A MO SMS B-Party Routing Configuration Procedures
Appendix B, MO SMS B-Party Routing Configuration Procedures, describes the procedures necessary to configure the EAGLE to perform global title translation on the MAP B-Party digits instead of the GTT called party address of the message.
A.1 Introduction
The MO SMS B-Party Routing feature allows global translation type (GTT) routing to be performed on IS41 MO SMDPP and GSM MO_FSM messages based on the SMS B-party digits from the MAP layer of the message.
If the B number is a short code, then a short message service (SMS) can be directed to a specific short message service center (SMSC) based on the short code dialed by the SMS sender. If the B number is the MSISDN/MDN of the SMS recipient, then the SMS can be directed to a specific SMSC based on subscriber groupings or types.
Provisioning the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature
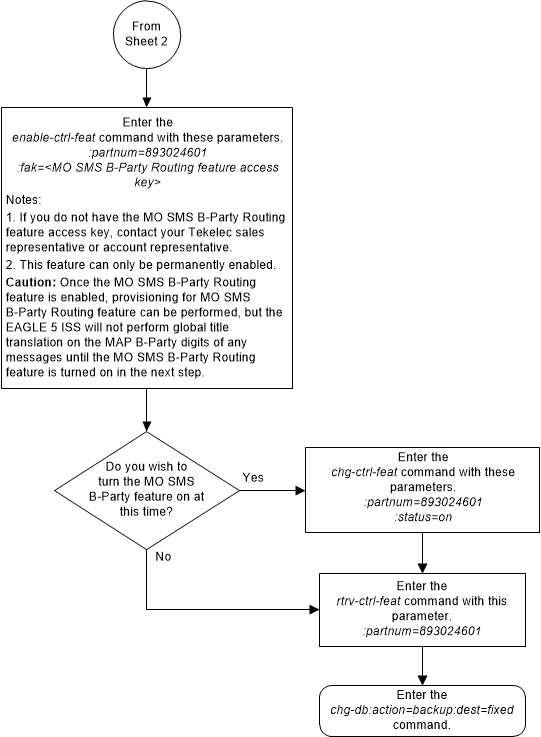
- Enable the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature using the
enable-ctrl-featcommand. Perform the procedure Activating the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature.Note:
The MO SMS B-Party Routing feature can be turned on in this step using thechg-ctrl-featcommand. If the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature is not turned on in this step, provisioning for the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature can still be performed. When the provisioning is completed, the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature can be turned on. The MO SMS B-Party Routing feature will not work until the feature is turned on. - Provision a GTT set that will be used by the MO SMS
B-Party Routing feature using the
ent-gttsetcommand. Perform the procedure Adding a GTT Set . - Assign the GTT set to the B-Party GTT set name
option. Perform one or both of these procedures.
- If global translation type (GTT) routing will be
performed on GSM MO_FSM messages, the GTT set name must be the value of the
bpartygttsnparameter of thechg-gsmsmsoptscommand. Perform the procedure Configuring the GSM MO SMS B-Party Routing Options. - If global translation type (GTT) routing will be
performed on IS41 MO SMDPP messages, the GTT set name must be the value of the
bpartygttsnparameter of thechg-is41smsoptscommand. Perform the procedure Configuring the IS-41 MO SMS B-Party Routing Options.
- If global translation type (GTT) routing will be
performed on GSM MO_FSM messages, the GTT set name must be the value of the
- Specify that global title translation needs to be
performed on the MAP B-Party digits of the message. Perform one or both of
these procedures.
- If global translation type (GTT) routing will be
performed on GSM MO_FSM messages, the value
mapbpartymust be specified for themosmsgttdigparameter of thechg-gsmsmsoptscommand. Perform the procedure Configuring the GSM MO SMS B-Party Routing Options. - If global translation type (GTT) routing will be
performed on IS41 MO SMDPP messages, the value
mapbpartymust be specified for themosmsgttdigparameter of thechg-is41smsoptscommand. Perform the procedure Configuring the IS-41 MO SMS B-Party Routing Options.
- If global translation type (GTT) routing will be
performed on GSM MO_FSM messages, the value
- Provision the service selectors for the MO SMS
B-Party Routing feature using the
ent-srvselcommand. Perform the procedure Adding a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature. - If the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature was not turned
on in step 1, turn the feature on using the
chg-ctrl-featcommand. Perform the procedure Activating the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature.
