3 Using Oracle Spatial Studio
Using Oracle Spatial Studio, you can create one or more projects, each of which can define one or more spatial datasets on which you can perform various spatial operations.
It is important you understand the following terminologies when working on Spatial Studio:
- A project contains Spatial Studio objects, such as datasets, that are logically related to some intended usage. For example, a project might be named New England Sales Territories, or Sales Territories and Customers, or Ohio Airports and Counties. When creating a project, you should know the purposes for which you want to identify and analyze spatial data in a geographic area.
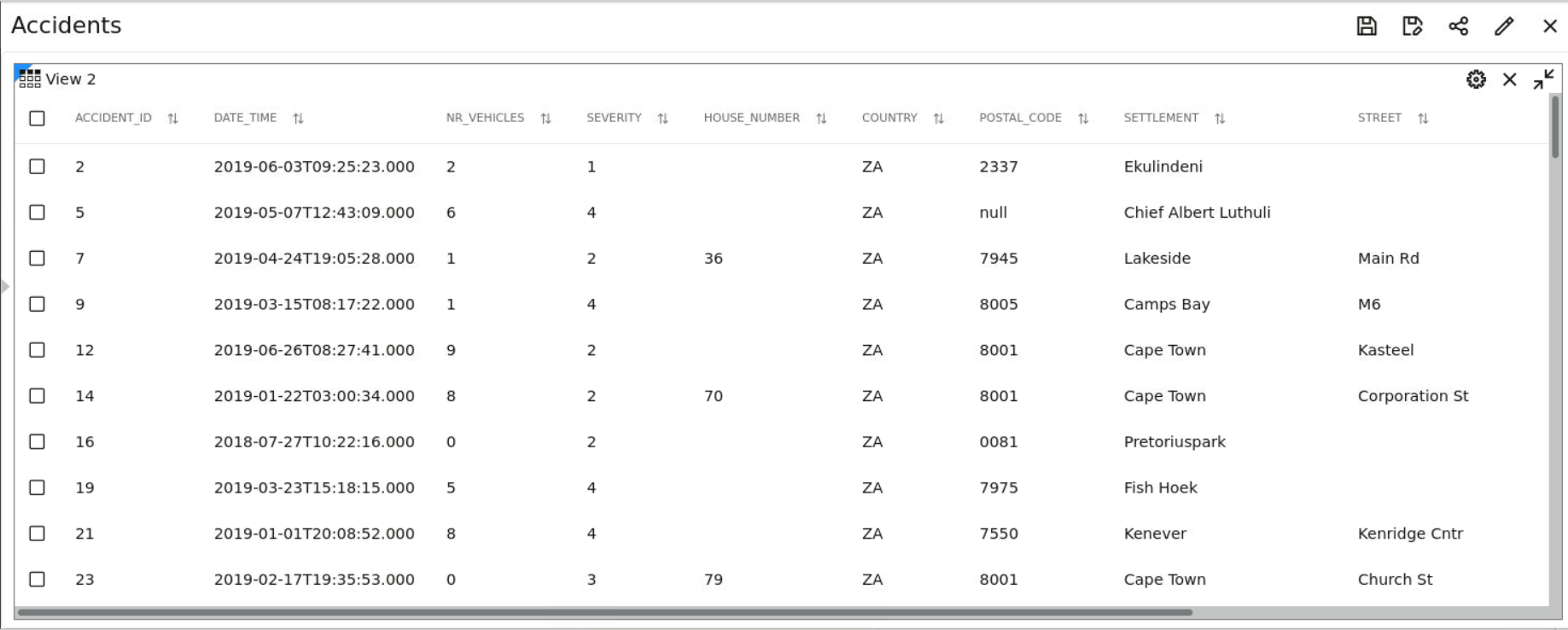
- A dataset is a collection of spatial features of a specific usage type and geometry type. For example, datasets might include Airports represented by polygon geometries, or Roadways represented by LRS line string geometries, or Accidents represented by point geometries.
- A connection specifies information for connecting to an Oracle Database schema where spatial data of interest resides: user name, password, system, port, database name, and so on. (It is similar to a SQL Developer connection.)
Note:
See also Spatial Studio Terminology for more information.The main landing page for Spatial Studio for a new user is as shown:
The overall layout of the Spatial Studio user interface comprises of:
- Header: The header at the top of the page contains the following
buttons:
 : to display or hide the side navigation menu
: to display or hide the side navigation menu
 : to help you get started on Spatial Studio by providing an overview of the tool and links to
other tutorial resources
: to help you get started on Spatial Studio by providing an overview of the tool and links to
other tutorial resources
 : displays the user profile details
: displays the user profile details
- Side Navigation Menu: A navigation panel on the left displays the menu items. You can expand or collapse the navigation drawer.
- User Workspace: The page specific details for the selected menu option is displayed on the right.
The navigation menu consists of the following menu options:
- Active Project: Directs you to the Active Project page where your recent working project is displayed.
