3 Implementing MSS Security
This chapter explains the security features of Oracle Communications MetaSolv Solution (MSS).
Securing the Application
MSS application security consists of two processes: authentication and authorization. Authentication is the process of identifying a user with a user ID and password combination. See MSS Installation Guide for authentication details. This chapter provides details about authorization, the process of granting or denying access to application functions.
Planning Application Authorization
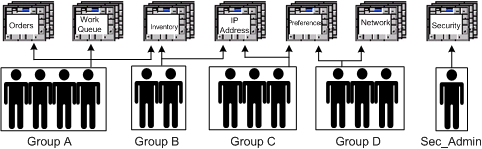
MSS security provides controlled, group-based access to specified parts of the MSS application and data. Users can be associated with groups, and users and groups can be restricted from specific areas of the software.
Figure 3-1 shows an example of group-based security.
Security is active when the application is installed. It cannot be deactivated. Only one user, the security administrator, has authorization to sign on. Only three groups are active at installation: DEFAULT, READ-ONLY, and SEC_ADMIN (security).
Note:
The group name READ-ONLY can be modified, if you already have READ-ONLY security group in MSS. See Knowledge Article 2472324.1 - New READ-ONLY Security Group Feature Available in Patch 27753924: MSS_6_3_0_B772 on the My Oracle Support website:https://support.oracle.com/epmos/faces/DocumentDisplay?id=2472324.1.
Every layer of the architecture has predefined superusers. A superuser has full control of all functions of the architecture layer. For MSS, the superuser is ASAP, the only user with security permissions (the only initial member of SEC_ADMIN).
Learning How the Application Works
Before planning the security model and creating users and groups, learn how MSS works at a high level so that you understand the main functions of the product. Next, meet with representatives from each department to define areas of the product they will be using. You will assign access to the users and groups you create based on this information.
Pre-Implementation Checklist
Gather the following information before beginning to set up security for MSS:
-
Person/group responsible for setting up new user IDs, maintaining general security features/permissions
-
Network user ID naming conventions
-
Company-wide standard on password change intervals
-
Policy for establishing temporary user IDs
-
Any existing group structure in legacy systems that might be leveraged for this implementation
Designing the Security Model
A security plan must be implemented after the product is installed and before it can be used. This section describes how to make decisions about the security model and provides tools for planning the security implementation.
Designing the security model for MSS involves:
-
Identifying the most logical groups of users
-
Creating matrixes for listing relevant users, groups, and processes
-
Completing the security planning matrixes
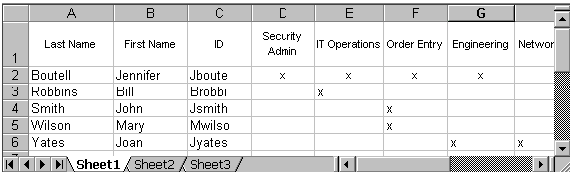
Use planning matrixes like the one shown in Figure 3-2. These matrixes give you a view of groups and permissions. Patterns become obvious and adjustments can be made before implementation.
Identifying MSS Users
When planning security, begin by listing all MSS users in the left-most column of an Employee/Group matrix. Include those users who may never enter data and only need to find information. The user name should match the Oracle user ID.
Understanding Groups and Permissions
When the users are added, they are automatically members of the group that is set in the system preference Default Security Group in the Security folder. The preference defaults to the DEFAULT security group and their security permissions are Not Set. This permission allows all users to access to all objects except security. Therefore, it is important to assign users to groups with restrictions and permissions. You can change the default value of the preference to other security groups. You can set the preference to READ-ONLY security group to limit all the newly added users to have read-only access throughout the application, by default.
Organizing users into groups eases security maintenance by reducing the number of permissions for individual users. For example, you might set up a Provisioner group, an Ordering group, and a Marketing group. If every user fits into one of those three groups, you need to set and maintain permissions for only three groups instead of for many individuals.
You can assign the MSS users to one or more groups. The groups are given permissions to access different aspects of the product.
