4 IDP A-Party Routing and IDP Service Key Routing Features
- IDP A-Party Routing uses the A-Party (CgPN) parameter of an IDP or IDPSMS message
- IDP Service Key Routing uses the ServiceKey and EventTypeBCSM parameters in the incoming IDP or IDPSMS message.
Feature Description
- IDP A-Party Routing - Part Number 893033301
- IDP Service Key Routing - Part Number 893033601
IDP A-Party Routing and IDP Service Key Routing are functions of the NPP IDPRCGPN service for IDP Relay that can be used independently and together. When used together, the IDP A-Party Routing function will be attempted first. If sufficient information is not available for routing, then execution of the IDP Service Key Routing function can be attempted as a fall-through option. The IDP Service Key Routing function is attempted as a fall-through option only if that desired behavior is configured. This allows both features to be enabled and turned on, yet only IDP A-Party Routing, only IDP SK Routing, or both can be selected.
Common Screening Lists, SCCP configuration options, and TTR configuration options control the operation of the two features. NPP processing for the features uses the IDP Relay feature IDPRCDPNIDPRCDPN, IDPRCDPN2, IDPRCDPN3, IDPRCDPN4, and IDPRCGPN services and specific Conditioning Actions and Service Actions.
IDP A-Party Routing
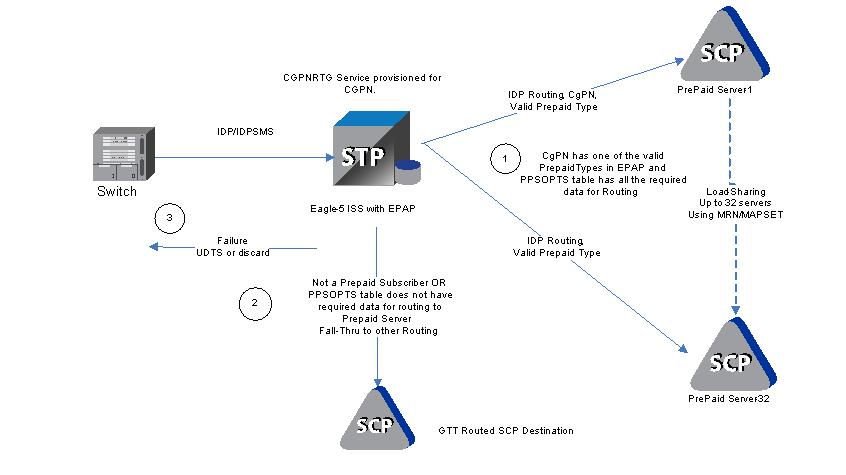
IDP A-Party Routing in the EAGLE is an extension of the Prepaid IDP Query Relay (IDP Relay) feature that uses the A-Party (CgPN) parameter of an IDP or IDPSMS message to provide a routing alternative to the default SCCP GTA routing.
The IDP A-Party Routing function is provided by an NPP Service Action, and by routing algorithms used during post-NPP processing. The routing algorithms use Prepaid Short Message (PPSOPTS) table data and MRNSET or MAPSET table data.
If all of the required data for A-Party routing is provisioned, then IDP A-Party Routing is attempted. In the case of successful routing, an IDP or IDPSMS message can be routed to one of the available Prepaid Servers from a list of provisioned servers in the MRNSET or MAPSET loadshare table. In the case of a routing failure, either a UDTS is sent back to the originator, or the message is discarded. If all of the required data for A-Party routing is not provisioned, then routing will fall through to either IDP Service Key Routing or GTT routing.
- Successful A-Party Routing to a prepaid server
- Fall-through to IDP Service Key Routing or GTT routing when the A-Party is not a prepaid subscriber or A-Party Routing does not have the complete data required for routing to the prepaid server
- Failed A-Party Routing; either a UDTS is sent back to the originator or the message is discarded
Figure 4-1 IDP A-Party Routing Message Flow
IDP Service Key Routing
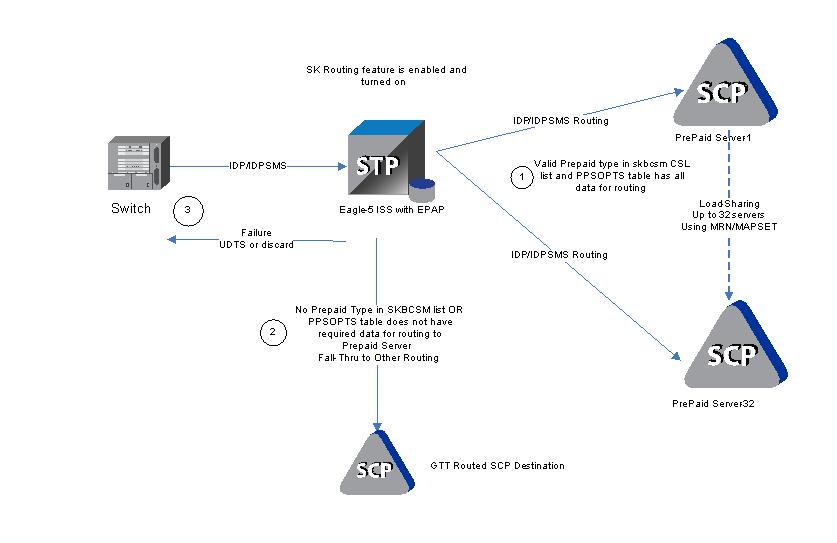
IDP Service Key Routing in the EAGLE is an extension of the Prepaid IDP Query Relay (IDP Relay) feature that provides a routing alternative to the default SCCP GTA routing during post-NPP processing, either independently or as a fall-through option for IDP A-Party Routing.
