20 Using Fetchlets
This chapter contains the following sections:
About Fetchlets
Enterprise Manager data retrieval is handled through predefined "fetchlets." A fetchlet is a parametrized data access mechanism that takes arguments (for example, a script, a SQL statement, a target instance's properties) as input and returns formatted data. Each fetchlet handles a specific type of data access. The fetchlets supplied with Enterprise Manager provide data retrieval capability for the most common data access methods, such as SQL, SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), HTTP, and DMS (Dynamic Monitoring Service). To handle more complex data access requirements, Enterprise Manager also provides an OS command fetchlet that allows developers to implement custom metric collection methods.
The following sections describe the fetchlets supplied with Enterprise Manager:
OS Command Fetchlets
The operating system (OS) command fetchlets allow you to obtain metric data by executing OS commands (either individually or from scripts) that return a standard out (stdout) data stream.
Three OS command fetchlets are available:
-
OS Fetchlet (raw)
-
OSLines Fetchlet (split into lines)
-
OSLineToken Fetchlet (tokenized lines)
OS Fetchlet
The OS fetchlet executes a given OS command and returns the command's output in a single cell table.
Input Parameters
Table 20-1 OS Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
command |
string |
Operating system command to be executed. |
Required |
|
ENVname |
string |
OSFetchlet parameters starting with "ENV" appear in the execution environment for the command as name environment variables |
Zero or more |
|
errStartsWith |
String |
When defined, this property allows you to define a custom prefix for error messages. If this property is not defined, the OSFetchlet defaults to "em_error=" as the message prefix. |
Optional |
|
script |
string |
Specifies the script to be executed if command property only provides an interpreter. For example, command might consist of "perl." script is then used to specify the particular perl script to be run. Although scripts can be specified directly from the command parameter, using the script parameter adds to stylistic clarity and readability when defining a target type metadata file. |
Optional |
|
args |
string |
A property that is taken as one or more arguments to the command and script properties. Although args can be specified directly from the command parameter, using the args parameter adds to stylistic clarity and readability when defining a target type metadata file. |
Optional |
|
separateErrorStream |
boolean |
If an error occurs while executing a command, this property instructs the fetchlet whether to return both the stdout and stderr to the user as an error message. When set to TRUE, only stderr output is sent to the user as an error message when there is a command error. When set to FALSE (default value), both the stdout and the stderr are sent to the user as an error message upon command failure. |
Optional. (TRUE/FALSE) |
|
em_metric_timeout |
integer |
Metric timeout period (in seconds). After the timeout period has finished, the Management Agent returns a timeout exception and terminates any child processes that may have been created. The Management Agent does not terminate any of the grandchild processes. Specify "-1" for no timeout period. |
Optional |
Example
You want to obtain metric data by executing the UNIX echo command.
To run the command from the shell environment, enter:
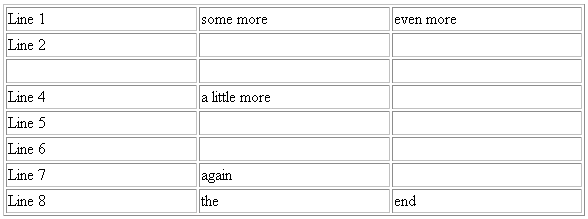
echo Line 1|some more|even more\nLine 2\n\nLine 4|a little more|\n|Line 5\n|Line 6|\n|Line 7|again|\nLine 8|the|end
The echo command produces the following standard output:
Line 1|some more|even more Line 2 Line 4|a little more| |Line 5 |Line 6| |Line 7|again| Line 8|the|end
Using the OS fetchlet with the given example command.
The fetchlet returns the following 1 x 1 table:
Figure 20-1 Table Returned by the OS Fetchlet
The raw output of the OS command is returned. Any standard error output is appended to the standard output.
Error Handling
Any problems encountered launching the command (For example, the command program no longer exists) results in an oracle.sysman.emSDK.emd.fetchlet.MetricSourceException wrapping a java.io.IOException. If the command exits with a non-zero exit value, the fetchlet throws an oracle.sysman.emSDK.emd.fetchlet.MetricSourceException wrapping an oracle.sysmand.emd.fetchlets.CommandFailedException.
Notes
Commands are not executed as if they are being run in a shell. This means that common shell symbols do not work, including piping, output redirection, and backgrounding.
Commands cannot read from standard input.
The fetchlet blocks and waits for the command to finish.
OSLines Fetchlet (split into lines)
The OS Lines fetchlet executes a given OS command and tokenizes the OS command's output. The output is tokenized by lines. The fetchlet returns the tokens in a single column table. The nth row in the table represents the nth line in the output of the OS command.
To get the raw, untokenized output of an OS command, use the OS fetchlet. To get the output of an OS command tokenized by lines and each line tokenized by a given delimiter, see the OS Line Token fetchlet.
Input Parameters
Table 20-2 OSLines Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
command |
string |
Operating system command to be executed. |
Required |
|
startsWith |
string |
Only lines starting with this string are included in the result. |
Optional; default = "" (all lines are included) |
|
ENVname |
string |
Parameters starting with "ENV" appear in the execution environment for the command as name environment variables |
Zero or more of these |
|
errStartsWith |
string |
When defined, this property allows you to define a custom prefix for error messages. If this property is not defined, the OSFetchlet defaults to "em_error=" as the message prefix. |
Optional |
|
script |
string |
Specifies the script to be executed if command property only provides an interpreter. For example, command might consist of "perl." script is then used to specify the particular perl script to be run. Although scripts can be specified directly from the command parameter, using the script parameter adds to stylistic clarity and readability when defining a target type metadata file. |
Optional |
|
args |
string |
A property that is taken as one or more arguments to the command and script properties. Although args can be specified directly from the command parameter, using the args parameter adds to stylistic clarity and readability when defining a target type metadata file. |
Optional |
|
separateErrorStream |
boolean |
If an error occurs while executing a command, this property instructs the fetchlet to whether to return both the stdout and stderr to the user as an error message. When set to TRUE, only stderr output is sent to the user as an error message when there is a command error. When set to FALSE (default value), both the stdout and the stderr are sent to the user as an error message upon command failure. |
Optional. (TRUE/FALSE) |
|
em_metric_timeout |
integer |
Metric timeout period (in seconds). After the timeout period has finished, the Management Agent returns a timeout exception and terminates any child processes that may have been created. The Management Agent DOES NOT kill any of the grandchild processes. Specify "-1" for no timeout period. |
Optional |
Example
Take the following UNIX command:
echo Line 1|some more|even more\nLine 2\n\nLine 4|a little more|\n|Line 5\n|Line 6|\n|Line 7|again|\nLine 8|the|end
It produces the following output:
Line 1|some more|even more Line 2 Line 4|a little more| |Line 5 |Line 6| |Line 7|again| Line 8|the|end
Running OSLinesFetchlet with the given example command produces the following single column table.
Figure 20-2 Table Returned by the OS LINES Fetchlet
Note that without content, "\n" results in a blank line inserted between Line 2 and Line 4.
Note:
Commands are not executed as if they are being run in a shell. This means that common shell symbols do not work, including piping, output redirection, and backgrounding.
Commands cannot read from standard input.
The fetchlet blocks and waits for the command to finish.
The standard output of the command is captured and the standard error is captured and appended to the standard output.
Lines are tokenized using "\n".
OSLineToken Fetchlet (tokenized lines)
The OS Line Token fetchlet executes a given OS command and tokenizes the output of the OS command. The output is tokenized first by lines, and then each line is tokenized by a given delimiter set. The fetchlet returns the tokens in a table. The nth row in the table represents the nth line in the output of the OS command. The nth column in the table represents the nth token in a line as determined by the given delimiter set.
To get the raw, untokenized output of an OS command, see OS Fetchlet.
Input Parameters
Table 20-3 OSLineToken Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
command |
String |
Operating system command to be executed. |
Required |
|
delimiter |
String |
Set of characters that act as delimiters to tokenize the lines |
Optional; default = "" (just breaks output into lines) |
|
startsWith |
String |
Only lines starting with this string are included in the result |
Optional; default = "" (all lines are included) |
|
ENVname |
String |
Parameters starting with "ENV" appear in the execution environment for the command as name environment variables |
Zero or more of these |
|
errStartsWith |
String |
When defined, this property allows you to define a custom prefix for error messages. If this property is not defined, the OSFetchlet defaults to "em_error=" as the message prefix. |
Optional |
|
script |
String |
Specifies the script to be executed if command property only provides an interpreter. For example, command might consist of "perl." The script is then used to specify the particular perl script to be run. Although scripts can be specified directly from the command parameter, using the script parameter adds to stylistic clarity and readability when defining a target type metadata file. |
Optional |
|
args |
String |
A property that is taken as one or more arguments to the command and script properties. Although args can be specified directly from the command parameter, using the args parameter adds to stylistic clarity and readability when defining a target type metadata file. |
Optional |
|
separateErrorStream |
Boolean |
If an error occurs while executing a command, this property instructs the fetchlet to whether to return both the stdout and stderr to the user as an error message. When set to TRUE, only stderr output is sent to the user as an error message when there is a command error. When set to FALSE (default value), both the stdout and the stderr are sent to the user as an error message upon command failure. |
Optional. (TRUE/FALSE) |
|
em_metric_timeout |
Integer |
Metric timeout period (in seconds). After the timeout period has finished, the Management Agent returns a timeout exception and terminates any child processes that may have been created. The Management Agent DOES NOT kill any of the grandchild processes. Specify "-1" for no timeout period. |
Optional |
Example
Take the following UNIX command:
echo Line 1|some more|even more\nLine 2\n\nLine 4|a little more|\n|Line 5\n|Line 6|\n|Line 7|again|\nLine 8|the|end
It produces the following output:
Line 1|some more|even more Line 2 Line 4|a little more| |Line 5 |Line 6| |Line 7|again| Line 8|the|end
Running OSLineTokenFetchlet with the given example command and a single character "|" for the delimiter generates the following table:
Figure 20-3 Table Returned by the OS Token Lines Fetchlet
Error Handling
Any problem launching the command (unable to find the command program) results in an oracle.sysman.emSDK.emd.fetchlet.MetricSourceException wrapping a java.io.IOException.
If the command exits with a non-zero exit value, the fetchlet throws a oracle.sysman.emSDK.emd.fetchlet.MetricSourceException wrapping a oracle.sysmand.emd.fetchlets.CommandFailedException.
Notes
Commands are not executed as if they are being run in a shell. This means that common shell symbols do not work, including piping, output redirection, and backgrounding.
The fetchlet promptly closes the input stream to the running command.
The fetchlet blocks and waits for the command to finish.
Lines are tokenized using "\n".
The delimiter can be a single character or a set of characters. For example, it can be "|+_", if the line should be broken up by pipes, pluses, and underscores. If two or more delimiters are together in the output text, such as "||" or "+|+", then it is as if there are empty string tokens between them. These empty strings get columns in the result table. It is not considered that there are empty strings preceding a delimiter that starts a line or following a delimiter that ends a line.
In order to express non-printable characters in the delimiter set (such as tabs) in XML, use "&#xHH;" where H is the hexadecimal identifier for the character.
Invoke an OS Fetchlet as a Specific User for Metric Collection
Depending on requirements, your plug-in may need to utilize the OS fetchlet to invoke a pre-existing script on the Management Agent monitoring a target to collect data for a specific metric as a specific user; that is, as a user other than the default "oracle" user.
Enterprise Manager supports the use of Privilege Delegation Providers (sudo and powerbroker) to invoke metric collections as a specific user. Enabling PDP for a plug-in requires credential setup on both the plug-in and on hosts where the target(s) being monitored are deployed.
