A E1 Interface
Appendix A, E1 Interface, contains general information about the E1 interface and how to provision it.
A.1 Introduction
The E1 interface terminates or distributes E1 facility signals for the purpose of processing the SS7 signaling links carried by the E1 carrier. The E1 interface can be either a an E1/T1 MIM card, an E5-E1T1-B card, or SLIC card as shown in Figure A-1, and Figure A-2. The E1/T1 MIM or E5-E1T1-B card can also be used as a T1 interface. This appendix describes how an E1 interface is configured using either the the E1/T1 MIM card or E5-E1T1-B card. The T1 interface configuration is described in T1 Interface.
Note:
The procedures in this appendix are used only to configure E1 signaling links on the E1/T1MIM card or E5-E1T1-B card. To configure an E1 high-speed signaling link (on the LIME1ATM card), go to the Adding an ATM High-Speed Signaling Link procedure.The E1/T1 MIM card contains up to eight signaling links and allows the EAGLE to contain more than 500 signaling links.
Figure A-1 E1/T1 MIM Block Diagram
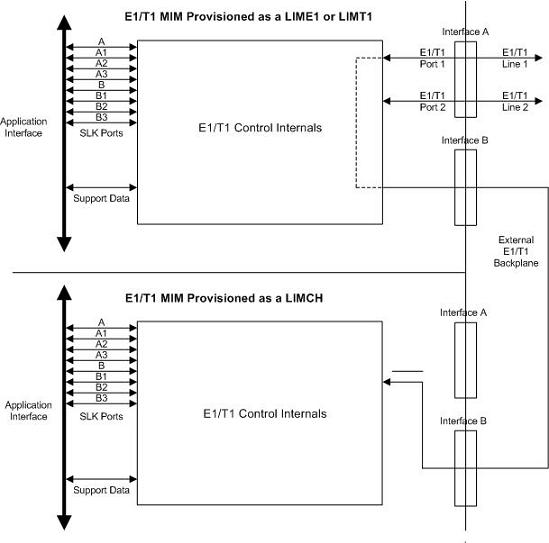
Figure A-2 E5-E1T1-B Block Diagram
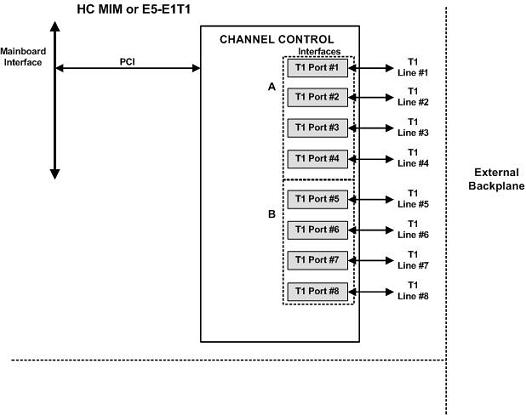
Table A-1 provides an overview of the functions of the E1 card and the channel card.
Table A-1 Functional Overview of the E1 and Channel Card
| Card | Function |
|---|---|
| E1 |
|
| Channel |
|
Configured as an E1 Card
Configured as an E1 card, two separate and independent E1 inputs can be terminated on an E1 card. If an E1/T1 MIM is being used, one to eight bi-directional channels are extracted from the E1 inputs and processed as SS7 signaling links. Implemented as E1 Link Interface Modules, up to thirty two separate and independent E1 inputs can be terminated in an Extension Shelf. The E1 card can support signaling links transmitting at either 56 kbps or 64 kbps.
Configured as a Channel Card
In an Extension shelf equipped with an E1 cabling backplane, an E1 card terminates one or two E1 inputs and connects the E1 port 1 input to one of eight available busses on the E1 cabling backplane. Channel cards also connected to the E1 cabling backplane are able to extract any eight signaling channels from the same E1 port 1 input. In this manner, up to 31 E1 channels can be used for signaling - the 32nd channel is reserved for E1 synchronization. The E1 card can support signaling links transmitting at either 56 kbps or 64 kbps.
Note:
An E5-E1T1-B card cannot be used as a channel card.High Capacity Multi-Channel Interface Module (HC-MIM) and Eagle 5 - E1 T1 Interface (E5-E1T1)
The EAGLE 5 - E1 T1-B Interface (E5-E1T1-B) provides access to eight E1 ports residing on backplane connectors A and B. Each data stream consists of 31 E1 DS0 signaling links assigned in a time-division multiplex manner. Each channel occupies a unique timeslot in the data stream and can be selected as a local signaling link on the interface card. A maximum of 64 E1 signaling links can be assigned to an appropriate card. A maximum of 32 E1 signaling links can be assigned to an E5-E1T1-B card.
To support the processing of signaling channels that are intermixed on trunks with voice or data channels, the E5-E1T1-B card allows E1 ports to be channel bridged. This allows better utilization of E1 bandwidth without dedicating entire trunks to signaling.
Figure A-3 Channel Bridging
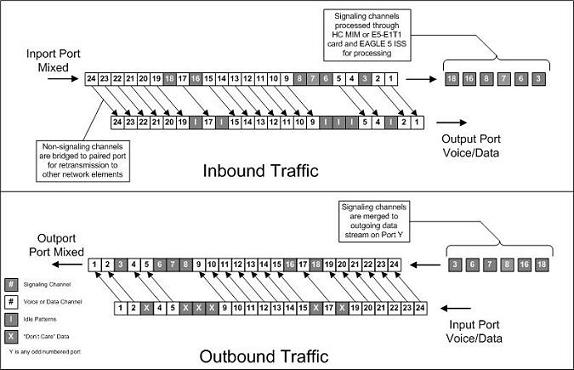
Channel bridging is implemented by pairing odd and even E1 ports. The E1 port selected for channel bridging is the odd numbered port (1, 3, 5, 7). When the E1 port is selected for channel bridging, it is paired with its adjacent even numbered port (2, 4, 6, 8) as shown in Table A-2.