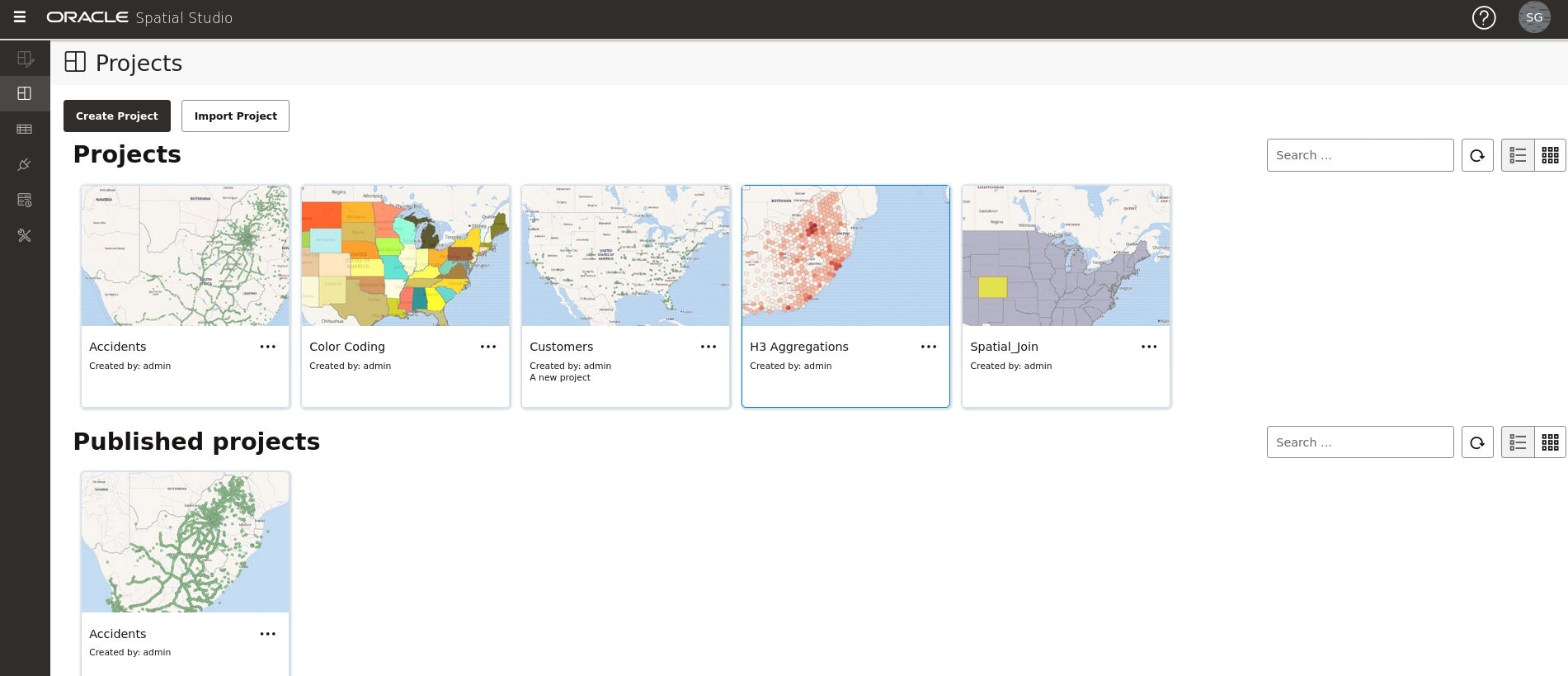
- Projects: Directs you to the Projects page where all your existing projects and published projects are listed.
- Datasets: Directs you to the Datasets page where all the datasets available to you are listed.
- Connections: Directs you to the Connections page where all the existing connections (data sources) available to you are listed.
- Jobs: Directs you to the Jobs page where the various background jobs started by Spatial Studio to process various requests are listed.
