7 Discovering and Monitoring the SOA Suite
This chapter describes how you can discover and configure the components of the SOA Suite 11g and 12c using Enterprise Manager Cloud Control.
In particular, this document covers the following:
List of Supported Versions
For the supported versions of the SOA Suite and the SOA Cloud Services (SOACS) for Enterprise Manager go to the Enterprise Manager certification matrix.
To access the Enterprise Manager certification matrix, follow these steps:
- Sign in to My Oracle Support:
http://support.oracle.com - Click the Certifications tab.
- In the Certification
Search, from the Product list, select
one of the following:
- Enterprise Manager Base Platform - OMS, to view the certification for OMS.
- Enterprise Manager Base Platform - Agent, to view the certification for Management Agent.
- From the Release list, select release version, and then click Search.
Monitoring Templates
The following Oracle-certified default templates are being shipped for Enterprise Manager and Enterprise Manager agents. Table 7-1 describes the available templates, and the agents to which they apply:
Table 7-1 Monitoring Templates
| Target Type | Template Name |
|---|---|
|
SOA Infrastructure |
Oracle Certified Fusion Middleware Template for SOA Infrastructure |
|
SOA Composite |
Oracle Certified Fusion Middleware Template for SOA Composite |
Discovering the SOA Suite
You can use a local or a remote Management Agent to perform the discovery process. as follows:
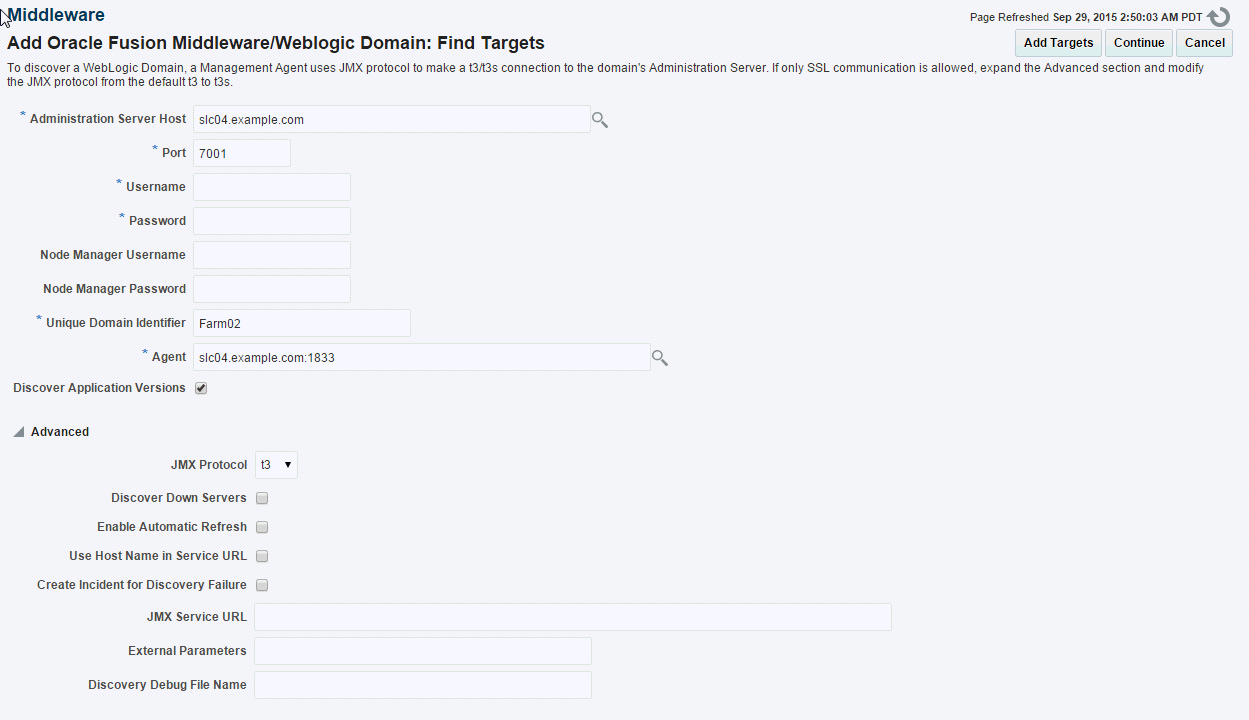
Discovering the SOA Suite Using a Local Agent
If you use a local agent, you need to use a Management Agent that is running on the same host as the Administration Server.
Discovering the SOA Suite Using a Remote Agent
You can discover the SOA Suite using a remote agent which may be running on a host that is different from the host on which the Administration Server is running. In this case, you may not be able to provision SOA Artifacts remotely, or capture the host metrics.
To collect metric data, ensure that you copy the jar files listed in Table 7-2 from the SOA HOME install location to the Agent Home Directory, which is located at: $AGENT_HOME/plugins/oracle.sysman.emas.agent.plugin_<plugin version>/archives/jlib/extjlib. If the extjlib directory does not exist, it can be created. This step is required only if you are using a remote agent to monitor the SOA Suite.
Table 7-2 Metric Data Collection
| SOA Target | Files Names |
|---|---|
|
SOA PS5 (11.1.1.6.0) and higher targets |
|
|
SOA 12c targets |
jrf-api.jar To enable Error Hospital and Instance Tracing, you additionally require:
|
|
To enable BPMN instance tracing |
For SOA 11g targets:
For SOA 12c targets:
|
Discovering the SOACS Instance Using the Hybrid Cloud Agent
You can discover a SOA instance on the Oracle Public Cloud in Enterprise Manager using the Hybrid Cloud Agent. To understand the architecture of the hybrid cloud see Enabling Hybrid Cloud Management in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator’s Guide. The steps required to discover the SOACS instance are also a part of the same chapter. However, a detailed listing of the steps along with the relevant links to the sections is given below.
Configuring the SOA Suite with Target Verification
As a prerequisite, verify the target monitoring setup before you perform any operations on the SOA infrastructure. Use the Target Setup Verification page to run a series of diagnostic scans and verify if you have met all functional as well as system-level prerequisites required for monitoring targets in Enterprise Manager. This helps you discover and repair all target monitoring setup-related issues beforehand.
This section describes the following:
Note:
You will not be able to click on the torch icon available next to the database system field in Dehydration Store repair pop-up if an association exists between the database system and SOA infrastructure. It is enabled only when the association is missing. When the association is missing, you can select appropriate database system target from target selector popup. Pop-up can be launched by clicking on the torch icon.
Running Functionality-Level Diagnostic Checks
To run diagnostic scans on the functionalities associated with an Enterprise Manager target and to identify any setup issues, follow these steps:
- From the Targets menu, select Middleware.
- On the Middleware page, click the target you are interested in. For example, SOA Infrastructure.
- On the Home page of the target, from the target-specific menu, select Target Setup, and click Verification.
- On the Target Setup Verification page, in the Functionality Check section, click Scan.
- If setup problems are detected, repair them. See Repairing Target Monitoring Setup Issues.
