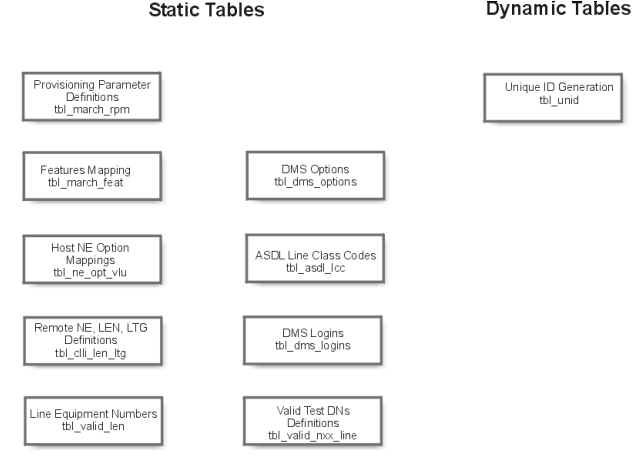
2 ASAP Database Tables
This chapter contains table information for the following databases:
Control database
This section describes the user-created database tables contained in the Control Database Data Dictionary.
User-created database tables
Following is the list of user-created database tables.
tbl_alarm_center
This static table defines the alarm centers where system alarm notifications are sent. You are responsible for maintaining this table. The initial data for this table is provided as part of the core system.
Table 2-1 tbl_alarm_center
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
alarm_center |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The unique code representing the alarm center. |
|
control_prog |
varchar2 |
14 |
0 |
The program to be executed to communicate to the alarm to this alarm center. For example, this could be a shell script written to send a message over the network, to a printer or pager, etc., although any UNIX executable can be provided. The alarm program passes alarm data as command line arguments for interpretation by the alarm program. The core system provides a shell script and a sample C program, control_prog.c, which can be used as a basis to generate user-created alarm programs. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
A description of the alarm center. |
|
opt#_type |
varchar2 |
2 |
1 |
The option name passed to the control program, where # is a number between 1 and 5. This is a UNIX executable option to the control program. Can be null or any single wildcard character ("-_"), for example, -d -w, etc. |
|
opt#_value |
varchar2 |
20 |
1 |
The option value that is passed to the control program corresponding to the previous option type, where # is a number between 1 and 5. |
Table indexes:
alarm_center
The following is an example of alarm centers tbl_alarm_center:
alarm_Center control_prog description opt1_type
opt1_value opt2_type opt2_value opt3_type
opt3_value opt4_type opt4_value opt5_type
opt5_value
------------ -------------- ---------------------------------------- ---------
ADMIN admin.sh Administration Alarm NULL
NULL NULL NULL NULL
NULL NULL NULL NULL
NULL
ADMINPGR adminp.sh Administration Pager NULL
NULL NULL NULL NULL
NULL NULL NULL NULL
NULL Each alarm center can invoke a program. This program is a UNIX executable or shell script. If set to NULL, no alarm program is invoked. In this example, two alarm programs, admin.sh and adminp.sh, are defined.
tbl_alarm_log
This dynamic table contains all of the system generated alarms.
Table 2-2 tbl_alarm_log
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
event_unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
The unique ID of the event generating the alarm. If an alarm is generated by this event, an alarm log entry is created in tbl_alarm_log with this event_unid value. |
|
alarm_code |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The alarm code of the generated alarm. |
|
alarm_unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
The unique ID that identifies the alarm. |
|
start_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The start date and time of the system alarm. |
|
escalation_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
If set, the date and time of the last alarm escalation. |
|
clear_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
If set, the date and time at which the alarm was cleared. |
|
ack_user |
varchar2 |
30 |
1 |
The user ID of the user who acknowledged the alarm. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
alarm_unid event_unid alarm_code
tbl_appl_proc
This static table contains ASAP application configuration information. The ASAP startup procedure uses this table to determine the applications to start, and their start sequence.
You are responsible for maintaining this table. The initial data for this table is provided as part of the core system.
Table 2-3 tbl_appl_proc
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
start_seq |
number |
38 |
0 |
Controls the sequence in which the applications are started. For example, certain client applications may be required to start before server applications, and other client applications after the server applications. |
|
appl_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Specifies the ASAP application type.
|
|
appl_cd |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical ASAP application code, for example, SARM, NEP01, NEP02, etc. The ASAP configuration file contains entries for the real name of each application. The real name appears as a parameter value for the application's logical name. |
|
control_svr |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The name of the logical ASAP application Control server that spawns the application and monitors its behavior. In a distributed ASAP configuration, there must be a Control server defined on each machine. In each ASAP configuration there is only one master Control server. This server is defined as having itself as a Control server. Remote Control servers are defined as having the master Control server as their Control server. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
A description of the ASAP application. |
|
diag_file |
varchar2 |
14 |
0 |
The name of the diagnostics log file where diagnostic messages are written. This file is created in the $LOGDIR directory under a dated directory, for example, $LOGDIR/yymmdd. |
|
auto_start |
char |
1 |
0 |
An auto start flag for the application. Values:
When starting ASAP with the command start_asap_sys, all applications with the autostart value of Y are started automatically. To configure the SRP in tbl_appl_proc, you must set auto_start to ‘N'. |
|
program |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The name of the UNIX executable to run. This UNIX program must reside in the $PROGRAMS directory and must be executable. |
|
diag_level |
varchar2 |
4 |
0 |
The diagnostic level of the ASAP application. The diagnostic level determines whether to log diagnostic information when the ASC_diag() API function call is used. Possible values are:
|
|
isactive |
char |
1 |
0 |
Flag denoting whether the ASAP application is currently active. This stops attempts at starting more than one instance of the same application. Set by CSP_start_server/CSP_start_client and reset by CSP_halt_server/CSP_halt_client functions. Possible values are:
|
|
last_start |
date |
- |
1 |
If set, identifies the last start date and time of the ASAP application. It is set by the administrative Control function, CSP_start_server. |
|
last_halt |
date |
- |
1 |
If set, identifies the last halt or termination date and time of the ASAP application. It is set by the administrative Control function CSP_halt_server/CSP_halt_client. |
|
last_abnormal |
date |
- |
1 |
If set, identifies the last abnormal termination of the ASAP application process. This is determined by the ASAP application Control server. |
|
svr_type |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Possible values include:
|
Table indexes:
Indexes
appl_cd start_seq
tbl_classA_secu
tbl_classA_secu is an internal ASAP table that contains login ID and password information for each ASAP server.
ASAP class A secure data includes the database login/password for each ASAP server. This information is initially configured during ASAP installation.
The ASAP security administrator can maintain secure data by using the ASAP security tool. The ASAP security tool enables users to initialize and maintain security for ASAP Class A components (each core ASAP server). Refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide for more information.
In addition to the ASAP security administator, the following action functions enable users to access the secure data: GET_SECUREDATA, SET_SECUREDATA. For more information on these action functions, see "GET_SECUREDATA" and "SET_SECUREDATA" respectively.
Table 2-4 tbl_classA_secu
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Name of key entry. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Encrypted value. |
|
class |
integer |
- |
0 |
Possible values:
|
|
secu_level |
integer |
- |
0 |
One of the following:
|
|
s_cache |
integer |
- |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
audit_level |
integer |
- |
Reserved |
Reserved for future use. |
|
c_date |
date |
- |
0 |
Creation date. |
|
alg |
integer |
- |
0 |
Type of cypher algorithm, currently supports only BLOWFISH alg (1). |
|
desc1 |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description. |
Table indexes:
name, value
tbl_classB_secu
tbl_classB_secu contains user ID, password, and other information used for custom components, particularly the C SRP API, C++ SRP API, Java-enabled NEP, and NEs.
User-defined secure data can be set up in the following ways: using the ASAP security administration tool or through APIs or action functions.
To import a large amount user-defined secure data into ASAP secure storage, it is recommended that the user compose a flat file containing essential secure data information. The format is "name:value:description" with semicolons used as delimiters. For example, a data file will reference secure data as follows:
TOR_NE:password1:Class B NE login info ENG_NE:password2:Class B NE login info
Note:
The ASAP security administration tool encrypts the value field.
Refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide for more information.
The user can access the secure ASAP data through security APIs or action functions.
The following security APIs from customized SRP and Java-enabled NEP. These security APIs include ASC_get_securedata, ASC_set_securedata. For more information on these APIs, see "ASC_get_securedata" and "ASC_set_securedata" respectively.
The following action functions enable users to access the secure data from customized or non-customized NEPs: GET_SECUREDATA, SET_SECUREDATA. For more information on these action functions,see "GET_SECUREDATA" and "SET_SECUREDATA" respectively.
Table 2-5 tbl_classB_secu
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Name of key entry. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The encrypted value. |
|
class |
integer |
- |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
s_cache |
integer |
- |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
c_date |
date |
- |
0 |
Creation date. |
|
desc1 |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description. |
Table indexes:
name, value
tbl_code_list
This static table is maintained within the Control database. It is used to track core and custom code used in ASAP. For instance, this table can identify code that tracks cartridges deployed within ASAP.
Table 2-6 tbl_code_list
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
code_type |
varchar2 |
4 |
0 |
Type of code. |
|
code |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The code entry. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
4 |
0 |
The code value. |
|
code_desc |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
A description of the code. |
|
parm1 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
General purpose parameter field. |
|
parm2 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
|
parm3 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
|
parm4 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
Table indexes:
code_type, code, value
tbl_component
This static table contains a list of ASAP processes for each ASAP territory and system. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
Table 2-7 tbl_component
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
territory |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The name of the ASAP territory. This allows the components of all ASAP systems in all territories to be specified and maintained in a single database. It is possible to have many territories in an ASAP implementation. Territories are generally mutually exclusive since there is no communication between ASAP systems in different territories. |
|
system |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The name of the ASAP system within an ASAP territory. |
|
component |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The ASAP application component within this territory. This refers to the application components listed in the appl_cd column in tbl_appl_proc. |
Table indexes:
territory, system, component
tbl_db_threshold
You can configure this static table to enable monitoring of data and transaction log sizes for a specific database by the ASAP Control server. You can specify the thresholds and the system events to be generated if such thresholds are exceeded. The Control server periodically performs this check.
Note:
The interval between checks is configured by the Control server application configuration variable, DB_MONITOR_TIME.
For information on DB_MONITOR_TIME, refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide.
The following is a an example of a database monitoring configuration.
Table 2-8 Sample database monitoring configuration
| asap_sys | db_name | data threshold (%) | data event |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PROD |
POOL_TS |
85 |
MAJOR-EVT |
|
PROD |
POOL_TS |
95 |
MAJOR-EVT |
Note:
For the db_name column, you must use the specific name of the tablespace (not the database name) where the databases that you want to monitor are located.
In this database configuration example, the MAJOREVT system event is generated on the production system if the POOL_TS database becomes 85% full. If the transaction log for the database exceeds 100 MB, the CRIT_EVT is generated by the system.
Table 2-9 tbl_db_threshold
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asap_sys |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The ASAP environment. This should be set equal to the value of the appropriate ASAP_SYS environment variable. The Control server only reads records from this table with values of asap_sys equal to the currently defined ASAP_SYS environment variable. |
|
db_name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the database in this asap_sys environment, for example, SDB_U01_asap. |
|
data_threshold |
number |
38 |
0 |
The data threshold above which the system event data_event is issued (in percentage 0-100). |
|
tran_threshold |
number |
38 |
1 |
Obsolete. |
|
data_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The system event to be issued if the data_threshold is exceeded. |
|
tran_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Obsolete. |
Table indexes:
asap_sys, db_name
tbl_event_log
This dynamic table contains a log of all system events generated by ASAP applications.
You can create these entries by using the ASC_event() API function from within the source code.
Table 2-10 tbl_event_log
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
appl_cd |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical name of the ASAP application that generated the system event. |
|
event_type |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The event type that specifies whether a system alarm is to be generated by accessing the static table, tbl_event_type. |
|
event_unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
A unique ID of this event. If an alarm is generated by this event, an alarm log entry is created in tbl_alarm_log with this event_unid value. |
|
source_file |
varchar2 |
14 |
0 |
The source file name where the event was generated. |
|
source_line |
number |
38 |
0 |
The line in the source file where the event was generated. |
|
reason |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
A description of the system event. |
|
event_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of the system event. |
|
ack_user |
varchar2 |
30 |
1 |
ID of the user who acknowledged the event. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
event_unid appl_cd, event_dts
tbl_event_type
This static table defines the system events an ASAP application may generate and if required, the system alarm code associated with the event. You can generate system events using customer-specific code. You can configure these system events to enable or disable system alarms, as required.
System events are logged in the Control database table, tbl_event_log. The ASAP core system specifies the system events generated by the core system. You are responsible for updating the existing system events and adding your own specific events.
This table is referenced by the customEvent element in ServiceModel.xsd. In other words, The customEvent must reference an event that has been defined in tbl_event_type in the control database.
Table 2-11 tbl_event_type
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
event_type |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The ASAP event type generated by the application. Each system event must have a record in this table. The core API includes the following system events:
|
|
The Control server can issue the following events:
|
||||
|
event_type (continued) |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The SARM can issue the following events:
The NEP can issue the following events:
|
|
description |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
A description of the event. If an alarm is generated by this event, the description is passed to the alarm program. |
|
alarm_code |
number |
8 |
1 |
The alarm code associated with the system event. If null, a database log entry is created, but no alarm is generated. |
|
alarm_action |
varchar2 |
2 |
1 |
The alarm action; specifically, the enabling or disabling of the associated system alarm. It allows system events to generate and stop system alarms. Possible values are:
|
|
notify_aims |
char |
0 |
1 |
Reserved for future use. |
Table indexes:
event_type
The following is an example of the tbl_event_type table:
event_type description alarm_code alarm_action ---------- ---------------------------------------- ---------- ------------ ABNORMAL Abnormal Process Termination - Application ABNORMAL E DB2FULL Database Space is Critical CRIT_NAC E DISK_ERR Critical Disk / Media Error - See Diagno CRIT_AC E FS2FULL File System Space is Critical CRIT_NAC E MAINTNCE Information: Host NE has gone into Maint MIN_AC E NTWK_ERR Application Network Connection Error - S MIN_AC E ROUT_ERR Error: SARM Routing Error - Unable to De MIN_AC E RPCSPACE Critical Database Resource Error - See D CRIT_NAC E RPC_ERR General Application RPC Error - See Diag MIN_AC E SRVOBJER Application Server Object Access Error - MIN_AC E SYS_ERR General Application Process Error MAJ_AC E SYS_INFO General Application Information SYS_WARN General Application Process Warning E TRANFULL Tranlog Space is Critical CRIT_NAC E UNIX_ERR UNIX System Call Error - See Diagnostics MIN_AC E WOINPROC Work Order(s) in Progress Longer than Sp MIN_AC E
tbl_fs_threshold
You can configure this static table to enable monitoring of the desired UNIX file system sizes by the ASAP Control server. If the thresholds are exceeded, you may specify both the thresholds and the system events to be generated. The Control server periodically performs this check.
Note:
You can configure the interval between checks by using the Control server application configuration variable, FS_MONITOR_TIME.
A possible configuration for this table is:
Table 2-12 Sample FS_MONITOR_TIME table
| asap_sys | file_system | full threshold (%) | full event |
|---|---|---|---|
|
PROD |
/ |
80 |
MAJOREVT |
|
PROD |
/DATA |
85 |
MAJOREVT |
With this threshold configuration, the MAJOREVT system event is generated on the test system if the “/" file system becomes 80% full. This function is platform-specific and may not work on all platforms.
The implementation of the file system monitor varies across different platforms. Before defining the FS threshold, consult your UNIX Administrator for the file system configuration.
ASAP reports less than what the UNIX file system actually uses since ASAP takes into account the 10% minimum free space requirement when determining the file system space available. Therefore, you must set the FS threshold lower than the actual threshold level. For example, if the file system full alarm FS_FULL is to be generated at an 80% level, you should set the FS threshold at 75%.
Table 2-13 tbl_fs_threshold
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asap_sys |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The ASAP environment. The Control server only reads records from the table with values of asap_sys equal to the currently defined ASAP_SYS environment variable. |
|
file_system |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the file system. |
|
full_threshold |
number |
38 |
0 |
The threshold above which the system event full_event is issued (in percentage 0-100). |
|
full_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The system event issued should the full_threshold be exceeded. |
Table indexes:
asap_sys, file_system
tbl_listeners
This table allows any ASAP server to set up socket listeners for receiving RPC requests. You must configure this table to allow the SARM to start up socket listeners for incoming SRP requests. As well, every Java-enabled NEP must maintain a dedicated connection to its JInterpreter.
Table 2-14 tbl_listeners
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srv_name |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
Name of the server that starts a socket listener. The SARM must start a socket listener to receive incoming Java SRP requests. For a Java-enabled NEP, this is the name of the NEP ($NEP). For the Java SRP, this column contains the SARM name. |
|
host_name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The host name or the IP address on which the server application resides. For the JInterpreter, this value must always be localhost. For the Java SRP, the host_name identifies the location of the SARM. |
|
listener_name |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The name of the listener thread. For a Java-enabled NEP, the listener name describes the listener in the Java process that accepts interpreter requests from the C process. This listener name must always be $NEP_jlistener. For the Java SRP, observe the naming convention of “<Java SRP application name>_jsrplistener". This column is used by the Java SRP to retrieve the listener configurations. |
|
port |
integer |
0 |
A free port on which the server can start the socket listener. |
Table indexes:
srv_name, listener_name
tbl_name_value_pair
This static table provides the facility to maintain miscellaneous name value pair information related to the Control database. You are responsible for maintaining this table.
Table 2-15 tbl_name_value_pair
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Nulls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The name of the parameter. |
|
value |
number |
38 |
0 |
The value of the parameter. |
Table indexes:
name
tbl_process_info
This table contains information on process system resource usage. This information is updated according to the frequency of polling, as specified by the PERF_POLL_PERIOD configuration variable.
Table 2-16 tbl_process_info
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Nulls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
appl_cd |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The name of the ASAP server. |
|
info_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of the ASAP process performance polling. |
|
sys_events |
smallint |
- |
0 |
The total number of system events generated by appl_cd since ASAP start up. |
|
user_cpu |
integer |
- |
0 |
User CPU time. |
|
system_cpu |
integer |
- |
0 |
System CPU time. |
|
proc_identity |
number |
20 |
0 |
The ID of the process. |
Table indexes:
appl_cd, info_dts
Note:
The user_cpu and system_cpu are gathered by each ASAP server by using the times() UNIX system call. The times are in units of 1/CLK_TCK seconds.
tbl_server_info
This static table stores OCA SRP server information required for the OCA applet to connect to different sessions. When the OCA SRP server starts, it sends an HTTP request to the IORManager servlet, which extracts the following information from the HTTP request:
-
OCA SRP server name
-
Name of host where WebLogic Server is deployed
-
Port number on which WebLogic Server is listening
The servlet then inserts the server, host name and port number string in the table.
When the OCA applet starts up, it reads the following information from the table.
Table 2-17 tbl_server_info
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
servername |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The name of the server. |
|
hostname |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The host on which the WebLogic server resides. |
|
info |
varchar2 |
512 |
0 |
The port number on which WebLogic Server is listening. |
For more information on configuring the OCA, refer to the ASAP Installation Guide.
tbl_system_alarm
This static table describes ASAP system alarms that can be generated by ASAP system events. You must populate and maintain this table. Some initial data is provided in the core system.