A.2 Activating the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature
This procedure is used to enable and turn on the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature using the feature’s part number.
The
enable-ctrl-feat command enables the
MO SMS B-Party Routing feature by inputting the feature’s access key and the
feature’s part number with these parameters:
:fak – The feature
access key provided. The feature access key contains 13 alphanumeric characters
and is not case sensitive.
:partnum – The issued
part number of the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature, 893024601.
The
enable-ctrl-feat command requires that
the database contain a valid serial number for the EAGLE, and that this serial
number is locked. This can be verified with the
rtrv-serial-num command. The EAGLE is
shipped with a serial number in the database, but the serial number is not
locked. The serial number can be changed, if necessary, and locked once the
EAGLE is on-site, with the
ent-serial-num command. The
ent-serial-num command uses these
parameters.
:serial – The serial
number assigned to the EAGLE. The serial number is not case sensitive.
:lock – Specifies
whether or not the serial number is locked. This parameter has only one value,
yes, which locks the serial number.
Once the serial number is locked, it cannot be changed.
Note:
To enter and lock the EAGLE’s serial number, theent-serial-num command must be entered
twice, once to add the correct serial number to the database with the
serial parameter, then again with the
serial and the
lock=yes parameters to lock the serial
number. You should verify that the serial number in the database is correct
before locking the serial number. The serial number can be found on a label
affixed to the control shelf (shelf 1100).
This feature cannot be temporarily enabled (with the temporary feature access key).
Once this feature is enabled, provisioning for this
feature can be performed, but the feature will not work until the feature is
turned on with the
chg-ctrl-feat command. The
chg-ctrl-feat command uses these
parameters:
:partnum – The issued
part number of the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature, 893024601.
:status=on – used to
turn the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature on.
Once the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature has been turned on, it be can be turned off. For more information on turning the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature off, refer to the procedure Turning the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature Off.