Running System-Level Diagnostic Checks
To run diagnostic scans on the system components that monitor an Enterprise Manager target and check their availability rate, follow these steps:
Metric and Collection Settings
For the following metrics the collection schedule is not available on the Metric and Collection Settings page. Detailed steps to update the collection intervals are listed in the following table:
Table 7-3 Metric and Collection Settings
| Target Type | Metric Name | Collection Interval Update Steps |
|---|---|---|
|
SOA Infrastructure |
Response |
Navigate to the associated weblogic server where SOA is deployed, to do so, follow these steps:
Note: This change is applicable to all the applications deployed in that WebLogic server. |
|
SOA Composite |
Response |
For SOA PS5 (11.1.1.6.0) or earlier, follow these steps:
For SOA PS6 (11.1.1.7.0) onwards, navigate to the associated SOA Infrastructure where SOA composite is deployed. To do so, follow these steps:
Note: This change is applicable to all the SOA composites which are deployed in that SOA Infrastructure |
|
SOA Composite |
SOA Composite - Component Detail Metrics |
Navigate to the associated SOA Infrastructure where soa composite is deployed. To do so, follow these steps:
|
|
SOA Composite |
SOA Composite - Recoverable And Rejected Messages |
Navigate to the associated SOA Infrastructure where soa composite is deployed. To do so, follow these steps:
|
Integration Workload Statistics (IWS)
Integration Workload Statistics (IWS) reports provide SOA system-wide reports that can help you analyze utilizations, identify potential bottlenecks and backlogs, and perform top-down analysis of your integration system.
So, for instance, if there are stressed components or endpoints in your SOA system that are slowing down the system, IWS reports can help you narrow down on these. For example, a slow FTP or database adapter reference endpoint can be identified in the reports. Likewise, a BPEL process running slower than usual can also be identified. You can look at internal queue backlogs, like BPEL queues and EDN queues. SOA composite-wise summaries are also available.
IWS reports can include metrics like system resource usage, composite statistics, statistics for internal system queues, statistics for synchronous and asynchronous business processes, and endpoint statistics. The components supported in this release include BPEL Service Engine, EDN, Web Service Binding, File Adapter, JMS Adapter, FTP Adapter, DB Adapter, AQ Adapter, and MQ adapter.
IWS takes periodic snapshots of performance statistics to generate these reports. You can enable or disable IWS data collection. You can also set the collection frequency and the granularity of data collected for your IWS reports. The following table illustrates the data collection levels, or statistics levels, and the data collected for each level.
| Data Collection Level/Statistics Level | Data Collected |
|---|---|
| MINIMUM | System-wide resource usage data. |
| BASIC | MINIMUM + Service and reference endpoint statistics, BPEL and EDN backup queue statistics, BPEL instance statistics. |
| NORMAL | BASIC + Data on BPEL activities like Receive, Invoke, Pick, and onMessage. |
| FINEST | NORMAL + Data on all BPEL activities. |
The sections contains the following topics:
Statistics in an IWS Report
An Integration Workload Statistics (IWS) report contains various statistics, depending on the data collection level that you have set. In addition to system-wide resource usage data, the report can include service and reference endpoint statistics, BPEL and EDN backup queue statistics, and BPEL instance statistics. Statistics on BPEL activities may also be included.
The IWS report contains the following broad sections when the data collection level is set to finest:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
System Resource Usage |
Statistics include Java Virtual Machine (JVM) statistics like CPU utilization and memory utilization (for JVM heap and non-heap memory), SOA Data Source statistics that show active connections and connection pool details, and SOA Work Manager statistics that include details on threads. |
|
Composite (Rollup) Statistics |
Aggregate composite-wise statistics that indicate flow rate (throughput/transactions per second) and latency (in milliseconds) for the composite endpoints and internal backup queues (EDN and BPEL queue). |
|
Slowest Composite Endpoints |
Aggregate composite-wise statistics that indicate the latency (in milliseconds) and flow rate (throughput) for the slowest endpoints. |
|
Backups in Internal Queues |
Aggregate statistics for the backups in internal system queues (BPEL queue and EDN queue). |
|
Longest Running Business Processes |
Aggregate statistics for top asynchronous and synchronous business (BPEL) process instances based on execution time. |
|
Most Time-Consuming Business Process Activities |
Aggregate statistics for top business process activities (BPEL activities like Receive, Invoke, etc) based on execution time. |
Enabling, and Configuring, or Disabling IWS
Integration Workload Statistics (IWS) snapshot data is collected at periodic intervals. You can enable snapshot data collection, configure snapshot interval, and the granularity of data collected.
To enable, and configure, or disable Integration Workload Statistics (IWS) follow the steps below:
Note:
The IWS Configuration feature is active only if the Preferred Credential for the Weblogic domain is set to an user having SOA Administrator role. The credentials can be updated using the SOA Infrastructure menu option - Target Setup Verification.
Generating an IWS Report
The Integration Workload Statistics (IWS) reports help you identify bottlenecks and backlogs in the system. IWS include metrics like system resource usage, composite statistics, statistics for internal system queues, statistics for synchronous and asynchronous business processes, and endpoint statistics.
To generate an IWS report, follow the steps below:
Note:
You must have already configured IWS data collection and set a snapshot interval before generating an IWS report. See Enabling, Disabling and Configuring IWS for more information.
Setting Up and Using SOA Instance Tracing
Instance Tracing allows you to trace the message flow across SOA Composites and SOA Infrastructures monitored by Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. The flow of message can be traced across servers, clusters, and WebLogic domains.
The section contains the following topics:
Configuring Instance Tracing (SOA 11g Targets Only)
Before enabling Instance Tracing, ensure that the SOA infrastructure is monitored by an Oracle Management Agent.
To enable Instance Tracing for any SOA Infrastructure 11g instances involved in executing composite instances:
- Set the host and the WebLogic Domain preferred credentials using Target Setup Verification. For details, see Configuring the SOA Suite with Target Verification.
- To view the state of the listed SOA instances, enable the Capture Composite State flag on the instance tracing page as follows:
- On the SOA Infrastructure home page, from SOA Infrastructure menu, select Fusion Middleware Control.
- Navigate to the home page of the SOA Infrastructure target.
- From SOA Infrastructure menu, select SOA Administration, and then click Common Properties.
- On the SOA Infrastructure Common Properties page, select the Capture Composite Instance State check box.
Setting Search Criteria for Tracing an Instance
Select the appropriate search link based on the version of your SOA target:
Instance Tracing for SOA 11g Targets
To search for faults and messages, enter details as described in the following table, and click Search.
Table 7-4 Setting Search Criteria
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Instance ID |
Specify the ID of the instance that is to be traced. The flow trace is a runtime trail of a message flow identified by an Instance ID. It enables you to track a message flow that crosses instances of different composites. |
|
Start Time From - To |
The time period the instances were initiated. |
|
Name |
The name of the instance. |
|
Conversation ID |
The conversation ID of the instance. |
|
Instance Count |
The number of instances that should be retrieved by the Search. |
|
ECID |
The ECID enables you to track the message flow across different SOA Composite instances that span across SOA Infrastructure. |
|
Composite Name |
The name of the composite. Use this to restrict your search for business flows to a specific composite. Note that wild-card search is supported. For example, ( |
Click Search after you have specified the required criteria. A list of Instance IDs that meet the criteria are displayed. Click Trace to generate trace data for the specified instance and period.