When a user belongs to a group, the user receives all the permissions of the group. If a user belongs to multiple groups, the least restrictive group permissions apply. A permission that is directly granted to a user overrides any group permission levels. Therefore, some users can have more or less restrictive permissions than other users in the same group if they are also restricted as individuals.
Oracle recommends always using groups to set permissions, even if it means a group might have only one member for a period of time. If your groups are well planned, other users will also be added. To routinely set permissions without using groups would require extensive setup time for implementation and ongoing maintenance for each individual. If you do not use groups, setting individual security may also require scanning too many windows and controls into the database. If you must scan objects into the database for each user, the number of records increases, increasing the possibility of negative performance impacts. This will be explained in more detail later in this chapter.
Identifying Logical Groups of Users
A quick way to designate groups within MSS is to identify the departments that use the product, and use those departments as the highest-level group names. If your departments are large or have diverse responsibilities, you can identify subsets of those departments as groups.
Another way to designate groups is:
-
Identify processes
-
Group processes into like functions
-
Map users to those groups
After determining the basic groups at your company, list them across the top of the Employee/Group matrix you used to list all user names.
Associating Users with Groups
With each user listed down the left side and each group listed across the top, fill in the matrix, associating each user with at least one group, as shown in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Security Matrix, Users and Groups
Description of "Figure 3-2 Security Matrix, Users and Groups"
Implementing Application Security
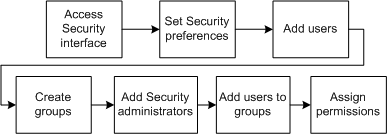
When planning is complete, the initial process for establishing security is straightforward and sequential, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 First Security Implementation Process
Description of "Figure 3-3 First Security Implementation Process"
Before you begin implementing security in MSS, be sure you have completed the following tasks:
-
Make sure there are no user restrictions on the servers where MSS resides.
-
Make sure the MSS server names are in the gateway.ini file using gateway parameters. See the discussion about gateway parameters in MSS System Administrator's Guide for more information.
-
Assign users read-only access to the network folders containing the application files.
To access MSS security:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
Click Administration on the navigation bar.
You can now add users, assign MSS permissions, and maintain groups. The rest of this chapter and the online Help provide details about procedures and descriptions of window and fields.
Adding New Users and Groups
All users are initially members of the security group that is set in the system preference Default Security Group and can remain in that group even when assigned to other groups.
Both users and groups can be members of groups. A user or a group can be unassigned from any group with which it is associated. Make sure that the unassigned user or group does not need the permissions being removed when it is disassociated from the parent group.
To add users or groups:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
On the navigation bar, select Administration, and then click Security Users and Groups.
The Security Users and Groups window is displayed.
-
In the right pane, do one of the following:
-
Right-click and select New, and then select User or Group.
The Add User or Add Group window is displayed, which enables you to add a new user or a group.
-
Double-click the Users or Groups folder, right-click a user or a group, and then select New From.
The New / From User or New / From Group window is displayed, which enables you to add a new user or a group from an existing user or group.
-
-
Enter the required information in the fields.
-
Click OK.
Note:
See "Adding New Users That Use a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution" for adding new users that use a non-Oracle authentication solution.
Adding New Users That Use a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution
This section provides instructions for adding new users that use a non-Oracle authentication solution.
Adding Users Using the New Option for a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution
To add users using the New option for a non-Oracle authentication solution:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
On the navigation bar, select Administration, and then click Security Users and Groups.
The Security Users and Groups window is displayed.
-
In the right pane, right-click and select New, and then select User.
The Add User window is displayed.
-
(Optional) Select the Create Database User For Access To MSS Utilities check box.
You must select this check box only if you need access to MSS utilities. If you opt to not select this check box, you will be able to access only the MSS application and not the MSS Utilities.
Note:
The Password Expires On, Password, and Confirm fields become active in the Add User window only after you select the Create Database User For Access To MSS Utilities check box.
-
Enter the required information in the User ID, Description, Password Expires On, Password, and Confirm fields.
-
Click OK.
The application creates the new user in both SECURITY_USERS table and Oracle database, thus enabling the user to access both the MSS application and MSS Utilities.
