration for dynamic clusters is included in this guide.
Mixed clusters (clusters that contains both dynamic and configured server instances) are not supported in the Oracle SOA Suite enterprise deployment.
Synchronizing the System Clocks
Before you extend the domain to include Oracle SOA Suite, verify that the system clocks on each host computer are synchronized.
Oracle recommends the use of the Network Time Protocol (NTP). See Configuring a Host to Use an NTP (time) Server.
To verify the time synchronization, query the NTP service by running the ntpstat command on each host.
Sample output:
$ ntpstat
synchronised to NTP server (10.132.0.121) at stratum 3
time correct to within 42 ms
polling server every 16 sPrerequisites for Creating the Managed File Transfer Domain
Before you create the Managed File Transfer domain, ensure that your existing deployment meets the following prerequisites.
-
Verify that you have installed a supported JDK.
-
You must have an existing Oracle home where you have installed the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure software binaries. This must be a dedicated Oracle home for the Managed File Transfer domain. The Oracle home is typically on shared storage and is available from MFTHOST1 and MFTHOST2. See Shared Storage Recommendations When Installing and Configuring an Enterprise Deployment.
Note that you should not configure the Infrastructure domain, only install the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure software.
To create the Infrastructure Oracle home, see Installing the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure on SOAHOST1.
-
Back up the installation. If you have not yet backed up the existing Fusion Middleware Home, Oracle recommends backing it up now.
To back up the existing Fusion Middleware Home and domain, see Performing Backups and Recoveries in the SOA Enterprise Deployments.
-
If you have not done so already, verify that the system clocks on each host computer are synchronized. You can do this by running the date command as simultaneously as possible on the hosts in each cluster.
Alternatively, there are third-party and open-source utilities that you can use for this purpose.
Installing the Software for an Enterprise Deployment
The procedure to install the software for an enterprise deployment is explained in this section.
Starting the Managed File Transfer Installer on MFTHOST1
To start the installation program:
When the installation program appears, you are ready to begin the installation.
Parent topic: Installing the Software for an Enterprise Deployment
Navigating the Installation Screens When Installing Managed File Transfer
The installation program displays a series of screens, in the order listed in the following table.
If you need additional help with any of the installation screens, click the screen name.
| Screen | Description |
|---|---|
|
This screen introduces you to the product installer. |
|
|
Use this screen to automatically search My Oracle Support for available patches or automatically search a local directory for patches that you have already downloaded for your organization. |
|
|
Use this screen to specify the location of your Oracle home directory. This Oracle home should already contain Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure. For more information about Oracle Fusion Middleware directory structure, see Selecting Directories for Installation and Configuration in Planning an Installation of Oracle Fusion Middleware. |
|
|
This screen verifies that your system meets the minimum necessary requirements. If there are any warning or error messages, you can refer to one of the documents in the Roadmap for Verifying Your System Environment section in Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure. |
|
|
Use this screen to verify the installation options that you selected. Click Install to begin the installation. |
|
|
This screen allows you to see the progress of the installation. Click Next when the progress bar reaches 100% complete. |
|
|
Review the information on this screen, then click Finish to dismiss the installer. |
Parent topic: Installing the Software for an Enterprise Deployment
Installing the Software on Other Host Computers
If you have configured a separate shared storage volume or partition for SOAHOST2, then you must also install the software on SOAHOST2. For more information, see Shared Storage Recommendations When Installing and Configuring an Enterprise Deployment.
Note that the location where you install the Oracle home (which contains the software binaries) varies, depending upon the host. To identify the proper location for your Oracle home directories, refer to the guidelines in File System and Directory Variables Used in This Guide.
Parent topic: Installing the Software for an Enterprise Deployment
Verifying the Installation
After you complete the installation, you can verify it by successfully completing the following tasks.
Parent topic: Installing the Software for an Enterprise Deployment
Reviewing the Installation Log Files
Review the contents of the installation log files to make sure that no problems were encountered. For a description of the log files and where to find them, see Understanding Installation Log Files in Installing Software with the Oracle Universal Installer.
Parent topic: Verifying the Installation
Checking the Directory Structure for Managed File Transfer
The contents of your installation vary based on the options that you select during installation.
Use the ls --format=single-colum command to check the list of directory and sub-directories in the /u01/oracle/products/fmw directory:
cfgtoollogs coherence em inventory mft OPatch oracle_common oraInst.loc osb oui soa wlserver
For more information about the directory structure you should see after installation, see What are the Key Oracle Fusion Middleware Directories? in Understanding Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Parent topic: Verifying the Installation
Creating the Managed File Transfer Database Schemas
Before you can configure an Managed File Transfer domain, you must install the required schemas in a certified database for use with this release of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
Starting the Repository Creation Utility (RCU)
To start the Repository Creation Utility (RCU):
Parent topic: Creating the Managed File Transfer Database Schemas
Navigating the RCU Screens to Create the Managed File Transfer Schemas
Schema creation involves the following tasks:
-
Task 6, "Verifying the Tablespaces for the Required Schemas"
-
Task 8, "Reviewing Completion Summary and Completing RCU Execution"
- Task 1 Introducing RCU
-
Click Next.
- Task 2 Selecting a Method of Schema Creation
-
If you have the necessary permission and privileges to perform DBA activities on your database, select System Load and Product Load. This procedure assumes that you have the necessary privileges.
If you do not have the necessary permission or privileges to perform DBA activities in the database, you must select Prepare Scripts for System Load on this screen. This option generates a SQL script, which can be provided to your database administrator to create the required schema. See Understanding System Load and Product Load in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
Click Next.
- Task 3 Providing Database Connection Details
-
Provide the database connection details for RCU to connect to your database.
-
In the Host Name field, enter the SCAN address of the Oracle RAC Database.
-
Enter the Port number of the RAC database scan listener, for example 1521.
-
Enter the RAC Service Name of the database.
-
Enter the User Name of a user that has permissions to create schemas and schema objects, for example SYS.
-
Enter the Password of the user name that you provided in step 4.
-
If you have selected the SYS user, ensure that you set the role to SYSDBA.
-
Click Next to proceed, then click OK on the dialog window confirming that the connection to the database was successful.
-
- Task 4 Specifying a Custom Prefix and Selecting Schemas
-
On this page, do the following:
-
Choose Create new prefix, and then enter the prefix that you want to use for the Managed File Transfer schemas. A unique schema prefix is required because you are creating a new domain for Managed File Transfer.
-
From the list of schemas, select the Managed File Transfer schema.
The following dependent schemas are selected automatically:
-
Common Infrastructure Services
-
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler
-
Oracle Platform Security Services
-
User Messaging Service
-
Audit Services
-
Audit Services Append
-
Audit Services Viewer
-
Metadata Services
-
Weblogic Services
-
The custom prefix is used to logically group these schemas together for use in this domain only; you must create a unique set of schemas for each domain as schema sharing across domains is not supported.
Tip:
For more information about custom prefixes, see Understanding Custom Prefixes in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
For more information about how to organize your schemas in a multi-domain environment, see Planning Your Schema Creation in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
Click Next to proceed, then click OK on the dialog window confirming that prerequisite checking for schema creation was successful.