Note:
To trace an instance, credentials must be set for the WebLogic domain of each SOA Infrastructure monitored by Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control and for the host on which the Management Agent monitoring each SOA Infrastructure application is present.
Click the Instance ID link to see the flow trace which includes the list of SOA Infrastructure instances involved in the flow, faults, the domain, and the list of faults.
Instance Tracing for SOA 12c Targets
To search for faults and messages, enter details as described in the following table, and click Search.
Table 7-5 Setting Search Criteria
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Time |
Use this filter to restrict your query to a specific time in the past. A time filter is required to search for faults. Ensure that you enter appropriate values in Instance Created From and Instance Created To fields. By default, all the instances created in the last one day are displayed. Additionally, you can add the following filters:
|
|
Composite |
Use to restrict your search for business flows to a specific composite. If you trace an instance at the composite level, then the Composite value is pre-populated. However, if you trace an instance at SOA infrastructure level, then select any of the following:
Click the torch icon. In the Search and Select Targets wizard, select the target name from the table and click Select. A faults search is performed on the selected composite. |
|
Sensor |
Ensure that you select a composite to view the sensors associated with it. |
|
Flow Instance |
Flow ID: Use this to search for the flow ID of the business flow instance. Flow Correlation ID: Use this to search for the flow correlation ID of the business flow instance. Initiating ECID: Use this to search for the ECID of the business flow instance. Flow Instance Name: Use this to search for unique system and business identifiers that help you isolate a specific flow instance Composite Instance Name: Use this to specify the name or title of the composite instance name. |
|
State |
Select one of the following states: Select Active to search active instances. If you select a blank, then the filtering is ignored.
Select Inactive to search inactive instances. If you select a blank, then the filtering is ignored.
|
|
Fault |
Use to limit your search for business flows to only those with faults. If you leave this field blank, the Fault filter is ignored. To search for faults in any state, select All. To search for faults in a particular state, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Type |
To search for all types of faults, select All To search for a particular type of fault, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Owner |
Use the Name field to enter a fault owner name. Ensure that the name entered is in the following format:
Use this to further filter your search for faulted business flows to stuck flows awaiting a particular type of recovery action from the administrator. To search for faults belonging to all the owners, select All. To drill down to a particular fault owner, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Details |
You can fine grain your search parameters to drill down to granular result by providing all or some of the following details:
Expand Other to display additional fields for filtering:
|
|
Restrict Search Rows |
By default, the search results are restricted to 10 rows in the table. If you want to modify this limit or restriction, enter a suitable value. The highest value you can enter as the limit depends on the limit set on the OMS. When no limit is set on the OMS, the limit that is honored by default is 2000, so the default range you can enter in the Restrict Search Result (rows) field is 1 to 2000. To modify this maximum limit set on the OMS, run the following command: Note: The higher the value you set as the limit, the longer the time it takes to retrieve the faults, and that entering a higher value than the default in Restrict Search Result (rows) can lead to longer time to get the faults, and hence a longer load time. |
Tracing an Instance Within a SOA Infrastructure
To trace an instance within the context of a SOA Infrastructure, follow these steps:
Tracing Instance Across SOA Infrastructures
To trace an instance across SOA Domains, follow these steps:
- In Cloud Control, from the Targets menu, select Middleware.
- On the Middleware page, click the target you are interested in. For example, SOA Infrastructure.
- From the SOA Infrastructure menu, select Trace Instance.
- On the Instance Tracing page, perform instance search. To do so, see Table 7-5.
- Select an instance, and Click Trace.
- In the Trace Instance dialog box, click Add to add the other SOA Infrastructure targets where this SOA instance has been executed.
- In the Search and Add targets dialog box, select the other SOA Infrastructure targets, and click Select.
- Click Set to set the WebLogic Domain Credentials, and Host Credentials if you haven't already set them.
- Click OK. A flow trace job is scheduled to run immediately to collect the instance trace data across domains. On completion, a status is displayed in Trace Job Status column. Click the status link to drill down to the Flow Trace page.
- Click OK.
Viewing Composite Heat Map
Composite heat map is a graphical representation of a set of metrics depicted as colored boxes.
To view the composite heat map follow the steps below:
Metric size represents the size of the block. The bigger the block the higher the numeric value of the metric size. Metric color represents the color code of the metric defined by you. In the color scroll bar, the left slider with a number indicates the number below which the metric is displayed as green and similarly the right slider with the number indicates the number above which the metric is displayed in red. The number range (metric range) between the left slider and the right slider is denoted by the range of colors in between green and red.
Note:
Heat map displays the blocks or nodes only for the composites that have values above 0.In the heat map display, if you want to view the details of a box, click the box. A complete summary of the service is displayed in a dialog box. You can view the details on a chart that helps you analyze how the service is being used over a period of time. The same analysis is available in a table format as well.
Monitoring Dehydration Store
The Dehydration Store Diagnostics feature provides a dedicated view that allows you to analyze the behavior of the SOA Dehydration database. You can monitor SQL performance metrics and table growth specifically in the context of the SOA Suite's use of the database. The view displays both throughput and wait bottleneck data which allows you to monitor the general health of the target database instance. Using Active Session History, you can track usage data and display it as a table space chart, a growth rate chart, or an execution chart.
Note:
In addition to monitoring Oracle standalone database, the Dehydration Store now supports reviewing the general health of the RAC database engine, and identifying problems that are causing performance bottlenecks.
You can also monitor Real Application Cluster (RAC) databases. For RAC, you can monitor Multi Data Source and GridLink Data Sources. In RAC scenario, the Dehydration Store Performance tab lists all the associated database nodes in the form of a drop down menu. You can select any particular instance from the Show Database Instance menu, and view the associated metric data.
Enabling Monitoring of the SOA Dehydration Store
To configure and enable monitoring of the SOA Dehydration Store, follow these steps:
- From the Targets menu, select Databases to check if the database target representing the SOA Dehydration Store has been discovered in Enterprise Manager.
- Check if at least one configuration for the SOA Infrastructure and WebLogic Server targets is available.
- Navigate to the Target Verification page to run the functionality check for dehydration store. For more details, see Configuring the SOA Suite with Target Verification.
If you do not see data after these configuration details have been specified, you must wait for the next collection interval.
Publishing a Service to UDDI
To publish a service to UDDI, navigate to the Services and References Home page, select a service from the table and click Publish to UDDI from the menu. The Publish Service to UDDI window is displayed with the following fields:
-
Service Name: The name of Web Service to be published to the UDDI Registry. This is a Read Only field.
-
Service Description: The description of the selected Web Service.
-
Service Definition Location: The URL location of the Service Definition. This is a Read Only field.
-
UDDI Source: A logical name for an external UDDI registry source. Select the UDDI Source from the drop-down list.
-
Business Name: The name of the data structure in the UDDI registry. Select a Business Name that has been registered with the UDDI from the list.
Click OK to start the process that publishes the web service to UDDI or click Cancel to cancel publishing the service.
Generating SOA Reports
This section describes the steps to use Enterprise Manager to print SOA reports using BI Publisher Enterprise Reports, or using Information Publisher.