Table A-2 Channel Bridging E1 Port Pairing
| Odd Numbered E1 Port (Bridging Master) | Even Numbered E1 Port Bridged to the Odd Numbered E1 Port (Bridging Slave) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 |
| 7 | 8 |
By pairing E1 ports, the adjacent even numbered E1 port could be used to allow data received on the bridging master (odd) E1 port to reach downstream network elements. This interface is a bi-directional interface so data is also able to enter the bridging slave (even) E1 port and leave the EAGLE through the bridging master (odd) E1 port. There is a 1 to 1 correspondence between the timeslots on the bridging master and slave E1 ports.
In order to use channel bridging without facility errors, both E1 ports (bridging master and slave) must be synchronous (timed off the same clock source). This may be accomplished in one of the following ways:
- The bridging master
E1
port and the bridging slave
E1
port use timing recovered from each other (using the
e1tsel=recoveredparameter with either theent-e1orchg-e1command). When provisioning channel bridged E1 port, only the bridging master E1 port is provisioned with theent-e1orchg-e1command. The bridging slave E1 port is automatically provisioned with the same attributes as the bridging master E1 port. - Both the bridging master and slave
E1
ports are using an external clock source (using the
e1tsel=externalparameter when provisioning the channel bridged E1 port with either theent-e1orchg-e1command).
Any other methods used for timing could cause problems on the E1 trunk and are not supported.
Idle patterns on the shadow channels, that is, the timeslots located on the bridging slave E1 port that have been not been dropped from the bridging master E1 port, are provided by the EAGLE. All other idle timeslots that are not dropped by the EAGLE must contain an idle pattern provided by the remote network elements connected to both E1 ports (bridging master and slave). Without these patterns on the idle timeslots, instability of the E1 signaling link may occur.
Provisioning of signaling links on the bridging slave E1 port is not allowed while the bridging master E1 port is channel bridged.
A.2 Determining the Configuration
External Interface Descriptions
The E1 Interface Backplane provides a method for extending individual E1 channels from the E1-configured cards to any channel-configured cards in use. Note the following issues regarding the E1 backplane:
-
Only one E1-configured card may be plugged into each bus on the backplane.
-
When installing non-E1 cards on the shelf equipped with the E1 interface backplane, ensure that none of the slots to be used are cabled to the E1 interface backplane. If a non-E1 card is installed in a slot that is connected to the E1 backplane, all E1 cards on that bus may fail.
-
Only one E1 card may be connected (via the B port) to each bus of the E1 cabling backplane, and all SS7 links derived from any particular E1 must be processed on the same shelf on which the incoming E1 is terminated.
-
Due to cable congestion, Oracle does not recommend use of the E1 cabling backplane on the control shelf.
-
If the control shelf is used, a maximum of 20 E1 interfaces can be utilized in the control shelf.
The E1 backplane is impedance-controlled for 120 Ohms and is designed for use with RS-485 transmission characteristics.
Descriptions of the T1 hardware and the procedures for installing the T1 hardware are contained in Hardware Reference and Installation Guide.
Possible Configurations
The E1 backplane was designed to allow the maximum number of possible customer setups. It allows the customer to choose between several levels of diversity and convenience. Configurations depend on the number of cards configured as E1 cards versus the number of cards configured as channel cards. The level of diversity required by the customer also affects the configuration requirements. Note that all signals labelled “E1 input” may be one or two E1 ports depending on the cable used.
Support of Two E1 Ports
The E1 card will support two E1 ports, which are independently configurable. On an E1 card, E1 port 1 will support channel cards. The second port of that E1 card will only support up to a maximum of eight time slots and will not support channel cards.
Clocking Options
Each E1 interface must independently operate in one of two clocking modes. When configured as a channel card, an E1 card is required for the channel card’s clocking source.
-
Slave Timing - The default receive clock on the E1 card will be used as the source of the transmit clock.
-
Master Timing - The transmit clock of the E1 card will originate on this board. The oscillator on the board provides the clock source. Note the oscillator is less accurate than the network clock.
The Master Timing feature allows an E1 signaling link to take its high-speed clock reference directly from an external high-speed master clock source.
Support of E1 Framing Options
The E1 interfaces will independently support the following E1 framing options. Selection of these options will be made by the crc4 and cas parameters of either the ent-e1 or chg-e1 commands.
-
Clear Channel Signaling (CCS)
-
Channel Associated Signaling (CAS)
-
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC4)
The following provide for zero bit suppression: HDB3 (High Density Bipolar encoding of order 3).
On any given E1 card, CCS and CAS are mutually exclusive and cannot be used together. However, CRC4 may be added to either CCS or CAS.