-
- Task 5 Specifying Schema Passwords
-
Specify how you want to set the schema passwords on your database, then specify and confirm your passwords. Ensure that the complexity of the passwords meet the database security requirements before you continue. RCU proceeds at this point even if you do not meet the password polices. Hence, perform this check outside RCU itself.
Tip:
You must make a note of the passwords you set on this screen; you need them later on during the domain creation process.
Click Next.
- Task 6 Verifying the Tablespaces for the Required Schemas
-
On the Map Tablespaces screen, review the information, and then click Next to accept the default values.
Click OK in the confirmation dialog box.
- Task 7 Creating Schemas
-
Review the summary of the schemas to be loaded, and click Create to complete schema creation.
Note:
If failures occurred, review the listed log files to identify the root cause, resolve the defects, and then use RCU to drop and recreate the schemas before you continue.
- Task 8 Reviewing Completion Summary and Completing RCU Execution
-
When you reach the Completion Summary screen, verify that all schema creations have been completed successfully, and then click Close to dismiss RCU.
Parent topic: Creating the Managed File Transfer Database Schemas
Verifying Schema Access
Verify schema access by connecting to the database as the new schema users created by the RCU. Use SQL*Plus or another utility to connect, and provide the appropriate schema names and passwords entered in the RCU.
./sqlplus
SQL*Plus: Release 11.2.0.4.0 Production on Fri Nov 1 08:44:18 2013
Copyright (c) 1982, 2013, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Enter user-name: FMW1221_MFT
Enter password: mft_schema_password
Connected to:
Oracle Database 11g Enterprise Edition Release 11.2.0.4.0 - 64bit Production
With the Partitioning, OLAP, Data Mining and Real Application Testing options
SQL>Parent topic: Creating the Managed File Transfer Database Schemas
Creating the Managed File Transfer Domain for an Enterprise Deployment
- Starting the Configuration Wizard
Start the Configuration Wizard as the first step to extend the existing enterprise deployment domain. - Navigating the Configuration Wizard Screens for MFT
Starting the Configuration Wizard
Start the Configuration Wizard as the first step to extend the existing enterprise deployment domain.
Note:
If you added any customizations directly to the start scripts in the domain, those are overwritten by the configuration wizard. To customize server startup parameters that apply to all servers in a domain, you can create a file called setUserOverridesLate.sh and configure it, for example, add custom libraries to the WebLogic Server classpath, specify Additional JAVA command line options for running the servers, or specify additional environment variables. Any customizations you add to this file are preserved during domain upgrade operations, and are carried over to remote servers when using the pack and unpack commands.
To start the Configuration Wizard:
Navigating the Configuration Wizard Screens for MFT
Follow the instructions in these sections to create and configure the domain for the topology, with static or dynamic clusters.
Configuring the Domain with Static Clusters
Follow the instructions in this section to create and configure the domain for MFT, with static clusters.
Domain creation and configuration includes the following tasks.-
Task 1, "Selecting the Domain Type and Domain Home Location"
-
Task 9, "Providing the GridLink Oracle RAC Database Connection Details"
-
Task 13, "Configuring the Administration Server Listen Address"
-
Task 25, "Reviewing Your Configuration Specifications and Configuring the Domain"
-
Task 26, "Writing Down Your Domain Home and Administration Server URL"
- Task 1 Selecting the Domain Type and Domain Home Location
-
You must select a Domain home directory location, optimally outside the Oracle home directory.
Oracle recommends that you locate your Domain home in accordance with the directory structure in What Are the Key Oracle Fusion Middleware Directories? in Understanding Oracle Fusion Middleware, where the Domain home is located outside the Oracle home directory. This directory structure helps avoid issues when you need to upgrade or reinstall software.
To specify the Domain type and Domain home directory:
-
On the Configuration Type screen, select Create a new domain.
-
In the Domain Location field, specify your Domain home directory.
For more information about this screen, see Configuration Type in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard
-
- Task 2 Selecting the Configuration Templates
-
On the Templates screen, make sure Create Domain Using Product Templates is selected, then select the following templates:
-
Oracle Managed File Transfer-12.2.1.3.0 [mft]
Selecting this template automatically selects the following dependencies:
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager
-
Oracle B2B Client
-
Oracle JRF
-
Oracle WSM Policy Manager
-
WebLogic Coherence Cluster Extension
-
For more information about the options on this screen, see Templates in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 3 Configuring High Availability Options
-
This screen appears for the first time when you create a cluster that uses Automatic Service Migration or JDBC stores or both. After you select HA Options for a cluster, all subsequent clusters that are added to the domain by using the Configuration Wizard, automatically apply HA options (that is, the Configuration Wizard creates JDBC stores and configures ASM for them).
On the High Availability Options screen:
-
Select Enable Automatic Service Migration with Database Basis.
-
Set JTA Transaction Log Persistence to JDBC TLog Store.
-
Set JMS Server Persistence to JMS JDBC Store.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you use JDBC stores, which leverage the consistency, data protection, and high availability features of an Oracle database and makes resources available for all the servers in the cluster. So, the Configuration Wizard steps assume that the JDBC persistent stores are used along with Automatic Service Migration.
When you choose JDBC persistent stores, additional unused File Stores are automatically created but are not targeted to your clusters. Ignore these File Stores.
If, for any reason, you want to use Files Stores, you can retain the default values for TLOGs and JMS persistent store options in this screen and configure them in a shared location later. See Task 12, "Selecting Advanced Configuration". Shared location is required to resume JMS and JTA in a failover scenario.
You can also configure TLOGs and JMS persistent stores manually in a post step. For information about the differences between JDBC and Files Stores, and for specific instructions to configure them manually, see Using Persistent Stores for TLOGs and JMS in an Enterprise Deployment.
Click Next.
-
- Task 4 Selecting the Application Home Location
-
On the Application Location screen, specify the value of the APPLICATION_HOME variable, as defined in File System and Directory Variables Used in This Guide.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Application Location in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 5 Configuring the Administrator Account
-
On the Administrator Account screen, specify the user name and password for the default WebLogic Administrator account for the domain.
Make a note of the user name and password specified on this screen; you need these credentials later to boot and connect to the domain's Administration Server.
- Task 6 Specifying the Domain Mode and JDK
-
On the Domain Mode and JDK screen:
-
Select Production in the Domain Mode field.
-
Select the Oracle Hotspot JDK in the JDK field.
Selecting Production Mode on this screen gives your environment a higher degree of security, requiring a user name and password to deploy applications and to start the Administration Server.
For more information about the options on this screen, including the differences between development mode and production mode, see Domain Mode and JDK in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
In the production mode, a boot identity file can be created to bypass the need to provide a user name and password when you start the Administration Server. See Creating the boot.properties File.
-
- Task 7 Specifying the Database Configuration Type
-
On the Database Configuration Type screen:
-
Select RCU Data to activate the fields on this screen.
The RCU Data option instructs the Configuration Wizard to connect to the database and Service Table (STB) schema to automatically retrieve schema information for the schemas needed to configure the domain.