In your plug-in, you must set the credential reference in the metric definition in the target metadata file. In the example, example Credentialref line has "your_cred". This value refers to monitoring credential set name.
Example: Credential Reference in Target Metadata
<TargetMetadata TYPE="my_type" NAME="my_target_name">
...
<Metric NAME="my_special_metric" TYPE="TABLE">
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="test" TYPE="STRING"/>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="OS">
<Property NAME="command" SCOPE="GLOBAL">%perlBin%/perl</Property>
<Property NAME="script" SCOPE="GLOBAL">%scriptsDir%/your_
script.pl</Property>
<CredentialRef NAME="OSCreds">your_cred</CredentialRef>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
...
</TargetMetadata>
On the Management Agent monitoring the target, a referenced credential type must be created that points to host:HostCreds, and allow the monitoring credential set be of the new type that you add. See Oracle Enterprise Manager Administrator's Guide for details on privilege delegation setup using Enterprise Manager.
The credential data will be persisted to the target metadata file (target.xml) for the Management Agent monitoring the target.
The following example defines the referenced credential type MyHostCreds in target.xml, which is of the credential type host:HostCreds.
Example: Credential Type Definition in Management Agent
<Target TYPE="<removed>" NAME="<removed>" DISPLAY_NAME="<removed>" ON_HOST="" EMD_URL="https://<removed>/emd/main/" TIMEZONE_REGION="" IDENTIFIER="TARGET_GUID=<removed>"> ... <CredentialType NAME="MyHostCreds"><CredentialTypeRef REF_NAME="HostRef" REF_TYPE="HostCreds" REF_TARGETTYPE="host" ASSOCIATION="host"><CredentialTypeRefColumn NAME="HostUserName" REF_TYPECOLUMN="HostUserName"/><CredentialTypeRefColumn NAME="HostPassword" REF_TYPECOLUMN="HostPassword"/></CredentialTypeRef></CredentialType> ... </Target>
When monitoring credentials are updated Enterprise Manager (via Setup->Security->Monitoring Credentials), the data shown above will be updated on the Management Agent automatically.
The next example defines the HostMonCredSet monitoring credential set, which is of type MyHostCreds (and therefore type host:HostCreds)
<CredentialSet NAME="HostMonCredSet" CREDENTIAL_TYPE="MyHostCreds" USAGE="MONITORING"><AllowedCredType TYPE="MyHostCreds"/> </CredentialSet>
SQL Fetchlet
The SQL fetchlet executes a given SQL statement on a given database as a given user and returns the table result.
Input Parameters
Table 20-4 SQL Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Connection Information |
|
|
|
|
MachineName |
String |
Database host |
Required |
|
Port |
Integer |
Database port |
Required |
|
SID |
String |
Database SID |
Required unless ServiceName is specified |
|
ServiceName |
String |
Database ServiceName |
Required unless SID is specified |
|
OracleHome |
String |
Database's Oracle Home (used in conjunction with OidRepSchemaName). |
Required when OidRepSchemaName is used. |
|
Credential Information |
|
|
|
|
UserName |
String |
user name |
Required |
|
password |
String |
user password |
Optional; default is "" |
|
Role |
String |
Role used when connecting to the database (e.g., SYSDBA) |
Optional; allowed choices are SYSDBA, SYSOPER, and NORMAL (default) |
|
General |
|
|
|
|
STATEMENT |
String |
SQL statement or PL/SQL block |
Required unless FILENAME is specified. |
|
FILENAME |
String |
Full path of the file containing the SQL statement or PL/SQL block |
Required unless STATEMENT is specified. |
|
NUMROWS |
Integer |
Maximum number of rows to output. |
Required |
|
Bind Parameters |
|
|
|
|
SQLINPARAM<position> |
String |
Value of input parameter at position <position> |
Zero or more, one for each input parameter. |
|
SQLOUTPARAMPOS |
Integer |
Position of output parameter, if it exists |
There can be exactly one output parameter, if it exists. |
|
SQLOUTPARAMTYPE |
String |
Type of the output parameter, if it exists. |
There can be exactly one output parameter type, if it exists. |
|
transpose |
TRUE/FALSE |
If TRUE, the result is transposed: rows to columns and columns to rows. |
Notes
The SQL statement or PL/SQL block can be specified either through the STATEMENT property, or via a file whose name is provided through the FILENAME property.
The SQL fetchlet supports input parameters. Input and output parameters are indicated in the SQL/PLSQL text in the usual way, by using ":<number>". Input parameters can be used to bind values to both SQL queries and PL/SQL blocks.
Input parameter values are specified as properties of the form SQLINPARAM<position>. There can be any number of input parameters. The input parameters need to be scalar: input parameters of type ARRAY and STRUCT are not supported.
The SQL fetchlet supports the execution of anonymous PL/SQL blocks (which may call other functions or procedures) to retrieve data. When executing a block of PL/SQL, data is returned to the fetchlet by means of an OUT parameter. There can be exactly one out parameter. It must be of type SQL_CURSOR (a PL/SQL REF CURSOR), or it must be a named type that represents an array of objects. In the latter case, each field of the object represents one column of the table; and each object instance in the array represents one complete row in the table. The OUT parameter position and type are specified by means of the properties SQLOUTPARAMPOS and SQLOUTPARAMTYPE. If an OUT parameter is specified, then the fetchlet assumes it is executing PL/SQL and treats the STATEMENT property as an anonymous PL/SQL block.
Note:
When using a SQLOUTPARAMTYPE of type 'ARRAY', you must identify the array as follows:
-
If you create the array type specified in the SQLOUTPARAMTYPE from SQL*Plus or any utility without using double quotation marks to surround the array name, then you must specify the array name using all upper-case letters in the target metadata file for this property. The reason for this because the RDBMS automatically changes the array name to all upper-case.
-
If you create the array type specified in the SQLOUTPARAMTYPE from SQL*Plus or any utility using double-quotation marks to surround the array name, then the RDBMS retains the case specified. For this reason, users must specify the array name using the same case used in the target metadata file.
If no OUT parameter is specified, the fetchlet assumes that it is executing a SQL query.
Note that all input parameters to the SQL fetchlet are strings. This means that all other datatypes will have to be converted to strings. This is straightforward for datatypes such as numbers, but not, for example, dates and timestamps. You can pass an absolute date or timestamp by passing a character representation of the value (using a DateFormat class). There is no way currently to pass in a date function, such as SYSDATE or SYSDATE+1. In such case, you could embed the date argument directly in the SQL, for example:
begin func1(:1, :2, SYSDATE); end;
The other caveat is passing null arguments to a procedure. Consider the following SQL:
STATEMENT=begin func1(:1,:2); end; SQLINPARAM1=null SQLOUTPARAMPOS=2 SQLOUTPARAMTYPE=fooret
Assume that the first argument is intended to be a varchar2. By parameterizing it and passing 'null' as the first argument, what we are really doing is passing the *string* 'null' to the argument, and not a null value. If you intend to pass a null value, do the following:
STATEMENT=begin func1(null, :1); end; SQLOUTPARAMPOS=1 SQLOUTPARAMTYPE=fooret
Examples
The following properties execute a query (get all users) with no parameters:
Example 1: Query With No Parameters
MachineName=skini-pc Port=1521 SID=o817 UserName=scott password=tiger STATEMENT=select * from all_users; NUMROWS=30
The following properties execute a query (get the first few objects of a specified type owned by a specified user) with input parameters:
Example 2: Query With Input Parameters
MachineName=skini-pc Port=1521 SID=o817 UserName=scott password=tiger STATEMENT=select * from all_objects where owner=:1 and object_type=:2 and rownum<:3tt> NUMROWS=30 SQLINPARAM1=SYSTEM SQLINPARAM2=INDEX SQLINPARAM3=10
The following example executes a PL/SQL procedure that returns a cursor and has input parameters:
Example 3: PL/SQL Procedure With Input Parameters
achineName=skini-pc Port=1521 SID=o817 UserName=scott password=tiger STATEMENT=begin :1 := skini_junk.func1(:2); end; NUMROWS=30 SQLINPARAM2=SYSTEM SQLOUTPARAMPOS=1 SQLOUTPARAMTYPE=sql_cursor
The following example specifies a PL/SQL procedure that returns an array of strings:
Example 4: PL/SQL Procedure Returning an Array of Strings
MachineName=skini-pc Port=1521 SID=o817 UserName=scott password=tiger STATEMENT=begin skini_junk.newproc(:1,:2); end; NUMROWS=30 SQLINPARAM1=SYSTEM SQLOUTPARAMPOS=2 SQLOUTPARAMTYPE=my_string_array
The following example specifies a PL/SQL package that returns an array of structures:
Example 5: PL/SQL Package Returning an Array of Structures
MachineName=skini-pc Port=1521 SID=o817 UserName=scott password=tiger STATEMENT=begin :1 := skini_junk.func2(:2,:3,:4,:5,:6); end; NUMROWS=30 SQLINPARAM2=somename SQLINPARAM3=someplace SQLINPARAM4=someanimal SQLINPARAM5=something SQLINPARAM6=22 SQLOUTPARAMPOS=1 SQLOUTPARAMTYPE=my_struct_array
The following example provides the PL/SQL used in the previous examples for reference.
Example 6: PL/SQL Used in Examples
create or replace type my_type as Object (
name varchar2(128),
place varchar2(128),
animal integer,
thing number,
thing2 number);
/
create or replace type my_struct_array as table of my_type;
/
create or replace type my_string_array as table of varchar2(3000);
/
create or replace type my_int_array as table of integer;
/
create or replace package skini_junk as
type Jcr is ref cursor;
function func1(username in varchar2) return Jcr;
function func2(name varchar2, place varchar2, animal integer,
thing number, thing2 number) return my_struct_array;
procedure newproc(name varchar2, outArray OUT my_string_array);
procedure newproc2(numrows in varchar2, outArray OUT my_int_array);
end skini_junk;
/
create or replace package body skini_junk as
function func1(username in varchar2) return Jcr is
cr Jcr;
begin
open cr for select object_name, object_type, status from all_objects where
owner=upper(username);
return cr;
end;
function func2(name varchar2, place varchar2, animal integer,
thing number, thing2 number) return my_struct_array IS
ret my_struct_array := my_struct_array();
begin
ret.extend(50);
for i in 1..50 loop
ret(i) := my_type(name || i,
place || i,
animal+i,
thing+i,
thing2+i);
end loop;
return ret;
end;
procedure newproc(name varchar2, outArray OUT my_string_array) IS
begin
outArray := my_string_array();
outArray.extend(100);
for i in 1..100 loop
outArray(i) := name || i;
end loop;
end;
procedure newproc2(numrows in varchar2, outArray OUT my_int_array) IS
begin
outArray := my_int_array();
outArray.extend(numrows);
for i in 1..numrows loop
outArray(i) := i;
end loop;
end;
end skini_junk;
/SNMP Fetchlet
An object identifier (OID) corresponds to either a MIB variable instance or a MIB variable with multiple instances. Given a list of OIDs, the SNMP fetchlet polls an SNMP agent on a given host for corresponding instances.
