A Deploying the OAM Service
This chapter describes how to optionally deploy and manage the Oracle Access Manager (OAM) service.
Required Software
The following software can be optional if you use an Identity Provider other than OAM:
-
Oracle Access Manager (OAM), included with Oracle Identity and Access Management 12c (12.2.1.4.0)
-
Oracle WebLogic Server 12c (12.2.1.4.0)
-
Oracle HTTP Server (OHS) 12c (12.2.1.4.0)
-
Oracle HTTP Server 12c WebGate for OAM
Install the following required software only if you use OAM or OHS for traditional UIM.
Note:
You can skip installing the following software if your Identity Provider supports SAML2.0.To install the required software, do the following:
-
Install Oracle WebLogic Server 12c and create the Oracle Middleware Home directory (MW_Home). This is the directory in which the Oracle Fusion Middleware products are installed.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle WebLogic Server 12c.
-
Install Oracle Access Manager (OAM) in the same Oracle Middleware Home directory that you created when you installed Oracle WebLogic Server 12c.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity and Access Management.
-
Install and configure Oracle HTTP Server, which is a Web server that acts as the front end to the Oracle WebLogic Server.
For more information, Oracle Fusion Middleware Installing and Configuring Oracle HTTP Server.
-
Install and configure Oracle HTTP Server WebGate for OAM.
A WebGate is a web-server plug-in for Oracle Access Manager (OAM) that intercepts HTTP requests and forwards them to the Access Server for authentication and authorization. For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Installing WebGates for Oracle Access Manager.
-
Install an external LDAP server. For example, Oracle Internet Directory (OID). Oracle recommends Oracle Internet Directory as an external LDAP store.
For information on installing and configuring Oracle Internet Directory, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity Management.
-
Configure the external LDAP as the user identity store in OAM.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Access Management.
-
Register the Oracle HTTP Server WebGate instance with OAM by using the Oracle Access Manager Administration Console.
For more information, see the chapter on “Registering Partners (Agents and Applications) by Using the Console" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle Access Manager with Oracle Security Token Service.
-
Continue with the steps in "Configuring UIM to Enable SSO Authentication" in UIM Installation Guide.
Note:
OAM, OHS, and WebGate are optional when you use UIM with ATA, and if you use any other identity provider.Building the OHS Image
To build OHS image:
- Go to WORKSPACEDIR that is created in "Unified Inventory and Topology Toolkit".
- Download V983369-01.zip: Oracle Fusion Middleware 12c (12.2.1.4.0) HTTP Server for Linux x86-64, 1.9 GB file from Oracle E-Delivery by searching for the file from Oracle HTTP Server 12.2.1.4.0 for (Linux x86-64) and copy them to the $WORKSPACEDIR/ohs-builder/staging/downloads/ folder.
- Modify
ohsBaseImage.package.pathin $WORKSPACEDIR/ohs-builder/bin/ohs_manifest.yaml with the filename of the downloaded OHS archive file. - Download
jdk-<version>_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzand copy to the $WORKSPACEDIR/ohs-builder/staging/downloads/java folder.Note:
See UIM Compatibility Matrix for the latest versions of software. - Modify the
ohsBaseImage.jdk.pathin $WORKSPACEDIR/ohs-builder/bin/ohs_manifest.yaml file with the name of the downloaded JDK file. - Run
build-all-images.shin bin directory to build all images on OHS.
Deploying OAM along with OHS for Authentication Service
Before deploying OAM using the COMMON CNTK scripts, ensure the following:
- WebLogic Operator is deployed and configured as per UIM_CNTK. See "Setting Up Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes Operator" in UIM Cloud Native Deployment Guide for more information.
- Namespace is registered with WebLogic Operator using the UIM_CNTK script. See "Registering the Namespace" in UIM Cloud Native Deployment Guide for more information.
- Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer is installed as per UIM_CNTK script. See "Installing the Traefik Container Image" in UIM Cloud Native Deployment Guide for more information.
- Pull the Oracle Access Manager Image or latest cpu image from Oracle
Container Registry as follows:
- Launch a browser and access the "Oracle Container Registry".
- Click Sign In and enter your username and password.
- In the Search field, enter Oracle Access Manager and press Enter.
- Click oam_cpu for the latest CPU patch image of Oracle Access Manager.
- In the Terms and Conditions box, select the language as English.
- Click Continue and accept Terms and Restrictions.
- On your Podman environment, log in to the Oracle Container
Registry and enter your Oracle SSO username and password when
prompted:
$ podman login container-registry.oracle.com Username: <username> Password: <password> $ podman pull <oam-cpu-image-name> - Pull the Oracle Access Manager Image or latest CPU image from Oracle
Container Registry as follows.
For example: Use the following command to pull OAM CPU image from Oracle Container Registry:
docker pull container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/oam_cpu:12.2.1.4-jdk8-ol7-221014
- Download Oracle Communications Unified Inventory Management Common Toolkit from Oracle Software Delivery Cloud.