-
Verify that the Vendor is Oracle and the Driver is *Oracle's Driver (Thin) for Service Connections; Versions: Any.
-
Verify that Connection Parameters is selected.
Note:
If you select Manual Configuration on this screen, you must manually fill in the parameters for your schema on the JDBC Component Schema screen.
After you select RCU Data, fill in the fields as shown in the following table:
Field Description DBMS/Service
Enter the service name for the Oracle RAC database where you install the product schemas. For example:
orcl.example.com
Be sure this is the common service name that is used to identify all the instances in the Oracle RAC database; do not use the host-specific service name.
Host Name
Enter the Single Client Access Name (SCAN) Address for the Oracle RAC database, which you entered in the Enterprise Deployment Workbook.
Port
Enter the port number on which the database listens. For example,
1521.Schema Owner
Schema Password
Enter the user name and password to connect to the database's Service Table schema.
This is the schema user name and password that was specified for the Service Table component on the Schema Passwords screen in RCU. See Creating the Database Schemas.
The default user name is
prefix_STB, whereprefixis the custom prefix that you have defined in RCU.Click Get RCU Configuration when you finished specifying the database connection information. The following output in the Connection Result Log indicates that the operating succeeded:
Connecting to the database server...OK Retrieving schema data from database server...OK Binding local schema components with retrieved data...OK Successfully Done.
Click Next if the connection to the database is successful.
For more information about the RCU Data option, see Understanding the Service Table Schema in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
For more information about the other options on this screen, see Datasource Defaults in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 8 Specifying JDBC Component Schema Information
-
Verify that the values on the JDBC Component Schema screen are correct for all schemas.
The schema table should be populated, because you selected Get RCU Data on the previous screen. As a result, the Configuration Wizard locates the database connection values for all the schemas required for this domain.
At this point, the values are configured to connect to a single-instance database. However, for an enterprise deployment, you should use a highly available Real Application Clusters (RAC) database, as described in Preparing the Database for an Enterprise Deployment.
In addition, Oracle recommends that you use an Active GridLink datasource for each of the component schemas. For more information about the advantages of using GridLink data sources to connect to a RAC database, see Database Considerations in the High Availability Guide.
To convert the data sources to GridLink:
-
Select all the schemas by selecting the checkbox in the first header row of the schema table.
-
Click Convert to GridLink and click Next.
-
- Task 9 Providing the GridLink Oracle RAC Database Connection Details
-
On the GridLink Oracle RAC Component Schema screen, provide the information that is required to connect to the RAC database and component schemas, as shown in following table.
Element Description and Recommended Value SCAN, Host Name, and Port
Select the SCAN check box.
In the Host Name field, enter the Single Client Access Name (SCAN) Address for the Oracle RAC database.
In the Port field, enter the SCAN listening port for the database (for example,
1521).ONS Host and Port
In the ONS Host field, enter the SCAN address for the Oracle RAC database.
In the Port field, enter the ONS Remote port (typically,
6200).These values are required when connecting to Oracle 11g databases but optional when connecting to Oracle database 12c and higher. If you are using an Oracle 12c database, the ONS list is automatically provided from the database to the driver.
Enable Fan
Verify that the Enable Fan check box is selected, so that the database can receive and process FAN events.
For more information about specifying the information on this screen, as well as information about how to identify the correct SCAN address, see Configuring Active GridLink Data Sources with Oracle RAC in the High Availability Guide.
You can also click Help to display a brief description of each field on the screen.
- Task 10 Testing the JDBC Connections
-
A green check mark in the Status column indicates a successful test. If you encounter any issues, see the error message in the Connection Result Log section of the screen, fix the problem, then try to test the connection again.
By default, the schema password for each schema component is the password you specified while creating your schemas. If you want different passwords for different schema components, manually edit them in the previous screen (JDBC Component Schema) by entering the password you want in the Schema Password column, against each row. After you specify the passwords, select the check box that correspond to the schemas that you changed the password in and test the connection again.
For more information about the other options on this screen, see Test Component Schema in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 11 Specifying the Keystore
-
Use the Keystore screen in the Configuration Wizard to specify details about the keystore to be used in the domain.
For a typical enterprise deployment, you can leave the default values. See Keystore in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard
- Task 12 Selecting Advanced Configuration
-
To complete domain configuration for the topology, select the following options on the Advanced Configuration screen:
-
Administration Server
This is required to properly configure the listen address of the Administration Server.
-
Node Manager
This is required to configure Node Manager.
-
Topology
This is required to add, delete, or modify the Settings for Server Templates, Managed Servers, Clusters, Virtual Targets, and Coherence.
Note:
-
When you use the Advanced Configuration screen in the Configuration Wizard, if any of the above options are not available on the screen, then return to the Templates screen and ensure that you have selected the required templates for this topology.
-
JDBC stores are recommended and selected in Task 3, "Configuring High Availability Options" so there is no need to configure File Stores.
If you choose File Stores in Task 3, "Configuring High Availability Options", you have to select the File Stores option here to configure them in a shared location in
ORACLE_RUNTIME/domain_name/MFT_Cluster/jms. Shared location is required to resume JMS and JTA in a failover scenario.
-
- Task 13 Configuring the Administration Server Listen Address
-
On the Administration Server screen:
-
In the Server Name field, retain the default value-AdminServer.
-
In the Listen Address field, enter the virtual host name that corresponds to the VIP of the ADMINVHN that you had procured in Procuring Resources for an Enterprise Deployment and had enabled in Preparing the Host Computers for an Enterprise Deployment.
For more information on the reasons for using the ADMINVHN virtual host, see Reserving the Required IP Addresses for an Enterprise Deployment.
-
Leave the other fields at their default values.
In particular, be sure that no server groups are assigned to the Administration Server.
-
- Task 14 Setting the Node Manager Type (Per Host)
-
Select Manual Node Manager Setup as the Node Manager type.
Note:
-
For more information about the options on this screen, see Node Manager in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
For more information about per domain and per host Node Manager implementations, see About the Node Manager Configuration in a Typical Enterprise Deployment.
-
For information about Node Manager configuration, see Configuring Node Manager on Multiple Machines in Administering Node Manager for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
- Task 15 Configuring Managed Servers
-
Use the Managed Servers screen to create the Managed Servers that are required in the Managed File Transfer domain.
-
Change the default server name to
WLS_MFT1in the Server name column. -
Click Add and repeat this process to create a second Managed Server named
WLS_MFT2. -
Use the information in Table 20-* to fill in the rest of the columns for each MFT Managed Server.
The Managed Server names suggested in this procedure (WLS_MFT1 and WLS_MFT2) are referenced throughout this document; if you choose different names then be sure to replace them as needed,
For more information about the options on this screen, see Managed Servers in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
Server Name Listen Address Listen Port Enable SSL SSL Listen Port Server Groups WLS_MFT1
MFTHOST1
7500
No
Disabled
MFT-MGD-SVRS
WLS_MFT2
MFTHOST2
7500
No
Disabled
MFT-MGD-SVRS
The selected server group ensures that the Managed File Transfer and Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) software is targeted to the Managed Server.