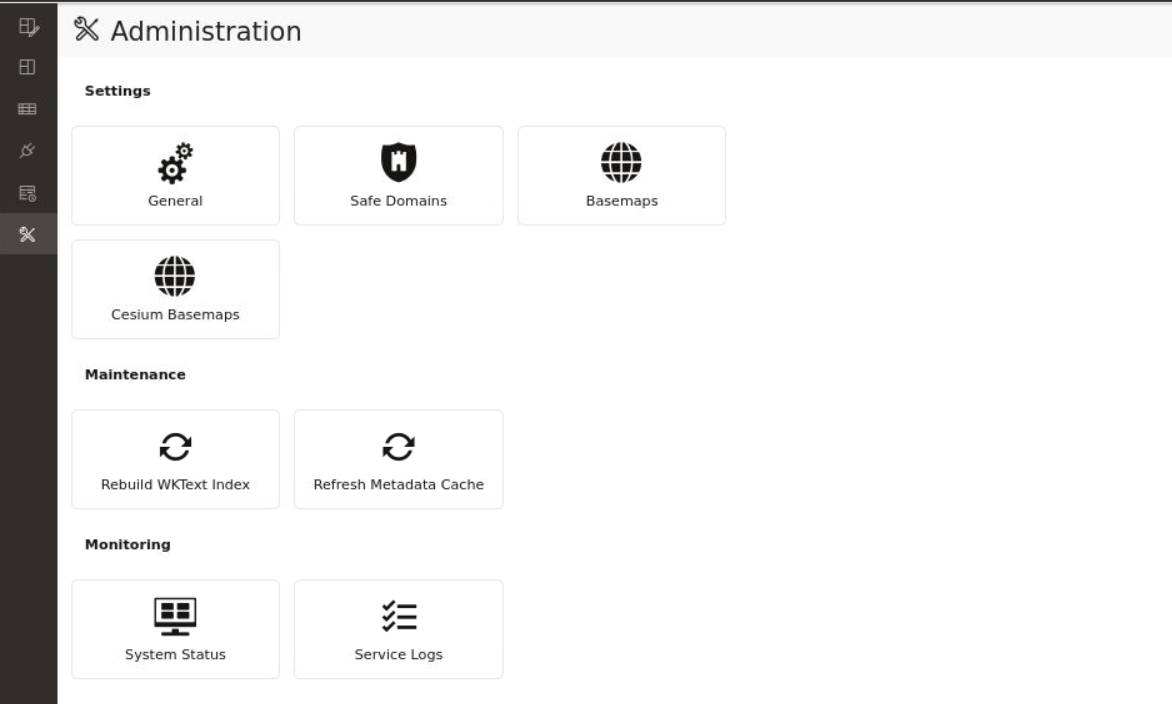
- Administration: Directs you to the Administration page where you can monitor the status and activity of Spatial Studio. It contains tabs for Settings, Maintenance, and Monitoring.
- Getting Started Using Spatial Studio
Spatial Studio includes a page with information and links to help you get started using the tool. - Spatial Studio Active Project Page
The Active Project page displays your current working project. - Spatial Studio Projects Page
The Projects page lists all the projects that have been created, both unpublished and published. - Spatial Studio Datasets Page
The Datasets page lets you view and edit existing datasets, and create new ones. - Spatial Studio Connections Page
The Connections page displays all the existing connections and also allows you to create a new connection. - Spatial Studio Administration Page
You can monitor the status and activity of Spatial Studio in the Administration Page. You can also view server logs, change global system configurations, manage custom basemaps, and configure safe domains. - Spatial Studio Jobs Page
The Jobs page displays details of all the background jobs that run in Spatial Studio. - Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
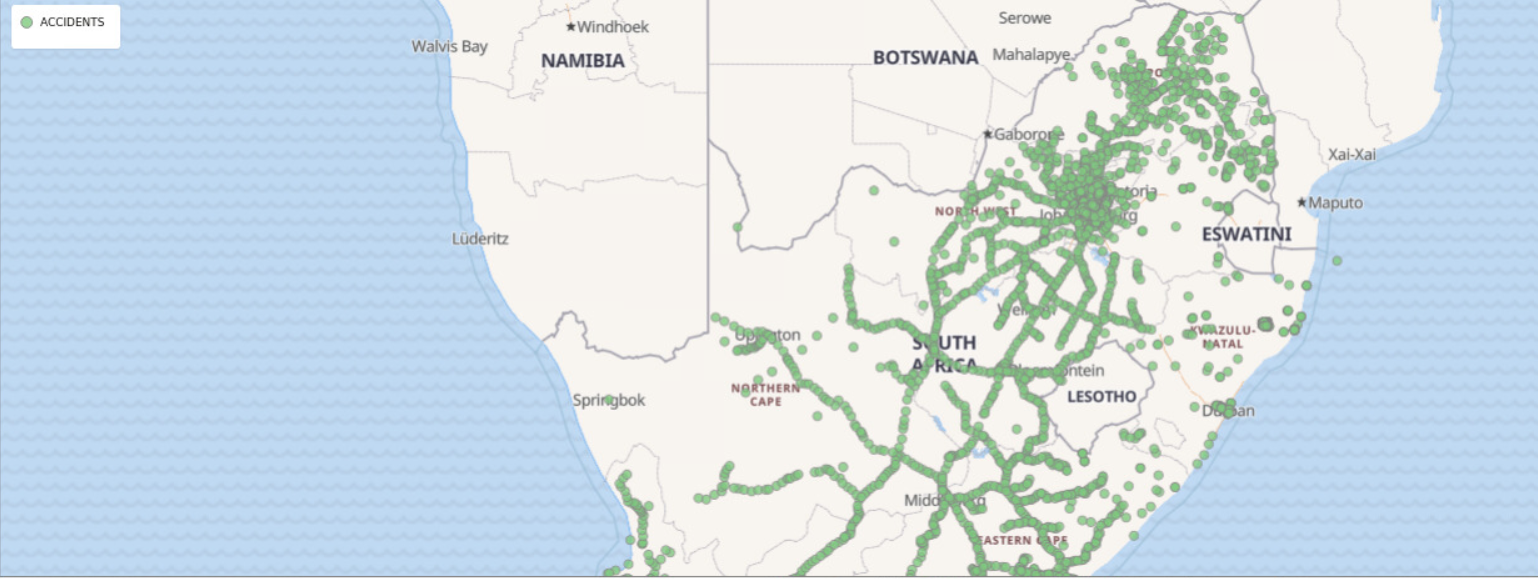
You can visualize your spatial data in Oracle Spatial Studio using different modes of visualization. - Performing Analyses in Spatial Studio
You can perform various spatial analyses (such as filtering by proximity, nearest neighbor analysis and so on) and visualize the results in Spatial Studio.