LIM-E1 Card to Channel Card Interface
Whether the E1/channel card is operating as an E1 card or a channel card, the card will map any eight channels from the E1 interfaces to an HDLC controller (ports A, B, A1, B1, A2, B2, A3, B3 for the E1/T1 MIM card). These channels could be dropped either both from E1 port 1 or one from E1 port 1 and the other from E1 port 2. When the E1/channel card is configured as an E1 card, it will support the external E1 cabling backplane interface from E1 port 1 (E1 port 2 will not have this capability) to additional E1/channel cards, within the same shelf, configured as channel cards. Idle time slots not assigned to an E1 card or a channel card will be filled with a one’s pattern.
Channel Support
The E1/channel card will independently support either 56 kbps or 64 kbps on any channel.
Configuring the Signaling Links
The main consideration for the provisioning of E1s is to determine the number of E1s existing in the network and the equipment needed for grooming into the EAGLE. To utilize the flexibility of the E1 interface feature, you may want to determine the minimum number of E1 cards needed to process the total number of SS7 links and then consider diversity for reliability reasons.
Use the following points as guidelines when considering diversity for E1:
-
If possible, no two E1s containing links from a common link set should be on the same E1/dual port channel card.
-
If possible, no two E1s containing links from a common link set should be on adjacent E1/dual port channel cards where they are powered from the same fuse position.
-
If possible, no two E1s containing links from a common link set should be terminated on the same shelf because of the shelf clock cabling, and is only an issue if using master clocking sync to the network
-
If possible, no two links in a link set should arrive at the EAGLE on the same E1.
-
If possible, for link sets containing more than two links, you should minimize the number of links in that link set on any given E1.
As an example, consider a network to be groomed into the EAGLE consisting of 30 E1s with a total number of 100 links where the largest link set size is 8. The most efficient way to provision the EAGLE would be to have four extension shelves equipped with the E1 cabling backplane, one E1 card, and 12 channel cards per shelf. Utilizing one B bus on each shelf, 25 signaling links would be terminated on each shelf for a total of 100. This is also the minimum number of E1 cards required for this example.
With the same example but using the third and fifth bullets above as a consideration, the EAGLE would be provisioned with eight extension shelves equipped with the E1 cabling backplane. Four of the shelves would be equipped with one E1 card and six channel cards, and the other four shelves would be equipped with one E1 card and five channel cards. Since the largest link set size is eight, a total of eight E1 cards is required. Utilizing one B bus on each shelf, 13 signaling links would be terminated on each shelf with six channel cards, and 12 signaling links would be terminated on each shelf with five channel cards.
Note:
When retrieving link information from the database, the links for an E1 or channel card is not displayed until after the card is allowed.E1 Configuration Form
Use the form provided below to record your E1 configuration. An example of the required input is shown in italics under each column heading.
Table A-3 E1 Signaling Link Configuration Form
| Card Location and Port (1201 A) | Timeslot (1) | E1 Number (1) | E1 Card Location (1201) | Adjacent Point Code (4001) | Linkset ( ST1ME ) | SLC (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
A.3 E1 Interface Configuration Procedures
This appendix contains these procedures because they contain information specific to the E1 Interface:
- Adding a LIM-E1 Card
- Removing a LIM-E1 Card
- Adding Channelized and non-Channel Bridged E1 Ports
- Adding Channel Bridged E1 Ports
- Adding Unchannelized E1 Ports
- Removing the E1 Interface Parameters
- Changing the Attributes of a Channelized E1 Port
- Changing the Attributes of an Unchannelized E1 Port
- Making a Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channelized E1 Port
- Making a Non-Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channel Bridged E1 Port
- Adding an E1 Signaling Link
Procedures for configuring the linksets and routes, for removing SS7 signaling links (which includes E1 signaling links), and for configuring the HC MIM temperature alarms are contained in SS7 Configuration interface, therefore, are not included in this appendix.
The procedures contained in this appendix use a variety of commands. If more information on these commands is needed, go to Commands User's Guide to find the required information.
A.4 Adding a LIM-E1 Card
The LIM-El card is provisioned as either an E1 card or a channel card in the database using the ent-card command. The card being provisioned in the database can be one of these cards shown in Table A-4.
Table A-4 E1 Card Part Numbers
| Card Type | Part Number |
|---|---|
|
E1/T1MIM |
870-2198-XX |
|
E5-E1T1 |
870-1873-XX |
The ent-card command uses these parameters.
:loc – The location of the card being added to the database.
Note:
The HC-MIM can be inserted only in a odd-numbered card location. The HC-MIM will not power up if it is inserted in an even-numbered card location. All the E1 backplane cabling should be removed from the B connector for the slot that the HC-MIM will occupy.The HC-MIM occupies two card locations, so the even numbered card location adjacent to the odd numbered slot where the HC-MIM has been inserted must be empty, as shown in Table A-5. The HC-MIM is connected to the network through the odd numbered card slot connector.
Table A-5 HC-MIM Card Locations
| Location of the HC-MIM | Empty Card Location | Location of the HC-MIM | Empty Card Location |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Slot 01 |
Slot 02 |
Slot 11 |
Slot 12 |
|
Slot 03 |
Slot 04 |
Slot 13 |
Slot 14 |
|
Slot 05 |
Slot 06 |
Slot 15 |
Slot 16 |
|
Slot 07 |
Slot 08 |
Slot 17 |
Slot 18 |
The E1, E1/T1 MIM and E5-E1T1 cards occupy one card location. These cards can be placed in any card location except for even numbered card locations whose adjacent odd numbered card location is occupied by a card that occupies two card locations.
:type – The type of card being added to the database. For this procedure, the value of this parameter is lime1 (E1 card) or limch (channel card).
Note:
The HC-MIM and E5-E1T1 card cannot be provisioned as a channel card.:appl – The application software that is assigned to the card. For this procedure, the value of this parameter is either ccs7itu or ss7ansi.
The shelf to which the card is to be added must already be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-shlf command. If the shelf is not in the database, see the Adding a Shelf procedure in Database Administration - System Management User's Guide.
The examples in this procedure are used to add the LIM-E1 cards in card locations 1201, 1202, 1203, 1204, 1211, and 1212 to the database.
Figure A-4 Adding a LIM-E1 Card
A.5 Removing a LIM-E1 Card
This procedure is used to remove either an E1 card or a channel card from the database using the dlt-card command. The card being removed must exist in the database.
If an E1 card is being removed, then no E1 interfaces can be assigned to the card. This can be verified with the rtrv-e1 command. Go to the Removing the E1 Interface Parameters procedure to remove the E1 interfaces assigned to the E1 card being removed from the database.
If only a channel card is being removed from the database, then no SS7 signaling links can be assigned to the card. This can be verified with the rtrv-slk command. Go to the Removing an SS7 Signaling Link procedure to remove the signaling links assigned to the channel card being removed from the database.
Caution:
If the E1 card or channel card is the last SS7LIM in service, removing this card from the database will cause SS7 traffic to be lost and isolate the EAGLE from the network.The examples in this procedure are used to remove the E1 cards in card locations 1202 and 1203.
Figure A-5 Removing a LIM-E1 Card
A.6 Adding Channelized and non-Channel Bridged E1 Ports
The channelized and non-channel bridged E1 ports are provisioned in the database using the ent-e1 command using these parameters.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) that is servicing the E1 signaling link. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter.
:e1port – The E1 port on the E1 card used to service the E1 signaling link. The e1port value cannot already be assigned to the E1 card specified by the loc parameter.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link. The default value is on (crc4=on).
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. The default value is CCS enabled (cas=off). The cas=on parameter cannot be specified for an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI. The default value is HDB3 encoding (encode=hdb3). AMI encoding can be specified only for an HC-MIM, or an E5-E1T1 card.
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master (external), slave (line), or recovered. The default value is slave timing (e1tsel=line).
The recovered timing source can be used only with the chanbrdg=on parameter and cannot be used in this procedure.
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3. The default value is 0 (si=0).
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31. The default value is 0 (sn=0).
The ent-e1 command contains other parameters that are not used in this procedure. These parameters and their usage are described in these sections:
e1tsel=recovered,chanbrdg, andforce=yes– Adding Channel Bridged E1 Ports.linkclassandminsurate– Adding Unchannelized E1 Ports.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-card command.
If the cas=on parameter is specified with the ent-e1 command, timeslot 16 cannot be used when the E1 signaling link is provisioned with the ent-slk command in Adding an E1 Signaling Link.
The E1 card cannot contain channelized and unchannelized E1 ports.
Figure A-6 Adding Channelized and non-Channel Bridged E1 Ports
Sheet 1 of 7
Sheet 2 of 7
Sheet 3 of 7
Sheet 4 of 7
Sheet 5 of 7
Sheet 6 of 7
Sheet 7 of 7
A.7 Adding Channel Bridged E1 Ports
The channel bridged E1 ports are provisioned in the database using the ent-e1 command using these parameters.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) that is servicing the E1 signaling link. The E1 card must be an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter.
:e1port – The E1 port on the E1 card used to service the E1 signaling link. The e1port value cannot already be assigned to the E1 card specified by the loc parameter.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link. The default value is on (crc4=on).
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. The default value is CCS enabled (cas=off). The cas=on parameter cannot be specified for an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI. The default value is HDB3 encoding (encode=hdb3).
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master (external) or recovered. The default value is slave timing (e1tsel=line) which cannot be used for a channel bridged E1 port.
The recovered timing source can be used only with the chanbrdg=on parameter and uses the even numbered member of the bridged-pair as a clock source, ensuring that port in the pair can recover the timing from its partner.
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3. The default value is 0 (si=0).
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31. The default value is 0 (sn=0).
:force=yes – Required when the even numbered E1 port being channel bridged is provisioned in the database before this procedure is performed.
:chanbrdg – Specifies whether or not the odd numbered E1 port specified in this procedure is channel bridged to its adjacent even numbered E1 port. Table A-9 shows the E1 ports that can be specified with the chanbrdg=on parameter and the even-numbered E1 ports that are bridged to the odd numbered E1 port.
Table A-9 Channel Bridging Ports
| Odd Numbered E1 Port | Even Numbered Bridged E1 Port |
|---|---|
|
1 |
2 |
|
3 |
4 |
|
5 |
6 |
|
7 |
8 |
The ent-e1 command contains the linkclass and minsurate parameters that are not used in this procedure. These parameters and their usage are described in Adding Unchannelized E1 Ports.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-card command.
The E1 card cannot contain channelized and un-channelized E1 ports.
Figure A-7 Adding Channel Bridged E1 Ports
Sheet 1 of 6
Sheet 2 of 6
Sheet 3 of 6
Sheet 4 of 6
Sheet 5 of 6
Sheet 6 of 6
A.8 Adding Unchannelized E1 Ports
The E1 interface parameters are provisioned in the database using the ent-e1 command using these parameters.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) that is servicing the E1 signaling link. The E1 card must be an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter.
:e1port – The E1 port on the E1 card used to service the E1 signaling link. The e1port value cannot already be assigned to the E1 card specified by the loc parameter.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link. The default value is on (crc4=on).