Deploying OAM Using Common Cloud Native Toolkit Scripts
To deploy OAM using COMMON_CNTK scripts:
- Go to the $WORKSPACEDIR/common_cntk folder created in Unified Inventory and Topology Toolkit and export the path to a variable COMMON_CNTK. See "Unified Inventory and Topology Toolkit" for more information.
- Modify the parameters in the
$SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yamlfile as follows:- inventory.host: Provide the inventory host IP or address where UIM traditional application is installed. This is a mandatory parameter. For UIM cloud native instance, the value is: <uimproject>-<uiminstance>-cluster-uimcluster.<uimproject>.svc.cluster.local
- inventory.port: Provide the inventory host port where the UIM on-perm is installed. This is a mandatory parameter. For UIM cloud native instance, the value is 8502.
- inventory.isSSL: If traditional UIM has the SSL port used, change the value to true, for Cloud Native Inventory always false.
- imagePullSecret: Provide the Kubernetes secret name containing the Docker secrets to pull images. This is a mandatory parameter. This secret should be accessible, which means that it must be created in the same namespace as OAM.
- persistentVolumeClaimName: Provide the existing pvc name for storage of OAM domain. This is a mandatory parameter.
- hostSuffix: By default it is .uim.org.
- loadBalancerPort: The load balancer port exposed by Traefik or external load balancer. Enter the Secure/SSL port.
- gcLogs: To enable GC logs for OAM, set enabled to
true and configure the number of files and size of each file. You
can uncomment values inside oam-server to override common values for
gcLogs.
For example:
gcLogs: enabled: true fileSize: 10M noOfFiles: 10 - tls.enabled: Flag to enable tls or ssl. By default, it is true. If true, create the certificate and the key mentioned in next step. Oracle recommends not to disable SSL in production environment.
- If SSL is enabled that is,
tls.enabledis true, create the certificate as follows:- Create
certsfolder in $COMMON_CNTK. - Copy your signed certificate and key into
certsfolder by renaming the certificate name ascommoncert.pemand renaming the key file name ascommonkey.pem.Note:
OAM supports wild card certificates. Your certificate can be updated with the
*.<hostSuffix>. By default, thehostSuffixvalue isuim.orgfrom applications.yaml. See "Using Wild Card Certificates" for more information. - (Optional) Run the following command to create Single
Certificate and Key for OAM, messaging-bus, UIM, and
ATA:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commonkey.pem -out $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commoncert.pem -subj "/CN=<instance>.<project>.admin.uim.org" -extensions san -config <(echo '[req]'; echo 'distinguished_name=req'; echo '[san]';echo 'subjectAltName=@alt_names'; \echo '[alt_names]'; \ echo 'DNS.1=<instance>.<project>.admin.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.2=<instance>.<project>.oam.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.3=<instance>.<project>.ohs.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.4=uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.5=<instance>.<project>.topology.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.6=localhost'; \ echo 'DNS.7=svc.cluster.local'; \ echo 'DNS.8=<instance>.<project>.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.9=admin.<instance>.<project>.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.10=t3.<instance>.<project>.uim.org'; \ )An example for project:sr and instance: quick:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commonkey.pem -out $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commoncert.pem -subj "/CN=quick.sr.admin.uim.org" -extensions san -config <(echo '[req]'; echo 'distinguished_name=req'; echo '[san]';echo 'subjectAltName=@alt_names'; \echo '[alt_names]'; \ echo 'DNS.1=quick.sr.admin.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.2=quick.sr.oam.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.3=quick.sr.ohs.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.4=uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.5=quick.sr.topology.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.6=localhost'; \ echo 'DNS.7=svc.cluster.local'; \ echo 'DNS.8=quick.sr.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.9=admin.quick.sr.uim.org'; \ echo 'DNS.10=t3.quick.sr.uim.org'; \ )Note:
Ensure that commoncert.pem and commonkey.pem files are present in the $COMMON_CNTK/certs folder.
OAM, UIM, ATA, and Message Bus support wildcard certificates. See "Using Wild Card Certificates" for more information.
- (Optional) To generate your own self-signed certificates, see "SSL Certificates".
- Create
- Create the secrets for OAM as follows:
- Create the mandatory secrets according to the system prompts as
follows:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/manage-app-credentials.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a oam create database,wlsadmin,ingressTLS Applications specified - oam ====create database,wlsadmin,ingressTLS secret for oam Application==== Provide Database credentials for 'sr-quick-oam' ... OAM DB Admin(sys) Username: <PDB-ADMIN-USER> OAM DB Admin(sys) Password: <PDB-ADMIN-PWD> OAM Schema Username: <OAM_SCHEMA_USER> OAM Schema Password: <OAM_SCHEMA_PWD> OAM DB Host: <DB_HOSTNAME> OAM DB Port: <DB_PORT> OAM DB Service Name: <SERVICE-NAME> Provide Weblogic Admin credentials for 'sr-quick-oam' ... Weblogic Admin Username: <WL_ADMIN_USER> Weblogic Admin Password: <WL_ADMIN_PWD> Provide Ingress TLS Credentials for OAM application 'sr-quick-oam' ... Ingress TLS Certificate Path (PEM file): $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commoncert.pem Ingress TLS Key file Path (PEM file): $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commonkey.pem secret/sr-quick-oam-rcu-credentials created secret/sr-quick-oam-wls-credentials created secret/sr-quick-oam-ingress-tls-cert-secret created Execution status of secrets for command - create: OAM MICROSERVICE...........OkNote:
The RCU Schema password guideline specifies that a valid password must be specified. The password should be alpha numeric only and can contain the following special characters: # , _ . The password should not start with a number or a special character.
