Additional Rf Features Alarms and Traps
Service-Context-ID Format
The Service-Context-ID AVP (461) located in the root ACR message is formatted as follows:
[[["extensions".]MNC.MCC.]"Release".]32260@3gpp.orgwhere
- extensions—This is operator specific information to any extensions in a service specific document. The value is configured by setting the diam-srvc-ctx-ext parameter.
- MNC.MCC—This identifies the operator implementing the service specific document, which is used to determine the specific requirements for the operator configurable parameters. Both MNC and MCC must be specified separated by a dot(.). The value is configured by setting the diam-srvc-ctx-mnc-mcc parameter as two integers separated by a dot. For example: 012.310
- Release—This indicates the
3GPP Release the service specific document is based upon e.g. 6 for Release 6.
The value is configured by setting the
diam-srvc-ctx-rel parameter with valid values
are >=1.
Note:
"32260@3gpp.org" is fixed.
Acme Excluded Attribute Range
You can select certain ACME specific AVPs to include in the Rf accounting records with the diam-acme-attr-id-range parameter. If this parameter is configured with one or more values, then all other valid Acme-specific AVPs, by number, are excluded. If by configuration, the SBC will exclude one (or more) individual ACME attributes, there will be no effect. If by configuration an Acme-specific attribute number that refers to a group is excluded, the SBC removes the complete grouped AVP from the ACR message.
Consider:
- Acme-specific attribute 1—The grouped AVP
- Acme-specific attributes 2-35—The individual AVPs that make up the group
If you configure diam-acme-attr-id-range 1,3- the SBC includes all attributes in the Acme group; This configuration aims to exclude only attribute 3 but is has no effect.
If you configure diam-acme-attr-id-range 2-, the SBC excludes the full Acme-specific group because Acme-Packet-Specific-Extension-Rf AVP (1) was not included.
The diam-acme-attr-id-range parameter’s syntax is as follows:
| Syntax | Meaning |
|---|---|
| X-Y | include range of attribute IDs from X to Y (X and Y are included) |
| -Y | include any attribute ID <= Y |
| X- | include any attribute ID >= X |
| - | include any attribute ID |
| X | include attribute ID = X |
Including the To Header in ACRs and CDRs
You can configure the SBC to support the Acme-SipHdr-TO AVP. This AVP conveys the value of TO headers in Rf deployments. The system uses this AVP to populate the string in the sipHdrTO from SIP methods into ACRs and CDRs. Enabling this feature causes the system record the SIP 'To:' header in ACRs for all endpoints.
When configured, the SBC uses this AVP (code 122), to capture TO headers from incoming SIP message and populate the Acme-SipHdr-TO in the Acme-Packet-Specific-Extension-Rf grouped AVP.
By default, the SBC does not populate this AVP. You configure the sip-tohdr-in-acr option in the account-config to enable this behavior.
ORACLE(account-config)#options +sip-tohdr-in-acrSupporting IOI AVPs for Unregistered Endpoints
You can configure the SBC to include the Originating-IOI and Terminating-IOI AVPs within ACRs and Diameter based CDRs for unregistered endpoints in addition to registered endpoints. Support for registered endpoints is available without special configuration. For unregistered endpoints, you enable the ioi-for-unregistered option within the account-config element.
The Inter-Operator-Identifier AVP (838) is a grouped AVP that includes the originating IOI AVP (839) and the terminating IOI AVP (840) for the purpose of tracking inter-service provider traffic. The SBC extracts this information from incoming P-Charging-Vector headers in the 200 OK of an initial INVITE from either side of a peering deployment. When applicable, the SBC populates these AVPs within:
- START ACR—Requires that you configure the generate-start parameter to OK in the account-config.
- INTERIM ACR
- STOP ACR
- EVENT ACR
If there is no IOI info in the P-Charging-Vector, the SBC does not include these AVPs in ACRs.
You configure the charging-vector-mode to pass to convey these AVPs for unregistered endpoints. If you also enable the realm-as-ioi option, however, the SBC ignores the value derived from the pass parameter and includes the ingress and egress realm names in the AVPs.
The table below presents the orig-ioi and term-ioi that the SBC would send in its ACRs based on your realm-as-ioi and ioi-for-unregistered options configurations. Assume the ingress and egress realm names are realm1 and realm2. For the bottom three rows, assume the following P-Charging-Vector contents.
