4 Database Transport Access (DTA) Configuration
Chapter 5, Database Transport Access (DTA) Configuration, describes the Database Transport Access (DTA) feature and the procedures necessary to configure the EAGLE to support this feature.
4.1 DTA Feature Overview
This feature allows data to be routed through the SS7 network using the SCCP protocol without relying on TCAP as the upper level protocol.
In the case of specialized applications, MSUs containing SCCP and proprietary data must be sent through the network to customer-specific databases. However, these MSUs may need additional processing before being routed to their final destination.
The DTA feature provides a mechanism for the redirection of specific MSUs to a customized database. The EAGLE uses gateway screening to qualify incoming MSUs for redirection.
Once gateway screening is passed, the original MSU is encapsulated into a new MSU and routed to its new destination.
Figure 4-1 shows a typical configuration for the DTA feature.
Figure 4-1 Example of Configuration for the DTA Feature
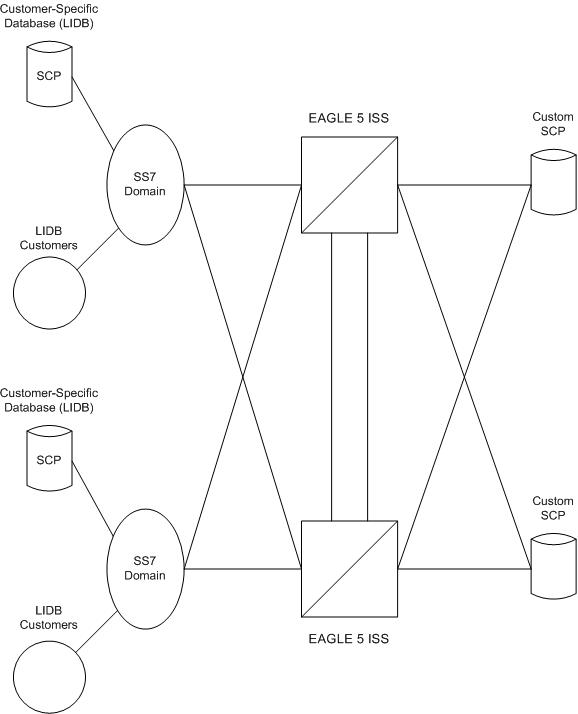
The new routing is specified by a redirection table that specifies the destination point code (DPC) and a new called party address. The routing indicator and the subsystem number are defined within the called party address.
The MSU is then passed to the SCP on the specified linkset where the application data is processed for a customized application.
Once the SCP has processed the user data, the SCP sends the MSU back to the EAGLE. At the EAGLE, the MSU is routed to its final destination in the SS7 network. The SCP determines the routing for the MSU, providing it in the routing label of the MTP portion of the MSU and in the SCCP called party address.
The SCP also provides new calling party address information to support billing applications. The SCP is considered as the originator (OPC) and the calling party.
4.2 Functional Description
The principal function within the EAGLE for this feature is gateway screening. This feature allows the EAGLE to examine all incoming MSUs and determine whether or not they should be allowed into the network. Gateway screening looks at the routing label of the incoming MSU and matches this information with the EAGLE’s gateway screening tables.
To support the DTA feature, a gateway screening stop action set containing the rdct (redirect) gateway screening stop action is assigned to the last screen in the screening process. The redirect gateway screening stop action selects the MSU that is redirected for the DTA feature. The screening table for the DTA feature examines the routing label (OPC, DPC) and the SIO fields of the MSU.
Once the MSU has been qualified for redirection by the gateway screening function, the original MSU is encapsulated into the data portion of SCCP within a new SS7 MSU, including all level two and level three headers. A redirect routing table identifies the DPC to be inserted into the routing label of the redirected MSU. In addition, the called party address in the SCCP portion of the MSU is modified according to the parameters set in the redirect routing table. Figure 4-2 illustrates the encapsulation process.