<OAM_SCHEMA_USER>should be less 12 characters and<OAM_SCHEMA_PWD>is the RCU Schema password. - Ensure the following secrets are created:
- Database secret : Contains the details of OAM database
schema. For example,
sr-quick-oam-rcu-credentials. - wlsadmin secret: Contains the credentials for
WebLogic and oamconsole. For example,
sr-quick-oam-wls-credentials. - ingressTLS: Contains certificate and key for
OAM. For example,
sr-quick-oam-ingress-tls-cert-secret.
- Database secret : Contains the details of OAM database
schema. For example,
- For traditional UIM, if SSL port is used, you must create
additional configmap to pass the inventory
certificate.
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/manage-app-credentials.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a oam create inventorySSL Provide Inventory SSL Credentials for OAM application 'sr-quick-oam' ... On-prem Inventory SSL Certificate Path (PEM file): <provide inventory certificate>
- Create the mandatory secrets according to the system prompts as
follows:
- Configure Ingress and Ingress Controller for OAM. See "Configuring Ingress and Ingress Controller for OAM" for more information.
- Create schema by running the following commands to install OAM DB and
ensure that database secret and image name for database.yaml are
correct:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/install-database.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/database.yaml -a oam -c 1 - Create OAM by running the following command to install OAM and ensure
that you updated applications.yaml
file:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/create-applications.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a oam
Using Wild Card Certificates
OAM, UIM, ATA and Message Bus supports wildcard certificates. You can generate wildCard Certificates with the hostSuffix value provided in applications.yaml. The default is uim.org.
To use wild card certificates:
- To create a self-signed wild card certificate, use the following
command:
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout $COMMON_CNTK/certs/wildcardkey.pem -out $COMMON_CNTK/certs/wildcardcert.pem -subj "/CN=*.uim.org" -extensions san -config <(echo '[req]'; echo 'distinguished_name=req'; echo '[san]';echo 'subjectAltName=@alt_names'; \echo '[alt_names]'; \ echo 'DNS.1=*.uim.org'; \ ) - Change the subDomainNameSeperator value from period (.) to hyphen
(-) so that the incoming hostnames match the wild card DNS
pattern.
Update the $SPEC_PATH/project/instance/applications.yaml file as follows:
#Uncooment and provide the value of subDomainNameSeparator, default is "." #Value can be changed as "-" to match wild-card pattern of ssl certificates. #Example hostnames for "-" quick-sr-topology.uim.org subDomainNameSeparator: "-" - If you have configured the above settings, the following are the hostnames to access
OAM application for project:sr, instance:quick, and hostSuffix:
uim.org:
oam-admin hostname: quick-sr-admin.uim.org oam-ohs hostname: quick-sr-ohs.uim.org oam hostname: quick-sr-oam.uim.org oam-policy hostname: quick-sr-policy.uim.org
Configuring Ingress and Ingress Controller for OAM
OAM supports standard Kubernetes ingress API and provides samples for integration. The following configuration provides the OAM required annotations for NGINX.
Any Ingress Controller that conforms to the standard Kubernetes Ingress API and supports annotations needed by OAM should work. Oracle does not certify any individual Ingress controllers to confirm this generic compatibility.
The annotations for OAM are:
- To use Annoation Base Generic Ingress Controller, update applications.yaml
from $SPEC_PATH/project/instance as
follows:
# Valid values are TRAEFIK, GENERIC ingressController: "GENERIC" ingress: className: nginx ##provide ingressClassName value, default value for nginx ingressController is nginx. annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity: "cookie" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/affinity-mode: "persistent" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/session-cookie-name: "nginxingresscookie" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "50m" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: 64k - To enable SSL, provide the following annotations in applications.yaml under
oam-server
tag:
oam-server: ingress: annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/configuration-snippet: | more_clear_input_headers "WL-Proxy-Client-IP" "WL-Proxy-SSL" "X-Custom-Request-Header" ; more_set_input_headers "X-Forwarded-Proto: https"; more_set_input_headers "WL-Proxy-SSL: true"; more_set_input_headers "IS_SSL: ssl"; - To use TRAEFIK Ingress Controller, update applications.yaml from
$SPEC_PATH/project/instance as
following:
# Valid values are TRAEFIK, GENERIC ingressController: "TRAEFIK"
Upgrading OAM
To upgrade OAM, you can use following command:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/upgrade-applications.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a oamNote:
This upgrade command will restart OAM and OHS deployments. If you want to update ingressTLS, inventorySSL secrets or want to make any changes in applications.yaml for OAM, you can perform this operation.
