7 Working with ADF Desktop Integration Table-Type Components
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Downloading Pending Insert and Pending Update Rows to an ADF Table Component
-
Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component Using an UploadAllOrNothing Action
-
Deleting ADF Table Component Rows in the Fusion Web Application
-
Adding a ModelDrivenColumnComponent Subcomponent to Your ADF Table Component
-
Configuring an ADF Table Component to Resize Columns Based on Data at Runtime
-
Limiting the Number of Rows Your Table-Type Component Downloads
About ADF Desktop Integration Table-Type Components
ADF Desktop Integration provides the ADF Table component to display structured data. It provides end users with the functionality to download rows of data. It also enables end users to edit or delete downloaded data, insert new rows of data, and to upload new and edited rows of data.
For this to happen, you must expose methods on data controls, create action bindings in your page definition file, and set properties for the ADF Table component that an Excel worksheet hosts. Figure 7-1 shows the ADF Table component.
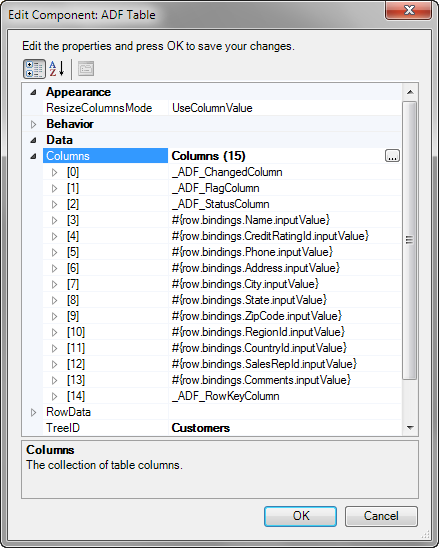
Figure 7-1 ADF Desktop Integration Table-Type Components
Description of "Figure 7-1 ADF Desktop Integration Table-Type Components"
Each ADF Table component contains a Key column. Do not remove the Key column as it contains important information that is used by ADF Desktop Integration for the proper functioning of the table. Removal of the Key column, or any modification in the Key column cell, results in errors and data corruption. For information about the Key column, see Configuring ADF Table Component Key Column.
The other ADF Desktop Integration components that you can use with these table-type components are described in Working with ADF Desktop Integration Form-Type Components and Working with Lists of Values .
ADF Desktop Integration Table-Type Components Use Cases and Examples
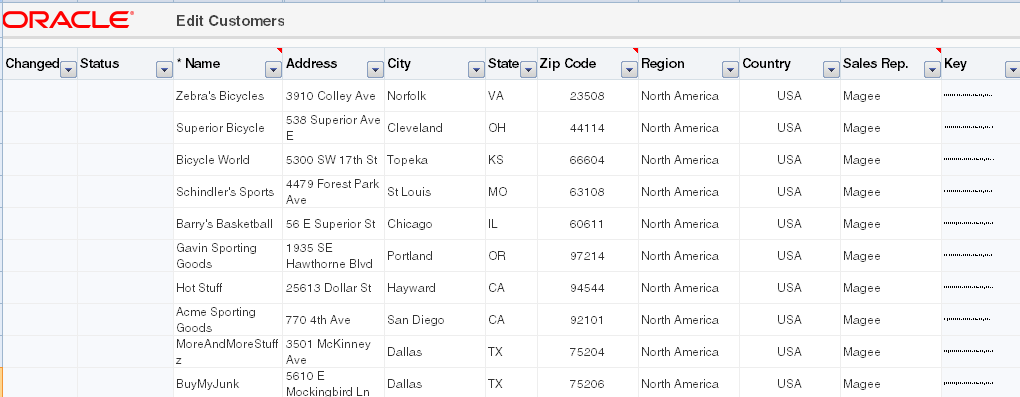
Tables are used to display the structured information. For example, Figure 7-2 shows an ADF Table component of Summit sample application for ADF Desktop Integration with data downloaded from the respective Fusion web application.
Figure 7-2 ADF Table Component with Downloaded Data
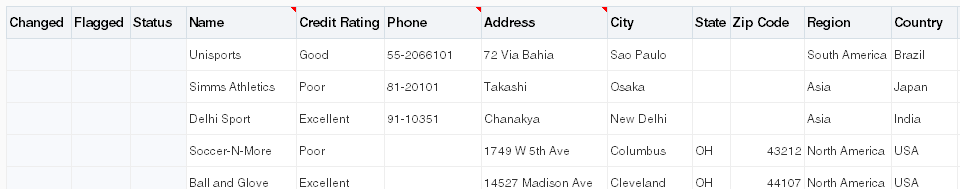
Description of "Figure 7-2 ADF Table Component with Downloaded Data"
Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components
After you have added a table component to your integrated Excel workbook, you may find that you need to add additional functionality to configure your table. Following are links to other functionality that table components can use.
-
Search and Select dialog: You can configure a
ModelDrivenColumnComponentsubcomponent in a table column, as described in Adding a Model-Driven List Picker to an ADF Table Component, to display a dialog where end users can search and select data. -
Dependent List of Values: You can add dependent list of values components in your table component. See Creating Dependent Lists of Values in an Integrated Excel Workbook.
-
Styles: You can configure the display of your form-type components using several predefined Excel styles. See Working with Styles.
-
Tooltips: You can configure tooltips to display additional information or instructional text to your end users. See Displaying Tooltips in ADF Desktop Integration Components.
-
EL Expressions: You can use EL expressions with table-type components. See ADF Desktop Integration EL Expressions.
Page Definition Requirements for an ADF Table Component
ADF Table components require that you expose specific control bindings in the page definition file in order to provide data-entry functionality.
The ADF Table component is one of the Oracle ADF components that ADF Desktop Integration exposes. It appears in the components palette of the ADF Desktop Integration Designer task pane and, after inserted into an Excel worksheet, allows the following operations:
-
Read-only
-
Insert-only
-
Update-only
-
Insert and update
Review the following sections for information about page definition file requirements specific to an ADF Table component.
Before you can configure an ADF Table component to provide data-entry functionality to your end users, you must configure the underlying page definition file for the Excel worksheet with ADF bindings. For general information about the page definition file requirements for an integrated Excel workbook, see Working with Page Definition Files for an Integrated Excel Workbook.
Expose the following control bindings when you create a page definition file for authoring an ADF Table component:
-
Tree binding that exposes the desired attribute bindings. Note that ADF Desktop Integration only supports scrollable and range paging access modes for view objects. The other access modes are not supported.
Consider using the range paging access mode when your integrated Excel workbook has to download large amounts of data. See Efficiently Scrolling Through Large Result Sets Using Range Paging in Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
If you decide to use the range paging access mode, make sure that the application's view object supports this access mode before using it with ADF Desktop Integration. For example, the view object must work properly with TOP-N queries described in Understanding How Oracle Supports "TOP-N" Queries of Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
In addition, note that view objects with range paging access mode cannot be scrolled with unposted rows. For this reason, make sure that ADF Desktop Integration action sets commit or roll back any pending changes as expected. If pending changes are not committed or rolled back before invoking an ADF Table component's
Downloadaction, the application reports the following exception:An attempt has been made to navigate a rowset in range paging mode when the rowset has pending changes.
Before inserting new rows, the iterator repositions to the first row, if necessary. This is because inserting new rows after the first row can result in unexpected scrolling. This behavior applies to the ADF Table component's
Uploadaction as well as double-click action sets for insert rows.Note:
Deleting rows may also result in unexpected scrolling with a view object in range paging access mode. Therefore, range paging access mode should not be used if the ADF Table component’sDeleteFlaggedRowsaction is exposed in the integrated Excel worksheet. -
Method action bindings and action bindings (such as
Execute,Commit, andCreateInsert) if you intend to configure values for the ADF Table component'sRowActionsandBatchOptionsgroups of properties. Examples of procedures where you set values for these groups of properties include:
Figure 7-3 shows the bindings that the ExcelCustomers.xml page definition file includes. This page definition file can support the use of an ADF Table component in the Excel worksheet that it is associated with.
Figure 7-3 ADF Bindings Supporting Use of an ADF Table Component
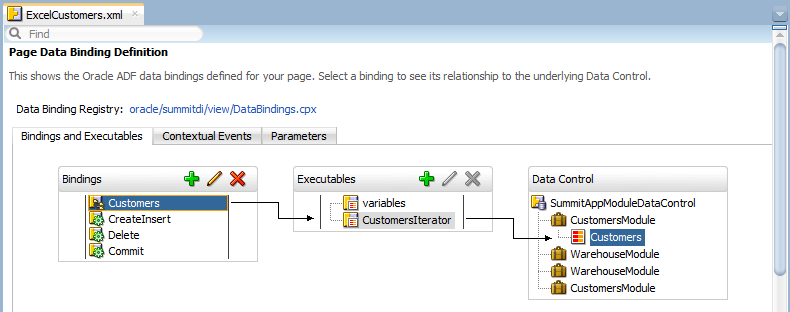
Description of "Figure 7-3 ADF Bindings Supporting Use of an ADF Table Component"
Inserting an ADF Table Component into an Excel Worksheet
After you configure a page definition file correctly, you can insert an ADF Table component into the worksheet and configure its properties to achieve the functionality you want. The ADF Table component enables you to download, edit, and upload rows of data.
How to Insert an ADF Table Component
You insert an ADF Table component using one of the following methods:
-
In the bindings palette of the ADF Desktop Integration Designer task pane, select the tree binding to use and click Insert Binding.
The following procedure describes how to insert an ADF Table component using the bindings palette. One benefit of this method over the other two is that you do not have to manually add each column that you want to appear in the component at runtime.
-
In the Oracle ADF tab, select ADF Table from the Insert Component dropdown list.