Table 2-18 tbl_system_alarm
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
alarm_code |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The alarm code. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
A description of the system alarm that is passed to the alarm program. |
|
alarm_level |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The level of the alarm. Possible values are:
|
|
escalation_code |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
escalation_time |
number |
38 |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
auto_clear |
char |
1 |
If this flag is set to Y, it automatically clears the alarm after being generated; otherwise, the alarm continues to go off until it is either manually turned off or a system event is triggered to disable it. For more information, see "tbl_event_type." You can use a Control Server administrative RPC, alarm_stop, to turn off a particular non-auto clearing system alarm. |
|
|
route#_period |
number |
38 |
Where # is a number between 1 - 5. The period in minutes from the alarm to the alarm center. |
|
|
route#_start |
number |
38 |
Where # is a number between 1 - 5. The daily start time in minutes after midnight for the alarms to go to the alarm center. A value between 0 and 1440. |
|
|
route#_end |
number |
38 |
Where # is a number between 1 - 5. The daily end time in minutes after midnight for the alarms to go to the alarm center. A value between 0 and 1440. |
|
|
route#_center |
varchar2 |
8 |
Where # is a number between 1 - 5. The alarm center to route alarms. |
Table indexes:
alarm_code alarm_code description alarm_level escalation_code
escalation_time auto_clear route1_period route1_start route1_end route1_Centre route2_period route2_start route2_end route2_Centre
---------- ---------------------------------------- ----------- --------------- ABNORMAL Abnormal Process Termination CRITICAL
NULL N 5 0 1440 ADMINPGR NULL NULL NULL
CRIT_NAC Critical ASAP System Alarm CRITICAL
NULL N 5 0 1440 ADMINPGR NULL NULL NULL
CRIT_AC Critical ASAP System Alarm CRITICAL
NULL Y 5 0 1440 ADMINPGR NULL NULL NULL
MAJ_NAC Major ASAP System Alarm MAJOR
NULL N 5 0 1440 ADMIN NULL NULL NULL
MAJ_AC Major ASAP System Alarm MAJOR
NULL Y 5 0 1440 ADMIN NULL NULL NULL
MIN_NAC Minor ASAP System Alarm MINOR
NULL N 5 0 1440 ADMIN NULL NULL NULL
MIN_AC Minor ASAP System Alarm MINOR
NULL Y 5 0 1440 ADMIN NULL NULL NULL
tbl_unid
You can use this dynamic table to manage unique IDs needed by other tables. It is present in most user databases and provides a method of generating a serial field.
Table 2-19 tbl_unid
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
unid_type |
char |
32 |
1 |
The unique ID type. You can maintain many different types of unid values with each generating a serial field by means of a suitable function. |
|
unid |
number |
38 |
1 |
The current unid value for the unid type. |
|
pad# |
char |
255 |
1 |
Where # is a number between 1 - 4. Forces each record to reside on a separate database page (allowing improved database concurrency). |
Table indexes:
unid_type
tbl_unload_param
This table is used by the utilities. It provides information about the parameters inserted or deleted by the stored procedures.
Table 2-20 tbl_unload_param
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
seq_no |
Number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence Number of the table |
|
col_no |
Number |
38 |
0 |
Column Number of the parameter in the table |
|
para_name |
Varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Name of the Parameter |
|
default_flag |
Number |
38 |
0 |
Default flag |
|
sp_type |
char |
3 |
0 |
Type of the stored procedure |
|
rows_int |
Number |
38 |
0 |
Number of Rows |
Table indexes:
seq_no, para_name, sp_type
This table will be available in the Control and SARM databases. It contains data relevant to the respective database it is in.
tbl_unload_sp
This table provides information about the stored procedures used to insert and delete data from ASAP tables. This table is used by utilities which modify these ASAP tables.
Table 2-21 tbl_unload_sp
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
seq_no |
Number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence Number of the table |
|
Tbl_name |
Varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
Name of the ASAP table |
|
New_sp |
Varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
Stored Procedure used to insert the data into the table |
|
Del_sp |
Varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
Stored Procedure used to delete data from the table |
|
List_sp |
Varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
Stored Procedure used to list the data in the table |
Table indexes:
seq_no
This table will be available in the Control and SARM databases. It contains data relevant to the respective database it is in.
SARM database
This section details the SARM database tables.
Work order audit information
This section describes the various methods of extracting work order audit information from the following tables:
-
tbl_wrk_ord – contains the current status of work orders.
-
tbl_info_parm – contains information parameters that are returned to the SRP from the NEP State Tables.
-
tbl_srq_log – contains information pertaining to the system's interaction with NEs and resulting changes to work order status and switch history information of the NE responses.
-
tbl_wo_audit – tracks the work order's status as it is processed. The level of information captured in tbl_wo_audit is governed by the ASAP configuration variable WO_AUDIT_LEVEL.
The level of logging for tbl_srq_log and tbl_wo_audit is governed by the ASAP.cfg configuration parameter WO_AUDIT_LEVEL. The following list explains the available audit levels:
-
0 – no auditing occurs. No information is placed in the tbl_wo_audit table.
-
1 – there is one audit entry per work order in the tbl_wo_audit table as it is tracked through the system.
-
2 – provides all functions of level 1 plus the audit level entries for all error states in the tbl_wo_audit table.
-
3 – provides all functions of level 2 plus it tracks the provisioning of a work order through the entire provisioning process in the tbl_wo_audit table. For example, when the ASDL was started, when it was placed in pending queue, where in the pending queue it is, when it was sent to the NEP etc.
-
4 – all events are inserted into the tbl_wo_audit table. This level is intended to debug the work order auditing process.
If the WO_AUDIT_LEVEL configuration parameter is set to 2 or greater, SRQ_ERROR_EVENTS are written to tbl_srq_log. Whenever it is set less than 2, WO_AUDIT_LEVEL events are not written into this table.
Events of other types, such as NE_RESP_EVENTs, NE_CMD_EVENTs and SRQ_INFO_EVENTs, are written into tbl_srq_log even when WO_AUDIT_LEVEL=0. These events track the information from the NEP's perspective, including:
-
response logging (commands sent to and responses received from the NE)
-
asdl_exit types and associated error messages
-
information such as when a command was sent to the NE.
Viewing work order audit information
The OCA client provides a work order audit function that displays events related to the processing of work orders contained in tbl_wo_audit. These events include, but are not limited to, the event text and the data and time of these events.
The asap_utils utility provides additional functions that are particularly related to the processing of work orders.
-
1. SARM - Service Requests in DB – lists the SRQs currently resident in the ASAP database. It details the order ID, status, priority, due date, parent order, batch group
-
2. SARM - In Proc Requests Summary – lists the number of requests currently in progress in the ASAP database (this is determined to be orders in a Loading or In Progress state).
-
3. SARM - In Proc Requests Details – lists details of any work orders currently in progress within the SARM.
-
4. SARM - Work Order Queue Summary – lists the number of orders in each of the SARM order queues. The queues include:
-
Ready Queue – orders currently in progress.
-
Rollback Queue – orders currently being rolled back.
-
Auto Held Queue – orders that are being held by the SARM and not released for some reason
-
-
5. SARM - Work Order Queue Details – provides the order details of each order in the SARM work order queues. Such queues are global to the SARM.
-
6. SARM - Work Order Lock States – lists the orders in progress and their respective lock states. Generally, an in progress order will have a local lock. Only in the high availability configuration will orders be remotely locked.
-
7. SARM - ASDL/NE Queue Summary – provides summary details about each NE in the system including:
-
the NE, technology and software load
-
the NEP managing the NE
-
the current state of the NE
-
Down, Connecting, Available, Maintenance, Disabled
-
the time estimate (sec.) for ASDL processing to that NE
-
the number of ASDLs pending to that NE (in a prioritized queue), the number currently in progress, the number of connections open to that NE, and the number of ASDLs waiting to be retried to that NE.
-
-
8. SARM - ASDL/NE Queue Details – provides details about each ASDL in the Pending, In Progress and Retry ASDL queues to each NE in the system.
A complete description of these and other asap_utils functions is located in the ASAP System Server Configuration Guide.
The level of logging is governed by the ASAP.cfg configuration parameter WO_AUDIT_LEVEL. The following list explains the available audit levels:
-
0 – no auditing occurs. No information is placed in the tbl_wo_audit table.
-
1 – there is one audit entry per work order in the tbl_wo_audit table as it is traced through the system.
-
2 – provides all functions of level 1 plus the audit level entries for all error states in the tbl_wo_audit table.
-
3 – provides all functions of level 2 plus it tracks the provisioning of a work order through the entire provisioning process in the tbl_wo_audit table. For example, when the ASDL was started, when it was placed in pending queue, where in the pending queue it is, when it was sent to the NEP etc.
-
4 – all events are inserted into the tbl_wo_audit table. This level is intended to debug the work order auditing process.
If the WO_AUDIT_LEVEL is set to 2 or greater, SRQ_ERROR_EVENTS are written to tbl_srq_log. Whenever it is set less than 2, WO_AUDIT_LEVEL events are not written into this table.
Events of other types, such as NE_RESP_EVENTs, NE_CMD_EVENTs and SRQ_INFO_EVENTs, are written into tbl_srq_log even when WO_AUDIT_LEVEL=0. These events track the information from the NEP's perspective, including:
-
response logging (commands sent to and responses received from the NE)
-
asdl_exit types and associated error messages
-
information such as when a command was sent to the NE.
SARM database tables
This section details the SARM database tables.
tbl_asap_srp
This static ASAP database table defines all Service Request Processors (SRPs) currently configured in the ASAP system. Any ASAP application process that communicates with the SARM as an SRP using the SRP API must be defined in this table.
Upon start up, the SARM opens one or more network connections to each SRP defined in this table. For each SRP, you can configure the SARM to issue an ASAP system event with each work order notification transmitted back to the SRP. The following are possible system events:
-
NO EVENT – No event is sent to the SRP.
-
NULL – The event is sent to the SRP or no system event is generated.
-
Others – The event is sent to the SRP or the system event is generated of the type specified. This allows the SARM to be configured by the SRP and not globally as it would if this was performed by means of a configuration variable.
For more information on event types, see "tbl_event_type."
The Java SRP must be configured to be a socket type connection.
You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
You can maintain this table in the following ways:
-
Using the Service Activation Configuration Tool (SACT). Refer to the ASAP Server Configuration Guide for instructions.
-
Using stored procedures, including:
-
SSP_new_srp adds new SRP definitions.
-
SSP_del_srp deletes SRP definitions from this table.
-
SSP_list_srp lists the contents of this table.
-
Table 2-22 tbl_asap_srp Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srp_id |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical SRP server name. |
|
srp_desc |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
A description of the SRP. |
|
srp_conn_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Connection protocol from the SARM to the SRP. Valid values are:
|
|
srp_host_name |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Name of the machine that the SRP resides upon. |
|
srp_host_port |
varchar2 |
6 |
1 |
The port number that the SRP is waiting on for socket connections. |
|
wo_estimate_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Work order estimate event. If you configure the SARM using the configuration variable WO_TIME_ESTIMATE_ON to perform this work order estimation calculation, the SARM determines the approximate number and processing time for ASDLs on the work order. The SARM then calculates an approximate time estimate for this work order. |
|
wo_failure_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Work order failure event. |
|
wo_complete_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Work order complete event. |
|
wo_start_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Work order start event. |
|
wo_soft_err_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
This notification is generated whenever an ASDL response on the work order is ‘Fail But Continue'. If the work order fails or completes, then this notification is followed by a Failure or Completion notification. If this event is not required by the SRP, you must specify NO_WO_EVENT_NOTIFICATION (NO EVENT). |
|
wo_blocked_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Not supported. |
|
wo_rollback_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Generated when a work order fails and rollback is configured on one or more CSDLs on the order. It is also generated when a completed work order is cancelled and the SARM rolls back any completed ASDLs on the work order. If this event is not required by the SRP, specify NO_WO_EVENT_NOTIFICATION (NO EVENT). |
|
wo_timeout_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Work order timeout event. |
|
ne_unknown_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
If defined, the system event issued by the SARM when an NE unknown notification is being transmitted back to the SRP from the SARM. This notification is transmitted to the SRP upon a Remote to Host NE, or DN to Host NE routing error. |
|
ne_avail_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
No longer used. |
|
ne_unavail_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
No longer used. |
|
wo_accept_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
If defined, the system event issued by the SARM when a work order acceptance notification is being transmitted back to the SRP from the SARM. |
|
aux_srp_id |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Specifies the auxiliary SRP to where the SARM opens network connections in the event that the primary SRP is unavailable. Set this field to NULL. |
|
aux_srp_conn_type |
char |
1 |
1 |
Connection protocol for SARM to auxiliary SRP communications. Valid values are:
|
|
aux_srp_host_name |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Name of the machine that the auxiliary SRP resides upon. |
|
aux_srp_host_port |
varchar2 |
6 |
1 |
The number of the port that the auxiliary SRP is waiting on for socket connections. |
Table indexes:
srp_id
tbl_asap_stats
tbl_asap_stats provides a way of gathering and analyzing statistics related to the ASAP provisioning process.
If you enable the ASAP statistics gathering by using the NEP configuration variable ASAP_STATS_ON, the dynamic table will contain a log of all the ASAP statistical entries. Statistical entries are made by the Interpreter State Table action, LOG_STAT, and are passed to relevant data fields.
Table 2-23 tbl_asap_stats Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
stats_unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
The unique ID of the statistical entry which is generated at insert time. |
|
stats_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time that the statistical entry was logged. |
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The work order to which this statistical entry is related. This is determined from the work order table at insert time. |
|
wo_stat |
number |
1 |
0 |
The status of the associated work order. This is determined from the work order table at insert time. An update trigger updates the work order status to match that of the work order. This means that when a work order is completed, all statistical entries associated with that work order is updated to ‘Completed'. The possible values for this field are the same as those in wo_stat in the SARM database table tbl_wrk_ord. See "tbl_wrk_ord (SARM)." |
|
user_id |
varchar2 |
64 |
0 |
The user ID associated with this log entry. The user ID is determined from the orig_login field in the SARM database table tbl_wrk_ord at insert time. See "tbl_wrk_ord (SARM)." |
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
The service request related to this statistical entry. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL being provisioned when the statistics log entry was created. |
|
mcli |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
If set, the Remote NE. |
|
hcli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE to which the ASDL currently being processed is routed. |
|
dn |
varchar2 |
24 |
1 |
If set, the directory number currently being provisioned. |
|
len |
varchar2 |
16 |
1 |
If set, the line equipment number currently being provisioned. |
|
ne_cmd |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
If set, the NE command string sent to the NE. |
|
cmd_type |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
If set, the type of NE command string. The possible values which form the basis for simple statistical gathering include:
You can customize this field and also specify other command types to better suit your statistical requirements. |
|
cmd_stat |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
If set, identifies the status of the NE command after transmission to the NE. The possible values which form the basis for statistical gathering include:
This field is customizable. You can specify other command states to better suit your statistical requirements. Refer to the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide for more detailed descriptions of these base_types. |
|
cmd_reason |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
If set, identifies the reason that the NE command failed. This is the error string returned from the NE. You can generate reports to determine the principal error conditions in the provisioning process. |
|
parm1 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Multi-purpose text field in which customer specific information is logged. This field logs additional information in this table. To allow this in a flexible manner, these miscellaneous parameter fields have been provided. |
|
parm2 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
|
parm3 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
|
parm4 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
|
parm5 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
|
parm6 |
varchar2 |
25 |
1 |
Same as parm1. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
stats_unid wo_id wo_stat, stats_dts cmd_stat, stats_dts
tbl_asdl_config
This static table defines the ASDL configuration information required to handle routing and rollback at the ASDL level. It is used by the SARM to determine which NEP to route the command to, whether rollback is required for this ASDL, and if so, the rollback ASDL to use. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_asdl_defn adds new ASDL configuration information to this table.
-
SSP_del_asdl_defn deletes ASDL configuration information from this table.
-
SSP_list_asdl_defn lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-24 tbl_asdl_config Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL command. |
|
reverse_asdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Only required if rollback is configured on the ASDL. If the ASDL requires rollback, the reverse ASDL command must be invoked. |
|
ignore_rollback |
char |
1 |
0 |
Ignore rollback flag. Possible values are:
Rollback can be initiated for this ASDL in two cases.
|
|
route_flag |
char |
1 |
0 |
Routing of the ASDL. Possible value is:
This value is defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. Deprecated. Column maintained for backward compatibility only. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
A description of the ASDL. |
|
asdl_timeout |
number |
8 |
0 |
The maximum number of seconds for an ASDL timeout. If there is no response in the given timeout value, the ASDL will timeout. For more information, see the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
|
asdl_retry_number |
number |
8 |
0 |
The maximum number of retries if an ASDL requests timeout. If the number of retries exceeds asdl_retry_number, the order is failed and rolled back. For more information, see the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
|
asdl_retry_interval |
number |
8 |
0 |
The time period in seconds between ASDL retries. For more information, see the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
Table indexes:
asdl_cmd
tbl_asdl_log
This dynamic table is used by the SARM to log the ASDLs as they are sent to the NEP to facilitate rollback.
Table 2-25 tbl_asdl_log Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
The service request ID uniquely identifying where the ASDL belongs. |
|
asdl_stat |
number |
1 |
0 |
Status of the ASDL. If defined, this field is updated while processing the ASDL and its rollback ASDL. Possible values include:
These values are defined in sarm_defs.h. |
|
asdl_unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
A unique ID identifying the ASDL log entry. This is a unique identifier and is assigned sequentially starting at the value1. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The sequence number uniquely identifying the CSDL on the SRQ that generated this ASDL. |
|
asdl_option |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Reserved. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL command. |
|
rollback_asdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
If rollback is required on this ASDL, use this command to roll back the original ASDL. It is set by the SARM once the rollback is completed as a history record. This field is NULL unless rollback of this ASDL is performed. |
|
comp_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The completion date and time of the ASDL processing. |
|
rollback_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time of the ASDL rollback. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE to which the ASDL is routed by the SARM. |
|
queue_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time when the ASDL was placed in the SARM provisioning queue. |
|
start_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time when provisioning starts for this ASDL. The difference between this value and the queue_dts represents the time the ASDL spent in the queue of pending ASDLs before being transmitted to the NEP for provisioning. |
|
retry_count |
number |
38 |
1 |
A count of the number of times the ASDL was retried at the NE. |
Table indexes:
srq_id, asdl_stat, asdl_unid
tbl_asdl_parm
A static table used by the SARM to define the parameter labels and values associated with a given ASDL. It also provides the mapping between the CSDL parameter labels received from the SRP (csdl_lbl) and the ASDL parameter labels (asdl_lbl) transmitted to the NEP for interpretation by the Interpreter State Tables.
For each CSDL label (csdl_lbl), the SARM checks the current CSDL parameter name value pairs for a matching label. If no matching label is found, it checks for a label in the work order global parameter name value pairs. If no matching label is found in either of these parameter name value pairs and the parameter type (param_typ) which is mandatory, the default value (default_vlu), is used.