This command will not make any changes to OAM domain. To update domain, you need to uninstall OAM and recreate.
Uninstalling OAM
To uninstall OAM:
- Delete OAM as
follows:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/delete-applications.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a oam - Delete OAM db schema as
follows:
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/install-database.sh -p sr -i quick -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/database.yaml -a oam -c 2 - Run the file
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/uninstall.sh.Note:
Ensure the domain folder and its contents on the PV_SHARED_PATH or PathsharedDomainPathon NFS are deleted after the uninstallation. That is, delete<project>-<instance>-oamand<project>-<instance>-oam-ohsfolders.
Specifying the Proxy Settings
Enter the following proxy settings:
- In the browser, go to network no-proxy settings and include the *<hostSuffix> value from $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml. By default, it is .uim.org that is, *.uim.org.
- In
/etc/hoststhe following may changed based on the<instance>,<project>, andhostSuffixvalues in $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml.
etc/hosts:
<k8s cluster ip> <instance>.<project>.oam.<hostSuffix> <instance>.<project>.admin.<hostSuffix> <instance>.<project>.policy.<hostSuffix> <instance>.<project>.ohs.<hostSuffix>
for example:
<k8s cluster ip> quick.sr.oam.uim.org quick.sr.admin.uim.org quick.sr.policy.uim.org traefik.uim.org quick.sr.ohs.uim.orgAccessing the WebLogic Server Administration Console and the OAM Console
You need to complete the proxy settings for accessing the WebLogic Server Administration console and the OAM console. The credentials for accessing WebLogic console or OAM console are stored in the wlsadmin secret.
https://<instance>.<project>.admin.<hostSuffix>:<loadBalancerPort>/consolehttps://quick.sr.admin.uim.org:30443/consolehttps://<instance>.<project>.admin.<hostSuffix>:<loadBalancerPort>/oamconsolehttps://quick.sr.admin.uim.org:30443/consoleConfiguring OAM
To configure OAM before using it for SSO authentication:
- Log in to Oracle Access Management (OAM)
Console:
https://<instance>.<project>.admin.<hostSuffix>:<loadBalancerPort>/oamconsole - Click Configuration at the top right corner of the Console to show Configuration Launch Pad.
- Click on Available Services and then click Enable Service for OAuth and OpenIDConnect Service.
- From Configuration Launch Pad, select Access Manager from the
View menu in the Settings section:
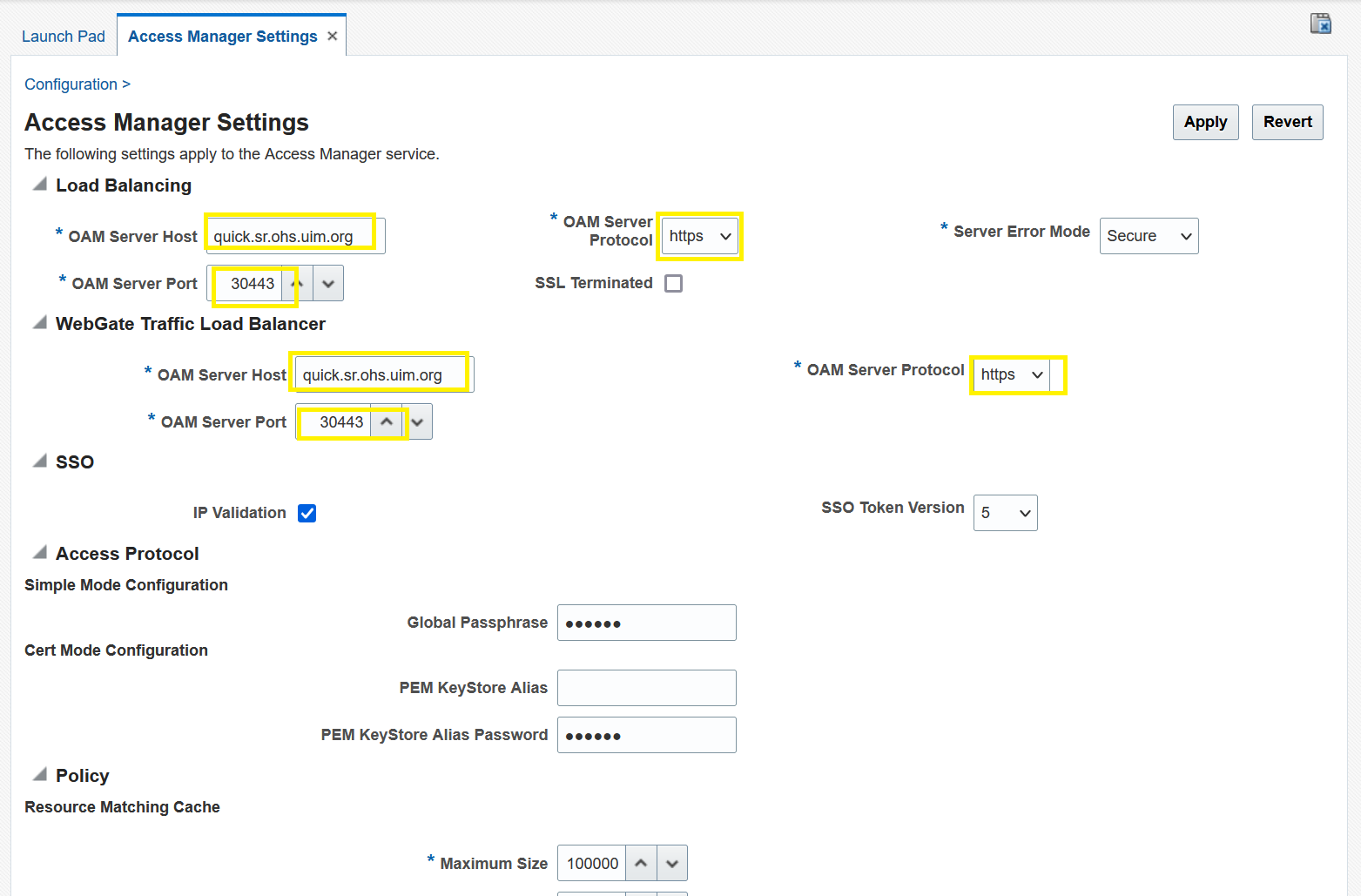
- Under Load Balancing and WebGate Traffic Load
Balancer, modify
OAM Server Hostwith<instance>.<project>.ohs.<hostSuffix >. ThehostSuffixvalue is taken from $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml. By default, it is .uim.org. - Modify
OAM Server Protocoltohttps. - Modify
OAM Server Portto<loadBalancerPort>. This value is from $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml. - Secure the load balancer port.
- Click Apply to save.
- Under Load Balancing and WebGate Traffic Load
Balancer, modify
- From Configuration Launch Pad, select User Identity Stores to
create an ID store for using the embedded LDAP of UIM:
- Click Create under the IDS Profiles section for creating an IDS profile.