Input Parameters
Table 20-5 SNMP Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
hostname |
String |
Host name of the SNMP agent |
Required. Default is "localhost" Examples: "bigip.host.example.com" "148.87.10.5" |
|
PORT |
String |
Port of the SNMP agent |
Optional. Default is "161" |
|
COMMUNITY |
String |
SNMP community string |
Optional. Default is "public" |
|
TIMEOUT |
String |
SNMP timeout. |
Optional. Default is five seconds |
|
OIDS |
String |
A list of substrings separated by delimiters. Each substring starts with an OID (in numerical dot notation), and can be optionally ended with *PlacementOID. (See notes for details.) |
Required. Examples: "1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.1.1.0,1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.1.3.0,1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.1.5.0" "1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.2 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.10 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.16" "1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.3 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.5 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1*1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.2 1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3*1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.2" |
|
DELIM |
String |
A delimiter to separate individual substrings in OIDS. |
Optional; default is whitespace characters, (dot), *(star) and 0-9 (digits) cannot be used as delimiters |
|
TABLE |
String |
Each OID in OIDS corresponds to a variable with multiple instances if this parameter is "TRUE" and to a single variable instance if it is "FALSE". |
Optional; default is "FALSE" |
|
PINGMODE |
Boolean |
Used for defining PINGMODE Response metric If set to TRUE, then a successful GetResponse generates a single-row, single-column table with the value "1" in its cell. A timeout generates a single-row, single-column table with the value "0". This is useful for defining a Response metric for an SNMP-based target. |
Optional. Default is "FALSE" |
|
IGNORE_TIMEOUT_ERR_BOOLEAN |
Boolean |
Specifies whether to generate an error when a non-PINGMODE invocation times out while waiting for a response. If set to TRUE, then a non-PINGMODE invocation that times out while waiting for a response should not generate a metric collection error. This is reasonable behavior for targets that define a PINGMODE Response metric. If that Response metric is going to generate an availability severity when the SNMP agent stops responding, then there is no need to generate metric errors on any non-Response metrics that happen to run before the Response metric can identify the problem. |
Optional. Default is "TRUE" |
|
MAX_NUM_ROWS_FETCH |
Integer |
The maximum number of rows to be returned by a TABLE invocation. The configuration property "SnmpTableMaxNumRowsFetch" can override the default value. |
Optional. Default is 1000 |
|
CONTEXT_NAME |
String |
Along with CONTEXT_ENGINE_ID, these two properties specify a set of SNMPv3 credentials, which replace the community string used by SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c. Note: If these two properties are specified, then the COMMUNITY and the VERSION parameters are ignored, and the sent request is an SNMPv3 request. |
Optional. No default value |
|
CONTEXT_ENGINE_ID |
String |
For information about this parameter, see the CONTEXT_NAME description. |
Optional. No default value |
|
VERSION |
String |
Specifies the SNMP version. If the following occurs, then VERSION is set to "v2c", indicating an SNMPv2c request:
If these previous conditions do not apply, then VERSION is set to "v1" indicating an SNMPv1 request. |
Optional. Default is "v1" |
|
disallowV1Requests |
Boolean |
This parameter enables the user to specify that the Management Agent should use SNMPv2c only when sending any request to a particular target |
Optional. Default is "FALSE" |
|
hasV2Types |
Boolean |
This parameter is a global-scoped property for an SNMP QueryDescriptor that includes OIDs for MIB variables whose types are 64-bit integer values. These are not representable in SNMPv1. Even if other requests for the same target instance are sent using SNMPv1, the target-type owner knows that this request must be SNMPv2c. |
Optional. Default is "FALSE" |
|
USE_GET_NEXT_ONLY |
Boolean |
If an SNMP QueryDescriptor is SNMPv2c, according to the conditions described in the VERSION description, and if TABLE is TRUE, then the multiple rows that the SNMP fetchlet returns will be fetched using the SNMPv2c GetBulk request, and not the GetNext request used in SNMPv1. If USE_GET_NEXT_ONLY is set to TRUE, then the SNMP fetchlet returns will be fetched using GetNext requests. |
Optional. Default is "FALSE |
Error Handling
MissingParameterException is thrown if either host name or OIDS is not given. FetchletException is thrown if TABLE is not equal to either TRUE or FALSE, an I/O error occurs while sending or receiving SNMP messages to or from the agent, or the agent responds with an SNMP error.
Notes
The table returned by the fetchlet contains a column for every OID in OIDS. If input OIDs correspond to single variable instances, the table will have just one row with those instances. On the other hand, if the OIDs correspond to variables with multiple instances, each column in the table will contain instances for its OID and each row will correspond to a different subidentifier. (A subidentifier is an OID extension that uniquely identifies a particular variable instance for some MIB variable.) OIDS must contain either all OIDs with subidentifiers or all OIDs without the subidentifiers.
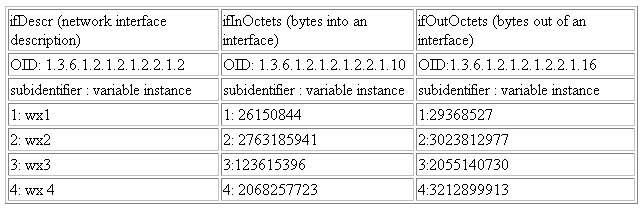
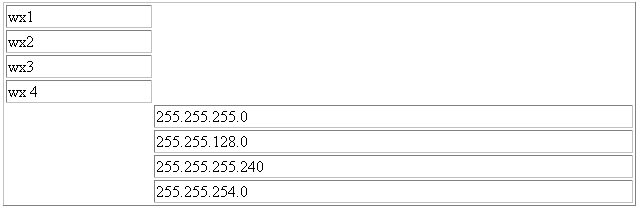
For example, to request the variable instances for the three OIDs: sysDescr, sysUpTime, and sysName, OIDS would have to be "1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.1.1.0 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.1.3.0 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.1.5.0". In this case, all OIDs contain the instance subidentifier, ".0". The return table appears as follows (the actual values may be different):
Alternatively, assume that some MIB contains the following 3 columns and 4 instances:
Figure 20-5 SNMP Fetchlet: Columns 3 and 4 Content
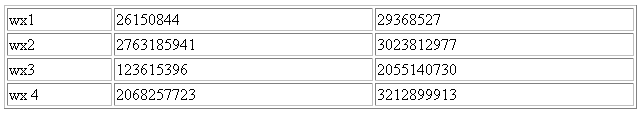
To construct a table with 3 columns corresponding to ifDescr, ifInOctets, and ifOutOctets, OIDS would be defined as follows
"1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.2 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.10 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.16"
The fetchlet returns the following:
Figure 20-6 SNMP Fetchlet:ifDescr, ifInOctets, and ifOutOctets OIDS
The rows correspond to subidentifiers 1,2,3,4 respectively.
Any OID in OIDS can be appended with another placement OID. The variable instances for the placement OID do not appear in the returned table. Instead, they determine the place for the variable instances of the original OID within a column. In particular, for every variable instance I with subidentifier S in the set of instances for the original OID, (a) there must exist a variable instance X with subidentifier S in the set of instances corresponding to the placement OID, and (b) X is used as the subidentifier for the instance I.
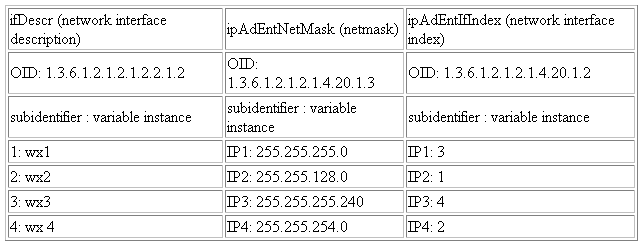
For example, consider a MIB containing the following 3 columns, each with 4 variable instances:
Figure 20-7 SNMP Fetchlet: MIB Content with 4 Variable Instances
To construct a table containing ifDescr and ipAdEntNetMask, OID of ipAdEntIfIndex would have to be used as the placement OID to "align" the columns. Thus, the OIDS input to the fetchlet would be "1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.2 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.4.20.1.3*1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.4.20.1.2". The fetchlet output will be as follows:
Figure 20-8 SNMP Fetchlet: Table Containing ifDescr and ipAdEntNetMask
If OIDS were "1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.2.2.1.2 1.3.6.1.2.1.2.1.4.20.1.3" for the previous example, the output would be as follows:
HTTP Data Fetchlets
The HTTP data fetchlets obtain the contents of a URL and returns the contents of the URL as data. Three fetchlets are available:
-
URL Fetchlet
-
URL Lines
-
URL Lines Token
URL Fetchlet (raw)
The URL fetchlet gets the contents of a given URL and returns the contents of the URL in a single cell table.
To get the output of a URL tokenized by lines and each line tokenized by a given delimiter, see the URL Line Token fetchlet.
Input Parameters
Table 20-6 URL Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
url |
URL to retrieve the contents of |
required |
|
proxyHost |
proxy host through which to make the URL connection. |
optional |
|
proxyPort |
proxy port through which to make the URL connection. |
optional |
Example
Take the following URL:
http://localhost/nhcities.txt
It has the following contents:
Line 1: Nashua, Keene,
Line 2: Concord
Line 3: , Conway, Manchester, Milford, Brookline,
Line 4:
Line 5: Hollis, Meredith
Now run the URL fetchlet with the given URL. The fetchlet returns the following one-by-one table:
The raw contents of the URL is returned.
Error Handling
MissingParameterException if URL parameter is missing. FetchletException if the URL is malformed or an I/O error occurs in retrieving the content of the URL.
URL Lines Fetchlet (split into lines)
The URL fetchlet gets the contents of a given URL and tokenizes the contents of the URL. The output is tokenized by lines. The fetchlet returns the tokens in a single column table. The nth row in the table represents the nth line of the URL contents.
Note:
To get the raw, untokenized contents of a URL, see the URL fetchlet. To get the contents of a URL tokenized by lines and each line tokenized by a given delimiter, see the URL Line Token fetchlet.
Table 20-7 URL Lines Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
url |
URL to retrieve the contents of |
required |
|
proxyHost |
proxy host through which to make the URL connection. |
optional |
|
proxyPort |
proxy port through which to make the URL connection. |
optional |
|
startsWith |
only lines starting with this string are included in the result |
optional; default = "" (all lines are included) |
Example
Take the following URL:
http://localhost/nhcities.txt
It has the following contents:
Line 1: Nashua, Keene,
Line 2: Concord
Line 3: , Conway, Manchester, Milford, Brookline,
Line 4:
Line 5: Hollis, Meredith
Now run the URL fetchlet with the given URL.
The fetchlet returns the following table:
Error Handling
MissingParameterException if URL parameter is missing.
FetchletException if the URL is malformed or an I/O error occurs in retrieving the content of the URL.
Notes
Lines are tokenized using "\n".
URL Line Token Fetchlet (tokenized lines)
The URL fetchlet gets the contents of a given URL and tokenizes the contents of the URL. The output is tokenized first by lines, and then each line is tokenized by a given delimiter set. The fetchlet returns the tokens in a table. The nth row in the table represents the nth line of the URL content. The nth column in the table represents the nth token in a line as determined by the given delimiter set.
To get the raw, untokenized contents of a URL, see the URL fetchlet.
Table 20-8 URL Line Token Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
url |
URL to retrieve the contents of |
required |
|
delimiter |
set of characters that act as delimiters to tokenize the lines |
optional; default = "" (just breaks output into lines) |
|
proxyHost |
proxy host through which to make the URL connection. |
optional |
|
proxyPort |
proxy port through which to make the URL connection. |
optional |
|
startsWith |
only lines starting with this string are included in the result |
optional; default = "" (all lines are included) |
Example
Take the following URL:
http://localhost/nhcities.txt
It has the following contents:
Line 1: Nashua, Keene,
Line 2: Concord
Line 3: , Conway, Manchester, Milford, Brookline,
Line 4:
Line 5: Hollis, Meredith
Now run the URL fetchlet with the given URL and a single character "," for the delimiter.
The fetchlet returns the following table:
Error Handling
MissingParameterException if URL parameter is missing.
FetchletException if the URL is malformed or an I/O error occurs in retrieving the content of the URL.
Notes
Lines are tokenized using "\n".