The status of the features in the EAGLE is shown with
the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command.
The MO SMS B-Party Routing feature requires that DSMs or
SLIC cards are installed and provisioned in the EAGLE. DSM cards are shown by
the entry
dsm in the
TYPE column and
vsccp in the
APPL column of the
rtrv-card output. SLIC cards are shown
as
type=dsm (in the odd numbered card
slots) or
type=slic (in the even numbered card
slots), and
appl=vsccp.
The MO SMS B-Party Routing feature also requires that
the Global Title Translation (GTT) and Enhanced Global Title Translation (EGTT)
features are turned on. The status of the Global Title Translation and Enhanced
Global Title Translation features are shown in the
rtrv-feat output.
Figure A-1 Activate the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature- Sheet 1 of 3
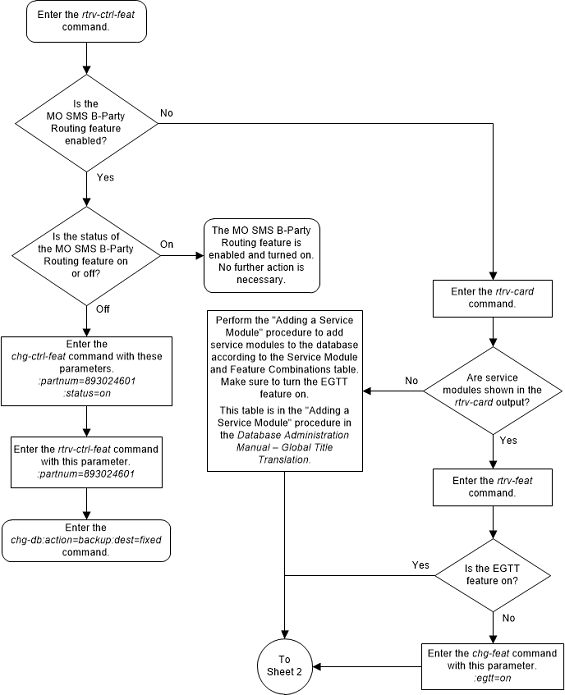
Figure A-2 Activate the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 2 of 3
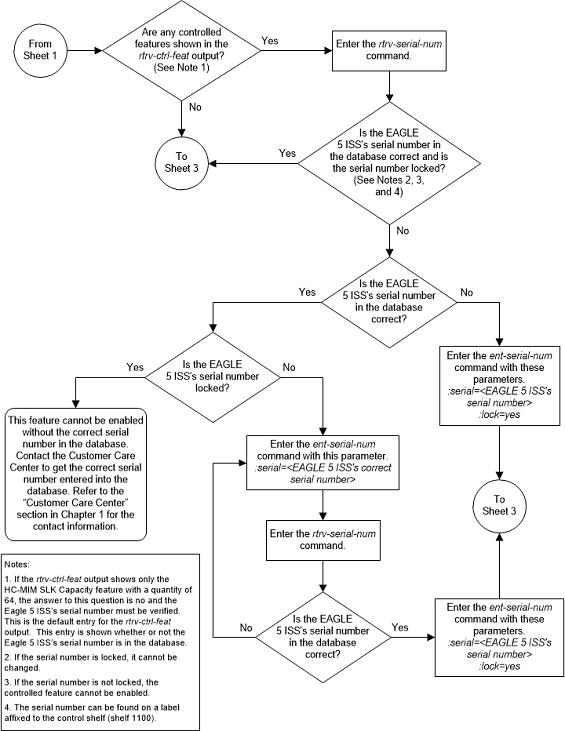
Figure A-3 Activate the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 3 of 3
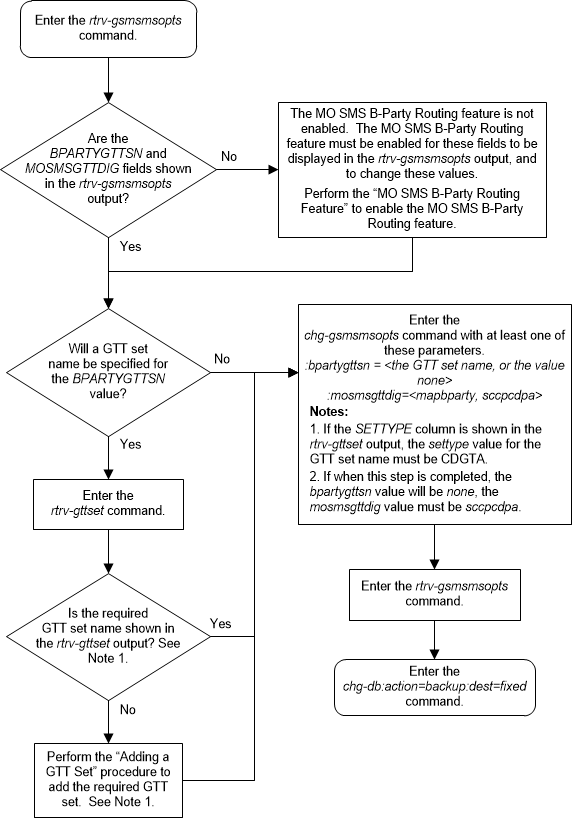
A.3 Configuring the GSM MO SMS B-Party Routing Options
This procedure is used to configure the MO SMS B-Party
routing options for GSM messages using the
chg-gsmsmsopts command with these
parameters:
:bpartygttsn – the name
of the GTT set, shown in the
rtrv-gttset output, global title
translation on the MAP B-Party digits of the GSM message will be performed on;
or the value
none indicating that global title
translation on the MAP B-Party digits of the GSM message will not be performed
on any GTT set.
:mosmsgttdig – the
digits that are used for global title translation.
sccpcdpa- the digits of the SCCP called party address portion of the message are used for global title translation.mapbparty- the MAP B-party number is used for global title translation.
The system default value for the
bpartygttsn parameter is
none. The system default value for the
mosmsgttdig parameter is
sccpcdpa.
This procedure can be performed only if the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature is enabled.
The set type of the GTT set name
that will be specified for the
bpartygttsn parameter must be
CDGTA. The set type of the GTT set is
shown in the
SETTYPE column of the
rtrv-gttset output. If the
SETTYPE column is not shown in the
rtrv-gttset output, all the GTT sets
are CDGTA GTT sets.
If the value of the
bpartygttsn parameter is
none when this procedure is completed,
the value of the
mosmsgttdig parameter must be
sccpcdpa.