Adding Users Using the New From Option for a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution
To add users using the New From option for a non-Oracle authentication solution:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
On the navigation bar, select Administration, and then click Security Users and Groups.
The Security Users and Groups window is displayed.
-
In the left pane, select Users.
-
In the right pane, right-click a user and then select New From.
The New / From User window is displayed.
Note:
When creating users using the New From option for a non-Oracle authentication solution, the Password and Confirm Password fields are not displayed in the New / From User window.
-
Enter the required information in the New User Id and New User Description fields.
-
Click OK.
The application creates the new user only in the SECURITY_USERS table and does not create the new user in the Oracle database, and therefore the newly created user can access only the MSS application and cannot access MSS Utilities.
To enable the user created using the New From option to also access MSS Utilities for a non-Oracle authentication solution, see "Enabling Users Created Using the New From Option to Access MSS Utilities for a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution".
Enabling Users Created Using the New From Option to Access MSS Utilities for a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution
To enable the user created using the New From option to also access MSS Utilities for a non-Oracle authentication solution:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
On the navigation bar, select Administration, and then click Security Users and Groups.
The Security Users and Groups window is displayed.
-
In the left pane, select Users.
-
In the right pane, right-click the user and select Edit.
The Edit User window is displayed.
-
Select the Create Database User For Access To MSS Utilities check box.
-
Enter the required information in the Password Expires On, Password, and Confirm Password fields.
The User ID field is non-editable because the MSS application already created the new user in the SECURITY_USERS table when you performed the tasks mentioned in "Adding Users Using the New From Option for a Non-Oracle Authentication Solution".
-
Click OK.
The new user is created in the Oracle database and this user can now access MSS Utilities.
Note:
If the user already exists in the Oracle database, the Create Database User For Access To MSS Utilities check box is not displayed in the Edit User window. In this situation, the Password button becomes active in the Edit User window. Clicking the Password button displays the Password Administration window, which enables you to modify the password for the existing user.
Authorizing System Administrators
Table 3-1 lists the administrator privileges and provides information on how to assign each privilege to authorize users.
Table 3-1 How to Assign Administrator Privileges
| Authorization | How to Authorize |
|---|---|
|
DBA identification |
Scripts are run during installation that provide the ASAP user with DBA authority. Use the ASAP user ID to perform MSS DBA tasks. |
|
Security administrator |
Add the user's ID to the Sec_Admin group or to another group that has some or all security permissions. See "Creating Additional Security Administrators". |
|
Access to configuration files |
Master configuration files reside on the Oracle WebLogic server. These files can be edited by any user unless password-protected by the IT department. When distributed to client computers, configuration changes can be made. |
|
Customize default desktop |
Log on with the ID specified in the DefaultPortalId parameter of gateway.ini file. |
|
Customize the navigation bar (Navbar) |
The user identified in the User parameter of the gateway.ini in the JNDI section can set the Allow Users to Customize My Desktop preference in MSS. This default determines whether users can customize the desktop Navbar, according to the instructions in the Help. |
|
Set system and global preferences |
A user can be assigned permission within application security to set these preferences that affect user setup in the MSS database. Instructions are in the online Help. |
|
Manage Oracle WebLogic Server |
See the Oracle WebLogic Server documentation for information on authorizing administrators. |
Validating API Logons
Some MSS API servers, such as PSR, LSR, and Work Management, have security features that are enabled by default.
The security validation for CORBA APIs works only if you are sending a ConnectReq CORBA object to the WDIRootImpl object. This does not apply to all APIs, because some, such as the LSR API, do their own transaction management.
Refer to the CORBA API Developer's Reference for details about coding the APIs. See the discussion about OrbProperties parameter in MSS System Administrator's Guide for information about setting up API logon validation.
Adding Registered Users to MSSRole for Accessing EJB Methods Externally
The MSS application implements security for EJB methods. You must add a registered user to the Global Role MSSRole to access the EJB methods externally.
To add a registered user to MSSRole:
-
Log on to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console by entering the following URL in your browser:
http://host:port/console
where:
-
host is the name of the administration server computer.
-
port is the administration server port number.
