2 Installing the RUEI Software
Note:
Before attempting to install RUEI components on any system, make sure that the latest OpenSSL patches are applied for your operating system using the appropriate commands (for example, yum update or up2date). Applying the latest OpenSSL patches helps improve the security of the system.
Prerequisites
This section describes the steps that should be taken before installing the RUEI software. Ensure that all preconditions described in this section are met before proceeding with the installation process.
Note:
RUEI installation is supported for RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 7.x, 8.x and 9.x. However for maximum reliability and security, upgrade the system to the latest patch version before installing RUEI.
Planning the Software Installation
For an introduction to RUEI data collection, see Data Collection. The following installation data collection options are available:
-
Network data collector: This option collects data that passes through the network and was the default option in previous releases and requires either a local or remote collector.
-
Tag data collector: This option, also called tag based monitoring, collects data by monitoring the request and processing of a specific web URL (the tag) which is inserted into all pages.
Table 2-1 Installation Overview and Data Collection Methods
| Network | Tag | |
|---|---|---|
|
Requirement |
Access to network traffic to perform Network Protocol Analysis. |
Access to application templates to insert Javascript code. |
|
Single Server (as in Figure 1-7) |
Use the |
Use the |
Planning the Software Installation Location
Depending on the installation location of the Reporter database and the RUEI software, the necessary disk space needs to be carefully planned. During operating system installation, you will need this information at hand for the disk partitioning phase.
The following table shows the disk space requirements for the RUEI installation components.
Table 2-2 Required Disk Space Specifications
| Partition | Min. RequiredDisk Space (GB) | Component |
|---|---|---|
| Reporter / Single Server | . | . |
| ORACLE_BASE (default /u01/app/oracle ) 1 | 600 | Database |
| RUEI_HOME (default /opt/ruei ) | 5 | RUEI Software |
| RUEI_DATA (default /var/opt/ruei/ ) | 400 | RUEI Data |
| Collector / Tag Collector | . | . |
| RUEI_HOME (default /opt/ruei ) | 5 | RUEI Software |
| RUEI_DATA (default /var/opt/ruei/ ) | 200 | RUEI Data |
| Database | . | . |
| ORACLE_BASE (default /u01/app/oracle ) 1 | 600 | Database |
This means that for a stand-alone RUEI server installation, a minimum of 1005 GB is required.
Note:
The Reporter and database servers require high-performance data storage. RAID-10 or RAID-5 (or equivalent) storage configurations with high-performance disks are recommended.
Configuring the Network Interface for Network Data Collection
If you want to use network data collection:
-
Ensure that a static IP address is assigned to the interface used to access the RUEI web interface. In addition, the assigned IP address and host name should be configured in the
/etc/hostsfile. If necessary, ensure that all Reporter and Collector systems are correctly defined in the DNS system. -
Ensure that the network interface(s) used for network packet monitoring are administratively up, but without an IP address.
Note:
Make the network interface up status permanent (after a reboot) by setting the
ONBOOTparameter of the capturing interfaces toyes. The network interfaces configuration can be found in the/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ethXfile (whereXrepresents the necessary network interface). Alternatively, use the graphical utility system-config-network to perform the above actions.
Configuring Operating System Security
When the system boots for the first time, a post-installation wizard appears, and allows you to finalize the operating system configuration settings.
You must ensure that Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is disabled. To disable SELinux set SELINUX=disabled in the /etc/selinux/config file. This is necessary for the correct operation of RUEI. Changing the SELinux setting requires rebooting the system so that the entire system can be re-labelled.
Please configure the operating system's firewall, if enabled, to allow access to the respective services, like (by default) TCP port 1521 for the database listener TCP port 443 for the web interface and TCP port 22 for the SSH server.
For security reasons, it is recommended that you select the Encrypt System check box during operating system installation so that all sensitive data is stored in a secure manner. A passphrase is required during booting the system.
Verify NTP Daemon Operation for Network Data Collection
Ensure that the date and time settings are correctly specified. The use of NTP is recommended and is required in a split-server deployment. In addition, all time zones specified for Reporter and Collector systems must be identical.
Note:
In distributed environments, all time zones specified for Reporter and Collector systems must be identical.
RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux
In RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux, NTP synchronization, timezone and other clock related settings are managed through the timedatectl tool:
Note:
This command will enable the NTP enabled option, which should also enable NTP synchronized option as well if the time server is set properly in the following chrony config file:/etc/chrony.conf# timedatectl
Local time: Wed 2017-10-04 09:42:09 BST
Universal time: Wed 2017-10-04 08:42:09 UTC
RTC time: Wed 2017-10-04 08:42:09
Time zone: Europe/London (BST, +0100)
NTP enabled: yes
NTP synchronized: yes
RTC in local TZ: no
DST active: yes
Last DST change: DST began at
Sun 2017-03-26 00:59:59 GMT
Sun 2017-03-26 02:00:00 BST
Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at
Sun 2017-10-29 01:59:59 BST
Sun 2017-10-29 01:00:00 GMT
Verify that NTP enabled and NTP synchronized show yes.