Figure 4-2 DTA Encapsulation
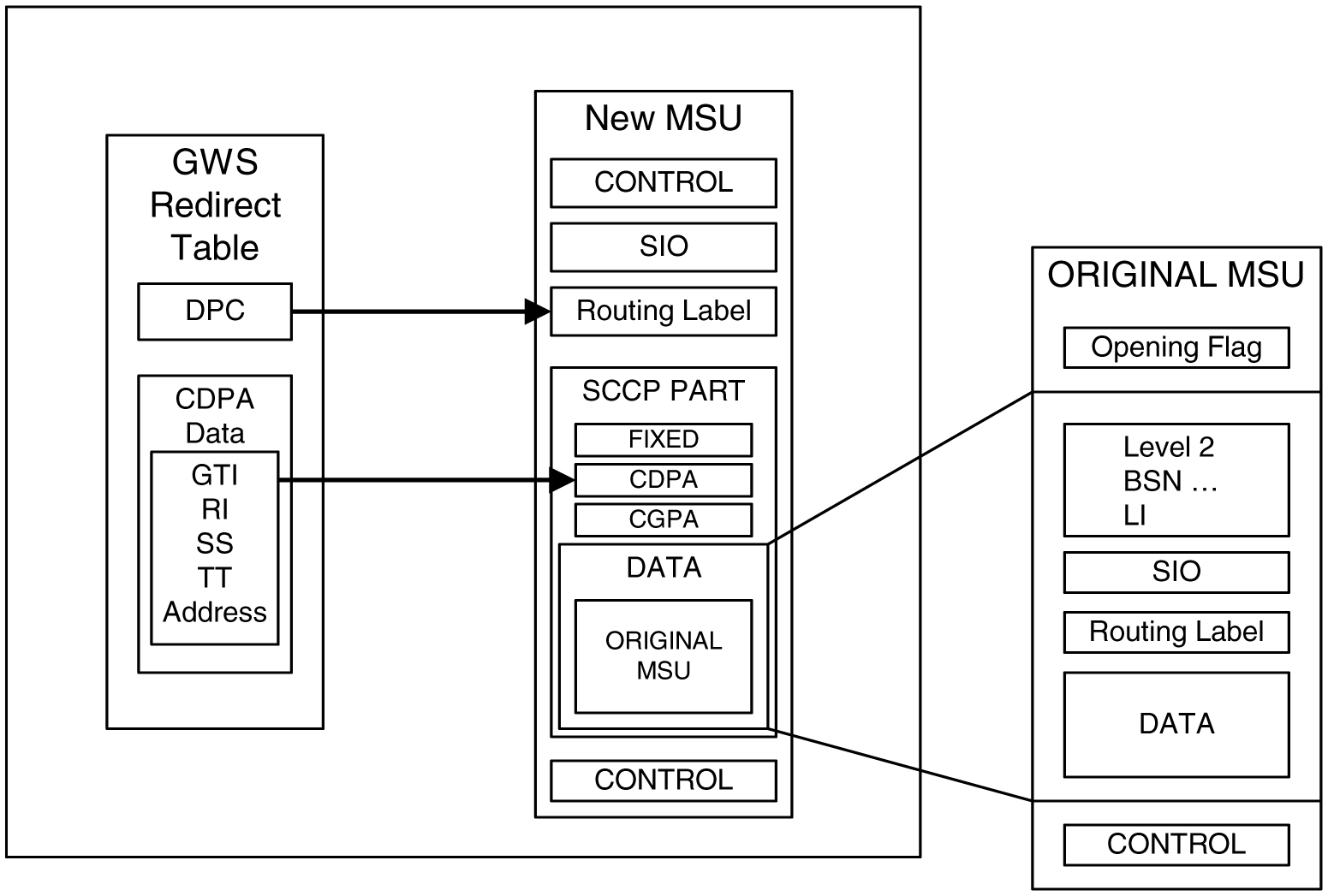
The global title function is used to determine which of the SCPs the MSU is routed to. In the event of subsystem failures, SCCP subsystem management determines which of the SCPs is available. The global title function provides the routing information and routes the MSU to the available SCP.
The global title function require service modules which contains the global title translation tables.
Once the MSU has received its routing information, the MSU can be sent to the appropriate SCP (specified by the EAGLE’s redirection table and global title). The SCP then processes the user data contained within the encapsulated MSU. Once processing has been completed, the MSU is sent back to the EAGLE for final routing.
The DTA feature will redirect MSUs to either ANSI or ITU nodes, depending on the value of the DPC in the redirect routing table, but the redirect routing table can contain only one DPC value. If the incoming message type is not the same as the DPC in the redirect routing table, the message is tunneled to the redirect DPC.