Figure A-4 Configure the GSM MO SMS B-Party Routing Options
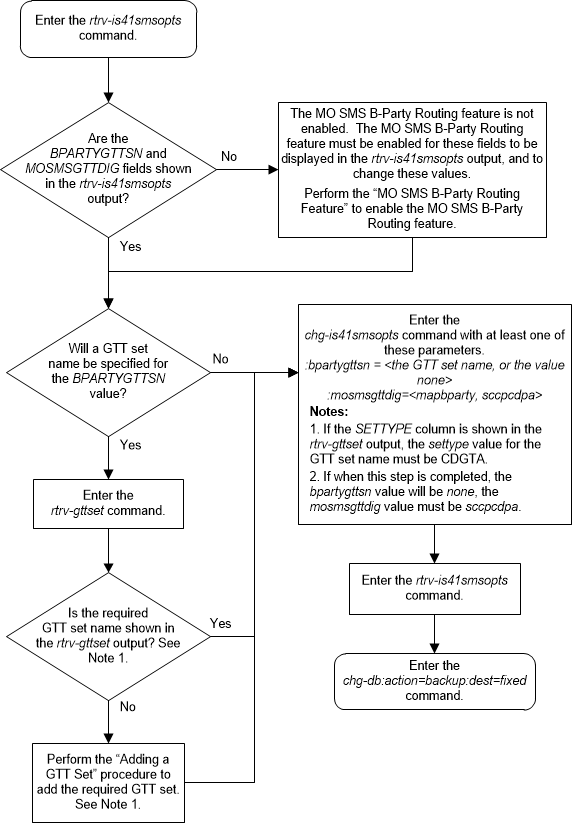
A.4 Configuring the IS-41 MO SMS B-Party Routing Options
This procedure is used to configure the MO SMS B-Party
routing options for IS-41 messages using the
chg-is41smsopts command with these
parameters:
:bpartygttsn – the name
of the GTT set, shown in the
rtrv-gttset output, global title
translation on the MAP B-Party digits of the IS-41 message will be performed
on; or the value
none indicating that global title
translation on the MAP B-Party digits of the IS-41 message will not be
performed on any GTT set.
:mosmsgttdig – the
digits that are used for global title translation.
sccpcdpa- the digits of the SCCP called party address portion of the message are used for global title translation.mapbparty- the MAP B-party number is used for global title translation.
The system default value for the
bpartygttsn parameter is
none. The system default value for the
mosmsgttdig parameter is
sccpcdpa.
This procedure can be performed only if the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature is enabled.
The set type of the GTT set name that will be specified
for the
bpartygttsn parameter must be
CDGTA. The set type of the GTT set is
shown in the
SETTYPE column of the
rtrv-gttset output. If the
SETTYPE column is not shown in the
rtrv-gttset output, all the GTT sets
are CDGTA GTT sets.
If the value of the
bpartygttsn parameter is
none when this procedure is completed,
the value of the
mosmsgttdig parameter must be
sccpcdpa.
Figure A-5 Configure the IS-41 MO SMS B-Party Routing Options
A.5 Adding a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature
This procedure is used to provision an entry in the
service selector table for the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature using the
ent-srvsel command.
The
ent-srvsel command uses these
parameters.
:gti/gtia/gtii/gtin/gtin24 – The global title
indicator. The GTI defines the domain as
gtiandgtia(ANSI) with GTI=2gtii(ITU international) with GTI=2 or GTI=4, andgtinandgtin24(ITU national) with GTI=2 or GTI=4.
The
gti and
gtia parameters are equivalent.
:serv – the DSM service
- smsmr.