P-Charging-Vector: icid-value=89000078phcsioo6ohb4jq46e9c6nk1zz9e432-6;
icid-generated-at=171.15.252.1;orig-ioi=AAAA;term-ioi=BBBB| realm-as-ioi | ioi-for-unregistered | IOI in ACR for unregistered endpoints | Orig-ioi, term_ioi in ACR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Disabled | Disabled | Not Present | Absent, Absent |
| Disabled | Enabled | From the PCV in 200OK, if all conditions fulfilled | AAAA, BBBB |
| Enabled | Disabled | Ingress and Egress realm names | realm1, realm2 |
| Enabled | Enabled | Ingress and Egress realm names | realm1, realm2 |
You configure the ioi-for-unregistered option in the account-config to include the IOI AVPs in Diameter CDRs for unregistered endstations. If this option is not set, the SBC adds IOI AVPs in Diameter CDRs for registered endstations only.
Configure the ioi-for-unregistered option using the syntax below.
ORACLE(account-config)# options +ioi-for-unregisteredIf you type options and then the option value without the plus sign, you overwrite any previously configured options. To add a new option to an options list, prepend the new option with a plus sign as shown in the previous example.
Managing IOI for Peering Endpoints
You can configure the SBC to manage P-Charging-Vector (PCV) headers and populate standard AVPs and CDRs with Originating and Terminating IOIs for peering deployments. This is separate from IOI management within access and P-CSCF applications. Configurations that apply to this feature include the ioi-for-unregistered option in the applicable account-config, and the charging-vector-mode settings on the applicable sip-interface elements.
This feature allows the SBC to do the following for peering applications, wherein endpoints do not register with the SBC:
- Manage the inclusion and contents of PCV headers with respect to the
IOI and ICID parameters in INVITEs, 18x and 2xx messages.
When you configure the ioi_for_unregistered option, the SBC refers to IOIs from SIP messages to generate ICID values. If the SIP message doesn’t contain the PCV header from the access side, however:
- The SBC generates and inserts an ICID.
- The SBC does not insert IOIs in SIP messages or ACRs.
- Include IOI AVPS 838, 839, and 840 in START, INTERIM, STOP, and EVENT
ACRs and subsequent CDRs for the applicable end points.
When you configure the charging-vector-mode on the access side sip-interface to insert_ioi_pass in conjunction with the ioi_for_unregistered option, the SBC inserts IOIs from the ingress SIP message in the applicable CDRs. In addition, configure the charging-vector-mode on the core side sip-interface to delete-and-respond. If available, uses the IOI received in the applicable SIP messages. The SBC inserts either Orig or Term IOIs, depending on the call flow.
The SBC sends the same values for the IMS-Charging-Identifier (AVP Code: 841) and Inter-Operator-Identifier (AVP Code: 838) AVPs in ACRs.
Caveats to consider when using this feature include:
- The feature is applicable to Peering deployments.
- The feature also supports registered calls, when setting the ingress interface charging-vector-mode to insert_ioi_pass.
- An IPX Hub does not change the IOI (orig / term) during a call. This means the SBC only needs to consider the initial IOI, which is received in an originating INVITE or 18x / 200 OK messages (terminating).
- Refer, Reinvite, Update, SMS, Register scenarios are not in the scope of this feature.
- This feature does not apply to SIP forking call flows.
Configuring this Feature
You configure this feature by enabling the ioi-for-unregistered option in the applicable account-config The code block below depicts this configuration.
ORACLE(account-config)# options +ioi-for-unregisteredIn addition, you set the charging-vector-mode on the access sip-interface to insert_ioi_pass, and the charging-vector-mode on the core sip-interface to delete-and-respond. The code block below depicts these configurations.
sip-interface
realm-id CoreRealm
sip-port
...
operator-identifier Core_Side
charging-vector-mode delete-and-respond
sip-interface
realm-id AccessRealm
sip-port
...
operator-identifier IPX_HUB
charging-vector-mode insert_ioi_passThe realm-as-ioi feature supersedes this feature. If you have configured the realm-as-ioi option, the SBC does not transmit the PCV from the 200 OK to the Rf server. Instead, the SBC sends realm names as IOIs for accounting in diameter, radius and local CDRs.