There is another server group called MFT-MGD-SVRS-ONLY that targets only MFT but not Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) to the server. This is typically used if you want to have Oracle Web Services Manager (OWSM) in a different server rather than with the MFT server.
The server groups target Fusion Middleware applications and services to one or more servers by mapping defined groups of application services to each defined server group. Any application services that are mapped to a given server group are automatically targeted to all servers that are assigned to that group. See Application Service Groups, Server Groups, and Application Service Mappings in Domain Template Reference.
-
- Task 16 Configuring a Cluster
-
Use the Clusters screen to create a new cluster:
-
Click the Add button.
-
Specify
MFT_Clusterin the Cluster Name field. -
Leave the Address field blank.
-
Specify
mft.example.comin the Frontend Host field. - Specify
80as the Frontend HTTP port and443as the Frontend HTTPS port. -
From the Dynamic Server Groups drop-down list, select
Unspecified.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Clusters in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 17 Assigning Server Templates
-
Click Next.
- Task 18 Configuring Dynamic Servers
-
Verify that all dynamic server options are disabled for clusters that are to remain as static clusters.
-
Confirm that the Dynamic Cluster, Calculated Listen Port, and Calculated Machine Names checkboxes on this screen are unchecked.
-
Confirm that the Server Template selection is Unspecified.
-
Click Next.
-
- Task 19 Assigning Managed Servers to the Cluster
-
Use the Assign Servers to Clusters screen to assign Managed Servers to the new cluster.
-
In the Clusters pane, select the cluster to which you want to assign the servers; in this case,
MFT_Cluster. -
In the Servers pane, assign
WLS_MFT1toMFT_Clusterby doing one of the following:-
Click once on
WLS_MFT1to select it, then click on the right arrow to move it beneath the selected cluster (MFT_Cluster)) in the Clusters pane.or
-
Double-click on
WLS_MFT1to move it beneath the selected cluster (MFT_Cluster) in the clusters pane.
-
-
Repeat these steps to assign the WLS_MFT2 Managed Server to MFT_Cluster.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Assign Servers to Clusters in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 20 Configuring Coherence Clusters
-
Use the Coherence Clusters screen to configure the Coherence cluster that is automatically added to the domain.
In the Cluster Listen Port, enter
9991.For Coherence licensing information, Oracle Coherence Products in Oracle Fusion Middleware Licensing Information User Manual.
- Task 21 Creating Machines
-
Use the Machines screen to create five new machines in the domain. A machine is required in order for the Node Manager to be able to start and stop the servers.
-
Select the Unix Machine tab.
-
Click the Add button to create five new UNIX machines.
Use the values in Table 20-1 to define the Name and Node Manager Listen Address of each machine.
-
Verify the port in the Node Manager Listen Port field.
The port number
5556, shown in this example, may be referenced by other examples in the documentation. Replace this port number with your own port number as needed.Note:
If you are installing on a host where additional domains were already configured, and you have already configured a per host Node Manager, then the address and port configured in this screen must be for the existing per host Node Manager.
Table 20-1 Values to Use When Creating Unix Machines
Name Node Manager Listen Address Node Manager Listen Port MFTHOST1
The value of the MFTHOST1 host name variable or MFTHOST1 alias. For example,
MFTHOST1.example.com.5556
MFTHOST2
The value of the MFTHOST2 host name variable or MFTHOST2 alias. For example,
MFTHOST2.example.com.5556
ADMINHOST
Enter the value of the ADMINVHN variable.
5556
For more information about the options on this screen, see Machines in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 22 Assigning Servers to Machines
-
Use the Assign Servers to Machines screen to assign the Administration Server and the two Managed Servers to the appropriate machine.
The Assign Servers to Machines screen is similar to the Assign Managed Servers to Clusters screen. Select the target machine in the Machines column, select the Managed Server in the left column, and click the right arrow to assign the server to the appropriate machine.
Assign the servers as follows:
-
Assign the AdminServer to the ADMINHOST machine.
-
Assign the WLS-MFT1 Managed Server to the MFTHOST1 machine.
-
Assign the WLS-MFT2 Managed Server to the MFTHOST2 machine.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Assign Servers to Machines in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 23 Creating Virtual Targets
-
Click Next.
- Task 24 Creating Partitions
-
Click Next.
- Task 25 Reviewing Your Configuration Specifications and Configuring the Domain
-
The Configuration Summary screen contains detailed configuration information for the domain that you are about to create. Review the details of each item on the screen and verify that the information is correct.
If you need to make any changes, you can go back to any previous screen either by using the Back button or by selecting the screen in the navigation pane.
Domain creation does not begin until you click Create.
In the Configuration Progress screen, click Next when it finishes.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Configuration Summary in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 26 Writing Down Your Domain Home and Administration Server URL
-
The Configuration Success screen shows the following items about the domain you just configured:
-
Domain Location
-
Administration Server URL
You must make a note of both items as you need them later; the domain location is needed to access the scripts used to start the Administration Server.
Click Finish to dismiss the Configuration Wizard.
-
After you have completed extending the domain with static clusters, go to Configuring Node Manager for the Managed File Transfer Domain.
Parent topic: Navigating the Configuration Wizard Screens for MFT
Configuring the Domain with Dynamic Clusters
Follow the instructions in this section to create and configure the domain for MFT, with dynamic clusters.
Domain creation and configuration includes the following tasks.-
Task 1, "Selecting the Domain Type and Domain Home Location"
-
Task 9, "Providing the GridLink Oracle RAC Database Connection Details"
-
Task 13, "Configuring the Administration Server Listen Address"
-
Task 24, "Reviewing Your Configuration Specifications and Configuring the Domain"
-
Task 25, "Writing Down Your Domain Home and Administration Server URL"
- Task 1 Selecting the Domain Type and Domain Home Location
-
You must select a Domain home directory location, optimally outside the Oracle home directory.
Oracle recommends that you locate your Domain home in accordance with the directory structure in What Are the Key Oracle Fusion Middleware Directories? in Understanding Oracle Fusion Middleware, where the Domain home is located outside the Oracle home directory. This directory structure helps avoid issues when you need to upgrade or reinstall software.
To specify the Domain type and Domain home directory:
-
On the Configuration Type screen, select Create a new domain.
-
In the Domain Location field, specify your Domain home directory.
For more information about this screen, see Configuration Type in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard
-
- Task 2 Selecting the Configuration Templates
-
On the Templates screen, make sure that Create Domain Using Product Templates is selected, then select the following templates:
-
Oracle Managed File Transfer-12.2.1.3.0 [mft]
Selecting this template automatically selects the following dependencies:
-
Oracle B2B Client
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager
-
Oracle WSM Policy Manager
-
Oracle JRF
-
WebLogic Coherence Cluster Extension
-
For more information about the options on this screen, see Templates in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 3 Configuring High Availability Options
-
This screen appears for the first time when you create a cluster that uses Automatic Service Migration or JDBC stores or both. After you select HA Options for a cluster, all subsequent clusters that are added to the domain by using the Configuration Wizard, automatically apply these HA options.