Generating SOA Reports Using BI Publisher
Note:
Beginning with Enterprise Manager Cloud Control 13c Release 5, Oracle Analytics Publisher (formerly BI Publisher) must be accessed from a standalone Oracle Analytics Server. For more information, see Oracle Analytics Server in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Administrator's Guide.
Generating SOA Reports Using Information Publisher
This section describes the procedure to create SOA Reports.
Note:
These reports can be generated only for SOA 11g targets. Information Publisher reports are not supported for SOA 12c targets.
-
From the Targets menu, select Middleware, and click on a SOA Infrastructure target. The SOA Infrastructure Home page appears.
-
From the SOA Infrastructure menu, select the Information Publisher Reports.
The out-of-box SOA reports are displayed under the SOA Performance Reports section.
-
Select a report from the section (for example, you can select Pending Instance Statistics) and click Create Like. The Create Report Definition page is displayed.
-
In the General page, enter the following details:
-
Enter the BPEL Process Name as the title.
-
Click the Set Time Period to set the time interval for the report.
-
Click the Run report using target privileges of the Report Owner (SYSMAN) check box in the Privileges section.
-
-
Click the Elements tab and click the Set Parameters icon for the Pending Instance Statistics Element in the table.
-
In the Set Parameters page, click the torch icon to select a Composite Name. The Result Set Size with default values for the Pending Instance Statistics report is displayed.
-
Select a Component Name from the list, enter the Result Set Size and click Continue to return to the Elements page.
-
The selected target name is displayed in the Elements table.
-
To schedule periodic report generation, click the Schedule tab.
-
Specify the schedule type and other details and click OK.
-
You will return to the Report Home page where the newly scheduled report is displayed in the table. Click the report name to view the details.
Generating SOA Diagnostic Reports
To collect the SOA diagnostics data from SOA Dehydration Store, and generate report, follow these steps:
Exporting a Composite .jar File
Exporting a Composite from a SOA instance provides you the option of deploying it on another SOA instance. The export feature allows administrators to:
-
Export a Composite from the on-premise SOA instance
-
Export a Composite from the SOACS on the cloud
To export a Composite .jar file perform the following steps:
Provisioning SOA Artifacts and Composites
The SOA Artifacts Deployment Procedure allows you to:
-
Provision SOA Artifacts from a reference installation or from a gold image.
-
Create a gold image of the SOA Artifacts.
-
Provision SOA Composites either from the Software Library or from another accessible location.
Note:
The features listed above are also supported on the SOA instances running on the cloud.For more details on the SOA Artifacts Deployment Procedure, see the Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patching.
Diagnosing Issues and Incidents
To access the diagnostic data for problems and incidents, access the Support Workbench page. To do so, navigate to the SOA Infrastructure Home page, and from the SOA Infrastructure menu, select Diagnostics, then select Support Workbench.
Enter the credentials for the host on which the WebLogic server is running and the WebLogic credentials for the WebLogic server. Click Continue to log into the Support Workbench page. On this page, you can do the following:
-
View problem or incident details.
-
View, create, or modify incident packages.
-
View health checker findings.
-
Close resolved problems.
Searching Faults in the SOA Infrastructure
This section describes how you can search faults in the SOA infrastructure. In particular, you can perform the following tasks:
Overview of Faults and Fault Types in SOA Infrastructure
The following are the types of SOA composite application faults displayed in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control:
-
Business: Application-specific faults that are generated when there is a problem with the information being processed (for example, a social security number is not found in the database).
-
System: Network errors or other types of errors such as a database server or a web service being unreachable.
-
Oracle Web Service Manager (OWSM): Errors on policies attached to SOA composite applications, service components, or binding components. Policies apply security to the delivery of messages.
The following are the categories of SOA composite application faults in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control:
-
Recoverable
-
Business faults and some specific system faults
-
Oracle Mediator input file path and output directory mismatch
-
An Oracle BPM Worklist user is not authorized to perform relevant (expected) actions
-
-
Nonrecoverable
-
Rejected messages
-
Most system faults
-
Non-existent references
-
Service invocation failures
-
Policy faults
-
-
Rejected Messages
A fault is classified as a rejected message based on where it occurs. If a fault occurs before entering a SOA composite, without generating a composite instance, it is classified as a rejected message. A system or a policy fault can be identified as a rejected message.
Overview of the Recovery Actions for Resolving Faults
Recovery actions enable you to recover or resolve the SOA composite application faults. The following describes the recovery actions supported for different SOA engines.
Table 7-6 Overview of the Recovery Actions for Resolving Faults
| Recovery Action | Description | Applicable To SOA Engine Type |
|---|---|---|
|
Retry |
Retries the instance directly. An example of a scenario in which to use this recovery action is when the fault occurred because the service provider was not reachable due to a network error. The network error is now resolved. |
|
|
Abort |
Terminates the entire instance. |
|
|
Continue |
Ignores the fault and continues processing (marks the faulting activity as a success). |
|
|
Rethrow |
Rethrows the current fault. BPEL fault handlers (catch branches) are used to handle the fault. By default, all exceptions are caught by the fault management framework unless an explicit rethrow fault policy is provided. |
|
|
Replay |
Replays the entire scope again in which the fault occurred. |
|
Prerequisites for Searching, Viewing, and Recovering Faults
Meet the following prerequisites before searching, viewing, and recovering SOA composite application faults:
Set the following as preferred credentials. These credentials can be set from the Target Setup Verification page. To do so, from the Targets menu, select Middleware. On the Middleware page, click the target you are interested in. For example, SOA Infrastructure. On the Home page of the target, from the target-specific menu, select Target Setup, and click Verification:
-
Credentials of the host on which the SOA server is running.
-
Administrator credentials of the Oracle WebLogic Domain.
Searching and Viewing Faults
To search and view SOA composite application faults, follow these steps:
Setting Search Criteria
To search for faults and messages, enter details as described in the following table, and click Search.
Table 7-7 Setting Search Criteria
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Time |
Use this filter to restrict your query to a specific time in the past. A time filter is required to search for faults. Ensure that you provide values in the Fault Time From and Fault Time To fields. For example, enter 1/13/14 5:33:25 AM and 2/13/14 5:33:25 AM in the respective fields to query for all the faults that have occurred in this one month time window. |
|
Composite |
Use to restrict your search for business flows to a specific composite. Click the torch icon. In the Search and Select Targets wizard, select the target name from the table and click Select. A faults search is performed on the selected composite. |
|
Flow Instance |
Enter the Flow ID to isolate a specific flow instance. For each workflow involving different composites a unique flow ID gets generated. When there is an error in any component in a particular flow, the ID gets listed on the Faults and Rejected Messages tab. This ID is useful in assessing the error trend. |
|
Fault |
Use to limit the search for business flows to only those with faults. If you leave this field blank, the Fault filter is ignored. To search for faults of any type, select All or blank. To search for faults in a particular type, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Type |
To search for all types of faults, select All. To search for a particular type of fault, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Owner |
Use this to further filter your search for faulted business flows to stuck flows awaiting a particular type of recovery action from the administrator. To search for faults belonging to all the owners, select All. To drill down to a particular fault owner, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Details |
You can fine grain your search parameters to drill down to granular result by providing all or some of the following details:
Expand Other to display additional fields for filtering:
|
|
Restrict Search Rows |
By default, the search results are restricted to 10 rows in the table. If you want to modify this limit or restriction, enter a suitable value. The highest value you can enter as the limit depends on the limit set on the OMS. When no limit is set on the OMS, the limit that is honored by default is 2000, so the default range you can enter in the Restrict Search Result (rows) field is 1 to 2000. To modify this maximum limit set on the OMS, run the following command: Note: The higher the value you set as the limit, the longer the time it takes to retrieve the faults, and that entering a higher value than the default in Restrict Search Result (rows) can lead to longer time to get the faults, and hence a longer load time. |
Finding Total Faults in the SOA Infrastructure
To find the total faults in the SOA infrastructure, follow these steps:
Limiting Faults Searched and Retrieved from the SOA Infrastructure
When you search for faults in the SOA infrastructure, the search might result in numerous faults. By default, the search results are restricted to 500 rows in the table. However, you can choose to modify this limit if you want.
