10 Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture Software Deployment
This topic describes about Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture software deployment.
Once everything is deployed, the managed servers. For each application, call the path /refresh for refreshing the configuration properties.
- Zookeeper Cluster Setup
This topic provides the systematic instructions to install Zookeeper cluster setup. - Kafka Cluster Setup
This topic provides the systematic instructions for Kafka cluster setup. - Kafka Security Setup
This topic describes about the Kafka Security setup. - Kafka Client Side Adoption
This topic provides the systematic instructions for Kafka cluster setup. - Tesseract Installation
This topic describes systematic instructions of Tesseract installation. - Conductor Installation
This topic provides the systematic instructions to install conductor. - Report Service Installation
This topic provides the systematic instructions to install report service.
10.1 Zookeeper Cluster Setup
This topic provides the systematic instructions to install Zookeeper cluster setup.
Note:
It is recommended to keep minimum number of zookeeper nodes as 3 or higher in odd numbers. The sample configs provided below are for 3 node setup.Note:
To restart the server, refer to the Restart Server section in Configuration and Deployment Guide.- JDK is installed in all node machines.
- Download kafka_2.13-3.7.0 and extract the binary in all node machines. Kafka can be found at <Unzip the file>/THIRD_PARTY_SOFTWARES/KAFKA/ARCHIVE
Note:
Please note that the zookeeper that we will be using is bundled within kafka.10.2 Kafka Cluster Setup
This topic provides the systematic instructions for Kafka cluster setup.
Note:
It is recommended to keep minimum number of kafka nodes as 3 or higher odd numbers. The sample configs provided below are for 3 node setup.- JDK is installed in all node machines.
- Download Kafka and extract the binary in all node machines. Kafka can be found at
<Unzip the file>/THIRD_PARTY_SOFTWARES/KAFKA/ARCHIVE.
Configure a Standalone Kafka Instance in Cluster Mode
If there is already a standalone Kafka instance with Oracle Banking Microservices Architecture services running on it, it is expected the topics are already created in the Kafka instances. In this case, use the below steps to enable replication of messages between Kafka brokers:
10.3 Kafka Security Setup
This topic describes about the Kafka Security setup.
Prerequisites
- JDK is installed in all node machines.
- Kafka is downloaded and extracted the binary in all node machines. Kafka can be found at
<Unzip the file>/THIRD_PARTY_SOFTWARES/KAFKA/ARCHIVE.
Generate Keystore
The items highlighted in bold are placeholders and should be replaced with suitable values when running the command.
keytool -genkeypair -alias alias -keyalg keyalg -keysize keysize -sigalg
sigalg -validity valDays -keystore keystoreTable 10-1 Generate Keystore - Keyword Description
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
alias |
Used to identify the public and private key pair created. |
keyalg |
It is a key algorithm used to generate the public and private key pair.
The RSA key algorithm is recommended. |
keysize |
It is the size of the public and private key pairs generated.
A key size of 1024 or more is recommended. |
sigalg |
It is the algorithm used to generate the signature.
This algorithm should be compatible with the key algorithm and should be one of the values specified in the Java Cryptography API Specification and Reference. |
valdays |
It is the number of days for which the certificate is to be considered valid.
Please consult with your CA on this period. |
keystore |
It is used to specify the location of the JKS file.
If no JKS file is present in the path provided, one will be created. |
Table 10-2 Certificate and Keystore - Attributes
| Attributes | Description |
|---|---|
| Keystore Password | Specify a password used to access the Keystore.
This password needs to be specified later when configuring the identity store in Kafka server. |
| Key Password | Specify a password used to access the private key stored in the Keystore.
This password needs to be specified later when configuring the SSL attributes of the Kafka Server. |
| First and Last Name (CN) | Enter the domain name of the machine. For example, www.example.com. |
| Name of your Organizational Unit | The name of the department or unit making the request.
Use this field to further identify the SSL Certificate you are creating, for example, by department or by physical server. |
| Name of your Organization | The name of the organization making the certificate request. For example, Oracle Financial Services.