:tt
– The global title translation. (0-255)
:ssn – The subsystem
number. (0-255, or *)
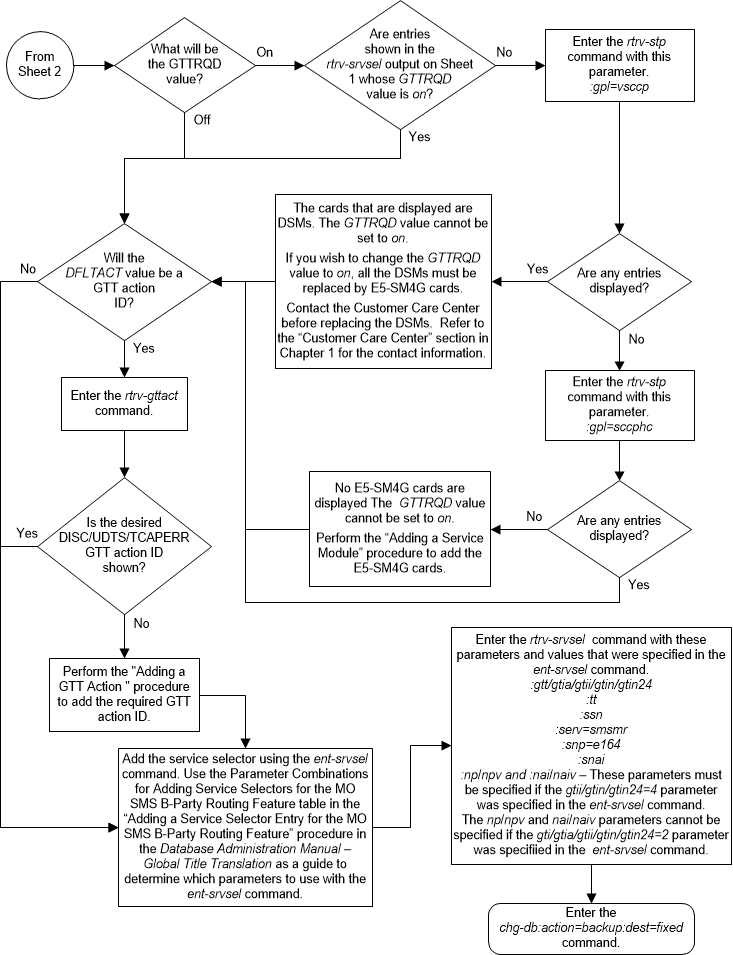
:dfltact - The default
action identifier that is associated with the service selector entry. This
parameter has one of these values.
- A GTT action identifier shown in the
rtrv-gttactoutput whoseACTIONvalue is eitherdisc,udts, ortcaperr. fallback- Fallback to the relay data. The relayed MSU is routed according to the routing data provided by the service.falltogtt- Fallback to GTT. If thegttselidparameter has a value other thannone, and the GTT selector search fails, the GTT selector search is performed again using thegttselid=noneparameter.
:on=gttrqd - Global
title translation is required after the service execution is complete and the
message is relayed by the service.
:off=gttrqd - Global
title translation is not required after the service execution is complete and
the message is relayed by the service.
:gttselid - The GTT
selector ID user for performing global title translation on messages that are
relayed by the service. (0 - 65534)
:nai or
:naiv – The nature of address
indicator. See
Table A-1
for NAI/NAIV.
Note:
The nature of address indicator parameters (naiv or
nai) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
naiv or
nai parameter.
Table A-1
shows the mapping between the
naiv and the
nai parameters.
:np or
:npv – The numbering plan. See
Table A-2
for NP/NPV mapping.
Note:
The numbering plan parameters (npv or
np) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
npv or
np parameter.
Table A-2
shows the mapping between the
npv and the
np parameters.
:snai – The service
nature of address indicator.
natl— National significant numberintl— International numberrnidn— Routing number prefix and international dialed/directory numberrnndn— Routing number prefix and national dialed/directory numberrnsdn— Routing number prefix and subscriber dialed/directory numberccrndn— Country code, routing number, and national directory numbersub— Subscriber number
:snp – The service
numbering plan - e164
Table A-1 NAIV/NAI Mapping
| NAIV | NAI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -- | Unknown |
| 1 | Sub | Subscriber Number |
| 2 | Rsvd | Reserved for national use |
| 3 | Natl | National significant number |
| 4 | Intl | International number |
| 5-127 | --- | Spare |
Table A-2 NPV/NP Mapping
| NPV | NP | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -- | Unknown |
| 1 | E164 | ISDN/telephony numbering plan |
| 2 | Generic | Generic numbering plan |
| 3 | X121 | Data numbering plan |
| 4 | F69 | Telex numbering plan |
| 5 | E210 | Maritime mobile numbering plan |
| 6 | E212 | Land mobile numbering plan |
| 7 | E214 | ISDN/mobile numbering plan |
| 8 | Private | Private network or network-specific numbering plan |
| 9-15 | --- | Spare |
To perform this procedure, the MO SMS B-Party Routing
feature must be enabled. Enter the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command with the MO SMS
B-Party Routing part number, 893024601, to verify whether or not the MO SMS
B-Party Routing feature is enabled. If the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature is
not enabled, perform the procedure
Activating the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature
to enable MO SMS B-Party Routing feature.
