Oracle Forms Services Architecture
Oracle Forms Services is a middle-tier application framework for deploying complex, transactional Forms applications to a network such as an intranet or the Internet.
The Forms Services architecture is made up of three-tiers. Developers build Forms applications with Forms Developer and deploy them with Forms Services. Developers can also take applications that were previously deployed in client/server and move them to a three-tier architecture. Some minor changes in application code may be required when moving to a three-tier architecture.
The three tiers of the architecture are as follows:
- Client Tier: The client tier (top of Figure -1) may contain one of the following two configurations:
- The Forms Standalone Launcher (FSAL) and a Java Runtime Environment or Java Development Kit (JDK).
- The Java Plug-In/Java Runtime (JPI/JRE), used to launch the application with Java Web Start (JWS).
Note:
Some browsers, such as Microsoft Edge with IE mode, may still include the required components for this configuration but this configuration is no longer recommended for use.
- Middle Tier: The middle tier (middle of Figure -1) is the application server, where application logic, server software, and compiled Forms application modules are stored.
The Forms Listener servlet and the Forms Runtime process also reside on the middle tier.
- Database Tier: The database tier (bottom of Figure -1) is the database server, where database server software is stored.
Figure -1 Three-tier configuration for running a form
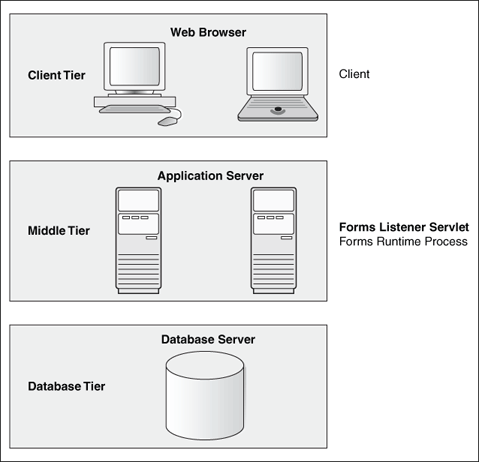
Description of "Figure -1 Three-tier configuration for running a form"
Forms Listener Servlet
The Forms Listener servlet is a broker between the Java client and the Forms Runtime process. The servlet takes connection requests from Java client processes and initiates a Forms Runtime process on their behalf.
If your application uses Forms REST integration, the calls to REST are executed by the Forms Listener servlet.
The Figure -2 shows how the client sends HTTP requests and receives HTTP responses from Forms Services. Oracle Forms Services uses the Forms Listener servlet to start, stop, and communicate with the Forms Runtime process. In this image, the client is to the left. In the center of the image, the HTTP Listener acts as the network endpoint for the client, keeping the other server computers and ports from being exposed at the firewall.
The Forms Runtime process, in the right side of the image, executes the code contained in a particular Forms application. The Forms Listener servlet manages the creation of a Forms Runtime process for each client and manages the network communications between the client and its associated Forms Runtime process.
Note:
The Forms Listener servlet is configured for you during the Oracle Fusion Middleware installation process.Figure -2 Architecture using the Forms Listener Servlet
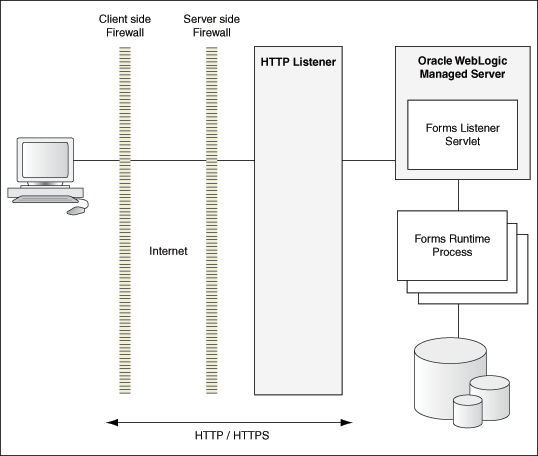
Description of "Figure -2 Architecture using the Forms Listener Servlet"
Forms Runtime Process
For each Oracle Forms session, there is one Oracle Forms Runtime process on the application server. This process is where Oracle Forms actually runs, and manages application logic and processing. It also manages the database connection; queries and updates data; runs any PL/SQL in the form; executes triggers; and so on. It uses the same forms, menus, and library files that were used for running in client/server mode.
The Forms Runtime process also uses a Java Virtual Machine (JVM), as needed, to run custom Java imported into the application, calls to Oracle Reports, or calls to Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher (also referred to as the Analytics Publisher). In order to limit the amount of memory consumed by the Forms Runtime process, the Forms JVM Controller can be configured and enabled. With the JVM Controller enabled, memory needed by this JVM can be shared across multiple JVMs, thereby reducing the total memory consumption and freeing more resources on the server. To manage JVM usage and pooling, see Configuring and Managing Java Virtual Machines.