On the High Availability Options screen, complete the following steps:
-
Verify that the Enable Automatic Service Migration option is not selected.
-
Verify that Default Persistent Store is selected as the JTA Transaction Log Persistence option.
-
Select JDBC Store as the JMS Service Persistence option.
You can configure only JMS Server persistence for Dynamic Clusters by using the Configuration Wizard. You cannot configure Service Migration and JTA Transaction Logs Persistence for Dynamic Clusters by using the Configuration Wizard, you have to configure them manually. Instructions are covered in later chapters of this guide.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you use JDBC stores, which leverage the consistency, data protection, and high availability features of an oracle database and makes resources available for all the servers in the cluster. So, the Configuration Wizard steps assume that the JDBC persistent stores are used along with Automatic Service Migration.
When you choose JDBC persistent stores, additional unused File Stores are automatically created but are not targeted to your clusters. Ignore these File Stores.
If, for any reason, you want to use Files Stores, you can retain the default values for TLOGs and JMS persistent store options in this screen and configure them in a shared location later. See Task 12, "Selecting Advanced Configuration". Shared location is required to resume JMS and JTA in a failover scenario.
You can also configure TLOGs and JMS persistent stores manually in a post step. For information about the differences between JDBC and Files Stores, and for specific instructions to configure them manually, see Using Persistent Stores for TLOGs and JMS in an Enterprise Deployment.
Click Next.
-
- Task 4 Selecting the Application Home Location
-
On the Application Location screen, specify the value of the APPLICATION_HOME variable, as defined in File System and Directory Variables Used in This Guide.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Application Location in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 5 Configuring the Administrator Account
-
On the Administrator Account screen, specify the user name and password for the default WebLogic Administrator account for the domain.
Make a note of the user name and password specified on this screen; you need these credentials later to boot and connect to the domain's Administration Server.
- Task 6 Specifying the Domain Mode and JDK
-
On the Domain Mode and JDK screen:
-
Select only Production in the Domain Mode field.
-
Select the Oracle Hotspot JDK in the JDK field.
Selecting Production Mode on this screen gives your environment a higher degree of security, requiring a user name and password to deploy applications and to start the Administration Server.
For more information about the options on this screen, including the differences between development mode and production mode, see Domain Mode and JDK in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
In the production mode, a boot identity file can be created to bypass the need to provide a user name and password when starting the Administration Server. See Creating the boot.properties File.
-
- Task 7 Specifying the Database Configuration Type
-
On the Database Configuration Type screen:
-
Select RCU Data to activate the fields on this screen.
The RCU Data option instructs the Configuration Wizard to connect to the database and Service Table (STB) schema to automatically retrieve schema information for the schemas needed to configure the domain.
-
Verify that the Vendor is Oracle and the Driver is *Oracle's Driver (Thin) for Service Connections; Versions: Any.
-
Verify that Connection Parameters is selected.
Note:
If you select Manual Configuration on this screen, you must manually fill in the parameters for your schema on the JDBC Component Schema screen.
After you select RCU Data, fill in the fields as shown in the following table:
Field Description DBMS/Service
Enter the service name for the Oracle RAC database where you install the product schemas. For example:
orcl.example.com
Be sure this is the common service name that is used to identify all the instances in the Oracle RAC database; do not use the host-specific service name.
Host Name
Enter the Single Client Access Name (SCAN) Address for the Oracle RAC database, which you entered in the Enterprise Deployment Workbook.
Port
Enter the port number on which the database listens. For example,
1521.Schema Owner
Schema Password
Enter the user name and password to connect to the database's Service Table schema.
This is the schema user name and password that was specified for the Service Table component on the Schema Passwords screen in RCU. See Creating the Database Schemas.
The default user name is
prefix_STB, whereprefixis the custom prefix that you have defined in RCU.Click Get RCU Configuration when you finished specifying the database connection information. The following output in the Connection Result Log indicates that the operation is successful:
Connecting to the database server...OK Retrieving schema data from database server...OK Binding local schema components with retrieved data...OK Successfully Done.
Click Next if the connection to the database is successful.
For more information about the RCU Data option, see Understanding the Service Table Schema in Creating Schemas with the Repository Creation Utility.
For more information about the other options on this screen, see Datasource Defaults in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 8 Specifying JDBC Component Schema Information
-
Verify that the values on the JDBC Component Schema screen are correct for all schemas.
The schema table should be populated, because you selected Get RCU Data on the previous screen. As a result, the Configuration Wizard locates the database connection values for all the schemas required for this domain.
At this point, the values are configured to connect to a single-instance database. However, for an enterprise deployment, you should use a highly available Real Application Clusters (RAC) database, as described in Preparing the Database for an Enterprise Deployment.
In addition, Oracle recommends that you use an Active GridLink datasource for each of the component schemas. For more information about the advantages of using GridLink data sources to connect to a RAC database, see Database Considerations in the High Availability Guide.
To convert the data sources to GridLink:
-
Select all the schemas by selecting the checkbox in the first header row of the schema table.
-
Click Convert to GridLink and click Next.
-
- Task 9 Providing the GridLink Oracle RAC Database Connection Details
-
On the GridLink Oracle RAC Component Schema screen, provide the information required to connect to the RAC database and component schemas, as shown in following table.
Element Description and Recommended Value SCAN, Host Name, and Port
Select the SCAN check box.
In the Host Name field, enter the Single Client Access Name (SCAN) Address for the Oracle RAC database.
In the Port field, enter the SCAN listening port for the database (for example,
1521).ONS Host and Port
In the ONS Host field, enter the SCAN address for the Oracle RAC database.
In the Port field, enter the ONS Remote port (typically,
6200).These values are required when connecting to Oracle 11g databases but optional when connecting to Oracle database 12c and higher. If you are using an Oracle 12c database, the ONS list is automatically provided from the database to the driver.
Enable Fan
Verify that the Enable Fan check box is selected, so that the database can receive and process FAN events.
For more information about specifying the information on this screen, as well as information about how to identify the correct SCAN address, see Configuring Active GridLink Data Sources with Oracle RAC in the High Availability Guide.
You can also click Help to display a brief description of each field on the screen.
- Task 10 Testing the JDBC Connections
-
A green check mark in the Status column indicates a successful test. If you encounter any issues, see the error message in the Connection Result Log section of the screen, fix the problem, then try to test the connection again.
By default, the schema password for each schema component is the password that you specified while creating your schemas. If you want different passwords for different schema components, manually edit them in the previous screen (JDBC Component Schema) by entering the password that you want in the Schema Password column, against each row. After you specify the passwords, select the check box that corresponds to the schemas that you changed the password in and test the connection again.
For more information about the other options on this screen, see Test Component Schema in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 11 Specifying the Keystore
-
Use the Keystore screen in the Configuration Wizard to specify details about the keystore to be used in the domain.
For a typical enterprise deployment, you can leave the default values. See Keystore in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 12 Selecting Advanced Configuration
-
To complete domain configuration for the topology, select the following options on the Advanced Configuration screen:
-
Administration Server
This is required to properly configure the listen address of the Administration Server.