Originating IOI Call Flow
Conditions for the access side call (IPX Hub) terminating at the Core side, depicted in the diagram below, include:
- The call is initiated from the IPX Hub side.
- You have configured the charging-vector-mode on the caller's sip-interface to insert_ioi_pass.
- The Orig_IOI present in the SIP P-Charging-Vector (PCV) header within the ingress INVITE.
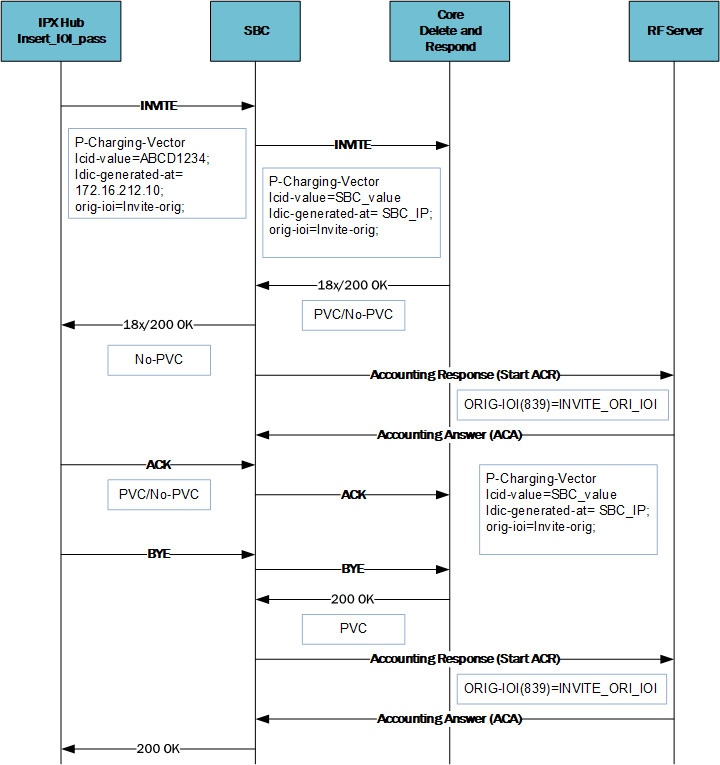
Processing for this call includes:
- In the egress Invite, while populating the P-Charging-Vector, the SBC uses the IOI from the ingress INVITE and generates the ICID values.
- The icid-generated-at parameter in the PCV is the IP address of the SBC sip-interface.
- The SBC replaces the ICID values received in the Ingress Invite with its own generated values.
- Because there are no IOI values provided from the core side (delete-and-respond), this scenario does not include any IOI values in the 18x/2xx messages.
- In this scenario, the SBC includes only the Originating-IOI in the ACR towards the Rf server.
Note:
The SBC handles any PCV parameters coming from the core side according to the configured charging-vector-mode.Note:
The SBC uses the initial/first IOI in the ACR towards the Rf server.Terminating IOI Call Flow
Conditions for the core side call terminating at the access side, depicted in the diagram below, include:
- The call is initiated from the core side.
- You have configured the charging-vector-mode on the caller's sip-interface to delete_and_respond causing the SBC to drop the PCV.
- The ingress 18x/2xx has the Term-IOI, which the SBC uses to populate the ACR and the egress response towards the core along with the ICID values from Initial INVITE.
