7 Installing Oracle Remote Management Agents
Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent) is one of the core components of Enterprise Manager that enables you to convert an unmanaged host to a managed host in the Enterprise Manager system. The Management Agent works in conjunction with the plug-ins to monitor the targets running on that managed host.
Management Agent Types
- Standalone agent: Agent installed on a local target. Also, known as local agent.
- Remote agent: Agent installed on host to monitor remote targets such as Host and Database.
- Central agent: Agent installed with the Enterprise Manager middleware. The OMS home and Agent home reside on it.
This chapter describes how you can install remote management agents on unmanaged hosts and convert them to managed hosts and be able to monitor targets on remote host.
Note:
For information about installing Management Agents (standalone agents) using agent gold images, see Installing Oracle Management Agents.
This chapter covers the following:
Overview of Installing Remote Agents
Remote agents are agents installed on a dedicated host to monitor targets on a remote host.
Enterprise Manager depends on agents to discover targets to allow them to be monitored and managed. Traditionally, this requires to install an agent on the same host where the software runs on therefore the installed agent can monitor the state of the target. Customers with software spread over very large numbers of hosts end up having a very large number of agents installed, and over time, managing the lifecycle of all these agents becomes a major operational cost.
What is a remote agent?
A remote agent allows Enterprise Manager to monitor and manage targets by using agents that are installed on separate hosts instead of requiring a local agent installation on the same host as the target. These agents use remote protocols for monitoring the host and database. If needed, use SSH to run commands on the target host.
Once targets on remote hosts are discovered by remote agents, the Enterprise Manager functionalities work as if they were being monitored by local agents. For example, the monitoring and management features such as job system, deployment procedures and patching are available.
A remote agent can monitor targets on many hosts which results in a significant reduction in the number of agents that need to be maintained by the Enterprise Manager administrator.
When checking agent availability, standalone/local agents only have to deal with the agents being unreachable due to hosts being down, while now with remote agents, there can be cases where the agent is up and monitoring targets on other hosts, but the host of the target being down.
Remote Cache: It's the area in the monitored remote host that stores all the remote agent configuration.
The remote agent maintains this area automatically on the monitored hosts. For example, replicating any patches that are applied to it or pushing any metric extension scripts into it. The remote cache also includes dependencies such as the java runtime, a Perl install and the client install which is used by Perl scripts to connect to the database.
Note:
- Local agents cannot be converted to remote agents.
- Remote agents cannot be patched through agent gold image.
This section covers the following:
Supported Operating Systems
Table 7-1 Remote Agents Supported Operating Systems
| Operating System | Version |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Linux x86-64 Red Hat Linux x86-64 |
See Package Requirements for Oracle Management Agent. |
Supported Enterprise Manager Targets
Remote Agent is supported only for Host and Database targets.
Database Targets Supported
All database-related target types can be discovered and monitored using a remote agent.
This includes Database Instance, Cluster Database, Automatic Storage Management, Autonomous Transaction Processing (ATP), Autonomous Data Warehouse (ADW), Cluster and all associated types.
- Database Machine (On-premises Exadata).
- Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance (ZDLRA).
Remote Agents Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
- Simplify agent lifecycle having less number of agent installed.
Enterprise Manager depends on agents to discover targets to allow them to be monitored and managed. Historically, this has required to install an agent on the same host that the target runs on. With remote agents, there's a less number of agents installed, becoming easier to manage them all.
-
When using remote agents, you have the ability to scale up to monitor targets on multiple hosts. For example, you can have a single remote agent to be monitoring more than 10 remote hosts, potentially even hundreds of remote hosts at the large scale.
Limitations
- Existing standalone/local agents cannot be changed to remote agents.
- The host or VM selected for remote agent deployment should not contain any software installs.
- Enterprise Manager targets already discovered cannot be updated or changed to remote agent.
- Cross platform monitoring between remote agent host and remote target host is not supported.
- Remote agent for ATP and ADW targets is not allowed if standby agent is configured.
Installing Remote Agents
At any point in time, if you want to monitor a target remotely running on a host, you must first convert that unmanaged host to a managed host by installing a remote agent.