It is recommended to use the company or organization's formal name, and this name entered here must match the name found in official records. |
| Name of your City or Locality | The city in which your organization is physically located. For example, Bengaluru. |
| Name of your State or Province | The state/province in which your organization is physically located. For example, Karnataka. |
| Two-letter Country Code for this Unit | The country in which your organization is physically located. For example, US, UK, IN, etc. |
Example 10-1 Execution
A sample execution of the command is mentioned below:
keytool -genkeypair -alias certificates -keyalg RSA -keysize 1024 -sigalg SHA512withRSA
-validity 365 -keystore /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerKeystore.jksEnter keystore password:<Enter a password to protect the keystore>
Re-enter new password:<Confirm the password keyed above>
What is your first and last name?
[Unknown]: <domain name>.oracle.com
What is the name of your organizational unit?
[Unknown]: <application name>
What is the name of your organization?
[Unknown]: Oracle Financial Services
What is the name of your City or Locality?
[Unknown]: Bengaluru
What is the name of your State or Province?
[Unknown]: Karnataka
What is the two-letter country code for this unit?
[Unknown]: IN Is CN= name.oracle.com, OU=Test, O=Oracle Financial Services, L= Bengaluru, ST= Karnataka, C=IN correct? [no]: yes
Enter key password for < password >
RETURN if same as keystore password): <Enter a password to protect the key>
Re-enter new password: <Confirm the password keyed above>
Export Private Key as Certificate
Export private key as certificate command is mentioned below:
keytool -export -alias <alias_name> -file <export_certificate_file_name_with_location.cer>
-keystore <keystore_name.jks> -keypass <Private key Password> -storepass <Store Password>Example:
keytool -export -alias certs -file /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaCert.cer
-keystore /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerKeystore.jks -keypass oracle123
-storepass oracle123If successful, the following message will be displayed:
Certificate stored in file < KafkaCert.cer>
Import the Cert and Generate TrustStore
To import the cert and generate TrustStore, the command is mentioned below:
keytool -import -alias alias -file cert_file -keystore truststore –storepass storepassTable 10-3 Certificate and TrustStore - Keyword Description
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
alias |
It is used to identify the public and private key pair.
Specify the alias of the key pair used to create the CSR in the earlier step. |
cert_file |
It is the location of the file containing the PKCS#7 formatted reply from the CA, containing the signed certificate. |
truststore |
It is the location where the TrustStore should be generated. |
storepass |
It is the password for the TrustStore. |
- One used for Kafka server
- One used for clients
Example:
keytool -import -alias certs -file /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaCert.cer
–keystore /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerTrustStore.jks -storepass oracle123keytool -import -alias certs -file /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaCert.cer
-keystore /scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaClientTrustStore.jks -storepass oracle123Table 10-4 Keystore Files
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
KafkaServerKeystore.jks |
Keystore file for Kafka brokers |
KafkaServerTrustStore.jks |
TrustStore file for server |
KafkaClientTrustStore.jks |
TrustStore file for client |
KafkaClientTrustStore.jks file.
Note:
The TrustStore files should be generated using the same CA. The user can generate and place these files on all the different servers of Kafka so that they can be accessed by server*.properties file. The KafkaClientTrustStore.jks should be placed on the server, which is accessible by the microservices also.
Create Users in Zookeeper
- Start the zookeeper.
Note:
Refer to Zookeeper Cluster Setup topic for more details. - Follow the below steps for user creation.
- Execute the admin command for admin user creation.
./kafka-configs.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --alter --add-config “SCRAM-SHA-256= [password=admin-secret],SCRAM-SHA-512=[password=admin-secret]” --entity-type users --entity-name adminNote:
The user created with admin as username and password is setup for the user for each scram mechanism. Here, the user admin is used for Kafka broker auth. - Execute the test command for test user creation.
./kafka-configs.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --alter --add-config “SCRAM-SHA-256= [iterations=8192,password=test-secret],SCRAM-SHA-512=[password=test-secret]” --entity-type users --entity-name testNote:
The user created with test as username and password is setup for the user for each scram mechanism. Here, the user test is used for client auth.
- Execute the admin command for admin user creation.
Configure Brokers
- Add the following properties to Kafka in the server.properties file.