The subsystem number in the called party address determines whether the MSU is processed as an ANSI MSU or an ITU MSU. If the subsystem number is 0, the MSU is an ANSI MSU. If the subsystem number is 250, the MSU is an ITU MSU (an MSU containing either a ITU-I point code, 14-bit ITU-N point code, ITU-I Spare point code, or 14-bit ITU-N Spare point code). If the subsystem number is 251, the MSU is an ITU-N24 MSU (an MSU containing a 24-bit ITU-N point code).
Tunneling uses an MTP2/MTP3/SCCP header based on the network type of the DTA DPC to allow any incoming message to be routed to the DTA DPC. A wrapper is placed around the message (an ANSI wrapper around an ITU message, or an ITU wrapper around an ANSI message), and sends the message to the DTA DPC. The destination removes the wrapper and processes the original information.
Discarding MSUs
MSUs can be discarded for these reasons:
-
Gateway screening is not available or the MSU does not pass gateway screening.
-
The gateway screening redirect function is disabled.
-
The MSU is too large to be encapsulated
-
The DPC for the gateway screening redirect function is prohibited or congested.
-
The EAGLE’s SCCP subsystem is prohibited.
The discarding of MSUs is controlled by gwsd linkset parameter. If the gwsd=on parameter is specified for the linkset, and one or more of the conditions in the previous list are encountered, MSUs on the linkset are discarded. If the gwsd=off parameter is specified for the linkset, and one or more of the conditions in the previous list are encountered, MSUs on the linkset are routed to its original destination. Each of the MSU discard conditions are discussed in the following paragraphs.
If gateway screening is not available or the MSU does not pass gateway screening, the MSU is discarded. An unsolicited alarm message (UAM) is not generated. This condition is not dependent on the linkset gwsd parameter value. The MSGWSDSLIM measurement is pegged.
If the redirect mode is set to ‘off’ in the redirect function, either with the chg-gws-redirect:enabled=off or dlt-gws-redirect commands, and the linkset gwsd=on parameter is specified for the linkset, the MSU is discarded, UIM 1084 is generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is pegged. If the linkset gwsd=off parameter is specified for the linkset, the MSU is routed to its original destination, UIM 1084 is not generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is not pegged.
If an MSU is too large to be encapsulated, the MSU may be discarded, depending on the linkset’s gwsd parameter value. The maximum length of the MSU is dependent on the number of digits contained in the global title address and on the network type of the DPC in the MSU, as shown in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1 Maximum Encapsulation Length per DTA DPC Type
| MSU DPC Type | GTA Length - 1 Digit | GTA Length - 21 Digits |
|---|---|---|
| ANSI | 250 bytes | 240 bytes |
| ITU-I | 253 bytes | 243 bytes |
| ITU-I Spare | 253 bytes | 243 bytes |
| ITU-N | 253 bytes | 243 bytes |
| ITU-N Spare | 253 bytes | 243 bytes |
| ITU-N24 | 250 bytes | 240 bytes |
MSUs that are too long are discarded based on the linkset gwsd parameter value. If the linkset gwsd=on parameter is specified for the linkset, the MSU is discarded, UIM 1084 is generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is pegged. If the linkset gwsd=off parameter is specified for the linkset, the MSU is routed to its original destination, UIM 1085 is generated, but the DTAMSULOST measurement is not pegged.
If the DPC of the gateway screening redirect function is the DPC of an external node, and if the route to this DPC is prohibited, or if this DPC is available, but the congestion level is above the priority of the MSU (for DTA, this priority is always 0), the MSU will not be encapsulated and will be discarded or routed according to the linkset’s gwsd parameter value. If the linkset’s gwsd value is on, the MSU is discarded, UIM 1084 is generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is pegged. If the linkset’s gwsd value is off, the MSU is routed to its original destination, UIM 1084 is not generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is not pegged.
If the DPC for the gateway screening redirect function is the EAGLE’s point code, the MSU is sent to the EAGLE’s SCCP subsystem for GTT processing. If the EAGLE’s SCCP subsystem is prohibited, the MSU will not be encapsulated and will be discarded or routed according to the linkset’s gwsd parameter value. If the linkset’s gwsd value is on, the MSU is discarded, UIM 1084 is generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is pegged. If the linkset’s gwsd value is off, the MSU is routed to its original destination, UIM 1084 is not generated, and the DTAMSULOST measurement is not pegged.
UIMs 1084 and 1085 are discussed in greater detail in Unsolicited Alarm and Information Messages Reference.