-
-
Create a user with the registered user name. See the WebLogic Server documentation for detailed information on creating users.
-
Add the registered user name to MSSRole. See the WebLogic Server documentation for detailed information on adding users to roles.
Adding Registered Users to Access External JMS Queues
The MSS application implements security for external JMS queues. You must add a registered user to the Integration Administrators group to access the external JMS queues.
To add a registered user to the Integration Administrators group:
-
Log in to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console by entering the following URL in your browser:
http://host:port/console
where:
-
host is the name of the administration server computer.
-
port is the administration server port number.
-
-
Create a user with the registered user name. See the WebLogic Server documentation for detailed information on creating users.
-
Add the registered user name to the Integration Administrators group. See the WebLogic Server documentation for detailed information on adding users to groups.
Adding APPJMSUser User for JMS Messaging Through Gateway Events
The following entries govern the processing of the gateway events messaging in the gateway.ini file:
APPJMSUser=app_jms APPJMSPwd=
MetaSolv Solution uses the WebLogic user mentioned in the APPJMSUser field to do the following:
-
Establish a connection with the application server for processing the gateway events messaging
-
Put the message in the mss.external.event.queue. The mss.external.event.queue is a secured JMS queue and only a valid user who belongs to the Integration Administrators group can access it.
You can create or change the encrypted password for the APPJMSUser user by using the Encrypt Passwords Security option in MetaSolv Solution Utilities.
After you create a new AES encrypted password for the APPJMSUser user, you must copy the encrypted password in the gateway.ini file. See the discussion about copying encrypted passwords to the gateway.ini file in the MSS System Administrator's Guide.
During MSS installation, the APP_JMS user is created by default and updated in the gateway.ini. If required, you can change the APPJMSUser and APPJMSPwd parameters in the gateway.ini file.
Accessing MSS Web Services Using a WebLogic User
The MSS Web Service operations are secured using WS-Security. You must be a registered WebLogic user to access the web service operations externally.
To create a valid WebLogic user:
-
Log on to the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console by entering the following URL in your browser:
http://host:port/console
where:
-
host is the name of the administration server computer.
-
port is the administration server port number.
-
-
Create a user with the registered user name. See the WebLogic Server documentation for detailed information on creating users.
Refer to the MSS Web Services Developer's Guide for more information on securing web services.
Tracking Logons
The appserver audit log file appserver_auditlog.xml (for 6.3.1.452 or earlier) or appserver_audit.log (for 6.3.1.558 or later) can tell you when users log on and off and when there are failed attempts. This capability can be used to identify unauthorized access attempts. See the discussion about managing MSS log files in MSS System Administrator's Guide for information about loggingconfig.xml parameters.
The following example shows the different types of audit messages recorded in this log file for logon/logout actions from a fictitious user ID named SCHINTAL.
-
Authentication failure
Message:
Login attempt failed for SCHINTAL. Exception: ORA-01017: invalid username/password; logon denied
Cause: Invalid user name or incorrect password.
Action: Please supply a correct username and password combination.
-
Authenticated (successful)
Message:
Login detected for SCHINTAL.
Cause: User has signed on.
Action: None.
-
User has signed off
Message:
Logout detected for SCHINTAL.
Cause: Logout by user or Client disconnected.
Action: None.
Managing Application Passwords
The security administrator manages the following application password tasks:
-
Setting the password preference
-
Specifying password expiration dates
-
Resetting passwords
-
With Oracle authentication, creating a new Oracle user ID for APIs to use when accessing the database
Setting the Password Preference
To set the password preference:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
Click Administration.
-
Click Preferences.
-
Double-click the Security folder.
-
Double-click the Change password upon initial logon preference.
-
(Optional) To require a password change at the first logon, select Change password upon initial logon.
Specifying a Password Expiration Date
To specify a password expiration date when adding a user:
-
Log in to MSS
-
Click Administration.
-
Click Security Users and Groups.
-
Do one of the following:
-
To add a user and accept the 90-day default password expiration date, retain the defaults.
-
Change the default password expiration date based on your business practices.
-
At any time after a user has been added, you can set a specific password expiration date or specify that the password does not expire.