- Specify Name as
UIMEmbeddedLDAP. - (Optional) Provide Description.
- Configure the Repository properties under Repository:
- Choose Repository Options by selecting Create New.
- Provide Directory Type as
Weblogic Server Embedded LDAP. - Provide Host Name as
<Inventory's AdminHost>and Port as<Inventory's AdminPort>under Hosts.Note:
In case of UIM Cloud Native Environment, provide AdminServer service name and port for<Inventory's AdminHost>:<Inventory's AdminPort>as<uim-project>-<uim-instance>-admin:8501 (sample: sr-quick-admin:8501). - If UIM onPrem admin server is SSL enabled, select SSL Enabled, for UIM Cloud Native environment not required.
- Provide the Bind DN as
cn=Admin. - Specify Bind Password provided for the embedded
LDAP in the WebLogic admin console. Ensure that the following steps
are performed in WebLogic console where UIM is deployed. In the
WebLogic Server admin console, change the credential for the
embedded LDAP server as follows:
Note:
In case of UIM Cloud Native environment, enter your WebLogic password in the Password field.- Expand Domain > Security > Embedded LDAP.
- In the Credential field, enter the new credential.
- In the Confirm Credential field, enter the new credential again.
- Click Save.
- Reboot the WebLogic server.
- Provide Base DN as
follows:
ou=myrealm,dc=<inventory application domain name>Note:
In case of UIM Cloud Native Environment, provide <inventory application domain name> as domain. On UIM CN, WebLogic domain name is set todomainby default.
- Configure the user properties to configure the LDAP user object under
User section:
- Provide Base DN as
ou=people,ou=myrealm,dc=<inventory application domain name>. - Provide Login ID Attribute as
uid.
- Provide Base DN as
- Configure the Group properties to configure the LDAP group object under Group section:
- Provide Base DN as
ou=groups,ou=myrealm,dc=<inventory application domain name>. - Click Test Connection on the top-right corner to ensure the connection to embedded LDAP is successful.
- Click OK to close the Connection Status dialog box.
- Click Create to create IDS profile.
Entries with the profile name are displayed in the IDS Profiles and IDS Repositories table.
- Click Sync IDS Profiles button on right side of OAM ID Stores section to see the IDSPROFILE-UIMEmbeddedLDAP entry displayed under OAM ID Stores table.
- Click Application Security at the top right corner of the Console to show the Application Security Launch Pad.
- Click Agents and then Search to show the UnifiedWebgate in the table.
- Select UnifiedWebgate from the table and click Edit to
modify the Webgate settings:
- Modify Logout Redirect URL as:
https://<instance>.<project>.ohs.<hostSuffix>:<loadBalancerPort/oam/server/logout - Modify the Access Server and Host Name under
Primary Server List as
Otherand<domainUID> -oam-server1 ' where domainUID is the <project>-<instance>-oam. By default, it issr-quick-oam-oam-server1. - Click Apply to save.
- Modify Logout Redirect URL as:
- From the Application Security Launch Pad, select Authentication Modules from
Plug-ins to create 'UIM Embedded LDAP Module' authentication module.
- Click Create LDAP Authentication Module in the Create dropdown, under Search Results section.
- Provide Name as UIM Embedded LDAP Module.