SSL-SCRAM Settings for SSL Configuration (Recommended)
listeners=SSL://localhost:9092
advertised.listeners=SSL://localhost:9092
ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=
ssl.truststore.location=/scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerTrustStore.jks
ssl.truststore.password=oracle123
ssl.keystore.location/scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerKeystore.jks
ssl.keystore.password=oracle123
ssl.key.password=oracle123
security.inter.broker.protocol=SSL
Entries in the properties table for each kafka consumer/producer service
- 'spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.ssl.truststore.location'
- 'spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.ssl.truststore.password'
- 'spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.security.protocol' value = ‘SSL’
- 'ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm' = ''
SSL-SCRAM Settings for SASL-SSL Configuration (Not recommended)
ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=
ssl.truststore.location=/scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerTrustStore.jks
ssl.truststore.password=orcl@123
ssl.keystore.location/scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaServerKeystore.jks
ssl.keystore.password=orcl@123
ssl.key.password=orcl@123
sasl.enabled.mechanisms= SCRAM-SHA-256
sasl.mechanism.inter.broker.protocol= SCRAM-SHA-256
security.inter.broker.protocol=SASL_SSL
listeners=SASL_SSL://whf00phz:9093
advertised.listeners=SASL_SSL://10.40.162.113:9093
listener.name.sasl_ssl.scram-sha-256.sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="admin" password="admin-secret"; - Specify the absolute path of the Kafka Server Truststore and Keystore and its respective passwords.
- Modify the host name and IP in the listeners and advertised.listeners properties field accordingly.
- Start the Kafka servers.
Note:
Refer to the command in Kafka Cluster Setup topic.
Clients Changes (Kafka Consumer and Producer Services)
Table 10-5 List of PROPERTIES
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers | <hostname:port> |
| spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zknodes | <hostname:port> |
| spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options.username | <Zookeeper user created for clients> |
| spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.jaas.options.password | <Zookeeper user encrypted password for clients> |
| spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.ssl.truststore.location | <location of client trust store certificate> |
| spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.configuration.ssl.truststore.password | <Pass code of client truststore certificate> |
To encrypt the password, use the following API of plato-config-service:
API: http://hostname:port/config-service/encrypt
Request Type: Text
Request Body: Password
For example, when the user clicks the above API for the following passwords, we get the response of encrypted value:
test-secret : 36c11a239ffafbe229d888e7d21f0508a38a2501fd5592b1fe54e30889dd57ed
While inserting to properties table, append the encrypted values with the keyword {cipher} to get it decrypted by the config-service during fetch as given in below example:
For more information on adding properties to plato-config-deploy.env, refer to the topic Method 3 – Using env files and setUserOverrides.sh file in Configuration and Deployment Guide.
Important Commands
ssl.truststore.location=/scratch/Data/Certificates/KafkaClientTrustStore.jks
ssl.truststore.password=orcl@123
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=
sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-256
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required \
username="obvam_new" \
password="obvam-secret";
Note:
Update the truststore location and the password.To view the messages getting sent in Kafka, save the below lines to a file and name it as ssl.properties.
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server kafka-server --topic topicName
--consumer.config absolute-path-of-consumer-config --from-beginning./kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic test_topic
--consumer.config =/scratch/kafka/config/ssl.properties --from-beginning10.4 Kafka Client Side Adoption
This topic provides the systematic instructions for Kafka cluster setup.
- plato-alert-management-services
- plato-orch-services
- plato-api-gateway
- conductor
- plato-batch-server
- -Dspring.cloud.stream.kafka.default.producer.sync=true
Note:
This property is not required on managed server where api-gateway is deployed. - -Dspring.cloud.stream.kafka.default.producer.configuration.max.block.ms=5000
- -Dspring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.replication-factor=3
- -Dspring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.required-acks=all
- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers: <all brokers separated by comma> e.g. localhost:9092,localhost:9093,localhost:9094
- spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes: <all zookeepers separated by comma> e.g. localhost:2181,localhost:2182,localhost:2183
10.5 Tesseract Installation
This topic describes systematic instructions of Tesseract installation.
Prerequisite
- GNU Autotools—autoconf, automake, libtool
- CMake (Optional, we use CMake if autoconf fails to build leptonica).
Both should be available inside Oracle yum.
