4 Getting Started with Developing Applications with Oracle JDeveloper
This chapter includes the following sections:
About Developing Applications with Oracle JDeveloper
JDveloper provides different types of windows, visual and code editing tools, and testing and analytical tools for developing applications.
The features for developing applications in JDeveloper include:
-
Different types of window for managing and working with different object types and resources associated with applications, projects, and files.
-
Several visual and code editing tools to facilitate the task of creating different types of source documents. The editors are integrated with other windows in the IDE, thus drag and drop operations and simultaneous, automatic updates among the various integrated tools are supported.
-
Tools to simplify the task of testing and analyzing source code, processes, and application modules or packages.
Creating Applications and Projects
An application heads the control structure view, while a project is positioned as the logical container for a program or part of a program. Create a new project, a new empty project, or open an external file into a new project to add a project to an application.
The application is the highest level in the control structure. It is a view of all the objects you need while you are working. An application keeps track of all your projects while you develop programs. A project is a logical container for a set that defines a JDeveloper program or portion of a program. A project might contain files representing different tiers of a multi-tier application, for instance, or different subsystems of a complex application. These files can reside in any directory and still be contained within a single project.
All of the projects within an application are displayed below that application. If you filter a project using the working set, the project is not displayed under the application. Closing an application or project closes all open editors or viewers for files in that application or project and unloads the files from memory.
You can remove application and project control files from the IDE without deleting them from the disk. (This is not true for other types of file, which will be deleted from the disk at the time that they are removed from the IDE.) JDeveloper can recognize many different file types, displaying each in its appropriate viewer or editor when you double-click the file.
When adding a project to an application, you can choose to:
-
Create a new project, with specific objects and attributes you define.
-
Create a new empty project, which inherits default project properties.
-
Open an existing set of files from outside JDeveloper into a new project.
Projects control their files lists directly through the directory. Applications and packages also define where and how the files within a project are stored.
Note:
The same object (physical file) can appear in more than one project. This means that any actions carried out on the object in one project will show up in the other project (although some effects will become apparent only after the project is compiled). For packages, two or more projects should not share a package unless, first, they also share a source path used to generate the package and, secondly, the package is already compiled and will never be changed.
How to Create an Application
An application is the highest level view of objects in the control structure that tracks projects. Use the procedure to create a new application with a specific feature scope.
The application is the highest level in the control structure. It is a view of all the objects you need while you are working. An application keeps track of all your projects while you develop programs..
To create a new application with a specific feature scope:
- Open the New Gallery by choosing File > New.
- In the New Gallery, in the Categories tree, under General, select Applications.
- In the Items list, double-click the application type you want to create.
- In the Create Application dialog, enter application details like the name and directory. For help with the wizard, press F1.
- Click Next to open the Project Name page, where you can optionally provide details for your project.
- When you are done, click Finish.
How to Create a Custom Application
You can either create an application with a specific feature, or create an application that can be customized to include any feature. Use the procedure to create a new custom application.
You can either create an application with a specific feature scope, or create a custom application that contains a single project that can be customized to include any features.
To create a new custom application:
- Open the New Gallery by choosing File > New.
- In the New Gallery, in the Categories tree, under General, select Applications.
- In the Items list, double-click Custom Application. The Create Custom Application wizard opens.
- In the Create Custom Application dialog, enter application details like the name and directory. For help with the wizard, press F1.
- Click Next to open the Project Name page, where you can optionally provide details for your project.
- When you are done, click Finish.
How to Create a Project
A project is a logical container for a program or part of a program. Use the procedure to create a new project with a specific feature scope.
A project is a logical container for a set of files that defines a JDeveloper program or portion of a program. You can create a project that is preconfigured with a specific set of features.
To create a new project with a specific feature scope:
- In the Applications window, select the application within which the project will appear.
- Click the Application Menu icon, and select New Project to open the Projects page of the New Gallery.
- In the Items list, double-click the project type you want to create.
- Complete the Create Project wizard, and click Finish. For help on the wizard, press F1.
The new project appears in the Applications window. It inherits whatever default properties you have already set. To alter project properties for this project, either double-click the filename or right-click and choose Project Properties.
Creating a New Custom Project
Use the procedure to create a new custom project.
To create a new custom project:
- In the Applications window, open the application that will contain the new project.
- Click the Application Menu icon, and select New Project to open the Projects page of the New Gallery.
- Under Items, select Custom Project.
- Click OK.
Managing Applications and Projects
Use the Applications window, which organizes projects to provide a logical view of the application, to manage applications and projects. View the contents within project folders in an application as a directory tree or a file list, or sort the nodes in packages and directories by type.
You can effectively manage your applications and projects using the Applications window. The Applications window organizes your projects in terms of higher-level logical components that gives you a logical view of your application and the data it contains. It provides an infrastructure that the different extensions can plug into and use to organize their data and menus in a consistent, abstract manner. While the Applications window can contain individual files (such as Java source files), it is designed to consolidate complex data. Complex data types such as entity objects, UML diagrams, EJB, or web services appear in this Applications window as single nodes. The raw files that make up these abstract nodes appear in the Structure window.