3.1 Getting Started Using Spatial Studio
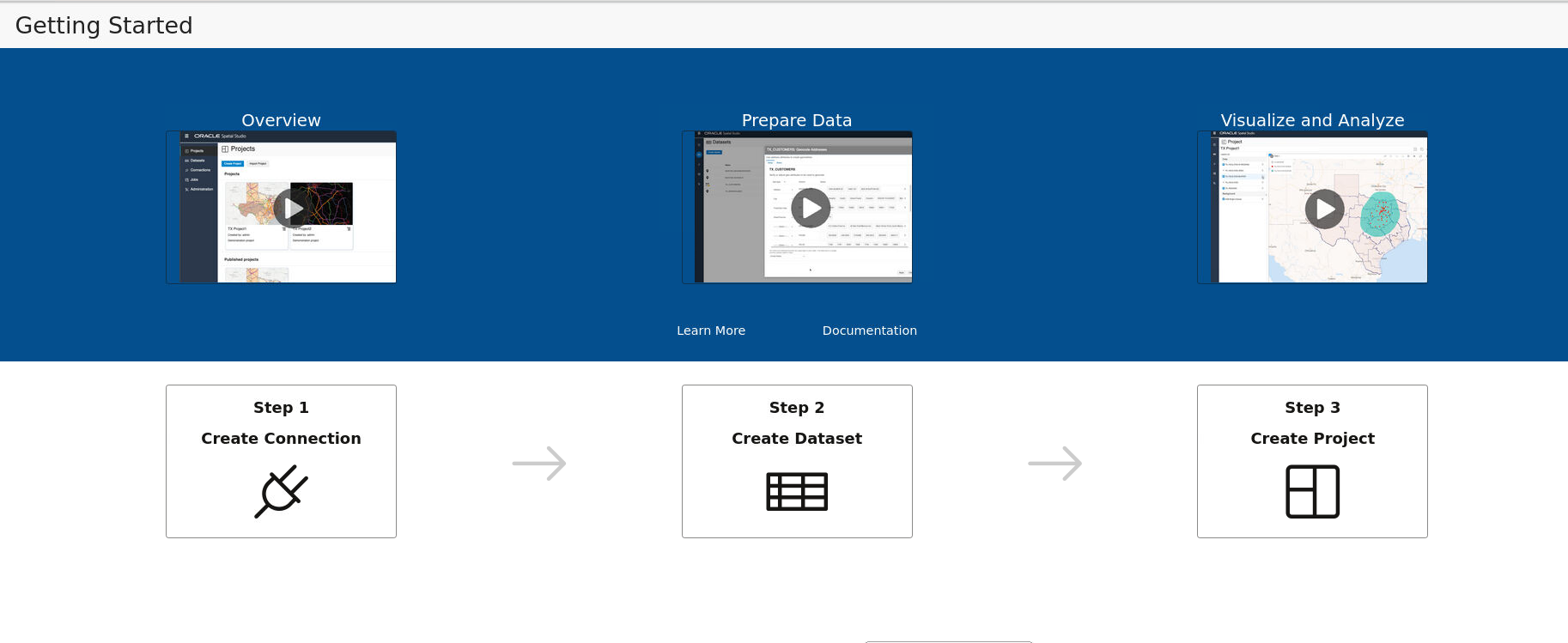
Spatial Studio includes a page with information and links to help you get started using the tool.
To display this page, click the small question mark icon (?) in the top right area of most pages (above the Create button) and click Getting Started from the context menu.
The Getting Started page opens as shown:
You can learn more about Spatial Studio by clicking one of the following options:
- Overview: Watch this video to understand the user interface and see how to perform the available actions.
- Prepare Data: Enable your business data for mapping and spatial analysis.
- Visualize and Analyze: Explore geographic patterns and relationships in your business data.
- Learn More: Visit our video library to learn more about Oracle Spatial Cloud.
- Documentation: See Oracle Spatial Studio Guide documentation to learn more about administering and using Spatial Studio.
- Get started using Spatial Studio through the
following workflow:
- Step1 - Create Connection: Begin by creating your database connection.