-
In the components palette of the ADF Desktop Integration Designer task pane, select ADF Table and click Insert Component.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of ADF Table component. See Inserting an ADF Table Component into an Excel Worksheet.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To insert an ADF Table component into an Excel worksheet:
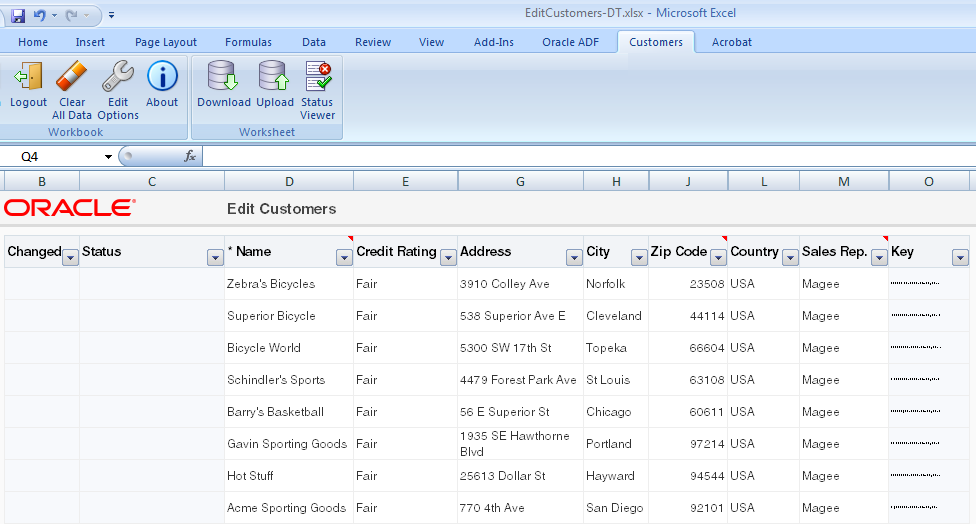
Figure 7-5 shows the ADF Table component in EditCustomers-DT.xlsx in design mode.
Figure 7-5 ADF Table Component in Design Mode
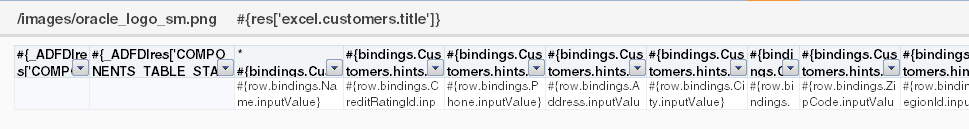
Description of "Figure 7-5 ADF Table Component in Design Mode"
Figure 7-6 shows the ADF Table component in EditCustomers-DT.xlsx at runtime.
For information about the properties that you can set for the ADF Table component, see ADF Table Component Properties and Actions.
To remove the table component, use the Delete ribbon command. See Removing ADF Desktop Integration Components.
How to Add a Column in an ADF Table Component
If you inserted the table without using the tree binding (for example, you inserted the table from the component palette) you add columns to the table to display the data for each attribute that you want to appear in the table. For example, a customers' table will have columns that displays customer name, phone, credit rating, and so on.
The procedure is the same if you want to add a column to table you inserted using the tree binding.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of ADF Table component. See Inserting an ADF Table Component into an Excel Worksheet.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To add a column in an ADF Table component:
ADF Desktop Integration does not limit the number of columns you can add to an ADF Table component. You can add as many columns as your version of Excel supports. However, a wide table can result in a poor user experience and slow performance. If you experience slow performance, try to reduce the number of table columns before investigating other causes. ADF Desktop Integration recommends configuring less than 30 columns per table when possible to optimize performance and user experience.
Downloading Data to an ADF Table Component
After you add an ADF Table component to a worksheet, configure an Oracle ADF component, such as a worksheet ribbon command, to invoke an action set. The action set must include the ADF Table component Download action among the actions that it invokes.
The number of rows that an ADF Table component contains expands or contracts based on the number of rows to download from a Fusion web application. You should not place anything to the left or right of a table-type component unless you want to replicate it when Excel inserts rows to accommodate the data that one of the table-type components downloads. You can place other components above or below a table-type component as they maintain their position relative to the table-type component at runtime.
How to Download Data to an ADF Table Component
Configure a ribbon command to invoke the ADF Table component Download action.
Before you begin:
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to configure ADF component to download data to an ADF Table data component. See Downloading Data to an ADF Table Component.
To download data to an ADF Table component:
What Happens at Runtime: How an ADF Table Component Downloads Data
The end user invokes the action set that you configured. The action set invokes the list of actions specified in order. These include an action that invokes the Download action of the ADF Table component. When invoked, the Download action downloads all rows from the tree binding referenced by the ADF Table component TreeID property.
Make a note of the following points when the Download action is invoked at runtime:
-
If any rows are marked as changed when the
Downloadaction is invoked, the end user is prompted to confirm the action and to continue (see Figure 7-8). If the end user chooses No, the action and the action set are cancelled without error. -
All existing Excel rows are removed from the table in Excel.
-
The status column is cleared of all messages.
-
Any criteria that has been applied to the worksheet using Excel's Filter functionality is automatically cleared prior to the Upload action.
-
Excel's precision for a specified number is confined to 15 significant figures. If server data has a higher precision, Excel silently changes the precision. For example,
1234567890123456789012345678901234567890is downloaded as1.23456789012345E+39.
Figure 7-8 Confirmation Prompt Before Downloading Data in ADF Table

Description of "Figure 7-8 Confirmation Prompt Before Downloading Data in ADF Table"
The number of rows that the action downloads depends on the values set for the RowLimit group of properties in the ADF Table component. See Limiting the Number of Rows Your Table-Type Component Downloads .
Downloading Pending Insert and Pending Update Rows to an ADF Table Component
ADF Desktop Integration provides pending insert rows and pending update rows that facilitate the insertion and update of data from the ADF Table component.
A Pending Insert row is a worksheet table row with data that, on upload, is inserted as a new data row in the iterator. For example, if the end user creates a new row in the table by using the Insert option in the right click context menu, the new row is treated as a pending insert row and is inserted to the iterator when being uploaded.
A Pending Update row is a worksheet table row with data that, on upload, updates an existing data row in the iterator. For example, if the iterator of the tree binding contains some rows retrieved from the database and when these rows are downloaded to the ADF table, they are treated as pending update rows. If the end user makes changes to these rows and uploads them, the existing rows in the iterator are updated with new values from the ADF Table row.
In most cases, rows in the iterator of the tree binding are downloaded as pending update rows into the ADF Table. If you want some rows to be downloaded as pending inserts, you need to set the state of these rows to STATUS_INITIALIZED. For information about how to set a row's state as STATUS_INITIALIZED, see the setNewRowState method in Oracle Fusion Middleware Java API Reference for Oracle ADF Model.
Note the following differences between pending insert rows and pending update rows:
-
Pending insert rows are populated with the value of the EL expression for the insert component that is associated with each column in the ADF Table component (if the
InsertUsesUpdatecolumn property is set toFalse), while pending update rows are populated with the value of the EL expression for the update component that is associated with each column in the ADF Table component. -
When evaluated for pending insert rows, the EL expression
#{components.componentID.currentRowMode}returnsInsert. In contrast, the same EL expression returnsUpdatefor pending update rows.Note that the
componentIDpart of the EL expression#{components.componentID.currentRowMode}references the ID of the ADF Table component.
For information about EL expressions, see ADF Desktop Integration EL Expressions.
What Happens at Runtime: Download Action is Invoked
When the Download action is invoked, it examines the state of each row in the iterator. Rows of state STATUS_INITIALIZED are downloaded as pending insert rows in the table, while rows of other states are downloaded as pending update rows.
Using STATUS_INITIALIZED Rows for Pending Inserts
You can use STATUS_INITIALIZED rows to pre-populate values for some, or all, attributes of the pending insert rows. As a STATUS_INITIALIZED row is not validated, you can configure an action to populate the STATUS_INITIALIZED row partially and insert it into the iterator before the Download action is invoked. The Download action then treats this row as a pending insert row so that a new row, based on the pre-populated row, can be inserted.
Note that STATUS_INITIALIZED rows are not automatically removed from the iterator during download. You can configure another action to remove STATUS_INITIALIZED rows after download. For example, you can configure an action set with the following actions:
-
ADFmActionthat createsSTATUS_INITIALIZEDrows -
Table.Downloadaction -
ADFmActionthat cleans upSTATUS_INITIALIZEDrows
What You May Need to Know About DownloadForInsert Action
ADF Desktop Integration also supports a table action called DownloadForInsert. DownloadForInsert is an obsolete action and can be replaced with the Download action. DownloadForInsert continues to work as it always has worked in previous releases. The key difference, with respect to Download, is that DownloadForInsert only considers rows in the iterator that are in the STATUS_INITIALIZED state.
Updating Existing Data in an ADF Table Component
Describes how you configure an ADF Table component so that end users can edit and upload changes to existing data rows in the table.
Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component describes how you can configure the ADF Table component so that end users can upload modified data rows.
How to Configure an ADF Table Component to Update Data
If you want the end user to be able to edit existing data, but want to restrict the addition or deletion of data rows, no additional configuration is required. Make sure that your project and the ADF Table component is configured as shown in the following procedure.
To configure an ADF Table component to update data:
Table 7-2 RowAction Properties of ADF Table Component
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 7-9 ADF Table RowActions Properties to Update Data
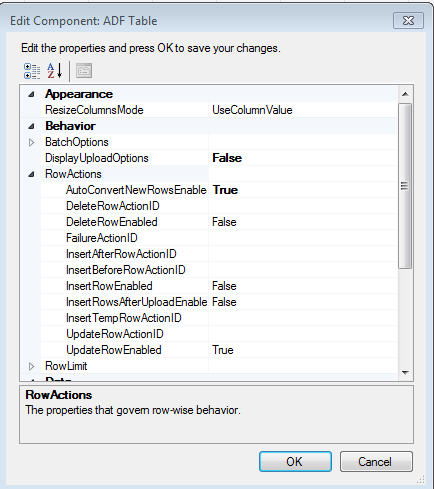
What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Updates Data
When the end user changes data in a row, ADF Desktop Integration marks the row and an upward pointing triangle appears in a row of the _ADF_ChangedColumn column.
Note:
You can also configure an ADF Table component to automatically refresh a row when an end user edits a value. See Configuring Automatic Row Refresh in an ADF Table Component.After updating the existing data, the end user initiates the upload process to save the changes. For information about the ADF Table component's upload process, see Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component.