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. The default value is CCS enabled (cas=off). The cas=on parameter cannot be specified for an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI. The default value is HDB3 encoding (encode=hdb3).
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master (external) or slave (line). The default value is slave timing (e1tsel=line).
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3. The default value is 0 (si=0).
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31. The default value is 0 (sn=0).
:linkclass – Indicates whether the E1 port supports channelized (linkclass=chan) or un-channelized (linkclass=unchan) E1 signaling links.
:minsurate – Specifies the minimum number of signaling units (FISUs and LSSUs) per second that are transmitted on the outbound E1 signaling link during idle periods or when there is an unused portion of the link’s bandwidth. The value of this parameter is from 500 to 2000 signaling units per second, with the default value of 1000 signaling units per second. The minsurate parameter can be specified only when an unchannelized E1 port (linkclass=unchan parameter) is being configured.
The ent-e1 command contains the e1tsel=recovered, chanbrdg, and force=yes parameters. These parameters are not used in this procedure. These parameters and their usage are described in Adding Channel Bridged E1 Ports.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-card command.
Figure A-8 Adding Unchannelized E1 Ports
Sheet 1 of 10
Sheet 2 of 10
Sheet 3 of 10
Sheet 4 of 10
Sheet 5 of 10
Sheet 6 of 10
Sheet 7 of 10
Sheet 8 of 10
Sheet 9 of 10
Sheet 10 of 10
A.9 Removing the E1 Interface Parameters
This procedure is used to remove an E1 interface from the database using the dlt-e1 command using these parameters.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) containing the E1 interface being removed.
:e1port – The E1 port on the E1 card containing the E1 interface being removed.
The E1 interface to be removed must exist in the database. This can be verified in step 1.
To remove the E1 interface information contained on an E1 card, all signaling links serviced by that E1 card must be removed from the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-e1 command, specifying the card location and E1PORT on the E1 card, and the rtrv-slk command, specifying the location of any cards (E1 or channel cards) shown in the rtrv-e1 output. If there are any signaling links being serviced by the E1 card, go to the Removing an SS7 Signaling Link procedure and remove these signaling links.
Even numbered E1 ports cannot be removed if the even numbered E1 port is channel bridged. Remove the corresponding odd numbered E1 port (see Table A-5) to remove the even numbered channel bridged E1 port.
Figure A-9 Removing the E1 Interface Parameters
A.10 Changing the Attributes of a Channelized E1 Port
chg-e1 command. A channelized E1 port is an E1 port whose LINKCLASS value is CHAN, shown in the LINKCLASS column in the rtrv-e1 output. Other actions can be performed on E1 ports. To perform these actions on the E1 ports, perform one of these procedures.
- To change the attributes of an unchannelized E1 port - Changing the Attributes of an Unchannelized E1 Port
- To make a channel bridged E1 port from a channelized E1 port - Making a Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channelized E1 Port
- To make a non-channel bridged E1 port from a channel bridged E1 port - Making a Non-Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channel Bridged E1 Port
To change the attributes of a channelized E1 port, these parameters are used with the chg-e1 command.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) that is servicing the E1 signaling link. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter. The E1 card can be either an E1/T1 MIM, an HC -MIM, or an E5-E1T1 card.
:e1port – The E1 port being changed in this procedure.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link.
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. The cas=on parameter cannot be specified for an HC-MIM, or an E5-E1T1 card.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI. AMI encoding can be specified only for an E1/T1 MIM, an HC-MIM, or an E5-E1T1 card.
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master timing (external), slave timing (line), or recovered.
The recovered timing source can be used only with the chanbrdg=on parameter and uses the even numbered member of the bridged-pair as a clock source, ensuring that port in the pair can recover the timing from its partner.
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3.
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-e1 command.
If either the crc4, cas, encode, or e1tsel values are being changed, all the signaling links serviced by the E1 card must be taken out of service.
If the signaling link being serviced by the E1 card is using timeslot 16, the cas=on parameter cannot be specified with the chg-e1 command.
Figure A-10 Changing the Attributes of a Channelized E1 Port
Sheet 1 of 4
Sheet 2 of 4
Sheet 3 of 4
Sheet 4 of 4
A.11 Changing the Attributes of an Unchannelized E1 Port
chg-e1 command. An unchannelized E1 port is an E1 port whose LINKCLASS value is UNCHAN, shown in the LINKCLASS column in the rtrv-e1 output. Other actions can be performed on E1 ports. To perform these actions on the E1 ports, perform one of these procedures.
- To change the attributes of a channelized E1 port - Changing the Attributes of a Channelized E1 Port
- To make a channel bridged E1 port from a channelized E1 port - Making a Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channelized E1 Port
- To make a non-channel bridged E1 port from a channel bridged E1 port - Making a Non-Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channel Bridged E1 Port
To change the attributes of an unchannelized E1 port, these parameters are used with the chg-e1 command.
:loc – The location of the E1 card that contains the unchannelized E1 port (card type lime1) that is servicing the E1 signaling link. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter. The E1 card can be either an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card.
:e1port – The E1 port being changed in this procedure.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link.
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. For an unchannelized E1 port, the cas value must be off.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI.
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master (external) or slave (line).
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3.
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31.
:minsurate – Specifies the minimum number of signaling units (FISUs and LSSUs) per second that are transmitted on the outbound E1 signaling link during idle periods or when there is an unused portion of the link’s bandwidth. The value of this parameter is from 500 to 2000 signaling units per second, with the default value of 1000 signaling units per second.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-e1 command.