To modify the limit, set the Restrict Search Result (rows) field to a suitable value while setting the search criteria (see Setting Search Criteria). Then search.
The highest value you can enter as the limit depends on the limit set on the OMS. When no limit is set on the OMS, the limit that is honored by default is 2000, so the default range you can enter in the Restrict Search Result (rows) field is 1 to 2000.
To modify the maximum value set on the OMS, run the following command:
emctl set property -name oracle.sysman.core.uifwk.maxRows -value <max_limit_value>
Caution:
The higher the value you set as the limit, the longer it takes to retrieve the faults. Entering a higher value than the default in Restrict Search Result (rows) field can lead to longer time to get the faults, and therefor result in a longer load time.
Searching Only Recoverable Faults
There might be numerous faults in the SOA infrastructure, but you can search and view only the recoverable faults. For example, there might be 700 faults in total, but there may be only 550 recoverable faults; you can search and list only those 550 faults if you want.
To search only for recoverable faults, while searching for faults, set the search criteria with the Fault State list set to Recoverable. If you set it to All, then faults that are recoverable and not recoverable are searched and listed.
For more information, see Searching and Viewing Faults.
Searching Faults in a Particular Service Engine
There might be faults across various service engines such as BPMN, Mediator, Business Rules, and Human Workflow. You can search and view only faults occurred in a particular service engine.
To search for faults in a particular service engine, set the search criteria with the Component Type list set to a particular service engine of interest. Then search.
For more information, see Setting Search Criteria.
Searching Faults by Error Message
There might be numerous errors in the SOA infrastructure, but you might be interested only in those errors that contain some keywords of your interest. For example, you might be interested only in errors that contain the word ORAMED. You can search and view faults with such keywords.
To search faults by error messages, set the search criteria with the Error Message Contains field set to some keywords of your interest. Then search.
Note:
-
By default, the entered keywords are searched anywhere in the error message.
-
The keywords you enter are case sensitive.
-
The only wildcard character permitted is
%,which signifies all or anything after, before, or between two keywords. For example,BPEL%faultwill result in faults with the error messageBPEL is a fault.
For more information, see Setting Search Criteria.
Filtering Displayed Search Results
When you set the search criteria and search for faults in the SOA infrastructure, and when the search results appear in the results table, you can filter the search results further to show only those rows or fault instances that interest you, based on a keyword entered in the column header.
For example, from the displayed fault instances, to filter and view only the bpel service engine's results, enter the keyword bpel in the textbox placed above the Component Type column header. This is essentially the value shown in the bpel fault instance row for the Component Type column.
To filter the displayed search results, follow these steps:
Recovering Faults in Bulk
The process of recovering similar type of faults in a single operation is called Bulk Recovery. In case of SOA 11g targets all the Recoverable faults can be recovered through bulk recovery option, and similarly for SOA 12c targets, all the Recovery required faults can be recovered through bulk recovery.
Note:
For SOA 12c targets, you can supply either the composite details or the fault details to recover faults. It is mandatory that you supply at least one of these parameters, if not, bulk recovery cannot be performed. For SOA 11g targets, you must supply the composite details.
Bulk recovery can be performed when the following criteria are met:
-
All faults to be recovered are in the same partition.
-
The recovery required count is greater than zero.
-
The Fault Owner type of the selected row is bpmn, mediator or bpel.
-
A state for the fault is specified.
You can perform bulk recovery from Faults and Rejected Messaged tab, or Error Hospital tab available on the SOA Infrastructure home page. This way, the context of the fault is maintained, and is accordingly pre-populated on the Create Bulk Recovery Page. However, if you access it from the Bulk Recovery Jobs page, you will need to enter all the details afresh.
In particular, this section covers the following:
Performing Bulk Recovery from the Bulk Recovery Jobs Page
To directly recover a large number of faults from the SOA database, follow these steps to perform a bulk recovery:
Note:
For a SOA 12c target, faults with following recovery states are recovered:
-
Admin Recovery
-
Mediator Recovery
-
BPEL Invoke Message Recovery
-
BPEL Callback Message Recovery
-
BPEL Activity Message Recovery
However, faults with recovery states EDN Recovery, Rejected Messages Recovery, and Human Workflow Recovery, cannot be recovered.
For a SOA 11g target, all faults with state Recoverable are recovered. However, faults with recovery states BPEL messages, rejected messages, and human workflow faults cannot be recovered.
Setting Fault Details for Recovering Faults in Bulk
To set the fault details while recovering faults in bulk, follow these steps:
-
In the Fault Details section, from the Engine Type menu, select an engine, so that fault search could be restricted to the selected type.
-
From the Fault Type menu, select the type of fault you want to recover. This could be, System Faults, Business Faults, or OWSM Faults.
-
In the Error Message Contains field, enter a keyword you are looking for in the error messages so that only faults with such error messages are recovered.
-
In addition to this, you can refine your fault search by providing details like Fault Name, Fault Code, HTTP Host, and JNDI Name.
Setting Recovery and Batch Details for Recovering Faults in Bulk
To set the recovery and batch details for recovering faults in bulk, follow these steps:
-
In the Recovery Options section, from the Recovery Action list, select a recovery action.
-
By default, Batch by Fault Time is enabled so that faults can be grouped into multiple, smaller units or batches based on the time they were created, and run sequentially. Oracle recommends that you keep the option enabled to simplify the fault recovery process. However, if you do not want to create batches for some reason, then deselect this option.
-
If you keep the Batch by Fault Time option enabled, then do the following:
-
By default, the batches are created with faults that occurred within every 60 minutes. If you want to change this time period, then enter a value in minutes in the Batch Time Period field. The minimum time period is 5 minutes and the maximum time period is 360 minutes.
-
By default, the delay time between two batches is set to 300 seconds. If you want to change this delay time, then enter a value in seconds in the Delay between batches (sec) field. The minimum delay time is 5 seconds and the maximum delay time is 900 seconds.