The libraries must be on the server. By default, they are available on Oracle Linux. If libraries are not present, please install through yum with the following command:
sudo yum install <LIBRARY_NAME>- libjpeg
- ibtiff
- zlib
- libjpeg-turbo
- libwebp
- libpng-devel
- libtiff-devel
- libwebp-devel
Note:
If you are using any distribution other than Oracle Linux, please install libraries from the official Oracle repo or any other repo available for that distribution.Download the installation files required to install and set up Tessract. Files are available at <Unzip the file>/THIRD_PARTY_SOFTWARES/Tesseract.
- leptonica-1.82.0.tar.gz
- tesseract-5.1.0.tar.gz
- eng.traineddata
- osd.traineddata
Leptonica Installation
Tesseract uses Leptonica internally for image processing. Leptonica can be built and installed by autoconf or CMake. The installation can be done using Autoconf and CMake.
Note:
If the user already have full access to all installation directory, then sudo is not required.>sudo LINUX_COMMAND (In case the user does not have file access permissions)
>LINUX_COMMAND (In case the user has all access. Example: DBA user, Root user)
Note:
In this topic, we execute all commands with sudo. The user can skip based on your user permission details.- Copy the downloaded leptonica tarball (leptonica-1.82.0.tar.gz) in server (installation directory). For eample: /scratch.
- Execute below commands sequentially to install
leptonica through
autoconf.
sudo tar xvf leptonica-1.82.0.tar.gz cd leptonica-1.82.0 sudo ./configure sudo make -j4Note:
In line 4, we used sudo make –j4. Here 4 is the number of CPU core. Generally, the user can use sudo make –jn where n is the number of core. It will make the build process much faster.Here, the core number is used as 4 to build the software.
If the processor does not have multiple cores, the user can use normal make command
sudo make.
Note:
If the installation is successful, then go to Leptonica Configuration . Else, go to Install through CMake.
- If the installation through Autoconf fails to
generate the configure file or has any other error, follow
the commands below to build through
CMake.
sudo tar xvf leptonica-1.82.0.tar.gz cd leptonica-1.82.0 sudo mkdir build cd build sudo cmake .. sudo make -j4
- Configure the Leptonica path so that the Tesseract Leptonica installation can be found.
- Add the leptonica installation directory in
library path. Example:
/usr/local/lib ,/usr/lib, /usr/lib64etc. - Configure the Leptonica header path.
Example:
/usr/local/include/leptonica. - Setup the Pkgconfig path and execute the below
mentioned commands to set the
path.
export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$PKG_CONFIG_PATH:/usr/local/lib/pkgconfig/ export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=$PKG_CONFIG_PATH:/usr/lib64/pkgconfig/ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/lib export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/lib export LIBLEPT HEADERSDIR=/usr/local/include/leptonicaNote:
Sometimes, tesseract still unable to find lept.pc file.It gives configuration errors. For example, Leptonica 1.82 or higher is required. In that case, locate the lept.pc file (usually present at /usr/local/lib/pkgconfig/) with the command locate lept.pc and copy the same in /usr/lib64 directory.sudo cp /usr/local/lib/pkgconfig/lept.pc /usr/lib64/pkgconfig/Similarly, some services might not be able to get Libleptonica shared object files (.so files, ex: liblept.so, libleptonica.so etc.).Note:
.so files are usually present in the server at /usr/local/lib. - Type whereis libleptonica or locate
libleptonica to find the path and copy the .so
files in /usr/lib64
path.
cd /usr/local/lib sudo cp -a *liblept* /usr/lib64
- Copy the Tesseract tarball tesseract-4.1.0.tar.gz
to the server (installation directory). For example,
/scratch. - Copy the Tesseract trained files eng.traineddata, osd.traineddata to the server.
- Execute below commands sequentially to build and
install
Tesseract.
sudo tar xvf tesseract 5.1.0.tar.gz cd tesseract-5.1.0 sudo ./autogen.sh sudo ./configure --prefix=/usr sudo make -j4 .Note:
/usr/binis the directory where tesseract binary will be present if you passprefix=/usrin configure. You can provide the path based on where you want to install. - Copy the traineddata files in tessdata
directory.