Measurements
Two measurements are provided to indicate the number of MSUs discarded: DTAMSULOST and MSGWSDSLIM.
The DTAMSULOST measurement counts the number of MSUs discarded because gateway screening is not available. This can be caused by a number of events, including congestion in the EAGLE.
The MSGWSDSLIM counts the number of MSUs discarded because the received MSU was too large to be encapsulated or because the redirect function was disabled.
DTAMSULOST and MSGWSDSLIM are explained in greater detail in Measurements Reference .
4.3 Summary of the Gateway Screening Redirect Table Commands
The following set of commands is used to administer the gateway screening redirect table.
Table 4-2 Commands for the Gateway Screening Redirect Table
| Command | Explanation and action |
|---|---|
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
|
|
The |
4.4 SCCP Subsystem Management
The EAGLE provides SCCP subsystem management for all transactions sent to an SCP. In the case of the DTA feature, subsystem management is provided for the customized SCP. The customized SCP is deployed in a quad configuration adjacent to the EAGLE. You must configure the links connecting the EAGLE and the SCP in such a way to support SCCP subsystem management. The application supported by the dual SCPs is duplicated in both entities. You can configure the applications in one of the following two modes: dominant or load-shared.
When configured as dominant, one SCP is configured to receive all queries. This assignment is made in EAGLE routing tables. In the event the dominant SCP fails, traffic is diverted by SCCP subsystem management to the mate application.
If load sharing is configured, both SCPs will receive queries. SCCP ensures that all associated transactions are sent to the same SCP. Load sharing allows traffic to be distributed to both SCPs evenly, preventing congestion at one SCP.
If there is a failure in a load sharing configuration, SCCP subsystem management diverts all traffic to the mate SCP. When the failed SCP is restored, the EAGLE resumes load sharing.
Figure 4-3 shows an EAGLE configured with primary and backup SCPs.
Figure 4-3 Configuration of GTT for Routing Management

4.5 EAGLE Requirements
There are no specific hardware requirements to support the DTA feature. However, if the following specific situations exist, the following cards are required.
Table 4-3 Cards Required in Specific Situations
| If | Required Card |
|---|---|
|
Subsystem management is used |
E5-SM4G, E5-SM8G |
4.6 Configuring the EAGLE for the DTA Feature
This procedure is used to add all the items to the EAGLE database that are necessary to implement the DTA feature.
The following features must be turned on:
- Gateway screening
- Global title translation
Verify that these features are turned on by entering the
rtrv-feat command. If any of these
features are turned off, they can be turned on by entering one of the following
commands:
chg-feat:gws=on– if the Gateway Screening feature is off (GWS = offin thertrv-featcommand output)chg-feat:gtt=on– if the Global Title Translation feature is off (GTT = offin thertrv-featcommand output)
Note:
After the Gateway Screening and Global Title Translation features are turned on with thechg-feat command, they cannot be turned
off.
The following items must be provisioned in the database before the EAGLE can be provisioned for the DTA feature:
- LIMs assigned to the
ss7ansiapplication that are necessary to implement the DTA feature – "Adding an SS7 LIM" procedure in Database Administration – System Management User's Guide. The LIMs can be verified by entering thertrv-cardcommand. - Service Module cards assigned
to the
vsccpapplications that are necessary to implement the DTA feature - Adding a Service Module procedure in Database Administration – GTT User's Guide. The Service Module cards can be verified by entering thertrv-cardcommand. - If you wish to redirect
MSUs on
IP cards (cards running the
iplim,iplimi,ss7ipgw,ipgwi, oripsgapplications), then IP cards assigned to theiplim,iplimi,ss7ipgw,ipgwi, oripsgapplications must be in the database - see the Adding an IPLIMx Card, Adding an IPGWx Card, or Adding an IPSG Card procedures in Database Administration - IP7 User's Guide. The IP cards can be verified by entering thertrv-cardcommand. If MSUs on IP cards are being redirected, the IP cards must be assigned to SCTP associations, and routing keys, if applicable, according to the application assigned to the IP card. The IP configuration can be verified by entering these commands, as appropriate:rtrv-appl-rtkey,rtrv-as,rtrv-assoc,rtrv-ip-lnk,rtrv-ls,rtrv-slk. Perform the procedures in Database Administration - IP7 User's Guide to update the IP7 Secure Gateway configuration as necessary. - Linksets whose
APCs are in the
SS7 domain that are
necessary to implement the
DTA feature – see
"Adding an