IDP Service Key Routing uses the Service Key and EventType BCSM parameters in the the incoming IDP or IDPSMS message, the provisioned prepaid type data in the SKBCSM Common Screening List, and data in the Prepaid Short Message (PPSOPTS), MRNSET, and MAPSET tables.
If all of the required data for Service Key routing is provisioned, then IDP Service Key Routing is attempted. In the case of successful routing, the IDP or IDPSMS message can be routed to one of the available Prepaid Servers from a list of provisioned servers in the MRNSET or MAPSET load share table. In the case of routing failure, either a UDTS is sent back to the originator, or the message is discarded. If all of the required data for Service Key routing is not provisioned, then routing will fall through to GTT routing.
- Successful Service Key Routing to a prepaid server
- Fall-through to GTT routing; either the SKBCSM list or the PPSOPTS table does not have the complete data required for routing to the prepaid server
- Failed Service Key routing; either a UDTS is sent back to the originator or the message is discarded
Figure 4-2 IDP Service Key Routing Message Flow
IDP A-Party Routing and Service Key Routing Interaction
The two features link together when both features are turned on and the A-Party Routing CGPNRTG NPP Service Action is provisioned.
- If the CGPNSKRTG option is ON, Service Key Routing will be considered if A-Party Routing is not attempted. A-Party Routing will not be attempted if sufficient data required for A-Party Routing is not provisioned.
- If the CGPNSKRTG option value is OFF, Service Key Routing will be skipped and the message falls through to GTT routing if A-Party Routing is not attempted.
Table 4-1 IDP A-Party Routing and IDP Service Key Routing Feature Interaction
| A-Party Routing Turned On | CGPNRTG Service Action Provisioned | SK Routing Turned On | TTROPTS CGPNSKRTG | Routing Decision | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | N/A | No | N/A | Fall through to GTT | |
| Yes | N/A |
SK Routing (Fail = UDTS, discard) (Insufficient Data=Fall through to GTT) |
|||
| Yes | No | No | N/A | Fall through to GTT | |
| Yes | N/A |
SK Routing (Fail = UDTS, discard) (Insufficient Data = Fall through to GTT) |
|||
| Yes | Yes | Insufficient Data | No | N/A | Fall through to GTT |
| Yes | Off | Fall through to GTT | |||
| On |
Fall through to SK Routing (Fail = UDTS, discard) (Insufficient Data = Fall through to GTT) |
||||
| Sufficient Data | N/A | N/A |
A-Party Routing (Fail = UDTS, discard) |
||
IDP A-Party Routing Service Action Handlers
- RTDB lookup
- Interpretation of results from RTDB lookups
- NPP processing of Service Actions that are used for IDP A-Party Routing
Table 4-2 provides a summary of the Service Actions used for IDP A-Party Routing.
Table 4-2 Summary of IDP A-Party Routing Service Actions
| Service Action | Description | Function | Precedence |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGPNRTG | CgPN A-Party or Service Key Routing | Determines whether CgPN routing and/or SK routing should be attempted during post-NPP processing. | 80 |
| CGPNSVCRQD | Calling Number lookup | Sets a flag to cause the IDPRCGPN service to be invoked for the message. | 60 |
CGPNRTG Service Action Handler
The CGPNRTG Service Action Handler performs an RTDB lookup on the conditioned CgPN to find the Portability Type, and determines whether CgPN routing, or Service Key routing, or both should be attempted during post-NPP processing.
Configuration Options Used
If the IDP A-Party Routing feature and the IDP Service Key Routing feature are on, the TTROPTS CGPNSKRTG option is used to determine if Service Key Routing should be used as a fall-back option for A-Party Routing.
Action Performed
The Portability Type from the RTDB lookup is examined to identify a prepaid subscriber.
If the IDP Service Key Routing feature is on and the IDP Service Key Routing feature is not enabled, Service Key Routing will not be attempted in post-NPP processing.
If both features are on, the CGPNSKRTG configuration option is used to determine whether only A-Party Routing will be attempted, or Service Key Routing is available if A-Party Routing fails, in post-NPP processing.
Terminating Action?
This is not a terminating action.
CGPNSVCRQD Service Action Handler
The CGPNSVCRQD Service Action Handler sets a flag to cause the IDPRCgPN service to be invoked for the message.
Configuration Options Used
None.
Action Performed
A flag is set to cause the IDPRCgPN service to be invoked for the message.
Terminating Action?
This is not a terminating action.
EAGLE Commands
EAGLE Commands describes commands that can be used for the configuration and maintenance of the IDP A-Party Routing and IDP Service Key Routing features.
Refer to Commands User's Guide for complete descriptions of the commands, including parameter names, valid values, and output examples for the commands.
Maintenance Commands
See Maintenance Commands for a list of maintenance commands that can be used with the IDP A-Party Routing and IDP Service Key Routing features.