Excel uploads modified rows from the integrated workbook in batches rather than row by row. You can configure the number of rows uploaded for each batch as well as the actions an ADF Table component invokes when it uploads and commits a batch of rows. For information about batch processing, see Batch Processing in an ADF Table Component.
For information about the properties that you can set for the ADF Table component, see ADF Table Component Properties and Actions.
Note:
Any criteria that has been applied to the worksheet using Excel's Filter functionality is automatically cleared prior to the Upload action.
Inserting Data in an ADF Table Component
You can configure an ADF Table component to allow end users to insert new data rows.
Once you complete this task, you may want to also configure the component to allow end users to upload new and modified data rows, as described Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component .
How to Configure an ADF Table Component to Insert Data Using a View Object's Operations
To commit the changes that an end user makes in an ADF Table component, you add action bindings to the page definition file that is associated with the Excel worksheet that hosts the ADF Table component and configure a number of ADF Table component properties.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to configure ADF Table component to insert data. See Inserting Data in an ADF Table Component.
For information about ADF Table component properties, see ADF Table Component Properties and Actions .
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure an ADF Table component to insert data using a view object's operations:
Note:
-
If you are using a polymorphic view object and want to insert a new row, the default
CreateInsertaction binding is not sufficient. You must create a custom method that also sets the discriminator value in the newly created row.While creating the custom method, you must expose the custom method as an action binding in the page definition file. The action binding must be specified as the
InsertBeforeActionIdrather thanCreateInsert. -
If the
InsertRowsAfterUploadEnabledproperty is set toFalseand the end user tries to upload the inserted rows again, an error message in the status column is displayed indicating that the row cannot be inserted more than once.
Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component
You configure the ADF Table component and the worksheet that hosts it so that end user can upload changes they make to data in the ADF Table component to the Fusion web application.
To configure this functionality, you decide what user gesture or worksheet event invokes the action set that invokes the ADF Table component's Upload action.
The Upload action commits all successful rows even when some other rows have failures. Use the UploadAllOrNothing action instead if you want no row changes to get committed if one, or more, row failures occur (see Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component Using an UploadAllOrNothing Action). To provide upload options to end users in a web page from the Fusion web application that differ from the default upload dialog, you must specify a Dialog action in the action set before the action that invokes the ADF Table Component's Upload action. See How to Create a Custom Upload Dialog.
Note:
In a master-detail relationship, ADF Desktop Integration does not support editing of the ViewLink source attributes, as the selections in the child view object would change as a result. To prevent any accidental editing, define the ViewLink source attributes to be read-only, or use a model configuration that does not include a view link between master and detail.
How to Configure an ADF Component to Upload Data from an ADF Table Component
Configure an ADF component, such as a worksheet ribbon command, to invoke an action set that, in turn, invokes the ADF Table component Upload action.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to configure ADF component to upload data from an ADF Table data component. See Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component .
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure an ADF component to upload changed data from an ADF Table component:
Note:
The action set does not include a call to a commit-type action as the ADF Table component's batch options already include calls to Commit. See How to Configure Batch Options for an ADF Table Component .
What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Uploads Data
At runtime, the end user invokes the action set through whatever mechanism you configured (ADF component, worksheet ribbon command, or worksheet event). This triggers the following sequence of events:
-
If the ADF Table component contains dynamic columns, ADF Desktop Integration verifies whether the dynamic columns that were expanded the last time the ADF Table component's
Downloadaction was invoked are still present in the Fusion web application. If the columns are not present, ADF Desktop Integration prompts the end user to determine whether to continue upload process. If the end user decides not to continue, ADF Desktop Integration returns an abort code to the executing action set. -
If the ADF Table component contains no pending changes to upload, the ADF Table component's
Uploadaction returns a success code to the executing action set. -
The ADF Table component uploads modified rows in batches, rather than row by row. You can configure the batch options using the
BatchOptionsgroup of properties. For information about batch options for the ADF Table component, see Batch Processing in an ADF Table Component.Each row of a batch is processed in the following way, and the process continues until all changed rows of each batch are processed:
-
For inserted rows, invoke the
InsertBeforeRowActionIDaction, if specified. -
For edited rows, position the tree binding iterator to the correct row.
-
Set attributes from the worksheet into the model, including any cached row attribute values.
-
For edited rows, invoke the
UpdateRowActionIDaction; and for inserted rows, invoke theInsertAfterRowActionIDaction, if specified. -
For each uploaded row, displays a status message indicating success or failure in the Status column. If a row fails to upload, the Status column displays a message (for example,
Update Failed). More detailed information about the failure is shown in the Status Viewer when the end user clicks in any cell on the row with the failure. See Using the Status Viewer to Report Error Messages to End Users.For information about the Status column, see Special Columns in the ADF Table Component .
-
For any row failure, the ADF Table component verifies the value of
AbortOnFail. IfAbortOnFailis set toFalse, it continues the upload process. Otherwise the component stops uploading data and invokes theCommitaction.
-
-
While uploading data, the ADF Table component returns a success or failure code to the executing action set based on the following:
-
If the ADF Table component commits all batches successfully, it returns the success status to the executing action set. If
Table.DisplayUploadOptionsproperty is set toTrueand the end user has selected the Download all rows after successful upload option in Upload Options dialog, the ADF Table component then downloads all rows from the Fusion web application. -
If the ADF Table component did not commit all batches successfully, the action set invokes the action specified by the
RowActions.FailureActionIDproperty, if an action is specified for this property. ADF Desktop Integration returns a failure code to the action set.
-
If the Table.DisplayUploadOptions property is set to True and the On failure, continue to upload subsequent rows checkbox is selected in the Upload Options dialog, the Upload action returns a success code to the action set even if some individual rows encountered validation failures.
Note:
When the Upload action is invoked on an ADF Table that has an Excel filter applied, Excel filter's criteria is cleared to show any hidden Excel worksheet rows, but the filter is not removed.
What Happens at Runtime: How the ReadOnly EL Expression Is Evaluated During Upload
At runtime, if an ADF Table component column's ReadOnly property evaluates to True, the ADF Table component's Upload action ignores all changes in the column's cells.
For information about change tracking, see Evaluating EL Expressions for ReadOnly Properties.
What Happens at Runtime: How Row Errors Are Handled During Upload
When the ADF Table component starts uploading data, ADF Desktop Integration creates a DataControlFrame savepoint before initiating the upload process (once per batch of uploaded rows). In case of any error, ADF Desktop Integration reverts back to the savepoint, ensuring the integrity of the server-side state of the Fusion web application.
For each row in a batch of uploaded rows, ADF Desktop Integration does the following:
-
Invokes configured actions, applies row attribute value changes, and performs data validation.
-
In case of any error, reverts back to the savepoint state.
Note:
A second iteration is performed, if required, to re-upload any successfully uploaded rows whose changes were reverted due to a subsequent upload error.
Since ADF Desktop Integration uses savepoints to manage model state during upload, any row-level action implementations should avoid calling commit or rollback actions.
For information about savepoints, see Using Trees to Display Master-Detail Objects in Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
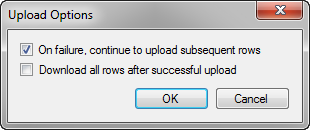
What You May Need to Know About Upload Options
At runtime, when the end user uploads data from the integrated Excel workbook to the Fusion web application, ADF Desktop Integration continues to upload subsequent data rows in case of any row failure, and does not refresh or download data of all rows after a successful upload.
If required, you can enable or disable the Upload Options dialog, as shown in Figure 7-11, by setting the Table.DisplayUploadOptions property. When DisplayUploadOptions is set to True, ADF Desktop Integration presents the Upload Options dialog.
Note:
The Table.DisplayUploadOptions property is set to True by default in ADF Table components of integrated Excel workbooks created with versions of ADF Desktop Integration that did not include Table.DisplayUploadOptions property.
Using the Upload Options dialog, end users can enable or disable the following options:
-
Continue to upload subsequent rows on failure. This is the default behavior.
When disabled, ADF Desktop Integration aborts the upload process in case of any row failure.
-
Download all data rows after a successful upload. This behavior is disabled by default.
When enabled, ADF Desktop Integration downloads the latest data from the view object cache after the successful upload.
Note:
If the Download all data rows after a successful upload checkbox is selected, ADF Desktop Integration downloads the data from the view object cache, not from the database.
Therefore, if another user happens to update the same rows that the end user has updated, the end user will not see the updates made by the other user after downloading data rows.
If the end user clicks Cancel in the Upload Options dialog, ADF Desktop Integration returns an abort code to the executing action set. If the end user clicks OK, the action set continues executing with the options specified in the dialog for the upload operation.
You may also create a custom upload dialog. See How to Create a Custom Upload Dialog.
How to Create a Custom Upload Dialog
You display a page from Fusion web application that offers end users different options to those presented in the default upload dialog. You add a Dialog action before the action that invokes the ADF Table component's Upload action in the action set.
Note:
You can prevent the appearance of the standard Upload Options dialog by setting the DisplayUploadOptions property to False, as described in What You May Need to Know About Upload Options.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to configure ADF component to upload data from an ADF Table data component. See Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component .
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To create a custom upload dialog:
What Happens at Runtime: Custom Upload Dialog
When a custom dialog appears, the page from the Fusion web application that you configure the Dialog action in the action set to display appears instead of the default upload dialog.
Note:
If there is no server connectivity when the end user tries to upload data, the end user gets an error when the Dialog action fails to find the custom upload page. ADF Desktop Integration does not revert to the standard dialog when server connectivity is not available.
For information about displaying a page from the Fusion web application, see Displaying Web Pages from a Fusion Web Application. Otherwise, the runtime behavior of the action set that you configure to upload data is as described in What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Uploads Data.
Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component Using an UploadAllOrNothing Action
The UploadAllOrNothing action provides an alternative method to upload data from the ADF Table component where the upload process commits all changed rows only if all rows are successfully uploaded.
ADF Desktop Integration commits all row changes that are successfully uploaded during a Table.Upload operation, even when one or more rows have failures. For example, if 100 rows are uploaded and only three rows contain failures, 97 rows are still committed to the database. For information, see Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component .