SS7 Linkset" procedure in
Database Administration –
SS7 User's
Guide. The
APCs of
SS7 linksets can be
either
ANSI,
ITU-I,
ITU-N,
ITU-I Spare,
ITU-N Spare, or
ITU-N24 point codes. The
linksets can be verified by entering the
rtrv-lscommand. The linksets whose traffic is to be redirected by the DTA feature, must have gateway screening allowed (specify thegwsa=onparameter) and must reference a gateway screening screen set. The name of the screen set is shown in theSCRNfield of thertrv-lscommand output. The name of the screen set is specified by thescrnparameter in either theent-lsorchg-lscommands. The screen set referenced by the linkset must be in the database. All gateway screening entities must be in the database before the necessary linkset can be added to the database or changed to reference the necessary screen set. See the "Gateway Screening Configuration" section to make sure that the necessary gateway screening entities are in the database for this feature. To enhance the reliability of the DTA feature, the gateway screening message discard function should be turned on with thegwsd=onparameter. - Signaling links assigned to linksets containing
SS7APCs that are necessary to implement the
DTA feature – "Adding
an
SS7 Signaling Link" procedure in
Database Administration –
SS7 User's
Guide. The
APCs of
SS7 linksets can be
either
ANSI,
ITU-I,
ITU-N,
ITU-I Spare,
ITU-N Spare, or
ITU-N24 point codes. The
signaling links can be verified by entering the
rtrv-slkcommand. - Routes assigned to linksets containing
SS7APCs that are necessary to implement the
DTA feature - "Adding a
Route Containing an
SS7DPC"
procedure in
Database Administration –
SS7 User's
Guide. The
DPCs of
SS7 routes and
APCs of
SS7 linksets can be
either
ANSI,
ITU-I,
ITU-N,
ITU-I Spare,
ITU-N Spare, or
ITU-N24 point codes. The
routes can be verified by entering the
rtrv-rtecommand.
Gateway Screening Configuration
The
DTA feature uses gateway
screening to select the messages that are redirected. A gateway screening stop
action set containing the
rdct (redirect) gateway screening stop
action must be assigned to one of these gateway screening entities where the
gateway screening process stops (the
NSFI of the screen is
STOP).
- Allowed OPC
- Blocked OPC
- Allowed SIO
- Allowed DPC
- Blocked DPC
- Allowed Destination Field
- Allowed ISUP Message Type
Enter the
rtrv-gws-actset command to display the
gateway screening stop action sets in the database. The database contains one
gateway screening stop action set that contain the
rdct gateway screening stop action as
shown in bold in the example output. This gateway screening stop action is
always in the database and cannot be changed or removed.
rlghncxa03w 06-10-07 00:17:31 GMT EAGLE5 36.0.0
ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT ACT
ID NAME 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
-- ------ ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----
1 copy copy
2 rdct rdct
3 cr copy rdct
GWS action set table is (3 of 16) 19% full
For more information on configuring gateway screening stop action sets, see the “Configuring Gateway Screening Stop Action Sets” procedure in Database Administration - GWS User's Guide.
Caution:
Redirecting SLTA/SLTM messages prevents SLTA/SLTM messages from being returned to the EAGLE. The signaling link carrying these messages will fail if these messages are not returned to the EAGLE. To prevent SLTA/SLTM messages from being redirected, gateway screening stop action sets containing the redirect stop action should not be assigned to the following screens:- Allowed OPC screens containing the adjacent point code of a linkset
- Allowed SIO screens containing the service indicator values 1 (SI=1) or 2 (SI=2)
- Allowed DPC screens containing the EAGLE’s point code.
To verify that the screen set being used with the gateway
screening redirect function, enter the
rtrv-scrset:scrn=<screen set name assigned to
the linkset being used> command. If the last screen in the screen
set is
OPC,
BLKOPC,
SIO,
DPC,
BLKDPC,
DESTFLD, or
ISUP, enter the gateway
screening retrieve command corresponding to the last screen in the screen set,
with the screening reference name shown in the
rtrv-scrset
output. For example, if the last screen in the screen set is
ISUP, enter the
rtrv-scr-isup command with the
sr parameter. If the
NSR/ACT value shown
in the retrieve output is a gateway screening stop action set name that
contains the
rdct stop action, shown in the
rtrv-gws-actset output, this screen set
can be used for the gateway screening redirect function. If you wish to use
this screen set, but the
rdct gateway screening stop action is
not assigned to the last screen in the screen set, go to
Database Administration - GWS User's Guide
and perform one of these procedures, as appropriate, to assign the
rdct gateway screening stop action to
the last screen in the screen set.