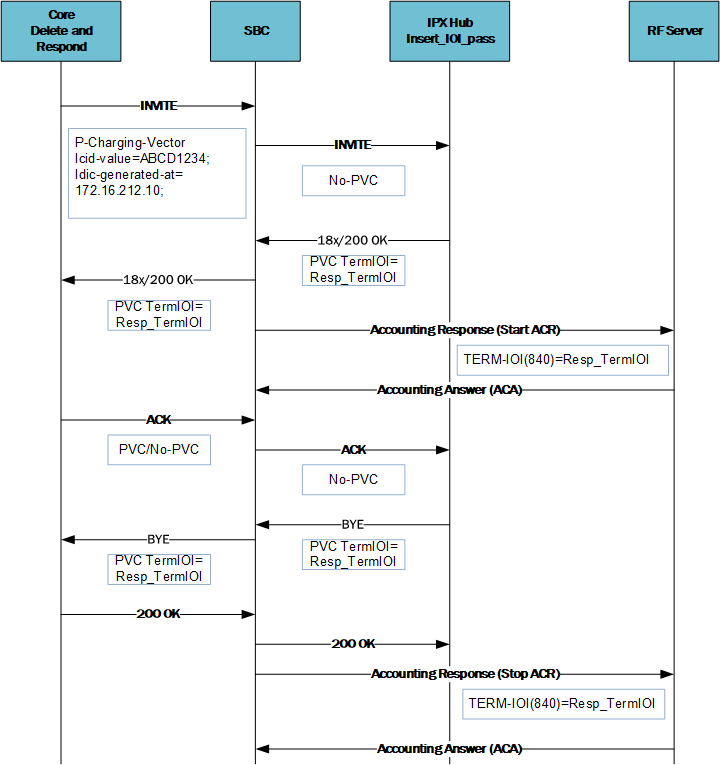
Processing for this call includes:
- The SBC does not include a PCV in the egress INVITE.
- The SBC inserts the stored PCV (icid-values) from Delete and Respond charging-vector-mode in the egress response.
- The SBC inserts the stored term-IOI from the ingress response (18x/2xx) in the egress response.
- The SBC includes only the Terminating-IOI from the 18x/2xx Term IOI values in the ACR towards the Rf server.
SNMP Trap Behavior
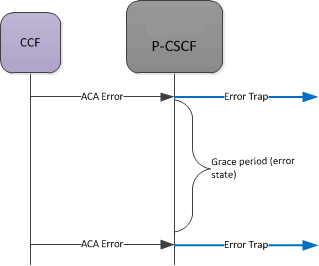
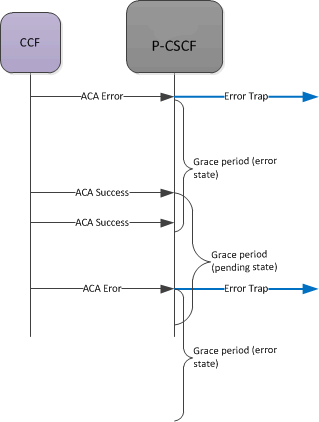
The SBC sends an SNMP trap (apDiameterSrvrErrorResult) upon a CCF returning an error-containing ACA. See the list of four errors (3002, 3004, 4002. 5012) which generate traps in the Alarms section. The frequency at which subsequent traps are sent is based upon configuring the diam result code trap grade period option configured in the account config.
When the SBC has sent a trap after receiving a bad ACA, it goes into an error state. The SBC waits one grace period before checking if it is still in an error state. If the state has not switched from errored back to pending, the SBC sends another error trap, after that first grace period ends (counting from the initial error) and then after the next error message is received.
If the CCF returns a successful message, the grace start in a pending state. When this second timer expires (pending no more errors or additional successes), on the next successful ACA, a success trap is sent.
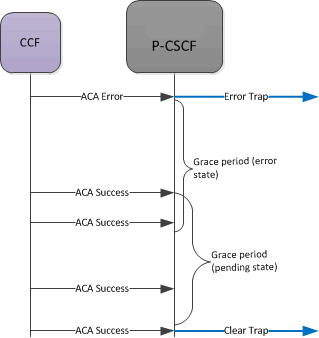
If, while in the pending grace period an ACA error is received, the SBC immediately sends an error trap, and begins the error state again. It also starts counting the initial grace period time again.
Alarms
A MINOR non health affecting Diameter Accounting Server Error alarm will be generated when one of the following Result Codes is received:
- 3002 (DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_DELIVER)
- 3004 (DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY)
- 4002 (DIAMETER_OUT_OF_SPACE)
- 5012 (DIAMETER_UNABLE_TO_COMPLY)
The alarm is cleared when a success (2XXX) code is received.
The rules for setting state of the failed server alarm are the same as the grace period rules described in the SNMP Trap Behavior section.
