1 Introduction to Enhanced Application Identification & Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library
Enhanced Application Identification allows the service to recognize an application based on domain name or sub-domain name, and allows users to steer application traffic to a defined service. Enhanced Application Identification leverages the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library of pre-defined categories and applications to simplify configuration while also supporting custom user-defined categories and applications. The Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library contains more than 100 pre-defined applications. Oracle will provide updates to the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library based on customer feedback. New signature libraries can be upgraded independently of software packages via the Oracle SD-WAN Edge configuration editor process.
Enhanced Application Identification is configured globally for ease of use. The user may define application policies to steer applications to the local Internet service or to hair-pin them back to the data center or NCN site. Application policies may be applied to Oracle SD-WAN Edge, to a single site, or to a subset of sites within Edge. When applications are steered to a Conduit service (as when hair-pinning to the data center or Edge), traditional QOS services are applied and users may map the application to a predefined classification or select their own classification from a pre-defined list.
Additionally, the appliance now provides an application dashboard view which allows the user to view top live and cumulative applications, bandwidth usage by service, application health information. These features are described in more detail in this document.
Capabilities
Oracle SD-WAN Edge's Enhanced Application Identification provides the capability to identify an application and match multiple configuration components to a policy. Some of these configurable components are pre-defined and some are user definable. These are included below with a brief definition, and described in more detail below:
Table 1-1 Idenfication Methods
| Component | Description | Used For | User Defined / Customizable | Pre-Defined | Optional Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Category | Group of Applications | Application Dashboard: Top Applications | YES | YES | YES |
| Application (Defined by User) | User-defined specific application (comprised by domain name, 5 tuple). Can be enabled or disabled at any time. | Application Dashboard | YES | NO | YES |
| Application (Defined by Oracle) | Applications part of the Application Signature Library (comprised of subdomains, 5 tuple. By default, this is disabled.) | Application Dashboard | YES | YES | YES |
| DNS Snooping | Enabling any application enables DNS snooping throughout SD-WAN Edge. (Default is disabled.) | Display of Applications with Domain Name Match | YES | YES | YES |
| Probing Intervals | Application probing frequency for an application can be enabled or disabled, and configured. Probing is only performed when an application includes one or more domain names as match criteria. | Application Health | YES | YES | YES |
| Response Times | Normal and Warning level application response times can be configured. (Default to 100 for Normal and 200 for Warning.) | Application Health | YES | YES | YES |
| Site Response Time Bias | Adjust the Normal and Warning level application response times on a per-site basis. (Default is 0.) | Application Health | YES | NO | YES |
Application Categories
Application Categories are used to group applications for the purpose of more easily defining policies that apply to multiple applications. Application Categories can be created by users, or users can leverage the Application Categories contained in the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library, or a combination of both. The Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library provides multiple pre-defined Application Categories, including Business, Music, News, Voice, and more. Users may add or remove Application Categories as desired. Application Categories may be used as one of the match criteria for Application Policies. Usage reporting is available for Application Categories via the Application Dashboard. (For more details, see the Application Dashboard Section.)
User Defined Applications
In addition to the applications included in the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library, users may define applications to match on protocol, port, network IP address or domain name, and DSCP tag or a combination of these items. Traffic will be evaluated against userdefined applications before being evaluated against the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Defined Applications that originate from the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature Library. Applications may be used as one of the match criteria for Application Policies. Usage reporting is available for applications via the Application Dashboard. (For more details see the Application Dashboard Section)
Oracle Defined Applications
Note:
Oracle Defined Applications imported from the Oracle SD-WAN Edge Application Signature library are disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled in the Configuration Editor. DNS snooping will only occur after an application has been enabled.Application Policies
Note:
Once the user defines an application policy or makes any changes to an application policy, the configuration must be saved and then applied to Oracle SD-WAN Edge to implement the policy. The user would use the Change Management process to activate the updated configuration file containing the new/edited application policies.Site Groups
Site Groups allow users to group multiple sites together for use with one or more Application Policies. There are three default site groups available for user convenience including: All Sites, ControllerSites, and NonControllerSites. Users may define additional site groups as desired for use in any Application Policies.
Network Objects
Network objects allow users to specify an IP address and subnet mask list for an application policy. Network Objects are user-defined.