If no default value is set, the SARM registers an ASDL parameter mapping failure. If the parameter is Indexed, the csdl_lbl must contain a “++" or the SARM will not start. There is considerable translation mapping logic related to both the tbl_csdl_asdl and this table.
Note:
By convention, the ++ notation appears at the end of the label within square brackets. This convention makes it easy to identify the index.
An example of this translation is contained in the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide. Refer to the section on dynamic routing scenarios.
You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_asdl_parm adds ASDL parameters to tbl_asdl_parm.
-
SSP_del_asdl_parm adds ASDL parameters to tbl_asdl_parm.
-
SSP_list_asdl_parm lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-26 tbl_asdl_parm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL command. |
|
parm_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The sequence number of the ASDL parameter within the parameter list. |
|
asdl_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL label used in transmitting the ASDL parameter name value pairs to the NEP for interpretation by the NE State Tables or Java methods. |
|
csdl_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL or global work order parameter label, which is transmitted to the SARM by the SRP or returned by the NEP State Tables or Java methods as a return CSDL global parameter. For an indexed or compound parameter, the CSDL command defined in this table is not exactly the same as the label transmitted by the SRP. This table stores the CSDL's base name. |
|
default_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
In the case when the CSDL parameter is not passed to the SARM, the SARM substitutes the default value for the csdl_lbl. This default parameter value is referenced only for Scalar parameters. |
|
param_typ |
char |
1 |
0 |
There are three ASDL parameter formats:
ASDL parameters can be either required or optional. Consequently, the possible parameter type values include:
For more information about XML and XPATH parameters, see ASAP Cartridge Development Guide. |
|
dep_asdl_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
An ASDL parameter that identifies the XML document that the XPATH is evaluated against. Applies only to parameter types P and Q. |
Table indexes:
asdl_cmd, parm_seq_no
For details and examples of various parameter types, refer to the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide.
tbl_asdl_response
In this ASDL Loopback testing table, the Interpreter must be placed in loopback mode by means of the Interpreter configuration parameter LOOPBACK_ON.
In loopback mode, when an ASDL completes successfully from the State Table, the Interpreter refers to this table to determine the action to take before completing the Interpreter ASDL invocation.
This table specifies a time interval to wait, (useful to test time-out conditions), for various State Table exit states and ASDL states returned by the Interpreter processing. You only need to perform the test to populate this table when loopback testing is being performed.
Table 2-27 tbl_asdl_response Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL for which loopback processing is provided. |
|
parm_option |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
exit_status |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The exit status returned to the Interpreter from the simulation. The possible values include:
|
|
asdl_status |
varchar2 |
20 |
1 |
The ASDL status returned to the SARM. This column is only used when exit_status is FAIL. The possible values include:
Refer to the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide for more detailed descriptions of these base_types. |
|
asdl_time |
number |
38 |
0 |
The time interval, in seconds, that the Interpreter waits before returning a response to the invoking server. This interval is used to simulate a delay in the processing of the NE responses to mimic usual run-time conditions. |
|
error_text |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
An error text description sent back to the SARM detailing the cause of the error. Error text can be viewed by the front-end user interface. If it is not explicitly specified, generic descriptive text is supplied. |
Table indexes:
asdl, asdl_option
tbl_aux_wo_prop
tbl_aux_wo_prop is a class A dynamic table that serves as an extension to tbl_wrk_ord. tbl_aux_wo_prop was designed to accommodate additional pre-defined work order properties to supplement the ones contained in tbl_wrk_ord. Currently, the only extended property supported in tbl_aux_wo_prop is WO_SECURITY_PROP. This property is maintained for each work order. If WO_SECURITY_PROP = 0, then work order information is eligible to be output to diagnostic files. If WO_SECURITY_PROP = 1, then no work order information is written to diagnostic files.
Refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide for more information on secure work order information.
When the work orders in the tbl_wrk_ord are deleted, the corresponding records in tbl_aux_wo_prop are deleted. This table can be purged using function SSP_db_admin. For guidelines and instructions on database purging, refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide.
Table 2-28 tbl_aux_wo_prop Columns
| Column Name | Type | Length | Nulls | Nulls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ID of the work order property. |
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the work order property. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The value given to the work order property. |
Table indexes:
Non-unique
wo_id
tbl_blackout
This static table contains date and time periods for which a particular Host NE is deemed unavailable by the user for ASAP updates.
The NEP State Table reads this table using the current time. If the current time is within a blackout period, the State Table returns a maintenance mode condition, therefore, disconnects from the Host NE. This process is continually retried until the Host NE is no longer blacked out. You can use this table when there are systems competing for limited ports on the Host NE. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
Note that if the dayname entry is present, then the configuration is considered to be Static. The implementation will check for the start time and end time alone, and assume that both fall on the same day. When configuring a blackout period that spans from one day to the next (e.g. from 22:00 until 01:00 the next day) you must configure two separate lines in tbl_blackout: one for 22:00:00 until 00:00:00 and one from 00:00:00 until 01:00:00.
Table 2-29 tbl_blackout Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE that is blacked out. |
|
dayname |
varchar2 |
10 |
1 |
If this field contains the valid name of a day of the week (for example, Sunday or Monday) then the date portions of start_tm and end_tm are ignored. If this field is empty than both the date and time portions from start_tm and end_tm will be used. If this field contains an invalid value, the blackout will not occur. |
|
start_tm |
date |
- |
0 |
The start date and time for the blackout interval. |
|
end_tm |
date |
- |
0 |
The end date and time for the blackout interval. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
A description of the NE blackout reason. |
Table indexes:
host_clli, start_tm, dayname
tbl_clli_route
This static table contains the mapping between a Remote NE and its Host NE. It is used to determine the Host NE when a Remote NE is provided on the work order. Given the Remote NE and ASDL, this table provides the Host NE to which this ASDL is routed.
If no Remote NE is present on the work order, the table tbl_nep_rte_asdl_nxx is used to route the ASDL by DN. This is only performed if the parameter MCLI is present on the ASDL and is set to the special literal SKIPCLLI. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_clli_map adds new CLLI-to-Host CLLI mapping definitions to tbl_clli_route.
-
SSP_del_clli_map deletes CLLI-to-Host CLLI mapping definitions in tbl_clli_route.
-
SSP_list_clli_map lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-30 tbl_clli_route Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mach_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Remote NE. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Host NE to which the Remote NE is connected. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The ASDL command for which this routing definition is valid. This is useful for services that require ASDL-dependent routing. |
Table indexes:
mach_clli, asdl_cmd
tbl_comm_param
This static table contains communication parameters required to communicate with various external systems. It is possible to specify such communication parameters by device type, for example, serial, TCP/IP Telnet, Generic, etc.
You can also specify communication parameters for:
-
Host NEs and all devices.
-
Host NEs and a particular device.
-
Specific Host NE and all devices.
-
Specific Host NE and a specific device.
If an entry exists for the Host NE and device of a particular Command processor in the NEP, it overrides any of the previous entries. You can also specify parameters in this table for particular Host NEs and devices or combinations.
Each parameter is made available to the State Table or Java method. tbl_comm_param specifies various parameters that are specific to the Host NE or device. It allows State Tables or Java methods to employ processing that is specific to the Host NE or device, where required. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_comm_param adds new communication parameters for a specified device type, host, and device into tbl_comm_param.
-
SSP_del_comm_param deletes parameter information from tbl_comm_param.
-
SSP_list_comm_param lists the contents of this table.
-
SSP_get_async_ne lists NEs which have an ASYNC_CONN communication parameter defined with a value of TRUE or FALSE.
Table 2-31 tbl_comm_param Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
dev_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
The device line type. The possible values include:
|
|
host |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE for which this parameter value applies. If specifying communication parameters for all Host NEs, set this parameter to COMMON_HOST (COMMON_HOST_CFG). |
|
device |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The device for which this parameter value applies. If specifying communication parameters for all devices, set this parameter to COMMON_DEVICE (COMMON_DEVICE_CFG). |
|
param_label |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The parameter label. There are many communication parameters that you must specify in this table in order for the ASAP communication library to function correctly. These communication parameters and their usage are detailed in the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
|
param_value |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The parameter value. |
|
param_desc |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description of the communication parameter. |
Table indexes:
dev_type, host, device, param_label
tbl_cp_mux
Specifies the mapping between command processor logical devices and NEP multiplexing devices.
Table 2-32 tbl_cp_mux Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
cp_device |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
A logical device used in the communications between a command processor thread and a multiplexing device. This device must be first configured in the table tbl_resource_pool. |
|
mux |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The name of the multiplexing device that the specified command processor logical device maps to. The multiplexing device must be first configured in the table tbl_nep_mux. |
Table indexes:
cp_device
tbl_csdl_asdl
This static table used by the SARM to map and sequence CSDL commands to ASDL commands. For each ASDL associated with a CSDL, SARM checks if the ASDL is valid for the CSDL. The final determination of whether the ASDL is valid depends on the ASDL parameter translation process specified by tbl_asdl_parm. To perform this translation, certain conditions must apply. These conditions are identified in columns cond_flag and eval_exp. An ASDL is valid only if both conditions are satisfied.
Examples of various configurations and instructions on configuring CSDL-to-ASDL translation are described in the ASAP System Administrator's Guide.
You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table using one of the following mechanisms:
-
using XML schemas and deploying these services using the Service Activation Deployment Tool (SADT). Refer to the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide for more information.
-
using stored procedures
-
SSP_new_CSDL_asdl adds a new CSDL-to-ASDL mapping definitions to tbl_csdl_asdl
-
SSP_del_CSDL_asdl deletes CSDL-to-ASDL mapping definitions from tbl_csdl_asdl
-
SSP_list_csdl_asdl lists the contents of this table.
-
Table 2-33 tbl_csdl_asdl Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
CSDL command that translates into one or more ASDL commands. |
|
asdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The sequence number of the ASDL command associated with the CSDL. This enables one CSDL to generate more than one ASDL command. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
ASDL command to which the CSDL translates. |
|
pnr |
number |
38 |
1 |
Values are:
|
Table indexes:
csdl_cmd, asdl_seq_no
tbl_csdl_asdl_eval
This table contains CSDL to ASDL mappings and the multiple condition expressions defined for the mappings
Table 2-34 tbl_csdl_asdl_eval Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Foreign key to tbl_csdl_asdl.csdl_cmd. |
|
asdl_seq_no |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The sequence number of the ASDL command associated with the CSDL. This enables one CSDL to generate more than one ASDL command. |
|
cond_flag |
char |
1 |
0 |
The conditions to be met for the ASDL to be executed for the CSDL. The values for this field are as follows:
The condition is checked for each ASDL associated with the CSDL. If the condition is satisfied, the ASDL is added to the list of ASDLs for the CSDL. If not, the ASDL is not executed. Validation is performed in the parameter validation stage in referencing the table tbl_asdl_parm. |
|
label |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The parameter label to test in the condition flag. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The parameter value associated with the label which is tested in the condition flag. |
|
eval_exp |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Contains combination of parameter names, operators, and values to which the parameters are compared. |
|
apply_from |
number |
38 |
1 |
The first indexed ASDL that this rule should apply to: Valid range is from 1 to 9999. Must be less than or equal to the value specified in column apply_to. If is not specified, then this rule will be applied to any indexed ASDL up to and including the one specified in column apply_to. |
|
apply_to |
number |
38 |
1 |
The last indexed ASDL that this rule should apply to: Valid range is from 1 to 9999. Must be greater than or equal to the value specified in column apply_from. If is not specified, then this rule will be applied to any indexed ASDL starting from the one specified in column apply_from. |
tbl_csdl_config
This static table contains the static CSDL configuration information that determines if the CSDL is configured for rollback, its provisioning sequence, and whether a failure of the CSDL generates a system event. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_csdl_defn adds new CSDL definitions to tbl_csdl_config.
-
SSP_del_csdl_defn deletes CSDL definitions from tbl_csdl_config.
-
SSP_list_net_elem lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-35 tbl_csdl_config Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL command. |
|
rollback_req |
char |
1 |
0 |
A flag indicating if rollback is required for this CSDL. In certain circumstances, it may be preferable for no rollback to occur. If any of the CSDLs on a work order require rollback, the dynamic work order structure in SARM's memory is flagged and the entire work order is rolled back if any CSDL fails. Possible values are:
In the SRP database, wo_rback must be set to Y or D for the CSDL to rollback. |
|
csdl_level |
smallint |
1 |
0 |
The level of the CSDL in the SRQ. An integer between 0 and 255 that indicates the sequence level for the CSDL command within the work order. The SARM uses this integer to determine the order in which to provision CSDL commands from an SRP. The SARM then provisions CSDL commands that have lower level numbers first. Sequence levels are only relevant for inter-dependent CSDL commands As the SARM receives the CSDLs from the SRP, it reorders them in a sequence that corresponds to their respective CSDL levels to ensure the correct provisioning sequence. This reordered sequence may not be the same as the sequence in which the SRP transmitted the CSDLs to the SARM. The field csdl_id in the table tbl_srq_csdl contains the SRP CSDL sequence of the CSDLs transmitted to the SARM. |
|
fail_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
If set, the system event to be triggered upon CSDL failure. This event can log or print error messages, trigger system alarms, etc. Use this column to immediately notify personnel of CSDL failure. |
|
complete_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
If set, the system event triggered upon CSDL completion. |
|
option_asdl |
number |
38 |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description of the CSDL command. This description field is displayed in front-end user interfaces only. |
Table indexes:
csdl_cmd
tbl_err_threshold
This static table specifies the threshold for the number of consecutive hard errors for a particular Host NE and ASDL. If the threshold is exceeded, the SARM requests the NEP to disable the specified Host NE. Such hard errors can either be generated directly by the State Tables or from user-defined exit types that map to hard errors. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_err_threshold adds a new threshold for a specific NE and ASDL command in tbl_err_threshold.
-
SSP_del_err_threshold deletes a threshold from tbl_err_threshold.
-
SSP_list_err_threshold lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-36 tbl_err_threshold Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL commands to be used to track consecutive hard errors. |
|
threshold |
number |
38 |
0 |
The threshold number of consecutive hard errors that must occur for the SARM to disable the specified Host NE. |
Table indexes:
host_clli, asdl_cmd
tbl_event_dataset
This table contains sets of parameters to be returned for events. Note that multiple trigger criteria (stored in "tbl_event_template") can map to a single set of return parameters. Also, the table can contain multiple rows for given template_name, with each row defining a particular parameter.
Table 2-37 tbl_event_dataset Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
template_name |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The name of the event template dataset. This is a unique user-defined identifier for a distinct return parameter dataset. |
|
parameter_type |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
Identifies the type of the parameter to be added to the event template dataset:
|
|
csdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The CSDL to apply the event template dataset to. The csdl parameter is only required if the parameter_type is CSDL_PARAMETER or INFO_PARAM: |
|
parameter_name |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
Name of the parameter to be added to the event template dataset. |
Table indexes:
template_name, parameter_type, cscl, parameter_name
tbl_event_template
This table maps event template names to event type / CSDL combinations. The name field maps to event template entries in tbl_event_dataset which detail extended event information to be returned in the work order header.
See "tbl_event_dataset" for more information.
Table 2-38 tbl_event_template Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The name of the event template. Points to a set of return parameters in tbl_event_dataset thus allowing for the case where multiple trigger criteria could map to a single set of return parameters. |
|
event_type |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
(Mandatory) The event type to apply the event template name to. Following are the event types:
Note: For each service action or just for the given service action, service action parameters are returned. |
|
csdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The CSDL to apply the event template to. Optional. Note: This field is applicable only when the event type is set to orderFailEvent. |
Table indexes:
event_type, csdl
tbl_ext_method_lib
This table provides the external method library details required by the SRT.
Table 2-39 tbl_ext_method_lib Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Name of the library |
|
type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of the library
|
|
library |
blob |
- |
1 |
The binary form of the library. |
tbl_host_clli
This static table contains the Host NE, technology, and software load of each Host NE in the ASAP system. It also contains records for each Host NE to which the NEPs interface. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table
-
SSP_new_net_host adds new network element definitions to this table.
-
SSP_del_net_host deletes network element definitions from this table.
-
SSP_list_net_host lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-40 tbl_host_clli Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE identifier. |
|
tech_type |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
Technology of the Host NE or SRP. |
|
sftwr_load |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
Software version of the Host NE, for example, BCS33, PAC4, or the token software load of the SRP. The technology and software load must be consistent with the values given in the table tbl_nep_asdl_prog in order to ensure that the State Table Interpreter or JInterpreter are able to translate an ASDL. |
Table indexes:
host_clli
tbl_id_routing
This static table is a routing database table that defines the mapping between an ASDL and the Host NE when using ID_ROUTING as an ASDL routing scheme.
-
SSP_new_id_routing adds a host NE and the ID_ROUTING mapping record to tbl_id_routing.
-
SSP_del_id_routing deletes a host NE and the ID_ROUTING mapping record from tbl_id_routing.
-
SSP_list_id_routing lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-41 tbl_id_routing Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE which the ASDL command is routed to. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The ASDL command that is being routed. |
|
id_routing_from |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The starting point of a range of ID_ROUTING. |
|
id_routing_to |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The end point of a range of ID_ROUTING. |
If a CSDL maps to multiple ASDLs that are routed to different host NEs, you must ensure that tbl_ne_routing contains an entry for each ASDL. Each entry references a different host NE. For example:
Table 2-42 ID Routing example
| fromRange | toRange | asdl_cmd | host_clli |
|---|---|---|---|
|
100 |
200 |
A-ADD_POTS_LINE |
HOUSTON |
|
100 |
200 |
A-OPTION_ON |
DALLAS |
The following example shows how ID_ROUTING operates for IP addresses:
Table 2-43 ID Routing example
| fromRange | toRange | asdl_cmd | host_clli |
|---|---|---|---|
|
10.9.1.0 |
10.9.10.255 |
A-ADD_POTS_LINE |
TORONTO |
|
10.9.11.0 |
10.9.18.255 |
A-ADD_POTS_LINE |
DALLAS |
In this case, if the ASDL references an IP address of 10.9.3.25, the ASDL would be routed to the TORONTO host NE. The IP address 10.9.12.255 would be routed to DALLAS.
Refer to $ASAP_BASE\samples\ASDL_ROUTE for a sample ID routing based on IP addresses.
Table index:
host_clli
Once the SARM starts, tbl_id_routing is loaded into memory from the SARM database.
For exact matching, the value of id_routing_from, and id_routing_to must be configured identically.
tbl_info_parm
This dynamic table contains information parameters that are returned to the SRP from the NEP State Tables. These parameters contain information that is returned to the requesting external system as Compound parameters. The SRP uses a query API function to retrieve the Information parameters associated with a particular work order.