Applications displayed in the Applications window contain one or more projects. Within the projects are the root folders for the paths in that project. You can choose to view project contents as a directory tree or file list, and packages by tree or list. And you can sort the nodes within packages and directories by type.
How to Open an Existing Application
You can either create a new application, or open an existing application. Use the procedure to open an existing application and add it to the Applications window.
You have the option of creating new applications from scratch or opening existing ones. As soon as you create or import the application, it is added to the Applications node in the Applications window.
To open an existing application and add it to the Applications window:
How to Open an Existing Project
A project that is created or imported is added to the selected application. Use the procedure to open an existing project and add it to an application.
As soon as you create or import a project, it is added to the selected application.
To open an existing project and add it to an application:
How to Quickly Add Items to a Project Using the New Menu
Use the project context menu to add components to features for a newly created project. Use the procedure to add items using the project context menu.
After you have created your project, you can directly create components related to the project's features using the project context menu.
To add items using the project context menu:
How to Import Existing Source Files into JDeveloper
Import a file into a project, or use it to create a new project.
You can create new files of various types from scratch or open existing ones. When opening existing files, you can import them, along with their file structure, into an existing project or build a completely new project around them.
Alternatively, you can add source files to projects you already have.
How to Import Existing Files into a New JDeveloper Project
Import a file into JDeveloper to create a new project. Use the procedure to open existing files, and import them into a new JDeveloper project.
You can import existing files of any type into JDeveloper, creating a new project as you do so.
To open existing files and import them into a new JDeveloper project:
You can fine tune your project directories structure, for example to point to resource directories, in the Project Properties dialog.
How to Import a WAR File into a New JDeveloper Project
When you import a WAR file, JDeveloper creates a new project into which its contents are extracted. Use the procedure to open a WAR file, and import it into a new JDeveloper project.
You can import a WAR file into JDeveloper, creating at the same time a new project to contain its extracted contents.
To open a WAR file and import it into a new JDeveloper project:
The wizard analyzes the WAR file and extracts its contents.
The new project appears under the selected application node, populated with the imported files.
How to Import an EAR File into a New JDeveloper Application
JDeveloper uses an imported EAR file to create a new application based on the extracted EAR modules. Use the procedure to open an EAR file, and import it into a new application.
When you import an EAR file, JDeveloper will always create a new application and populate it with projects based on the EAR modules extracted. You cannot add the contents of an EAR file to an existing application or project.
You should not use this procedure to import an EAR file that you simply wish to deploy using JDeveloper. To do this, create a new application and project, then copy your EAR file into the project directory (or add its location to the project's content). The EAR file will then appear in the Applications window under the project's Application Sources node. From here, you can deploy the file by right-clicking it and choosing Deploy to.
To open an EAR file and import it into a new JDeveloper application:
How to Import Files into a Project
Use an imported file in a project, or create a new project with an imported file. Use the procedure to open an existing file, and add it to a project using the Import Existing Sources wizard.
You can create new files of various types from scratch or open existing ones. When opening existing files, you can import them, along with their file structure, into an existing project or build a completely new project around them.
You can also create new projects from existing source.
Note:
You can use the Import Existing Sources wizard to add.zip or.jar files to projects. You cannot use it to add.war or.ear files. A .war file requires the Import WAR File wizard to property extract its contents into the project. An EAR file requires the Import EAR File wizard, which extracts its contents into a new application.
To open an existing file and add it to a project using the Import Existing Sources wizard:
Managing Folders and Java Packages in a Project
JDeveloper enables you to create custom folders or Java packages within your project to better organize your project files.
How to Create a Folder or Java Package
Within projects, create custom folders or Java packages to organize project files. Use the procedure to create a folder or Java package.
To create a folder or Java package:
- In the Applications window, select the project or folder within which you want to create the custom folder.
- On the File menu, select New.
- In the New Gallery, under Categories, select General.
- Under Items, select Folder to create a new folder. To create a Java Package, under Items, select Java Package.
- In the Create Folder or Create Java Package dialog, specify the name of the folder or Java package, and the directory you want to create it in.
How to Delete a Folder or Java Package
Use the procedure to delete a folder or Java package.
To delete a folder or Java package:
- Select the folder or Java package that you want to delete.
- On the File menu, select Delete.
- On the Confirm Delete Folder dialog, confirm the deletion of the folder or Java package. Click Show Folder Files to see the files contained in the folder or Java package.
How to Manage Working Sets
Configure the Applications window with Working sets to view a subset of files from the project. Use All Files to return to the default view.
Working sets allow you to configure the Applications window to show you a subset of files from your project. This is particularly useful when working with large projects. Until you create a working set, there are no default working sets. After you create a working set, the option All Files lets you to get back to the default view.
How to Group Objects into a Working Set
Run and debug a working set of a large application so that neither the whole application nor performance is affected. Use the procedure to group objects in the Applications window into a working set.
You can run and debug a working set in just the same way as you run and debug a project. This allows you to work on just a subset of a large application, for example a Java EE application, without affecting the entire application or incurring a performance hit.