-
Batch Recovery esures that all the faults that occurred in the specified fault time period are recovered in a phased manner. For example, lets assume: Fault time period: 1 Mar 2013 2.00am to 1 Mar 2013 3.00am Batch time period: 10mins Batch Delay: 300secs (i.e 5mins) This means, there are 60mins/10mins = 6 batches in all. The first batch recovers faults between 2.00am to 2.10am. The second batch recovers faults between 2.10am to 2.20am, and so on. After each batch runs, there is a delay of 300secs (5mins), after which the next batch execution begins.
Scheduling Bulk Recovery Jobs to Run Once or Repeatedly
To schedule bulk recovery jobs, on the Create Bulk Recovery page, in the Job Parameters section, select one of the following options:
-
To run the jobs only once, select one of these options:
-
Immediately, if you want to run the job immediately.
-
Later, if you want to run the job just once, at a schedule date and time, and not immediately.
-
-
To run the jobs repeatedly at a set frequency, select an appropriate value from the Repeat menu, and set the corresponding frequency.
Note: For a repeating job, ensure that you do not set a custom time period. If you do so, the job cannot track the faults properly, and in-turn recovers the same faults again and again. Instead, you can set a relative time period. For example, select Last 1Day from the Fault Occurred menu.
-
To set a grace period, select Do not run if it cannot start within, and set an appropriate grace period.
A grace period is a period of time that defines the maximum permissible delay when attempting to run a scheduled job. If the job system cannot start the execution within a time period equal to the scheduled time + grace period you set, then it skips the job. By default, all jobs are scheduled with indefinite grace periods.
Performing Bulk Recovery from Faults and Rejected Messages Tab
To recover a large number of faults from the SOA database, follow these steps:
Note:
For a SOA 12c target, faults with following recovery states are recovered:
-
Admin Recovery
-
Mediator Recovery
-
BPEL Invoke Message Recovery
-
BPEL Callback Message Recovery
-
BPEL Activity Message Recovery
However, faults with recovery states EDN Recovery, Rejected Messages Recovery, and Human Workflow Recovery, cannot be recovered.
For a SOA 11g target, all faults with state Recoverable are recovered. However, faults with recovery states BPEL messages, rejected messages, and human workflow faults cannot be recovered.
Performing Bulk Recovery from the Error Hospital Tab
To recover a large number of faults from the SOA database, follow these steps:
Note:
For a SOA 12c target, faults with following recovery states are recovered:
-
Admin Recovery
-
Mediator Recovery
-
BPEL Invoke Message Recovery
-
BPEL Callback Message Recovery
-
BPEL Activity Message Recovery
However, faults with recovery states EDN Recovery, Rejected Messages Recovery, and Human Workflow Recovery, cannot be recovered.
For a SOA 11g target, all faults with state Recoverable are recovered. However, faults with recovery states BPEL messages, rejected messages, and human workflow faults cannot be recovered.
Tracking Bulk Recovery Jobs
This section describes the following:
Tracking Bulk Recovery Jobs, and Viewing Their Results and Errors
To track bulk recovery jobs and view their results and errors, follow these steps:
Creating Bulk Recovery Jobs Using EMCLI and Web Services
You can create Bulk Recovery Jobs for a SOA Infrastructure Target from the command line using EM CLI, from EM Job Systems using Web-Service Interface, or from Cloud Control UI.
This section contains the following sections:
Creating Bulk Recovery Jobs Using EMCLI
In EM CLI, use EM job system's get_jobs command to submit bulk recovery jobs. The inputs to the job are supplied using a properties file.
To create the bulk recovery job using EMCLI, follow these steps:
-
Log in to EMCLI. For example:
emcli login -username=sysman
-
Find out the input parameters to be entered in the property file to run the bulk recovery job. To do so, run the following command:
emcli describe_job_type -type=SOABulkRecovery
-
Use any editor to open the properties file, and provide your inputs. You can then save and close the properties file.
Using any editor, create a new text file. For example,
temp.propertiesHere is a sample Property File: target_list=<soa-infra target name>:oracle_soainfra variable.CompositeList=<composite1 target name>, <composite 2 target name> variable.BatchDelay=300 variable.BatchSize=10 variable.EnableBatching=1 variable.EngineType=BPEL variable.ErrorMsg=xxxx variable.FaultStartTime=01-01-2013 00:00:00 PST variable.FaultEndTime=01-02-2013 00:00:00 PST variable.FaultTimePeriod=Custom variable.RecoveryAction=ContinueNote:
Currently, Oracle supports only one SOA-Infrastructure target to be entered in the target_list property.
-
Run the following command to submit a bulk recovery job with the updated property file as an input:
emcli create_job -name=bulk522 -job_type=SOABulkRecovery -input_file=property file:/tmp/temp.properties
-
Set the preferred credentials or named credentials for the WebLogic Domain and SOA Server Host. By default, the job uses the preferred credentials, that is, WebLogic Administrator Credentials for the WebLogic domain and Normal Host Credentials for the SOA Server hosts.
To set the preferred credentials, run the following commands:
Setting WebLogic Domain Credentials: emcli set_preferred_credential -target_type=weblogic_domain -target name=<weblogic domain target name> -set_name=WLCredsNormal -credential name=<existing named credential name> -credential_owner=<user> Setting SOA Host Credentials: emcli set_preferred_credential -target_type=host -target_name=<host target name> -set_name=HostCredsNormal -credential_name=<existing named credential name> -credential_owner=<user>
Alternately, you can override the preferred credentials by supplying the named credentials as an input to the property file for the current submission.
Following example describes how to set the named credentials for the WebLogic Domain and SOA Server host:
target_list=<SOA-Infra TargetName>:oracle_soainfra cred.SOAAgentHostCred.<slc01nbo.us.example.com>:<host>=NAMED:xxxx cred.SOADomainCreds.<target_name>:<target_type>=NAMED:xxxx
Viewing the Submitted Jobs and Outputs Using EMCLI
The following table describes certain other operations that can be performed using EMCLI commands.
Table 7-8 EMCLI Commands For Bulk Recovery
| EMCLI Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
|
This EMCLI command to view all the Bulk Recovery Jobs that have been submitted. |
|
|
|
This EMCLI command to view the output of the Bulk Recovery job execution. To view the details of the job steps, you need to supply the Execution ID of the job. Note: The output of the job that is displayed using the EMCLI command is unstructured. For a complete and structured report of the output, log in to Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. From Enterprise menu, select Job, and then click Activity. On the Job Activity Page, in the Advanced Search region, enter the name of the job, and then click Go. Select the job, and drill down to the steps by click Expand All. |
Run the following command to get the Execution ID of the job:
Use the Execution ID in the following command to view the details of the job submitted:
|
Creating Bulk Recovery Jobs through Web-Service
In addition to EM User Interface and EMCLI, you can also use Web-Service Interface provided by EM job system to create Bulk Recovery Jobs. The web-service interface of the Job System is available by default in an EM installation, and the URL for the WSDL is as follows:
<protocol>://<machine>:<port>/em/websvcs/extws/JobControlService?wsdl
The EM job system web services are implemented as Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) end-points. Client programs can access these end-points using a variety of languages like Java, C++, and Ruby. The web service is used by sending a SOAP request message to one of the end-points, and retrieving the corresponding response message.