Using the UploadAllOrNothing action, you can configure the upload process to commit all changed rows only if all rows are successfully uploaded. For example, if 100 rows are uploaded, and if any row fails, no rows are committed to the database.
Uploading a large number of changed worksheet rows with the UploadAllOrNothing action can result in significant memory consumption on the application server. This is because the UploadAllOrNothing action commits only after all rows are processed successfully. For this reason, the UploadAllOrNothing action is not intended for use with large data sets. You can limit the amount of data that the UploadAllOrNothing action can upload using the UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit servlet parameter. For information about the UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit servlet parameter, see Limiting the Amount of Changed Data That Can Be Uploaded With UploadAllOrNothing Action.
How to Configure an ADF Component to use UploadAllOrNothing Action
Configure an ADF component, such as a worksheet ribbon command, to invoke an action set that, in turn, invokes the ADF Table component UploadAllOrNothing action.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to configure ADF component to upload data from an ADF Table data component. See Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component Using an UploadAllOrNothing Action.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure an ADF component to use UploadAllOrNothing action:
What Happens at Runtime: UploadAllOrNothing Action is Invoked
If you have chosen the UploadAllOrNothing action, ADF Desktop Integration commits row changes only when all rows are uploaded successfully.
Note:
The UploadAllOrNothing action uploads data in the same way as the Upload action. For information about how data gets uploaded during Upload as well as UploadAllOrNothing, see What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Uploads Data.
During the UploadAllOrNothing action, ADF Desktop Integration uploads all changed worksheet rows prior to invoking the action specified by CommitBatchActionID. If one, or more, row-level failures occur, the action specified by FailureActionID is invoked and the action specified by CommitBatchActionID is not invoked.
In the event of a failure, all values in the Changed column remain unchanged. The Status column displays failure messages for the rows that contain errors, but remains empty for all rows without errors. When all rows successfully commit, the Changed column values are cleared and the Status column for the uploaded rows reports success.
Note:
-
The
UploadAllOrNothingaction is only supported for DataControls that support database transactions. -
If
CommitBatchActionIDis not configured and an action set contains theUploadAllOrNothingaction, a validation error is reported. -
The
UploadAllOrNothingaction treats all update and insert rows as a single batch. This means that the action bindings specified by the ADF Table componentRowData.BatchOption'sStartBatchActionIDandCommitBatchActionIDproperties get invoked one time per operation.
Limiting the Amount of Changed Data That Can Be Uploaded With UploadAllOrNothing Action
Uploading a large number of changed worksheet rows with the UploadAllOrNothing action can result in significant memory consumption on the application server. For this reason, it is not intended for use with large data sets. To prevent end users from uploading too much data during the UploadAllOrNothing action, set the UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit servlet parameter (specified in Kb) to limit the total amount of changed data that can get uploaded. If no parameter value is specified, a default limit of 10,240 Kb is used. If you specify a value for this servlet parameter larger than the default, performance and scalability testing and analysis should be performed to measure the impact on the application server.
If the total amount of changed data uploaded exceeds the UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit value, an error message is reported to the end user, and the UploadAllOrNothing action is aborted. Note that the action specified by Table.RowActions.FailureActionID is invoked when the changed data limit is exceeded.
To alter the limit for the amount of changed data that can be uploaded:
Example 7-1 web.xml File With UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit Servlet Parameter
<servlet>
<servlet-name>adfdiRemote</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>oracle.adf.desktopintegration.servlet.DIRemoteServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit</param-name>
<param-value>10240</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
Example 7-1 shows the entry for UploadAllOrNothing.ChangedDataLimit in the Summit sample application for ADF Desktop Integration's web.xml file.
Deleting ADF Table Component Rows in the Fusion Web Application
The ADF Table component exposes an action (DeleteFlaggedRows) that, when invoked, deletes the rows in the Fusion web application that correspond to the flagged rows in the ADF Table component.
A flagged row in an ADF Table component is a row where the end user has double-clicked or typed a character in the cell of the _ADF_FlagColumn column as described in Batch Processing in an ADF Table Component. The _ADF_FlagColumn column must be present in the ADF Table component to configure it to delete rows in the Fusion web application.
In addition, the page definition file that you associate with the worksheet that hosts the ADF Table component must expose a Delete action binding.
How to Configure an ADF Table Component to Delete Rows in the Fusion Web Application
To delete rows from an ADF Table component, you must add the Delete action binding to the page definition file, configure the RowActions group of ADF Table component properties, and configure an action set to invoke the DeleteFlaggedRows action.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to configure ADF Table component to delete data rows in Fusion web application. See Deleting ADF Table Component Rows in the Fusion Web Application.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure an ADF Table component to delete rows in a Fusion web application:
What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Deletes Rows in a Fusion Web Application
The end user flags rows to delete, as described in Row Flagging in an ADF Table Component. The end user then invokes the action set. The following sequence of events occurs:
-
If specified, the action binding referenced by the
BatchOptions.StartBatchActionIDproperty is invoked.Failures from this step are treated as errors. An error stops the action set invoking. It also returns the error condition to the action set. If an action binding is specified for the
ActionSet.FailureActionIDproperty, the action set invokes the specified action binding.For information about configuring batch options, see Batch Processing in an ADF Table Component.
-
For each flagged row in the ADF Table component, the action set positions the tree binding iterator to the correct row, then it invokes the delete-type action binding specified by
RowActions.DeleteRowActionID.Note:
Rows inserted since the last invocation of the ADF Table component's
Downloadaction but not uploaded to the Fusion web application are ignored even if flagged for deletion. -
For each flagged row in the ADF Table component, if the delete-type action binding specified by
RowActions.DeleteRowActionIDfails, the next event depends on the value you specified for theDeleteFlaggedRowsaction'sOptions.AbortOnFailureproperty. IfFalse, the action set attempts to delete all flagged rows without stopping at the first failure it encounters. If the action set fails to delete a flagged row, that row:-
Remains in the ADF Table component
-
Is marked as
Failedin the ADF Table component's Status column -
Is skipped while the action set commits the batch of successfully deleted flagged rows
-
Remains flagged in the Flagged column cell
If the
DeleteFlaggedRowsaction'sOptions.AbortOnFailureproperty is set toTrue(the default value), the ADF Table component stops invocation of theDeleteFlaggedRowsaction. -
-
If an action binding is specified for the
BatchOptions.CommitBatchActionIDproperty, the action set invokes it. If this step fails, the action set stops processing batches. If no failures occur, the action set processes the next batch by invoking the action binding specified by theBatchOptions.StartBatchActionIDproperty, and so on until the action set processes all batches. -
If the action set processes all batches successfully, it invokes the action binding specified by its
ActionOptions.SuccessActionIDproperty if an action binding is specified for this property. It then removes the rows deleted in the Fusion web application by invocation of the delete-type action binding specified byRowActions.DeleteRowActionIDfrom the worksheet and returns a success code to the action set.If failures occur while the action set processes the batches, the action set invokes the action binding specified by its
ActionOptions.FailureActionIDproperty if an action binding is specified for this property. This action binding returns a failure code to the action set. -
If an unexpected exception occurs while the action set invokes its actions, an error code is returned to the action set. All relevant error messages are available in the Status Viewer. See Using the Status Viewer to Report Error Messages to End Users.
Note:
When the DeleteFlaggedRows action is invoked on an ADF Table that has an Excel filter applied, Excel filter's criteria is cleared to show any hidden Excel worksheet rows, but the filter is not removed.
Batch Processing in an ADF Table Component
The ADF Table component's Upload and DeleteFlaggedRows actions both commit changes in batches rather than row-by-row in order to optimize performance and scalability. You can configure batch option properties that determine the size of batches and what actions the ADF Table component invokes when it uploads a batch.
How to Configure Batch Options for an ADF Table Component
The ADF Table component has a group of properties (BatchOptions) that allow you to configure how the ADF Table component manages batches of rows. Information about these properties can be found in ADF Table Component Properties and Actions .
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how ADF Table components upload data, delete data, and batch process both tasks. See What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Uploads Data, What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Component Deletes Rows in a Fusion Web Application, and Batch Processing in an ADF Table Component.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure batch options for an ADF Table component:
Note that a failure at the entity-level is not considered a batch failure. A failure at the commit level (for example, a wrong value for a foreign key attribute) is considered a batch failure.
Troubleshooting Errors While Uploading Data
End users may see reports of errors under certain circumstances while uploading data from ADF Table components. After posting changes from a batch, ADF Desktop Integration runs the action specified by the CommitBatchActionID. Rows from a batch that experiences a failure executing the action specified by the CommitBatchActionID display the details of the failure in the Status Viewer. Any rows in the batch that had changes posted successfully on the server before the failure show Batch Failed in the Status column.
Errors that occur during the commit action might continue to be reported on subsequent batch commit actions, even though subsequent batches of records do not contain errors. This can happen when any pending model updates are not automatically reverted when the CommitBatchActionID action fails. To avoid any such error, you must explicitly revert pending model updates that exist after a commit failure. For example, you could create a custom action for the CommitBatchActionID that first attempts to commit the pending model changes. However, if an exception occurs during commit, the custom method should first roll back the pending model changes, so that any subsequent batch commit attempts can succeed.
Note:
It is important that the commit exception gets thrown again after rollback so that the commit errors are reported as expected on the client.
Special Columns in the ADF Table Component
By default, the ADF Table component includes some columns when you insert an ADF Table component in a worksheet. You can retain or remove these columns, if required.