If you use
prefix=/usr, tessdata directory is present at/usr/share. If you useprefix=/usr/local, tessdata directory is present at/usr/local/share.sudo cp osd.traineddata /usr/share/tessdata sudo cp eng.traineddata /usr/share/tessdata
- Execute the below commands to set the Tesseract
library
path.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/lib export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/lib - Sometimes services are unable to find
libtesseractshared object files (.so files) present in system (Usually at/usr/lib). In that case copy thelibtesseractfiles in/usr/lib64.cd /usr/lib sudo cp -a *libtesseract* /usr/lib64 - Some programs search for the
tessdatadirectory in a different path (usr/share/tesseract/4/tessdata). Copy the existing tessdata directory to the path (either in/usr/share or /usr/local/sharebased on your installation).cd /usr/share sudo mkdir tesseract(execute if tesseract directory is not p resent) cd tesseract sudo mkdir 4 cd /usr/share sudo cpR tessdata /usr/share/tesseract/4 - Run the below command to set tessdata
prefix.
export TESSDATA_PREFIX=/usr/share/tesseract/4/tessdataThe Tesseract is now installed.
- Verify the version with below
command.
tesseract --versionIt shows the tesseract version (5.1.0), leptonica version (1.82.0) along with other default libraries (libjpeg, libjpeg-turbo, libpng, libtiff, zlib).
10.6 Conductor Installation
This topic provides the systematic instructions to install conductor.
Before proceeding, ensure that the below steps are done.
- Make sure that the
datasource jdbc/PLATO-Ois created. The maximum capacity attribute of the datasource connection pool must be greater than 100. - Make sure that the Domain and cluster configuration steps are completed.
Note:
The conductor-server.war file needs to be deployed on a separate manged server due to its load and size.
10.7 Report Service Installation
This topic provides the systematic instructions to install report service.
Before proceeding, ensure that the below steps are done.
- Make sure that the data source is created.
Table 10-7 Data Source List
Data source Name Data source JNDI Targets PLATOCMC jdbc/CMNCORE Plato Common Core Server PLATOSMS jdbc/sms Plato-SMS-Server REPORTSERIVCE jdbc/REPORTSERVICE Plato-Report-Service-Server - Make sure that the below wars are installed along with the ones mentioned above.
- CMC Core Service
- CMC Base Service
- CMC Currency Service
- CMC Component Service
- Plato Report Service
- SMS Component Server
- App Shell
Install setUserOverrides.sh file
Perform the following steps:
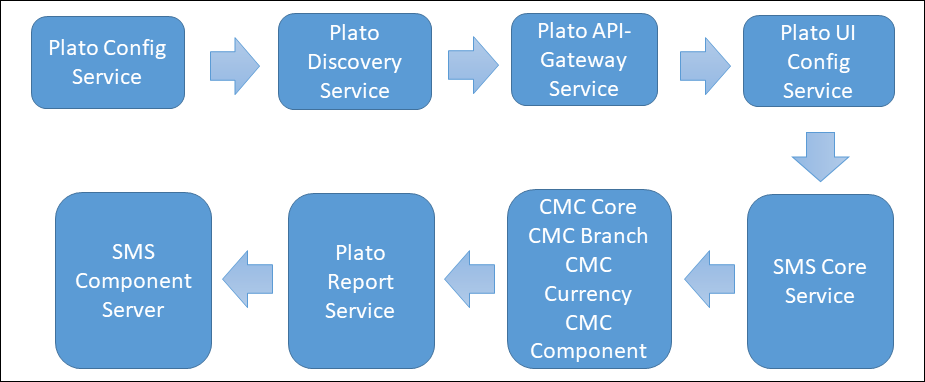
Figure 10-1 Plato Reporting Deployment Order
Table 10-8 Installation Summary for Plato Reporting Service:
| Application | Archive name | OSDC path | Targets |
|---|---|---|---|
| sms-core-Service | sms-core-Service-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\sms-core-service\ | Sms-core-Service |
| cmc-base-services | cmc-base-services-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\cmc-base-service\ | cmc-base-Service |
| cmc-branch-services | cmc-branch-services-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\cmc-branch-service\ | cmc-branch-Service |
| cmc-currency-services | cmc-currency-services-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\cmc-currency-service\ | cmc-currency-Service |
| cmc-component-server | cmc-component-services-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\cmc-component-service\ | cmc-component-Service |
| plato-report-Services | plato-report-Services-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\plato-report-services\ | Plato-report-Server |
| sms-component-server | sms-component-services-{version}.war | {unzip the file}PLATO\sms-component-service\ | sms-component-Service |
Note:
Refer to OSDC file for the exact version number for each service.