The delimiter can be a single character or a set of characters. For example, it can be "|+_", if the line should be broken up by pipes, pluses, and underscores. If two or more delimiters are together in the output text, such as "||" or "+|+", then it is as if there are empty string tokens between them. These empty strings get columns in the result table. It is NOT considered that there are empty strings preceding a delimiter that starts a line or following a delimiter that ends a line.
In order to express non-printable characters in the delimiter set (such as tabs) in XML, use "&#xHH;" where H is the hexadecimal identifier for the character.
URLXML Fetchlet
The URL XML fetchlet obtains the XML content of a given URL, and extracts information based on a given pattern. A pattern is a list of "chunks" of XML to match against. The return table is a table with a column for each grabber (*) in the pattern in order and a row each time the pattern chunk matches in the XML content.
Input Parameters
Table 20-9 URLXML Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
url |
URL to retrieve the contents of |
Required. |
|
pattern |
The pattern used to extract information from XML; this is a list of XML chunks that that is compared against the XML content of the URL. Each chunk contains one or more "grabbers" (*) in the text portion of the elements that define what should the flattened into text and extracted. |
Required. |
|
proxyHost |
The proxy host through which to make the URL connection. |
Optional. |
|
proxyPort |
The proxy port through which to make the URL connection. |
Optional. |
|
ignoreDtd |
If set to TRUE, specifies that the DTD file referenced by the content XML should be ignored. This is useful in cases where the DTD file cannot be accessed. |
Optional. |
|
generateKey |
If set to true, a unique key will be generated for each row. The key will occupy the first column of the result, and will be numeric. |
Optional. |
|
throwConnException |
If set to TRUE, a java.net.ConnectException will be thrown. Otherwise, it will be caught and an empty result set will be returned. Setting this property to FALSE provides behavior which is consistent with the DMSFetchlet. |
Optional. The default value is TRUE. |
Example
Take the following URL:
http://localhost/urlxmltestfile.xml
It has the following content:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<testfile>
<test>Simple text</test>
<test><level>A little more complex</level></test>
<test></test>
<notatest></notatest>
<test>Yet more complexity<level>Even a little more complex</level>Will it ever stop?</test>
<test1>must match<level>extract me!</level></test1>
<test1>must match here<level>extract me, too!</level></test1>
</testfile>
Running the URL XML fetchlet with the given URL and the pattern:
<testfile><test>*<level>*</level></test></testfile>
returns the following table:
Error Handling
MissingParameterException if URL or pattern parameters are missing.
A FetchletException is generated if:
-
The URL is malformed.
-
An I/O error occurs in retrieving the content of the URL.
-
The URL contents or pattern contains invalid XML.
Notes
Setting the proxy host and/or port changes these settings for the java.net package for the whole Java environment and is not thread-safe if the proxy settings are changing.
URL Timing Fetchlet
The URL Timing fetchlet gets the contents of a given URL, timing not only the base page source but any frames or images in the page as well.
Input Parameters
Table 20-10 URL Timing Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
url# |
URL(s) to download. "url0" is required but any number of URLs can be specified beyond url0 that following the convention: url0, url1, url2, url3. |
Required. |
|
proxy_host |
Proxy host used to make a URL connection. |
Optional. Specifies the proxy to be used for accessing URLs. If the proxy_host_override value is provided, then that value will be used instead. |
|
proxy_port |
Port used by the proxy host used make the URL connection. |
Optional. |
|
dont_proxy_for |
Domains for which the proxy will not be used. |
Optional. For example, .us.example.com, .uk.example.com |
|
use_proxy |
When used in conjunction with the proxy override input parameters, use_proxy specifies a proxy to be used in lieu of the original proxy. When set to false without the proxy override parameters set, no proxy is used. |
Optional. Parameter can be set to true or false. |
|
proxy_host_override |
Alternate proxy host used to make the URL connection. |
Optional. Overrides proxy_host. |
|
proxy_port_override |
Alternate proxy port used to make the URL connection. |
Optional. Overrides proxy_port. |
|
dont_proxy_override |
Do not use the proxy for domains. |
Optional. Parameter can be set to true or false. |
|
internet_cert_loc |
Path pointing to the location of a certificate to be used to access a secure (HTTPS) URL. |
Optional. |
|
auth_realm |
Realm for the Basic Authentication log on. If the realm is not specified for the authentication, authentication does not occur and the download of the page fails with a 401 response code. |
Optional. |
|
auth_user |
User name for Basic Authentication. |
Optional. |
|
auth_password |
Password for Basic Authentication. |
Optional. |
|
retries |
Number of times to retry the url if it initially fails. |
Optional. Default = 1 |
|
connection_timeout |
Wait time (in milliseconds) allowed to establish a connection to a server. This time also includes time required for name resolution. |
Optional. Default= 60000 milliseconds (1 minute) |
|
read_timeout |
Idle time in the read waiting for the server to respond. For example, if no data is received from the server during the specified timeout period, the operation is considered failure. |
Optional. Default = 12000 milliseconds (2 minutes) |
|
timeout |
Number of milliseconds after which the page download is considered a failure. This will detect if the site is functional but is extremely slow. |
Optional. Default = 300000 ms (5 minutes) |
|
status_comparator |
When collating the rows to make a single row, the status_comparator parameter will indicate whether all URLs should have been a success (and) or any URLs should have been a success (or). |
Optional. Default = and |
|
cache |
Indicates whether to use a cache when accessing an URL. Set the parameter to "n" to specify that no cache be used. |
Optional. Default = yNote: The scope of the cache is per request. There is no persistent cache across multiple get metric requests. |
|
output_format |
Specifies the output format to be used: summary, detailed, repeat_column. For more information on output formats, see Metric Columns and Output Modes. |
Required. summary : gives a default set of metrics in a single row for all urlsdetailed: gives a default set of metrics for each url.repeat_column : gives a single row of metric with timing for each of the url. |
|
metrics |
Specifies which metric columns need to be returned. For more information on metrics columns returned for each output format, see Table 20-12 |
Optional. Allows you to specify of what needs to be returned from the fetchlet and in which order.Example: status, status_description, total_response_time |
Metric Columns and Output Modes
The format of information and specific metric information returned are controlled by the "output_format" and "metrics" input parameters. Table 20-11 lists the format categories and the metrics (columns) returned by each. For a description of available metric columns, see Table 20-12
Table 20-11 URLTIMING Fetchlet: Output Formats
| Output Format | Description | Metric Columns |
|---|---|---|
|
summary |
Returns a default set of metrics in a single row for all URLs If the metrics input parameter is specified, then only the columns specified will be returned. |
computed_response_time, status, status_description, dns_time, connect_time, redirect_time, first_byte_time, html_time, content_time, total_response_time, rate, max_response_time, avg_response_time, avg_connect_time, avg_first_byte_time, broken_count, broken_content |
|
detailed |
Returns a default set of metrics for each url. If the metrics input parameter is specified, then only the columns specified will be returned. |
url, computed_response_time, status, status_description, dns_time, connect_time, redirect_time, first_byte_time, html_time, content_time, total_response_time, rate, redirect_count, html_bytes, content_bytes, total_bytes, avg_connect_time, avg_first_byte_time, broken_count, broken_details |
|
repeat_column |
Returns a single row of metrics with timing for each of the URLs. If the metrics input parameter is specified, then those columns will be returned for each URL followed by overall status and status_description. (Note the output will always be single row). |
total_response_time repeated for each URL followed by overall status and status_description. |
Metric Columns
Table 20-12 shows the metric columns returned by the URLTIMING fetchlet.
Table 20-12 URLTIMING Fetchlet: Metric Columns
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
status |
The overall status of all URLs. By default AND is used to compute overall status but this can be changed using the status_comparator input parameter. |
|
connect_time |
The time to connect to the server and send the request. |
|
first_byte_time |
Time taken between sending the request and reading the first byte from the response. |
|
total_response_time |
Time taken for fetching ALL urls and associated content (gif, css, javascript, and so on). |
|
max_response_time |
Also referred as Slowest page time. This the time taken by the slowest URL. |
|
avg_response_time |
Average response time for URL. Computed as total response time / number of pages (urls). |
|
rate |
Kilo Bytes per second. This is computed by total bytes received / total time taken to receive them. |
|
html_time |
Total time taken to download the html part of all pages. This time excludes time to fetch images and other contents. (Includes time to fetch frame html). |
|
content_time |
Time taken to download the page content (gif, javascripts, css, and so on). |
|
redirect_time |
Total time taken for all redirects occurring while fetching the set of urls specified. |
|
redirect_count |
Number of redirects. |
|
total_bytes |
Total number of bytes. |
|
html_bytes |
Total number of HTML bytes. (Includes bytes for frame html). |
|
content_bytes |
Total number of content bytes. |
|
status_description |
This is present only when the status is down. Corresponds to HTTP Status description. |
|
request_count |
Number of request made. (Includes all html as well as content requests). |
|
broken_count |
Number errors while fetching images or other content elements. |
|
broken_details |
List of images or other content elements that could not be fetched. This has format of url[broken list], url[broken list... |
|
computed_response_time |
This time approximates the time it would have taken for a client (like browser) to fetch all the pages in the transaction. This number is computed as if the contents of every page (gifs, css, and so on) were fetched using multiple threads. |
|
avg_connect_time |
Total connect_time / total number of connections made. |
|
avg_first_byte_time |
Total First Byte Time / Number of requests made (either to fetch HTML or content). |
|
dns_time |
Time to resolve host name (not implemented, always returns zero). |
|
url |
Returns the url, can only be used in 'detailed' output_format. |
Example
Take the following URL:
url0=http://www.example.com/
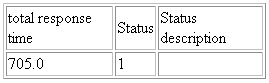
With the input parameter output_format=summary, the fetchlet returns the following table (minus the headers on the columns):
With output_format = summary and metrics = total_response_time, status, status_description the fetchlet returns the following table (minus the headers on the columns):
Figure 20-15 Summary Output Format with Specified Metric Columns
With output_format = summary and metrics = total_response_time, status, status_description the fetchlet returns the following table (minus the headers on the columns) and the server is giving error:
Figure 20-16 Summary Output Format with Specified Metric Columns and Internal Server Error
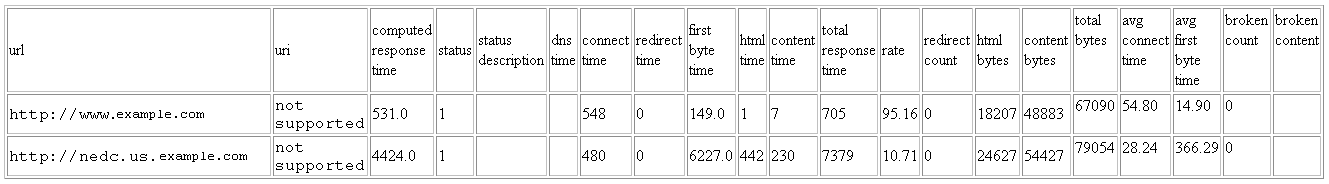
Take the following URL:
url0=http://www.example.com/ url1=http://nedc.us.example.com/
With the output_format=summary, the fetchlet returns the following table (minus the headers on the columns). Here the numbers are time taken for fetching both the urls.
Figure 20-17 Summary Output Format for Two URLs
With the output_format=detailed, the fetchlet returns the following table (minus the headers on the columns):
With the output_format=repeat_column, the fetchlet returns the following table (minus the headers on the columns):
Error Handling
Metric error if the URL parameter is missing, malformed, or if the metric cannot be computed.
Notes
The time required to perform a retry will be added on to the total time of the page. For example, if two retries are performed and then a success occurs, the total page time will be the time of the page that succeeded plus the time it took for the two retries to fail.