To group objects in the Applications window into a working set:
How to Create a Working Set by Defining File and Directory Filters
Select files or containers in the Applications window, or provide include and exclude filters in Manage Working Sets to define a working set. Use the procedure to create a working set by defining file and directory filters.
You can define a working set by selecting from files or containers in the Applications window, or by providing include and exclude filter patterns through the Manage Working Sets dialog.
To create a working set by defining file and directory filters:
How to Create a Working Set From Search Results in the Log Window
Exercise the option to save search results as a working set. Use the procedure to create a working set from the results of a search in the Log window.
You can create one or more sets of files for working on within a project. Based on the scope of your search, the action to save the search results as a working set is available.
To create a working set from the results of a search in the Log window:
- In the Log window, right-click and choose Save as Working Set from the context menu.
- In the Create Working Set dialog, enter a name for the working set.
How to Identify the Current Working Set
Focusing the mouse pointer over Working Sets in the Applications window displays the name of the current working set as a tooltip.
A tooltip in JDeveloper identifies the working set you are currently using:
-
In the Applications window, hover the mouse over the Working Sets icon. The name of the current working set is displayed as a tooltip. Alternatively, click the Working Sets icon to bring up a menu in which the active working set is checked.
How to Change the Active Working Set
Use the procedure to edit files and projects in a working set.
To change the active working set:
-
In the Applications window, click the Working Sets icon and select the working set you want to open.
Files not belonging to the working set are removed from the Applications window but no editors are closed.
How to Edit Files and Projects in a Working Set
Use the procedure to edit files and projects in a working set.
To edit files and projects in a working set:
How to Show All Files in the Applications window
Use the All Files option in Working Sets from the Applications window to show all files in the Applications window.
To restore the view in the Applications window to show all files:
-
In the Applications window, click the Working Sets icon and select (All Files).
How to Run and Debug a Working Set
A working set for debugging must include the projects that represent the Java EE modules. Use the procedure to run and debug a working set.
Before you begin, ensure that you are using the working set you want to run or debug. This should include the projects that represent the Java EE modules (Web applications, EJB modules) that you are working on and any dependencies.
Be aware that any projects that are explicit dependencies (in the Dependencies page of the Project Properties dialog) will be included even if they are excluded from the working set.
To run and debug a working set:
How to Browse Files in JDeveloper Without Adding Them to a Project
JDeveloper allows you to browse files without adding them to a project. Use the procedure to browse files in JDeveloper without adding them to a project.
Sometimes, you may not want to add files directly to a project, but yet have them handy for browsing. You can bring files into the JDeveloper IDE, without adding them to a project.
To browse files in JDeveloper without adding them to a project:
How to View an Archive
Open an archived file and view its contents, or add the contents to a new or existing project. Use the procedure to open an archive in JDeveloper and view its contents.
You can easily inspect the contents of any archive, after first opening the archived file in JDeveloper. You can add the contents of an archive to an existing or new JDeveloper project.
To open an archive in JDeveloper and view its contents:
How to View an Image File in JDeveloper
You can view image files in JDeveloper. Use the procedures to open and view an image in JDeveloper, and to view an image already imported into JDeveloper.
You can easily view any.gif, .jpg, .jpeg, or .png file from within JDeveloper.
To open and view an image in JDeveloper:
-
From the main menu, choose File > Open.
As you are only going to view the image, it doesn't matter which node in the Applications window is currently selected.
-
Navigate to the image or images to be opened. Be sure that the file type field either specifies all file types or the image types.
-
Select the image.
-
With your selection made, click Open.
The image is displayed in the main working area of JDeveloper.
To view an image already imported into JDeveloper:
- In the Applications window, select the image file.
- Double-click the file, or right-click and choose Open.
Setting Default Project Properties
The project properties specified in the Project Properties dialog apply only to individual projects. The project properties specified in the Default Project Properties dialog apply to all projects across applications.
The project properties you specify in the Default Project Properties dialog apply to all subsequent projects you create across applications. Those you specify in the Project Properties dialog apply only to the current project. You can also set custom properties to override the properties set in a current project. This is particularly useful in a multiuser development environment. Custom properties are not stored in the .jpr file.
How to Set Default Project Properties
Overrides to the default project values apply only to individual projects. Use the procedure to view or change the default settings for a project.
When you set project properties for an individual project, you override the default values for that project alone.
The procedures you follow for setting default project properties are identical to those for setting properties for individual projects — with the exception that, as you are in default properties, you do not need to first select an individual project. Note that some project properties cannot be set from the Default Project Properties dialog.
To view or change the default settings for a project:
- From the main menu, choose Application > Default Project Properties.
- In the Default Project Properties dialog, select the appropriate category.
- View or set the various properties as desired.
- When finished, click OK.
How to Set Properties for Individual Projects
Properties can be set for any individual project, or for all subsequent projects.
You can set the project properties for all subsequent projects, or fine-tune the properties for any individual project.
Additional project properties are also available, based upon specific tasks such as compiling, or debugging.
How to View or Change the Current Output Path for an Individual Project
Setting project properties for an individual project overrides the default project properties. Use the procedure to view or change the current output path for an individual project.
When you set project properties for an individual project, you override the default values for that project alone.