Application Match Functionality
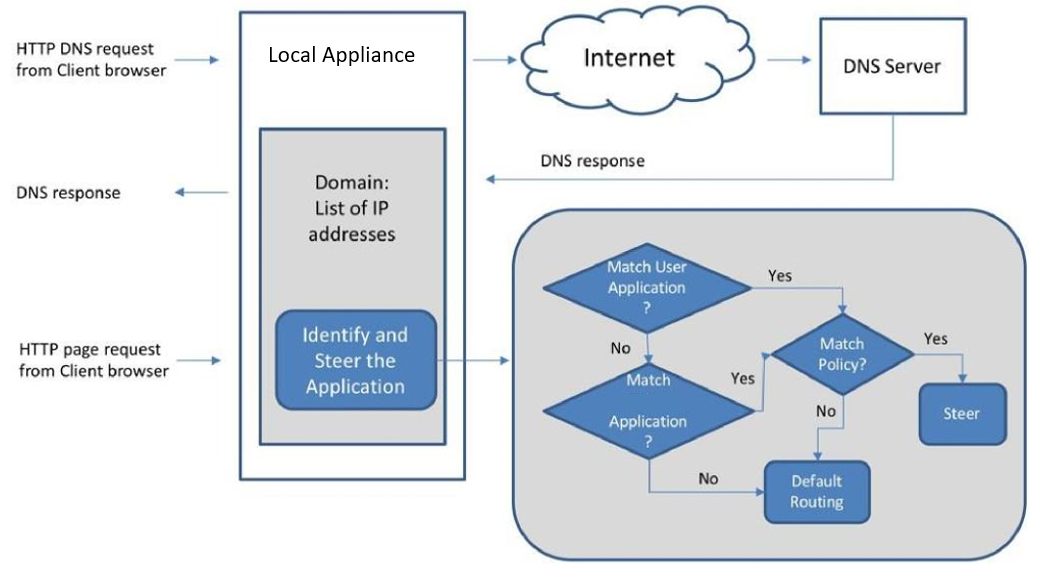
Oracle has supported application identification in the past by leveraging a 5-tuple match where the user would configure IP address or ports based on the application flow. In addition, Oracle has also supported the concept of DNS proxy which allowed the system to learn DNS resolution information from DNS replies.
Note:
Since the appliance must be able to read DNS information in order to identify applications, Application Identification is not supported in conjunction with Encrypted DNS.Note:
Application Identification only matches the first connection when multiple DNS A records resolve to the same IP address. Subsequent connections using the same IP address will be attributed to the original application match, and will block the addition of that IP address as a match for other applications. For example, if Application A uses the domain name “domain1.com” as one of its match criteria and Application B uses the domain name “domain2.com” as one of its match criteria, if the DNS resolution for both domains is “1.2.3.4” then all connections using that address will be assigned to the first application the record is matched against.Application Policy Processing
The priority for matching on a defined policy is as follows:
- User-defined application policies
- Oracle SD-WAN Edge-defined applications
All policies are listed in priority order, with lower-numbered policies processed first. Once a session matches an application policy, additional policies will not be evaluated for that session. The user defined applications take priority over the Oracle defined applications when matching an application policy. If the session does not match an application policy, the session will default to the routing table. If the application policy is steered to a service that is down, the routing table is used to forward the flow to the appropriate destination service. Currently, users cannot configure a failover policy as the routing table is used if the service associated with an application policy is down. If the user steers an application to a service, the service must exist at the destination site. For example, if the application policy is steering to the local Internet service of a site, the Internet service must exist at that site when defining the application policy. If the service does not exist at a site, the decision to forward the packets/flow is based on the appliance routing table.
Application Health
Note:
Health information for applications is only available when probing is enabled. Probing is only performed on applications which include a domain name in the match criteria.When probing is enabled and the application domain name is resolved by DNS snooping, a TCP request will be sent to the IP(s) associated with the application and the RTT time will be calculated based on the response (details below). For applications with more than one associated IP address, the top 5 addresses used will be probed and an average RTT calculated from the results. The TCP SYN contains the timestamp in the Options field and the expectation is that the Server will respond with a Timestamp. If the server does not respond with a timestamp the RTT is not calculated at this time. These probes will also show up in the flow table – source IP address will be an Oracle VIP address with the destination IP being that of the application domain. These will be TCP based using a source port of 2156 and a destination port of 443. The RTT is compared to the timer thresholds specified in the configuration (default or user-defined) to determine application health. Applications which are at or below the normal response time will be classified as Normal. Applications which are at or below warning response time but above the normal response time will be classified as Warning. Applications which are above the warning threshold will be classified as Critical. The user has the ability to change these values per application.
Since different sites may have different acceptable thresholds, an additional timer delay (the site bias normal / warning timer) is configurable on a per-site basis. This value is added to the value defined within each application.