Maintaining User Passwords
To assign or change a password expiration date for an existing user:
-
Click Administration.
-
Click Security Users and Groups.
-
Double-click the user whose password expiration date you want to specify.
The Edit User window is displayed.
-
Click the Password Expires On field, which displays the current calendar.
-
Do one of the following:
-
Select a date.
-
Clear the field to indicate no expiration date.
-
-
Click OK.
Creating Additional Security Administrators
To create additional administrators:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
Click Administration.
-
Click Security Users and Groups.
-
Add the user to the Sec_Admin group or create a new sub-group for Sec_Admin.
You can create sub-groups with subsets of permissions, such as:
-
Access to the Security Permissions window
-
Access to Security reports
-
Access to the Users and Groups window
-
Access to work management task editing
-
Access to the security system preference
-
Users to change global preferences
-
Assigning MSS Permissions
Permissions are controlled through the MSS UI. Permissions control what users and groups can access in the application. Permissions (inclusive or restrictive) are assigned as a means of controlling feature access and on-screen displays. Features and windows can be disabled and fields can be made invisible.
To access permissions:
-
Log in to MSS.
-
Click Administration.
-
Click Security Permissions.
The Security Permissions window appears.
-
In the left-most pane, expand the menu tree to display a list of MSS windows.
The right-most pane displays a list of permissions for the user or group displayed in the User/Group list.
-
Follow directions in the online Help to assign permissions.
Understanding Permissions
Permissions determine what a user can do and which items can be seen within the application. Permissions can be assigned to a group or to a specific user.
The rules for determining access include the following:
-
When a user is assigned to multiple groups, the least restrictive group permissions apply.
-
Not Set allows access to objects as a default.
When an individual user is assigned a permission, it overrides group permissions.
Different objects are associated with different types of permissions. The next sections describe the permissions for each type of object.
Window Permissions
There are four levels of permissions that you can assign to a window:
-
Read Only: Users can see and access the window but cannot make changes.
-
Enabled: Users have explicit permission to use the window and make changes.
-
No Access: Users cannot see or use the window.
-
Not Set: Users can access the window. It is similar to Enabled, but it does not override other permissions when the system determines the least restrictive permissions for a user.
Control Permissions
Objects such as lists, tree view buttons, tabs, columns, check boxes, and fields are known as controls. Control names are not preloaded into the MSS database.
If you want to secure a control and the name does not appear in Security, it does not exist in the MSS database. To add the control to the database, refer to "Scanning Windows and Controls Into the Database".
Controls are associated with the following permissions:
-
Enabled: Users have explicit permission to access the control and make changes.
-
Disabled: The control is non-functional.
-
Invisible: The control is grayed out.
-
Not Set: Users can access the control. It is similar to Enabled, but it does not override other permissions when the system determines the least restrictive permissions for a user.
Pop-Up Menu Permissions
You can secure an entire pop-up menu or a specific item on a pop-up menu. Pop-up menus are preloaded into Security and cannot be added or customized other than setting permissions.
Pop-up menus are associated with the following permissions:
-
Enabled: Users have explicit permission to use the pop-up menu and make changes.
-
Disabled: The pop-up menu is non-functional.
-
Invisible: The pop-up menu does not appear.
-
Not Set: Users can access the pop-up menu. It is similar to Enabled, but it does not override other permissions when the system determines the least restrictive permissions for a user.
Check Point Permissions
Check points secure certain logical functions in MSS that do not correspond to window objects. Because these functions can have far-reaching impacts, check points are preloaded into Security and cannot be added or customized. The Sec_Admin group can access all security check points.
The following processes are protected by check points:
-
MSAG Override settings
-
Cascade Reconcile
-
Mass DLR Reconcile
-
IP Addresses - External
-
Reset Supp Type
-
Order Management: w_row_in_use
-
PSR External Service Key
-
Security Permissions
-
Security Users and Groups
-
Users and Groups
-
Security Reports
-
Partition Groups
-
Assign Permissions
-
Preferences
-
Software Options
-
Password Policy
-
PBDatabaseTrace
-
Shared Views
-
Exception Queue Access
-
View All Work Queues
-
Edit Tasks
-
System Queue Access
-
Encrypt Passwords
Note:
At installation, only the security administrator can change a completion date on the Work Management Work Queue Manager window - Task Detail tab. The security administrator can assign that access to groups or users using the Edit Tasks check point.