To view or change the current output path for an individual project:
How to Set the Target Java SE for a Project
Specify the Java SE that JDeveloper will use when compiling and running a project. Use the procedure to view or change the current Java SE for an individual project.
Setting the target Java SE specifies which Java SE JDeveloper will use when compiling and running your project.
To view or change the current Java SE for an individual project:
How to Manage Project Dependencies
If a project that is related to another project through dependencies is compiled, the related project is also compiled. Use the procedure to manage the project dependencies for an individual project.
Complex applications generally comprise multiple projects, which may be related though dependencies. That is, project A must depend on project B when project A uses classes or resources from project B. When this dependency is set, compiling project A will automatically compile project B.
Deployment profile dependencies are created and edited in the Project Properties dialog available from the Tools menu.
To manage the project dependencies for an individual project:
- In the Applications window, select the appropriate project.
- From the main menu, choose Application > Project Properties, or right-click and choose Project Properties.
- Select the Dependencies node.
- On the Dependencies page, view the current dependency hierarchy for the project.
- Select or deselect projects as desired.
- To change the current dependency ordering, click Ordering.
- When finished, click OK.
How to Associate Features with a Project Via a Template
Use a template in a project to avail the features available in the template. Use the procedure to associate features with a project by means of its template.
When you create a project from a template, the project will inherit all the features available in the template. More features are added dynamically to the project as you create content in your project. Go to Project Properties > Features > Reconcile to filter the list of features that are actually in use in the project.
To associate features with a project via its project template:
Note:
This procedure is applicable only for new projects created from a template.
How to Associate Features with an Individual Project
The JDeveloper design time filters the features to be associated with a project. Use the procedure to associate features with an individual project.
When features are associated with a project, JDeveloper's design time filters the choices you see based upon what you are most likely to need for a project of this type.
To associate features with an individual project:
- In the Applications window, select the appropriate project.
- From the main menu, choose Application > Project Properties, or right-click and choose Project Properties.
- Select the Features node.
- On the Features page, click the Add Features button.
- In the Add Features dialog, select the features to be associated with the project in the Project Features list.
- Click the shuttle button to transfer your selection to the Selected list.
- Click OK.
How to Set Javadoc Properties for a Project
Every JDeveloper project comes with defaults that you can replace. Use the procedure to set Javadoc properties for an individual project.
Every project you create carries the JDeveloper project defaults or those you have supplied yourself for all projects. You can also replace these defaults on a project-by-project basis. Setting these properties is the same in either case: only the location, and application, of the information differs.
To set Javadoc properties for an individual project:
- In the Applications window, select the project.
- From the main menu, choose Application > Project Properties, or right-click and choose Project Properties.
- Under Profiles, select the active profile node.
- Under the active profile node, select the Javadoc node.
- When finished, click OK to close the Project Properties dialog.
How to Manage Libraries
Internal library definitions persist within the project file, cannot be shared, and are added using the Project Properties dialog. External libraries persist in stand-alone library definition files, can be shared, and their URLs too get added when they are added to a project.
There are two categories of library: internal and external. Internal library definitions are persisted within the project file itself (that is, within the .jpr file) and are thus always available to anyone opening that project. However, internal library definitions are not sharable among any other projects. You can add an internal library to a project by going to the Libraries and Classpath page of the Project Properties dialog, and clicking Add JAR/Directory.
External library definitions are persisted within their own stand-alone library definition file (that is, the .library file). As such, external libraries can be checked into source control, referenced by any number of projects, and can be shared among all users in a team environment in the same way that java source files are. Since external libraries have their own unique URL, adding an external library to a project adds that URL to the project.
How to Add Application-level Libraries and Classpaths
Libraries that are added at the application level are added to the libraries and classpaths of all projects within the application. Use the procedure to add an application-level library.
Libraries are often required across many or all projects within an application. All libraries that you add at the application level are implicitly added to the libraries and classpaths of all projects within the application and are readily available at design and compile time.
Any library or classpath added at the application level for use during deployment are included in the packaged EAR lib directory and is selected for deployment by default.
To add an application-level library:
- Right-click the application in the application window.
- Select Application Properties from the contextual menu.
- Select the Libraries and Classpath node.
- Click Add Library.
- Locate the required library in the selection tree and click OK.
Libraries added at the application-level do not appear in the in the project properties Libraries and Classpath page by default. Check Show Application Libraries in the project properties Libraries and Classpath page to see all application-level libraries (this option is disabled if no application-level libraries exist). You can move the list of application-level libraries as a block to the top or bottom of the classpath entries using the Move to Top or Move to Bottom arrows. You cannot move an individual application-level library.
You can create and add an application-level library in the same way as described in How to Create a New Library and Add it to a New Project.
How to View the Current Libraries in a Project
Use the procedure to view the current libraries for an individual project. The classpath of a library is added to the project classpath when the library is added to the project.
When you include libraries in a project, the source paths defined for those libraries automatically become part of the project's classpath.
To view the current libraries for an individual project:
How to Add an Existing Library to a Project
Use the procedure to add an existing library to a project.
You can add an existing library to a project.
To add an existing library to a project:
- With the project selected in the Applications window, open the Project Properties dialog.