Proposed usage:
-
For basic monitoring:
Use url0=<URL to be monitored> , output_mode=summary and specify metrics=status, computed_response_time, status_description
-
For getting all columns:
Use url0=<url to be monitored> , output_mode=summary
Dynamic Monitoring Service (DMS) Fetchlet
The Dynamic Monitoring Service (DMS) fetchlet contacts an Application Server (AS) and then collects the metrics instrumented by the DMS.
The DMS allows application and system developers to measure and export customized, component-specific performance metrics. The Oracle Management Agent allows software components to import runtime performance data into Oracle Enterprise Manager.
The DMS fetchlet is an Oracle Management Agent plug-in module that allows the Management Agent to import the performance data that is exported by the DMS. Using the DMS fetchlet, any component that is instrumented using DMS API calls may share its performance data with Enterprise Manager.
Advantages to Using DMS for Oracle Management Agent Integration
With DMS, a component can insulate itself from the operational details of the Management Agent. A component would not need to deploy (or maintain) its own fetchlet or deploy (or maintain) a Tcl script or shell script to plug into one of the existing fetchlets. A component would not need to devise its own new way of measuring or exporting performance metrics. Performance metrics can be measured and reported in a consistent way across components. The DMS fetchlet contacts the remote DMS runtime directly with no need for forking shell scripts or Tcl scripts. Most importantly, DMS automatically produces the long, complicated metadata document for you and thereby saves many hours of tedious and error-prone hand editing.
Input Parameters
Table 20-13 DMS Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
oraclehome |
String |
Top directory under which the monitored IAS instance is installed. It is used only for monitoring local IAS processes. For monitoring remote IAS processes, users should give it an empty value and specify property "opmnremoteport" and/or "machine" instead. |
Required. Example: "/private/oracle/ias" |
|
version |
String |
AS Version number of the target. It is used to distinguish the version of monitored AS instance. |
Optional Example: "9.0.4" |
|
opmnport |
Integer |
Oracle Process Monitoring and Notification (OPMN) port. It is used primarily for monitoring remote AS processes. It should be specified together with property "machine". If it is present and valid , property "oraclehome" and "httpport" are ignored. |
Optional Example: "6200" |
|
httpport |
Integer |
HTTP port is used primarily for monitoring stand-alone processes. It should be specified together with property "machine". It will be ignored, if property "opmnport" is present. If it is present and valid, property "oraclehome" is ignored. |
Optional Example: "7777" |
|
machine |
String |
Host name where the Internet Application Server (AS) instance runs. It should be specified together with property "opmnport". If it is not present, the local host is assumed. |
Optional Example: "my-sun.us.example.com" |
|
metric |
String |
Name of the table-type metric. |
Required Example: "Servlets" |
|
columnOrder |
String |
A list of metric column names separated by ";". The column names must be specified in same order as they appear in the target type metadata file. Do not include "name", "host", "process" and "fullname" columns. |
Required Example: "processTimes;totalRequest;requestRate" |
|
usecache |
String |
Whether to cache this metric. The legal values are "true", "false" and "refreshall" with "true" being the default. The "refreshall" value tells the DMS to delete its cache data and retrieve the most recent data from all targets. |
Optional. Example: "false" Setting "usecache" to "false" will bypass DMS caching |
|
proxyHost |
String |
Proxy host through which to make the HTTP connection |
Optional Example: "proxy.us.example.com" |
|
proxyPort |
Integer |
Proxy port through which to make the HTTP connection |
Optional Example: "80" |
|
dontProxyFor |
String |
Domains for which the proxy will not be used. |
Optional Example: ".us.example.com" or "18.219.0" |
|
useDefaultProxy |
String |
When used in conjunction with the proxy override parameters, this variable specifies a proxy other than the original one. When set to false without the proxy override parameters set, no proxy at all is used. |
Optional Example: "true" or "false" |
|
proxyHostOverride |
String |
proxy host through which to make the HTTP connection |
Optional Example: "www-proxy.us.example.com" |
|
proxyPortOverride |
Integer |
proxy port through which to make the HTTP connection |
Optional Example: "80" |
|
authrealm |
String |
Realm for the Basic Authentication logon. If the realm is not specified for the authentication, authentication does not occur and the download of the page fails with a 401 response code. |
Optional Example: "Please input your flex account login:" |
|
authuser |
String |
Username for Basic Authentication |
Optional "superuser" |
|
authpwd |
String |
Password for Basic Authentication |
Optional Example: "welcome" |
Error Handling
The DMS fetchlet throws MissingParameterException if any of the properties "oraclehome", "metric", "columnOrder", "opmnport", or "httpport" is missing. It throws FetchletException if any of the ports given is not valid.
Notes
The first four columns of the metric table returned are always column "name", "fullname", "host" and "process". Therefore, do not include them in columnOrder string. Property "machine" should be specified together with either properties "opmnport" or "httpport". In this case, the property "oraclehome" is ignored.
DMS Fetchlet/Oracle Management Agent Integration Instructions
DMS has been used in several components (such as Apache, JServ, OSE, and Portal) to provide a consistent performance monitoring infrastructure for Oracle 9i Application Server. The Sensors are easy to use and save most of the work related to performance measurement because they hide most of the details related to timing, counting, and categorization. Finally, DMS hides many Management Agent details from component developers and much of the Management Agent integration effort.
Integrating DMS Data with the Management Agent
As mentioned earlier, DMS allows application and system developers to measure and export customized, component-specific performance metrics. The Oracle Management Agent enables software components to import runtime performance data into Enterprise Manager. This section describes how to integrate DMS performance metrics with the Management Agent.
Step 1: Install AS
Step 2: Install Enterprise Manager
Step 3: Instrument your Component with DMS
To enable DMS metrics for Enterprise Manager, you must follow two additional rules:
-
Rule 1: All Nouns exported to the Management Agent must have types Noun types can be set either by specifying the "type" parameter in the Noun.create() methods or by using the Noun.setType(String) method. The idea is that every Noun type will be converted automatically to a Management Repository table. Every Noun of a given type will become a row in the type's corresponding Management Repository table. The metrics contained by a Noun become columns in the Management Repository table metric. Any Noun without a type will not be exported to Management Agent.
-
Rule 2: All Nouns of a given type must contain a consistent set of Sensor names Because the metrics contained by a Noun become columns in a management repository table, you must make sure that all Nouns of a given type contain the same Sensors. This ensures that each row of the corresponding Management Repository table has the same set of columns. DMS does not check this constraint for you.
For example, the following Java snippet shows how to create typed Nouns that contain a consistent set of Sensors. DMS will automatically convert these into a Management Repository table named "MyType":
/* first create the nouns*/
Noun n1 = Noun.create("/myExample/myComponent/noun1", "MyType");
Noun n2 = Noun.create("/myExample/myComponent/noun2", "MyType");
/* next, create the Sensors */
PhaseEvent pe1 = PhaseEvent.create(n1, "criticalPhase", "a critical interval");
PhaseEvent pe2 = PhaseEvent.create(n2, "criticalPhase", "a critical interval");
Event e1 = Event.create(n1, "importantEvt", "an important event");
Event e2 = Event.create(n2, "importantEvt", "an important event");
/* here is a third set that shows the use of Noun.setType(String) */
PhaseEvent pe3 = PhaseEvent.create(
"/myExample/myComponent/noun3/criticalPhase",
"a critical interval");
Event e3 = PhaseEvent.create(
"/myExample/myComponent/noun3/importantEvt",
"an important event");
Noun n3 = Noun.get("/myExample/myComponent/noun3");
n3.setType("MyType");
For this example, the "MyType" table will contain three rows and four columns. Besides the columns corresponding to the two Sensors, there will be a "name" column and a "path" column that will contain the DMS path name including the process name and "/myExample/myCom...".
If these Nouns/Sensors are created in several servlet engines within the AS site, then the AggreSpy will find each of the servlet engines and will aggregate all of the Nouns/Sensors into a single MyType table.
Step 4: Generate your Target Metadata Document
You can generate the Target Metadata Document using your browser. Point your browser to your AS site that you want to monitor using the following URL:
http://YOUR_AS_HOST:YOUR_AS_PORT/YOUR_SERVLET_PATH/AggreSpy?format=targetmetadata
You should use the actual host, port and servlet path of your AS installation in the above URL. The servlet path usually defaults to "servlet". The XML document you get is the Target Metadata Document for your AS site. The first comment of the XML document explains where you can obtain the Target Metadata Document and instructions telling you what needs to be done to this document.
Step 5: Install the Target Metadata Document
Follow the steps described in the first comment of the XML document. Save the XML document to a file called "oracle_dms.xml" under the "metadata" directory of your Enterprise Manager installation (OMS_ORACLE_HOME/sysman/admin/metadata/). If you want to monitor a subset of the metrics or merge the metrics with the ones in the existing "oracle_dms.xml" file, you should save this new definition to a separate file called target_name.xml. You will also need to change the Target Type entry in the generated metadata document.
Next, you should add the target instance information of your AS site to your "targets.xml" file residing under the top directory of your Enterprise Manager installation. You can find a block of XML tags in the comment you read. They look like:
<Target Type='oracle_dms' NAME='DMS_YOUR-IAS-HOST_YOUR-IAS-PORT' VERSION='2.0'> <Property NAME='host' VALUE='YOUR_IAS_HOST' /> <Property NAME='port' VALUE='YOUR_IAS_PORT' /> <Property NAME='dmsPath' VALUE='YOUR_SERVLET_PATH' /> </Target>
Copy this block and paste it to the targets.xml file between <targets> and </targets> tags.
Finally, to add the new target metadata file and target instance information from the targets.xml file to Enterprise Manager, you must run the following command:
>$ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl reload
Step 6: View Your Metrics
You are ready to view your metrics using Enterprise Manager's Metric Browser. First, make sure that AS and your component are still running. Next, restart the Oracle Management Agent. Finally, point your browser to your Management Agent installation using the following URL:
http://YOUR_AGENT_HOST:YOUR_AGENT_PORT/emd/browser/main
The Management Agent port information can be found in the $AGENT_HOME/sysman/config/emd.properties file at the EMD_URL line.
You should use the actual host and port of your Management Agent installation in the above URL. You will find your AS site listed as the target "DMS_YOUR-AS-HOST_YOUR-AS-PORT". If you click the link, you will see a list of metric IDs. You can browse your metrics by clicking on the respective metric IDs.
JDBC Fetchlet
Call-level interfaces such as JDBC permit external access to SQL database manipulation and update commands. The Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) fetchlet allows you to execute common JDBC commands and obtain their response time for any type of database.
Input Parameters
Table 20-14 JDBC Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
Transaction Name |
(Standard) |
Required. |
|
Beacon Name |
(Standard) |
Required. |
|
Connect String |
Connection string provided by the user. The Connect String must comply with the URL format specified by the vendor of the database to which the user is trying to connect. Examples: Format required by Oracle: jdbc:oracle:thin:@hostname:port Format required by MySQL: jdbc:mysql://hostname:port |
Required. |
|
Class Name String |
The driver class name to be used for connections. Example: oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver You have two options for configuring the Agent to use the .jar file containing the driver:
|
Required. |
|
Username |
User name to be used when connecting to the database. |
Required. |
|
Password |
Password to be used when connecting to the database. |
Required. |
|
Role |
User Role |
Required. |
|
Statement |
SQL statement to be executed. Use of PL/SQL is possible by using prepareCall() API. |
Required. |
Table 20-15 Metric Columns Collected
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
Status |
Status of the test. Status is 'down' if there is a SQLException generated by the fetchlet. |
|
Total Time |
Time required for the fetchlet to execute the test. |
|
Connect Time |
Time required for DriverManager.getConnection() to complete. |
|
Prepare Time |
Time required for conn.prepareStatement() to complete. |
|
Execute Time |
Time required for stmt.executeQuery() to complete. |
|
Fetch Time |
Time required for while(rs.next()) { rs.getRow() } to complete. |
|
Close Time |
Time required for closing resultset, statement, connection to complete. |
|
Number of rows |
Number of rows fetched. |
|
Total time per row |
|
|
Fetch time per row |
Example: Properties Passed to JDBC Fetchlet
The following example provides the properties passed to the JDBC fetchlet when invoked.