The following list describes the columns and the purpose they serve:
-
_ADF_ChangedColumnThe cells in this column track changes to the rows in the ADF Table component. If a change has been made to data in a row of the ADF Table component since download or the last successful upload, a character that resembles an upward pointing arrow appears in the corresponding cell of the
_ADF_ChangedColumncolumn. This character toggles (appears or disappears) when a user double-clicks a cell in this column. Figure 7-12 shows an example.Figure 7-12 Changed Column in an ADF Table Component
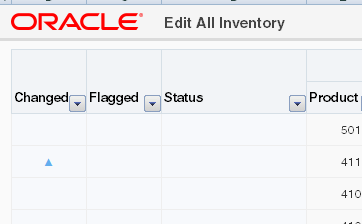
Description of "Figure 7-12 Changed Column in an ADF Table Component"Note:
If the end user does not want the ADF Table component's
Uploadaction to upload changes in the rows marked by this column, the user must clear the entry that appears in the corresponding cell.When an ADF Table component invokes its
Uploadaction, it uploads all rows with non-empty cells in the_ADF_ChangedColumncolumn. See Uploading Changes from an ADF Table Component . -
_ADF_FlagColumnWhen the end user double-clicks a cell in this column, the corresponding row is flagged for flagged-row processing. A solid circle character appears to indicate that the row is flagged for flagged-row processing. For information about the use of this column, see Row Flagging in an ADF Table Component.
Note:
By default, the solid circle character indicates a row flagged for flagged-row processing. However, any nonempty cell in a
_ADF_FlagColumnflags the corresponding row for flagged-row processing. -
_ADF_StatusColumnThis column reports the results of invocation of ADF Table component actions, such as
DeleteFlaggedRowsandUpload.A message appears in the cell of the
_ADF_StatusColumnto indicate the result of the invocation for the corresponding row. If the end user invokes aDoubleClickActionSetdefined in an ADF Table column and an error occurs, the errors are also reported in the Status column of the corresponding row. Figure 7-13 shows an example of a Status column message for a row where an update failed. More detailed information about status appears in the Status Viewer, as described in Using the Status Viewer to Report Error Messages to End Users.Figure 7-13 Status Column in an ADF Table Component
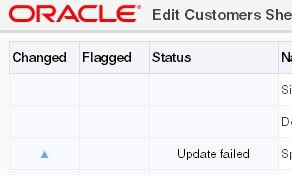
Description of "Figure 7-13 Status Column in an ADF Table Component" -
_ADF_RowKeyColumnThis column, also referred to as the Key column, contains important information about the ADF Table component used by ADF Desktop Integration at runtime. The column appears both at runtime and design time. Do not remove the Key column because it is required for the proper functioning of the ADF Table component. You can configure its appearance-related properties.
For information about the
_ADF_RowKeyColumn,see Configuring ADF Table Component Key Column.
The ADF Table component treats the properties of the _ADF_ChangedColumn, _ADF_FlagColumn, _ADF_RowKeyColumn, and _ADF_StatusColumn columns differently from the properties of other columns that it references. It ignores the values set for properties such as InsertComponent, InsertUsesUpdate, and UpdateComponent unless it invokes the DisplayRowErrors action described in Table A-12. It reads the values for properties related to style and appearance, for example CellStyleName and HeaderStyleName.
Row Flagging in an ADF Table Component
By default, the ADF Table component includes a column, _ADF_FlagColumn, that facilitates the selection of rows for flagged-row processing. Double-clicking a cell of the _ADF_FlagColumn column flags the corresponding row for processing by actions invoked by a component action.
When the end user double clicks a cell of the _ADF_FlagColumn column, a solid circle appears, or disappears, in the cell to indicate that the row is flagged, or not. Figure 7-14 shows an example of a flagged column.
Figure 7-14 Flagged Column in ADF Table Component
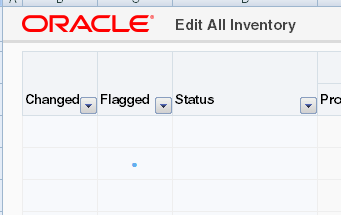
Note:
By default, the solid circle character indicates a row flagged for flagged-row processing. However, any nonempty cell in a _ADF_FlagColumn column flags the corresponding row for flagged-row processing.
The following component actions can be invoked on flagged rows:
-
DeleteFlaggedRows -
DownloadFlaggedRows
You can use the FlagAllRows component action to flag all rows, and the UnflagAllRows component action to unflag all rows of the ADF Table component.
Note:
-
The ADF Table component's
DownloadFlaggedRowsaction does not support changes in table column structure after the last invocation of theDownloadorDownloadForInsertaction. The table column structure usually changes if you are using dynamic columns, or if the table contains columns with complex expressions in theVisibleproperty. -
The
DownloadFlaggedRowsaction is not applicable to inserted rows.
Use of these component actions is dependent on the appearance of the _ADF_FlagColumn column in the ADF Table component. If you remove the _ADF_FlagColumn column from the ADF Table component, you cannot invoke any of these component actions. For information about these component actions, see ADF Table Component Actions.
At runtime, the end user can invoke any of the previously listed component actions from an action set. The invoked component action processes all flagged rows. For example, it downloads or deletes all flagged rows. For information about configuring an action set to invoke a component action, see How to Invoke Component Actions in an Action Set.
Configuring ADF Table Component Key Column
When you add ADF Table to your integrated Excel workbook, the Key column (column ID: _ADF_RowKeyColumn) appears automatically at design time.
The Key column contains important information that is used by ADF Desktop Integration for proper functioning of the table. Note that you must not remove the Key column at runtime.
How to Configure the Key Column
You can configure the Key column's position, style properties, and header label. By default, the Key Cell style is applied to it.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the Key column in the ADF Table component. See Configuring ADF Table Component Key Column.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure the Key column:
How to Manually Add the Key Column At Design Time
If you are using the integrated Excel workbook prepared and configured using an earlier version of ADF Desktop Integration, the Key column will not be available at design time. It will appear only at runtime. To configure the Key column properties, you can add it in the workbook at design time.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of the Key column in the ADF Table component. See Configuring ADF Table Component Key Column.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To manually add the Key column at design time:
Note:
You must specify the ID property of the new column as _ADF_RowKeyColumn; otherwise, the column will not be considered to be a Key column, and another Key column will automatically appear at runtime.
Adding a Dynamic Column to Your ADF Table Component
You can add dynamic columns to an ADF Table component so that the ADF Table component expands or contracts at runtime depending on the available attributes returned by the view object.
The DynamicColumn property of the Columns group in the TableColumn array controls this behavior. To make a column dynamic, set the DynamicColumn property to True. A dynamic column in the TableColumn array is a column that is bound to a tree binding or a tree node binding whose attribute names are not known at design time. A dynamic column can expand to more than a single worksheet column at runtime.
The ADF Table component's dynamic column supports the following subcomponent types:
-
ModelDrivenColumnComponent
-
Input Text
-
Output Text
Note:
ADF Desktop Integration does not support the subcomponent type TreeNodeList in a dynamic column.
Support for Model-Driven List of Values
You can also configure a dynamic column to support the List of Values subcomponent where the subcomponent type is determined from model configuration at runtime. At design time, specify the subcomponent type as ModelDrivenColumnComponent for the UpdateComponent or InsertComponent properties. At runtime, during dynamic column expansion, the model-driven runtime component is determined before caching the list of values. The remote servlet allows the client to retrieve Model configuration, allowing the client to choose the desired column subcomponent type. See Adding a ModelDrivenColumnComponent Subcomponent to Your ADF Table Component and Creating a List of Values in an ADF Table Component Column.
Note:
In cases where the ADF Table component uses a tree binding containing multiple <nodeDefinition> elements, model-driven lists used in dynamic columns must have unique names across all nodes.
How to Configure a Dynamic Column
You configure a dynamic column by specifying an EL expression with the following format for the Value property of the component specified by the ADF Table component column's InsertComponent property as a subcomponent:
#{bindings.TreeID.[TreeNodeID].AttributeNamePrefix*.inputValue}
or:
#{bindings.TreeID.AttributeNamePrefix*.inputValue}
where:
-
TreeIDis the ID of the tree binding used by the ADF Table component -
TreeNodeIDis an optional value that specifies the tree node binding ID. If you omit this value, all matching attributes from the tree binding display regardless of which tree node binding the attribute belongs to. -
AttributeNamePrefixidentifies a subset of attributes that exist within the tree binding's underlying iterator. If you do not specify a value forAttributeNamePrefix, all attributes for the tree binding or tree binding node are returned. Always use the*character.
Note:
While adding a dynamic column, ensure that tree node attribute names are not specified in the page definition file. At runtime, the tree node object returns all attribute names from the underlying iterator. If there are attribute names specified in the page definition file, the tree node object limits the list of available attribute names based on that list.
The following example returns all attributes that begin with the name "period" in the model.EmpView node of the EmpTree binding:
#{bindings.EmpTree.[model.EmpView].period*.inputValue}
Support for View Objects with Declarative SQL Mode
To support view objects that are configured with declarative SQL mode and customized at runtime, expose a tree binding in the page definition file that has no attributes defined. For example:
<tree IterBinding="DeclSQLModeIterator" id="DeclSQLModeTree">
<nodeDefinition Name="DeclSQLModeTreeNode"/>
</tree>
At runtime, the tree binding returns the selected attributes from the underlying declarative SQL mode view object to the integrated Excel worksheet.
What Happens at Runtime: How Data Is Downloaded or Uploaded In a Dynamic Column
When the ADF Table component's Download or DownloadForInsert action is invoked, the ADF Table component automatically updates the dynamic columns so that they contain an up-to-date set of matching attributes. For each invocation of Download, ADF Desktop Integration requires that all rows must have the same set of attributes for the dynamic column. It may generate errors if the set of attributes changes from row to row during Download.
If a dynamic column supports both Insert and Update operations, you should specify the same EL expression for the Value properties of the dynamic column's InsertComponent and UpdateComponent subcomponents. At runtime, the ADF Table component expands to include a dynamic column that displays the value of the attribute binding returned by the EL expression.
Typically the set of matching attributes does not change between invocation of the ADF Table component's Download and Upload actions. However, if previously downloaded attributes no longer exist in the tree binding when the ADF Table component invokes the Upload action, the integrated Excel workbook prompts the end user to determine if the end user wants to continue to upload data. For information about how to avoid the scenario just described (downloaded attributes no longer exist in the tree binding), see Using an Integrated Excel Workbook Across Multiple Web Sessions.
Note:
The ADF Table component ignores the value of a column's Visible property when you configure a column to be dynamic. For information about ADF Table component column properties, see Table A-11.