- Select the Libraries and Classpath node
- On the Libraries and Classpath page, click Add Library.
- Locate the required library in the selection tree and click OK.
How to Create a New Library and Add it to a New Project
Use the procedure to create a new library, and add it to a project.
You can create a new library and add it to a new project.
To create a new library and add it to a project:
- With the project selected in the Applications window, open the Project Properties dialog.
- Select the Libraries and Classpath node.
- On the Libraries and Classpath page, click Add Library.
- On the Add Library dialog, click New.
- In the Create Library dialog, enter a name for the new library and select its location.
- For each path type, click Add Entry or Add URL as appropriate. To remove a path, or correct an addition, click Remove. To rearrange the order of entries, use the reordering buttons to the right of the display area.
- Once you have clicked either Add Entry or Add URL, in the resulting selection dialog enter the filename or browse through the list to select one. When your entry is complete, click Select.
- In the Create Library dialog, click OK.
- On the Libraries and Classpath page, if finished click OK.
How to Edit an Existing Library in a Project
Use the procedure to edit an existing library in a project.
You can edit an existing library in a project.
To edit an existing library in a project:
- With the project selected in the Applications window, open the Project Properties dialog.
- Select the Libraries and Classpath node.
- On the Libraries and Classpath page, select the library to be altered from the Classpath Entries list.
- Click Edit. (This button remains the View button if the library is not editable.)
- In the Edit Library Definition dialog, the appropriate library's name should appear in the first field. Make any desired changes to the library name by typing directly into the field.
- For each Edit Path dialog, click Add Entry or Add URL as appropriate. To remove a path, or correct an addition, click Remove. To rearrange the order of entries, use the reordering buttons to the right of the display area.
- Once you have clicked either Add Entry or Add URL, in the resulting selection dialog enter the directory name or browse through the list to select one. When your entry is complete, click Select.
- In the Edit Library dialog, click OK.
- On the Libraries and Classpath page, if finished click OK.
How to Remove Libraries from a Project
The classpath of a library is removed from the project classpath when the library is removed from the project. Use the procedure to remove a library from a project.
When you remove libraries from a project, the source paths defined for those libraries no longer form part of the project's classpath.
To remove a library from a project:
- In the Applications window, select the appropriate project.
- From the main menu, choose Application > Project Properties, or right-click and choose Project Properties.
- Select the Libraries and Classpath node.
- On the Libraries page, select the desired library or libraries from the Libraries list and click Remove.
- If finished, click OK.
How to Import Libraries or Java SEs Outside the Project Scope
Work with libraries outside a JDeveloper project so that they are available to a project or a group of users. Use the procedure to work with libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project.
You can work with libraries completely outside the JDeveloper project scope, setting them up to be either available to you for use in any of your projects or available to a group of users across an installation.
To work with libraries or Java SEs outside of the scope of a project:
- From the main menu, choose Tools > Manage Libraries.
- In the Manage Libraries dialog, select either the Libraries or the Java SE Definitions tab.
- Select the User node to import libraries for your own use. Select the Extension node to import libraries for use across a group.
- Click Load Dir.
- In the Load Directories dialog, navigate to the library that you wish to import and click Select.
- When finished, click OK.
How to Create Libraries or Java SEs Outside the Project Scope
Create libraries outside the JDeveloper project so that they are available to a project or a group of users. Use the procedure to create libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project.
You can work with libraries completely outside the JDeveloper project scope, setting them up to be either available to you for use in any of your projects or available to a group of users across an installation.
To create libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project:
- From the main menu, choose Tools > Manage Libraries.
- In the Manage Libraries dialog, select either the Libraries or the Java SE Definitions tab.
- Select the User node to create libraries for your own use. Select the Extension node to create libraries for use across a group.
- Click New.
- In the Create Library dialog or the Create Java SE dialog, complete the details for the new library or Java SE.
- When finished, click OK.
How to Edit Libraries or Java SEs Outside the Project Scope
Work with libraries outside the JDeveloper project so that they are available to a project or a group of users. Use the procedure to edit libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project.
You can work with libraries completely outside the JDeveloper project structure, setting them up to be either available to you for use in any of your projects or available to a group of users across an installation.
To edit libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project:
How to Delete Libraries or Java SEs Outside the Project Scope
Work with libraries outside the JDeveloper project so that they are available to a project or a group of users. Use the procedure to delete libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project.
You can work with libraries completely outside the JDeveloper project scope, setting them up to be either available to you for use in any of your projects or available to a group of users across an installation.
To delete libraries or Java SEs outside the scope of a project:
How to Manage Application and Project Templates
Use application and project templates to create applications with the specified combination of features.
Application and project templates provide you with a quick way to create the project structure for standard applications with the appropriate combination of features already specified. The new application created from template appears in the Applications window already partitioned into tiered projects, with the associated features set.
The application template you select determines the initial project structure, the named project folders within the application. The project templates define the associated features. You can then filter the work you do in JDeveloper such that the choices available are focused on the features you are working with.
How to Define a New Application Template
To standardize application development, use application templates that provides templates for projects. Use the procedure to define a new application template.