For example:
327703 835778540 5 2012-03-13 13:03:34 2012-03-13 13:03:34
Count Description
1 Diameter Accounting Server Returned Error Result Code|172.30.0.135:3869-5012|172.30.69.211:3868-3002SNMP MIBs and Traps
ApDiamResultCode Textual Convention
ApDiamResultCode ::= TEXTUAL-CONVENTION
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"The Result-Code AVP (268) value
RFC 3588, 7.1. Result-Code AVP"
SYNTAX INTEGER {
diameterMultiRoundAuth(1001),
diameterSuccess(2001),
diameterLimitedSuccess(2002),
diameterCommandUnsupported(3001),
diameterUnableToDeliver(3002),
diameterRealmNotServed(3003),
diameterTooBusy(3004),
diameterLoopDetected(3005),
diameterRedirectIndicatoion(3006),
diameterApplicationUnsupported(3007),
diameterInvalidHdrBits(3008),
diameterInvalidAvpBits(3009),
diameterUnknownPeer(3010),
diameterAuthenticationRejected(4001),
diameterOutOfSpace(4002),
electionLost(4003),
diameterAvpUnsupported(5001),
diameterUnknownSessionId(5002),
diameterAuthoriszationRejected(5003),
diameterInvalidAvpValue(5004),
diameterMissingAvp(5005),
diameterResourcesExceeded(5006),
diameterContradictingAvps(5007),
diameterAvpNotAllowed(5008),
diameterAvpTooManyTimes(5009),
diameterNoCommonApplication(5010),
diameterUnsupportedVersion(5011),
diameterUnableToComply(5012),
diameterInvalidBitInHeader(5013),
diameterInvalidAvpLength(5014),
diameterInvalidMessageLength(5015),
diameterInvalidAvpBitCombo(5016),
diameterNoCommonSecurity(5017)
}apDiameterSrvrErrorResultTrap
apDiameterSrvrErrorResultTrap NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { apDiamAcctSrvrHostName,
apDiamAcctSrvrIPPort,
apDiamAcctSrvrOriginRealm,
apDiamAcctSrvrOriginHost,
apDiamAcctSrvrTransportType,
apDiameterResultCode
}
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
" The trap can be generated when the Diameter Server
returns 3xxx (Protocol Errors), 4xxx (Transient Failures), or
5xxx (Permanent Failure) Result-Code AVP (268)"
::= { apDiamNotifications 5 }apDiameterSrvrSuccessResultTrap
apDiameterSrvrSuccessResultTrap NOTIFICATION-TYPE
OBJECTS { apDiamAcctSrvrHostName,
apDiamAcctSrvrIPPort,
apDiamAcctSrvrOriginRealm,
apDiamAcctSrvrOriginHost,
apDiamAcctSrvrTransportType,
apDiameterResultCode
}
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
" The trap can be generated when the Diameter Server
returns a 2xxx (Success) Result-Code AVP (268)
after an error result"
::= { apDiamNotifications 6 }apDiamACCTResultObjectsGroup Object Group
apDiamACCTResultObjectsGroup OBJECT-GROUP
OBJECTS {
apDiameterResultCode
}
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A collection of mib objects accessible only to traps."
::= { apDiamNotificationGroups 3 }apDiamACCTResultNotificationsGroup Notification Group
apDiamACCTResultNotificationsGroup NOTIFICATION-GROUP
NOTIFICATIONS {
apDiameterSrvrErrorResultTrap,
apDiameterSrvrSuccessResultTrap
}
STATUS current
DESCRIPTION
"A collection of traps defined for ACCT Result Code."
::= { apDiamNotificationGroups 4 }SNMP Varbind Definitions
- apDiamAcctSrvrHostName—contains the account-server hostname.
- apDiamAcctSrvrIPPort—This object contains the account-server IP address and port number in the following format:
XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX:PORT
- apDiamAcctSrvrOriginRealm—contains the origin realm, which is a concatenation of the account-server realm and suffix in the following format:
[ account-server realm][ account-server suffix]
- apDiamAcctSrvrOriginHostName—contains the origin host name, which is a concatenation of the accounting-config host name, account-server realm and account-server suffix in the following format:
[accounting-config host name].[ account-server realm][ account-server suffix]
- apDiamAcctSrvrTransportType—contains the transport type.
- apDiameterResultCode—contains the Result-Code AVP (268) value as defined in RFC 3588, 7.1. Result-Code AVP