-
Node Manager
This is required to configure Node Manager.
-
Topology
This is required to add, delete, or modify the Settings for Server Templates, Managed Servers, Clusters, Virtual Targets, and Coherence.
Note:
-
JMS JDBC stores are recommended and selected in Task 3, "Configuring High Availability Options" so there is no need to configure File Stores.
If you choose JMS File Stores in Task 3, "Configuring High Availability Options", you have to select the File Stores option to configure them in a shared location in
ORACLE_RUNTIME/domain_name/MFT_Cluster/jms. Shared location is required to resume JMS and JTA in a failover scenario. -
When you use the Advanced Configuration screen in the Configuration Wizard, if any of the above options are not available on the screen, then return to the Templates screen and ensure that you have selected the required templates for this topology.
-
- Task 13 Configuring the Administration Server Listen Address
-
On the Administration Server screen:
-
In the Server Name field, retain the default value-
AdminServer. -
In the Listen Address field, enter the virtual host name that corresponds to the VIP of the ADMINVHN that you had procured in Procuring Resources for an Enterprise Deployment and had enabled in Preparing the Host Computers for an Enterprise Deployment.
For more information on the reasons for using the ADMINVHN virtual host, see Reserving the Required IP Addresses for an Enterprise Deployment.
-
In the Listen Port field, enter the port number to access the administration server. This guide recommends you to use the default port 7001.
Leave the other fields at their default values. In particular, be sure that no server groups are assigned to the Administration Server.
-
- Task 14 Setting the Node Manager Type (Per Host)
-
Select Manual Node Manager Setup as the Node Manager type.
Note:
-
For more information about the options on this screen, see Node Manager in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
For more information about per domain and per host Node Manager implementations, see About the Node Manager Configuration in a Typical Enterprise Deployment.
-
For information about Node Manager configuration, see Configuring Node Manager on Multiple Machines in Administering Node Manager for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
- Task 15 Configuring Managed Servers
-
On the Managed Servers screen, a new Managed Server for Oracle Managed File Transfer appears in the list of servers.
Static Managed Server definitions are not needed for dynamic cluster configurations. To remove the default Managed Server, complete the following steps:
-
Delete the default Managed Server.
-
Click Next to proceed to the next screen.
-
- Task 16 Configuring a Cluster
-
Use the Clusters screen to create a new cluster:
-
Click the Add button.
-
Specify
MFT_Clusterin the Cluster Name field. -
Leave the Address field blank.
-
Specify
mft.example.comin the Frontend Host field. - Specify
80as the Frontend HTTP port and443as the Frontend HTTPS port. -
From the Dynamic Server Groups drop-down list, select
MFT-DYN-CLUSTER.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Clusters in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 17 Assigning Server Templates
-
Use the Server Templates screen to configure the template:
-
Verify that
mft-server-templateis selected in the Name field. -
Specify
7499in the Listen Port field. -
Leave the Enable SSL option unchecked.
-
Click Next.
-
- Task 18 Configuring Dynamic Servers
-
Use the Dynamic Clusters screen to configure the required clusters:
-
Specify
MFT_Clusterin the Cluster Name field. -
Specify
WLS_MFTin the Server Name Prefix field. -
From the Server Template drop-down list, select
MFT-server-template. -
Specify
2in the Dynamic Cluster Size field. -
Specify
MFTHOST*in the Machine Name Match Expression field and select Calculated Machine Names.Note:
The dynamic cluster Calculated Machine Names and Machine Name Match Expression attributes control how server instances in a dynamic cluster are assigned to a machine. If the Calculated Machine Names attribute is set to False, the dynamic servers are not assigned to a machine. If the Calculated Machine Names attribute is set to True, the Machine Name Match Expression attribute is used to select the set of machines that is used for the dynamic servers. If the Machine Name Match Expression attribute is not set, all of the machines in the domain get selected. Assignments are made by using a round robin algorithm.
To make things easier regardless of your actual physical hostname, Oracle recommends that you use MFTHOSTn as your WebLogic machine names, as explained in Task 20, "Creating Machines", where n is a sequential number. This convention makes it easy for dynamic clusters to determine where to start each cluster member. If you want to follow this convention, in the Machine Match Expression field, enter MFTHOST*.
If you do not adopt this convention, the cluster members are started on each machine that you define in Task 20, "Creating Machines", including that of ADMINHOST. This situation is undesirable as you would end you with two cluster members that run on the same physical server but are attached to two different domain homes.
-
Select the Calculated Listen Ports and Dynamic Cluster check boxes.
Note:
Dynamic clusters with the Calculated Listen Port option selected have incremental port numbers for each dynamic managed server that is created automatically: dynamic server 1 uses Listen Port+1, dynamic server 2 uses Listen Port+2.
Since the Listen Port that is configured is 7499 and calculated ports is checked, MFT dynamic servers uses the following port numbers:
-
WLS_MFT1 server listens in 7500 port
-
WLS_MFT2 server listens in 7501 port
-
-
Click Next.
Note:
The Configuration Wizard does not allow you to specify a specific listen address for dynamic servers. For information about setting a specific listen address for WebLogic servers that are members of a dynamic cluster, see Configuring Listen Addresses in Dynamic Cluster Server Templates.
-
- Task 19 Configuring Coherence Clusters
-
Use the Coherence Clusters screen to configure the Coherence cluster that is automatically added to the domain.
In the Cluster Listen Port, enter
9991.For Coherence licensing information, Oracle Coherence Products in Oracle Fusion Middleware Licensing Information User Manual.
- Task 20 Creating Machines
-
Use the Machines screen to create three new machines in the domain. A machine is required in order for the Node Manager to be able to start and stop the servers.
-
Select the Unix Machine tab.
-
Click the Add button to create three new UNIX machines.
Use the values in Table 20-2 to define the Name and Node Manager Listen Address of each machine.
-
Verify the port in the Node Manager Listen Port field.
The port number
5556, shown in this example, may be referenced by other examples in the documentation. Replace this port number with your own port number as needed.Note:
If you are installing on a host where additional domains were already configured, and you have already configured a per host Node Manager, then the address and port configured in this screen must be for the existing per host Node Manager.
Table 20-2 Values to Use When Creating Unix Machines
Name Node Manager Listen Address Node Manager Listen Port MFTHOST1
The value of the MFTHOST1 host name variable or MFTHOST1 alias. For example,
MFTHOST1.example.com.5556
MFTHOST2
The value of the MFTHOST2 host name variable or MFTHOST2 alias. For example,
MFTHOST2.example.com.5556
ADMINHOST
Enter the value of the ADMINVHN variable.
5556
Note:
The name of the machine should reflect the value that you have specified in the Machine Match Expression field with the addition of a sequential number. That is , if you have specified SOAHOST* in the Machine Match Expression field, then the names of your machines should be SOAHOST1, SOAHOST2, and so on.
Tip:
More information about the options on this screen can be found in Machines in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
-
- Task 21 Assigning Servers to Machines
-
Use the Assign Servers to Machines screen to assign the Administration Server and the two Managed Servers to the appropriate machine.
The Assign Servers to Machines screen is similar to the Assign Managed Servers to Clusters screen. Select the target machine in the Machines column, select the Managed Server in the left column, and click the right arrow to assign the server to the appropriate machine.
Assign the server AdminServer to the ADMINHOST machine.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Assign Servers to Machines in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 22 Creating Virtual Targets
-
Click Next.
- Task 23 Creating Partitions
-
Click Next.
- Task 24 Reviewing Your Configuration Specifications and Configuring the Domain
-
The Configuration Summary screen contains detailed configuration information for the domain that you are about to create. Review the details of each item on the screen and verify that the information is correct.
If you need to make any changes, you can go back to any previous screen, either by using the Back button or by selecting the screen in the navigation pane.
Domain creation does begin until you click Create.
In the Configuration Progress screen, click Next when it finishes.
For more information about the options on this screen, see Configuration Summary in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- Task 25 Writing Down Your Domain Home and Administration Server URL
-
The Configuration Success screen shows the following items about the domain that you just configured:
-
Domain Location
-
Administration Server URL
You must make a note of both items as you need them later; the domain location is needed to access the scripts used to start the Administration Server.
Click Finish to dismiss the Configuration Wizard.
-
Parent topic: Navigating the Configuration Wizard Screens for MFT
Configuring Node Manager for the Managed File Transfer Domain
The Managed File Transfer domain uses a per host Node Manager, which allows the Node Manager to control multiple domains on the same host.
If you are configuring Node Manager for the first time on MFTHOST1, then follow the steps described in Configuring a Per Host Node Manager for an Enterprise Deployment. Note that the domain name and directories must match the values for the Managed File Transfer domain.
If you have already configured a per host Node Manager on MFTHOST1, then you can add the new domain to the existing Node Manager configuration:
Creating the boot.properties File
You must create a boot.properties if you want to start the Administrator Server without being prompted for the Administrator Server credentials. This step is required in an enterprise deployment. When you start the Administration Server, the credentials that you enter in this file are encrypted.
To create a boot.properties file for the Administration Server:
Starting the Node Manager on MFTHOST1
After you manually set up the Node Manager to use a per-host Node Manager configuration, you can start the Node Manager on MFTHOST1by using the startNodeManager.sh script.
Configuring the Node Manager Credentials and Type
By default, a per-host Node Manager configuration does not use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) for Node Manager-to-server communications. As a result, you must configure each system in the domain to use a communication type of plain, rather than SSL. In addition, you should set the Node Manager credentials so that you can connect to the Administration Server and Managed Servers in the domain.
The following procedure temporarily starts the Administration Server with the default start script, so that you can perform these tasks. After you perform these tasks, you can stop this temporary session and use the Node Manager to start the Administration Server.
Configuring the Domain Directories and Starting the Servers on MFTHOST1
After the domain is created and the node manager is configured, you can then configure the additional domain directories and start the Administration Server and the Managed Servers on MFTHOST1.
- Disabling the Derby Database
- Starting the Administration Server Using the Node Manager
After you have configured the domain and configured the Node Manager, you can start the Administration Server by using the Node Manager. In an enterprise deployment, the Node Manager is used to start and stop the Administration Server and all the Managed Servers in the domain. - Validating the Administration Server
Before you proceed with the configuration steps, validate that the Administration Server has started successfully by making sure that you have access to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control; both of these are installed and configured on the Administration Servers. - Creating a Separate Domain Directory for Managed Servers on MFTHOST1
When you initially create the domain for enterprise deployment, the domain directory resides on a shared disk. This default domain directory is used to run the Administration Server. You can now create a copy of the domain on the local storage for both MFTHOST1 and MFTHOST2. The domain directory on the local (or private) storage is used to run the Managed Servers. - Starting and Validating the WLS_MFT1 Managed Server on MFTHOST1
After you have configured Node Manager and created the Managed Server domain directory, you can use Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control to start the WLS_MFT1 Managed Server on MFTHOST1.
Disabling the Derby Database
Starting the Administration Server Using the Node Manager
After you have configured the domain and configured the Node Manager, you can start the Administration Server by using the Node Manager. In an enterprise deployment, the Node Manager is used to start and stop the Administration Server and all the Managed Servers in the domain.
To start the Administration Server by using the Node Manager:
Validating the Administration Server
Before you proceed with the configuration steps, validate that the Administration Server has started successfully by making sure that you have access to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control; both of these are installed and configured on the Administration Servers.
To navigate to Fusion Middleware Control, enter the following URL, and log in with the Oracle WebLogic Server administrator credentials:
ADMINVHN:7001/em
To navigate to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, enter the following URL, and log in with the same administration credentials:
ADMINVHN:7001/consoleCreating a Separate Domain Directory for Managed Servers on MFTHOST1
When you initially create the domain for enterprise deployment, the domain directory resides on a shared disk. This default domain directory is used to run the Administration Server. You can now create a copy of the domain on the local storage for both MFTHOST1 and MFTHOST2. The domain directory on the local (or private) storage is used to run the Managed Servers.
Placing the MSERVER_HOME on local storage is recommended to eliminate the potential contention and overhead cause by servers writing logs to shared storage. It is also faster to load classes and jars need from the domain directory, so any tmp directory or cache data that the Managed Servers use from the domain directory is processed quicker.
As described in Preparing the File System for an Enterprise Deployment, the path to the Administration Server domain home is represented by the ASERVER_HOME variable, and the path to the Managed Server domain home is represented by the MSERVER_HOME variable.
To create the Managed Server domain directory:
Propagating the Domain and Starting the Servers on MFTHOST2
After you start and validate the Administration Server and WLS_MFT1 Managed Server on MFTHOST1, you can then perform the following tasks on MFTHOST2.
Unpacking the Domain Configuration on MFTHOST2
Now that you have the Administration Server and the first WLS_WSM1 Managed Server running on MFTHOST1, you can configure the domain on MFTHOST2.
Starting the Node Manager on MFTHOST2
Starting and Validating the WLS_MFT2 Managed Server on MFTHOST2
Use the procedure that is explained in Starting and Validating the WLS_MFT1 Managed Server on MFTHOST1 to start and validate the WLS_MFT2 Managed Server on MFTHOST2.
Modifying the Upload and Stage Directories to an Absolute Path
After you configure the domain and unpack it to the Managed Server domain directories on all the hosts, verify and update the upload and stage directories for Managed Servers in the new clusters. See Modifying the Upload and Stage Directories to an Absolute Path in an Enterprise Deployment.
Configuring Listen Addresses When Using Dynamic Clusters
The default configuration for dynamic managed servers in dynamic clusters is to listen on all available network interfaces. In most cases, the default configuration may be undesirable. To limit the listen address to a specific address when you use dynamic clusters, see Configuring Listen Addresses in Dynamic Cluster Server Templates. Reverify the test URLs that are provided in the previous sections after you change the listen address and restart the clustered managed servers.
Configuring the Web Tier for the Extended Domain
Configure the web server instances on the web tier so that the instances route requests for both public and internal URLs to the proper clusters in the extended domain.
For additional steps in preparation for possible scale-out scenarios, see Updating Cross Component Wiring Information.
- Configuring Oracle Traffic Director for Managed File Transfer
Oracle Traffic Director can be used as an alternative to Oracle HTTP Server on the web tier. Similar to Oracle HTTP Server, it can route HTTP requests from the front-end load balancer to the application-tier WebLogic Managed Servers. However, only Oracle Traffic Director provides TCP load balancing and failover. As a result, Oracle Traffic Director is required by Oracle Managed File Transfer, which requires TCP for the routing of secure FTP requests. - Configuring the WebLogic Proxy Plug-In
Configuring Oracle Traffic Director for Managed File Transfer
Oracle Traffic Director can be used as an alternative to Oracle HTTP Server on the web tier. Similar to Oracle HTTP Server, it can route HTTP requests from the front-end load balancer to the application-tier WebLogic Managed Servers. However, only Oracle Traffic Director provides TCP load balancing and failover. As a result, Oracle Traffic Director is required by Oracle Managed File Transfer, which requires TCP for the routing of secure FTP requests.
For complete instructions on configuring Oracle Traffic Director, see Configuring Oracle Traffic Director for an Enterprise Deployment.
Parent topic: Configuring the Web Tier for the Extended Domain
Configuring the WebLogic Proxy Plug-In
Before you can validate that requests that are routed correctly through the Oracle HTTP Server or Oracle Traffic Director instances, you must set the WebLogic Plug-In Enabled parameter for the clusters that you just configured. To configure the WebLogic Proxy Plug-in:
Parent topic: Configuring the Web Tier for the Extended Domain
Validating the Managed File Transfer URLs Through the Load Balancer
Configuring and Enabling the SSH-FTP Service for Managed File Transfer
The Oracle Managed File Transfer enterprise deployment topology is based on the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for file transfer. SFTP is a separate protocol, packaged with SSH and designed to work similar to FTP, but over a secure connection.
SFTP allows you to limit the number of ports used for file transfer connections. It is preferable to FTP because of its underlying security features and ability to use a standard SSH connection.
- Generating the Required SSH Keys
To enable SFTP, you must generate SSH keys. This procedure needs to be done only once on one of the Managed Servers, because Managed File Transfer shares the same SFTP key for all the servers in the cluster. - Configuring the SFTP Ports
Before you can use the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for Oracle Managed File Transfer, you must configure the SFTP Ports. - Additional SFTP Configuration Steps for Managed File Transfer
There are several additional configuration steps that you should perform when you use SFTP with Managed File Transfer.
Generating the Required SSH Keys
To enable SFTP, you must generate SSH keys. This procedure needs to be done only once on one of the Managed Servers, because Managed File Transfer shares the same SFTP key for all the servers in the cluster.
Without a valid private key, SSH-FTP server fails to start. To comply with security best practices, you should always use a password-protected private key. The password you use must match the one specified in the Managed File Transfer Console. To locate the password in the Console, select Keystores > SSH Keystores > Private Key Password.
Configuring the SFTP Ports
Before you can use the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) for Oracle Managed File Transfer, you must configure the SFTP Ports.
Creating a New LDAP Authenticator and Provisioning Users for Managed File Transfer
When you configure an Oracle Fusion Middleware domain, the domain is configured by default to use the WebLogic Server authentication provider (DefaultAuthenticator). However, for an enterprise deployment, Oracle recommends that you use a dedicated, centralized LDAP-compliant authentication provider.
Enabling JDBC Persistent Stores for Oracle Managed File Transfer
Oracle recommends that you use JDBC stores, which leverage the consistency, data protection, and high availability features of an oracle database and makes resources available for all the servers in the cluster.
Follow these guidelines to ensure that you use JDBC stores, when you use static or dynamic clusters:
-
For static clusters
If you have made the following selections in the High Availability Options screen, as recommended in this guide for static clusters, then JDBC persistent stores are already configured for both JMS and TLOGS:
-
Set JTA Transaction Log Persistence to JDBC TLog Store.
-
Set JMS Server Persistence to JMS JDBC Store.
-
-
For dynamic clusters
You can configure only JMS Server persistence for dynamic clusters by using the Configuration Wizard. JTA Transaction Logs Persistence must be configure manually, if required. If you have made the following selections in the High Availability Options screen, as recommended in this guide for dynamic clusters, then JDBC persistent stores are already configured for JMS.
-
Set JMS Server Persistence to JMS JDBC Store.
-
Verify that JTA Transaction Log Persistence is set to Default Persistent Store.
Additional steps are needed to configure JTA Transaction Log with JDBC store. See Roadmap for Configuring a JDBC Persistent Store for TLOGs.
-
In case you did not select JDBC for JMS and TLOGS persistent in the High Availability Options screen, you can still configure JDBC stores manually in a post step. For specific instructions to configure them manually, see Using JDBC Persistent Stores for TLOGs and JMS in an Enterprise Deployment.
Note:
The High Availability Options screen appears during the Configuration Wizard session for the first time when you create a cluster that uses Automatic Service Migration or JDBC stores or both. All subsequent clusters that are added to the domain by using the Configuration Wizard, automatically apply the selected HA options.
Enabling Automatic Service Migration for Oracle Managed File Transfer
To ensure that Oracle Managed File Transfer (MFT) is configured for high availability, you must configure the MFT Servers for service migration.
Follow these guidelines to ensure that you provide the required high availability for Weblogic services when you use static or dynamic clusters:
-
For static clusters
Automatic Service Migration is already configured if you select Enable Automatic Service Migration with Database Basis in the High Availability Options screen.
The Database Leasing is already configured and the migratable targets are created with the appropriate policies for the cluster. If you have implemented these settings, validate the configuration, as described in Validating Automatic Service Migration in Static Clusters.
In case you do not select this option during the Configuration Wizard session, you can configure automatic migration manually in a post step. For instructions to complete the steps for static clusters, see Configuring Automatic Service Migration in an Enterprise Deployment.
-
For dynamic clusters
You cannot configure Service Migration for dynamic clusters by using the Configuration Wizard, it needs to be configured manually. The following steps are needed:
-
Configure the database leasing for the cluster.
-
Set the appropriate migration policies for JTA Service and JMS Persistent Stores.
For instructions to complete the steps for dynamic clusters, see Configuring Automatic Service Migration in an Enterprise Deployment.
-
Note:
The High Availability Options screen appears during the Configuration Wizard session for the first time when you create a cluster that uses Automatic Service Migration or JDBC stores or both. All subsequent clusters that are added to the domain by using the Configuration Wizard, automatically apply the selected HA options.
Backing Up the Configuration
It is an Oracle best practices recommendation to create a backup after you successfully extended a domain or at another logical point. Create a backup after you verify that the installation so far is successful. This is a quick backup for the express purpose of immediate restoration in case of problems in later steps.
The backup destination is the local disk. You can discard this backup when the enterprise deployment setup is complete. After the enterprise deployment setup is complete, you can initiate the regular deployment-specific Backup and Recovery process.
For information about backing up your configuration, see Performing Backups and Recoveries for an Enterprise Deployment.