- Step2 - Create Dataset: Create a Dataset and load spatial data.
- Step3 - Create Project: Create a Project for visualizing and analyzing the spatial data.
Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
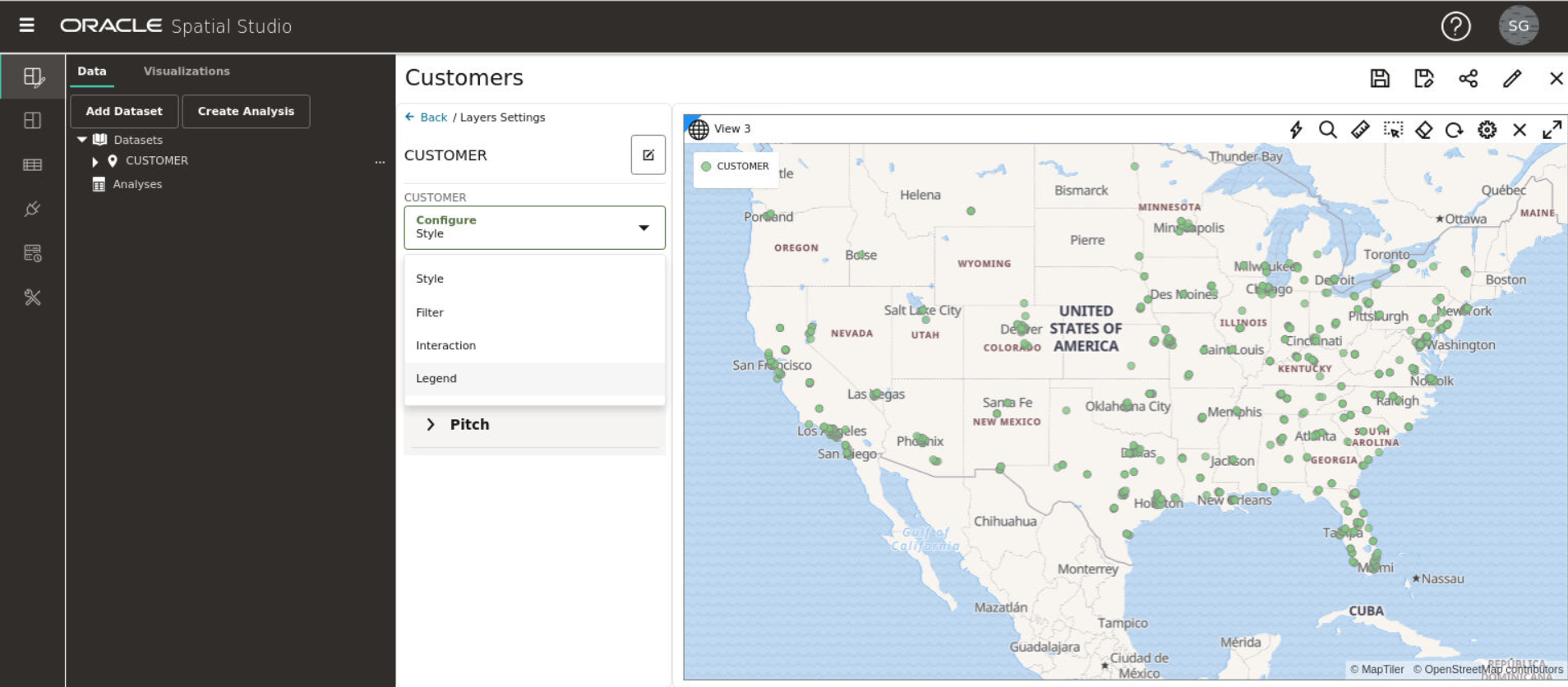
3.2 Spatial Studio Active Project Page
The Active Project page displays your current working project.
You can switch to your working project at any time from the other pages when working in Spatial Studio.
The following figure shows a layout of the Active Project page:
- Creating a table or map visualization.
- Adding or removing datasets from your project.
- Adding or removing data from a visualization layer.
- Adjusting the style setting or the zoom resolution for your
visualization layer. You can click the menu selector next to the dataset name in
the Data tab to display the following available options:
- Settings: Shows display options for Style, Filter, Interaction, and Legend.
- Spatial Analysis: Allows you to perform many spatial operations (All, or filtered by type: Filter, Combine, Transform, Measure), such as Add a buffer of a specified distance, Return shapes having spatial relationship to another, and Calculate area.
- Zoom to Layer: Zooms the display (out or in) to fit the entire layer.
- Refresh Layer: Refreshes the layer to reflect all user actions.
- Configure Animation: Allows you to configure animation settings to visualize a moving object.
- Remove: Removes the layer from the project.
The following icons are displayed on the top-right area of the Active Project page:
They are as follows:
- Save Project : Saves your updates to the project
- Save Project as : Creates a new copy of the project
- Publish Project : Publishes the project
- Edit: Allows you to edit the project details (such as, Name, Created By and Description)
- Close Project: Closes the project
Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
3.3 Spatial Studio Projects Page
The Projects page lists all the projects that have been created, both unpublished and published.
Figure 3-1 shows the layout of the Projects page.
You can perform the following actions on the Projects page:
- You can select a project to work or for viewing the details.
- You can create a new project by clicking Create Project.
- You can import a project by clicking Import and selecting a project zip file in the Import Project dialog.
- You can open, export or delete a project by clicking the
 icon for any of the listed projects.
icon for any of the listed projects.
- You can alter the display settings to have the projects listed as cards or in a tabular format.
- You can search for both unpublished and published projects.
Note:
For the first two actions, the project will be opened in the Active Project page.Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
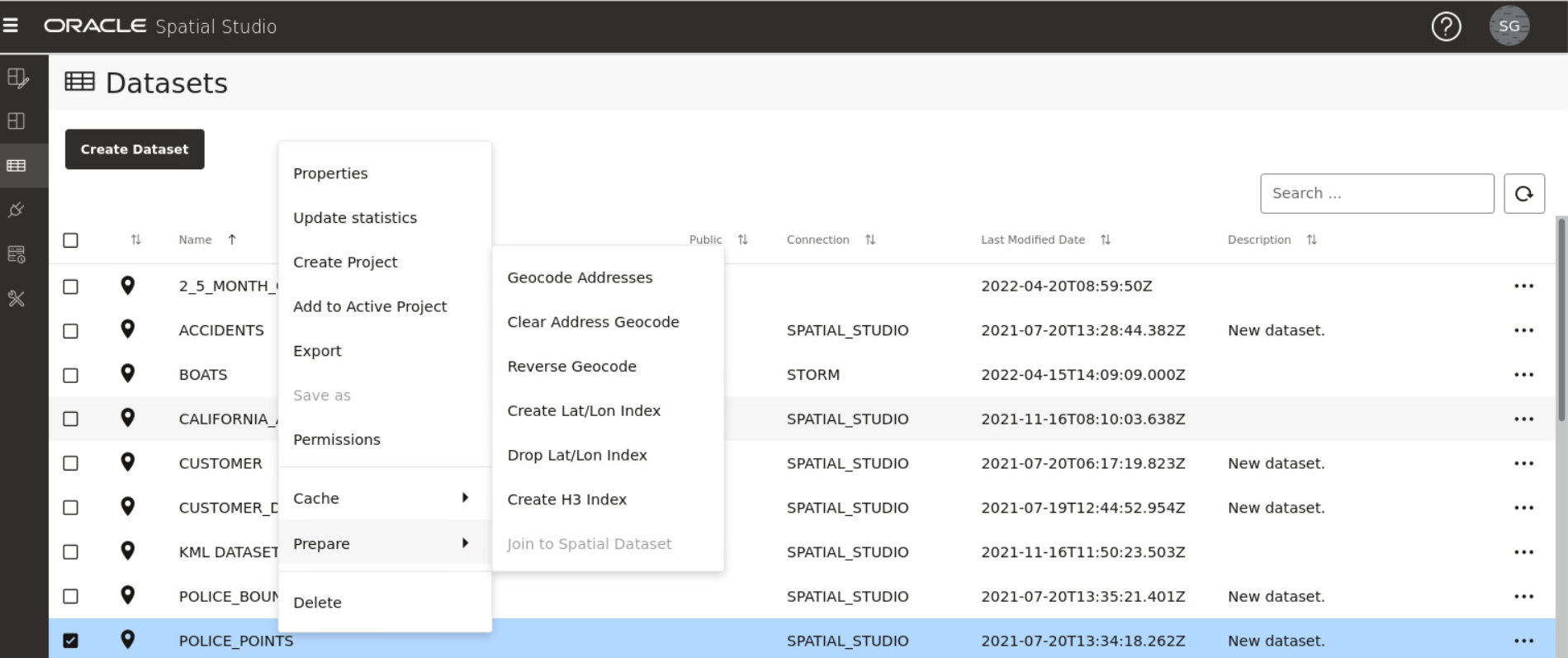
3.4 Spatial Studio Datasets Page
The Datasets page lets you view and edit existing datasets, and create new ones.
The following figure shows the Datasets page:
You can perform the following actions on the Datasets page:
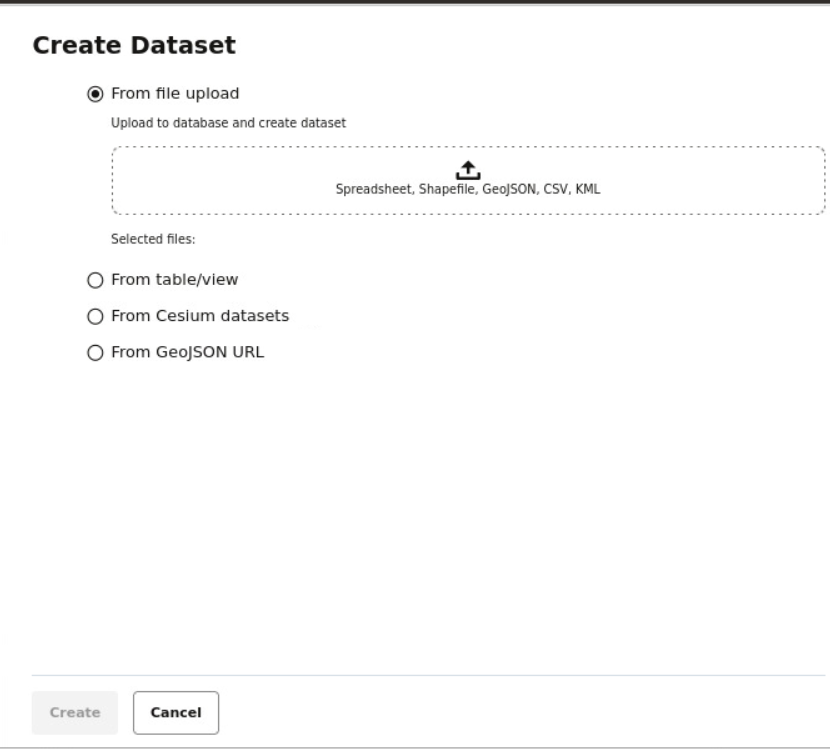
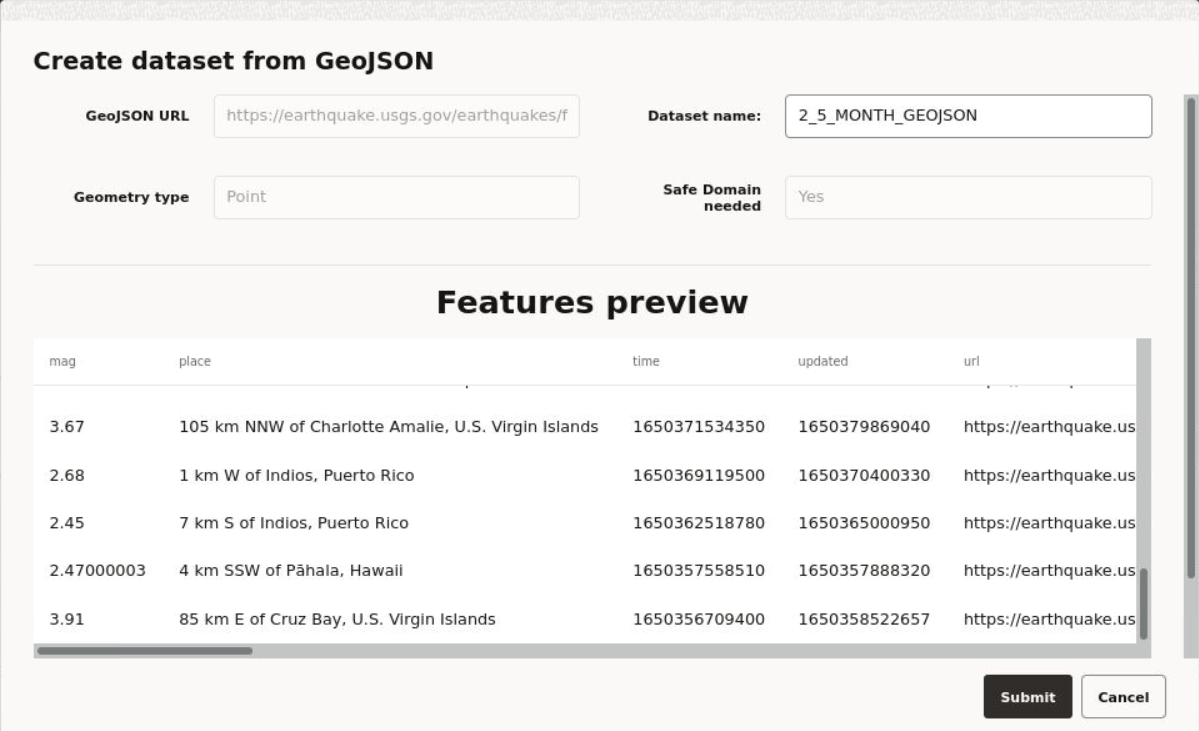
- You can create a new dataset, by clicking Create Dataset.