Permissions that can be assigned to check points are:
-
Enabled: Users have explicit permission to pass the check point.
-
Not Set: Users can access the window. It is similar to Enabled, but it does not override other permissions when the system determines the least restrictive permissions for a user.
No user outside of the Sec_Admin group can pass a check point without the security administrator providing explicit permission to access the protected object or function and providing a special password for the pop-up that appears when trying to access the area. The Sec_Admin group can access all security check points.
Scanning Windows and Controls Into the Database
The list of windows in the Security Permissions window uses development window names and not the names that appear on the UI. The list contains all of the JSP windows in the application and many PowerBuilder windows. Not all PowerBuilder windows are listed. If a window you need is not listed, you can scan the controls on the window into the MSS database and then assign permissions to those controls.
To scan a window:
-
Open the window containing the controls you want to secure.
-
Press F2.
-
Make a note of the highlighted window name when the dialog box appears.
-
Assign permissions to the controls on that window using the Assign Permissions window.
Creating MSS Security Reports
Security reports provide information on the aspects of MSS system security, as listed in Table 3-2.
Table 3-2 Security Reports
| Report | Description |
|---|---|
|
Individual Detail |
Lists controls and statuses for the selected user or group. |
|
Hierarchy Detail |
Lists controls and statuses for the Ancestor Hierarchy of the selected user. |
|
Ancestor Hierarchy |
Shows the parent groups of the selected group/user, recursively. |
|
Descendant Hierarchy |
Shows the groups/users who are assigned to the selected group. |
|
User Exception |
Shows users who are not members of the Default group. |
See the online Help for detailed instructions on creating security reports.
Managing Utilities Security
A separate authorization is required to access security in the tbs_util.exe file, the MSS utilities. Leaving the utilities unsecured allows an authorized user to purge database records. See the online Help for instructions on using the MSS utilities security feature.
MSS utilities security permissions work exactly like MetaSolv Solution security. You can assign permissions to windows, controls, pop-up menus, and check points. Permissions are controlled through the MSS utilities UI. Permissions control what users and groups can access in the application. See "Assigning MSS Permissions" and Scanning Windows and Controls Into the Database for more details.
To access permissions in MSS utilities:
-
Log in to MSS utilities.
-
Click File.
-
Click Security and select Assign Permissions.
The Security Permissions window appears.
-
In the left-most pane, expand the menu tree to display a list of MSS utilities windows.
The right-most pane displays a list of permissions for the user or group displayed in the User/Group list.
-
Follow the directions in the online Help to assign permissions.
Managing File Permissions
On UNIX systems, the newly created files are given a permission of 640. Some files like executable files need additional permissions and they are individually assigned permissions.
Table 3-3 lists the custom permissions that the installer grants for specific file types.
Table 3-3 Custom Permissions
| Folder | Owner | Group | Other |
|---|---|---|---|
|
config |
read and write |
read and write |
- |
|
ior |
read and write |
read and write |
read and write |
|
gateway |
read and write |
read and write |
- |
|
logs |
read and write |
read |
- |
|
sample |
read, write, and execute |
read, write, and execute |
- |
|
others |
read, write, and execute |
- |
- |
Note:
On Windows systems, the system administrator must review the installation folders and restrict file permissions.
Changing Role Passwords
Only the database administrator can change passwords for the roles ADMIN_ROLE and WOTSTWTWWOO by running the following stored procedure:
===========pl/sql should be run by dba for changing role's password========== DECLARE C_NAME VARCHAR2(200); C_PASSWORD VARCHAR2(200); BEGIN C_NAME := 'role_name'; /*specify the role name, ADMIN_ROLE OR WOTSTWTWWOO*/ C_PASSWORD := 'password'; /*specify the password*/ SP_CREDSTORE_CHG_ROLE_PWD(C_NAME, C_PASSWORD); END;