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="JDBC"> <Property NAME="TxnName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">TxnName</Property> <Property NAME="BeaconName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">BeaconName</Property> <Property NAME="connstring" SCOPE="INSTANCE">connString</Property> <Property NAME="username" SCOPE="INSTANCE">username</Property> <Property NAME="password" SCOPE="INSTANCE">password</Property> <Property NAME="statement" SCOPE="GLOBAL">select * from user_tables</Property> <Property NAME="classstring" SCOPE="GLOBAL">oracle.jdbc.none</Property> <Property NAME="role" SCOPE="GLOBAL" OPTIONAL="TRUE">DBA</Property> <Property NAME="useconnpool" SCOPE="GLOBAL" OPTIONAL="TRUE">FALSE</Property> <Property NAME="GetTimingData" SCOPE="GLOBAL">TRUE</Property> </QueryDescriptor>
WBEM Fetchlet
The WBEM fetchlet accesses a CIMOM and retrieves requested information using the specified CIM class. The CIM class is mapped to a Management Repository table metric. The name of the CIM class is the name of the table metric that is returned, and the properties defined for the CIM class are used to name the table columns for the metric. The properties of interest must be specified during metric definition.
The fetchlet returns the instances that have been instantiated for the CIM class as rows of the Management Repository table metric.
Input Parameters
Table 20-16 WBEM Fetchlet Input Parameters
| Name | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
hostname |
String |
Host name of the CIMOM |
Optional; default is "localhost" |
|
port |
Integer |
Port for the CIMOM |
Optional; default is 5988 |
|
namespace |
String |
CIM Namespace |
Optional; default is "root/cimv2" |
|
username |
String |
User name to use for CIMOM authorization on the host where the CIMOM is running |
Required |
|
password |
String |
Password to use for CIMOM authorization on the host where the CIMOM is running |
Required |
|
CIMclassname |
String |
Name of the CIM class whose instances will be returned |
Required for all operations except STATUS. STATUS operations just check whether the CIMOM is running, so a class name is not needed. |
|
operation |
String |
Operation to be performed. Supported operations include COUNT, which returns a count of the number of instances in the class, VALUES, which returns the values of the specified properties for each instance of the class, or STATUS, which provides status information about the CIMOM. |
Optional, default is VALUES |
|
properties |
String |
The property names from the CIM class definition that we are interested in collecting. |
Required for VALUES operation. If the operation is VALUES, we can have 1 to N of these, separated by a semicolon. If the operation is VALUES, and no properties are provided, an error is returned. Properties are handed to the EMD in the order that they are specified. |
Error Handling
The following types of errors have been identified for the WBEM fetchlet.
MissingParameterException occurs when:
-
No CIM Class parameters match.
Fetchlet exception occurs when:
-
The class name is not found in the CIMOM namespace.
-
The namespace is not found.
-
The connection to the CIMOM does not have valid credentials.
-
The connection to the CIMOM failed because the CIMOM was not running.
-
The CIM class property does not exist
-
An unsupported operation was specified
-
No properties were specified.
Notes
Ports: Some CIMOM client interfaces expose the port that the CIMOM is listening on while some clients do not. To cover both cases, the port is exposed as an optional input parameter that defaults to port 5988. This is the default Pegasus CIMOM listener port. The Java API that is provided through Sun's Wbem Services does not expose the CIMOM port.
Protocols: Most CIMOMs support either an RMI or HTTP protocol for communicating with the CIMOM. The testing that has been done shows that the HTTP protocol is not as stable, and in some cases, not fully implemented in the CIMOM. Because of this, the protocol currently defaults to RMI. The actual parameters for the WBEM Services CIMOM for the protocol are: CIMClient.CIM_RMI or CIMClient.CIM_XML.
Fetchlet Operations: The WBEM APIs are very flexible at allowing clients to traverse the class hierarchies that are defined and their associations. At this point in time, the options on accessing CIM data from an EMD are restricted to counting, getting the properties of classes, and CIMOM status. These are the more important operations that need to be performed for monitoring. As additional requirements come in, we can add new operations to support them if necessary. For the prototype, only the count operation has been implemented.
Authentication: Most CIMOMs provide APIs to support authentication through a user identity mechanism. The majority of the CIMOMs have not implemented the API, so this capability is really a no-op. In any case, we've supplied the capability in the fetchlet so that as CIMOM implementations catch up with the standard, we'll have the necessary support in place.
Examples
The Wbem fetchlet supports three basic operations. At this point, the fetchlet only handles one operation at a time, so you cannot mix count, status, and value operations within a single fetchlet call. Example 1 shows how to write the metadata for a COUNT operation:
Example 1: COUNT Operation Metadata
<Metric NAME="Load" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_cimom_load">Load</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="Active Clients" TYPE="NUMBER" IS_KEY="FALSE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_cimom_active_clients">Active CIMOM Clients</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="Wbem">
<Property NAME="username" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="password" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="CIMClassname" SCOPE="GLOBAL">EX_SFLProvider</Property>
<Property NAME="operation" SCOPE="GLOBAL">COUNT</Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>The FETCHLET_ID is identified as Wbem. Property names are passed to the fetchlet for the required parameters user name, password, and CIMClassname. The operation is identified as COUNT.
The following example shows how to implement a Response Status metric to determine whether the CIMOM is running or not. It returns a value of 1 if the connection to the CIMOM is successful, otherwise 0.
Example 2: Response Status Metric
<Metric NAME="Response" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_cimon_response">Response</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="Status" TYPE="NUMBER" IS_KEY="FALSE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_cimom_response_status">Status</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="Wbem">
<Property NAME="username" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="password" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="operation" SCOPE="GLOBAL">STATUS</Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
The default operation is the VALUES operation. It is used to fetch the values of a class that is defined in the CIMOM.
In the final example, the EX_Teacher class is accessed and fetches the name column. Name is the key of the class and of the new metric being defined, so the IS_KEY property is set to true. The CIM class properties will be mapped to the Enterprise Manager columns in the order that they are specified in the properties property. In this case, there is only 1 property - Name.
Example 3: Single Property Fetched for a Class
<Metric NAME="EX_Teacher" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_EX_Teacher">EX_Teacher Class</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="Name" TYPE="STRING" IS_KEY="TRUE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_ex_teacher_name">Name</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="Wbem">
<Property NAME="username" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="password" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="CIMClassname" SCOPE="GLOBAL">EX_Teacher</Property>
<Property NAME="properties" SCOPE="GLOBAL">Name</Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
If multiple properties are fetched for a class, semi-colons should separate them. The properties should be provided in the order that the column descriptors are specified for the metric table definition.
Example 4: Multiple Properties Fetched for a Class
<Metric NAME="EX_SFLProvider" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_EX_SFLProvider">EX_SFLProvider Class</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="Name" TYPE="STRING" IS_KEY="TRUE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_ex_sfl_name">Name</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="Win" TYPE="NUMBER" IS_KEY="FALSE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_ex_sfl_win">Win</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor NAME="Lost" TYPE="NUMBER" IS_KEY="FALSE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="wbem_ex_sfl_lost">Lost</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="Wbem">
<Property NAME="username" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="password" SCOPE="GLOBAL">guest</Property>
<Property NAME="CIMClassname" SCOPE="GLOBAL">EX_SFLProvider</Property>
<Property NAME="properties" SCOPE="GLOBAL">Name;Win;Lost</Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>JMX Fetchlet
The JMX fetchlet retrieves Java Management Extensions (JMX) attributes (or invokes a JMX operation) from an MBean and returns the result as a (table) metric. If the ObjectName specified is an ObjectName pattern, then multiple rows are returned. Each row corresponds to an MBean matching the specified ObjectName pattern.
Input Parameters
Table 20-17 JMX Fetchlet Major Input Parameters
| Name | Type | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
|
MachineName |
String |
MBean server host name |
Optional |
|
Port |
Port on which the MBean server is listening for new connections |
Optional |
|
|
UserName |
String |
User name for JMX connections, if required |
Required |
|
password |
String |
Password for JMX connections, if required |
Required |
|
protocol |
String |
Protocol used for the connection |
Optional |
|
service |
String |
Service used for connection |
Optional |
|
serviceURL |
String |
serviceURL used for JMX connection. This is instead of the previous MachineName, Port, protocol, and service properties. Note: For middleware targets, the serviceURL can be obtained from either the farm or managedServer association depending on whether metric needs to be collected from AdminServer or the managed server. |
Required (unless MachineName and Port are specified) |
|
Metric |
String |
Mbean object name (or if MetricService=true, the DMS table name) |
Required |
|
columnOrder |
String |
Semi colon separated list of JMX attributes for the previous MBean corresponding to the column definitions in the TableDescriptor of the metric. |
Required |
|
operation |
String |
Name of the JMX operation to be invoked.In this case, the columnOrder represents the values from the return object to be populated in the Metric. (Oracle recommends using jmxcli to generate this). |
Optional |
|
arguments |
String |
The XML representing the arguments for the JMX operation. Oracle recommends using jmxcli to generate this. |
Optional |
|
MetricService |
Boolean |
MetricService=true implies that the metric is retrieved by the Oracle-specific DMS Metric Service. In this case the previous columnOrder property is a list of column names and the ‘metric' property indicates the actual DMS table name. |
Optional |
|
identityCol |
String |
The Mbean object name key (or a semi-colon separated list of keys) that will be extracted from the Mbean ObjectName and surfaced as key columns in the resultant metric.If the value ‘canonical' is specified, an additional key metric column with the complete Mbean object name is returned by the fetchlet.This property makes sense only if the previous metric property is an ObjectName pattern that matches more than one Mbean on the server. |
Optional |
|
autoRowID |
String |
Prefix for an automatically generated key column. The suffix is sequential numbers starting at 1.For example, autoRowID set to ROW_ generates a key column at position 0 with values ROW_1, ROW_2, and so on up to the number of rows returned.This is usually the case if none of the other columns (JMX attributes selected) are unique and multiple rows are returned as a result of multiple mbeans matches and mbean pattern. |
Optional |
|
useCache |
Boolean |
Applicable only when MetricService=true and indicates if metric service cache needs to be used |
Optional |
|
ServerNames |
String |
Applicable only when MetricService=true and is a semicolon list of server names from which the DMS metrics need to be retrieved. This is relevant only when collecting these metrics from the AdminServer (that is, serviceURL points to AdminServer through farm association), which has metrics from all managed servers |
Optional |
|
valueWhenNoMBean |
Number |
Typically used for response metrics and has the value that the fetchlet returns as a single row and column when no mbeans are found that match the given mbean pattern (in the previous metric property). |
Optional |
|
valueWhenDown |
Number |
Typically used for response metrics. This has the value that the fetchlet returns as a single row and column when the connection to the server fails due to a connection exception (indicating that the server is down). |
Optional |
|
admlMap |
String |
Applicable only when MetricService=true and is an XML snippet that indicates what adml parameters need to be passed for this adml table.(Oracle recommends using jmxcli to generate this). |
Optional |
Notes:
Web Service Fetchlet
In target metadata files generated by the Web Services Command-Line tool, the <QueryDescriptor> element specifies the properties that will be passed to the Web Services fetchlet when being invoked.