An application template organizes one or more project templates which specify the project types expected in the application. Using such templates enables you to standardize the way you develop an application.
To define a new application template:
The application template appears in the New Gallery in the Applications category of the Business Tier.
How to Define a New Project Template
Project templates provide standards for projects within an application. Use the procedure to define a new project template.
Project templates specify the various types of projects expected in a given application. Project templates are contained within application templates.
To define a new project template:
The project template appears in the New Gallery in the Projects category.
How to Share Application and Project Templates
Application or project templates are created in a location that can be accessed by other users. Use the procedure to create a shared template.
You can create an application or project template in a shared location. Other users can read templates from the shared location and use the same templates for their application and projects.
To create a shared template:
- Choose Application > Manage Templates.
- In the Manage Templates dialog, select either the Application Templates or Project Templates node and click the Add a shared location icon.
- In the Add Templates Directory dialog, enter or browse to the location where you want the shared template to be stored.
The shared templates folder is listed under both the Application Templates and Project Templates node.
How to Edit an Existing Application or Project Template
Users can edit templates to suit requirements. Use the procedure to edit an existing application or project template.
You can edit existing user-defined application or project templates.
To edit an existing application or project template:
How to Delete an Existing Application or Project Template
Application or project templates can be deleted. Use the procedure to delete an existing application or project template.
You can delete existing user-defined application or project templates.
To delete an existing application or project template:
How to Manage File Templates
You can create file templates with custom data for applications within JDeveloper. Use the procedures to create a template, and to edit an existing template.
JDeveloper allows you to create file templates with pre-populated custom data and use them in your application. For example, you can create a Java class file template that contains basic header tagging, then when you need to add a Java class file in your application, you would start from your created template and that would save you from manually entering basic header data in every single Java class.
You can create templates for all the files types supported in JDeveloper such as Java, html, xml, etc.
There are two workflows for managing file templates: you can edit an existing template and you can create a new template. The workflows are described below.
To edit an existing template:
-
Open your application in JDeveloper and navigate to Tools > Preferences > File Templates. JDeveloper provides an out-of-the-box Java class template.
-
In the File Templates dialog go to the folder directory and navigate to General > Java.
-
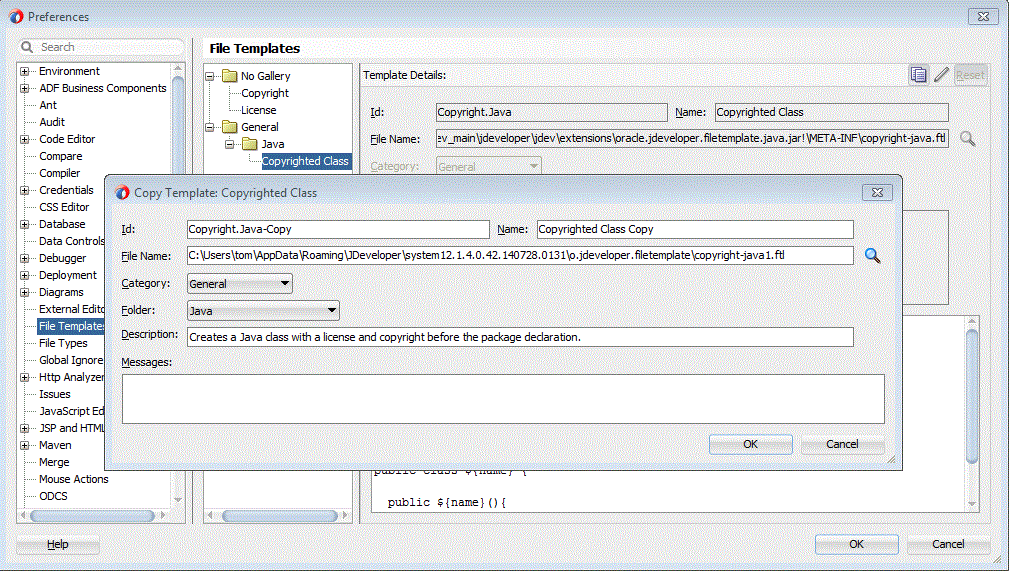
Click the provided template, Copyrighted Class. The template details and template content appears on the right pane.
By default the built-in templates are not editable. If you start typing to modify the content of the template, you will be prompted to confirm that you want to modify the built-in template.