Typically, the operations exposed by Job system in the Web-Service Interface is very similar to the EMCLI operations such as create_job, describe_job_type, and so on.
WorkFlow Examples for Bulk Recovery
This section covers the following examples:
Running Bulk Recovery Job Every Night
To schedule a bulk recovery job that runs at 12.00am every night, to recovers faults that have occurred through the day:
-
In the composites section, add the desired composites.
-
In the Time section, enter the following values:
-
For a SOA 12c target, from Instance Created menu, select Custom, and provide the custom values. To recover instances created during the day alone, select Last 1 Day.
-
From the Fault Occurred menu, select Last One Day.
-
Click Estimate Faults to view the number of faults that will be recovered.
-
-
In the Fault Details section, enter appropriate values.
-
In the Recovery Option section, enter the following values:
-
Select Batch by Fault Time.
-
In Batch Time Period, enter 10 mins. This would mean that, every batch would recover faults in 10mins time window. Since you have already selected Last One day (Fault Time From value), there will be 24*60 / 10 = 124 batches in all.
-
In Delay Between Batches, enter 200 secs. This will be the delay between each batch. The main intention behind a delay is to allow the SOA System time to stabilize after each recovery.
-
-
In the Job Parameters section, enter the following values:
-
Select Immediately to start the job as soon as it is submitted.
-
From repeat menu, select Every N Days.
-
Enter Frequency as 1 day.
-
-
Click Submit.
One Time Job with Specific Time Interval to Recover Faults
To schedule a bulk recovery job that runs one time, and recover faults in a specific time interval, follow these steps:
-
In the composites section, add the desired composites.
-
In the Time section, enter the following values:
-
For a SOA 12c target, from Instance Created menu, select Custom, and provide the custom values. To recover instances created during the day alone, select Last 1 Day.
-
From the Fault Occurred menu, select Custom. Enter 3:00 am in Fault Time From field, and 4:00 am in Fault Time To fields.
-
Click Estimate Faults to view the number of faults that will be recovered.
-
-
In the Fault Details section, enter appropriate values.
-
In the Recovery Option section, enter the following values:
-
Select Batch by Fault Time.
-
In Batch Time Period, enter 10 mins. This would mean that, every batch would recover faults in 10mins time window. Since you have selected a time window of one hour (3:00 am to 4:00 am), there will be 60 / 10 = 6 batches in all.
-
In Delay Between Batches, enter 200 secs. This will be the delay between each batch. The main intention behind a delay is to allow the SOA System time to stabilize after each recovery.
-
-
In the Job Parameters section, enter the following values:
-
Select Later, and provide a date and time to schedule the job.
-
From repeat menu, select Do not repeat.
-
Enter Frequency as 1 day.
-
-
Click Submit.
Generating Error Hospital Reports
Use the Error Hospital page to view an aggregate count of errors that have occurred in all SOA Composites deployed in the SOA Infrastructure. This page does not list out individual faulted instances. To view the individual flows that have faults, go to the Faults and Rejected Messages tab on the SOA Infrastructure Home page.
The Error Hospital page is available at the SOA Infrastructure level, where system-wide faults data is aggregated. When accessed at the partition level, the Error Hospital page is limited to faults data associated only with that partition.
The Error Hospital page is arranged in the following sections:
-
Search Region: You can update the necessary filters available in the Search section to drill down to a more granular result that meets your requirements. By default, the total faults that have occurred across all instances created in the last 24 hours is displayed. You must provide the Instance Created From and Instance Created To values as they are mandatory fields. In addition to these values, you may specify a time window for the fault to restrict your query to a specific time in the past.
Additionally, you can select the fault attribute by which data is aggregated. For example, if you select Fault Code, each row in the first column represents a specific code and the remaining columns show the fault statistics aggregated for each code.
-
Error Hospital Report Table: This table displays a report based on the filters specified in the search region. The data is always aggregated by one of the primary fault attributes selected from the list such as Fault Name, Fault Code, and so on. The default aggregation is by Fault Name. This report enables you to assess the error trends. For example, aggregate by Fault Code to see which code has the most faults. You can then select a single row which has maximum faults from the table, and perform a bulk recovery.
-
Charts Region: The details of the Error Hospital Report are also available in a chart form. Essentially, the top faults aggregated by Fault Name are represented in a bar chart. The pie chart depicts the recovery required faults as against non-recoverable faults.
The major advantages are:
-
Error Hospital Report acts as a quick view of fault count for administrators to determine the error trends.
-
A consolidated report with all an aggregate error count is available on a single page.
-
You can also perform bulk recovery on a selected group of similar faults in a single operation.
-
Autoretries feature allows system to continuously retry a recoverable fault. When a fault is in recovery required state and an autoretry is setup, then a automated system call is generated at a certain interval to try and recover the error. This feature greatly benefits the Administrator as they have lesser faults to manually track.
-
Trace Instance option allows you to navigate to the Instance Tracing page based on the fault group selected.
To set the search criteria for Error Hospital, enter details as described in the following table, and click Search.
Table 7-9 Setting Search Criteria for Error Hospital
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Time |
Use this filter to restrict your query to a specific time in the past. A time filter is required to search for faults. Ensure that you enter appropriate values in Instance Created From and Instance Created To fields. By default, all the instances created in the last one day is displayed. Additionally, you can add the following filters:
|
|
Composite |
Use to restrict your search for business flows to a specific composite. You can select the following option:
Click the torch icon. In the Search and Select Targets wizard, select the target name from the table and click Select. A faults search is performed on the selected composite. |
|
State |
Select one of the following states: Select Active to search active instances. If you select a blank, then the filtering is ignored.
Select Inactive to search inactive instances. If you select a blank, then the filtering is ignored.
|
|
Fault |
Use to limit the search for business flows to only those with faults. If you leave this field blank, the Fault filter is ignored. To search for faults of any type, select All or blank. To search for faults in a particular type, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Type |
To search for all types of faults, select All To search for a particular type of fault, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Owner |
Use the Name field to enter a fault owner name. Ensure that the name entered is in the following format:
Use this to further filter your search for faulted business flows to stuck flows awaiting a particular type of recovery action from the administrator. To search for faults belonging to all the owners, select All. To drill down to a particular fault owner, select one of the following:
|
|
Fault Details |
You can fine grain your search parameters to drill down to granular result by providing all or some of the following details:
Expand Other to display additional fields for filtering:
|
|
Restrict Search Rows |
By default, the search results are restricted to 10 rows in the table. If you want to modify this limit or restriction, enter a suitable value. The highest value you can enter as the limit depends on the limit set on the OMS. When no limit is set on the OMS, the limit that is honored by default is 2000, so the default range you can enter in the Restrict Search Result (rows) field is 1 to 2000. To modify this maximum limit set on the OMS, run the following command: Note: The higher the value you set as the limit, the longer the time it takes to retrieve the faults, and that entering a higher value than the default in Restrict Search Result (rows) can lead to longer time to get the faults, and hence a longer load time. |
In particular, you can perform the following tasks from this page:
Generating an Error Hospital Report
To generate and view an error counts that have occurred across all SOA Composites using the search fields, follow these steps:
Recovering BPMN Messages
To find recoverable instances of the BPEL or BPMN Service Engine, follow these steps:
Troubleshooting
This section describes the errors you might encounter while discovering the SOA Suite 11g and the workaround steps you can follow to resolve each of them.