Note:
From Release 13.1 onwards, the Web Service fetchlet is available from the Enterprise Manager for Fusion Apps and the Enterprise Manager for Fusion Middleware plug-ins.
To use this fetchlet, you must have the Enterprise Manager for Fusion Apps and the Enterprise Manager for Fusion Middleware plug-ins deployed on both the OMS and the Management Agent.
Input Parameters
Table 20-18 lists the supported properties:
Table 20-18 Web Service Fetchlet Properties
| Name | Description | Use | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ServiceName |
Web service name |
Required. Service Name must be prefixed with a valid namespace. |
All referenced namespaces are specified by the property "Namespace" |
|
PortName |
Web service port name |
Required. Port Name must be prefixed with a valid namespace. |
All referenced namespaces are specified via the property "Namespace" |
|
OperationName |
Web service operation name |
Required. Operation Name must be prefixed with a valid namespace. |
All referenced namespaces are specified by the property "Namespace" |
|
ServiceEndpoint |
Web service endpoint |
Required. A valid URL. |
|
|
WsdlURL |
Web service WSDL URL |
Optional. A valid URL. |
Required only if it is a RPC/Encoded Web service |
|
ParameterStyle |
SOAP parameter mapping style |
Optional. - BARE - WRAPPED |
Optional only if it is a RPC/Encoded or REST-ful Web service |
|
Payload |
Web service operation request payload |
Required. Must be specified using the CDATA section. |
|
|
SOAPBindingStyle |
SOAP binding style |
Optional. - DOCUMENT - RPC |
Optional only if it is a RPC or Encoded Web service |
|
SOAPBindingUse |
SOAP binding use |
Optional - ENCODED - LITERAL |
Optional only if it is a RPC or Encoded Web service |
|
SOAPVersion |
SOAP version |
Optional - SOAP_1_1 - SOAP_1_2 |
Optional only if it is an RPC or Encoded Web service |
|
MessageType |
Web service message type |
Optional - SOAP - REST |
Optional only if it is a RPC or Encoded Web service |
|
SecurityPolicy |
Security policy |
Required - NONE - BASIC_AUTHENTICATION |
|
|
Namespace |
Set of all namespaces referenced |
Optional. Contains all the namespaces referenced in the metric Specify using notation: [ns0="uri0"][ns1="uri1"] Example: [ns0="http://type.abc.com"] [ns1="http://app.abc.com"] |
|
|
ColType |
Collection result column type |
Required List of metric column type (separated by comma) Example: msgId:STRING,source:STRING,detail:STRING |
|
|
RowType |
Collection result row type |
Required List of XPath expression corresponding to metric columns (separated by comma) For example: //ns0:eventResponse/msgId, //ns0:eventResponse/source, |
|
|
SSLKeyStoreCredential |
SSL keystore credentialSet name |
Optional A valid CredentialSet of a Store Credential Type defined in the <CredentialInfo> |
Must be defined as a monitoring credential. |
|
SSLTrustStoreCredential |
SSL truststore credentialset name |
Optional A valid CredentialSet of a StoreCredential Type defined in the <CredentialInfo> |
Must be defined as a monitoring credential. |
|
UserCredential |
User token credentialset name |
Optional A valid CredentialSet of a AliasCredential or CSFKeyCrdential Type defined in the <CredentialInfo> |
Must be defined as a monitoring credential. |
|
ValueWhenDown |
Default response when target is down |
Required (only for response metric). Not required for regular metric. For Response metric, when a target is down, this value (if specified) will be returned. |
A target is considered as down when the Fetchlet catches a ConnectionException. |
Examples
Example 1 provides an example of a metric definition for Remote Procedure Call (RPC) or encoded Web services and Example 2 provides an example of a metric definition for doc or literal Web services.
Example 1: Metric Definition for RPC or Encoded Web Service
<Metric NAME="getVacantRooms" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="NLSID_GET_VACANT_ROOMS">getVacantRooms</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="TRUE" NAME="roomID" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_ROOM_ID">roomID</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="floor" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_FLOOR">floor</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="number" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_NUMBER">number</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="rate" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_RATE">rate</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="roomType" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_ROOM_TYPE">roomType</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="smoking" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_SMOKING">smoking</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="available" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_AVAILABLE">available</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="OWSM_WSF">
<Property NAME="SecurityPolicy" SCOPE="INSTANCE">NONE</Property>
<Property NAME="WsdlURL" SCOPE="INSTANCE">wsdlURL</Property>
<Property NAME="ServiceEndpoint" SCOPE="INSTANCE">serviceURL</Property>
<Property NAME="ServiceName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">ns0:SimpleHotelServiceRE</Property>
<Property NAME="PortName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">ns0:HotelService</Property>
<Property NAME="OperationName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">getVacantRooms</Property>
<Property NAME="MessageType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SOAP</Property>
<Property NAME="SOAPBindingStyle" SCOPE="GLOBAL">RPC</Property>
<Property NAME="SOAPBindingUse" SCOPE="GLOBAL">ENCODED</Property>
<Property NAME="ParameterStyle" SCOPE="GLOBAL">BARE</Property>
<Property NAME="SOAPVersion" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SOAP_1_1</Property>
<Property NAME="Namespace" SCOPE="GLOBAL"><![CDATA[[ns1="http://hotel.apps.muws/"][ns0="http://hotel.apps.muws/rpc/"]]]></Property>
<Property NAME="RowType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/@roomID,//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/floor,
//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/number,//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/rate,//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/roomType,
//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/smoking,//ns1:getVacantRoomsResponse/return/item/available</Property>
<Property NAME="ColType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">roomID:STRING,floor:STRING,number:STRING,rate:STRING,roomType:STRING,smoking:STRING,available:STRING</Property>
<Property NAME="Payload" SCOPE="GLOBAL"><![CDATA[<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"
xmlns:ns="http://hotel.apps.muws/"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:soapenc="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/">
<soap:Body soap:encodingStyle="">
<ns:getVacantRooms/>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>]]></Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
Example 2: Metric Definition for Doc or Literal Web Service
<Metric NAME="square" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="NLSID_SQUARE">square</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="arg0" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_ARG0">arg0</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="OWSM_WSF">
<Property NAME="SecurityPolicy" SCOPE="INSTANCE">NONE</Property>
<Property NAME="ServiceEndpoint" SCOPE="INSTANCE">serviceURL</Property>
<Property NAME="ServiceName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">ns0:CalculatorService</Property>
<Property NAME="PortName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">ns0:CalculatorPort</Property>
<Property NAME="OperationName" SCOPE="GLOBAL">square</Property>
<Property NAME="MessageType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SOAP</Property>
<Property NAME="SOAPBindingStyle" SCOPE="GLOBAL">DOCUMENT</Property>
<Property NAME="SOAPBindingUse" SCOPE="GLOBAL">LITERAL</Property>
<Property NAME="ParameterStyle" SCOPE="GLOBAL">WRAPPED</Property>
<Property NAME="SOAPVersion" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SOAP_1_1</Property>
<Property NAME="Namespace" SCOPE="GLOBAL"><![CDATA[[ns0="http://tests.jaxws.oracle.com/"]
[ns1="http://www.oracle.com/jaxws/tests"]]]></Property>
<Property NAME="RowType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">//ns1:squareResponse/arg0</Property>
<Property NAME="ColType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">arg0:STRING</Property>
<Property NAME="Payload" SCOPE="GLOBAL"><![CDATA[<soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body xmlns:ns1="http://www.oracle.com/jaxws/tests">
<ns1:square>
<arg0>%square.arg00001%</arg0>
</ns1:square>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>]]></Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
Using Credentials for Authentication
If basic authentication is required, then you must configure or define the following in the metric definition:
Example: Using Keystore and Truststore for SSL
…………
<Property NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredential" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet</Property>
<Property NAME="SSLKeyStoreCredential" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet</Property>
NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet">SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet</CredentialRef>
<CredentialRef NAME="SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet">SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet</CredentialRef>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
<CredentialInfo>
<CredentialType NAME="StoreCredential">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_TYPE">Store Credential Type</Label>
</Display>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StoreLocation">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_LOCATION">Store Location</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StoreType">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_TYPE">Store Type</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StorePassword">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_PASSWORD">Store Password</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
</CredentialType>
<CredentialSet NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet" USAGE="MONITORING">
<AllowedCredType TYPE="StoreCredential"/>
</CredentialSet>
<CredentialSet NAME="SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet" USAGE="MONITORING">
<AllowedCredType TYPE="StoreCredential"/>
</CredentialSet>
</CredentialInfo>
WS-Management Fetchlet
In target metadata files generated by the wsmancli Command-Line Tool, the <QueryDescriptor> element specifies the properties that will be passed to the WSManagement fetchlet when being invoked.
Note:
From Release 13.1 onwards, the WS-Management fetchlet is available from the Enterprise Manager for Fusion Middleware plug-in.
To use this fetchlet, you must have the Enterprise Manager for Fusion Middleware plug-in deployed on both the OMS and the Management Agent.
Input Parameters
Table 20-19 provides a complete list of the supported properties:
Table 20-19 WS Management Fetchlet Properties
| Name | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|
|
ResourceURI |
URI of a resource class representation or instance representation (wsman:ResourceURL) |
Required Any valid URI according to RFC 3986 |
|
To |
Transport address of a service (wsa:To). |
Required Any valid network transport address. |
|
Action |
wsa:Action identifies which operation is to be carried out against the resource. |
Required Current release only supports "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/transfer/Get". |
|
TransferOperation |
Name of the WS-Transfer operation. |
Required Current release only supports "GET". |
|
Locale |
Specifies the language that the client requests (and sometimes requires) and the response text to be translated into (wsman:Locale) |
Optional Any valid value for the standard XML attribute xml:lang |
|
MaxEnvelopeSize |
The size to indicate that client expects a response whose total SOAP envelope does not exceed the specified number of octets (wsman:MaxEnvelopeSize) |
Optional Value should not be less than 8192 |
|
OperationTimeout |
The value to indicate that client expects a response or a fault within the specified time (wsman:OperationTimeout). |
Optional Specify the value using format xs:duration (see http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema:duration). |
|
OptionSet |
A set of switches to the service to modify or refine the nature of the request (wsman:OptionSet). |
Optional Specify the values using the notation: [<OptionName1>, value:<value1>, type:<type1>, mustComply:<true|false>][<OptionName2>, value:<value2>, type:<type>, mustComply:<true|false>][...] |
|
ReplyTo |
The header to be present in all request messages when a reply is required (wsa:ReplyTo). |
Optional It should be either a valid address for a new connection using any transport supported by the service or the URI http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/08/addressing/role/anonymous (see WS-Addressing) |
|
SelectorSet |
Set of selectors that identify the instance of resource to be accessed (wsman:SelectorSet) |
Required Specify the value using the format below: [S1, V1][S2, V2]...[Sn, Vn] Where - S1, S2, ..., Sn are Selector names - V1, V2, ..., Vn are Selector values |
|
SecurityPolicy |
Security policy |
Required - NONE - BASIC_AUTHENTICATION |
|
Namespace |
Set of all namespaces referenced |
Required Specify using notation: [ns0="uri0"][ns1="uri1"].. Example: [ns0="http://type.abc.com"][ns1="http://app.abc.com"] |
|
ColType |
Collection result column type |
Required List of metric column types (separated by comma) Example: msgId:STRING,source:STRING,detail:STRING |
|
RowType |
Collection result row type |
Required List of XPath expression corresponding to metric columns (separated by comma) For example: //ns0:eventResponse/msgId,//ns0:eventResponse/source |
|
SSLKeyStoreCredential |
SSL keystore credentialSet name |
Optional A valid CredentialSet of a Store Credential Type defined in the <CredentialInfo> |
|
SSLTrustStoreCredential |
SSL truststore credentialSet name |
Optional A valid CredentialSet of a StoreCredential Type defined in the <CredentialInfo> tag. |
|
UserCredential |
User token credentialSet name |
Optional A valid CredentialSet of a AliasCredential or CSFKeyCrdential Type defined in the <CredentialInfo> tag. |
|
ValueWhenDown |
Default response when target is down |
Required (only for response metric). Not required for regular metric. For Response metric, when a target is down, this value (if specified) will be returned. A target is considered as down when the Fetchlet catches a ConnectionException |
Example: Metric definition for using the WS-Management Fetchlet
The following example provides an example of a metric definition using the WS-Management fetchlet.