If either the crc4, cas, encode, or e1tsel values are being changed, all the signaling links serviced by the E1 card must be taken out of service.
Figure A-11 Changing the Attributes of an Unchannelized E1 Port
Sheet 1 of 2
Sheet 2 of 2
A.12 Making a Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channelized E1 Port
chg-e1 command. A channelized E1 port is an E1 port whose LINKCLASS value is CHAN, shown in the LINKCLASS column in the rtrv-e1 output. A non-channel bridged E1 port is an odd numbered E1 port that contains dashes in the CHANBRDG column in the rtrv-e1 output. Other actions can be performed on E1 ports. To perform these actions on the E1 ports, perform one of these procedures.
- To change the attributes of a channelized E1 port - Changing the Attributes of a Channelized E1 Port
- To change the attributes of an unchannelized E1 port - Changing the Attributes of an Unchannelized E1 Port
- To make a non-channel bridged E1 port from a channel bridged E1 port - Making a Non-Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channel Bridged E1 Port
To make a channel bridged E1 port from a channelized E1 port, these parameters are used with the chg-e1 command.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) that contains the odd numbered channelized E1 port. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter. The E1 card can be either an HC-MIM, or an E5-E1T1 card.
:e1port – The E1 port being changed in this procedure. Only the odd numbered E1 ports, 1, 3, 5, or 7, can be specified for a channel bridged E1 port.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link.
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. For a channel bridged E1 port, the cas parameter value must be off.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI.
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master (external) or recovered.
The recovered timing source uses the even numbered member of the bridged-pair as a clock source, ensuring that port in the pair can recover the timing from its partner.
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see the Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface procedure.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3.
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31.
:chanbrdg – Specifies whether or not the odd numbered E1 port specified in this procedure is channel bridged to its adjacent even numbered E1 port. Table A-15 shows the E1 ports that can be specified with the chanbrdg=on parameter and the even-numbered E1 ports that are bridged to the odd numbered E1 port.
Table A-15 Channel Bridging Ports
| Odd Numbered E1 Port | Even Numbered Bridged E1 Port |
|---|---|
|
1 |
2 |
|
3 |
4 |
|
5 |
6 |
|
7 |
8 |
:force=yes – required when the even numbered E1 port being channel bridged is provisioned in the database before this procedure is performed.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-e1 command.
If either the crc4, cas, encode, or e1tsel values are being changed, all the signaling links serviced by the E1 card must be taken out of service.
Figure A-12 Making a Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channelized E1 Port
Sheet 1 of 6
Sheet 2 of 6
Sheet 3 of 6
Sheet 4 of 6
Sheet 5 of 6
Sheet 6 of 6
A.13 Making a Non-Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channel Bridged E1 Port
chg-e1 command. A channel bridged E1 port is an odd numbered E1 port that contains the entry MASTER in the CHANBRDG column in the rtrv-e1 output. Other actions can be performed on E1 ports. To perform these actions on the E1 ports, perform one of these procedures.
- To change the attributes of a channelized E1 port - Changing the Attributes of a Channelized E1 Port
- To change the attributes of an unchannelized E1 port - Changing the Attributes of an Unchannelized E1 Port
- To make a channel bridged E1 port from a channelized E1 port that is not channel bridged - Making a Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channelized E1 Port
To make a non-channel bridged E1 port from a channel bridged E1 port, these parameters are used with the chg-e1 command.
:loc – The location of the E1 card (card type lime1) that contains the channel bridged E1 port. The location of a channel card (card type limch) cannot be specified for this parameter. The E1 card can be either an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card.
:e1port – The E1 port being changed in this procedure. Only the odd numbered E1 ports, 1, 3, 5, or 7, can be specified for a channel bridged E1 port.
:crc4 – Specifies whether or not CRC4 is enabled on the E1 signaling link.
:cas – Specifies whether CAS or CCS is used on the E1 signaling link. CAS is enabled with the cas=on parameter. CCS is enabled with the cas=off parameter. Only HC-MIMs or E5-E1T1 cards can contain channel bridged E1 ports. For HC-MIMs or E5-E1T1 cards, the cas parameter value must be off.
:encode – Specifies the type of encoding or decoding that is used on the E1 signaling link, either HDB3 or AMI.
:e1tsel – The timing source for the E1 signaling link, master (external) or slave (line). If the e1tsel value for the channel bridged E1 port is recovered, the e1tsel value must be changed to either line or external when the channel bridged E1 port is changed to a non-channel bridged E1 port.
Note:
To use an external high-speed master clock source other than RS-422, TDMs 870-0774-15 or later must be installed in card locations 1114 and 1116, and the TDM Global Timing Interface options must be configured. For more information, see Configuring the Options for the TDM Global Timing Interface.:si – Specifies the value of the two spare international bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 3.
:sn – Specifies the value of the five spare national bits of NFAS data, from 0 to 31.
:chanbrdg=off – Specifies that the odd numbered E1 port specified in this procedure is not channel bridged to its adjacent even numbered E1 port.
The E1 card specified in this procedure must be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-e1 command.
If either the crc4, cas, encode, or e1tsel values are being changed, all the signaling links serviced by the E1 card must be taken out of service.
Figure A-13 Making a Non-Channel Bridged E1 Port from a Channel Bridged E1 Port
Sheet 1 of 2
Sheet 2 of 2
A.14 Adding an E1 Signaling Link
This procedure is used to add an E1 signaling link to the database using the ent-slk command and these parameters.