-
Modify the template by adding a simple line of text above the @author line. For example,
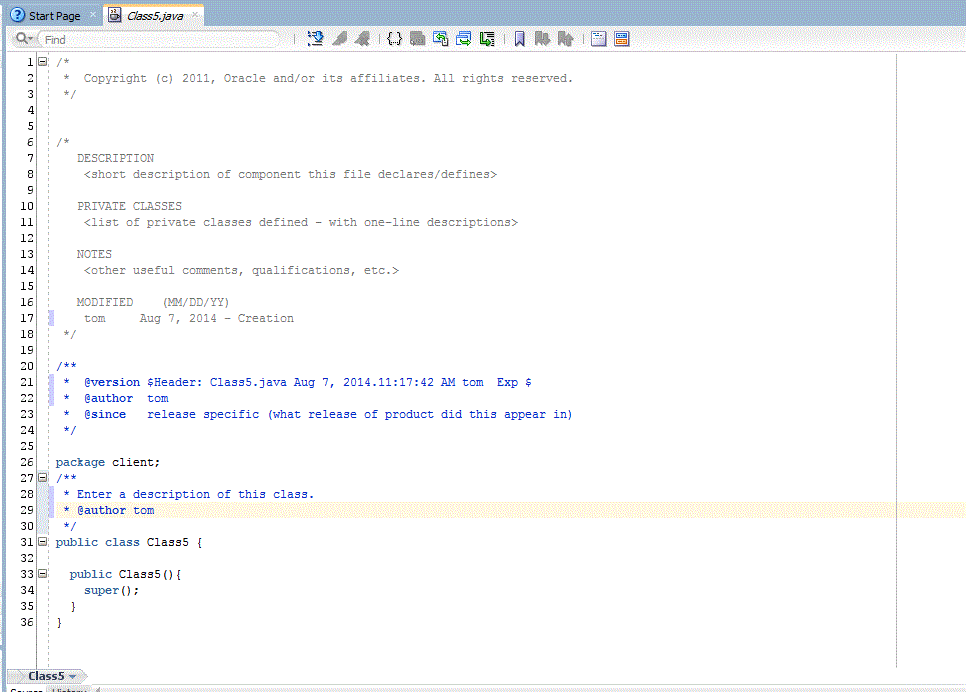
* Enter a description of this class.
Note:
JDeveloper provides out of the box variables to use in your templates. To understand those variables see, Available File Template Variables.
You can use the Reset button on the top-right corner of the page to revert the template to its original text.
-
Click OK to close the Preferences dialog.
-
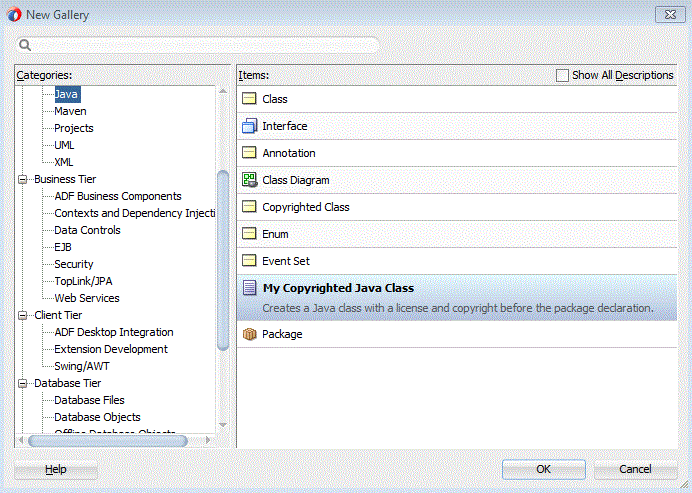
To use the template in your application, navigate to New > Gallery > General > Java and you will see on the right pane the Copyrighted Class template.
-
Select the template and click OK.
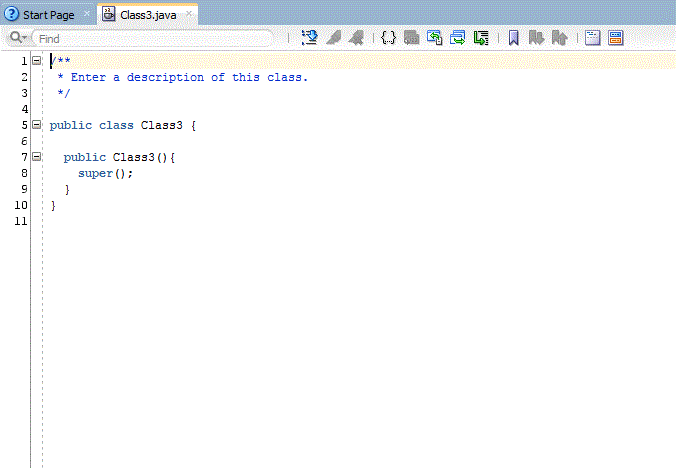
After defining the File Name, the new class is created using the text in the created template.
Line 28 shows the text that you added to the template on step 4.
To create a new template:
Available File Template Variables
JDeveloper provides name, nameAndExt, date, package, time, dateTime, and user File Template Variables.
JDeveloper provides the following File Template Variables out-of-the-box:
-
name—the name, without extension, of the file that will be created
-
nameAndExt—the name, without extension, of the file that will be created
-
date—the current time, in this format: Feb 16, 2008 from DateFormat.getDateInstance() during template processing
-
package—the current package is specified
-
time—the current time, in this format: 7:37:58 PM from DateFormat.getTimeInstance() during template processing.
-
dateTime—the current date, from DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance() during template processing
-
user—the current user name, as returned from System.getProperty("user.name")
How to Save an Application or Project
Use the Save or Save All options to save an application or project.
You can save an application or project in several ways.
To save all the components across applications, including all projects:
-
From the main menu, choose File > Save All or click the Save All icon.
Alternately, you can save components individually by using File > Save.