- Choose User Identity Store as IDSPROFILE-UIMEmbeddedLDAP that is created above.
- Click Apply to save.
- From the Application Security Launch Pad, select Authentication schemas from
Access Manager to create 'UIM Embedded LDAP Schema' authentication
schema.
- Click Create under Search Results section.
- Provide Name as UIM Embedded LDAP Schema.
- Provide Description as UIM Embedded LDAP Schema.
- Modify the Authentication Level as 2.
- Provide Challenge Method as FORM.
- Provide Challenge Redirect URL as /oam/server/.
- Choose Authentication Module as UIM Embedded LDAP Module.
- Provide Challenge URL as /login.jsp.
- Choose Context Type as customwar.
- Provide Context Value as /customConsent.
- Click Apply to save.
- From the Application Security Launch Pad, select Application
Domains from Access Manager to edit UnifiedWebgate application
domain.
- Click Search to show the UnifiedWebgate in the table.
- Select UnifiedWebgate from the table and click Edit to modify the Application Domain settings.
- Select Authentication Policies tab and select the Protected Resource Policy table item.
- Click Edit button to open Protected Resource Policy authentication policy settings.
- Choose Authentication Schema as UIM Embedded LDAP Schema from the drop down.
- Click Apply to save.
Configuring OAuth Service Settings
Complete the proxy settings as mentioned in the above section.
Ensure environment variable NO_PROXY is set with
<hostSuffix>.
Run the following commands from the machine on which the proxy settings are done:
export CREDS=`echo -n "<OAM_Domain_Username>:<password>" | base64 -w 0`
export OAMHOST=<instance>.<project>.admin.<hostSuffix> (example, quick.sr.admin.uim.org)
export OAMPORT=<loadBalancerPort> (the value provided in $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml)
Creating an OAuth Identity Domain
Run the following curl statement to create the UnifiedIdDomain identity domain with custom-consent enabled and using
IDSPROFILE-UIMEmbeddedLDAP as the identity
provider:
curl -i -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization:Basic ${CREDS}" --cacert $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commoncert.pem --noproxy $NO_PROXY --request POST https://${OAMHOST}:${OAMPORT}/oam/services/rest/ssa/api/v1/oauthpolicyadmin/oauthidentitydomain -d '{"consentPageURL":"/customConsent/customConsent.jsp","issueTLSClientCertificateBoundAccessTokens":false,"tokenSettings":[{"tokenType":"ACCESS_TOKEN","tokenExpiry":3600,"lifeCycleEnabled":false,"refreshTokenEnabled":true,"refreshTokenExpiry":86400,"refreshTokenLifeCycleEnabled":false},{"tokenType":"AUTHZ_CODE","tokenExpiry":3600,"lifeCycleEnabled":false,"refreshTokenEnabled":true,"refreshTokenExpiry":86400,"refreshTokenLifeCycleEnabled":false},{"tokenType":"SSO_LINK_TOKEN","tokenExpiry":3600,"lifeCycleEnabled":false,"refreshTokenEnabled":true,"refreshTokenExpiry":86400,"refreshTokenLifeCycleEnabled":false}],"customAttrs":"{\"allowedCustomPlugins\":\"OAuthCustomClaimsPlugin\"}","name":"UnifiedIdDomain","description":"Unified Identity Domain","identityProvider":"IDSPROFILE-UIMEmbeddedLDAP","errorPageURL":"/oam/pages/servererror.jsp","keyPairRolloverDurationInHours":48}'Creating a Resource
Run the following curl statement to create UnifiedRserver resource
with default scope as Info:
curl -i -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization:Basic ${CREDS}" --cacert $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commoncert.pem --noproxy $NO_PROXY --request POST https://${OAMHOST}:${OAMPORT}/oam/services/rest/ssa/api/v1/oauthpolicyadmin/application -d '{"tokenAttributes":[],"resServerType":"CUSTOM_RESOURCE_SERVER","resourceServerNameSpacePrefix":"UnifiedRserver.","name":"UnifiedRserver","description":"Unified Resource Server","audienceClaim":null,"scopes":[{"scopeName":"Info","description":"null"},{"scopeName":"DefaultScope","description":"DefaultScope"}],"idDomain":"UnifiedIdDomain","resourceServerId":"1f50f6f4-06a9-4d1b-8347-bc5672a12e56"}'Creating a Client
Run the curl statement to create topologyClient client.