ITU service selectors (defined by either the
gtii,
gtin, or
gtin24 parameters) can be specified
only if the ANSIGFLEX STP option is not enabled. Enter the
rtrv-stpopts command to verify whether
or not the ANSIGFLEX STP option is enabled.
Figure A-6 Add a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 1 of 3
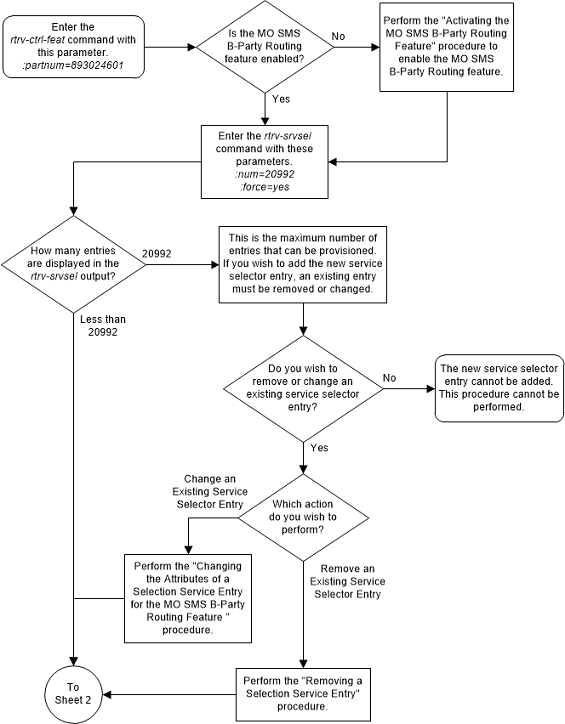
Figure A-7 Add a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 2 of 3
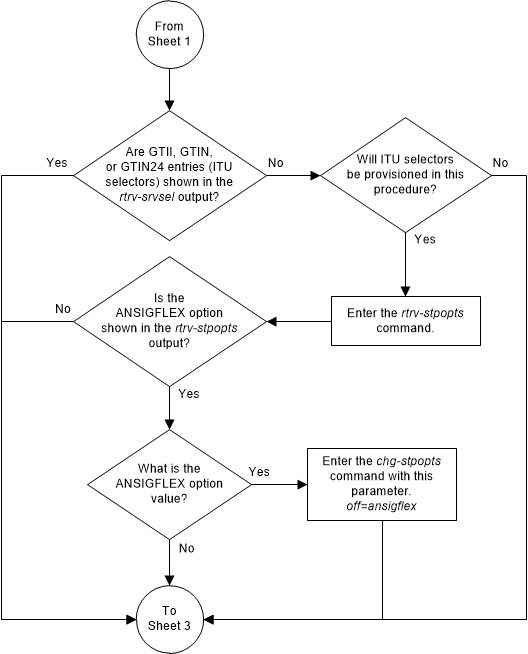
Figure A-8 Add a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 3 of 3
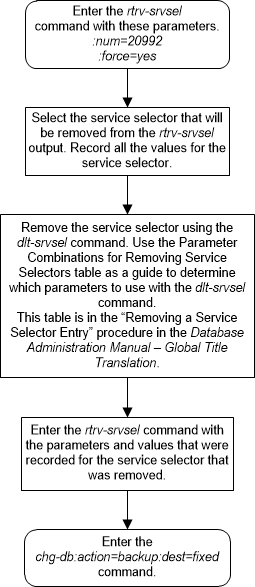
A.6 Removing a Service Selector Entry
This procedure is used to remove a service selector
using the
dlt-srvsel command.
The
dlt-srvsel command uses these
parameters.
:gti/gtia/gtii/gtin/gtin24 – The global title
indicator. The GTI defines the domain as
gtiandgtia(ANSI) with GTI=2gtii(ITU international) with GTI=2 or GTI=4, andgtinandgtin24(ITU national) with GTI=2 or GTI=4.
The
gti and
gtia parameters are equivalent.
:tt
– The global title translation value shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being removed.
:ssn – The subsystem
number value shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being removed.
:nai or
:naiv – The nature of address
indicator value shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being removed. (See
Table A-4
for NAI/NAIV mapping)
Note:
The nature of address indicator parameters (naiv or
nai) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
naiv or
nai parameter.
Table A-4
shows the mapping between the
naiv and the
nai parameters.
:np or
:npv– The numbering plan value shown
in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being removed. (See
Table A-5
for NP/NPV mapping)
Note:
The numbering plan parameters (npv or
np) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
npv or
np parameter.