- “Changing an Allowed ISUP Message Type Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed Affected Destination Field Screen”
- “Changing a Blocked DPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed DPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed SIO Screen”
- “Changing a Blocked OPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed OPC Screen”
If the last screen in the screen set is
CGPA,
TT,
CDPA, or
AFTPC, it is recommended
that either this screen set is changed so that the last screen in the screen
set is
OPC,
BLKOPC,
SIO,
DPC,
BLKDPC,
DESTFLD, or
ISUP with the
rdct gateway screening stop action, or
that another screen set with
OPC,
BLKOPC,
SIO,
DPC,
BLKDPC,
DESTFLD, or
ISUP as the last screen in
the screen set with the
rdct gateway screening stop action be
used. To find another screen set, enter the
rtrv-scrset command, then enter the
rtrv-scrset command again with one of
the screen set names shown in the first
rtrv-scrset output. If the last screen
in the screen set is
OPC,
BLKOPC,
SIO,
DPC,
BLKDPC,
DESTFLD, or
ISUP, enter the gateway
screening retrieve command corresponding to the last screen in the screen set,
with the screening reference name shown in the
rtrv-scrset output. Repeat this
entering the
rtrv-scrset commands until a desirable
screen set is found. If a desirable screen set cannot be found, either add a
new screen set, or change the existing screen set. To add a new screen set, go
to
Database Administration - GWS User's Guide
and perform one of these procedures, as appropriate, and assign the
rdct gateway screening stop action to
the last screen in the screen set.
- “Adding an Allowed ISUP Message Type Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed Affected Destination Field Screen”
- “Adding a Blocked DPC Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed DPC Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed SIO Screen”
- “Adding a Blocked OPC Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed OPC Screen”
If you wish to change the existing screen set, go to
Database Administration - GWS User's Guide
and perform one of these procedures, as appropriate. Make sure the last screen
in the screen set has the
rdct gateway screening stop action
assigned.
- “Changing an Allowed ISUP Message Type Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed Affected Destination Field Screen”
- “Changing a Blocked DPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed DPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed SIO Screen”
- “Changing a Blocked OPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed OPC Screen”
Verify that the necessary gateway screening entities have
been configured with the required gateway screening stop action set, by
entering the appropriate gateway screening retrieve command specifying the
actname parameter with the gateway
screening stop action name shown in the
rtrv-gws-actset command output.
rtrv-scr-opc:actname=rdct– to display the allowed OPC screensrtrv-scr-blkopc:actname=rdct– to display the blocked OPC screensrtrv-scr-sio:actname=rdct– to display the allowed SIO screensrtrv-scr-dpc:actname=rdct– to display the allowed DPC screensrtrv-scr-blkdpc:actname=rdct– to display the blocked DPC screensrtrv-scr-destfld:actname=rdct– to display the allowed destination field screensrtrv-scr-isup:actname=rdct– to display the allowed ISUP message type screens
If a gateway screening entity is configured to redirect,
the entry
STOP appears in the
NSFI field, the
NSR/ACT field contains the name of the
gateway screening stop action set specified in the gateway screening retrieve
command (see the following example).
rlghncxa03w 06-10-07 00:17:31 GMT EAGLE5 36.0.0
SCREEN = ALLOWED OPC
SR NI NC NCM NSFI NSR/ACT
opc1 010 010 010 STOP RDCT
opc1 010 010 012 STOP RDCT
If the necessary gateway screening entities are not in the database, add them to the database using one of these procedures in the Database Administration - GWS User's Guide.
- “Adding an Allowed ISUP Message Type Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed Affected Destination Field Screen”
- “Adding a Blocked DPC Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed DPC Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed SIO Screen”
- “Adding a Blocked OPC Screen”
- “Adding an Allowed OPC Screen”
If the necessary gateway screening entities are in the database, use one these procedures in the Database Administration - GWS User's Guide to assign the redirect gateway screening stop action to them.