Note:
Before proceeding, ensure you have reviewed Overview of Installing Remote Agents.This section covers the following:
Workflow of Installing Remote Agents
Table 7-2
| Task | Information |
|---|---|
| Review remote agents prerequisites | See Prerequisites for Installing Remote Agents |
| Deploy remote agents | See Installing Remote Agents Using the Console |
| Review postinstallation tasks | See Performing Postinstallation Tasks for Remote Agents |
| Perform recommended tasks for host monitoring | See:
|
Prerequisites for Installing Remote Agents
Review the following prerequisites for installing remote agents using the Console or EM CLI:
Table 7-3 General Prerequisites for Installing Remote Agents
| Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
|
Hardware Requirements |
See My Oracle Support Doc ID 3076694.1.
|
| Operating System Requirements | See Supported Operating Systems. |
|
Destination Host Requirements |
Confirm that the remote host has not been discovered by Enterprise Manager. The remote agent host should not contain any local targets. Ensure the host you are selecting for remote agent installation is free from any software installation. |
|
Destination Host Credential Requirements |
SSH key or password-based credentials are required. If you choose SSH credentials, the SSH keys are required to get configured prior installing the remote agent. |
|
sudo/pbrun/sesu/su SSH Requirements |
Use Power broker is not supported in Enterprise Manager 24ai Release 1. |
| Check if user needs to configure passwordless sudo | During the Add Remote Host Targets configuration, the following credentials are available:
|
| Check if Passwordless sudo is configured for the user on the remote host |
Monitoring user on the remote host should be configured not to prompt for password. To check, do the following:
|
For additional prerequisites, see Meeting the Generic Prerequisites for Installing Standalone Management Agents Using Add Host Targets Wizard or EM CLI.
Installing Remote Agents Using the Console or EM CLI
You can install remote agents using one of the following methods:
Note:
-
Use
sudowhen adding named credentials using Add Remote Host Targets wizard or EM CLI. Power broker is not supported in Enterprise Manager 24ai Release 1. -
To install remote agents using silent mode, see Installing Oracle Remote Management Agent in Silent Mode in the Enterprise Manager Advanced Installation and Configuration Guide.
Installing Remote Agents Using the Console
This section describes how to install remote agents.
Follow these steps:-
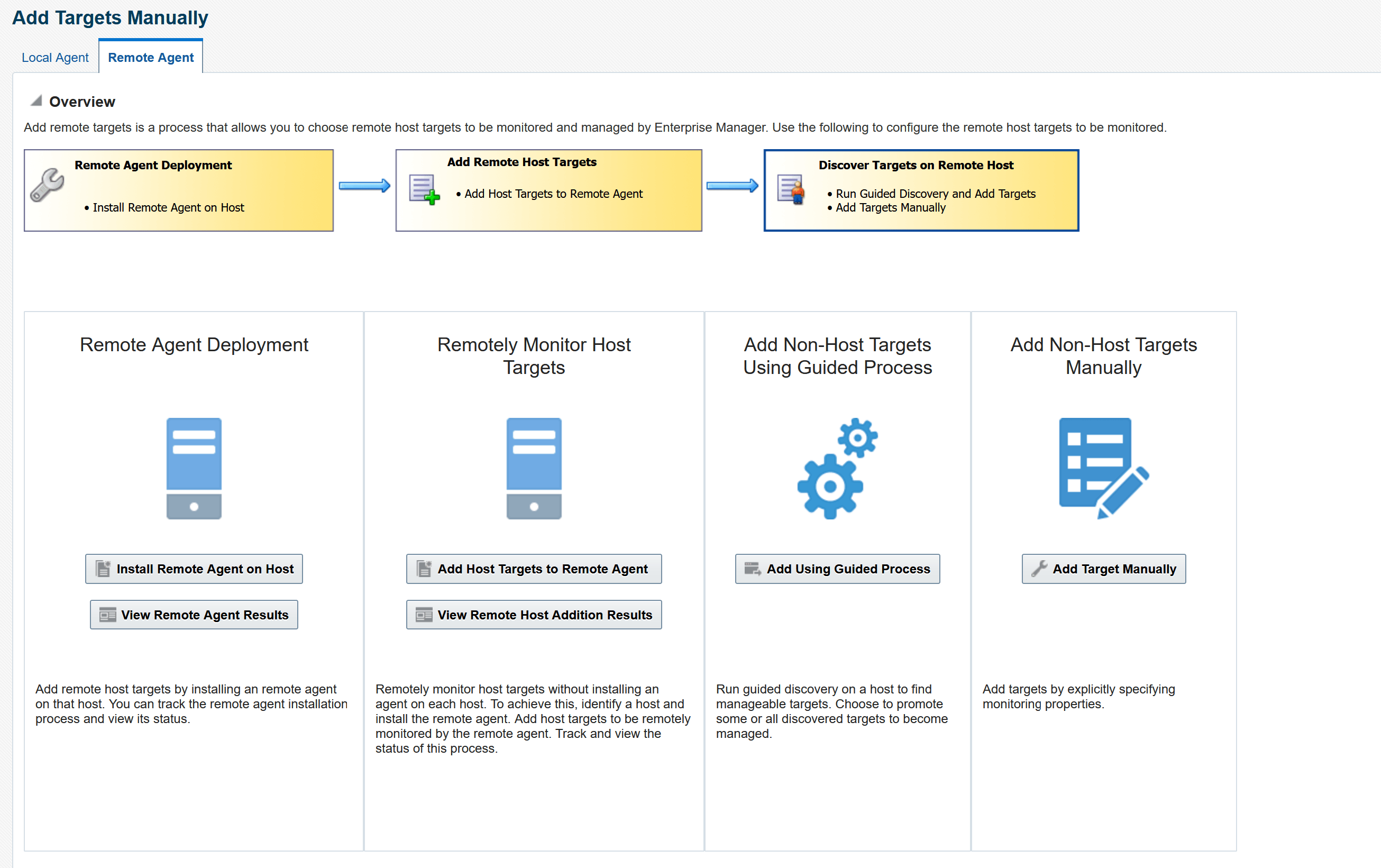
Open the navigation menu located in the upper-left corner of the Console and click Setup.
- Under Setup, select Add Target, and then Add Targets Manually.
- Select the Remote Agent tab.
- Under Remote Agent Deployment, select Install Remote Agent on Host.
-
On the Install Remote Agent on Host: Host and Platform Details page, do the following:
- Accept the default name assigned for this session or enter
a unique name of your choice.
The custom name you enter can be any intuitive name, and need not necessarily be in the same format as the default name. For example,