Table A-5
shows the mapping between the
npv and the
np parameters.
Table A-4 NAIV/NAI Mapping
| NAIV | NAI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -- | Unknown |
| 1 | Sub | Subscriber Number |
| 2 | Rsvd | Reserved for national use |
| 3 | Natl | National significant number |
| 4 | Intl | International number |
| 5-127 | --- | Spare |
Table A-5 NPV/NP Mapping
| NPV | NP | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -- | Unknown |
| 1 | E164 | ISDN/telephony numbering plan |
| 2 | Generic | Generic numbering plan |
| 3 | X121 | Data numbering plan |
| 4 | F69 | Telex numbering plan |
| 5 | E210 | Maritime mobile numbering plan |
| 6 | E212 | Land mobile numbering plan |
| 7 | E214 | ISDN/mobile numbering plan |
| 8 | Private | Private network or network-specific numbering plan |
| 9-15 | --- | Spare |
The service selector that is being removed from the
database must be shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output.
Figure A-9 Remove a Service Selector Entry
A.7 Changing the Attributes of a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature
This procedure is used to provision an entry in the
service selector table for the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature using the
chg-srvsel command.
The
chg-srvsel command uses these
parameters.
:gti/gtia/gtii/gtin/gtin24 – The global title
indicator. The GTI defines the domain as
gtiandgtia(ANSI) with GTI=2gtii(ITU international) with GTI=2 or GTI=4, andgtinandgtin24(ITU national) with GTI=2 or GTI=4.
The
gti and
gtia parameters are equivalent.
:nserv – the DSM
service - smsmr.
:tt
– The global title translation type value shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being changed.
:ssn – The subsystem
number shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being changed.
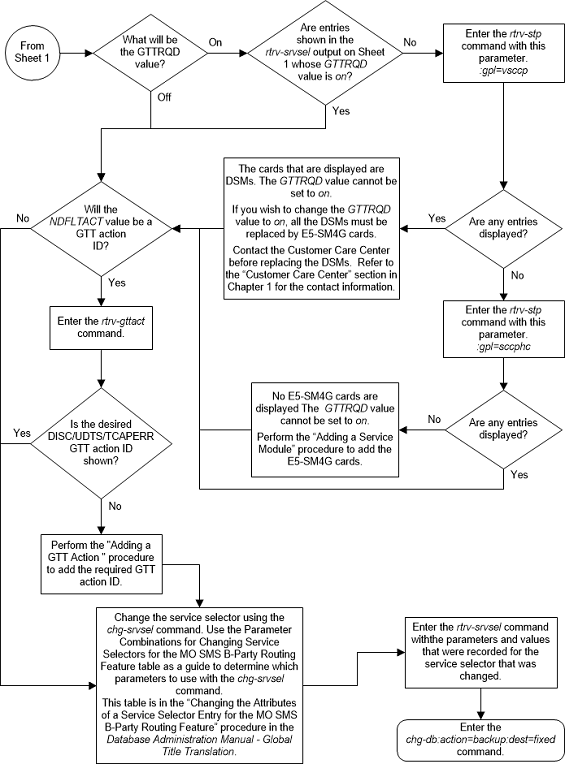
:ndfltact - The default
action identifier that is associated with the service selector entry. This
parameter has one of these values.
- A GTT action identifier shown in the
rtrv-gttactoutput whoseACTIONvalue is eitherdisc,udts, ortcaperr. fallback- Fallback to the relay data. The relayed MSU is routed according to the routing data provided by the service.falltogtt- Fallback to GTT. If thegttselidparameter has a value other thannone, and the GTT selector search fails, the GTT selector search is performed again using thegttselid=noneparameter.
:on=gttrqd - Global
title translation is required after the service execution is complete and the
message is relayed by the service.
:off=gttrqd - Global
title translation is not required after the service execution is complete and
the message is relayed by the service.
:ngttselid - The GTT
selector ID user for performing global title translation on messages that are
relayed by the service. (0 - 65534, or none)
:nai or
:naiv – The nature of address
indicator shown in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being changed. See
Table A-7
for NAI/NAIV mapping.
Note:
The nature of address indicator parameters (naiv or
nai) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
naiv or
nai parameter.
Table A-7
shows the mapping between the
naiv and the
nai parameters.