:loc – The card location of the card that the E1 signaling link will be assigned to.
:link – The signaling link on the card specified in the loc parameter.
:lsn – The name of the linkset that will contain the signaling link.
:slc – The signaling link code. The SLC must be unique within the linkset. It must be the same at both the EAGLE location and the distant node.
:bps – The transmission rate for the link in bits per second.
:ecm – Error correction method, either basic or pcr. The default value for this parameter is basic.
:pcrn1 – The threshold of the number of MSUs available for retransmission. If the error correction method being used is PCR (:ecm=pcr), and this threshold is reached, no new MSUs or FISUs are sent. The retransmission cycle is continued up to the last MSU entered into the retransmission buffer in the order in which they were originally transmitted.
:pcrn2 – The threshold of the number of MSU octets available for retransmission. If the error correction method being used is PCR (:ecm=pcr), and this threshold is reached, no new MSUs or FISUs are sent. The retransmission cycle is continued up to the last MSU entered into the retransmission buffer in the order in which they were originally transmitted.
:ts – The timeslot on the E1 card or channel card being used for the E1 signaling link.
:e1port – The E1 port on the E1 card that is servicing the timeslot selected for the E1 signaling link.
:e1loc – The location of the E1 card servicing the timeslot selected for the E1 signaling link. This parameter can be specified only when provisioning E1 signaling links on channel cards.
:l2tset – The level 2 timer set table assigned to the E1 signaling link. The type of linkset the E1 signaling link is assigned to and the E1 card’s application determines the value of the l2tset parameter. The level 2 timer set tables are defined in Changing Level 2 Timers .
The ent-slk command contains other optional parameters that can be used to configure a signaling link. These parameters are not shown here because they are not necessary to provision an E1 signaling link. These parameters are explained in more detail in Adding an SS7 Signaling Link, or in the ent-slk command description in Commands User's Guide.
These items must be configured in the database before an E1 signaling link can be added:
-
Shelf – see Adding a Shelf in Database Administration - System Management User's Guide
- E1 Card (card type
lime1) or ChannelCard (card typelimch) running either thess7ansiorccs7ituapplications – see Adding a LIM-E1 Card procedure - Destination Point Code – see the Adding a Destination Point Code procedure.
- Linkset – Adding an SS7 Linkset .
Verify that the link has been physically installed (all cable connections have been made).
Timeslot 16 (ts=16) cannot be specified for an E1 signaling link if the E1 interface servicing this link has CAS enabled. This is shown by the entry on in the CAS field of the rtrv-e1 output.
If the E1 signaling link is assigned to a channel card (card type limch), the e1port parameter cannot be specified. The e1port parameter value defaults to 1.
All E1 signaling links in a linkset can use either the 56000 or 64000 transmission rate. The transmission rate for the E1 signaling links in the linkset do not have to be the same.
The values for the ts parameter must be from 1 to 31.
The linkset must be in the database. The number of signaling links in a linkset cannot exceed 16. This can be verified with the rtrv-ls command.
The APC of the linkset assigned to the signaling link must be in the SS7 domain. Use the rtrv-dstn command to verify the domain of the APC of the linkset.
The pcrn1 or pcrn2 parameters can only be specified if the ecm=pcr parameter is specified.
If the E1 signaling link is being assigned to an unchannelized E1 port (shown by the entry UNCHAN in the LINKCLASS field in the rtrv-e1 output), you cannot specify the ts parameter. An E1 signaling link containing an unchannelized E1 port can be assigned only to an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card. A maximum of two E1 signaling links containing an unchannelized E1 port can be assigned to an HC-MIM. The link parameter value for these links must be either a or b. A maximum of one E1 signaling link containing an unchannelized E1 port can be assigned to an E5-E1T1 card. The link parameter value for this link must be a. The transmission rate (bps parameter) for an unchannelized E1 signaling link is 1984000 bits per second. The bps parameter is optional, and if not specified with the ent-slk command, the bps parameter value defaults to 1984000 bits per seconds.
If the E1 signaling link is being assigned to a channel bridged E1 port (shown by the entries MASTER or SLAVE in the CHANBRDG field in the rtrv-e1 output), the E1 port value for the signaling link must be the odd numbered ( MASTER ) E1 port.
If the E1 card is not an HC-MIM or an E5-E1T1 card, a maximum of 2 or 8 E1 signaling links can be assigned to the card. The range of link parameter values is dependent on the type of E1 card the signaling link is assigned to. If the E1 card is an E1/T1MIM, the link parameter values are A - A3, or B - B3, allowing a maximum of 8 signaling links on the card.
If the E1 signaling link is being assigned to a channelized E1 port (shown by the entry CHAN in the LINKCLASS field in the rtrv-e1 output) on an HC-MIM, the link parameter values are A - A31 or B - B31. An HC-MIM can contain a maximum of 64 channelized E1 signaling links. If signaling links A16 to A31, or B16 to B31 will be assigned to the card, the FAN feature must be turned on. The status of the FAN feature is shown in the rtrv-feat command output. The shelf containing the HC-MIM being added in this procedure must have fans installed. If the fans are not installed on the shelf containing the HC-MIM, go to Installation Guide and install the fans.
If the E1 signaling link is being assigned to a channelized E1 port (shown by the entry CHAN in the LINKCLASS field in the rtrv-e1 output) on an E5-E1T1 card, the link parameter values are A - A15 or B - B15. An E5-E1T1 card can contain a maximum of 32 channelized E1 signaling links.