add_host_operation_1.A unique deployment activity name enables you to save the installation details specified in this deployment session and reuse them in the future without having to enter all the details all over again in the new session.
- From the Add menu, select
Manually to enter the fully qualified name of
the Host and select the
Platform of the remote host on which you want
to install the remote agent.
The remote host names that are retrieved from the system for the installation may include IP addresses and short names. However, it is recommended that you provide fully qualified host names, such as
foo.example.com,which persist over the life of the remote host targets. This is recommended for ease of maintenance and overall security.Note:
-
Oracle recommends you to enter the fully qualified domain name of the remote host. For monitoring purpose, Enterprise Manager adds that remote host and the Management Agent with the exact name you enter here.
-
You must enter only one remote host name per row. Entering multiple remote host names separated by a comma is not supported.
-
You must ensure that the remote host name does not contain underscores('_').
Alternatively, from the Add menu, you can select either From File to add the remote host names stored in a file, or Discovered Hosts to add the remote host names from a list of hosts discovered by Enterprise Manager. For information on how the host name entries must appear in the host file, see Format of the Host List File.
Note:
When you select Discovered Hosts from the Add menu, and add remote hosts from a list of discovered hosts, the host's platform is automatically detected and displayed. The platform name is detected using a combination of factors, including hints received from automated discovery and the platform of the OMS host. This default platform name is a suggestion, so Oracle strongly recommends you to verify the platform details before proceeding to the next step.
Note:
-
If you reach this page (Host and Platform page) from the Auto Discovery Results page, then the hosts you selected on that page automatically appear in the table. In this case, you need to only validate the host names and their platforms.
-
- Click Next.
- Accept the default name assigned for this session or enter
a unique name of your choice.
-
On the Install Remote Agent on Host: Installation Details page, do the following:
- In the Deployment Type section, confirm it says: Remote Agent Install.
- From the table, select the first row that indicates the hosts grouped by their common platform name.
- Under the Agent Installation Details section, provide the installation details common to the hosts selected in Step 3 (b).
- For Installation Base Directory,
enter the absolute path to the agent base directory where you want the
software binaries, security files, and inventory files of the Management
Agent to be copied.
For example,
/u01/software/em24/agentbasedir/If the path you enter does not exist, the application creates a directory at the specified path, and copies the Management Agent software binaries, security files, and inventory files there.