The following is an example for creating a client with <project> as sr and <instance> as quick:
curl -i -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization:Basic ${CREDS}" --cacert $COMMON_CNTK/certs/commoncert.pem --noproxy $NO_PROXY --request POST https://${OAMHOST}:${OAMPORT}/oam/services/rest/ssa/api/v1/oauthpolicyadmin/client -d '{"clientType":"CONFIDENTIAL_CLIENT","issueTLSClientCertificateBoundAccessTokens":false,"name":"topologyClient","grantTypes":["PASSWORD","CLIENT_CREDENTIALS","JWT_BEARER","REFRESH_TOKEN","AUTHORIZATION_CODE"],"description":"null","attributes":[{"attrName":"customeAttr1","attrValue":"CustomValue","attrType":"STATIC"}],"id":"topologyClient","secret":"<secret>","scopes":["UnifiedRserver.Info"],"defaultScope":"UnifiedRserver.Info","redirectURIs":[{"url":"https://quick.sr.topology.uim.org:30443/topology","isHttps":true},{"url":"https://quick.sr.topology.uim.org:30443/redirect/ata-ui","isHttps":true}],"idDomain":"UnifiedIdDomain"}'Add topology service specific redirect URLs under redirectURIs attribute in json data and update <secret>:
- For ATA-API:
redirect-uri: "https://<instance>.<project>.topology.<hostSuffix>:<port>/topology" - For ATA-UI:
redirect-uri: https://<instance>.<project>.topology.<hostSuffix>:<port>/redirect/ata-ui
Note:
"redirectURIs":[{"url":"https://quick.sr.topology.uim.org/topology","isHttps":true},
{"url":"https://quick.sr.topology.uim.org/redirect/ata-ui","isHttps":true}]Debugging and Troubleshooting
The following are some common issues.
Unable to create Domain or Admin Server is not coming up
To troubleshoot the issue:
- Check if a folder with the domain name already exists at the
persistentVolumeClaim location.
If there is a Domain Exists error, the following message appears:
The domain will be created using the script /u01/weblogic/create-domain-script.sh ERROR: The create domain job will not overwrite an existing domain. The domain folder /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/accessdomain already exists - Ensure RCU schema creation is
successful.
kubectl -n <NAMESPACE> get pods - Check the logs of
<project>-<instance>-oam-dbschema(kubectl -n <NAMESPACE>), which ends withRepository Creation Utility - Create : Operation Completedline. - Check the logs of
<project>-<instance>-oam-create-infra-domain-job-<podsuffix>.
To resolve the issue:
- If a folder with the same domain name already exists, delete the domain folders (<project>-<instance>-oam and <project>-<instance>-oam-ohs) and its contents.
- Uninstall OAM. See Uninstalling OAM for more information.
- If RCU Schema creation is not successful, then check the rcuDatabaseURL and
rcuSchemaPrefix values provided.
Note:
Same
rcuSchemaPrefixvalue cannot be used for different domains with in the same database. - Resolve the database issues and run the scripts again.
- Resolve the errors appeared in the logs of
<project>-<instance>-oam-create-infra-domain-job-<podsuffix>:- If you see
mkdir: cannot create directory ... : Permission deniederror, then ensure the PVC/sharedDomainPath has permissions. For example:chmod 777 /scratch/shared. - If there are no errors or exceptions in logs, ensure the <NAMESPACE> is registered with the WebLogic operator as mentioned in prerequisites for running scripts.
- If you see
-
Before running the scripts again, remove the Helm releases that are partially installed as follows to get the helm releases in the namespace:
helm ls -n <NAMESPACE> -
Unable to Access OAM Console
Unable to access OAM Console using:
https://admin.<DOMAIN_NAME><hostSuffix>:<loadBalancerPort>/oamconsole
To troubleshoot the issue:
- Ensure the OHS service is up and running the following
commands:
kubectl -n <NAMESPACE> logs <project>-<instance>-oam-ohs-<podSuffix> - Ensure the
loadBalancerPortis correct and provide secure port if SSL is enabled. - Ensure proxy settings are done.
To resolve the issue, identify and uninstall the failed pod as follows:
-
Check if there are any pods that are failed or in the Error state using:
kubectl -n <NAMESPACE> get pods -
Check the release of the pods using the following Helm command:
helm ls -n <NAMESPACE> -
If RCU Schema creation has failed, uninstall
<project>-<instance>-oam-dbschemarelease using:helm -n <NAMESPACE> uninstall <project>-<instance>-oam-dbschema -
If OAM domain creation has failed, uninstall
<project>-<instance>-oam-createdomainrelease using:helm -n <NAMESPACE> uninstall <project>-<instance>-oam-createdomain - Run
$COMMON_CNTK/scripts/delete_applications.sh -p <project> -i <instance> -f $SPEC_PATH/sr/quick/applications.yaml -a oamthen ensure the<DOMAIN_NAME>folder and<DOMAIN_NAME>-ohsfolder (if exists) from the PVC/sharedDomainPathis deleted.
Inventory UI is not appearing after successful login
To troubleshoot the issue, check if you have the credentials to view UIM and check the logs of ATA-UI service.
The following error appears if you have recreated UIM.
Failure of Web Server bridge:
No back-end server available for connection: timed out after 10 seconds or idempotent set to OFF or method not idempotent.
To resolve the issue:
- Restart the OHS pod.
- Get the OHS pod name using
kubectl -n <namespace> get podscommand where the name of the pod is<project>-<instance>-oam-ohs-<podsuffix>.Note:
The pod name starts withPod name starts with <project>-<instance>-oam-ohs-<number>. -
Open the OHS pod using:
kubectl -n oamns exec -it <OHS_POD_NAME> –- bash. - Run the command:
echo '<DOMAIN_USER_PWD>' | /u01/oracle/ohssa/user_projects/domains/<project>-<instance>-oam-ohs/bin/restartComponent.sh ohs1 - Exit from the pod using
exit.