Table 2-44 tbl_info_parm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The work order ID. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The parameter label. |
|
parm_group |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
NE parameter group information returned to the Host system. This parameter group is set in the State Tables before the Information parameters are returned to the SARM. The SRP API routines specify parameters belonging to particular parameter groups in the Information parameter retrieval. |
|
parm_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The value associated with the parameter label. All control characters x0 to x1F, except x9, xA, and xD (tab, cr and nl), are stripped from the event text after it is retrieved from the database and before used in the XML document. This behavior is in compliance with XML 1.0 specification. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The CSDL sequence number in the work order that is being processed when the Information parameter is generated. |
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL command being processed when the Information parameter is generated from the Interpreter State Table. |
|
csdl_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
The ID of the CSDL being processed when the Information parameter is generated. This CSDL ID is the same as in table tbl_srq_csdl and enables the SRP to track which CSDL the information parameter belongs to. |
|
vlu_hint |
char |
1 |
0 |
Indicates whether the parameter value is a real value or an XML document or XPath expression. Can be one of the following:
|
Table indexes:
wo_id, parm_lbl, parm_group
tbl_label_value
This dynamic table stores event subscription information from the old CORBA SRP clients to handle event servers between CORBA SRP client and server. The new OCA SRP does not use this table.
Table 2-45 tbl_label_value Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
key_1 |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
Work Order ID. |
|
key_2 |
number |
- |
1 |
Event type. Possible values are defined oca.idls as follows:
|
|
label |
varchar2 |
600 |
0 |
An external system ID that is passed with the Work Order. It is not used by the SARM, but it is used by the SRP for proper routing to upstream systems. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
128 |
1 |
A sister external system ID that is passed with the Work Order. It is not used by the SARM, but it is used by the SRP for proper routing to upstream systems. |
Table indexes:
key_1, key_2, label
tbl_large_data
This table stores XML data, XPath expressions or other large data for future use by the SRT.
Table 2-46 tbl_large_data Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ref_id |
number |
20 |
0 |
Reference ID returned by the Database for the XML Order Data. |
|
data |
blob |
- |
1 |
Raw XML Data, XPath Expression or other large data. |
tbl_msg_convert
This static table contains the language and format of events logged by the SARM as it processes requests. Log messages are sent back to the Host system, and therefore, it is important they are in the user's native language. This table provides you with a mechanism to insert your own event text in your own language by populating this table with suitable data.
The core system provides the base event text in the language USA English. If you want to use another language, you are responsible for populating this table with the events in that language.
-
SSP_new_intl_msg adds a new international message record to tbl_msg_convert.
-
SSP_del_intl_msg deletes an international message from tbl_msg_convert.
-
SSP_list_intl_msg lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-47 tbl_msg_convert Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
lang_cd |
varchar2 |
3 |
0 |
The language code. This code determines the text message and format the SARM utilizes. The language code that the SARM uses is set by the SARM configuration variable LANGUAGE_OF_MSG. The default is USA. |
|
msg_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
Unique message identifier for messages referenced within the SARM. |
|
msg_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
This field specifies the type of message formatting. Possible values are:
|
|
message |
char |
255 |
0 |
The message text. If the type field is S, this field resembles a printf() format string. If the type field is D, no parameter substitution is performed. |
|
var_description |
char |
40 |
1 |
Description of the substitutable fields within the message. |
|
wo_audit |
char |
1 |
1 |
The destination for this log message. Possible values are:
|
Table indexes:
lang_cd, msg_id
tbl_ne_config
This static table, which is used by the SARM and the NEP, contains configuration information for each Host NE within ASAP. It also identifies the NEP that manages each Host NE.
This table is read by the SARM to determine the NEs managed by each NEP. This allows the SARM to route the ASDLs to the appropriate NEP that is managing the Host NE. It defines attributes that are particular to each Host NE regardless of the number and nature of the connections to that NE.
This table is read by the NEP to determine the NEs to be managed by that NEP and the Session Managers to be spawned to control all interaction with the NEs. It also specifies the primary resource pools of devices used to connect to the NEs.You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_net_elem() adds new network element definitions to this table.
-
SSP_del_net_elem() deletes network element definitions from this table.
-
SSP_list_net_elem() lists the contents of this table.
-
SSP_set_ne_loopback() updates the table when the loopback state is set to ON, OFF, or GLOBAL through asap_utils.
-
SSP_new_net_element() creates an extra throughput column with the default value of 0.
-
SSP_set_ne_throughput() sets the minimum time for a transaction in milliseconds on the NE.
Table 2-48 tbl_ne_config Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE. This is the name of the SessionManager thread within the NEP which manages all interaction with the Host NE and all connections to it. For dynamic routing, this is the name of the template. |
|
nep_svr_cd |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical name of the NEP server that connects to the Host NE. |
|
primary_pool |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
The primary resource pool used by the NEP managing the Host NE. It determines the primary devices used to connect to the Host NE. The primary pool is dedicated to a specific NE. The Host NE Session Manager within the NEP uses entries in this primary pool before attempting to use entries in the NEP's secondary resource pool to connect to this Host NE, as defined in tbl_nep. |
|
max_connections |
number |
2 |
0 |
The maximum number of concurrent connections allowed to the Host NE. This includes connections from both primary and secondary pools. For multiple dedicated Command Processors to a Host NE, configure the spawn threshold to 1 and the kill threshold to 0. This ensures that multiple Command Processors are used. For dynamic routing, this information can be provided on each order. |
|
drop_timeout |
number |
2 |
0 |
The maximum provisioning activity idle time, in minutes, that must elapse before the Session Manager managing the Host NE disconnects the primary connection to the NE. Until this threshold is exceeded, the Session Manager managing the NE maintains a dedicated Command Processor with a dedicated connection to the NE when there are no pending ASDL requests (maximum idle time). This time-out interval only applies to the primary connection to the NE, as all auxiliary connections have reached their kill_threshold by this point. For a busy Host NE, this time interval should be set high as there is a high probability of an incoming ASDL for the Host NE in that period. However, this value should be set low for a less active Host NE as the resource pool device in use by the Command Processor may be required by another Session Manager to communicate with another Host NE. This is most likely the case when the device is from the NEP's resource pool (the secondary pool which is also accessible to all Session Managers). For dynamic routing, drop timeout information can be provided on each order. |
|
throughput |
smallint |
1 |
0 |
NE instance throughput control – the minimum number of milliseconds a transaction takes per NE instance. The value 0 disables NE instance thoughput control. |
|
spawn_threshold |
number |
2 |
0 |
The number of ASDL requests in the SARM's “ASDL Ready Queue" destined to the NE. When this number is exceeded, the SARM requests the NEP Session Manager to open a new auxiliary connection to the NE. As the number of ASDLs in the SARM ASDL Ready Queue continues to exceed this spawn threshold, the SARM continues to request the NEP establishment of auxiliary connections to the NE. For example, the spawn threshold to a particular NE is 10. Once the ASDL Ready Queue size reaches 11, the SARM requests the NEP to establish an auxiliary connection to the NE. If the ASDL Ready Queue size reaches 12, the SARM requests another auxiliary connection be established by the NEP, and so on. This spawn threshold value should always be above the kill threshold if multiple connections are required to a particular NE. For dynamic routing, spawn threshold information can be provided on each order. |
|
kill_threshold |
number |
2 |
0 |
Upon receiving an ASDL completion, the SARM determines whether the current ASDL Ready queue size is less than the kill threshold. If so, it checks whether the ASDL was completed by an auxiliary connection. If so, the SARM transmits a disconnect request to the NEP Session Manager which disconnects the auxiliary connection. If the ASDL completion was performed on the primary connection, the SARM will not issue a disconnect request. For example, if the spawn_threshold is 10 and the kill threshold is 5, when the SARM receives an ASDL completion when its ASDL Ready queue size is 4 or less, it checks whether the ASDL completion was performed by an auxiliary connection. If so, it issues a disconnect request to the NEP Session Manager managing this NE. If the ASDL completion was not performed by an auxiliary connection, as would be the case when the spawn threshold was never exceeded, the SARM will not issue a disconnect request. For multiple dedicated connections, set the relevant number of connections in max_connections, the spawn threshold to 1, the kill threshold to 0, and the appropriate number of devices in the primary and secondary resource pools. For dynamic routing, kill threshold information can be provided on each order. |
|
template_flag |
Char ('Y','N') |
1 |
0 |
Flag to indicate if this network element entry identifies a static NE (N) or a dynamic network element template (Y). The default value is 'N'. |
|
loopback_on |
Char ('Y', 'N', 'G') |
1 |
0 |
Y: The NE is in loopback state regardless of the LOOPBACK_ON ASAP configuration parameter. N: The NE is not in loop back state regardless of the LOOPBACK_ON ASAP configuration parameter. G: The NE loop back state is determined by the LOOPBACK_ON ASAP configuration parameter. The default value is 'G'. |
|
request_timeout |
number |
8 |
0 |
The maximum number of seconds for an NE request timeout. If there is no response in the given timeout value, the associated ASDL will timeout. For more information, see the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
|
request_retry_number |
number |
8 |
0 |
The maximum number of retries, if the NE requests timeout. If the number of retries exceeds request_retry_number, the order is failed and rolled back. For more information, see the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
|
request_retry_interval |
number |
8 |
0 |
The time period in seconds between NE retries. For more information, see the ASAP System Administrator's Guide. |
Table indexes:
nep_svr_cd, host_clli
tbl_ne_event
This table contains NE-related log messages.
Table 2-49 tbl_ne_event Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
event_identity |
number |
20 |
0 |
Unique ID of this log message in this table. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE identifier if an NE or the SRP name if an SRP. |
|
event_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The time when the event was generated. |
|
state |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The current state of the NE. Possible states are:
|
|
evt_text |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Description of the event. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
evt_identity host_clli, event_dts event_dts
tbl_ne_monitor
Maintains the status of all NEs.
Note:
The tbl_ne_monitor table has been deprecated from ASAP 4.6.x onwards due to impact on the performance and so NE state information is no longer populated in it by default. However, this functionality can be turned on when you set the variable WO_TIME_ESTIMATE_ON to 1 in the ASAP.cfg file. On turning this configuration variable on the SARM database table tbl_ne_monitor gets populated with the NE state information and a new event WO_ESTIMATE_EVT is added to the SARM database table tbl_wo_event_queue. Oracle recommends not to use this feature in production.
Table 2-50 tbl_ne_monitor Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE where the ASDL is routed by the SARM. Even though one Host NE is specified on the CSDL, different ASDLs on that CSDL can be routed to different Host NEs. |
|
nep_svr_cd |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
Name of the NEP server. |
|
state |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The current state of the NE. Possible states are:
|
|
asdl_time_est |
number |
38 |
0 |
Estimated time to process an ASDL. |
|
pending_count |
number |
38 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs pending. |
|
in_progress_count |
number |
38 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs in progress. |
|
connect_count |
number |
38 |
0 |
Number of connections to the NE. |
|
retry_count |
number |
38 |
0 |
The number of times the ASDL was retried at the NE. |
|
held_count |
number |
38 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs held. |
|
consec_fail_count |
number |
38 |
0 |
Number of consecutive failures. |
|
connect_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date/time stamp of the last connection. |
|
disconnect_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date/time stamp of the last disconnect. |
|
avail_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date/time stamp of the last time mode available. |
|
maint_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date/time stamp of the last time it was put into maintenance mode. |
|
err_disable_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date/time stamp of the last time an error disabled the NE. |
|
err_enable_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date/time stamp of the last time the NE was enabled after an error. |
|
adm_disable_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The last time an administrator disabled the NE. |
|
adm_enable_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The last time an administrator enabled the NE. |
|
swd_sessions |
number |
38 |
1 |
Number of switch direct sessions. |
|
swd_start_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The last time a session started. |
|
swd_end_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The time when a switch direct session ended. |
|
swd_user_id |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
Switch direct user. |
|
pad1 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Padding to make a table row occupy a page. This reduces concurrence on the database data page by different database processes. |
|
pad2 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad3 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad4 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
Table indexes:
host_clli
tbl_ne_strsub
Enables you to configure substitutions for unknown or unwanted control characters.
Table 2-51 tbl_ne_strsub Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
strsub_type |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
TBD |
|
description |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
TBD |
|
asdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Name of the ASDL associated with the character. If no value is provided, the substitution will be made for all ASDL commands. |
|
csdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Name of the CSDL associated with the character. If no value is provided, the substitution will be made for all CSDL commands. |
|
ne_vendor |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Name of the software vendor for the network element associated with the character. If no value is provided, the substitution will be made for all network element vendors. |
|
tech_type |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Technology type for the network element associated with the character. If no value is provided, the substitution will be made for all technology types. |
|
sftwr_load |
varchar2 |
16 |
1 |
Software load for the network element associated with the character. If no value is provided, the substitution will be made for all software loads. |
|
ne_str_pattern |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
TBD |
|
ne_replace_pattern |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
TBD |
Table indexes:
strsub_type, csdl, asdl, ne_vendor, tech_type, sftwr_load, ne_str_pattern, ne_replace_pattern
tbl_nep
This static table, referenced by the SARM and NEP, maintains the relationship between the NEP and the secondary pool of devices which is used by the NEP to establish auxiliary connections to Host NEs.
The SARM references this table upon start up to determine the NEPs configured within the system. For each NEP, the SARM opens one or more network connections to that NEP. You can configure the number of connections.
Each NEP references this table upon start up to determine the secondary pool of devices available to all Session Managers within that NEP. It spawns a Command Processor thread for each device in this secondary pool of devices. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_nep adds a new pool of devices to this table.
-
SSP_del_nep deletes a pool of devices from this table.
-
SSP_list_nep lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-52 tbl_nep Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
nep_svr_cd |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical name of the NEP managing the secondary pool of devices. It is not the physical environment specific name listed in the interfaces file. |
|
dialup_pool |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
Secondary pool of devices available to all Session Managers within the NEP. If specified, you must define this resource pool in tbl_resource_pool. If null, there are no secondary devices available in the NEP. |
Table indexes:
nep_svr_cd
tbl_nep_asdl_prog
This static table is used by the State Table Interpreter or the JInterpreter within an application server to determine the State Table program or Java class to invoke for:
-
a given technology such as DMS, AXE, S12, etc.
-
software load such as BCS33, PAC4, etc.
-
ASDL
It is referenced by any process using the Interpreter library. It is also referenced by NEPs, SRPs, and ISPs within ASAP.
If the Interpreter executes an ASDL's State Table and is not listed in the table, it assumes that the State Table name is the same as the ASDL name. This is useful when sftwr_load and tech have no meaning, such as invoking State Tables within an SRP.
Any invocations of the CHAIN or CALL Interpreter actions require that the ASDL being chained or called has a mapping specified in this table. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_asdl_map adds a new ASDL-to-State Table mappings to tbl_nep_asdl_prog.
-
SSP_del_asdl_map deletes ASDL-to-State Table mappings from tbl_nep_asdl_prog.
-
SSP_list_asdl_map lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-53 tbl_nep_asdl_prog Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tech |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
The technology or type of the NE with which the Interpreter interacts, for example, DMS, S12, etc. |
|
sftwr_load |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
The Software Load of the software currently running on the NE. Since this field is non-null, you must place a value in the field even if there is no defined software load for this NE type. The table tbl_host_clli also adheres to the same convention for the software load value. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL command passed to the Interpreter that determines the Interpreter State Table program to be loaded and executed, or passed to the JInterpreter that determines the Java program to be executed. ASAP reserves some special ASDL commands to map special requirements, such as LOGIN or CONNECTION_HANDLER, to a program. |
|
program |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the Interpreter State Table program in tbl_nep_program to load and execute, or name of the Java connection class or Java provisioning method for JInterpreter to execute. State Tables within the NEP execute and receive the MML commands and responses. The State Tables within the SRP generally assist with the SRP work order translation process. |
|
interpreter_type |
varchar2 ['S','J'] |
1 |
0 |
A value of “S" indicates a State Table interpreter, whereas a value of “J" indicates a JInterpreter. A null value defaults to “S". |
Table indexes:
tech, sftwr_load, asdl_cmd
tbl_nep_mux
Stores the configuration of the NEP multiplexing devices.
Table 2-54 tbl_nep_mux Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mux |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The name of the multiplexing device. Communication parameters for this device are specified in tbl_comm_param. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The NE that the multiplexing device communicates with. You must first configure the NE in tbl_ne_config. |
|
mux_dev_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
The type of communications protocol or interface used in the interactions between the multiplexing device type and the NE. |
|
cp_dev_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
The type of communications protocol used in the interactions between the multiplexing device type and the command processor threads. |
Table indexes:
mux
tbl_nep_jprogram
This table stores the mapping between a Java class name and its binary representation which is analogous to a state table name and the state table.
Table 2-55 tbl_nep_jprogram Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
program |
varchar |
255 |
0 |
Name of the java class in the form package.class name. |
|
jclass |
blob |
The binary form of the java class. |
Table indexes:
primary key
program
tbl_nep_program
This static table is used by the Interpreter within an application server and contains the State Table Program information required to perform specific processing. For example, in the NEP, interact using MML commands and responses with the appropriate NE.
Records are maintained in NPG flat files for easier editing and then compiled into their respective table records. These State Tables are called by an Interpreter in any ASAP application Server, although more frequently in NEPs and SRPs.
You are responsible for populating and maintaining the State Table program NPG files.
-
SSP_new_nep_program adds State Table actions based on the specified program name and/or line number to tbl_nep_program.
-
SSP_del_nep_program deletes State Table actions based on the specified program name and/or line number from tbl_nep_program.
-
SSP_list_nep_program lists the contents of this table
Table 2-56 tbl_nep_program Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
program |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The name of the State Table Program. With this program the ASDL, Technology, and Software load map in the tbl_nep_asdl_prog static database table. |
|
line_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The line number in the State Table program which acts as a label for that instruction. The line number is similar to the ones used in BASIC programs. |
|
action |
varchar2 |
32 |
0 |
An action string to identify the particular action performed by the Interpreter in the Command Processor. A number of State Table actions are provided by various ASAP component libraries, for example, Interpreter, NEP, SRP, etc. You can add action functions and overwrite existing action functions as required. |
|
act_string |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The action string associated with the State Table action. This field is required depending on the specified State Table action. |
|
act_int |
number |
38 |
1 |
The action integer which, if set, represents the next line number in the State Table program. The next line number is where execution of the State Table should continue or there is a numeric field specific to the particular action function. If the action integer points to an invalid line number or is absent from the State Table program, the Interpreter registers a run time error and fails the operation. This field is required depending on the specified State Table action. |
Table indexes:
program, line_no
tbl_nep_program_source
Stores State Table source code. The compiled version is saved in tbl_nep_program.
Table 2-57 tbl_nep_program_source Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
program |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The name of the State Table program. With this program the ASDL, Technology, and Software load, map in the tbl_nep_asdl_prog static database table. |
|
line_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The line number in the State Table program which acts as a label for that instruction. The line number is similar to the ones used in BASIC programs. |
|
seq |
number |
38 |
0 |
Order of the source code. |
|
source |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Line of the State Table source code. |
Table indexes:
program, line_no, seq
tbl_nep_rte_asdl_nxx
ASAP can receive work orders with no Remote NE information. This static table was created to route the ASDLs to the relevant Host NE by means of a DN and ASDL command. If the Host system is unable to determine the Remote NE, the routing logic involving this table is employed in the SARM.
This table is not read into the internal memory within the SARM because such routing is rarely used in comparison to the Remote to Host NE routing mechanism. A parameter with label MCLI and value, and SKIPCLLI must be present on the ASDL for this routing logic to be employed. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table
SSP_new_dn_map adds new ASDL command routings by directory number to tbl_nep_rte_asdl_nxx.
SSP_del_dn_map deletes ASDL command routings from tbl_nep_rte_asdl_nxx.
SSP_list_dn_map lists the contents of this table
Table 2-58 tbl_nep_rte_asdl_nxx Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL command that provides ASDL specific routing capabilities by telephone number. This is important for such services as Voice Mail which is routed to separate NEs based on the ASDL. |
|
npa |
varchar2 |
3 |
0 |
The NPA is the first three digits in a telephone number. |
|
nxx |
varchar2 |
3 |
0 |
The NXX is the second three digits in a telephone number. |
|
from_line |
varchar2 |
4 |
0 |
The starting point of a range of telephone LINE numbers. It is the remaining four numbers in a telephone number which provide routing. |
|
to_line |
varchar2 |
4 |
0 |
The end point of a range of telephone LINE numbers to provide routing. |
|
cont_typ |
varchar2 |
1 |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
cont_nm |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
Reserved for future use. |
|
queue_nm |
varchar2 |
64 |
0 |
The Host NE to which this ASDL is routed. The SARM determines the NEP managing this Host NE and routes the ASDL appropriately. |
Table indexes:
asdl_cmd, npa, nxx, from_line, to_line, cont_typ
tbl_order_events
This table provides the order translation details for the SRT.
Table 2-59 tbl_order_events Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
translation_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the Translation Object. |
|
query_type |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Type of the Query. |
|
type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of the object.
|
|
parm |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Name of the parameter. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Value for the parameter. |
tbl_order_translation
This table contains the order translation script details for the SRT.
Table 2-60 tbl_order_translation Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
A unique name given to the translation script as an identifier. |
|
script_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Name of the script file that implements translation. |
|
translation_type |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Type of Translation to be executed. Possible values are XSLT and DO_NOT_FORWARD. |
|
type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of the translation object |
|
parm |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Name of the parameter |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Value of the parameter |
|
message_direction |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Translation Direction which indicates the whether this translation is for incoming orders, responses or events. Possible values are UPSTREAM, EVENT and RESPONSE. |
|
script |
BLOB |
- |
1 |
Binary form of the library/script. |
tbl_resource_pool
This static table defines collections of devices which may be used by the NEP to establish connections to NEs. Such groups of devices are called resource pools.
Each NE configuration (tbl_ne_config record) determines a primary resource pool which defines one or more devices the NEP uses to connect to that NE. Such devices are not used to connect to other NEs.
Each NEP has a secondary resource pool (defined in tbl_nep) containing devices used by the NEP to establish connections to any NE managed by that NEP. Such primary and secondary resource pools are defined in this table. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
-
SSP_new_resource adds new device definitions to this table.
-
SSP_del_resource deletes device definitions from this table.
-
SSP_list_resource lists the contents of this table
Table 2-61 tbl_resource_pool Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asap_sys |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
This is the environment in which this database record is to be used. As the ASAP databases are environment independent, only logical representations of physical entities exist within them.
At run time, only those records with this field defined to be the same as the environment variable asap_sys, are loaded by the NEP. |
|
pool |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The name of the pool of devices. It is referenced by:
|
|
device |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
The device name. This is the name of the logical device used to establish a connection to an NE. The device corresponding to this logical device is specified by means of the communications parameter table, tbl_comm_param. |
|
line_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
The communication protocol used by this device. The possible values include:
This is enforced by the associated data rule on the datatype. For the X.25 protocol, you can use both G and M. For the X.29, you can only use G because the X.29 does not support message-based type. Such definitions are defined in the header file nep_core.h. |
|
vs_key |
number |
38 |
- |
Reserved. The shared memory segment identifier for the Virtual Screen buffer. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
asap_sys, pool asap_sys, device
tbl_srq
This dynamic table is used by the SARM and contains Service Requests (SRQs) created by the SARM from details passed by an SRP during work order translation. There is a one-to-one mapping between work orders and SRQs in the SARM. The SRQ provides a unique ID that references to the work order within ASAP.
Table 2-62 tbl_srq Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
SRQ unique ID. |
|
srq_dd |
date |
- |
0 |
Due date and time of this SRQ. This is the same as the sched_dts in the work order table. |
|
grp_cd |
char |
1 |
0 |
The action of the SRQ. Possible values include:
This action field is important to the order in which SRQs are processed within the same work order and between work orders. These values are defined in asap_core.h. |
|
srq_pri |
char |
1 |
0 |
Priority of this SRQ as assigned by the Host order system. It is equal to the work order priority. Possible values include:
These values are defined in asap_core.h. This priority field is the first field in the internal composite ASAP SRQ priority within the ASAP core followed by the SRQ due date and the SRQ action such as Remove, Change, or Add. |
|
srq_stat |
number |
38 |
0 |
SRQ status that is updated while the SRQ is being processed by the SARM. Possible values include:
These definitions are defined in sarm_defs.h. |
|
evt_dt_tm |
date |
- |
0 |
Last date and time that this SRQ record was updated. |
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ID of the work order that this SRQ belongs to. |
|
srq_chg |
char |
1 |
1 |
Indicates whether the SRQ has been altered since being received by ASAP. Possible values include:
|
|
proc_typ |
char |
1 |
1 |
Type of processing required for this SRQ. Possible values include:
Batch requests have lower priority than immediate requests. Values are defined in sarm_defs.h. |
|
cur_csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
1 |
The sequence number of the current CSDL being processed within this SRQ. This serves as a pointer into the CSDL table which enables the SARM to determine which CSDL it had been processing. This is used by the SARM upon restarting an In Progress work order. |
|
cur_csdl_st |
number |
38 |
1 |
The status of the current CSDL being processed within this SRQ. This field and the sequence number are updated by the SARM as the SRQ is being processed. Possible values of this field are detailed in the csdl_st field of the tbl_srq_csdl table. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The Host NE associated with the latest ASDL on the SRQ. This is updated by the SARM to the value of the current ASDL Host NE value. There may be multiple Host NEs associated with a CSDL since each ASDL may be routed to a different Host NE. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
srq_id wo_id
tbl_srq_asdl_parm
This dynamic table contains parameter name value pairs associated with a Service Request (SRQ). It allows the ASDL and rollback parameters to be defined and, where possible, provides a pointer to their location in other database tables.
Table 2-63 tbl_srq_asdl_parm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
The SRQ ID that the parameter name value pairs are associated. |
|
unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
If the ASDL type is ROLLBACK_TYPE, (according to tbl_asdl_log) then this field is set to the value of the ASDL unique ID (asdl_unid) in the ASDL log table (tbl_asdl_log). This allows the ASDL log table to determine the rollback parameters associated with a particular ASDL. These parameter types are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The parameter label, for example, LEN, or DN. |
|
parm_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The parameter value associated with the parameter label. |
|
vlu_hint |
char |
1 |
0 |
Indicates whether the parameter value is a real value or an XML document or XPath expression. Can be one of the following:
|
Table indexes:
srq_id, unid, parm_lbl
tbl_srq_csdl
This dynamic table contains the CSDLs for each Service Request (SRQ) listed in the SRQ table. Each SRQ can have multiple CSDLs.
Table 2-64 tbl_srq_csdl Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
Unique ID of the SRQ that is associated with the CSDL. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number that distinguishes CSDLs within the SRQ. |
|
actn_noun_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
CSDL command. |
|
csdl_st |
number |
38 |
0 |
Status of the CSDL. Possible values include:
CSDL status values are defined in sarm_defs.h. |
|
asdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The sequence number of the ASDL currently being processed by the SARM on the CSDL. It is updated dynamically by the SARM as the ASDLs are processed. The SARM uses this field to determine the current ASDL to be provisioned upon restart. |
|
index_parm_cnt |
number |
38 |
0 |
Current index value in Indexed ASDL parameters. This field is dynamically updated by the SARM as it provisions an ASDL with a set of Indexed parameters. When the SARM restarts an In Progress order, it uses the value in this field to determine the relevant set of Indexed ASDL parameters to transmit with this ASDL. Use the getParam method to retrieve the value of the given input parameter as passed down to the JInterpreter by the SARM. Use the getIntParam method to retrieve the value of the given input parameter as passed down to the JInterpreter by the SARM and casts this value to an integer. Refer to the ASAP Online Reference for more information. |
|
csdl_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
The CSDL ID in the SRP transmitted to the SARM. When the SRP transmits a CSDL to the SARM, it passes this CSDL ID which SARM stores in the field. With this, the SARM generates the csdl_seq_no field value once it receives all CSDLs from the SRP and orders them according to their respective levels. This field is maintained by the SARM so that the SRP can query the SARM for CSDL specific information. It is used by the SRP to correlate the CSDL in the SRP with the CSDL in the SARM. |
|
asdl_route |
char |
1 |
0 |
Specifies the routing of the current ASDL on the CSDL. The CSDL is mapped to one or more ASDLs by the table tbl_csdl_asdl. Once the SARM acknowledges the ASDL, it looks up the appropriate entry in the tbl_asdl_config to determine the routing for this ASDL. Possible values include:
This value is defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. |
|
csdl_type |
char |
1 |
1 |
The type of CSDL. |
|
orig_seq_no |
number |
38 |
1 |
The original sequence number of the CSDL on the SRQ. |
|
estimate |
number |
38 |
1 |
The time estimate to provision the CSDL. |
|
start_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the CSDL started provisioning. |
|
abort_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the CSDL was aborted. |
|
failure_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the CSDL failed provisioning. |
|
comp_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the CSDL completed provisioning. |
|
update_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the CSDL was last updated. |
|
update_uid |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
The user who last updated the CSDL. |
|
prov_sequence |
number |
38 |
1 |
The provisioning sequence of the CSDL on the SRQ. You can specify an alternate provisioning sequence to the one originally received from the originating system. |
Table indexes:
srq_id, csdl_seq_no
tbl_srq_log
This dynamic table contains information logged for each SRQ. The log is a history of events that occurred on each SRQ, including Switch History information of the NE responses. If the Switch History is greater than 195 characters, the entry splits into two entries.
Through an API, the SARM and NEP write to this database table during the provisioning process. The SRP queries this table through an API to retrieve selected records for a particular work order.
You can view audit log information through the OCA Client. For more information, refer to the ASAP OCA User Guide.
Table 2-65 tbl_srq_log Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
ID of the Service Request. |
|
srq_log_identity |
number |
20 |
0 |
Unique ID of the log message in this table. This is an identity field automatically generated by the RDBMS upon insertion. This replaces the earlier field for performance reasons. |
|
evt_dt_tm |
date |
- |
0 |
Date and time of the logged event. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL within the SRQ that the event is associated with. This is the same as the csdl_seq_no field in the CSDL table. |
|
srq_stat |
number |
38 |
0 |
Status of the SRQ at the time the event occurred. For possible values, see srq_stat in tbl_srq, "tbl_srq." |
|
csdl_st |
number |
38 |
0 |
Status of the CSDL when the event occurred. For possible values, see csdl_st in tbl_srq_csdl, "tbl_srq_csdl." |
|
srq_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The SRQ Log Event. The SRP may inquire for the SRQ log by specifying particular SRQ events of interest in the inquiry RPCs. Possible values include:
These values are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. You must set WO_AUDIT_LEVEL in ASAP.cfg to 2 to generate SRQ_ERROR_EVENTS. |
|
evt_text |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Text description of the event. For NE responses, it contains 255 characters at a time (including newline characters) from the NE generated report. This should be considered when the information is being displayed by a front-end user interface. This allows each log record to contain more NE response information than if one NE response record was contained in each SRQ log record. If generated by an application, this text describes the event as displayed to you. All control characters x0 to x1F, except x9, xA, and xD (tab, cr and nl), are stripped from the event text after it is retrieved from the database and before used in the XML document. This behavior is in compliance with XML 1.0 specification. |
|
asdl_unid |
number |
38 |
1 |
The ID of the ASDL that generated the log entry. If there is no current ASDL for the log entry, set this field to null. |
Table indexes:
srq_id, srq_log_identity
tbl_srq_parm
This dynamic table contains global and CSDL name value pairs associated with an SRQ. It allows different types of parameters to be defined and where possible, provides a pointer to their location in other database tables. There is an index on this table which allows efficient query access to the global and CSDL parameters.
Table 2-66 tbl_srq_parm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
The SRQ ID that is associated with the parameter name value pairs. |
|
parm_typ |
char |
1 |
0 |
The type of SRQ parameter. Possible values include:
These parameter types are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. |
|
unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
If the parameter type is CSDL_TYPE, this field equals the CSDL sequence number (csdl_seq_no) in the CSDL tbl_srq_csdl. This field is not used if the parameter type is GLOBAL_TYPE. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The parameter label, for example, LEN or DN. |
|
parm_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The parameter value associated with the parameter label. |
|
parm_subvlu |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Contains the first 32 bytes of the global or CSDL parameter value. |
|
vlu_hint |
char |
1 |
0 |
Indicates whether the parameter value is a real value or an XML document or XPath expression. Can be one of the following:
|
Table indexes:
Indexes
srq_id, parm_typ, unid, parm_lbl parm_subvlu, parm_lbl
tbl_srt_bundle
This table contains SRT service bundles and/or its spawning details for the SRT.
Table 2-67 tbl_srt_bundle Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
service_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Service Identifier. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
1024 |
1 |
Description of the bundle or service action. |
|
spawn_parm |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Name of the spawning parameter on the order that will cause this service bundle or service action to be added to the order if it has the correct value |
|
spawn_value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Value of the spawning parameter that will cause the service bundle or service action to be added to the order. |
|
service_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
The service_type field indicates whether the table entry is a service bundle or a service action.
|
tbl_srt_bundle_csdl
This table contains the service action spawning information for the SRT.
Table 2-68 tbl_srt_bundle_csdl Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
service_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Service Identifier. |
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Name of the CSDL. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
20 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL. |
|
cond_flag |
char |
1 |
0 |
Conditional flag for the CSDL. Possible values are:
|
|
label |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The parameter label. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Value of the parameter. |
|
eval_exp |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Contains combination of parameter names, operators, and values to which the parameters are compared. |
|
inc_ord_resp |
char |
1 |
1 |
Identifies whether order data need to be included in the response or not.
|
|
description |
varchar2 |
1024 |
1 |
Description of the service bundle or service action. |
tbl_srt_config_reload
This table specifies the SRT configuration reload time.
Table 2-69 tbl_srt_config_reload Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
load_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
Date and time at which the SRT configuration was reloaded. |
tbl_srt_correlation
This table provides the correlation details for the SRT work order.
Table 2-70 tbl_srt_correlation Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
correlation_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
SRT Correlation identifier |
|
asap_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
ASAP Work Order identifier |
tbl_srt_csdl_parm
This table provides the service action parameter mapping details for the service bundle.
Table 2-71 tbl_srt_csdl_parm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
service_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Service Identifier. |
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL command. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
20 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL. |
|
parm_seq_no |
number |
20 |
0 |
Sequence number of the parameter. |
|
bundle_label |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The upstream label used in transmitting the parameters for provisioning. |
|
csdl_label |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL label used in transmitting the parameters for provisioning. |
|
default value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Default Value. |
|
parm_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of the parameter. Possible values include:
|
tbl_srt_ctx
This table provides the correlation details for the SRT work order.
Table 2-72 tbl_srt_ctx Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asap_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
ASAP identifier. |
|
name |
varchar2 |
1024 |
0 |
Name of the parameter. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
1024 |
0 |
Value of the parameter. |
|
type |
varchar2 |
1024 |
0 |
Type of the parameter. |
srt_header_mapping
This table enumerates XPath names and values to allow additional event XML message body data to be placed in the JMS header properties. This supports the inclusion of extended event data in JMS headers without additional database queries. If there are no entries in this table, then the default behavior occurs for JMS header creation. See "tbl_event_dataset" and "tbl_event_template."
The table contains of XPath names and values. The SRT iterates through the table entries and runs the configured XPaths. The returned name/value pairs are added to the JMS header properties.
If the XPath in the configuration name attribute returns multiple results, all returned values are added to the header. The values of these parameters are the result list of the value attribute. The name/value pairs are paired in the order they were returned by the XPath functions.
If the parameter name XPath returns more results than the value XPath the remaining values will be left blank.
If the parameter name XPath returns fewer results than the value XPath results, extra value XPath results are ignored.
Note: An XPath within single quotes represents a constant.
Table 2-73 srt_header_mapping Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
xpath_name |
varchar2 |
1024 |
0 |
xpath to generate a name. |
|
xpath_value |
varchar2 |
1024 |
0 |
xpath to generate a value |
Examples:
To return a specific information parameter on all event types, create a record with values similar to the following:
Name – 'IMSI'
Value – /*[name()=mslv-sa:completeEvent]//extendedWoProperties/extendedWoProperty[name='IMSI']/value
To return all extendedWoProperties on a completed event, create a record with values similar to the following:
Name – /*[name()=mslv-sa:completeEvent]//extendedWoProperties//name
Value – /*[name()=mslv-sa:completeEvent]//extendedWoProperties//value
tbl_srt_lookup
This table provides lookup details used by the SRT.
Table 2-74 tbl_srt_lookup Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the lookup. |
|
type |
varchar2 |
128 |
0 |
Type of the lookup. |
|
cache_scope |
varchar2 |
32 |
1 |
Scope of the lookup. Scope can be either: NONE, NODE or SYSTEM. |
|
cache_timeout |
varchar2 |
20 |
1 |
The amount of time in milliseconds to cache a value if the scope is SYSTEM. |
|
cache_max_size |
number |
20 |
1 |
The maximum number of entries to cache if the scope is SYSTEM. Once MaxSize is reached, least recently used values will be dropped. |
tbl_srt_lookup_input
This table provides lookup input details used by the SRT.
Table 2-75 tbl_srt_lookup_input Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
lookup_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the lookup |
|
parm_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the input parameter |
|
parm_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of the parameter. Possible values are:
|
|
parm_value |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Value of the parameter associated with the parameter name. If parm_type is L then parm_value contains an XPath, otherwise parm_value contains an instance string value. |
|
parm_source |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Indicates the source XML document for the order data. Possible values are:
|
tbl_srt_lookup_output
This table provides lookup output details used by the SRT.
Table 2-76 tbl_srt_lookup_output Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
lookup_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the lookup. |
|
parm_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the output parameter. |
|
parm_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of the parameter. Possible values is:
|
|
parm_value |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Value of the parameter. |
tbl_srt_query_spawn
This table provides query spawning details for the SRT.
Table 2-77 tbl_srt_query_spawn Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
parm_name |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Name of the parameter |
|
req_exp |
varchar2 |
1024 |
0 |
Regular expression used by the SRT. |
|
eval_cond |
char |
1 |
0 |
Evaluation condition |
tbl_stubs
This dynamic table is used in the ASAP High Availability configuration to maintain a copy of the critical data relating to any work order in either ASAP site. As the SARM processes a work order locally, the other SARM is notified of any critical updates performed on the order by means of SARM to SARM communication. The other SARM updates its stub table with the critical update information.
Table 2-78 tbl_stubs Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Work order ID |
|
wo_stat |
number |
38 |
0 |
The status of the work order. Refer wo_stat in "tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)" for a list of possible status values. |
|
wo_cmd |
number |
38 |
0 |
The work order command. |
|
srp_id |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The SRP from which this work order originated. |
|
sched_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The due date and time of the work order. |
|
crit_seq_no |
number |
38 |
1 |
The critical sequence number representing the current critical update that was last applied to the work order. |
|
parent_wo |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The parent work order of this order. |
Table indexes:
Wo_id, parent_wo
tbl_test_rpc_parm
This table provides the details about the RPC parameters used by SRT.
Table 2-79 tbl_test_rpc_parm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
rpc |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Work order ID |
|
seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The status of the work order. Refer wo_stat in "tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)" for a list of possible status values. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The work order command. |
|
parm_typ |
char |
1 |
0 |
The SRP from which this work order originated |
|
default_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The due date and time of the work order |
Table indexes:
rpc, seq_no
tbl_stat_text
Stores labels for the OCA client.
-
SSP_new_stat_text adds new static text labels to tbl_stat_text.
-
SSP_del_stat_text deletes static text labels from tbl_stat_text.
-
SSP_list_stat_text lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-80 tbl_stat_text Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
stat_id |
varchar2 |
10 |
0 |
ID for a group of labels. |
|
status |
number |
38 |
1 |
Integer key field for grouping. |
|
code |
varchar2 |
20 |
1 |
String key field for grouping. |
|
stat_text |
varchar2 |
100 |
0 |
Text describing the label. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
stat_id, status stat_id, code
tbl_unload_sp
This table provides information about the stored procedures used to insert/delete/ data to/from the ASAP tables. This table will be used by the utilities to load/unload the data in the ASAP tables.
This table is available in both the Control and SARM databases, containing data appropriate to the respective database.
Table 2-81 tbl_unload_sp Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the table. |
|
tbl_name |
varchar2 |
40 |
0 |
Name of the ASAP table. |
|
new_sp |
varchar2 |
40 |
1 |
Stored procedure used to insert the data into the table. |
|
del_sp |
varchar2 |
40 |
1 |
Stored procedure used to delete the data from the table. |
|
list_sp |
varchar2 |
40 |
1 |
Stored procedure used to list the data in the table. |
Table indexes:
seq_no
tbl_unload_param
This table is used by utilities. It provides information about the parameters inserted/deleted by stored procedures.
This table is available in both the Control and SARM databases, containing data appropriate to the respective database.
Table 2-82 tbl_unload_param Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the table. |
|
col_number |
number |
38 |
0 |
Column number of the parameter in the table. |
|
para_name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Name of the Parameter. |
|
default_flag |
number |
38 |
0 |
Default Flag. |
|
sp_type |
char |
3 |
0 |
Type of the stored procedure. |
|
rows_int |
number |
38 |
0 |
Number of rows. |
Table indexes:
seq_no, para_name, sp_type
temp_wrk_ord
This dynamic table details the supplemental work order information required by the ASAP functionality. The columns are similar to tbl_wrk_ord table. For details, refer to "tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)."
Table 2-83 temp_wrk_ord Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The work order ID that uniquely identifies the work order in the ASAP core. |
|
sched_dts |
Date |
- |
0 |
The scheduled date and time for provisioning to occur on work orders due in the future. For immediate work orders, set it to the current time. |
|
wo_stat |
number |
38 |
0 |
The status of the work order. It is updated by the SARM as the work order is being processed. For possible values, refer to the "tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)" table. |
|
comp_dts |
Date |
- |
1 |
The completion date of all provisioning associated with the work order in ASAP. |
|
srp_id |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical name of the front-end SRP that notifications and results are sent to for a particular work order. |
|
update_dts |
Date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of the last update on the work order within the ASAP core. |
|
org_unit |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The Organization Unit of the person or group to whom notification is sent should particular events occur on the work order. |
|
orig_login |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
The original login ID of the user who initiated the work order in the Host order system. This information is used for display, notification, and diagnostic purposes. |
|
revs_flag |
char |
1 |
0 |
The revisions flag on the work order to indicate if the work order was revised by the OCA client. |
|
exceptions |
char |
1 |
0 |
Exceptions flag indicating to the SRP if there are any exceptions in the completion of the work order. For more details, refer to the "tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)" table. |
|
pend_cancel |
char |
1 |
1 |
This flag indicates whether there is a pending order cancellation for this work order. |
|
rollback_stat |
number |
38 |
0 |
The rollback status of the work order. |
|
command |
number |
38 |
0 |
This field is transmitted by the SRP to the SARM and informs the SARM processing command to apply it to the work order. |
|
crit_seq_no |
number |
38 |
1 |
The sequence number of the last critical update performed on this work order. This is updated each time a critical update to the work order has been performed. |
|
lock_uid |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
The user who last locked the work order for updating. |
|
lock_dts |
Date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the work order was last locked for updating. |
|
start_dts |
Date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the work order started provisioning. |
|
asdl_timeout |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the ASDL time-out interval to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter ASDL_TIMEOUTS. |
|
parent_wo |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
If set, the parent work order on which the work order is dependent. The parent order must be completed for the work order to begin provisioning. |
|
wo_timeout |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the work order time-out interval to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter ORDER_TIMEOUT. |
|
asdl_retry_num |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the number of ASDL retries to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter NUM_TIMES_RETRY. |
|
asdl_retry_int |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the time period in seconds between ASDL retries to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default. |
|
wo_rback |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set to:
|
|
stub_update_req |
char |
1 |
1 |
Indicates whether Stub update is required or not. |
|
asdl_delay_fail |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set, a flag which specifies whether or not to treat hard errors encountered on the work order as delayed failures, therefore allowing the work order to finish processing before failing. |
|
max_delay_fail |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the number of ASDL delayed failures to allow before failing a batch work order. This allows the overriding of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter, BATCH_THRESHOLD. |
|
srq_id |
number |
38 |
1 |
The ID of the latest SRQ associated with the work order. There is a single SRQ related to a given work order. |
|
is_future_dated |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set to:
|
|
batch_group |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The batch group ID of the work order. |
|
extsys_di |
varchar2 |
128 |
1 |
An external system ID that is passed with the work order. It is not used by the SARM, but is used by the SRP for proper routing to upstream systems. |
|
rollback_exceptions |
char |
1 |
0 |
The rollback exceptions flag returned by the SARM on the work order rollback completion notification. Indicates whether there are exceptions (i.e. ASDL failure) during rollback of a work order. |
|
point_of_no_return |
number |
38 |
0 |
Values are:
|
|
failure_reason |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Provides the failure reason for a work order that fails during provisioning. |
Table indexes:
wo_id, srq_id
tbl_uid_pwd
If the SARM configuration variable SECURITY_CHECK is enabled, this static table is referenced to authorize access to the SARM from the SRP as part of the SRP to SARM protocol.
For the security check to be validated, the user ID and password on the work order must be defined in the table with an active status. If a security violation is detected, the SARM rejects the work order with a security violation, ASAP_STAT_SECURITY_VIOLATION (103).
This provides a central security mechanism to ensure that only properly validated work orders are received by the SARM from all SRPs in the system.
-
SSP_new_userid adds a new user account for the SARM to control access from the SRP in tbl__uid_pwd.
-
SSP_del_userid deletes a user account for the SARM to control access from the SRP in tbl__uid_pwd.
-
SSP_list_userid lists the contents of this table.
Table 2-84 tbl_uid_pwd Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
userid |
varchar2 |
64 |
0 |
The user ID for the security check. |
|
pwd |
varchar2 |
30 |
0 |
The associated password. |
|
status |
varchar2 |
40 |
1 |
Your current status. If set to ACTIVE, then you can access. If not, access is denied. |
Table indexes:
userid
tbl_unid
This dynamic table manages unique IDs required by other tables. It is present in most user-created databases and provides a method of generating a serial field.
Table 2-85 tbl_unid Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
unid_type |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
A unique code identifying the UNID type. This allows there to be many different UNID values for different types of UNID. |
|
unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
The UNID value for a particular type. |
|
pad1 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Padding to make a table row occupy a page. This reduces concurrence on the database data page by different database processes. |
|
pad2 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad3 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad4 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
Table indexes:
Unique
unid_type
tbl_user_err
This static table provides a mechanism to define user exit codes and map them to one of the base ASDL exit types. For more information on user exit types, see the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide.
If the State table returns a user-defined exit type, the NEP checks whether there is a base exit type defined for the specified ASDL and exit type. If so, then the base exit type is used. If not, the NEP determines whether there is a user-defined error type associated with the user-defined exit type.
Some initial data is provided as part of the core system. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
Pattern matching is ordered by length (search_pattern), csdl, asdl, ne_vendor, sftwr_load and tech_type. Pattern matching starts from the most specific specification to the least specific. The most specific specification is one that has all columns within the table filled.
-
SSP_new_err_type adds a new mapping of user-defined error types.
-
SSP_del_err_type deletes the mapping of user-defined error types.
-
SSP_list_err_type list the contents of this table
Table 2-86 tbl_user_err Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
csdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The CSDL that is executing. Error types can be defined for user_type and CSDL combinations. |
|
asdl |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The ASDL that is executing. Error types can be defined for user_type and ASDL combinations. |
|
vendor |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The vendor of the network element. |
|
tech_type |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The technology of the network element. |
|
sftwr_load |
varchar2 |
16 |
1 |
Software version of the host network element. |
|
search_pattern |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Regular expression pattern that is used to match on network element responses. |
|
user_type |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
User-defined ASDL exit type. |
|
base_type |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The base ASDL exit type where this user specified ASDL exit type maps to. The base types include:
Refer to the ASAP Cartridge Development Guide for more detailed descriptions of these base_types. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description of the user exit type. |
Table indexes:
Unique
csdl, asdl, ne_vendor, tech_type, sftwr_load, search_pattern, user_type
tbl_user_err_threshold
With this static table you can specify thresholds for a specific user exit from the Interpreter State Table by Host NE and ASDL command.
The SARM maintains three counters for each Host NE, ASDL, and user exit type. If a counter exceeds its user configured threshold, the SARM issues the appropriate event, if defined. In the Control database you can configure any system events generated from this table to map to relevant system alarms as required.
-
SSP_new_user_err_threshold adds a new user-defined error threshold or set of thresholds to tbl_user_err_threshold.
-
SSP_del_user_err_threshold deletes a user-defined error threshold or set of thresholds from tbl_user_err_threshold.
-
SSP_list_user_err_threshold lists the contents of this table
Table 2-87 tbl_user_err_threshold Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE. |
|
asdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL command. |
|
user_type |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The user State Table exit type. |
|
minor_threshold |
number |
4 |
1 |
The number of user exits for this Host NE and ASDL before the minor event is generated. |
|
minor_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
The minor system event to be generated. |
|
major_threshold |
number |
4 |
1 |
The number of user exits for this Host NE and ASDL before the major event is triggered. |
|
major_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
The major system event generated. |
|
critical_threshold |
number |
4 |
1 |
The number of user exits for this Host NE and ASDL before the critical event is triggered. |
|
critical_event |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
The critical system event generated. |
Table indexes:
Unique
host_clli, asdl_cmd, user_type
tbl_usr_wo_prop
This table is used to dynamically configure work order properties. It consists of WO ID and name/value pair for a user-defined work order properties. This table supports only string type user-defined work order properties.
Table 2-88 tbl_usr_wo_prop Columns
| Column Name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ID of the work order. |
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the work order property. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The value given to the work order property. |
|
value_hint |
char |
1 |
0 |
Indicates whether the parameter value is a real value (XML document) or a reference ID (XPATH expression). Can be one of the following:
|
Table indexes:
Unique
wo_id, name
tbl_wo_audit
This dynamic table tracks the work order status. It is populated based on the wo_audit column in "tbl_msg_convert" and the WO_AUDIT_LEVEL parameter in ActivationConfig.xsd and ASAP.cfg.
You can view audit log information through the OCA Client. For more information, refer to the ASAP OCA User Guide.
Table 2-89 tbl_wo_audit Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ID of the work order. |
|
wo_audit_log_identity |
number |
20 |
0 |
Unique ID of the audit message. This is an identity field automatically generated by the RDBMS upon insertion. |
|
wo_stat |
smallint |
1 |
0 |
The status of the work order internally within ASAP. It is updated by the SARM as the work order is being processed. Possible values for this field include:
These values are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h |
|
srq_evt |
varchar2 |
8 |
1 |
The SRQ Log Event. The SRP may inquire for the SRQ log by specifying particular SRQ events of interest in the inquiry RPCs. Possible values include:
These values are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. |
|
evt_dt_tm |
date |
- |
1 |
Last date and time the SRQ record was updated. This value is referenced when performing audit log queries in the OCA client. |
|
evt_text |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description of the event. |
|
user_id |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
The user ID. |
|
sched_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The scheduled date and time for provisioning to occur on this work order. It is used for work orders that are due in the future. For immediate work orders, set it to the current time. This value is referenced when performing work order queries in the OCA client. |
|
priority |
varchar2 |
21 |
0 |
Priority of the SRQ as assigned by the Host order system. It is equal to the work order priority. Possible values include:
These values are defined in asap_core.h. This priority field is the first field in the internal composite ASAP SRQ priority within the ASAP core followed by the SRQ due date and the SRQ action such as Remove, Change, or Add. |
|
batch_group |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The batch group ID of the work order. |
|
parent_wo |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
If set, the parent work order on which this order is dependent. The parent work order must be completed for provisioning to begin. |
|
org_unit |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The Organization Unit of the person or group to whom notification is sent should particular events occur on the work order. It is used for notification purposes and user group determination. |
|
grp_cd |
char |
1 |
0 |
The action of the SRQ. Possible values include:
This field determines the order in which SRQs are processed within the same work order and SRQs between work orders. These values are defined in asap_core.h. |
|
wo_event_time |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the work order event was placed into the audit log. |
|
wo_event_location |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The location of the work order event. For example, which pending queue the ASDL was placed in. |
Table indexes:
wo_id, wo_audit_log_identity
tbl_wo_event_queue
This dynamic table stores a back-up copy of all SRP events generated. Completed events are purged on a periodic basis.
Table 2-90 tbl_wo_event_queue Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The work order ID. |
|
event_unid |
number |
4 |
0 |
A unique ID of this event. If an alarm is generated by this event, an alarm log entry in tbl_alarm_log is created with this event unid value. |
|
event_type |
number |
4 |
0 |
The event type. It specifies if a system alarm is generated by accessing the static table, tbl_event_type. |
|
event_status |
number |
4 |
0 |
The current status of the event. |
|
srp_id |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical name of the front end SRP where notifications and results are sent for this particular work order, for example, SRP_EMUL. |
|
event_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of the system event. |
|
start_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of when provisioning starts for the ASDL. The difference between this value and queue_dts represents the time the ASDL spent in the queue of pending ASDLs to that Host NE before being transmitted to the NEP for provisioning. |
|
complete_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of when the ASDL provisioning is completed. |
|
estimate |
number |
4 |
1 |
The work order processing estimate returned to the SRP by the SARM after the work order was transmitted to the SARM by the SRP. |
|
misc |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
This field specifies miscellaneous information received by the SARM through the asap_wo_begin RPC. It contains another work order identifier associated with the primary work order. |
|
rev_flag |
char |
1 |
1 |
The revisions flag returned by the SARM on the work order completion notification. |
|
exceptions |
char |
1 |
1 |
The exceptions flag returned by the SARM on the work order completion notification. |
|
mach_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Remote NE. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Host NE to which the Remote NE is connected. |
|
reason |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
A description of the system event. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
4 |
1 |
Sequence number of the CSDL within the logical work order. |
|
csdl_id |
number |
4 |
1 |
The ID of the CSDL being processed when the Information parameter is generated. This CSDL ID is the same as the ID in tbl_srq_csdl. It allows the SRP to track the CSDL that this information parameter belongs to. |
|
timeout_status |
number |
4 |
1 |
The status of the work order when a timeout occurs. Possible values include:
|
|
queue_tm |
float |
8 |
1 |
Timestamp when the event was generated. |
|
xaction_type |
varchar2 |
16 |
1 |
The type of SRP event to be sent. Possible values include:
|
|
old_wo_stat |
number |
4 |
1 |
The previous status of the work order in the SARM. |
|
new_wo_stat |
number |
4 |
1 |
Status of the new work order. |
|
status |
number |
4 |
1 |
The current status of the work order in the SARM. |
|
extsys_id |
varchar2 |
128 |
1 |
An external system ID passed with the work order. It is not used by the SARM, but is used by the SRP for proper routing to upstream systems. |
|
rollback_exceptions |
char |
1 |
1 |
The rollback exceptions flag returned by the SARM on the work order rollback completion notification. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
wo_id, event_unid event_status, srp_id
tbl_wrk_ord (SARM)
This dynamic table details the essential work order information required by the ASAP core functionality. It contains details required by the provisioning process but does not contain customer-specific work order details.
Table 2-91 tbl_wrk_ord (SARM) Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The work order ID that uniquely identifies the work order in the ASAP core. This ID is the same as the one used in the Host system and allows easier user reference to orders in the OCA client. |
|
sched_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The scheduled date and time for provisioning to occur on work orders due in the future. For immediate work orders, set it to the current time. |
|
wo_stat |
number |
1 |
0 |
The status of the work order. It is updated by the SARM as the work order is being processed. Possible values include:
These values are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. |
|
comp_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The completion date of all provisioning associated with the work order in ASAP. |
|
srp_id |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The logical name of the front-end SRP that notifications and results are sent to for a particular work order. |
|
update_dts |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time of the last update on the work order within the ASAP core. |
|
org_unit |
varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
The Organization Unit of the person or group to whom notification is sent should particular events occur on the work order. |
|
orig_login |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
The original login ID of the user who initiated the work order in the Host order system. This information is used for display, notification, and diagnostic purposes. |
|
revs_flag |
char |
1 |
0 |
The revisions flag on the work order to indicate if the work order was revised by the OCA client. The possible values include:
This flag is passed back to the SRP by the SARM in the Work Order Completion Event. Such values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
|
exceptions |
char |
1 |
0 |
Exceptions flag indicating to the SRP if there are any exceptions in the completion of the work order. Such exceptions are generally the result of a “Fail but Continue" status being returned to the SARM for one of the ASDLs on the work order. This field is set by the SARM and communicated to the relevant SRP, which then requests the exception details. The possible values include:
The flag is passed back to the SRP by the SARM in the Work Order Completion Event. The values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
|
pend_cancel |
char |
1 |
1 |
This flag indicates if there is a pending order cancellation for this work order. Upon completion of the next ASDL on the order, the SARM checks this flag. If set, the SARM initiates rollback if configured at the ASDL level on the work order. The possible values are:
|
|
rollback_stat |
number |
1 |
0 |
The rollback status of the work order. If any CSDL on the work order requires rollback, this field is set to (201) RBACK_REQUIRED. Otherwise, it is set to (200) BACK_NOT_REQUIRED and no rollback takes place if the work order fails. If rollback is required, it starts on the work order and the SARM updates this field to (202) RBACK_IN_PROGRESS. This is a transient state and at the end of the rollback (Complete or Failed), the rollback status reverts back to its original state. If the rollback procedure fails, the field is updated to (204) RBACK_FAILED, otherwise (203) RBACK_COMPLETE to denote successful rollback. These values are defined in the header file sarm_defs.h. |
|
command |
number |
4 |
0 |
This field is transmitted by the SRP to the SARM and informs the SARM processing command to apply it to the work order. Possible values are:
These values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
|
crit_seq_no |
number |
4 |
1 |
The sequence number of the last critical update performed on this work order. This is updated each time a critical update to the work order has been performed. |
|
lock_uid |
varchar2 |
64 |
1 |
The user who last locked the work order for updating. |
|
lock_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the work order was last locked for updating. |
|
start_dts |
date |
- |
1 |
The date and time that the work order started provisioning. |
|
asdl_timeout |
number |
4 |
1 |
If set, the ASDL time-out interval to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter ASDL_TIMEOUTS. |
|
parent_wo |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
If set, the parent work order on which the work order is dependent. The parent order must be completed for the work order to begin provisioning. |
|
wo_timeout |
number |
4 |
1 |
If set, the work order time-out interval to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter ORDER_TIMEOUT. The order timeout behavior is governed by two parameters: the wo_timeout parameter on the work order and the ORDER_TIMEOUT configuration parameter in ASAP.cfg. If wo_timeout has a value greater than one, it is used. If wo_timeout has a value of zero, work orders do not time out. If wo_timeout has a value less than zero, ORDER_TIMEOUT is used. If wo_timeout has a value less than zero and ORDER TIMEOUT has a value of zero or less than zero, work orders do not time out. The work order/ASDL timer starts after the work order has been submitted and the first ASDL starts provisioning. This threshold can be exceeded if, for example, the connection to an NE is interrupted after the connection has been established. |
|
asdl_retry_num |
number |
4 |
1 |
If set, the number of ASDL retries to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter NUM_TIMES_RETRY. |
|
asdl_retry_int |
number |
4 |
1 |
If set, the time period in seconds between ASDL retries to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default. |
|
wo_rback |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set to:
|
|
stub_update_req |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
asdl_delay_fail |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set, a flag which specifies whether or not to treat hard errors encountered on the work order as delayed failures, therefore allowing the work order to finish processing before failing. This is used to override the behavior of the NEP State Table. |
|
max_delay_fail |
number |
4 |
1 |
If set, the number of ASDL delayed failures to allow before failing a batch work order. This allows the overriding of the system-wide SARM default which is specified by the configuration parameter, BATCH_THRESHOLD. |
|
srq_id |
number |
4 |
1 |
The ID of the latest SRQ associated with the work order. There is a single SRQ related to a given work order. |
|
is_future_dated |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set to:
|
|
batch_group |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The batch group ID of the work order. |
|
extsys_id |
varchar2 |
128 |
1 |
An external system ID that is passed with the work order. It is not used by the SARM, but is used by the SRP for proper routing to upstream systems. |
|
rollback_exceptions |
char |
1 |
0 |
The rollback exceptions flag returned by the SARM on the work order rollback completion notification. Indicates whether there are exceptions (i.e. ASDL failure) during rollback of a work order. |
|
point_of_no_return |
number |
38 |
0 |
Values are:
|
|
failure_reason |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Provides the failure reason for a work order that fails during provisioning. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
wo_id wo_stat, sched_dts, org_unit parent_wo batch_group
temp_csdl_estim
A temporary storage table for the Oracle SSP_csdl_list function. Data from this table is automatically maintained by the function; therefore, you should not manually add or remove data.
Table 2-92 temp_csdl_estim Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sess_id |
number |
22 |
1 |
Oracle session ID of the session executing the function. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
4 |
1 |
CSDL sequence number. |
|
estimate |
number |
4 |
1 |
CSDL estimate. |
Table indexes:
sess_id
temp_csdl_list
A temporary storage table for the Oracle SSP_csdl_list function. Data from this table is automatically maintained by the function; therefore, you should not manually add or remove data.
Table 2-93 temp_csdl_list Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sess_id |
number |
22 |
1 |
Oracle session ID of the session executing the function. |
|
csdl_cmd |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
CSDL command. |
|
csdl_st |
number |
1 |
1 |
CSDL status. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
4 |
1 |
CSDL sequence number. |
|
csdl_id |
number |
4 |
1 |
CSDL ID. |
|
description |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description of the CSDL. |
|
prov_sequence |
number |
4 |
1 |
Provisioning sequence of the CSDL. |
|
asdl_seq_no |
number |
4 |
1 |
ASDL sequence number. |
Table indexes:
sess_id
NEP database
This section details the NEP Database tables.
User-created database tables
Following is a list of user-created database tables.
tbl_asdl_lcc
This static table contains the line class codes for certain ASDLs. It is only used by NE State Table queries.
Table 2-94 tbl_asdl_lcc Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
asdl |
char |
80 |
0 |
The ASDLs that add an access line. |
|
lcc |
char |
5 |
0 |
The Line Class Code (LCC) for a specific ASDL adding an access line. |
Table indexes:
asdl
tbl_clli_len_ltg
This static table contains specific line information. For example, site code, line treatment group, intercept information, etc. This table is referenced by the GET_INCPT and GET_LTG State Table actions.
Table 2-95 tbl_clli_len_ltg Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Nulls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mach_clli |
varchar2 |
128 |
0 |
Remote NE. |
|
nxx |
varchar2 |
3 |
0 |
The NXX or Exchange working from this Remote NE. |
|
site |
char |
4 |
1 |
Site code associated with this Remote NE and NXX. |
|
ltg |
number |
38 |
1 |
Line treatment group for determining if calls are toll calls. |
|
pub_incpt |
char |
4 |
1 |
Indicates if the intercept on the line is for a directory-published number. |
|
non_pub_incpt |
char |
4 |
1 |
Indicates if the intercept on the line is for a non-published directory number. |
|
clli_desc |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
Description on the Remote NE. |
|
from_len |
varchar2 |
7 |
0 |
Start of LEN (Line Equipment Number) range. |
|
to_len |
varchar2 |
7 |
0 |
End of LEN range. |
|
host_clli |
char |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE managing the Remote NE. |
Table indexes:
Indexes
mach_clli, nxx, from_len host_clli, site, from_len
tbl_dms_logins
This static table is used by the NEP and contains the login user IDs and passwords for the connections to the DMS NEs. You are responsible for populating and maintaining this table.
Table 2-96 tbl_dms_logins Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
char |
80 |
0 |
Host NE. |
|
login_id |
char |
30 |
0 |
The login user ID that ASAP uses for this Host NE. |
|
password1 |
char |
30 |
0 |
The first NE password in a sequence of two passwords which are alternated. |
|
password2 |
char |
30 |
0 |
The second NE password. |
|
last_changed |
date |
- |
0 |
Date and time that the password was last changed. |
Table indexes:
host_clli, login_id
tbl_dms_options
This static table is used to specify DMS specific options.
Table 2-97 tbl_dms_options Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tech |
char |
16 |
0 |
The technology of the Host NE. |
|
sftwr_load |
char |
16 |
0 |
The software load of the Host NE. |
|
dms_option |
varchar2 |
10 |
0 |
The DMS option. |
Table indexes:
tech, sftwr_load, dms_option
tbl_march_feat
This static table provides the ability to map a generic option to a switch specific option. It is referenced by the GET_SW_FEAT State Table action.
Table 2-98 tbl_march_feat Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
generic_feat |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The generic feature. |
|
tech |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
The technology of the Host NE. |
|
switch_feat |
varchar2 |
20 |
0 |
The switch specific option. |
Table indexes:
generic_feat, tech
tbl_march_rpm
This static table provides the NEP State Tables access to provisioning parameters that are specific to a particular Host NE. The action, GET_P_PARMS, uses a variety of action strings that depend on the provisioning parameters being accessed.
Only the values of the parameters (ASDL parameters or State Table program local variables) are used, therefore the order of the parameters is fixed. The following is the order of the various parameter types:
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %NXX)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %USOC)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %USOC, %NXX)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %FEAT)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %PIC)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %USOC, %LCC)
-
(%TYPE, %MCLI, %USOC, %NXX, %LCC)
Table 2-99 tbl_ne_opt_vlu Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
host_clli |
char |
80 |
0 |
The Host NE. |
|
param_type |
varchar2 |
10 |
0 |
The type of provisioning parameter. The following values include:
|
|
usoc |
varchar2 |
10 |
1 |
The recent change Universal Service Order Code (USOC). |
|
nxx |
char |
3 |
1 |
The NXX (Network Number Exchange). |
|
lcc |
varchar2 |
10 |
1 |
The line class code. |
|
feat |
varchar2 |
20 |
1 |
Switch feature name. |
|
param_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Parameter label. |
|
param_vlu |
varchar2 |
30 |
1 |
Parameter value. |
Table indexes:
host_clli, param_type, usoc, nxx, lcc, feat, param_lbl
tbl_ne_opt_vlu
This static table is used by the State Tables. It contains the option string to be sent to the Network Element.
Table 2-100 ttbl_ne_opt_vlu Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tech |
char |
255 |
0 |
Technology of the Host Network Element. |
|
sftwr_load |
char |
16 |
0 |
Software Version of the Host Network Element |
|
asdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
0 |
The ASDL Command for which the option string needs to be sent to the NE. |
|
mask_lbl |
char |
10 |
1 |
A masking label for the option format |
|
opt_vlu |
char |
80 |
1 |
Option Value |
|
ne_opt_vlu |
char |
80 |
0 |
The option value for the particular NE Type and Software Load. |
Table indexes:
tech, sftwr_load, asdl_cmd, mask_lbl, opt_vlu
tbl_unid
This dynamic table provides a method of generating a serial field. You can manage unique IDs required by other tables. It is present in most user-created databases.
Table 2-101 tbl_unid Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
unid_type |
varchar2 |
12 |
0 |
A unique code identifying the UNID type. This allows many different UNID values for different types of UNID. |
|
unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
The UNID value for the type. |
|
pad1 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Padding to make a table row occupy a page. This is to reduce concurrence on the database data page by different database processes. |
|
pad2 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad3 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad4 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
Table indexes:
unid_type
tbl_valid_len
This static table contains a set of line equipment numbers that ASAP accesses in a non-production environment. This table is checked from the CHECK_DATA Interpreter ASDL when the ASAP_SYS environment variable does not equal PROD, and the Interpreter is not in loopback mode.
The CHECK_DATA State Table program and tbl_valid_len database table are included as samples so that you may create your own data checking tables.
tbl_valid_len is used to safeguard line equipment numbers (other than those listed in this table) when system testing is being conducted on a production NE. If validation is requested and a particular LEN is not found in this check table, then the order is failed.
Table 2-102 tbl_valid_len Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mcli |
char |
80 |
0 |
Remote NE of the LEN. |
|
len |
char |
7 |
0 |
Valid testing Line Equipment Number (LEN). |
Table indexes:
mcli, len
tbl_valid_nxx_line
This static table contains a set of telephone numbers that the ASAP system accesses in a non-production environment. This is a search table for the CHECK_DATA Interpreter State Table program when the ASAP_SYS environment variable does not equal PROD and the Interpreter is not in loopback mode.
The CHECK_DATA State Table program and tbl_valid_nxx_line database table are included as samples so that you may create your own data checking tables.
This table is to safeguard telephone numbers (other than those listed in this table) when system testing is being conducted on a production NE. If validation is requested and a particular DN is not found in this check table, the ASDL is failed.
Table 2-103 tbl_valid_nxx_line Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
nxx |
char |
3 |
0 |
Valid test NXX. |
|
line |
char |
4 |
0 |
Valid test line. |
Table indexes:
nxx, line
Admin database
This section describes the Admin database tables.
In addition to the user-created database tables described in the following section, the Admin database contains a WLStore table that is populated and managed by WebLogic Server to maintain persistence in their JMS destinations. It is recommended that you manually clean this tables during development if you want to start with a fresh environment. Otherwise, old undelivered messages occupy the queues and may cause problems when trying to debug or test. For production environments, you should design applications to handle undelivered messages. For instance, you can configure an error destination to use if a message fails to be delivered after a configurable number of attempts.
For more information on either of these two tables, refer to WebLogic Server documentation.
User-created database tables
Following is a list of user-created database tables.
tbl_asap_sarm
Defines the relationship between which Admin servers monitor which type of SARM servers.
Table 2-104 tbl_asap_sarm Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
adm_svr |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the Admin server. |
|
sarm |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the SARM server. |
Table indexes:
adm_svr, sarm
tbl_oca_svr
This table provides details about the number of active sessions maintained by the old CORBA SRP Server, if the load balancing feature is enabled. The new OCA SRP does not use this table.
Table 2-105 tbl_oca_svr Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
svr_name |
Varchar2 |
8 |
0 |
Name of the CORBA SRP Server. |
|
host_name |
Varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the host on which the CORBA SRP server application resides. |
|
session_no |
Number |
38 |
0 |
The number of sessions that the CORBA SRP Server is holding. |
|
status |
Varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
Status of the sessions. |
tbl_perf_asdl
Contains ASDL performance information retrieved from the SARM server in the ASAP system which continually maintains the data in memory. The frequency of the retrieval is controlled by the POLL_TIMER_ASDL configuration parameter.
You can view CSDL performance information using the asap_utils function: 22. Admin - ASDL Stats. For more information, refer to the ASAP Server Configuration Guide.
Table 2-106 tbl_perf_asdl Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sarm |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the SARM server providing the data. |
|
date_recvd |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time stamp of the record. |
|
time_elapse |
float |
8 |
0 |
Number of seconds since last performance data was received. |
|
record_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of record recorded. Possible values include:
|
|
asdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
1 |
The ASDL command. |
|
num_execute |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDL executions. |
|
num_failed |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDL failures. |
|
num_complete |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of successful ASDL completions. |
|
parm_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average number of parameters on the ASDL. |
|
parm_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum number of parameters on the ASDL. |
|
parm_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum number of parameters on the ASDL. |
|
num_rollback |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of times the ASDL was rolled back. |
|
num_soft_err |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of soft errors on the ASDL. |
|
num_retries |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of times the ASDL was executed. |
|
num_skipped |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of times the ASDL was skipped in processing. |
|
comp_tm_avg |
number |
8 |
0 |
The average time in seconds for the ASDL to complete. |
|
comp_tm_min |
float |
8 |
0 |
The minimum time in seconds for the ASDL to complete. |
|
comp_tm_max |
float |
8 |
0 |
The maximum time in seconds for the ASDL to complete. |
|
parm_count |
number |
4 |
1 |
Number of ASDL parameters. |
|
comp_tm |
float |
8 |
1 |
Total ASDL processing time in seconds. |
Table indexes:
sarm, asdl_cmd, date_recvd, record_type
tbl_perf_csdl
Contains CSDL performance information retrieved from the SARM server in the ASAP system which continually maintains the data in memory. The frequency of the retrieval is controlled by the POLL_TIMER_CSDL configuration parameter.
You can view CSDL performance information using the asap_utils function: 21. Admin - CSDL Stats. For more information on asap_utils, refer to the ASAP Server Configuration Guide.
Table 2-107 tbl_perf_csdl Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sarm |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the SARM server providing the data. |
|
date_recvd |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time stamp of the record. |
|
time_elapse |
float |
8 |
0 |
Number of seconds since last performance data was received. |
|
record_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of record recorded. Possible values include:
|
|
csdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
1 |
The CSDL command. |
|
num_received |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of times the CSDL was received by the SARM. |
|
num_complete |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of successful CSDL completions. |
|
num_failed |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of CSDL failures. |
|
comp_tm_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average completion time in seconds of the CSDL. |
|
comp_tm_min |
float |
8 |
0 |
Minimum completion time in seconds of the CSDL. |
|
comp_tm_max |
float |
8 |
0 |
Maximum completion time in seconds of the CSDL. |
|
num_asdl_comp |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of completed ASDLs on the CSDL. |
|
num_asdl_skip |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of skipped ASDLs on the CSDL. |
|
parms_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average number of CSDL parameters. |
|
parms_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum number of CSDL parameters. |
|
parms_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum number of CSDL parameters. |
|
asdl_comp_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average number of completed ASDLs on the CSDL. |
|
asdl_comp_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum number of completed ASDLs on the CSDL. |
|
asdl_comp_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum number of completed ASDLs on the CSDL. |
|
asdl_skip_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average number of ASDLs skipped on the CSDL. |
|
asdl_skip_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum number of ASDLs skipped on the CSDL. |
|
asdl_skip_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Total number of ASDLs skipped on the CSDL. |
|
asdl_comp_tot |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total ASDL Processing time. |
|
asdl_comp_count |
number |
4 |
1 |
Number of ASDLs completed. |
|
asdl_skip_count |
number |
4 |
1 |
Number of ASDLs skipped. |
|
comp_tm_tot |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total ASDL processing time. |
|
parm_count_tot |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total number of CSDL parameters. |
Table indexes:
sarm, csdl_cmd, date_recvd, record_type
tbl_perf_ne
Contains NE performance information retrieved from the SARM server in the ASAP system which continually maintains the data in memory. The frequency of the retrieval is controlled by the POLL_TIMER_NE configuration parameter.
You can view NE performance information using the asap_utils function: 23. Admin - NE Stats. For more information on asap_utils, refer to the ASAP Server Configuration Guide.
Table 2-108 tbl_perf_ne Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sarm |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the SARM server providing the data. |
|
date_recvd |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time stamp of the record. |
|
time_elapse |
float |
8 |
0 |
Number of seconds since the last performance data was received. |
|
record_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of record. Possible values include:
|
|
nep |
char |
8 |
1 |
The NEP server. |
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The Host NE. |
|
tech |
char |
16 |
1 |
The technology of the Host NE. |
|
sftwr_load |
char |
16 |
1 |
The software load of the Host NE. |
|
state |
char |
10 |
1 |
The Host NE state. |
|
num_estimate |
number |
4 |
0 |
The ASDL estimate for the NE. |
|
num_pending |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs in the Pending queue to the Host NE. |
|
num_in_prog |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs in the In Progress queue to the Host NE. |
|
num_connect |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of connections to the Host NE. |
|
num_retry |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs in the Retry queue to the Host NE. |
|
time_tot_avail |
float |
8 |
0 |
Total time in seconds the NE is available. |
|
time_curr_avail |
float |
8 |
0 |
Current time in seconds the NE has been available. |
|
num_asdl_comp |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs completed to the Host NE. |
|
num_asdl_fail |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs failed to the Host NE. |
|
num_asdl_retry |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs retried to the Host NE. |
|
num_asdl_recvd |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs received for the Host NE. |
|
num_asdl_xfer |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of ASDLs transferred. |
|
perc_ne_usage |
float |
8 |
0 |
Percentage of time that ASAP is provisioning the Host NE while it has open connections to the Host NE. |
|
asdl_comp_tm_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average time in seconds required to complete an ASDL to the Host NE. |
|
asdl_comp_tm_min |
float |
8 |
0 |
Minimum time in seconds required to complete an ASDL to the Host NE. |
|
asdl_comp_tm_max |
float |
8 |
0 |
Maximum time in seconds required to complete an ASDL to the Host NE. |
|
asdl_q_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average ASDL Pending queue size to the Host NE. |
|
asdl_q_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum ASDL Pending queue size to the Host NE. |
|
asdl_q_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum ASDL Pending queue size to the Host NE. |
|
pend_q_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average number of ASDLs in the SARM. |
|
pend_q_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum number of ASDLs in the SARM. |
|
time_tot_maint |
float |
8 |
0 |
Total time in seconds the Host NE is in Maintenance mode. |
|
time_curr_maint |
float |
8 |
0 |
Current time in seconds that the NE is in Maintenance mode. |
|
comp_tm_tot |
float |
8 |
1 |
Total ASDL processing time. |
|
q_time_tot |
float |
8 |
1 |
Total ASDL queue time. |
|
tot_pq_sz |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total Pending queue size. |
|
pq_samples |
number |
4 |
1 |
Number of Pending queue samples. |
Table indexes:
sarm, host_clli, date_recvd, record_type
tbl_perf_ne_asdl
Collects the frequency of exit conditions for the various NEs and ASDLs. The frequency of the retrieval is controlled by the POLL_TIMER_NE_ASDL configuration parameter.
You can view pseudo real-time statistical information related to SARM NE / ASDL processing using the asap_utils function: 24. Admin - NE/ASDL Stats. For more information on asap_utils, refer to the ASAP Server Configuration Guide.
Table 2-109 tbl_perf_ne_asdl Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sarm |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the SARM server providing the data. |
|
date_recvd |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time stamp of the record. |
|
time_elapse |
float |
8 |
0 |
Number of seconds since the last performance data was received. |
|
record_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of record. Possible values include:
|
|
host_clli |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
The host NE where the ASDL command is routed by the SARM. Although one host NE is specified on the CSDL, different ASDLs on the CSDL is routed to different Host NEs based on the ASDL command. |
|
asdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
1 |
The ASDL command. |
|
user_exit_type |
char |
20 |
1 |
The user-defined ASDL exit type. |
|
counter |
number |
4 |
0 |
The number of times the user_exit_type occurred. |
Table indexes:
sarm, host_clli, asdl_cmd, user_exit_type, date_recvd, record_type
tbl_perf_order
Contains work order performance information retrieved from the SARM server in the ASAP system which continually maintains the data in memory. The frequency of the retrieval is controlled by the POLL_TIMER_ORDER configuration parameter.
You can view work order performance information using the asap_utils function: 20. Admin - WO Stats. For more information on asap_utils, refer to the ASAP Server Configuration Guide.
Table 2-110 tbl_perf_order Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
sarm |
char |
8 |
0 |
Name of the SARM server providing data. |
|
date_recvd |
date |
- |
0 |
The date and time stamp of the record. |
|
time_elapse |
float |
8 |
0 |
Number of seconds since the last performance data was received. |
|
record_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Type of record recorded. Possible values include:
|
|
org_unit |
char |
8 |
1 |
Organization unit associated with the work order. |
|
ord_type |
char |
1 |
1 |
Work order type. |
|
num_recorded |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of work orders recorded in the SARM. |
|
num_cancelled |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of cancelled work orders. |
|
num_received |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of received work orders. |
|
num_future |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of future-dated work orders. |
|
num_immed_fail |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of immediate failed work orders. |
|
num_immed_comp |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of immediate completed work orders. |
|
num_tran_err |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of translation errors received. |
|
num_timeout |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of timed out work orders. |
|
num_rollback |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of rolled back work orders. |
|
num_update |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of work orders updated after the original was sent. |
|
num_collision |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of work order collisions. |
|
num_route_err |
number |
4 |
0 |
Number of work orders that have routing errors. |
|
global_p_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average number of global parameters on the work order. |
|
global_p_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum number of global parameters on the work order. |
|
global_p_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum number of global parameters on the work order. |
|
latency_avg |
float |
8 |
0 |
Average work order replication latency in seconds. |
|
latency_min |
number |
4 |
0 |
Minimum work order replication latency in seconds. |
|
latency_max |
number |
4 |
0 |
Maximum work order replication latency in seconds. |
|
num_fut_fail |
number |
4 |
0 |
The number of future-dated work orders that have failed. |
|
num_fut_comp |
number |
4 |
0 |
The number of future-dated work orders that have completed. |
|
latency_tot |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total work order replication latency in seconds. |
|
latency_count |
number |
4 |
1 |
Number of work order replication latencies that have occurred. |
|
global_p_tot |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total number of global parameters on all work orders. |
|
global_p_count |
number |
4 |
1 |
Total number of global parameters that have occurred. |
Table indexes:
sarm, org_unit, ord_type, date_recvd, record_type
tbl_aims_msg_convert
This table stores translations of all localizable ASAP strings to the destination languages.
Table 2-111 tbl_aims_msg_convert Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
lang_cd |
varchar2 |
32 |
0 |
The language code. |
|
msg_id |
varchar2 |
64 |
0 |
Unique message identifier to identify the messages referenced in other tables. |
|
type |
varchar2 |
16 |
0 |
Specifies the type of message, such as CSDL description, ASDL description, etc. |
|
message |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
The message test. |
|
var_description |
varchar2 |
40 |
1 |
Description of the message, for example, the substitutable fields within it. |
tbl_aims_preference
This dynamic table stores preferences in the OCA client.
Table 2-112 tbl_aims_preference Columns
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
user_id |
varchar2 |
30 |
0 |
User ID. |
|
name |
varchar2 |
100 |
0 |
Name of the preference. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
200 |
1 |
Value for the preference. You are responsible to convert the preference to a string. |
Table indexes:
user_id, name
C++ SRP API emulator database
SRP emulator is used for performance benchmarking, system testing, and the prototyping of new SRPs. The SRP emulator is a generic SRP that submits work orders to the SARM. The SRP emulator makes use of the SRP, Interpreter, Server Application, and Common API libraries.
Figure 2-2 C++ SRP API Emulator Database Tables
Description of "Figure 2-2 C++ SRP API Emulator Database Tables"
Note:
If you shut down and restart the C++ SRP API Emulator when USE_RAW_WO_ID is set to 0, it may result in a unique work order name containing a recurring prefix.
User-created database tables
Following is a list of user-created database tables.
tbl_aux_wo_prop
tbl_aux_wo_prop is a class A dynamic table that serves as an extension to tbl_wrk_ord. tbl_aux_wo_prop was designed to accommodate additional pre-defined work order properties to supplement the ones contained in tbl_wrk_ord. Currently, the only extended property supported in tbl_aux_wo_prop is WO_SECURITY_PROP. This property is maintained for each work order. If WO_SECURITY_PROP = 0, then work order information is eligible to be output to diagnostic files. If WO_SECURITY_PROP = 1, then no work order information is written to diagnostic files.
Refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide for more information on secure work order information.
When the work orders in the tbl_wrk_ord are deleted, the corresponding records in tbl_aux_wo_prop are deleted. This table can be purged using function SSP_db_admin. For guidelines and instructions on database purging, refer to the ASAP System Administrator's Guide.
Table 2-113 tbl_aux_wo_prop
| Column Name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ID of the work order property. |
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the work order property. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The value given to the work order property. |
Table indexes:
Unique
wo_id, name
tbl_csdl
Used only in conjunction with the SRP Emulator.
This static table contains all CSDLs for each logical work order listed in the tbl_wo_def table. Each logical work order can have one or more associated CSDLs.
Table 2-114 tbl_csdl
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_def_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Unique ID of the logical work order associated with the CSDL. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL within the logical work order. |
|
csdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL command. |
|
csdl_st |
number |
38 |
0 |
Initial status of the CSDL that gets transmitted to the SARM along with the rest of the work order details. Possible values include:
Values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
Table indexes:
Unique
wo_def_id, csdl_seq_no
tbl_csdl_parm
This static table contains all CSDL parameters associated with a specific CSDL.
Table 2-115 tbl_csdl_parm
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_def_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
The logical work order ID. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL within the logical work order. |
|
parm_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL parameter within the CSDL. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
CSDL parameter label; for example, DN, EN, etc. |
|
parm_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
CSDL parameter value associated with the parameter label. |
Table indexes:
Unique
wo_def_id, csdl_seq_no, parm_seq_no
tbl_srp_event_status
This dynamic table contains work order status information.
Table 2-116 tbl_srp_event_status
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_def_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Logical work order ID. |
|
event_name |
varchar2 |
50 |
0 |
Name of the event to test. |
|
event_status |
number |
38 |
0 |
The status that is assigned to the event.
|
Table indexes:
Unique
wo_def_id, event_name
tbl_tst_rqst
This dynamic table contains all test requests sent to the C++ SRP API Emulator. It contains test details to be used by the C++ SRP API Emulator, such as the test suite to use, type of test to run, number of instances of each work order in the test suite, etc. A test request is an instance of a test suite.
Table 2-117 tbl_tst_rqst
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tst_rqst_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
Unique test request ID. |
|
tst_suite_cd |
char |
96 |
0 |
Test suite code that specifies which test suite to use. |
|
sync_test |
char |
1 |
0 |
Specifies whether the test is synchronous, for example, waiting for test completion, or asynchronous. Possible values are:
|
|
repeat_cnt |
number |
38 |
0 |
Specifies how many instances are created of each logical work order in the test suite and runs stress tests of the system. |
|
all_wos_sent |
char |
1 |
0 |
A flag indicating whether all work orders associated with the test request have been sent to the SARM. You can use this field to determine if the test is complete, for example, if all_wos_sent = “Y" and wo_cnt = wo_cmp_cnt, the test is complete. Possible values are:
|
|
wo_cnt |
number |
38 |
1 |
Number of work orders in the test request. To be initialized to 0 by the user. The C++ SRP API Emulator updates the count as each work order is created and the wo_cnt determines if the test is complete. |
|
wo_cmp_cnt |
number |
38 |
1 |
A count of the completed work orders in the test. You must set this to 0. The C++ SRP API Emulator updates the count as each work order is completed and determines if the test is complete. |
|
tst_userid |
char |
32 |
1 |
The ID of the user. This field is only for diagnostic purposes. |
Table indexes:
Unique
tst_rqst_id
tbl_tst_suite
You can use this static table to create test suite definitions. Each test suite has a list of logical work orders associated with it. A test request is an instance of a test suite.
Table 2-118 tbl_tst_suite
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tst_suite_cd |
char |
96 |
0 |
Identifies a test suite. This column is a foreign key in tst_rqst. |
|
tst_suite_desc |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
A description of a test suite. |
|
create_dt |
date |
- |
0 |
Test suite creation date. |
Table indexes:
Unique
tst_suite_cd
tbl_unid
Use this dynamic table to manage unique IDs required by other tables in this database. It is present in most created databases and provides a method of generating a serial field.
Table 2-119 tbl_unid
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
unid_type |
char |
32 |
0 |
A unique code identifying the UNID type. This allows many different UNID values for different types of UNID. |
|
unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
The UNID value for that particular type. |
|
pad1 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Padding to make a table row occupy a database page. This reduces concurrence on the database data page by different database processes. |
|
pad2 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad3 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
|
pad4 |
char |
255 |
0 |
Same as pad1. |
Table indexes:
Unique
unid_type
tbl_usr_wo_prop
This table is used to dynamically configure a work order property. It consists of WO ID and name/value pair for a user-defined work order property, and is used mainly for work order queries. This table supports only string type user-defined work order properties (also known as extended work order properties). Extended work order properties are only applicable to the work order where they are defined.
Table 2-120 tbl_usr_wo_prop
| Column Name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The ID of the work order property. |
|
name |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The name of the work order property. |
|
value |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
The value given to the work order property. |
Table indexes:
Unique
wo_id, name
tbl_wo_def
This static table contains all logical work orders in the C++ SRP API Emulator database.
Table 2-121 tbl_wo_def
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_def_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Logical work order ID. |
|
wo_def_desc |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
A description of the work order definition. |
|
origin |
varchar2 |
64 |
0 |
The user who created the logical work order. |
|
org_unit |
char |
8 |
0 |
Organization Unit for the work order. This is set to the C++ SRP API Emulator Application server name. |
|
srp_stat |
char |
1 |
0 |
The SRP state of the logical work order. You can use this field to determine the operation field to transmit from the SRP to the SARM on the wo_begin RPC. You can find the field definitions in the local header file, srp_emul.h. |
|
priority |
char |
1 |
0 |
The provisioning priority. Possible values include:
Values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
|
srq_type |
char |
1 |
0 |
Service Request type. Possible values include:
Values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
|
userid |
varchar2 |
64 |
0 |
Specifies the user ID to be used for SARM security authorization. This is required only if the SARM security checking logic is currently configured. |
|
password |
char |
30 |
0 |
Specifies the password to be used for SARM security authorization. |
|
asdl_timeout |
number |
38 |
0 |
Specifies the ASDL time-out interval to be used on the work order provided that the configuration parameter ASDL_TIMEOUTS is set to 1. If the value of the ASDL_TIMEOUTS is zero (0), the ASDL timeout feature is not used, regardless of the asdl_timeout value. This value is passed to the SARM in the work order transaction to allow the specification of a work order dependent ASDL time-out interval. |
|
parent_wo |
char |
80 |
1 |
If set, the parent work order upon which this work order is dependent. This work order will not begin provisioning until the parent work order has been completed. |
|
wo_timeout |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the work order time-out interval in seconds to be used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default (specified by the configuration parameter ORDER_TIMEOUT in ASAP.cfg). The order timeout behavior is governed by two parameters: the wo_timeout parameter on the work order and the ORDER_TIMEOUT configuration parameter in ASAP.cfg. If wo_timeout has a value greater than one, it is used. If wo_timeout has a value of zero or less than zero, ORDER_TIMEOUT is used. If wo_timeout has a value of zero or less than zero and ORDER TIMEOUT has a value of zero or less than zero, work orders do not time out. The work order/ASDL timer starts after the work order has been submitted and the first ASDL starts provisioning. This threshold can be exceeded if, for example, the connection to an NE is interrupted after the connection has been established. |
|
asdl_retry_num |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the number of ASDL retries used on the work order instead of the system-wide SARM default. |
|
asdl_retry_int |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the time in seconds between retries of an ASDL used on this work order instead of the system-wide SARM default. |
|
wo_rback |
char |
1 |
1 |
Possible values:
If a value is not specified, the default is D. This means that the rollback depends on the CSDL parameter rollback_req. If rollback_req is set for a CSDL, then the work order rolls back when it times out or fails |
|
propagate |
char |
1 |
1 |
Reserved. |
|
asdl_delay_fail |
char |
1 |
1 |
If set, a flag specifying whether to treat hard errors encountered on the work order as delayed failures. The order then finishes processing before failing. You can use this field to override the behavior of the NEP State Table. |
|
delay_threshold |
number |
38 |
1 |
If set, the number of ASDL delayed failures given before failing a batch work order. This permits the overriding of the system-wide SARM default. |
|
batch_group |
char |
80 |
1 |
Batch group for the work order. |
|
extsys_id |
varchar2 |
128 |
1 |
ID of the source of the work order (optional). |
Table indexes:
wo_def_id
tbl_wo_list
This static table contains all logical work orders associated with each test suite listed in tbl_tst_suite.
Table 2-122 tbl_wo_list
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tst_suite_cd |
char |
96 |
0 |
The test suite code to which the logical work order list belongs. |
|
wo_list_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the logical work order within the test suite. |
|
wo_def_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Logical work order ID. |
|
delay |
number |
38 |
0 |
The delay in seconds after the transmission of the work order to the SARM. This allows the specification of time intervals between different work orders or copies of the same order. |
|
operation |
number |
38 |
0 |
The work order operation to be transmitted to the SARM. Possible values include:
These values are defined in the header file asap_core.h. |
|
status |
char |
1 |
0 |
The internal status of the work order to be transmitted to the SARM. Possible values include:
|
|
due_offset |
date |
- |
0 |
The due date increment to be applied to the work order when transmitting the work order to the SARM. |
|
parent_wo |
char |
80 |
1 |
If set, the parent work order upon which the work order is dependent. This work order will not begin provisioning until the parent work order has been completed. |
|
batch_group |
char |
80 |
1 |
Batch group for the work order. |
|
extsys_id |
varchar2 |
128 |
1 |
Source of the work order (optional). |
Table indexes:
tst_suite_cd, wo_list_seq_no
tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)
Note:
This table differs from the table of the same name that is located in the SARM database. See "tbl_wrk_ord (SARM)."
This dynamic table contains instances of logical work orders that belong to a specific test request listed in tbl_tst_rqst. A test request may have one or more work orders.
Table 2-123 tbl_wrk_ord (user-created database table)
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
tst_rqst_id |
number |
38 |
0 |
Unique ID of the test request to which the work order belongs. |
|
wo_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Work order ID. The numeric value is the same as wo_unid. This can be useful if some conversion of the work order ID format is required between this database and the work order ID transmitted to SARM. |
|
wo_def_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Logical work order ID. |
|
asap_stat |
char |
1 |
0 |
Determines the operation field to transmit on the wo_begin RPC from the SRP to the SARM. If HELD_ORDER_STAT (defined in sarm_defs.h) is specified, the work order transmits to the SARM and is held awaiting operator intervention. |
|
estimate |
number |
38 |
0 |
The work order processing estimate returned to the SRP by the SARM after the work order has been transmitted. |
|
revs_flag |
char |
1 |
1 |
The revisions flag returned by the SARM on the work order completion notification. |
|
exceptions |
char |
1 |
1 |
The exceptions flag returned by the SARM on the work order completion notification. |
Table indexes:
wo_id
tbl_wrk_ord_log
This dynamic table contains the information logged for each work order and provides a history of the events that occurred to the work order.
Table 2-124 tbl_wrk_ord_log
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Identifies the work order. |
|
event_dt |
date |
- |
0 |
Date and time of the logged event. |
|
asap_stat |
char |
8 |
0 |
ASAP status of the work order at the time the event occurred. Possible values are detailed for asap_stat in tbl_wo_list. |
|
log_unid |
number |
38 |
0 |
Unique ID of the log wo_log message. |
|
log_msg |
varchar2 |
255 |
1 |
A description of the event. |
Table indexes:
wo_id, log_unid
tbl_wrk_ord_parm
This dynamic table contains work order parameters.
Table 2-125 tbl_wrk_ord_parm
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Nulls |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Unique work order ID to which the parameters belong. |
|
parm_grp |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
The parameter group associated with the work order ID. |
|
csdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL associated with the work order parameters. |
|
csdl_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
The sequence number of the CSDL within the SRQ. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Work order parameter label, for example DN, LEN, etc. |
|
parm_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
Work order parameter value associated with the work order parameter label. |
|
event_dt |
date |
- |
0 |
Date and time of the logged event. |
|
parm_identity |
number |
20 |
0 |
Unique ID of the parameter. This is an identity field that is automatically generated by the RDBMS upon insertion. |
Table indexes:
wo_id, parm_lbl, parm_grp, parm_identity
tbl_wrk_ord_rev
This dynamic table contains work order revision information.
Table 2-126 tbl_wrk_ord_rev
| Column_name | Type | Length | Nulls | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
wo_id |
char |
80 |
0 |
Work order ID. The numeric value is the same as wo_unid. This is useful if some conversion of the work order ID format is required between the database and the work order ID transmitted to the SARM. |
|
flag |
char |
1 |
0 |
The revisions flag that is set to (Y)es or (N)o. |
|
csdl_cmd |
char |
80 |
0 |
The CSDL associated with the work order parameters. |
|
parm_seq_no |
number |
38 |
0 |
Sequence number of the CSDL parameter. |
|
parm_lbl |
varchar2 |
80 |
0 |
Work order parameter label, for example DN, LEN, etc. |
|
parm_vlu |
varchar2 |
255 |
0 |
CSDL parameter value associated with the parameter label. |
|
parm_desc |
varchar2 |
80 |
1 |
Description of the parameter. |
Table indexes:
wo_id, csdl_cmd, parm_seq_no