<Metric NAME="trafficLight" TYPE="TABLE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="NLSID_TRAFFIC_LIGHT">trafficLight</Label>
</Display>
<TableDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="YES" NAME="name" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_NAME">name</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="color" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_COLOR">color</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="x" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_X">x</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
<ColumnDescriptor IS_KEY="FALSE" NAME="y" TYPE="STRING">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="COL_Y">y</Label>
</Display>
</ColumnDescriptor>
</TableDescriptor>
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="WSManagementFetchlet">
<Property NAME="SecurityPolicy" SCOPE="INSTANCE">NONE</Property>
<Property NAME="ResourceURL" SCOPE="INSTANCE">resourceURL</Property>
<Property NAME="To" SCOPE="INSTANCE">To address</Property>
<Property NAME="OptionSet" SCOPE="INSTANCE">optionSet</Property>
<Property NAME="Locale" SCOPE="INSTANCE">locale</Property>
<Property NAME="MaxEnvelopeSize" SCOPE="INSTANCE">maxEnvelopeSize</Property>
<Property NAME="OperationTimeout" SCOPE="INSTANCE">operationTimeout</Property>
<Property NAME="Namespace" SCOPE="GLOBAL"> <![CDATA[[ns1="http://schemas.wiseman.dev.java.net/traffic/1/light.xsd"]
[ns0="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"]
[wsa="http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing"]
[env="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope"]]]></Property>
<Property NAME="RowType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">//ns1:trafficlight/ns1:name,//ns1:trafficlight/ns1:color,//ns1:
<Property NAME="ColType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">name:STRING,color:STRING,x:STRING,y:STRING</Property>
<Property NAME="ReplyTo" SCOPE="GLOBAL">http://www.w3.org/2005/08/addressing/role/anonymous</Property>
<Property NAME="Action" SCOPE="GLOBAL">http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2004/09/transfer/Get</Property>
<Property NAME="TransferOperation" SCOPE="GLOBAL">GET</Property>
<Property NAME="SelectorSet" SCOPE="GLOBAL">[name,Light1]</Property>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
Using Credentials
If basic authentication is required, then configure or define in the metric definition:
Example: Using Keystore and Truststore for SSL
…………
<Property NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredential" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet</Property>
<Property NAME="SSLKeyStoreCredential" SCOPE="GLOBAL">SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet</Property>
<CredentialRef NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet">SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet</CredentialRef>
<CredentialRef NAME="SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet">SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet</CredentialRef>
</QueryDescriptor>
</Metric>
<CredentialInfo>
<CredentialType NAME="StoreCredential">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_TYPE">Store Credential Type</Label>
</Display>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StoreLocation">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_LOCATION">Store Location</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StoreType">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_TYPE">Store Type</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StorePassword">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_PASSWORD">Store Password</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
</CredentialType>
<CredentialSet NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet" USAGE="MONITORING">
<AllowedCredType TYPE="StoreCredential"/>
</CredentialSet>
<CredentialSet NAME="SSLKeyStoreCredentialSet" USAGE="MONITORING">
<AllowedCredType TYPE="StoreCredential"/>
</CredentialSet>
</CredentialInfo>
REST Fetchlet
The REST fetchlet provides target monitoring for RESTful web resources. Based on input properties, this fetchlet can construct a request to communicate with the managed targets using HTTP standards. It can retrieve relevant data from the response to build and return monitoring metrics.
This release supports the following RESTful web services only:
-
HTTP methods
-
GET: Define a reading access of the source without any side-effects. The resource is never changed through a GET request.
-
POST: Update an existing resource or create a new resource.
-
HEAD: vCheck if a given path is serviceable.
-
-
Media type of request or response representations
-
application/xml (both request and response)
-
application/json (both request and response)
-
text/xml (response only)
-
application/x-www-form-urlencoded (request only)
-
-
Authentication scheme
Supports BASIC authentication.
Response Processing
The fetchlet relies on response data to construct monitoring metrics. Because the response media type can be application/xml, application/json, or text/xml, different mechanisms are adapted to process the response. Table 20-20 describes the different mechanisms for each response media type.
Table 20-20 Resonse Processing Mechanism
| Media Type | Mechanism |
|---|---|
|
application/xml |
XPath Query is used for processing XML data. The fetchlet property, RowType, specifies a list of XPath expressions corresponding to metric columns (separated by comma) for retrieving column data. For example: <records>
<ns2:Record xmlns:ns2="urn:com.office.directory">
<name>Peter</name>
<phone>+1 (650) 555-0100</phone>
</ns2:Record>
<ns2:Record xmlns:ns2="urn:com.office.directory">
<name>John</name>
<phone>+1 (650) 555-0185</phone>
</ns2:Record>
</records>
Assume the monitoring metric has two columns (name and phone). The corresponding XPath expressions are:
The following is an example of extracted data: Peter, +1 (650) 555-0100 John, +1 (650) 555-0185 |
|
application/json |
JSONPath is used for processing JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) data. JSONPath expressions refer to a JSON structure in the same way as XPath expressions are used in an XML document. For example: {
“Record":
[
{
“name":"Peter"
“phone":"+1 (650) 555-0100"
},
{
“name":"John"
“phone":"+1 (650) 555-0185"
},
]
}
Assume the monitoring metric has two columns (name and phone). The corresponding JSONPath expressions are:
The following example is an example of extracted data: Peter, +1 (650) 555-0100 John, +1 (650) 555-0185 |
|
text/xml |
Because text is a non-structural representation, there is no way to extract any specific data from it. Instead, the entire response is returned. |
Input Parameters
Table 20-21 provides a complete list of the supported properties.
Table 20-21 REST Fetchlet Properties
| Name | Description | Optional |
|---|---|---|
|
BaseURI |
Base URI of the RESTful web service |
No |
|
RequestElementPayload |
Request element payload (XML/JSON) in string format. Must be specified using the CDATA section if it is XML |
Yes |
|
RequestMetadata |
Request metadata in XML format |
No |
|
SecurityPolicy |
Specifies authentication scheme. Either NONE or BASIC_AUTHENTICATION |
No |
|
Namespace |
Set of all namespaces referenced in the metric. Specify using notation: [ns0="uri0"][ns1="uri1"]... For example: [ns0="http://type.abc.com"][ns1="http://app.abc.com"] |
No |
|
ColType |
Collection result column type. List of metric column type (separated by comma). For example: msgId:STRING,source:STRING,detail:STRING |
No |
|
RowType |
Collection result row type. List of path (XPath or JsonPath) expressions corresponding to metric columns (separated by comma). For example: //ns0:eventResponse/msgId,//ns0:eventResponse/source,//ns0:eventResponse/detail |
No |
|
SSLKeyStoreCredential |
SSL keystore credential set name. It must be defined as a monitoring credential and contain these credential columns: Location, Type, Password |
Yes |
|
SSLTrustStoreCredential |
SSL truststore credentialset name. It must be defined as a monitoring credential and contain these credential columns: Location, Type, Password |
Yes |
|
UserCredential |
User token credentialset name. It must be defined as a monitoring credential and contain these credential columns: Alias, Password |
Yes |
|
ProxyHost |
Host name of the proxy server to make the URL connection |
Yes |
|
ProxyPort |
Port number of the proxy server to make the URL connection |
Yes |
The following example shows an example of the Fectchlet Query Descriptor from a target metadata file. For more information about the target metadata files, see Creating Target Metadata Files.
Note:
The fetchlet ID is RESTFetchlet.
Example: Fetchlet Query Descriptor
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="RESTFetchlet">
<Property NAME="SecurityPolicy" SCOPE="INSTANCE">ListAll.SecurityPolicy</Property>
<Property NAME="BaseURI" SCOPE="INSTANCE">ListAll.BaseURI</Property>
<Property NAME="Namespace" SCOPE="GLOBAL">
<![CDATA[[ns0="urn:com.office.directory"]]]></Property>
<Property NAME="RowType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">//ns0:Record/name,//ns0:Record/title,
//ns0:Record/phone,//ns0:Record/building,//ns0:Record/floor,
//ns0:Record/office</Property>
<Property NAME="ColType" SCOPE="GLOBAL">name:STRING,title:STRING,phone:STRING
,building:STRING,floor:STRING,office:STRING</Property>
<Property NAME="RequestMetadata" SCOPE="GLOBAL">
<![CDATA[<Resource path="/">
<Resource path="lookup/list">
<Method elementDefined="false"
accept="application/xml" name="GET"/>
</Resource>
</Resource>
</Property>]]>
<Property NAME="UserCredential" SCOPE="GLOBAL">UserCredentialSet</Property>
<CredentialRef NAME="UserCredentialSet">UserCredentialSet</CredentialRef>
</QueryDescriptor>
Using HTTPS and Self-Signed Certificates
When calling an HTTPS URL with a self-signed SSL certificate from a REST fetchlet, the credential set must be specified in the target metadata file.
<QueryDescriptor FETCHLET_ID="RESTFetchlet">
......
<Property NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredential" SCOPE="GLOBAL">
SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet</Property>
<CredentialRef NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet">
SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet</CredentialRef></QueryDescriptor>
<CredentialInfo>
<CredentialType NAME="StoreCredential">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_TYPE">Store Credential Type</Label>
</Display>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StoreLocation" IS_SENSITIVE="FALSE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_LOCATION">Store Location</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StoreType" IS_SENSITIVE="FALSE">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_TYPE">Store Type</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
<CredentialTypeColumn NAME="StorePassword">
<Display>
<Label NLSID="CRED_STORE_PASSWORD">Store Password</Label>
</Display>
</CredentialTypeColumn>
</CredentialType>
<CredentialSet NAME="SSLTrustStoreCredentialSet" USAGE="MONITORING" CONTEXT_TYPE="TARGET">
<AllowedCredType TYPE="StoreCredential"/>
</CredentialSet>
</CredentialInfo>
In Enterprise Manager, a new fetchlet property, “SSLTrustServerCert", was added. If set to “TRUE", the fetchlet uses the non-validating mode for the server certificate, and there is no need to provide or specify the SSL trust store.
<Property NAME="SSLTrustServerCert" SCOPE="GLOBAL">TRUE</Property>
Using REST CLI to Generate Metadata
REST CLI is a client command line tool for generating target metadata and default collection files to enable the Management Agent to monitor RESTful web resources through invoking the REST fetchlet.
Use the following emctl command to invoke REST CLI:
emctl restcli
Table 20-22 provides a list of the command-line arguments that you can use with the emctl restcli command.
Table 20-22 Command-line Arguments Supported by REST CLI
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Generate target metadata |
|
|
|
WADL location |
|
|
|
WSDL location |
|
|
|
User name to log in to the host |
|
|
|
Host name of the proxy server |
|
|
|
Port number of the proxy server |
|
To use REST CLI: