Workflow for Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator
Learn about the various steps involved in using the Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator utility for migrating your NoSQL data.
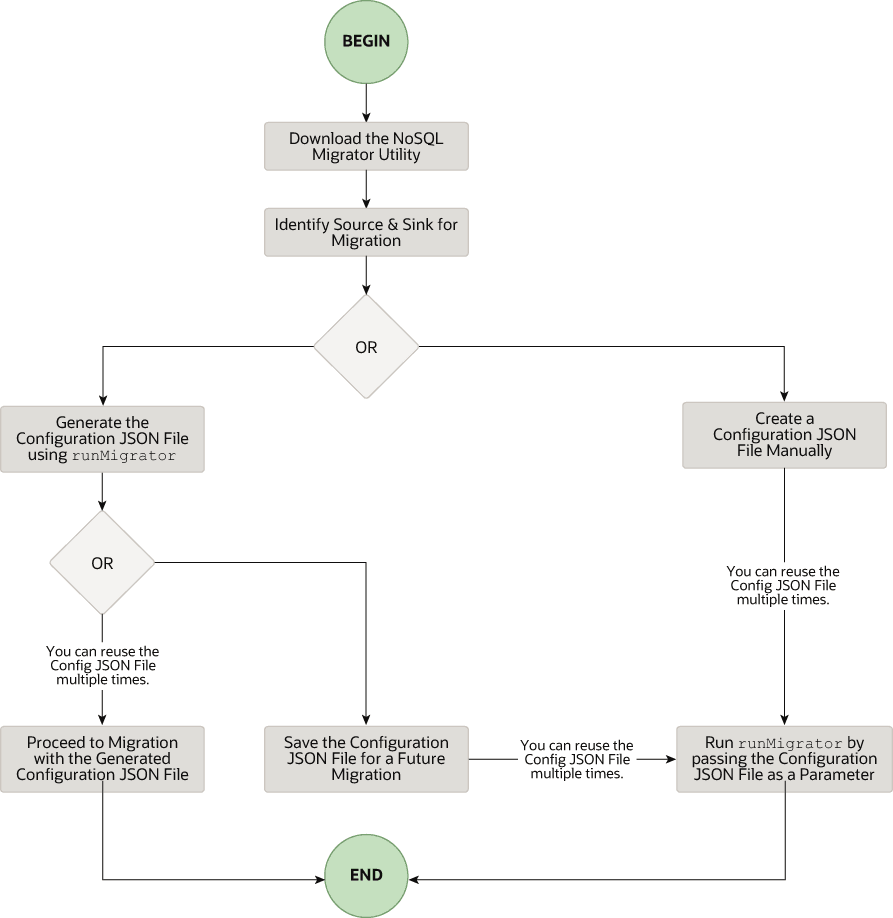
The high level flow of tasks involved in using NoSQL Database Migrator is depicted in the below figure.
Download the NoSQL Data Migrator Utility
runMigrator command from the command line interface.
Note:
Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator utility requires Java 11 or higher versions to run.Identify the Source and Sink
- Identify sink table schema: If the sink is Oracle NoSQL Database on-premises or cloud, you must identify the schema
for the sink table and ensure that the source data matches with the target
schema. If required, use transformations to map the source data to the sink
table.
-
Default Schema: NoSQL Database Migrator provides an option to create a sink table with the default schema without the need to predefine the schema for the table.
MongoDB-formatted JSON:
If the source is a MongoDB-formatted JSON file, the default schema for the table will be as follows:CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS <tablename>(id STRING, document JSON,PRIMARY KEY(SHARD(id))Where:
— tablename = value provided for the table attribute in the configuration.
— id = _id value from each document of the MongoDB exported JSON source file.
— document = For each document in the MongoDB exported file, the contents excluding the_idfield are aggregated into the document column.Note:
- If the _id value is not provided as a string in the MongoDB-formatted JSON file, NoSQL Database Migrator converts it into a string before inserting it into the default schema.
- If the table <tablename>
already exists in Oracle NoSQL Database
on-premises or cloud, and you want to migrate data
to the table using the
defaultSchemaconfiguration, you must ensure that the existing table has the ID column in lower case (id) and is of the type STRING.
DynamoDB-formatted JSON:
If the source is a DynamoDB-formatted JSON file, the default schema for the table will be as follows:CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS <tablename>(DDBPartitionKey_name DDBPartitionKey_type, [DDBSortKey_name DDBSortKey_type],DOCUMENT JSON, PRIMARY KEY(SHARD(DDBPartitionKey_name),[DDBSortKey_name]))Where:
— tablename = value provided for the sink table in the configuration
— DDBPartitionKey_name = value provided for the partition key in the configuration
— DDBPartitionKey_type = value provided for the data type of the partition key in the configuration
— DDBSortKey_name = value provided for the sort key in the configuration if any
— DDBSortKey_type = value provided for the data type of the sort key in the configuration if any
— DOCUMENT = All attributes except the partition and sort key of a DynamoDB table item aggregated into a NoSQL JSON column
If the source format is a CSV file, a default schema is not supported for the target table. You can create a schema file with a table definition containing the same number of columns and data types as the source CSV file. For more details on the Schema file creation, see Providing Table Schema.
Other valid sources:
For all the other sources, the default schema will be as follows:CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS <tablename> (id LONG GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY, document JSON, PRIMARY KEY(id))Where:
— tablename = value provided for the table attribute in the configuration.
— id = An auto-generated LONG value.
— document = The JSON record provided by the source is aggregated into the document column.
-
- Providing Table Schema:
NoSQL Database Migrator allows the source to provide schema
definitions for the table data using schemaInfo attribute. The schemaInfo attribute is available in all the data sources
that do not have an implicit schema already defined. Sink data stores can
choose any one of the following options.
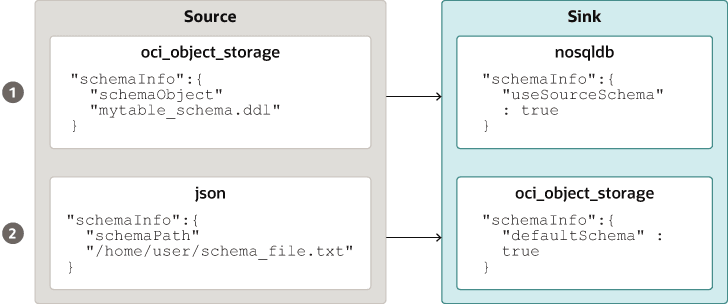
- Use the default schema defined by the NoSQL Database Migrator.
- Use the source-provided schema.
- Override the source-provided schema by defining its own schema. For example, if you want to transform the data from the source schema to another schema, you need to override the source-provided schema and use the transformation capability of the NoSQL Database Migrator tool.
The table schema file, for example,mytable_schema.ddlcan include table DDL statements. The NoSQL Database Migrator tool executes this table schema file before starting the migration. The migrator tool supports no more than one DDL statement per line in the schema file. For example,CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS(id INTEGER, name STRING, age INTEGER, PRIMARY KEY(SHARD(ID)))Note:
Migration will fail if the table is present at the sink and the DDL in theschemaPathis different than the table. - Create Sink Table: Once you identify the sink table
schema, create the sink table either through the Admin CLI or using the
schemaInfoattribute of the sink configuration file. See Sink Configuration Templates .Note:
If the source is a CSV file, create a file with the DDL commands for the schema of the target table. Provide the file path in schemaInfo.schemaPath parameter of the sink configuration file.
Run the runMigrator command
The runMigrator executable file is available in the extracted NoSQL Database Migrator files. You must install Java 11 or higher version and bash on your system to successfully run the runMigrator command.
runMigrator command in two ways:
- By creating the configuration file using the runtime options of the
runMigratorcommand as shown below.[~]$ ./runMigrator configuration file is not provided. Do you want to generate configuration? (y/n) [n]: y ... ...- When you invoke the
runMigratorutility, it provides a series of run time options and creates the configuration file based on your choices for each option. - After the utility creates the configuration file, you have a choice to either proceed with the migration activity in the same run or save the configuration file for a future migration.
- Irrespective of your decision to proceed or defer the migration activity with the generated configuration file, the file will be available for edits or customization to meet your future requirements. You can use the customized configuration file for migration later.
- When you invoke the
- By passing a manually created configuration file (in the JSON format) as a runtime parameter using the
-cor--configoption. You must create the configuration file manually before running therunMigratorcommand with the-cor--configoption. For any help with the source and sink configuration parameters, see Sources and Sinks.[~]$ ./runMigrator -c </path/to/the/configuration/json/file>
Logging Migrator Progress
NoSQL Database Migrator tool provides options, which enables trace, debugging, and progress messages to be printed to standard output or to a file. This option can be useful in tracking the progress of migration operation, particularly for very large tables or data sets.
- Log Levels
To control the logging behavior through the NoSQL Database Migrator tool, pass the --log-level or -l run time parameter to the
runMigratorcommand. You can specify the amount of log information to write by passing the appropriate log level value.$./runMigrator --log-level <loglevel>Example:$./runMigrator --log-level debugTable 1-1 Supported Log Levels for NoSQL Database Migrator
Log Level Description warning Prints errors and warnings. info (default) Prints the progress status of data migration such as validating source, validating sink, creating tables, and count of number of data records migrated. debug Prints additional debug information. all Prints everything. This level turns on all levels of logging. - Log File:
You can specify the name of the log file using --log-file or -f parameter. If --log-file is passed as run time parameter to the
runMigratorcommand, the NoSQL Database Migrator writes all the log messages to the file else to the standard output.$./runMigrator --log-file <log file name>Example:$./runMigrator --log-file nosql_migrator.log
Limitation
Oracle NoSQL Database Migrator does not lock the database during backup and block other users. Therefore, it is highly recommended not to perform the following activities when a migration task is running:
- Any DML/DDL operations on the source table.
- Any topology-related modification on the data store.