- “Changing an Allowed ISUP Message Type Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed Affected Destination Field Screen”
- “Changing a Blocked DPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed DPC Screen”
- “Changing an Allowed SIO Screen”
- “Changing a Blocked OPC Screen”
- “Changing an
Allowed OPC Screen”
Caution:
When Gateway Screening is in the screen test mode, as defined by the linkset parametersgwsa=offandgwsm=on, the gateway screening action in the gateway screening stop action set specified by theactnameparameter of the gateway screening screen set at the end of the gateway screening process will be performed.
A screen set is required to start the screening process.
Enter the
rtrv-scrset command to verify that the
necessary screen set is in the database. If the necessary screen set is not in
the database, use the “Adding a
Screen Set” in the in
Database Administration - GWS User's Guide
and add the necessary screen set to the database. If the necessary screen set
is in the database and the next screening function identifier (NSFI) needs to be changed, use the “Changing a
Screen Set” in the in
Database Administration - GWS User's Guide
to change the
NSFI of the screen set.
Canceling the
RTRV-GTT and
RTRV-GTA Commands
Because the
rtrv-gtt and
rtrv-gtacommands used in this procedure
can output information for a long period of time, the
rtrv-gtt and
rtrv-gtacommands can be canceled and
the output to the terminal stopped. There are three ways that the
rtrv-gtt and
rtrv-gtacommands can be canceled.
- Press the
F9function key on the keyboard at the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered. - Enter the
canc-cmdwithout thetrmparameter at the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered. - Enter the
canc-cmd:trm=<xx>, where<xx>is the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered, from another terminal other that the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered. To enter thecanc-cmd:trm=<xx>command, the terminal must allow Security Administration commands to be entered from it and the user must be allowed to enter Security Administration commands. The terminal’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-secu-trmcommand. The user’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-userorrtrv-secu-usercommands.
For more information about the
canc-cmd command, go to
Commands User's Guide.
Figure 4-4 Configuring the EAGLE for the DTA Feature
Sheet 1 of 11
Sheet 2 of 11
Sheet 3 of 11
Sheet 4 of 11
4.7 Changing the Gateway Screening Redirect Parameters
To change the configuration to support the
DTA feature, one or more
of the gateway screening redirect function’s attributes can be changed using
the
chg-gws-redirect command. This
procedure shows the steps necessary to change these attributes.
The gateway screening redirect function’s data must be in
the database and the gateway screening redirect function must be enabled, shown
by the entry
on in the enabled field of the
rtrv-gws-redirect command output.
Any of the gateway screening redirect function’s attributes can be changed. The new attributes, and any database entities required to support these attributes, must be in the database.
Canceling the
RTRV-GTT and
RTRV-GTA Commands
Because the
rtrv-gtt and
rtrv-gtacommands used in this procedure
can output information for a long period of time, the
rtrv-gtt and
rtrv-gtacommands can be canceled and
the output to the terminal stopped. There are three ways that the
rtrv-gtt and
rtrv-gtacommands can be canceled.
-
Press the
F9function key on the keyboard at the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered. -
Enter the
canc-cmdwithout thetrmparameter at the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered. -
Enter the
canc-cmd:trm=<xx>, where<xx>is the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered, from another terminal other that the terminal where thertrv-gttorrtrv-gtacommands were entered. To enter thecanc-cmd:trm=<xx>command, the terminal must allow Security Administration commands to be entered from it and the user must be allowed to enter Security Administration commands. The terminal’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-secu-trmcommand. The user’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-userorrtrv-secu-usercommands.
For more information about the
canc-cmd command, go to
Commands User's Guide.
The examples in this procedure are used to change the gateway screening redirect function’s attributes to these values. The routing indicator is not being changed.
-
:dpc– 009-003-001 -
:ssn– 45 -
:tt– 175 -
:gta– 3365841342
Figure 4-5 Changing the Gateway Screening Redirect Parameters
Sheet 1 of 4
Sheet 2 of 4
Sheet 3 of 4
Sheet 4 of 4
4.8 Disabling the Gateway Screening Redirect Function
This procedure is used to turn off the gateway screening
redirect function using either the
dlt-gws-redirect or
chg-gws-redirect commands. Turning off
the gateway screening redirect function also turns off the
DTA feature.
Figure 4-6 Disabling the Gateway Screening Redirect Function
Sheet 1 of 7
Sheet 2 of 7
Sheet 3 of 7
Sheet 4 of 7
Sheet 5 of 7
Sheet 6 of 7
Sheet 7 of 7