By default, the chrony package is installed to provide NTP synchronization. If time is not synchronized, in /etc/chrony.conf, provide at least one valid (and reachable) timeserver through at least one server directive.
After editing /etc/chrony.conf, restart the chronyd daemon:
systemctl restart chronyd
After that, the timedatectl command should display NTP synchronized as yes.
systemctl status chronyd.service -l as shown in the following example.systemctl status chronyd.service -l
chronyd.service - NTP client/server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/chronyd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-04-14 12:59:17 PDT; 2h 14min ago
Docs: man:chronyd(8)
man:chrony.conf(5)
Main PID: 12783 (chronyd)
Memory: 324.0K
CGroup: /system.slice/chronyd.service
\u2514\u250012783 /usr/sbin/chronyd
Apr 14 12:59:17 host1 systemd[1]: Starting NTP client/server...
Apr 14 12:59:17 host1 chronyd[12783]: chronyd version 3.2 starting (+CMDMON +NTP +REFCLOCK +RTC +PRIVDROP +SCFILTER +SECHASH +SIGND +ASYNCDNS +IPV6 +DEBUG)
Apr 14 12:59:17 host1 chronyd[12783]: Frequency -8.954 +/- 7.631 ppm read from /var/lib/chrony/drift
Apr 14 12:59:17 host1 systemd[1]: Started NTP client/server.
Apr 14 13:01:27 host1 chronyd[12783]: Selected source 10.128.128.1Installing the RUEI Prerequisites
The procedure described in this section is only required for a Reporter system. The procedure depends on whether you are using RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 7.x, 8.x or 9.x.
Installing All Requirements Using a Yum Repository
Depending on the OS flavor (RedHat or Oracle) and version you use, you may also need to enable the use of the "optional" (or "optional latest") repository to satisfy all dependencies.
The procedure depends on whether you are using RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 7.x, 8.x or 9.x.
Installing RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 7.x Prerequisites
After performing a minimum RedHat Enterprise / Oracle Linux 7.x installation, complete the following. A graphic environment is not required.
Install the necessary Reporter prerequisite packages running the following commands:
yum -y install httpd \
mod_ssl \
php \
php-ldap \
php-soap \
php-mbstring \
librsvg2-tools \
rsync \
libpcap \
ncurses \
zlib \
net-snmp \
net-snmp-libs \
net-snmp-utils \
*-fontsInstalling RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 8.x Prerequisites
After performing a minimum RedHat Enterprise / Oracle Linux 8.x installation, complete the following. A graphic environment is not required.
Install the necessary Reporter prerequisite packages running the following commands:
yum -y install httpd \
mod_ssl \
php \
php-ldap \
php-soap \
php-mbstring \
php-json \
php-xml \
librsvg2-tools \
rsync \
libpcap \
ncurses \
zlib \
net-snmp \
net-snmp-libs \
net-snmp-utils \
*-fonts
Installing RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 9.x Prerequisites
After performing a minimum RedHat Enterprise / Oracle Linux 9.x installation, complete the following. A graphic environment is not required.
Install the necessary Reporter prerequisite packages running the following commands:
yum -y install httpd \
mod_ssl \
php \
php-ldap \
php-soap \
php-mbstring \
php-json \
php-xml \
librsvg2-tools \
rsync \
libpcap \
ncurses \
zlib \
net-snmp \
net-snmp-libs \
net-snmp-utils \
*-fonts \
compat-openssl11Installing Oracle Database
Download and install Oracle Database Enterprise Edition from the Oracle database software downloads page at the following location:
https://www.oracle.com/database/technologies/oracle-database-software-downloads.html
The procedure for installing the Oracle database is fully described in the product documentation. It is available from the Oracle Database Documentation Library. The path user and group names used in this guide are based on the Oracle database product documentation.
Note:
For supported database versions, please see the certification list in My Oracle Support.
Note:
While Oracle Database is also available as an RPM package, instructions and scripts in this guide assume the .zip packages and Universal Installer are used to install the database software.
Obtaining the RUEI Software
The RUEI software is available from the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud web site (http://edelivery.oracle.com). To download the software, do the following:
- Sign in to the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud web site.
- From the Category search text field, enter "Oracle Real User Experience Insight" and select it from the drop-down list.
- From the search results, click " DLP: Oracle Real User Experience Insight 13.5.1.0.0". It will be added to your Cart.
- Click Checkout.
- Check to make sure the contents of your Cart are correct. Click Continue.
- Accept the Oracle License Agreement and click Continue.
- Click Download.
Unpacking the RUEI Software
Copy the downloaded RUEI zip file to /root directory on the server, and unzip it. Run the following commands:
cd /root
unzip package_name.zip
The following directories and files are extracted and provide the software required to complete the RUEI installation:
/root/ruei/db_templates/ruei_database.dbt/root/ruei/mkstore/mkstore-11.2.0.4.0.tar.gz/root/ruei/extra/oracledb/root/ruei/extra/ruei-clean.sh/root/ruei/extra/ruei-collector-failover.sh/root/ruei/extra/ruei-migrate/root/ruei/extra/ruei-reporter-failover.sh/root/ruei/extra/ruei.conf/root/ruei/extra/upgradeCheck.php/root/ruei/rpms/ux-*.rpm/root/ruei/ruei-check.sh/root/ruei/ruei-install.sh/root/ruei/ruei-prepare-db.sh/root/ruei/ruei-upgrade.sh/root/ruei/sql_scripts/*.sql
Generic Installation Tasks
The steps described in this section must be performed regardless of your planned installation (that is, a Reporter with local database, a Reporter with remote database, or a Collector).
Check The RUEI Configuration File
The /etc/ruei.conf file specifies the settings used within your installation. A template of this file is provided in the /root/ruei/extra directory of the RUEI distribution zip. All components in your RUEI environment (such as the remote database and Collectors) require the same global /etc/ruei.conf configuration file.
Note:
Be aware that all variables specified in the following table are the values used throughout this guide, and can be modified as required.
Table 2-3 RUEI Configuration Settings
| Setting | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Home directory of the RUEI software. Do not set to any path beginning with Note: The directory name cannot exceed 50 characters in length. RUEI_HOME and RUEI_DATA must be independent paths. For example, if RUEI_HOME is /opt/ruei, then RUEI_DATA cannot be set to /opt/ruei/data. Also, RUEI_HOME cannot be set to a subdirectory of /var/opt/ruei and that RUEI_DATA cannot be set to a subdirectory of /opt/ruei. |
|
|
|
Directory for RUEI data files. Do not set to any path beginning with Note: The directory name cannot exceed 50 characters in length. RUEI_HOME and RUEI_DATA must be independent paths. For example, if RUEI_HOME is /opt/ruei, then RUEI_DATA cannot be set to /opt/ruei/data. Also, RUEI_HOME cannot be set to a subdirectory of /var/opt/ruei and that RUEI_DATA cannot be set to a subdirectory of /opt/ruei. |
|
|
|
The RUEI operating system user. |
|
|
|
The RUEI operating system group. |
|
|
|
The database instance name. Note: The database instance name cannot exceed 8 characters in length. |
|
|
|
The configuration tablespace name Note: A database table space name cannot exceed 30 characters in length. |
|
|
|
The statistics tablespace name Note: A database table space name cannot exceed 30 characters in length. |
|
|
|
The database user name. Note: The database user name cannot exceed 30 characters in length. |
|
|
|
The Reporter database connect string. Note: The alias name cannot exceed 255 characters in length. |
|
|
|
The Reporter database connect string. Note:
|
$RUEI_DB_TNSNAME or |
|
|
The export database connect string. Note: The database user name cannot exceed 30 characters in length. |
|
|
|
The location of the |
|
|
|
The PHP timezone setting. Note: This should be the appropriate timezone setting, and must be valid for Linux, PHP and the Oracle Database. For Linux, you can use thetzselect utility, and for PHP use the following location: http://www.php.net/manual/en/timezones.php. See the Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for more information on time zones for the Oracle Database. Please note that it is required to set ORA_SDTZ (the database session time zone) to TZ in ruei.conf. See the ruei.conf installation template file in /root/RUEI/extra for instructions on how to do this.
|
|
|
DEFAULT_TABLESPACE |
The name for the default RUEI tablespace. |
|
|
REMOTE_DB |
Default is 0. Set to 1 for remote database. Note: Necessary when you do not have command-line access to the remote database host and running ruei-prepare-db.sh there is not an option. (See Setting up RUEI Against a Remote Database Service) |
|
|
DBCONNECT |
Fully qualified database connection string to remote database |
|
|
INSTANTCLIENT_DIR |
The path to the Oracle Instant Client library, needed for data processing and the UI. Note: The default value corresponds to Oracle Instant Client version 21. |
/usr/lib/oracle/21/client64 |
|
JAVA_HOME |
The path to your Java 8 Runtime Environment installation. |
/usr/java/jre |
Important
The TZ, RUEI_HOME, RUEI_DATA, RUEI_USER and RUEI_GROUP settings described in Table 2-3 must be specified in terms of literal values. Therefore, the following is not permitted:
RUEI_BASE=/my/ruei/dir export RUEI_HOME=$RUEI_BASE/home
Note:
If you change settings in /etc/ruei.conf after the installation of a RUEI system, you must restart system processing to make these changes effective (System > Maintenance > System reset > Restart system processing).
Failover Reporter Configuration Settings
Table 2-4 shows the settings that are used to configure a failover Reporter, and are only relevant to Reporter systems. For information on the configuration procedure, see Configuring a Failover Reporter System.
Table 2-4 RUEI Failover Reporter Configuration Settings
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The primary Reporter IP address. |
|
|
The secondary Reporter IP address. |
|
|
The virtual Reporter IP address. |
|
|
The network interface used to connect to the virtual Reporter IP address. |
|
|
The network mask of the virtual Reporter IP address. |
Failover Collector Configuration Settings
Table 2-5 shows the settings that are used to configure a failover Collector, and are only relevant to Collector systems. For information on the configuration procedure, see Configuring a Failover Collector System.
Table 2-5 RUEI Failover Collector Configuration Settings
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The primary Collector IP address. |
|
|
The secondary Collector IP address. |
|
|
The virtual Collector IP address. |
|
|
The network interface used to connect to the virtual Collector IP address. |
|
|
The network mask of the virtual Reporter IP address. |
cp /root/ruei/extra/ruei.conf /etc/In case of a remote Reporter database installation, the ruei.conf file needs to be identical to that of the Reporter system.
Creating a RUEI User and Directories
-
Create the
moniforcegroup andRUEI_USERuser. The home directory ofmoniforceshould be set to/var/opt/ruei, with read permissions for group members./usr/sbin/groupadd moniforce /usr/sbin/useradd moniforce -g moniforce -d /var/opt/ruei chmod -R 750 /var/opt/ruei chown -R moniforce:moniforce /var/opt/ruei
Note:
The login shell for the
moniforce(RUEI_USER) user must be set to/bin/bash. -
The RUEI directory locations are flexible, however it is necessary to use the exact directory name described as configured in the
/etc/ruei.conffile. Create the RUEI application root directory running the following commands:mkdir -p /opt/ruei chmod 755 /opt/ruei
Note:
The specified $RUEI_HOME and $RUEI_DATA directories must have 755 permissions defined for them. For more information on these directories, see Table 2-3 .
- Ensure the file is readable by the RUEI_USER user by issuing the following commands:
chmod 644 /etc/ruei.conf chown moniforce:moniforce /etc/ruei.conf
Installing Java
For Reporter and Collector systems, you need to install the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) version 8. Please download a 64 bit (x64) Linux version from https://www.java.com/en/download/linux_manual.jsp
The installation instructions below (and default value of JAVA_HOME in /etc/ruei.conf) are based on the non-RPM (.tar.gz) version
-
Run the following commands:
mkdir -p /usr/java chmod 755 /usr/java cd /usr/java tar xzf <path-of-download>/jre-8u*-linux-x64.tar.gz -
This installs the necessary Java software in the directory
/usr/java/jre1.8.0_<version>. To make the install directory version independent, create a more generic symlink running the following command:ln -s /usr/java/jre1.8.0_* /usr/java/jre
System Pre-installation Check
To verify if the system is ready for RUEI to be installed, it is advised to run the RUEI system check.
Running the System Check
To run the system check:
cd /root/ruei./ruei-check.sh <installation option> <check>
Depending on the installation option for the system, the check will need to be called with different arguments. The following table shows a list of available arguments.
Table 2-6 RUEI System Check Command Line Arguments
| Installation Option | System pre-installation check |
|---|---|
| Single Server | ./ruei-check.sh reporter system --role reporter |
| Reporter | . |
|
./ruei-check.sh reporter system --role reporter |
|
./ruei-check.sh reporter system --role reporter --with-remote-db |
| Collector | ./ruei-check.sh collector pre-install --role collector |
| Database | ./ruei-check.sh database pre-install --role database |
Note 1: Single Server and Reporter have the same ruei-check.sh command line because of the similar system requirements.
Note 2: In case of installation issues, please provide Oracle Customer Support with the RUEI check log file /tmp/ruei-check.log.
Note 3: Make sure you had set up and checked the /etc/ruei.conf file on each system as described in Check The RUEI Configuration File.
Reporter Installation
This section describes the procedure for installing the required components for a Reporter system. These include the Apache web server and the Oracle database Instant Client.
Installing the Apache Web Server and PHP
This section describes the installation and configuration of the Apache web server, and the components that use it.
PHP Configuration
-
Ensure that the web server starts automatically after re-boot by running the following command:
-
RedHat Enterprise / Oracle version 7.x/8.x:
systemctl enable httpd -
RedHat Enterprise / Oracle version 9.x:
systemctl enable httpd systemctl enable php-fpm
-
-
Create the following settings in the
/etc/php.d/ruei.inifile:session.gc_maxlifetime = 14400 memory_limit = 192M upload_max_filesize = 128M post_max_size = 128M
Avoiding RSVG Warnings
RUEI uses RSVG for graph generation. In order to avoid warnings about a missing directory, create the empty .gnome2 directory using the following command:
mkdir -p /var/www/.gnome2
Securing Apache Web Server
In order to protect sensitive data on RUEI, it is strongly recommended that access to the Reporter interface is restricted to HTTPS. Use the following command as the root user:
sed -i -e 's/^Listen 80/#Listen 80/' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
In addition to the already disabled SSLv2, also disable support for SSLv3 in the web server using the following command as the root user, if neccessary.
sed -i -e 's/^SSLProtocol all -SSLv2/SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3/' /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
Changing MPM Module in Apache Configuration
In order to enable PHP execution, you will need to modify the /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.conf file.
Note:
When running on RedHat Enterprise / Oracle Linux 9.x, it is not required to change the MPM Module.Run the following commands as the root user:
sed -i -e 's/^LoadModule mpm_event_module/#LoadModule mpm_event_module/' /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.confsed -i -e 's/^#LoadModule mpm_prefork_module/LoadModule mpm_prefork_module/' /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/00-mpm.confInstalling the Oracle Database Instant Client
Download the Oracle Database Instant Client (Basic) and SQL*Plus (version 19.x and above) package from Oracle Instant Client Downloads for Linux x86-64 (64-bit), and install by running the following commands as the root user:
cd /root/ruei/ic
rpm -Uhv oracle-instantclient*-basic-*.rpm
rpm -Uhv oracle-instantclient*-sqlplus-*.rpmInstalling the php-oci8 Module
As a prerequisite download and install the Oracle database Instant Client SDK (devel) package for your version of PHP, based on your yum, for your version of Instant Client from Oracle Instant Client Downloads for Linux x86-64 (64-bit).
You can find detailed installation instructions for the php-oci8 module at https://www.php.net/manual/en/oci8.installation.php
Note:
The version of oci8 you need to install depends on your PHP version. Consult the Description field at https://www.php.net/manual/en/oci8.installation.php .Example commands:
-
Install the Oracle database Instant Client SDK (devel) package:
yum install php-pear php-devel yum install <path-of-download>/oracle-instantclient-devel-*.x86_64.rpm pear config-set http_proxy <url_of_proxy>:<port>Note:
This step is optional, if a proxy is needed for internet access.pecl install oci8-<version>Note:
When prompted for a path to the library, you can choose the default ofautodetect.-
Create a file named
/etc/php.d/oci8.iniand add the following to it:#enable oci8 extension module extension=oci8.so -
Restart httpd:
systemctl restart httpdNote:
If your OS is RedHat Enterprise / Oracle version 9.x, also restart php-fpm:
systemctl restart php-fpm
Creating the Reporter Database Instance
Note:
If you intend to use RUEI with Enterprise Manager, you require the RUEI wallet password described below. Without the correct wallet password you cannot associate RUEI with Enterprise Manager.
The procedure described in this section should be skipped if you are installing a secondary (failover) Reporter system (see Configuring a Failover Reporter System), and you should continue at Installing the Reporter Software.
The Reporter database can reside either locally (that is, on the Reporter server) or on a remote database server. In this section you will create the database instance required for RUEI, and generate the "connection data" required for the Reporter to connect to this database instance. As an alternative for the database setup described in this chapter, you can follow the procedure described in Generic Database Instance Setup.
If you are using a remote database and you do not have command-line access to the remote database server because, for example, you want to configure RUEI using a “Pluggable Database", see Setting up RUEI Against a Remote Database Service.
You will need the following scripts to be present on the system where the database instance (RUEI_DB_INST) will be created:
-
ruei-prepare-db.sh: creates the database instance, Oracle wallet, and database connect files. This script will only run on Linux. If you are installing the Oracle database on a different operating system, see Generic Database Instance Setup. -
sql_scripts: this directory contains a number of SQL scripts that are called by theruei-prepare-db.shscript. -
db_templates: this directory contains templates for the RUEI database instance that is created by theruei-prepare-db.shscript. -
ruei-check.sh: this is a hardware and environment check utility, and is automatically invoked byruei-prepare-db.sh. The script can also be used as a stand-alone troubleshooting utility. For a complete description of the script, refer to RUEI System Check Tool.
For creating the database autologin wallet in this section and, optionally, for the integration with Enterprise Manager later on, a specific version of the "mkstore" utility is needed. You can set up this utility as follows. This needs to be done on the system where the database instance (RUEI_DB_INST) will be created as well as the reporter if those are separate systems.
-
Run the following commands:
cd /usr/local tar xzf /root/ruei/mkstore/mkstore-11.2.0.4.0.tar.gz
-
This installs the mkstore utility to /usr/local/mkstore-11.2.0.4.0. To make the install directory version independent, create a more generic symlink using the following command:
ln -s /usr/local/mkstore-11.2.0.4.0 /usr/local/mkstore
-
Make the following change to /etc/ruei.conf:
* export MKSTORE_BIN=/usr/local/mkstore/mkstore
-
If you are executing these steps on a database server separate from the reporter system, make the following change to /etc/ruei.conf:
* export JAVA_HOME=$ORACLE_HOME/jdk/jre
The four connection data files created during the procedure described in this section are as follows:
-
cwallet.sso -
ewallet.p12 -
sqlnet.ora -
tnsnames.ora
Note:
These files will be created in the RUEI_DATA directory.The RUEI configuration file (/etc/ruei.conf) also needs to be present on the database server and configured as described in Check The RUEI Configuration File and the instructions for setting up mkstore, given earlier in this section.
Do the following:
-
Copy the
ruei-prepare-db.shandruei-check.shscripts, and thesql_scriptsanddb_templatesdirectories to the server on which you intend to run the database instance, and make them executable for theoracleuser. These scripts and directories can be found in the RUEI distribution zip (/root/ruei/). -
Review the settings in the
/etc/ruei.conffile to match your needs as described in Check The RUEI Configuration File. If you want to use different names for the configuration and statistics tablespaces make sure these names are set before continuing. The same tablespace names must be used on the RUEI reporter and on the remote database. -
Log in to the database server as the
oracleuser on the database server, and set theORACLE_HOMEenvironment variable. You need to run theruei-prepare-db.shscript as theoracleuser. This script creates the $RUEI_DB_INST database, but only after a number of hardware and software environment checks have been performed. The actual checks performed depend on the system type you are currently installing.The script prompts you for the Reporter database user password.. This enables the RUEI application to login to the database automatically. The script also creates the "connection data" files for you now.Note:
The database password is also used as the Oracle wallet password. Both passwords must be 8-30 characters in length, and contain both numbers and letters. For information on changing the Oracle wallet password, please consult the appropriate Oracle documentation.
The script also prompts you for a default tablespace name to be used for this installation, and then creates the connection data files.
Run the following commands:
chmod +x ruei-prepare-db.sh ruei-check.sh chmod -R +r /home/oracle/sql_scripts/ chmod -R +r /home/oracle/db_templates/ export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/12.1.0/dbhome_1 Note: This line requires customization based on your database version and installation path. ./ruei-prepare-db.sh createYou are prompted whether you want the installation script to check your system. It is recommended that you do so. The checks performed are fully described in RUEI System Check Tool.
If you ran the above commands on a combined Reporter/Database server, you can skip step 4 and proceed to step 5.
-
This step only applies when using a remote database.
In case of a Reporter system using a remote database, you will need to copy the generated
/tmp/ruei-database-configuration.tarfile in step 3 from the database server to the Reporter system. The/tmp/ruei-database-configuration.tarfile must be extracted on the Reporter server in the directory/var/opt/ruei(RUEI_DATA). The permissions of the files need to be set so that the specifiedRUEI_USER(moniforce) can use them.Copy the generated .
tarfile, which holds connection data files to the Reporter system. Log in to the Reporter server and extract the .tarfile using the following commands:cd /var/opt/ruei tar xvfpath-to-tar-file/ruei/database-configuration.tar chown moniforce:moniforce cwallet.sso ewallet.p12 sqlnet.ora tnsnames.ora -
Because logging of the database can consume a large amount of disk space, it is recommended that you install a clean-up script to avoid the usage of unnecessary disk space. Copy the (example) script to the
oracleuser directory and activate it throughcronrunning the following commands:mkdir -p /home/oracle/bin cp /root/ruei/extra/ruei-clean.sh /home/oracle/bin chmod +x /home/oracle/bin/ruei-clean.sh su - oracle -c 'echo "10 0 * * * /home/oracle/bin/ruei-clean.sh" | crontab'
To validate the Database Instance creation, run the RUEI post-installation check using the following commands:
For Reporter with local Database or a Single Server system:
cd /root/ruei/
./ruei-check.sh database post-install --role reporterFor a Database server system:
cd /root/ruei/
./ruei-check.sh database post-install --role database
Installing the Reporter Software
The procedure described in this section is relevant to all configurations described in Scaling Scenarios and Planning the Software Installation. Installing the reporter software also installs the collector and processor software.
-
Make the
apacheandmoniforcemembers of two additional groups running the following commands:/usr/sbin/usermod -aG moniforce apache /usr/sbin/usermod -aG dialout apache /usr/sbin/usermod -aG dialout moniforce
-
Go to the directory that holds the RUEI software, and run the following commands:
cd /root/ruei chmod +x ruei-install.sh
-
Use one of the following options to run the pre installation check and install the reporter software:
-
If you are installing a reporter in a split server configuration or you want to use only network based data collection as described in Planning the Software Installation:
./ruei-check.sh reporter pre-install ./ruei-install.sh reporter
Note:
Investigate and fix any issues reported by the per installation check, before continuing with the RUEI reporter software installation. -
If you are installing on a single server and you want to use tag based data collection as described in Planning the Software Installation (This option also supports network based data collection):
./ruei-check.sh reporter,tag-server pre-install ./ruei-install.sh reporter-tag
Note:
Investigate and fix any issues reported by the per installation check, before continuing with the RUEI reporter software installation.
For information on monitoring an application based on tagging, see Defining Applications in the Identifying and Reporting Web Pages chapter of the RUEI Users Guide.
-
-
Re-start the Apache web server running the following command:
For Linux 7.x/8.x
/bin/systemctl restart httpd.service
-
As the
rootuser, add the following lines to the.bash_profilefile of theRUEI_USER(RUEI_DATA/.bash_profile):source /etc/ruei.conf source $RUEI_HOME/bin/env.sh
-
Verify that the RUEI software was correctly installed:
-
If you are installing a reporter in a split server configuration or you want to use only network based data collection as described in Planning the Software Installation:
./ruei-check.sh reporter post-install -
If you are installing a reporter in a split server configuration or you want to use only tag based data collection as described in Planning the Software Installation:
./ruei-check.sh reporter,tag-server post-install
-
-
This step should not be performed if you are installing a secondary (failover) Reporter system (see Configuring a Failover Reporter System). You should continue at Configuring the Network Interface.
As the
moniforceuser, set the RUEIadminuser password to enable logging onto the RUEI interface running the following commands:su - moniforce set-admin-password
You are prompted to enter and confirm the password.
Password Requirements
When defining the admin user password, bear the following in mind:
-
The password must have at least eight characters, and contain at least one non-alphanumeric character (such as $, @, &, and !).
-
The initial password must be changed within seven days.
-
The user name and password are case sensitive.
Remote Tag Data Collector Installation
The procedure described in this section is only relevant to remote tag-based data Collector systems, see Planning the Software Installation and Scaling Scenarios.
Log in to the Collector system as the root user, and do the following:
-
Make sure that the rsync and libpcap packages are installed. For example, enter the following commands to install the packages using Yum:
yum -y install rsync yum -y install libpcap
-
Install Apache running the following command:
rpm -Uhv httpd-2.2.15-*..x86_64.rpm
-
Ensure that the web server starts automatically after re-boot by running the following command:
/sbin/chkconfig httpd on
-
Change to the RUEI root directory and run the
ruei-install.shscript running the following commands:cd /root/ruei chmod +x ruei-install.sh ruei-check.sh
-
Install the tag based data collector as described in Planning the Software Installation:
./ruei-check.sh collector pre-install --role collector ./ruei-install.sh tag-server
Note:
Investigate and fix any issues reported by the per installation check, before continuing with the RUEI reporter software installation. -
Re-start the Apache web server running the following command:
/bin/systemctl restart httpd.service
-
As the
rootuser, add the following lines to the .bash_profile file of the RUEI_USER (RUEI_DATA/.bash_profile):source /etc/ruei.conf source $RUEI_HOME/bin/env.sh
-
Verify that the RUEI software is correctly installed by running the following command:
./ruei-check.sh reporter,tag-server post-install
-
Set up a password-less remote login from the Reporter system to the newly created Collector system. The necessary configuration steps are described in Configuring Reporter Communication (Split-Server Setup Only).
Remote Network Data Collector Installation
The procedure described in this section is only relevant to remote network data Collector systems, see Planning the Software Installation and Scaling Scenarios.
Logon to the Collector system as the root user, and do the following:
-
Make sure that the rsync and libpcap packages are installed. For example, enter the following commands to install the packages using Yum:
yum -y install rsync yum -y install libpcap
-
Change to the RUEI root directory and run the
ruei-install.shscript running the following commands:cd /root/ruei chmod +x ruei-install.sh ruei-check.sh
-
Install the network based collector as described in Planning the Software Installation:
./ruei-check.sh collector pre-install --role collector ./ruei-install.sh collector
Note:
Investigate and fix any issues reported by the per installation check, before continuing with the RUEI reporter software installation. -
As the
rootuser, add the following lines to the .bash_profilefile of the RUEI_USER (RUEI_DATA/.bash_profile):source /etc/ruei.conf source $RUEI_HOME/bin/env.sh
-
Configure the network interfaces as described in Configuring the Network Interface.
-
Verify that the RUEI software is correctly installed by running the following command:
./ruei-check.sh collector post-install
-
Set up a password-less remote login from the Reporter system to the newly created Collector system. The necessary configuration steps are described in Configuring Reporter Communication (Split-Server Setup Only)
Configuring the Network Interface
This section is only relevant to network data Collector systems.
Make the monitoring network interface up status permanent (after a reboot) by setting the ONBOOT parameter of the capturing interfaces to yes in the interface configuration files. The network interfaces configuration can be found in the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ethX file (where X represents the necessary network interface). Alternatively, use the graphical utility system-config-network to set the appropriate interfaces to activate device when computer starts.
Mail (MTA) Configuration (Optional, Reporter Only)
This section is only relevant to the Reporter system.
RUEI assumes a working local MTA for sending PDF reports and E-mail alerts. By default, Linux uses the Sendmail MTA. By default, Sendmail delivers the E-mail directly to the destination MTA. If this behavior is not according to your needs or policies, sending mail through a SmartHost (relay) might be an alternative. To configure a SmartHost in Sendmail, do the following:
-
Install the Sendmail configuration utility by going to the directory containing the uploaded RPM and running the following command for RedHat Enterprise/Oracle Linux 7 and 8.x:
yum install sendmail-cf
-
Find the line which contains the Smart Host setting in
/etc/mail/sendmail.mc. Modify theSMART_HOSTsetting to your needs. For example:define('SMART_HOST', 'my.example')dnl -
Generate the new configuration into a new
sendmail.cfby running the following command:make -C /etc/mail
-
Restart Sendmail running the following command:
service sendmail restart
Note:
Extensive information about the configuration of the Sendmail MTA is available at http://www.sendmail.org.
Configuring Automatic Browser Redirection (Optional)
This section is only relevant to Reporter systems.
To have the browser automatically redirected to the correct RUEI path, create the file /var/www/html/index.html with the following content:
<head>
<meta http-equiv="REFRESH" content="0;URL=/ruei/">
</head>Configuring Reporter Communication (Split-Server Setup Only)
This section is only relevant to a Reporter system with remote Collector(s).
A password-less SSH connection must be setup between the Moniforce user from the Reporter system to each Collector system. Do the following:
-
Log in to the Reporter server as
root. Run the following commands:su - moniforce ssh-keygen -P ""
Press Enter to accept the defaults.
-
Log in as
rootto each of the Collector systems and become themoniforceuser by running the following command:su - moniforce
-
Create the
.sshdirectory (if it does not already exist) for themoniforceuser on each Collector system by running the following commands:mkdir ~/.ssh chmod 700 ~/.ssh
-
Copy the SSH key on the Reporter system to the required location on the Collector system by running the following commands:
cd ~/.ssh ssh root@Reportercat /var/opt/ruei/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> authorized_keys(you will need to specify the Reporter system
rootpassword)chmod 600 authorized_keys
-
Check if it is now possible to execute a remote command (as
moniforceuser) on the Reporter system without using a password. For example:-
Log in as
rooton the Reporter server. -
Log in as
moniforceuser:su - moniforce. -
Execute a remote pwd command:
sshCollectorpwd. -
Enter yes to the question "Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?".
-
The command should return
/var/opt/ruei.
-
-
The above steps must be performed for each Collector!
Note:
If the connection between the Reporter and the Collector(s) has not been correctly configured, you will receive an authorization error when you try to register the remote Collector.
Verifying Successful Installation of RUEI
After completing the Initial Setup Wizard (described in Performing Initial RUEI Configuration), verify your installation by running the following commands on the Reporter system:
cd /root/ruei
./ruei-check.sh diagnosticsNote 1: The RUEI systems may require some time to settle after completing the Inital Setup Wizard. Once settled, the check “Reporter ~ post-install-settled” >> “System Status Overview” should report [ OK ], as shown below: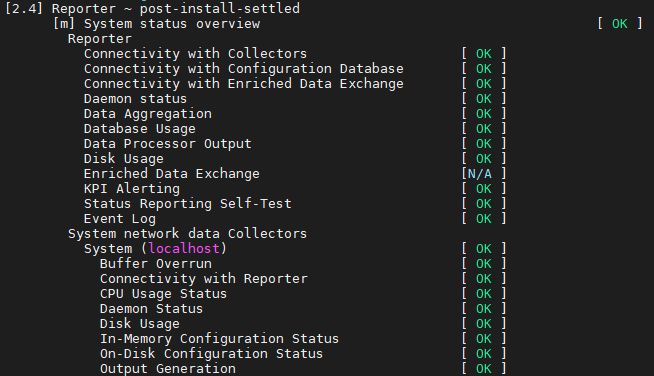
Note 2: The RUEI system check, verifies many parts of the system, including the “System Status Overview”. The “System Status Overview” can also be accessed using the UI by selecting System, then Status.
Note 3: For more information on the RUEI system check see RUEI System Check Tool.
Using RUEI with Oracle Enterprise Manager
You can set up a connection to the Oracle Enterprise Manager Repository so that KPIs defined for the applications, suites, and services that comprise your business applications can be reported as events in Incident Manager. The use of the business application facility is described in Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control Oracle Fusion Middleware Management Guide.