:np or
:npv– The numbering plan value shown
in the
rtrv-srvsel output for the service
selector that is being changed. See
Table A-8
for NP/NPV mapping.
Note:
The numbering plan parameters (npv or
np) can be specified by supplying
either a mnemonic or an explicit value. At no time may both the mnemonic and
the explicit value be specified at the same time for the same parameter. You
can specify either the
npv or
np parameter.
Table A-8
shows the mapping between the
npv and the
np parameters.
:nsnai – The service
nature of address indicator.
natl— National significant numberintl— International numberrnidn— Routing number prefix and international dialed/directory numberrnndn— Routing number prefix and national dialed/directory numberrnsdn— Routing number prefix and subscriber dialed/directory numberccrndn— Country code, routing number, and national directory numbersub— Subscriber number
:nsnp – The service
numbering plan - e164
Table A-7 NAIV/NAI Mapping
| NAIV | NAI | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | --- | Unknown |
| 1 | Sub | Subscriber Number |
| 2 | Rsvd | Reserved for national use |
| 3 | Natl | National significant number |
| 4 | Intl | International number |
| 5-127 | --- | Spare |
Table A-8 NPV/NP Mapping
| NPV | NP | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | --- | Unknown |
| 1 | E164 | ISDN/telephony numbering plan |
| 2 | Generic | Generic numbering plan |
| 3 | X121 | Data numbering plan |
| 4 | F69 | Telex numbering plan |
| 5 | E210 | Maritime mobile numbering plan |
| 6 | E212 | Land mobile numbering plan |
| 7 | E214 | ISDN/mobile numbering plan |
| 8 | Private | Private network or network-specific numbering plan |
| 9-15 | --- | Spare |
To perform this procedure, the MO SMS B-Party Routing
feature must be enabled. Enter the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command with the MO SMS
B-Party Routing part number, 893024601, to verify whether or not the MO SMS
B-Party Routing feature is enabled. If the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature is
not enabled, perform the procedure
Activating the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature
to enable MO SMS B-Party Routing feature.
Figure A-10 Change the Attributes of a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 1 of 2
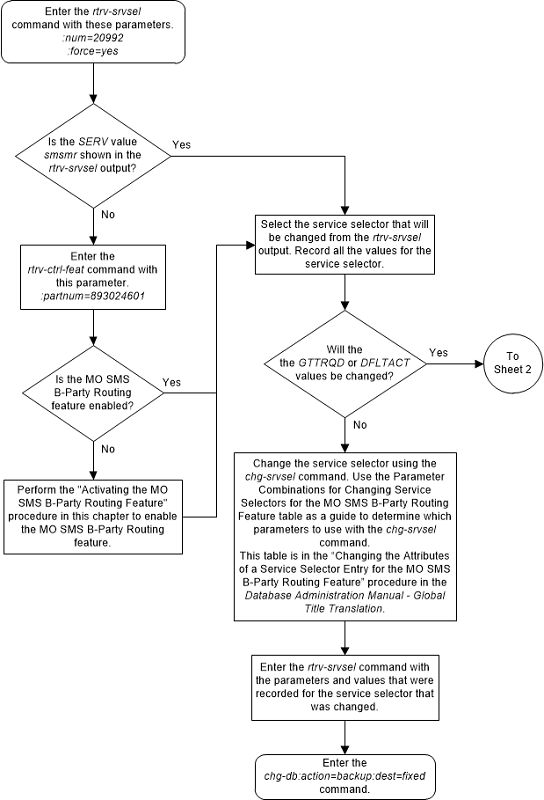
Figure A-11 Change the Attributes of a Service Selector Entry for the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature - Sheet 2 of 2
A.8 Turning the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature Off
This procedure is used to turn off the MO SMS B-Party
Routing feature using the
chg-ctrl-feat command.
The
chg-ctrl-feat command uses the
following parameters:
:partnum - The part
number of the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature, 893024601.
:status=off – used to
turn off the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature.
The status of the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature must be
on and is shown with the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command.
Caution:
If the MO SMS B-Party Routing feature is turned off, provisioning for MO SMS B-Party Routing can be performed with thechg-gsmsmsopts,
chg-is41smsopts,
ent-srvsel,
dlt-srvsel, and
chg-srvsel commands. The EAGLE will
not perform global title translation on the MAP B-Party digits of the message.
Figure A-12 Turn the MO SMS B-Party Routing Feature Off