Alternatively, you can restart OHS by rolling out restart from deployments as follows:
kubectl -n <namespace> get deployments
kubectl -n <namespace> rollout restart deployment <project>-<instance>-oam-ohsUIM UI Not Accessible on Using SSL Port of Traditional UIM Instance
Check the OHS logs and if you observe SSL Handshake error message in logs. For example,
wl_ssl_open : SSL Handshake failed onserror : Success, error : 29024,
status : 2, perform the following resolution steps:
-
Identify the Inventory certificate file (.pem) and copy it into OHS pod.
kubectl -n <NAMESPACE> cp <inventory-certificate-file> <NAMESPACE>/<OHS_POD_NAME>:/u01/oracle/ohssa/user_projects/domains/<project>-<instance>-oam-ohs/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/instances/ohs1/keystores/ -
Enter the OHS pod using:
kubectl -n <NAMESPACE> exec -it <OHS_POD_NAME> bash - Run the below commands inside the OHS
pod:
cd /u01/oracle/ohssa/user_projects/domains/<project>-<instance>-oam-ohs/config/fmwconfig/components/OHS/instances/ohs1/keystores /u01/oracle/ohssa/oracle_common/bin/orapki wallet create -wallet <wallet-name> -auto_login_only /u01/oracle/ohssa/oracle_common/bin/orapki wallet add -wallet <wallet-name> -trusted_cert -cert <inventory-certificate-file> -auto_login_only cd .. vim mod_wl_ohs.conf #edit the file for the locations mentioned as below <Location /Inventory> WLSRequest On WebLogicHost <inventory.host> WeblogicPort <inventory.port> #WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON SecureProxy ON WLSSLWallet "${ORACLE_INSTANCE}/config/fmwconfig/components/${COMPONENT_TYPE}/instances/${COMPONENT_NAME}/keystores/<wallet-name>" SetHandler weblogic-handler </Location> <Location /InventoryWS> WLSRequest On WebLogicHost <inventory.host> WeblogicPort <inventory.port> #WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON SecureProxy ON WLSSLWallet "${ORACLE_INSTANCE}/config/fmwconfig/components/${COMPONENT_TYPE}/instances/${COMPONENT_NAME}/keystores/<wallet-name>" SetHandler weblogic-handler </Location> <Location /InventoryRSOpenAPI> WLSRequest On WebLogicHost <inventory.host> WeblogicPort <inventory.port> #WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON SecureProxy ON WLSSLWallet "${ORACLE_INSTANCE}/config/fmwconfig/components/${COMPONENT_TYPE}/instances/${COMPONENT_NAME}/keystores/<wallet-name>" SetHandler weblogic-handler </Location> <Location /cartridge> WLSRequest On WebLogicHost <inventory.host> WeblogicPort <inventory.port> #WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON SecureProxy ON WLSSLWallet "${ORACLE_INSTANCE}/config/fmwconfig/components/${COMPONENT_TYPE}/instances/${COMPONENT_NAME}/keystores/<wallet-name>" SetHandler weblogic-handler </Location> <Location /mapviewer> WLSRequest On WebLogicHost <inventory.host> WeblogicPort <inventory.port> #WLProxySSL ON WLProxySSLPassThrough ON SecureProxy ON WLSSLWallet "${ORACLE_INSTANCE}/config/fmwconfig/components/${COMPONENT_TYPE}/instances/${COMPONENT_NAME}/keystores/<wallet-name>" SetHandler weblogic-handler </Location> - Restart the OHS
server:
echo '<WL_ADMIN_PWD>' | /u01/oracle/ohssa/user_projects/domains/<project>-<instance>-oam-ohs/bin/restartComponent.sh ohs1 - See the Configuring a Plug-In for One-Way SSL section from Using Oracle
WebLogic Server Proxy Plug-Ins 12.2.1.4.0 and perform the
following:
Note:
Perform this in UIM administrator console.-
Log into the Oracle WebLogic Server administration console.
- In the Domain Structure pane, expand the Environment node. If the server instances that are used to proxy the requests from Oracle HTTP Server are in a cluster, select Clusters. Otherwise, select Servers.
-
Select the server or cluster that you want to proxy the requests from Oracle HTTP Server.
-
In the Configuration: General tab, scroll down to the Advanced section and expand it.
- Do one of the following:
- To enable one-way SSL, select WebLogic Plug-In Enabled.
- To enable two-way SSL where client certificates are used to authenticate, select Client Cert Proxy Enabled.
- To enable two-way SSL with client certificates, select Both.
- If you have selected Servers in Step 2, repeat steps 3 and 4 for the other servers to which you want to proxy the requests from Oracle HTTP Servers.
-
Click Save.
- For the change to take effect, you must restart the server instances.
-
See the "Configuring the SSL Policy/Certificate" section from UIM System Administrator's Guide for configuring SSL with Oracle WebLogic server.