Note:
The Installation Base Directory is essentially the agent base directory. Ensure that the directory you provide is empty. If a previously run deployment session had failed for some reason, then you might see an ADATMP_<timestamp> subdirectory in the agent base directory. In this case, either delete the subdirectory and start a new deployment session, or retry the failed session from the Install Remote Agent on Host page.
- For Instance Directory, accept the
default instance directory location or enter the absolute path to a
directory of your choice where all Management Agent configuration files
can be stored.
For example,
/u01/software/em24/agentbasedir/agent_instIf you are entering a custom location, ensure that the directory has write permission. Oracle recommends maintaining the instance directory inside the agent base directory.
If the path you enter does not exist, the application creates a directory at the specified path, and stores all the Management Agent-related configuration files there.
- From Named Credential dropdown list,
select an appropriate profile whose credentials can be used for setting
up the SSH connectivity between the OMS and the remote hosts, and for
installing a Management Agent on each of the remote hosts.
Note:
-
If you do not have a credential profile, or if you have one but do not see it in the Named Credential list, then click the plus icon against this list. In the Create New Named Credential window, enter the credentials and store them with an appropriate profile name so that it can be selected and used for installing the Management Agents. Also set the run privilege if you want to switch over from the Named Credential you are creating, to another user who has the privileges to perform the installation.
-
If the plus icon is disabled against this list, then you do not have the privileges to create a profile with credentials. In this case, contact your administrator and either request him/her to grant you the privileges to create a new profile or request him/her to create a profile and grant you the access to view it in the Named Credential list.
-
Power Broker is not supported when creating named credential using Install Remote Agent on Host. You need to use
sudoinstead.
-
- From the Root Credential list, select an appropriate root credential to obtain privileges of a root user. This is an optional field. You may use this option only when your credentials do not have certain privileges as that of a root user. Use this along with your credentials.
- For Privileged Delegation Setting,
validate the Privilege Delegation setting to be used for running the
root scripts. By default, it is set to the Privilege Delegation setting
configured in Enterprise Manager.
For example, you can specify one of the following for the Privileged Delegation Setting field:
/usr/bin/sudo -u %RUNAS% %COMMAND% /usr/bin/sudo -u -S %RUNAS% %COMMAND% (if a pseudo terminal is required for remote command execution via SSH) /usr/bin/sesu - %RUNAS% -c "%COMMAND%" /usr/bin/su - %RUNAS% -c "%COMMAND%"Note:
Power Broker is not supported for Remote Agent.If you leave the Privileged Delegation Setting field blank, the root scripts will not be run by the wizard; you will have to run them manually after the installation.
This setting will also be used for performing the installation as the user set in the Run As attribute of the selected Named Credential if you had set the user while creating that Named Credential.
Note:
In the Privilege Delegation setting, the
%RUNAS%is honored as the root user for running the root scripts and as the user set in the Run As attribute of the Named Credential for performing the installation. - For Port, accept the default port (3872)
that is assigned for the Management Agent to communicate, or enter a
port of your choice.
The custom port you enter must not be busy. If you are not sure, you can leave this field blank. Enterprise Manager automatically assigns the first available free port within the range of 1830 - 1849.
- (Optional) In the Optional Details
section, enter the absolute path to an accessible location where the preinstallation and
postinstallation scripts
you want to run are available. Note that only shell scripts are
supported, and only one preinstallation or one postinstallation script
can be specified.
If you want to run the script as
root, then select Run as Root. If the script is on the host where OMS is running and is not on the host where you want to install the Management Agent, then select Script on OMS. In this case, the script will be copied from the OMS host to the destination hosts, and then run on the destination hosts. - (Optional) For Additional
Parameters, enter a whitespace-separate list of
additional
parameters
that you want to pass during the installation. For a complete list of
supported additional parameters, see Table 6-2.
For example, if you want to provide the inventory pointer location file, enter:
-invPtrLoc INVENTORY_LOCATION=/u01/oraInventoryThe above parameter is supported only on UNIX platforms, and not on Microsoft Windows platforms.
- Repeat Step 3 (b) to Step 3 (i) for every other row you have in the table.
- Click Next.
-
If you want to deploy Management Agents on the selected hosts in a rolling manner, such that the deployment proceeds continuously from one deployment phase to another, ignoring the failed hosts in each deployment phase, specify the following in the
$ORACLE_HOME/sysman/prov/agentpush/agentpush.propertiesfile:oracle.sysman.prov.agentpush.continueIgnoringFailedHost=true -
Under the Review page, review the details you have provided for the installation and do one of the following:
-
If you want to modify the details, then click Back repeatedly to reach the page where you want to make the changes.