How to Specify Header Labels for Dynamic Columns
Use the following syntax to write EL expressions for the HeaderLabel property of a dynamic column:
#{bindings.TreeID.[TreeNodeID].hints.AttributeNamePrefix*.label}
or:
#{bindings.TreeID.hints.AttributeNamePrefix*.label}
Specify the same tree binding ID, tree node binding ID, and attribute name prefix values in the HeaderLabel property of the dynamic column as the values you specify for the Value properties of the dynamic column's InsertComponent and UpdateComponent if the dynamic column supports Insert and Update operations.
If you want the mandatory columns, where the end user must enter a value, to be marked with a character or a string, you must configure the HeaderLabel property. Use the following syntax to write EL expression to add a character or string to all mandatory columns:
=IF(#{bindings.TreeID.[TreeNodeID].hints.*.mandatory}, "<prefix_for_mandatory_cols>", "") & "#{bindings.TreeID.[TreeNodeID].hints.*.label}"
For example, the following EL expression adds an asterisk (*) character to the mandatory columns label:
=IF(#{bindings.MyTree.[myapp.model.MyChildNode].hints.*.mandatory}, "* ", "") & "#{bindings.MyTree.[myapp.model.MyChildNode].hints.*.label}"
How to Specify Styles for Dynamic Columns
If the same style can be applied for all expanded columns, specify the literal style name for the CellStyleName property of a dynamic column.
However, if different styles are needed for different expanded columns, an EL expression must be specified for the CellStyleName property of a dynamic column.
You can specify different styles for each attribute using a custom attribute property, for example, adfdiCellStyle. The following syntax would be used for the CellStyleName EL expression:
#{bindings.TreeID.[TreeNodeID].hints.*.adfdiCellStyle}
For information about custom attribute properties, see Using ADF Desktop Integration EL-based Properties with Custom Attribute Properties.
Alternatively, you can specify different styles for each attribute using more complex EL expressions to compute the style name.
In the following example, the MyDateStyle style is applied to all date columns, and MyDefaultStyle is applied to other data type columns:
=IF("#{bindings.MyTree.[myapp.model.MyChildNode].hints.*.dataType}"="date", "MyDateStyle", "MyDefaultStyle")
For information about EL expressions, see ADF Desktop Integration EL Expressions.
Adding a ModelDrivenColumnComponent Subcomponent to Your ADF Table Component
The ModelDrivenColumnComponent is the default subcomponent when you insert an ADF Table component. The column subcomponent type is determined at runtime by the column's attribute Control Type hint specified on the server.
At design time for a column, specify the subcomponent type as ModelDrivenColumnComponent for the UpdateComponent or InsertComponent properties. At runtime, if there is a model-driven list associated with the attribute, then the column uses a dropdown list containing the model-driven list items.
Note:
-
To use the (optional) date picker for a model-driven column with a date attribute, set the
Compatibility.TableComponents.ModelDrivenColumns.DatePickerEnabledproperty toTrue. See ADF Desktop Integration Compatibility Properties. -
If there is no model-driven list associated with the attribute, or if any non-list-based control type is specified, then the column uses an Input Text subcomponent. If there is a model-driven list whose control type is
combo_lov, then the column uses an Input Text subcomponent. -
In a dependent list of values implementation, ADF Desktop Integration determines if each list subcomponent depends on another model-driven list when an ADF Table component uses multiple
ModelDrivenColumnComponentsubcomponents. To do this, it verifies that the bind variable specified for a list references an attribute bound to another list. See Table 8-1.
For information about creating a model-driven list, see How to Create a Model-Driven List in Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
Configuring an ADF Table Component to Resize Columns Based on Data at Runtime
You can configure column widths of an ADF Table component so that they are automatically resized at runtime.
The columns can be resized using Excel's AutoFit column width feature, which determines the width based on the data values in the column. ADF Desktop Integration can also resize the columns using explicit width values derived from EL expressions.
The resizing behavior of ADF Table columns is configured at the table level. You can then override them at the column level.
Resizing a column's width at runtime is a two-step process. First, you configure the table column with the desired width-related property values. Secondly, add the ADF Table component's ResizeColumns action to the desired action set. Typically, you add this action after the ADF Table component's Download action in the action set. The EditCustomers-DT.xlsx workbook in the Summit sample application, described in Introduction to the ADF Desktop Integration Sample Application, demonstrates this implementation.
How to Configure an ADF Table Component to Resize Columns at Runtime
You can use the design-time ResizeColumnsMode property to specify the common resizing behavior for all columns of the ADF Table component. Use the ResizeColumns table component method to control when the resizing occurs. To override resizing behavior of a particular column, use the column's ResizeMode property.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of configuring resizing behavior of ADF Table columns. See Configuring an ADF Table Component to Resize Columns Based on Data at Runtime.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure resizing behavior of ADF Table columns:
How to Configure an Action Set to Resize Columns of an ADF Table Component at Runtime
You can configure the action set in a worksheet ribbon command or a worksheet event to invoke the ADF Table component ResizeColumns action.
Note that resizing a table with many columns and many rows might take a noticeable amount of time.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of configuring resizing behavior of ADF Table columns. See Configuring an ADF Table Component to Resize Columns Based on Data at Runtime and Using Action Sets.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To configure an action set to resize Columns of an ADF Table component:
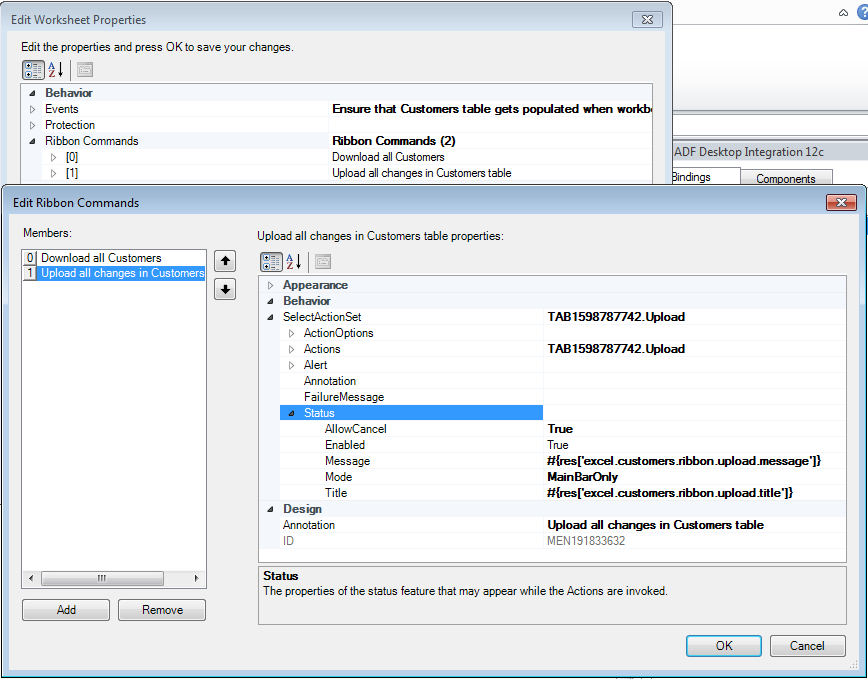
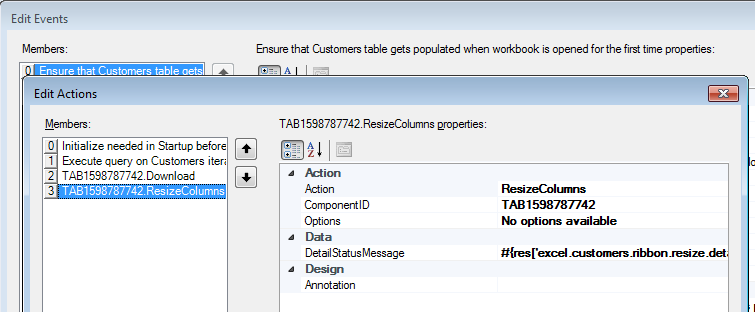
Figure 7-15 shows the ResizeColumns action at design-time that is configured in the worksheet Events property of the EditCustomers-DT.xlsx workbook.
Note:
If you configure an action set that is invoked by the worksheet Startup event and this action set invokes the ADF Table component's ResizeColumns action after the Download action, make sure that the action set invokes the ADF Table component's Initialize action before the Download action. Figure 7-15 demonstrates this configuration.
Figure 7-15 ResizeColumns Action
What Happens at Runtime: How the ADF Table Columns are Resized
The ADF Table columns are resized as the result of running of Table.ResizeColumns component action in an action set (see How to Configure an Action Set to Resize Columns of an ADF Table Component at Runtime).
What You May Need to Know About Resizing Columns of an ADF Table Component at Runtime
The entire worksheet columns containing the ADF Table component columns are resized depending on the values in the Table.ResizeColumnsMode and Column.ResizeMode properties. Resizing the table columns affects the contents of the cells or any other components (such as form components) located in the same Excel worksheet column outside of the table's boundaries.
If a worksheet contains two or more ADF Table components configured with action sets to resize columns at runtime, all ADF Table components attempt to resize their columns independently. However, the ADF Table component's ResizeColumns action that runs last sets the column width.
Tip:
For worksheets that contain more than one ADF Table component, call the ResizeColumns action only on the primary table
Note:
-
The
Column.Widthproperty does not support row-specific bindings. -
A common strategy is to call
ResizeColumnsafter one of the Download actions. See Figure 7-15 for an example. -
Resizing the columns for a large table may take a significant amount of time. The end user may perceive a download to be slower due to this extra work. Be sure to test your workbook with typical data loads to determine whether resizing is worth the delay for your use case.
-
Excel internally rounds the specified
Widthvalues to the nearest whole pixel value. For example, a value of 8.5 characters rounds to 8.43, which equates to 64 pixels. -
Using one of the AutoFit resizing modes on cells that have Wrap Text selected in their style definition may not resize as expected. Using
SpecifiedWidthmode, explicitly setting the row height of table cells at design time, or removing the Wrap Text setting from the style may produce better results. -
It may help to make Excel columns wider at design time if you use one of the AutoFit resizing modes and want to avoid text wrapping at runtime. This is due to the way that Excel's AutoFit resizing modes work.
Grouping Columns Together in an ADF Table Component
You can render group headers for columns that render in an ADF Table component to, for example, provide your end users with a more intuitive interface by using descriptive labels for groups of columns.
Figure 7-22 shows an example where the EditAllInventory-DT.xlsx workbook from the Summit sample application for ADF Desktop Integration groups the Product to Restock Date columns into an Inventory Details group header while the Warehouse to Country columns have been grouped into a Warehouse Details group of columns.
Figure 7-16 Providing a Grouping Header for Columns in an ADF Table Component
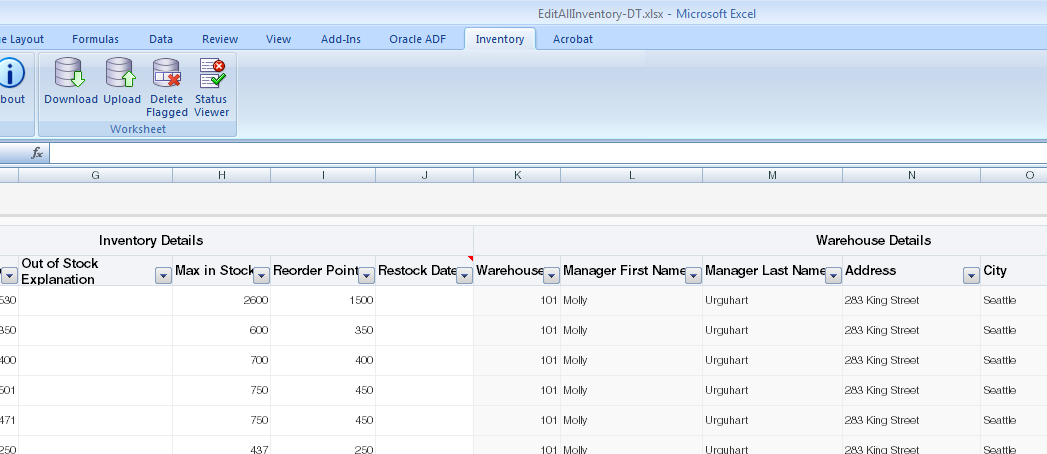
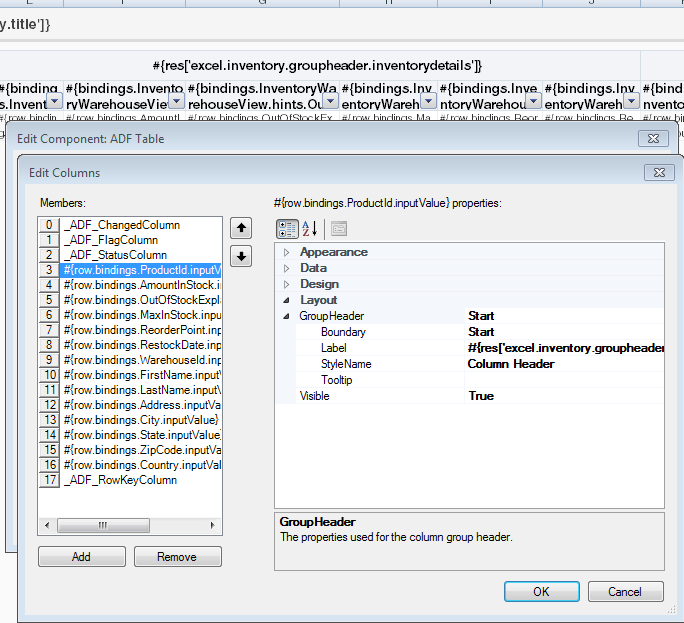
ADF Desktop Integration implements the functionality shown in Figure 7-16 by rendering an extra table header row above the ADF Table component's regular table header row at runtime. It renders this extra table header row if you configure the GroupHeader properties in one of the column definitions of the ADF Table component. You can also implement this functionality for dynamic columns. If you want to implement this functionality for dynamic columns, you must define custom attributes, as described in How to Group Columns that Render in a Dynamic Column. For information about how to configure the GroupHeader properties for static and dynamic columns, see How to Group Columns in an ADF Table Component.
Leave the row above the ADF Table component empty of data and styles if you want to render an extra table header row to group columns because, at runtime, existing data and styles will be overwritten to render the extra table header row.
How to Group Columns in an ADF Table Component
You group columns in an ADF Table component by configuring the GroupHeader properties for the start and end columns in the group of columns.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how you can group columns in an ADF Table component. See Grouping Columns Together in an ADF Table Component.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
Define custom attribute properties, as described in How to Group Columns that Render in a Dynamic Column, if you want to group header columns that render in a dynamic column. This step is not required if you want to group header columns in static columns.
To group columns in an ADF Table component:
How to Group Columns that Render in a Dynamic Column
A dynamic column can expand to more than a single worksheet column at runtime. At runtime, the integrated Excel workbook evaluates EL expressions defined for the GroupHeader properties after the dynamic column expands. Depending on the results of evaluating the GroupHeader properties, column groups form and the integrated Excel workbook renders grouped headers for the dynamic column.
To configure GroupHeader properties for columns that render in a dynamic column, you first define custom attribute properties on the view object attributes that render in the dynamic column's columns at runtime.
Define custom attribute properties for the attributes that you want to render the start and end boundaries of the grouped header in the dynamic column at runtime. Configure custom attribute properties for the start attribute that the GroupHeader Boundary, Label, StyleName, and Tooltip properties reference at runtime using EL expressions. Configure a custom attribute property for the end attribute that the GroupHeader Boundary property references at runtime using an EL expression.
For information about defining custom attribute properties, see Using ADF Desktop Integration EL-based Properties with Custom Attribute Properties.
Figure 7-18 shows an attribute (Address) that defines custom attribute properties to start a grouped header.
Figure 7-18 Custom Attribute Property to Start a Grouped Header in a Dynamic Column
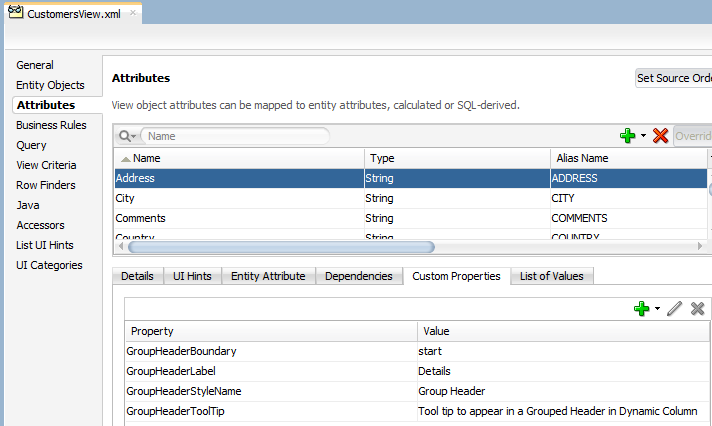
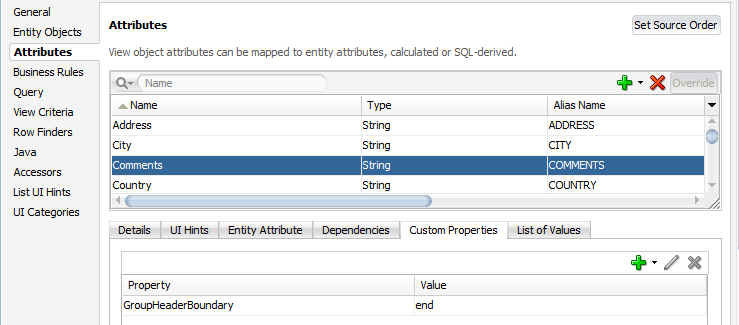
Figure 7-19 shows an attribute (Comment) that defines custom attribute property to end a grouped header.
Figure 7-19 Custom Attribute Property to End a Grouped Header in a Dynamic Column
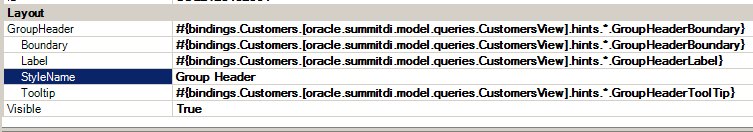
At runtime, a dynamic column expands to render columns for the view object's attributes. For this example the expanded columns are Address, City, and Comments that are configured to render a grouped header. Figure 7-20 shows the GroupHeader properties that you configure in the dynamic column at design time. At runtime, the EL expressions retrieve and evaluate the values of the configured custom attribute properties shown in Figure 7-18 and Figure 7-19. A grouped header labeled Details forms for the Address, City, and Comments columns.
For information about how to configure the GroupHeader properties, see How to Group Columns in an ADF Table Component.
Figure 7-20 Starting a Grouped Header in a Dynamic Column
What Happens at Runtime: How an ADF Table Component Groups Columns
An extra table header row renders above the ADF Table component's regular table header row at runtime if you configure values for the GroupHeader properties. The values you specify for the Label, StyleName and Tooltip properties of the start column in each group determines the label, style and tooltip of the group header. Any values that you configure for those GroupHeader properties of other columns in the column group are ignored.
The style specified by the GroupHeader.StyleName property in the column that you configure as the start column is applied on the extra table header cells of all columns in the group. The horizontal alignment of the group header label centers across the extra table header cells of all columns in the group.
The tooltip defined by the GroupHeader.Tooltip property in the start column renders on the extra table header cell of the end column in the group, as shown in Figure 7-21.
Figure 7-21 Grouped Columns Rendering Styles and Displaying a Tooltip
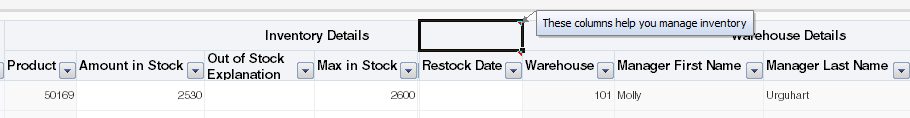
Description of "Figure 7-21 Grouped Columns Rendering Styles and Displaying a Tooltip"
Make sure that columns you configure as start and end columns render at runtime. If a column that you configure as a start column does not render at runtime, no column group forms. For example, if you configure Column 1 as a start column and Column 3 as an end column and Column 1 does not render at runtime because its Visible property returns false, no column group forms. Similarly, if Column 3 does not render, no column group forms that spans Column 1, Column 2, and Column 3. Instead, Column 1 renders as a single-column group.