To configure the EAGLE to perform circular routing detection test on the signaling links, perform the Configuring Circular Route Detection procedure.
Note:
Circular route detection is not supported in ITU networks.To provision a EAGLE with more than 1200 signaling links, the EAGLE must have certain levels of hardware installed. See the Requirements for EAGLEs Containing more than 1200 Signaling Links section for more information on these hardware requirements.
The EAGLE can contain a mixture of low-speed, E1, T1, ATM high-speed, and IP signalling links. The Determining the Number of High-Speed and Low-Speed Signaling Links section describes how to determine the quantities of the different types of signaling links the EAGLE can have.
Configuring Signaling Links on LIM-E1 Cards
The main consideration for the provisioning of LIM-E1 cards into the EAGLE is to determine the number of LIM-E1 cards existing in the network and the equipment needed for expanding the signaling link capacity of the EAGLE. To utilize the flexibility of the E1 interface feature, you may want to determine the minimum number of LIM-E1 cards needed to process the total number of SS7 links and then consider diversity for reliability reasons.
Use the following points as guidelines when considering diversity for E1:
- If possible, no two LIM-E1 cards containing links from a common link set should be on the same E1/dual port ChannelCard.
- If possible, no two LIM-E1 cards containing links from a common link set should be on adjacent E1/dual port Channel Cards where they are powered from the same fuse position.
- If possible, no two LIM-E1 cards containing links from a common link set should be terminated on the same shelf because of the shelf clock cabling, and is only an issue if using master clocking sync to the network
- If possible, no two links in a link set should arrive at the EAGLE on the same LIM-E1 card.
- If possible, for link sets containing more than two links, you should minimize the number of links in that link set on any given LIM-E1 card.
As an example, consider a network consisting of 30 LIM-E1 cards with a total number of 100 links where the largest link set size is 8. The most efficient way to provision the EAGLE would be to have 4 extension shelves equipped with the E1 Cabling Backplane, 1 E1Card, and 12 Channel Cards per shelf. Utilizing 1 “B” bus on each shelf, 25 signaling links would be terminated on each shelf for a total of 100. This is also the minimum number of LIM-E1 Cards required for this example.
With the same example but using the third and fifth bullets above as a consideration, the EAGLE would be provisioned with 8 extension shelves equipped with the E1 Cabling Backplane. Four of the shelves would be equipped with 1 E1Card and 6 Channel Cards, and the other 4 shelves would be equipped with 1 E1Card and 5 Channel Cards. Since the largest link set size is 8, a total of 8 LIM-E1 Cards is required. Utilizing 1 “B” bus on each shelf, 13 signaling links would be terminated on each shelf with 6 Channel Cards, and 12 signaling links would be terminated on each shelf with 5 Channel Cards.
Example Signaling Link Configuration
This examples used in this procedure are based on Table A-18.
Table A-18 E1 Signaling Link Configuration Table
| SLK LOC | SLK LINK | LSN | SLC | TYPE | BPS | TS | E1PORT | E1LOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1201 |
A |
LSNE12 |
0 |
LIME1 |
64000 |
1 |
2 |
N/A |
|
1202 |
A |
LSNE12 |
1 |
LIMCH |
64000 |
5 |
1 |
1201 |
|
1203 |
A |
LSNE13 |
0 |
LIME1 |
64000 |
8 |
2 |
N/A |
|
1204 |
A |
LSNE13 |
1 |
LIMCH |
64000 |
12 |
1 |
1203 |
|
1211 |
A |
LSNE145 |
0 |
LIME1 |
56000 |
10 |
2 |
N/A |
|
1212 |
A |
LSNE145 |
1 |
LIMCH |
56000 |
14 |
1 |
1211 |
|
1212 |
A |
LSNE145 |
2 |
LIMCH |
56000 |
20 |
1 |
1211 |
|
1301 |
A |
LSN6 |
0 |
LIME1 |
1984000 |
N/A |
4 |
N/A |
|
1303 |
B |
LSN7 |
0 |
LIME1 |
1984000 |
N/A |
7 |
N/A |
Canceling the REPT-STAT-SLK and RTRV-SLK Commands
Because the rept-stat-slk and rtrv-slk commands used in this procedure can output information for a long period of time, the rept-stat-slk and rtrv-slk commands can be canceled and the output to the terminal stopped. There are three ways that the rept-stat-slk and rtrv-slk commands can be canceled.
- Press the
F9function key on the keyboard at the terminal where therept-stat-slkorrtrv-slkcommands were entered. - Enter the
canc-cmdwithout thetrmparameter at the terminal where therept-stat-slkorrtrv-slkcommands were entered. - Enter the
canc-cmd:trm=<xx>, where<xx>is the terminal where therept-stat-slkorrtrv-slkcommands were entered, from another terminal other that the terminal where therept-stat-slkorrtrv-slkcommands was entered. To enter thecanc-cmd:trm=<xx>command, the terminal must allow Security Administration commands to be entered from it and the user must be allowed to enter Security Administration commands. The terminal’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-secu-trmcommand. The user’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-userorrtrv-secu-usercommands.
For more information about the canc-cmd command, go to the Commands User's Guide.
Figure A-14 Adding an E1 Signaling Link
Sheet 1 of 4
Sheet 2 of 4
Sheet 3 of 4
Sheet 4 of 4