-
If you want to cancel the deployment session for some reason, click Cancel. You are automatically taken to the Add Targets Manually page.
-
If you are satisfied with the details, then click Deploy Agent to install the remote agent. You are automatically taken to the Install Remote Agent on Host page that enables you to monitor the progress of the deployment session.
If you want to cancel a running deployment session, then under the Remotely Monitor Host Targets page, click Cancel. Once you cancel the session, you cannot track or resume the session in any way. However, the currently launched commands on the remote hosts will continue to run until they are completed.
-
-
If a particular installation phase has failed or has a warning, review the details provided for each phase in the Agent Deployment Details section of the Install Remote Agent on Host page, and do one of the following:
Note:
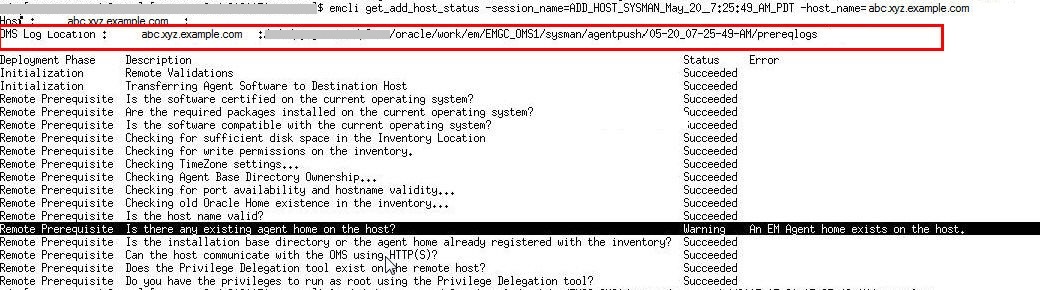
To find the cause of a failure, review the log files. One log file is generated per host, so if you installed Management Agents on multiple hosts, then review all the log files. For information on how to access the log files, refer to Overview of the Installation and Configuration Log Files in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Installation and Configuration Guide.
-
Fix the problem by reviewing the error description carefully, understanding its cause, and taking action as recommended by Oracle.
-
You can retry the deployment of remote agents with the same installation details.
To do so, on the Install Remote Agent on Host page, click Retry and select Retry Using Same Inputs.
-
You can retry the deployment of remote agents with modified installation details.
To do so, on the Install Remote Agent on Host page, click Retry and select Update Inputs and Retry.
-
-
Ignore the warning or failure, and continue with the session if you prefer.
-
You can choose to proceed with the deployment of remote agents only on those remote hosts that have successfully cleared the checks, and you can ignore the ones that have Warning or Failed status.
To do so, on the Install Remote Agent on Host page, click Continue and select Continue, Ignoring Failed Hosts.
-
You can choose to proceed with the deployment of remote agents on all the hosts, including the ones that have Warning or Failed status.
Note that choosing this option will ignore the prerequisites in order to allow the remote agent installation to proceed. If you want to proceed with this option, you must ensure that all the prerequisites are met through manual methods. The practice of ignoring prerequisite checks must be done only with the help of Oracle Support, or with a clear understanding of the impact of bypassing these checks.
To do so, on the Install Remote Agent on Host page, click Continue and select Continue, All Hosts.
-
-
-
Next step: Add Host Targets to Remote Agent.
Once the remote agent deployment is successful, you receive a message indicating the next required step: Add Host Targets to Remote Agent (located within Remotely Monitor Host Targets).
This step adds a remote host target to the remote agent that just got installed to allow host monitoring. For details, see Adding Remote Hosts to the Remote Agent in the Enterprise Manager Monitoring Guide.
Installing Remote Agents Using EM CLI
To install remote agents using EM CLI, follow these steps:
Note:
For more information on how to use the EM CLI verbs mentioned in this section, refer EMCLI Overview and Concepts in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface.
Performing Postinstallation Tasks for Remote Agents
Follow these postinstallation tasks after you install a remote agent using the Console or EM CLI:
Note:
-
You can repoint your existing Management Agents to a new Oracle Management Service (OMS). For information on how to do this, see Redirecting Oracle Management Agent to Another Oracle Management Service in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Installation Guide.
When you repoint your existing Management Agents to a new OMS, you cannot move the targets monitored by the Management Agents, the target history, and the Management Agent history. The monitored targets and the history data is lost.