This section covers the following:
Discovery
The following error occurs when the SOA instances are being discovered.
Table 7-10 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
New SOA Composite deployed on the SOA Server from JDeveloper are not displayed automatically in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. |
To discover the newly deployed SOA Composites in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, you must run the Refresh Farm menu option for the associated WebLogic Domain. |
Monitoring
The following error occurs when the collection frequency causes a delay in the collection of configuration data.
Table 7-11 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
All metrics are not displayed. |
Enterprise Manager Cloud Control uses the Management Agent to collect metric data. For the first collection, the agent may need 15 minutes to upload the metric data. |
Metric Collection |
If target setup verification is not run, you may see metric collections errors for a few metrics. Collection is suspended for these metrics till you unsuspend them. To batch unsuspend metrics with collection errors for SOA infrastructure targets, use the |
Instance Tracing Errors
The following error occurs when the instance is traced.
Instance Search Fails - Same reason as BPEL first column. If Management Agent is down or unreachable.
Table 7-12 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Instance Tracing Job Fails |
|
Recent Faults
The following errors occur when:
-
All instances with faults are not displayed as only the last 10 values are collected.
-
The most recently collected fault instances do not appear in the Faults and Messages page.
Table 7-13 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
All instances with faults are not populated in Enterprise Manager Cloud Control. |
By default, you can only view the latest 10 faults collected during the last 15 minutes. To view additional faults, navigate to Fusion Middleware by clicking the link in the General section on the target Home page. |
Fault Management
This section contains the troubleshooting information for fault management:
Bulk Recovery
In general when there is a Bulk Recovery Error, follow these steps to navigate to the page that describes the errors:
-
In Cloud Control, from the Targets menu, select Middleware.
-
On the Middleware page, click the SOA Infrastructure target.
-
On the SOA Infrastructure target page, from the SOA Infrastructure menu, select Fault Management, then select Bulk Recovery.
-
On the Bulk Recovery Jobs page, select the job that has failed.
-
On the Bulk Recovery Job Details page, in the Job Failure Error section, check the Parsed Error Message and Error Details fields to understand about the error because of which the job failed.
The following are some of the error messages that you may see in the Parsed Error Message field along with their suggested fixes:
Table 7-14 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
java.lang.IllegalArgumentExcept on: Invalid Job Identifier! The specified identifier does not match any valid fault recovery jobs. java.lang.IllegalStateException The results job xxxx are not available because the processing has not yet completed. |
|
t3://slc03dms.us.example.com:8001 javax.naming.CommunicationExce ption [Root exception is java.net.ConnectException: t3://slc03dms.us.example.com:8001 /soa-infra: Destination unreachable; nested exception is: java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused; No available router to destination] |
Ensure that the SOA Infrastructure is up and running, and submit another bulk recovery job with the same parameters. |
Fault Search and Recovery
The following error occurs when you are unable to connect to the SOA Infrastructure target:
Table 7-15 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Error connecting to SOA Infra t3://slc03dms.us.example.com:80 01. |
Ensure that the SOA Infrastructure is up and running. |
Fault Management and Instance Tracing Errors
The following errors occur when the SOA database is not functional:
Table 7-16 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Error occured when getting faults Java.rmi.RemoteException: EJB Exception: ; nested exception is: java.lang.RuntimeException: java.lang.RuntimeException: weblogic.jdbc.extensions.PoolD isabledSQLException: weblogic.common.resourcepool.R esourceDisabledException: Pool SOALocalTxDataSource is Suspended, cannot allocate resources to applications. |
Ensure the SOA Database is up and running. |
t3://slc03dms.us.example.com:80 01 javax.naming.CommunicationExce ption [Root exception is java.net.ConnectException: t3://slc03dms.us.example.com:80 01/soa-infra: Destination unreachable; nested exception is: java.net.ConnectException: Connection refused; No available router to destination] |
Ensure the SOA Database is up and running. |
Error occured when getting faults oracle.sysman.emSDK.agent.comm .exception.ConnectException: Unable to connect to the agent at https://slc03dms.us.example.com :3872/emd/main/ [Connection refused] |
Ensure the SOA Database is up and running. |
Information Publisher Reports
This section lists report related errors.
Table 7-17 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Report generation fails due to invalid database details. |
|
No targets found message for Oracle SOA Composite Reports. |
You cannot use the out-of-box reports directly. You must use the Create Like option to generate custom reports based on the SOA Composite Target type. |
Report generation fails due to invalid host details. |
Set valid credentials for the host target on which the SOA Infrastructure instance is running. |
BI Publisher Reports
This section lists BI Publisher report related errors.
Table 7-18 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Exception Encountered For One of SOA BIP Report If SOA Dehydration Is Not Configured |
If the SOA Dehydration store details are not configured in BI Publisher, the SOA Composite Report (from Dehydration Store) is not generated, and the following exception message is displayed:
To work around this issue, you must manually create the SOA database connection by choosing JDBC Connection from the Administration menu after the BI Publisher setup has been configured. The name of the data source name should be EMSOA 12. Use the following steps to create the EMSOA data source:
Once you have created the EMSOA data source, the issue should be resolved. |
Systems and Services
The following error occurs when you try to refresh a service that has not been created.
Table 7-19 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Create Service option does not work. |
System and service creation depends on the configuration collection of the SOA Infrastructure and related targets. Check the log file for details. |
Refresh Service option does not work. |
The Refresh Service function works for an existing Infrastructure service. In case the service does not exist, it should be created using the Create Service menu option. |
BPEL Recovery
The following error occurs when invalid credentials are provided.
Table 7-20 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Invalid Host and WebLogic Domain Credentials |
For the BPEL Recovery functionality to work, the host credentials and WebLogic Domain credentials must to be available in the preferred credential store. Set the valid credentials and try again. |
SOA License Issue
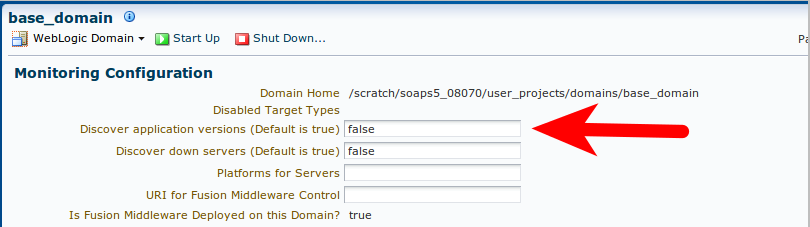
The following error occurs if the SOA Management Pack EE has not been enabled.
Table 7-21 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
The page requested is part of the SOA Management Pack EE. |
The SOA Management Pack EE must be enabled for the specific SOA Infrastructure target. To enable the license, follow these steps:
|
Dehydration Store Issue
Data is not displayed on the Dehydration Store page.
Table 7-22 Error Message
| Error Message | Workaround Steps |
|---|---|
Data is not displayed in the Dehydration Store page. |
This error may occur if there is a data mismatch between the values specified for the database target and the WebLogic Server Datasource. To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
|