Configuring an ADF Table Component to be Read-only
Describes how to configure an ADF Table component to be read-only.
The ADF Table component offers multiple features that are not available in the ADF Read-Only Table component, described in Creating an ADF Read-Only Table Component. Examples of features available in the ADF Table component include dynamic columns, the ability to group columns together and the ability to resize columns. For this reason, you may want to create an ADF Table component and configure it to be read-only rather than creating an ADF Read-only Table component. The CustomerSearch-DT.xlsx workbook in the Summit sample application contains an ADF Table component that is configured to be read-only.
How to Configure an ADF Table Component to be Read-only
You make an ADF Table component read-only by setting the RowActions UpdateRowEnabled and InsertRowEnabled properties to False and deleting the _ADF_ChangedColumn, _ADF_FlagColumn, and _ADF_StatusColumn columns from the ADF Table component.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of ADF Table component. See Configuring an ADF Table Component to be Read-only.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
Insert an ADF Table component in your integrated Excel workbook, as described in Inserting an ADF Table Component into an Excel Worksheet.
To configure an ADF Table component to be read-only:
Creating an ADF Read-Only Table Component
At runtime, the ADF Read-only Table component renders a table across a continuous range of cells that displays data from the tree binding that the ADF Read-only Table component references. Use this component to display data that you do not want the end user to edit.
Note:
The ADF Table component offers multiple features that are not available in the ADF Read-Only Table component. For this reason, you may want to consider creating an ADF Table component and configure it to be read-only rather than creating an ADF Read-Only Table component. See Configuring an ADF Table Component to be Read-only.
The ADF Read-only Table component supports several properties, such as RowLimit, that determine how many rows the component downloads when it invokes its Download action. It also includes a group of properties (Columns) that determine what columns from the tree binding appear at runtime in the Excel worksheet. The TreeID property specifies the tree binding that the component references. More information about these properties and others that the ADF Read-only Table component supports can be found in ADF Read-only Table Component Properties and Actions.
Note:
-
At runtime, inserting a row into the ADF Read-only Table component results in a new Excel row that behaves as if it is part of the downloaded data set, but the new row exists only in Excel. The data from the new row is not uploaded to the server, and does not affect the Fusion web application data.
-
Read-only columns include double-click action sets. However, these actions cannot reliably position on the current row. So, the results of using row-level action sets with the ADF Read-only Table component is not consistent. If you need to use row-level action sets with reliable row positioning, use the ADF Table component instead of the ADF Read-only Table component.
How to Insert an ADF Read-only Table Component
You use the ADF Desktop Integration Designer task pane to insert an ADF Read-only Table component into a worksheet.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of ADF Read-only Table component. See Creating an ADF Read-Only Table Component.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To insert an ADF Read-only Table component:
Limiting the Number of Rows Your Table-Type Component Downloads
You can configure the number of rows that an ADF Table or ADF Read-only Table component downloads by setting values for the component's RowLimit group of properties.
You can also display a warning message, if desired, that alerts the end user when the number of rows available to download exceeds the number of rows specified for download.
How to Limit the Number of Rows a Component Downloads
Specify the number of rows that the component downloads when it invokes its Download action as a value for the RowLimit.MaxRows property. Optionally, write an EL expression for the RowLimit.WarningMessage property so that the end user receives a message if the number of rows available to download exceeds the number specified by RowLimit.MaxRows.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how to limit the number of rows while downloading data in your ADF Table component. See Limiting the Number of Rows Your Table-Type Component Downloads.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To limit the number of rows a table-type component downloads:
Figure 7-22 shows the Edit Component dialog in the EditCustomers-DT.xlsx workbook where the row limit of an ADF Table component is configured.
Figure 7-22 Limiting Number of Rows of an ADF Table Component
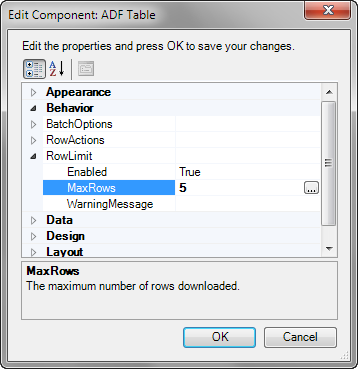
Description of "Figure 7-22 Limiting Number of Rows of an ADF Table Component"
What Happens at Runtime: How the RowLimit Property Works
When invoked, the Table-type component's Download action downloads the number of rows that you specified as the value for RowLimit.MaxRows from the Fusion web application. A message dialog similar to the one in Figure 7-23 appears if you specify an EL expression for RowLimit.MaxRows or do not modify its default value.
Figure 7-23 Row Limit Exceeded Warning Message
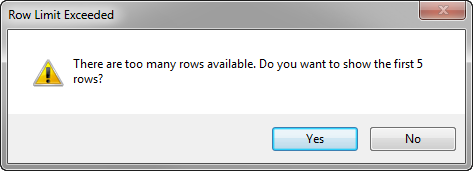
Description of "Figure 7-23 Row Limit Exceeded Warning Message"
Tracking Changes in an ADF Table Component
End users can create or modify data in the cells of an integrated Excel workbook that hosts an ADF Table component.
If a column is updatable and not read-only, change tracking is activated. End users can make the following changes to activate change tracking:
-
Edit cell values
-
Insert or delete cell values
-
Paste values to cells in the ADF Table component column that they copied elsewhere
A character that resembles an upward pointing arrow appears in a row of the _ADF_ChangedColumn column if the end user makes a change to data in a corresponding row. Figure 7-24 shows an example.
Figure 7-24 Changed Column in an ADF Table Component

This character appears if the end user makes a change to data hosted by a component where the component's ReadOnly property value is False. Various subcomponents, such as the ModelDrivenColumnComponent, have a ReadOnly property. You can write an EL expression or a literal string for this ReadOnly property that evaluates to True or False. If you write a static string or an EL expression that evaluates to True, no character appears in the _ADF_ChangedColumn column. For information about ReadOnly EL expressions and change tracking, see Evaluating EL Expressions for ReadOnly Properties.
Evaluating EL Expressions for ReadOnly Properties
If a table column's ReadOnly property EL expression contains a binding expression (for example, #{row.bindings.color.inputValue}), the runtime evaluation of that expression will be different depending on when the evaluation occurs.
The evaluation happens during the following:
-
Downloading data (
Download,DownloadFlaggedRows,DownloadForInsert) -
Uploading data (
Upload,UploadAllOrNothing), and change tracking
What Happens at Runtime: Evaluating EL Expression While Downloading Data
During Download, the EL expression is evaluated with the current binding value as expected.
What Happens at Runtime: Evaluating EL Expression While Uploading Data or Tracking Changes
During Upload, or when the end user changes values in the editable table, the EL expression is evaluated differently than Download. Specifically, an empty string is substituted for the binding expression prior to evaluation of the EL expression.
For example, if you have the following EL expression in an editable cell:
=IF("#{row.bindings.color.inputValue}"="RED", True, False)
During Upload, or when the end user changes values in the editable table, the EL expression evaluates to =IF(""="RED", True, False), and always returns False.
Note:
During change tracking, column component Value properties are not evaluated. So, for example, cell values will be blank for newly inserted rows regardless of the configured Value EL expression.
What You May Need to Know About Evaluating EL Expression While Uploading Data or Tracking Changes
During Upload and change tracking, an extra round trip to the server would be required to retrieve the binding values, in order to evaluate the EL expression properly. The extra round trip to the server would impact performance negatively, and could even require a new login if the end user did not have a currently valid session.
Note:
The same EL expression evaluation behavior also applies to the CellStyleName EL expression property when inserting new worksheet rows during table change tracking.
Due to the difference in behavior, if possible, you should avoid ReadOnly EL Expressions that contain binding expressions. However, if it is important for a given use case to use an attribute value in the ReadOnly expression, you should consider setting the worksheet protection to Automatic. For information about worksheet protection, see Using Worksheet Protection.
For example, if you have the following EL expression in a cell:
=IF("#{row.bindings.color.inputValue}"="RED", True, False)
During Download, the RED cells in this column will be set to Locked and the end user will not be able to edit those cells.
Displaying Error Messages in an Error Message Column
You can configure your ADF Table component to display a message column where row-level error messages appear at runtime.
At runtime, ADF Desktop Integration populates the cells in the error message column with the row-level error messages captured during invocation of the Upload, UploadAllOrNothing, and DeleteFlagged actions. End users of the integrated Excel workbook can use Excel’s Filter, Sort, and Find capabilities to locate errors that display the same error message to efficiently resolve errors before resubmitting corrected rows.
Excel’s Filter and Sort capabilities can be found by default in Excel’s Home ribbon tab, in the Editing ribbon group. Filter and Sort can also be invoked by selecting a cell in the error message column and right-clicking to display the context menu where you choose Filter followed by the appropriate sub-menu option. When Excel worksheet protection is enabled, access to the Filter and Sort capabilities are disabled. This is expected behavior.
The cell in the error message column displays one error message row. If an action reported multiple errors, the end user needs to resolve the displayed error and replay the action before they can see the next error message in the cell. In this scenario, your end user should refer to the Status Viewer where all errors for a row appear simultaneously, in addition to details such as cause and actions to take to resolve the error.
For action sets that contain both Upload and DeleteFlagged actions, the error message column shows the message from the failed action. Where both Upload and DeleteFlagged actions produce row-level errors for the same row, the error message column shows the error from the second action in the action set.
How to Display Error Messages in an Error Message Column
You add a new column to your ADF Table component and set the ID of the new column to _ADF_ErrorColumn.
Before you begin:
It may be helpful to have an understanding of how you can display an error column in an ADF Table component. See Displaying Error Messages in an Error Message Column.
You may also find it helpful to understand the functionality that can be added using other ADF Desktop Integration features. See Additional Functionality of Table-Type Components.
To display error messages in an error message column: