1 Overview
This topic describes about the overview for Multi Entity feature.
Banks have multiple implementations across geographies that support Multiple entities.
Multi Entity: This feature introduced to Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture products, which enables a single instance of the product (and the underlying Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture platform) to onboard the multiple entities of the bank onto the platform.
As part of the Multi-Entity feature, below are the functionality supported in all Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture products.
- Creation of "Multi-Entity Admin" user(s)
- Entity Definition and Maintenance
- Creation of "Entity Admin" User(s) & regular users
- Mapping of users (entity admins or regular users) to one or more entities - The users of the application will be central in nature and users can have access to one or more entities.
- User Entitlement will be local to the entity
- Deployment Diagram
This topic describes about the deployment diagram for Multi-Entity based deployment model. - Entity Creation
This topic describes about the various entity creations for Multi-Entity feature. - Users
This topic describes the information to configure a new users. - Switch Between Entities
This topic describes about the information to switch between entities.
1.1 Deployment Diagram
This topic describes about the deployment diagram for Multi-Entity based deployment model.
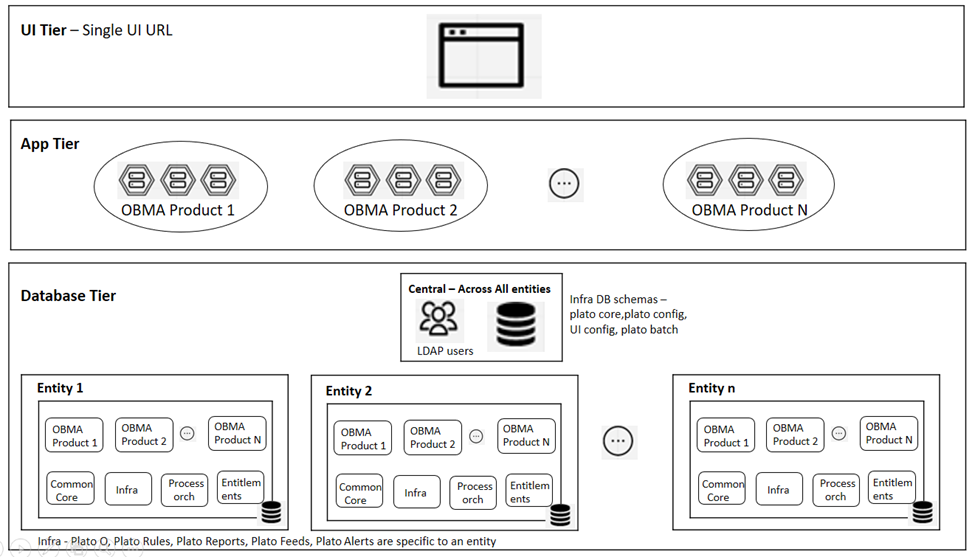
Deployment diagram depicts Multi-Entity based deployment model. Entities based on geographies are considered as an example in the deployment diagram.
UI Tier – UI Domain will be shared across multiple entities for a bank and the same UI URL will be used.
A user can map to one or more entities and a single home entity. During login, the user redirects to the home entity, and an option is provided to switch any of the other associated entities.
Multi Entity admin user has the special access to create/modify new entities in the system.
App Tier – One or more managed servers that host all the microservices are to be deployed for a product.
This includes the below list:
- Infrastructure services – OBMA Infra services (Plato Discovery, Plato API Gateway, Plato Batch, etc…) that are used across all products
- SMS service – for Role Based Authorization
- Common Core and Mid-office Common core services - Common domain related services that are used across by one or more products
- Domain services – micro-services related to Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture products (Oracle Banking Trade Finance Process Management, Oracle Banking Credit Facilities Process Management, Oracle Banking Liquidity Management, Oracle Banking Virtual Account Management, etc...)
Same as UI tier and App tier will be shared across multiple entities. Based on the entity ID provided in the request header, DB schema to the entity will be accessed for all CRUD operations.
Database Tier – The segregation of entities should be done in the DB layer. Separate DB schemas should be defined and used for the entities.
- LDAP users
- few infrastructure related DB schemas - Plato Config, Plato UI config, Plato core, and Plato Batch
- Infra related schemas - Plato O, Plato Rules, Plato Reports, Plato Feeds, and Plato Alerts
- User entitlements – SMS schema
- Common core schema
- Product specific DB schemas (each product will have multiple schemas; ideally 1 schema per microservice/sub-domain)
Banks that have a single entity should follow the same architecture but with "DEFAULT_ENTITY" configured in the system.
Parent topic: Overview
1.2 Entity Creation
This topic describes about the various entity creations for Multi-Entity feature.
- Default Entity Creation
This topic describes about the default entity creation. - Single Entity Setup
This topic provides the systematic instruction to setup the single entity for the bank. - Multi Entity Setup
This topic provides the systematic instruction to setup the multi entity for the bank.
Parent topic: Overview
1.2.1 Default Entity Creation
This topic describes about the default entity creation.
During environment setup, when microservices are deployed, DMLs/DDLs related to “DEFAULT_ENTITY” will be executed through flyway scripts.
Note:
Two Multi entity admin users must be created to manage and authorize entity and users in the system.The bank must pre-determine if the application will be set-up as single or multiple entity system based on the actual implementation requirement. User can directly refer the Single Entity Setup or Multi Entity Setup topics. By default, the system will create an entity with name DEFAULTENTITY and the name is allowed to be modified only once and must be manually controlled.
Parent topic: Entity Creation
1.2.2 Single Entity Setup
This topic provides the systematic instruction to setup the single entity for the bank.
- View Entities
This topic describes the systematic instructions to view and modify the single entity.
Parent topic: Entity Creation
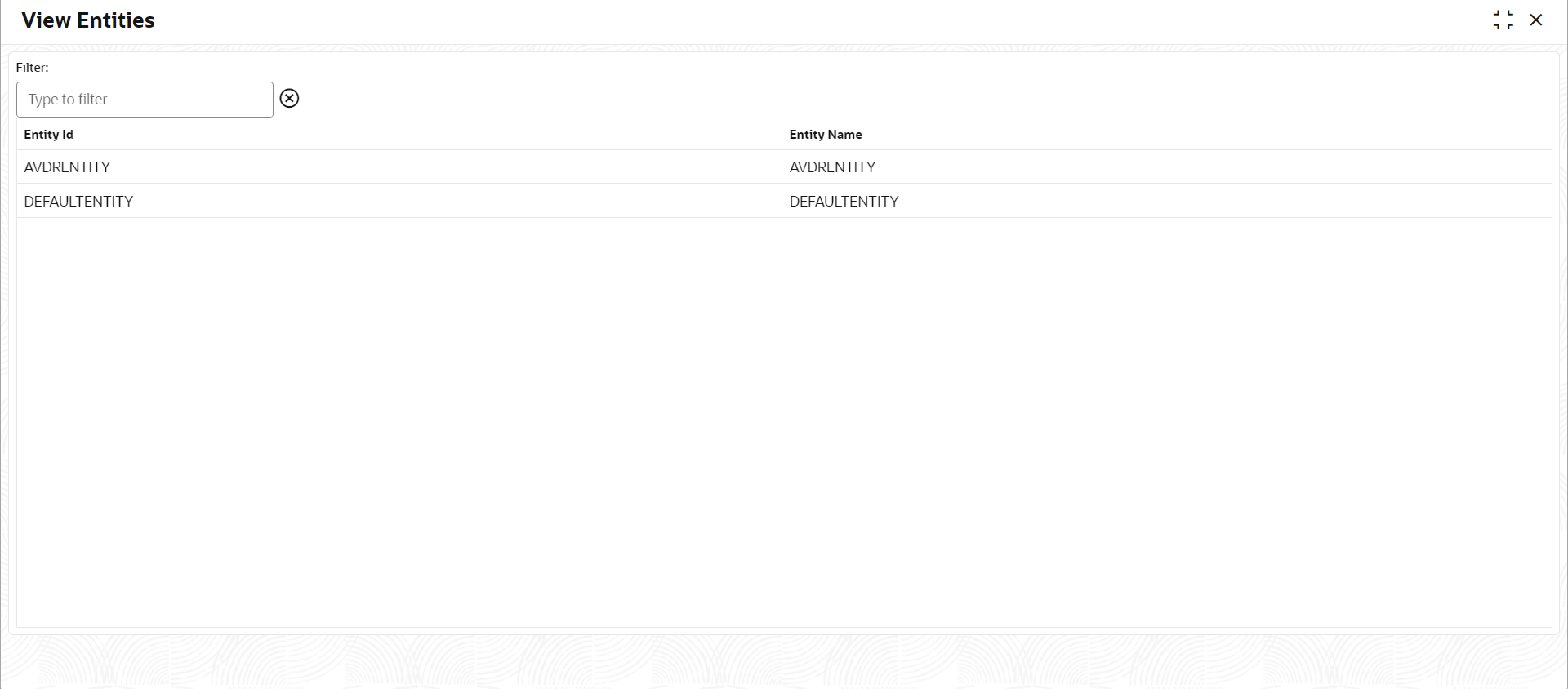
1.2.2.1 View Entities
This topic describes the systematic instructions to view and modify the single entity.
Parent topic: Single Entity Setup
1.2.3 Multi Entity Setup
This topic provides the systematic instruction to setup the multi entity for the bank.
- Create Entity
This topic describes the systematic instructions to configure a new entity for multi entity admins. - View Entities
This topic describes the systematic instructions to view the list of all entities.
Parent topic: Entity Creation
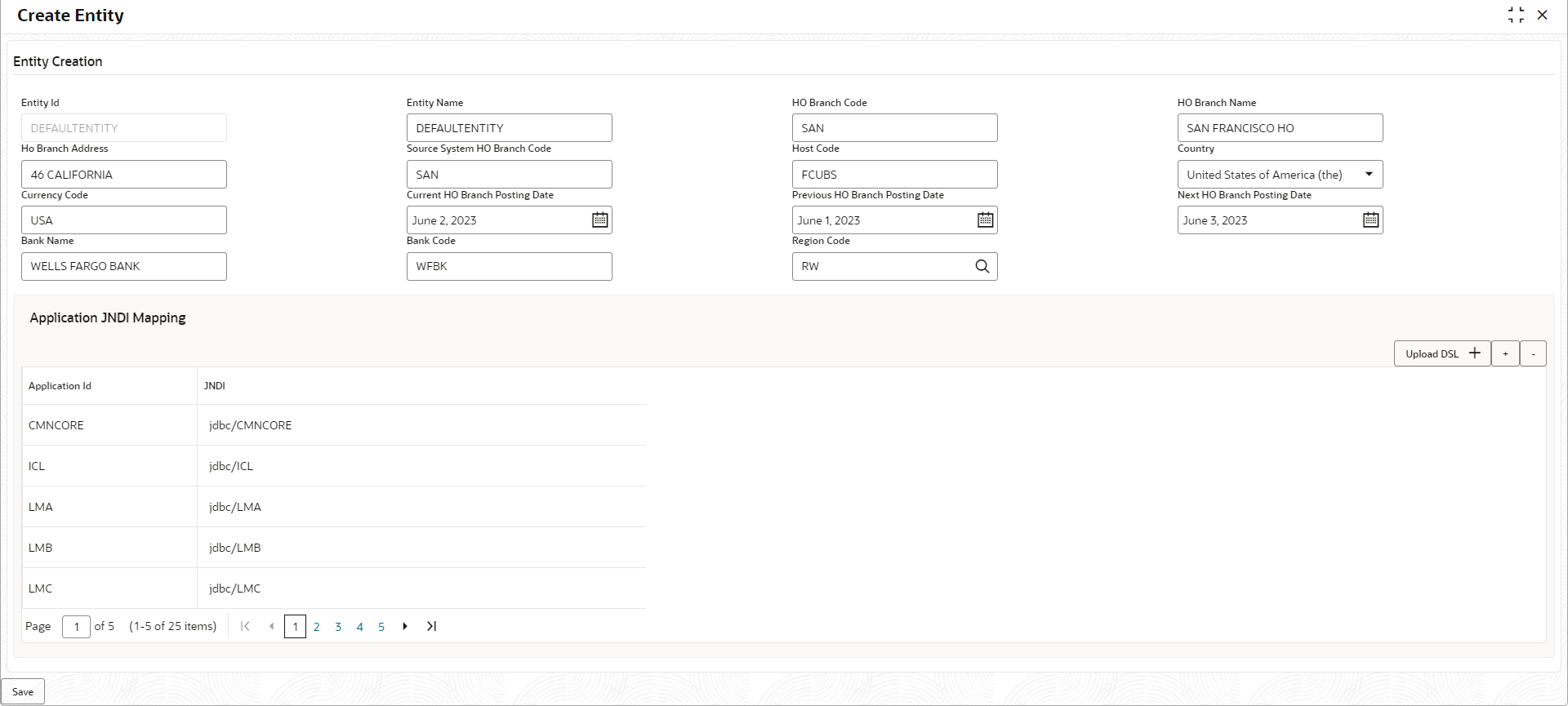
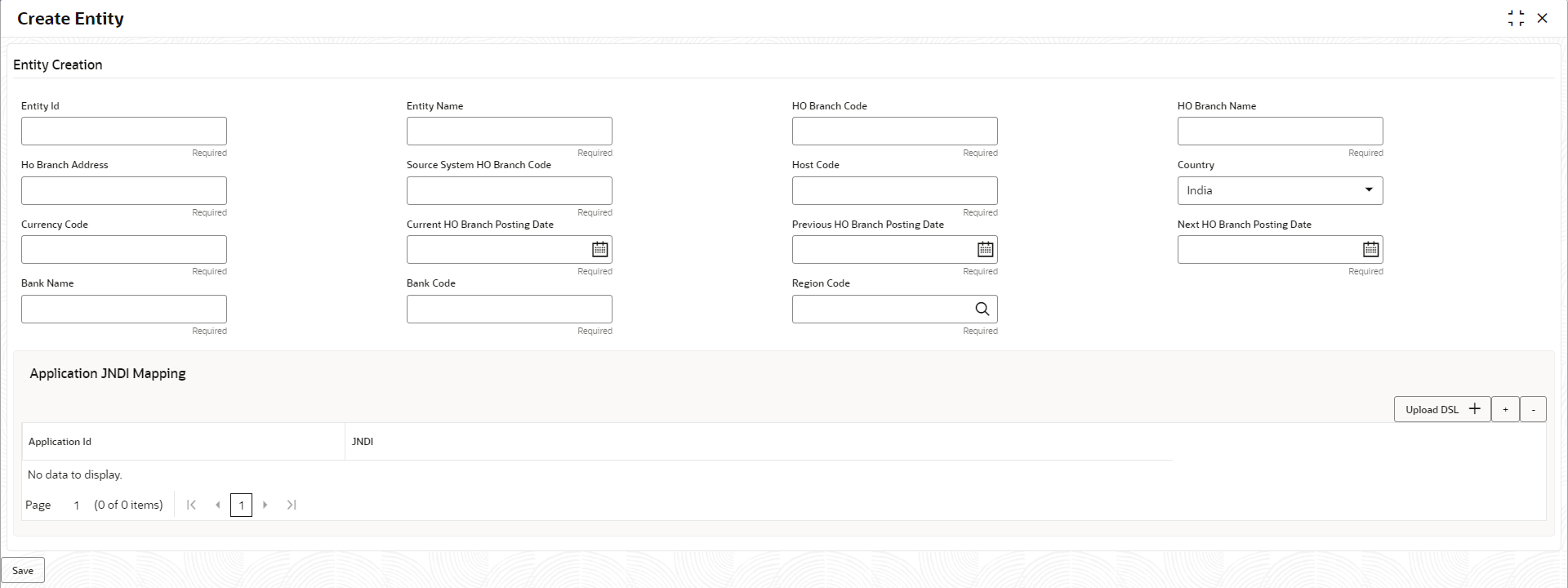
1.2.3.1 Create Entity
This topic describes the systematic instructions to configure a new entity for multi entity admins.
Parent topic: Multi Entity Setup
1.2.3.2 View Entities
This topic describes the systematic instructions to view the list of all entities.
Parent topic: Multi Entity Setup
1.3 Users
This topic describes the information to configure a new users.
Multi entity admins can create entity admins and users.
This topic contains the following subtopics:
- Create User
This topic describes the systematic instructions for the multi entity admins to configure a new user. - View Users
This topic describes the systematic instructions to view the list of configured users.
Parent topic: Overview
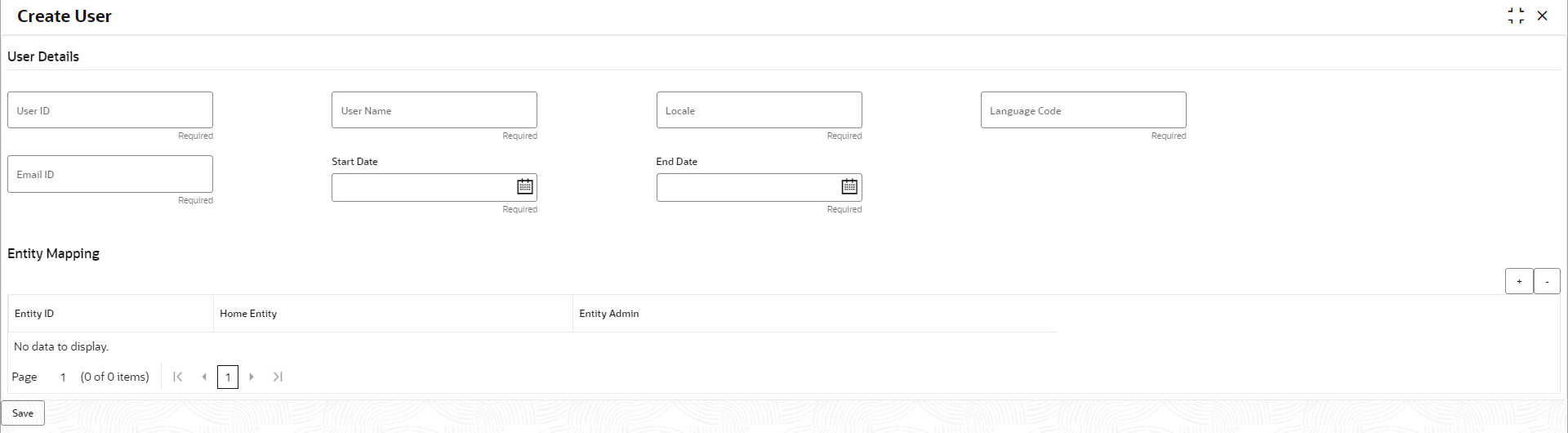
1.3.1 Create User
This topic describes the systematic instructions for the multi entity admins to configure a new user.
- Entity admin user will have default access to these core maintenance and security management screen.
Core Maintenance
- Currency definition
- Country code
- Language code
- Local Holiday
- System Dates
- External Branch Parameters
- External Bank Parameters
- Host code
Security Management
- Role
- User
- The core maintenances which are automatically created during the creation of an entity can be enhanced further by entity admin user. User can also perform new core maintenance for the new entity. For more information on Core Maintenance, refer to the Common Core User Guide.
- Normal users can be created in Create User screen by disabling Entity Admin toggle.
- Unlock and enrich the normal users created by mapping the required user role branches and user applications. Authorize the same. For more information, refer to the Oracle Banking Security Management System User Guide.
Parent topic: Users
1.3.2 View Users
This topic describes the systematic instructions to view the list of configured users.
Parent topic: Users
1.4 Switch Between Entities
This topic describes about the information to switch between entities.
- User can be mapped to one or more entities during the user creation, but only one among the entities should be made as Home Entity.
- If a user is mapped to 2 or more entities, then the user is allowed to switch between the entities.
- Users can switch between the entities only if :
- Same user should be available across the entities.
- Same branch should be available across the entities.
- User should have proper user role branch mapping done.
Parent topic: Overview