It is important to note that saving the application or project container (.jws, .jpr) file alone does not save the individual files governed by that application or project. Nor does saving individual contained files save the container node.
Each node is an independent entity and must be saved as such. Using Save All takes care of changes to these container files, as well as all content files.
Using Save or Save As on a selected application or project node saves or duplicates the .jws or .jpr file only: it does not save or duplicate the files contained within the node.
Note too that if you do a Save As on an application or a project container file, that container is replaced, but the files contained are not altered. If you do a Save As on an individual file, that file is duplicated. However, if you want to rename a file, you should use File > Rename.
How to Save an Individual Component or File
Use the Save or Save As on a selected application or project node to save the node. Use the procedure to save an individual component or file.
Saving the application or project container (.jws, .jpr) file alone does not save the individual files governed by that application or project. Nor does saving individual contained files save the container node.
Each node is an independent entity and must be saved as such. Using Save All takes care of changes to these container files, as well as all content files.
Using Save or Save As on a selected application or project node saves or duplicates the .jws or .jpr file only: it does not save or duplicate the files contained within the node.
You can rename an individual file or component using File > Rename.
Note that if you do a Save As on an application or a project container file, that container is replaced, but the files contained are not altered. If you do a Save As on an individual file, that file is duplicated.
To save an individual component or file:
How to Rename an Application, Project, or Individual Component
You can rename application files. Use the procedure to rename an application or project container, or an individual source file.
You can rename application control files, project control files, and individual files. The correct way of renaming Java classes is to use refactoring.
To rename an application or project container, or an individual source file:
Alternately, you can use File > Save As. Note that Rename always replaces the target file. Save As replaces application or project container (.jws, .jpr) files, but duplicates source files.
When you are saving files, remember that saving a container file alone does not save the contents of the entire application or project. For that, you need to use Save All.
How to Relocate an Application, Project, or Project Contents
Files associated with projects or projects with applications can be moved using the Applications window. Use the procedures to move an individual file, an entire application or directory, or a group of files from one project to another.
The Applications window presents a visual representation of the logical structure of applications and projects. It is not a file directory. It does not necessarily represent the physical location of those files.
To change the physical location of individual files, you can work in JDeveloper. To change the physical location of a group of files, it is easier to work through your operating system's file manager.
To change the association of files with projects or projects with applications, you would work in the Applications window, adding or removing as appropriate.
Note:
The best practice for relocating Java classes is to use the options available on the Refactor menu.
To change the physical location of an individual file, whether within the project or a container (.jws or .jpr) file:
-
In the Applications window, select the file to be moved.
-
From the main menu, choose File > Rename. If you have chosen a Java file, the Rename File dialog will open. You will be able to relocate the file only if you choose the option Rename the file only, do not update references in this dialog.
-
In the Rename dialog, navigate to the new location for the file and change the file's name if you wish.
-
Click Save.
The file is now physically stored in the new directory. Its logical representation does not change in the Applications window unless you explicitly alter it.
To change the physical location of an entire application or directory:
-
In your operating system's file manager, navigate to the directory in which the files currently reside. Files stored in the JDeveloper default directory reside in the
myworkfolder. -
Select the entire directory (application, project, or files within a project) to be moved and move it to the new location.
The files have now been moved, but JDeveloper no longer knows where they are.
-
When you return to JDeveloper, in the Applications window, and choose Open Application from the drop-down list.
-
Navigate to the new physical location of the application or project and click Open.
To change the physical location of a group of files from one project to another:
How to Close an Application, Project, or Other File
Any application, project, or file that is closed in the Applications window is unloaded from memory. Use the procedure to close an application or project.
When you close an application, project, or file in the Applications window, that application or project is unloaded from memory. When an application or project is closed, it appears in its unexpanded form in the Applications window.
In addition, you can remove applications, projects, or files from the Applications window, which removes them only from the list, or you can delete them permanently, wherever they reside, from within JDeveloper.
To close an application or project:
You can close a file opened in a viewer or an editor by clicking on the close box of the corresponding document tab above the editor window.
How to Remove a File from a Project
You can either remove files from a project, or you can delete them permanently. Use the procedure to remove a file from a project.
You can remove files from a project, which removes them only from the Applications window list, or you can delete them permanently, wherever they reside, from within JDeveloper.
To remove a file from a project:
- In the Applications window, select the file or files you wish removed.
- Select File > Delete.
- The Confirm Delete Dialog is displayed. If you are certain that you want to delete the file, click Yes.
How to Remove a Project from an Application
Delete the project control file to remove a project from an application. Use the procedure to remove a project from an application.
You can remove projects from the application by deleting the project control file (.jpr) from within JDeveloper.
To remove a project from an application:
- In the Applications window, select the project you wish to remove.
- Select File > Delete Project.
- The Confirm Delete Project Dialog is displayed. To confirm the deletion, click Yes.
How to Remove an Application
Use the procedure to remove an application from the IDE.
You can close an application and remove it from the Applications window. If you want to delete the application
To remove an application from the IDE:
- In the Applications window, click the Application Menu.
- Select Close Application.
- The Confirm Close Application Dialog is displayed. Select an option based on your preference.
- Select Application > Delete to delete the application and its contents.