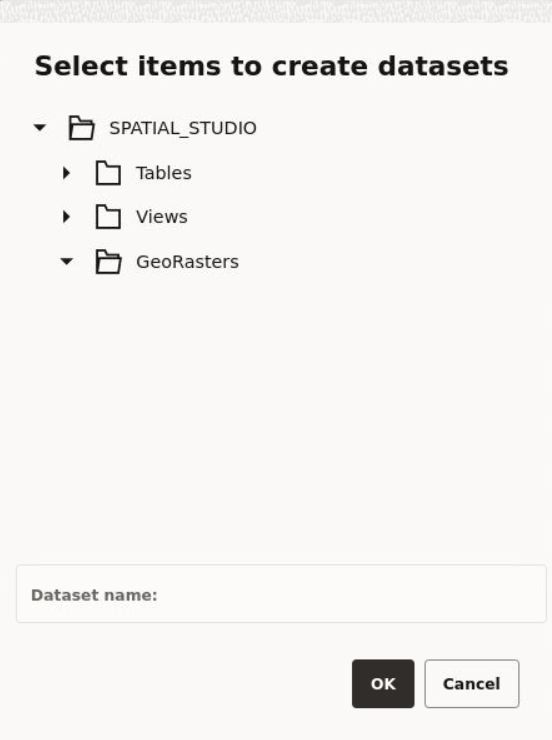
You can create a dataset from the following sources:
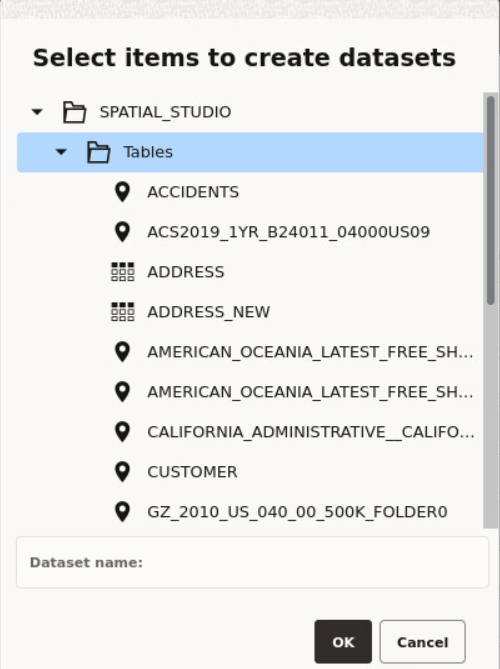
- Oracle Database table or view using a database connection
- By uploading dataset files with different formats to the database, such as
:
- Spreadsheet file
- Shapefile
- GeoJSON file
- CSV file
- KML file
- By importing 3D Tiles Tileset
By clicking ![]() against any displayed dataset or by right-clicking a dataset row, you can
perform the following actions :
against any displayed dataset or by right-clicking a dataset row, you can
perform the following actions :
- Properties: View or modify properties of the dataset
- Update Statistics: Update the dataset statistics
- Create Project: Create a new project using the dataset
- Add to Active Project: Add the dataset to the project in the Active Project page
- Export: Export the dataset (in GeoJSON or CSV file format)
- Save as: Make a new copy of the dataset
- Permissions: Configure dataset sharing and permissions
- Cache: Control map tiles pre-caching activities
- Prepare: Prepare a dataset for any of the following options:
- Geocode Addresses: Add geocoded information such as geographic coordinates to the dataset
- Clear Address Geocode: Remove geocoded information from the dataset
- Reverse Geocode: Add address information from a set of geographic coordinates to the dataset
- Create Lat/Lon Index: Create latitude/longitude index
- Drop Lat/Lon Index: Remove latitude/longitude index
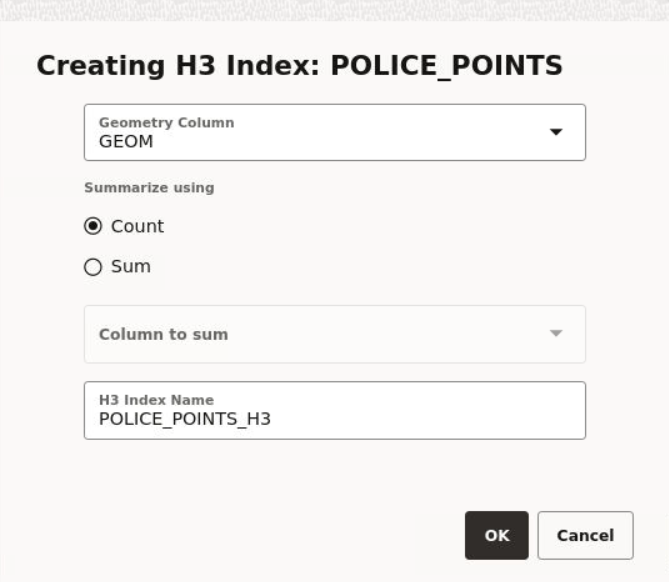
- Create H3 Index: Prepare an H3 aggregation dataset
- Join to Spatial Dataset: Prepare a non-spatial dataset for map visualization by joining to a spatial dataset
- Delete: Delete the dataset
- Creating a Dataset
- Datasets with Issues
- Geocoding a Dataset
- Reverse Geocoding a Dataset
- Preparing a Non-Spatial Dataset for Analysis
Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
3.4.1 Creating a Dataset
Parent topic: Spatial Studio Datasets Page
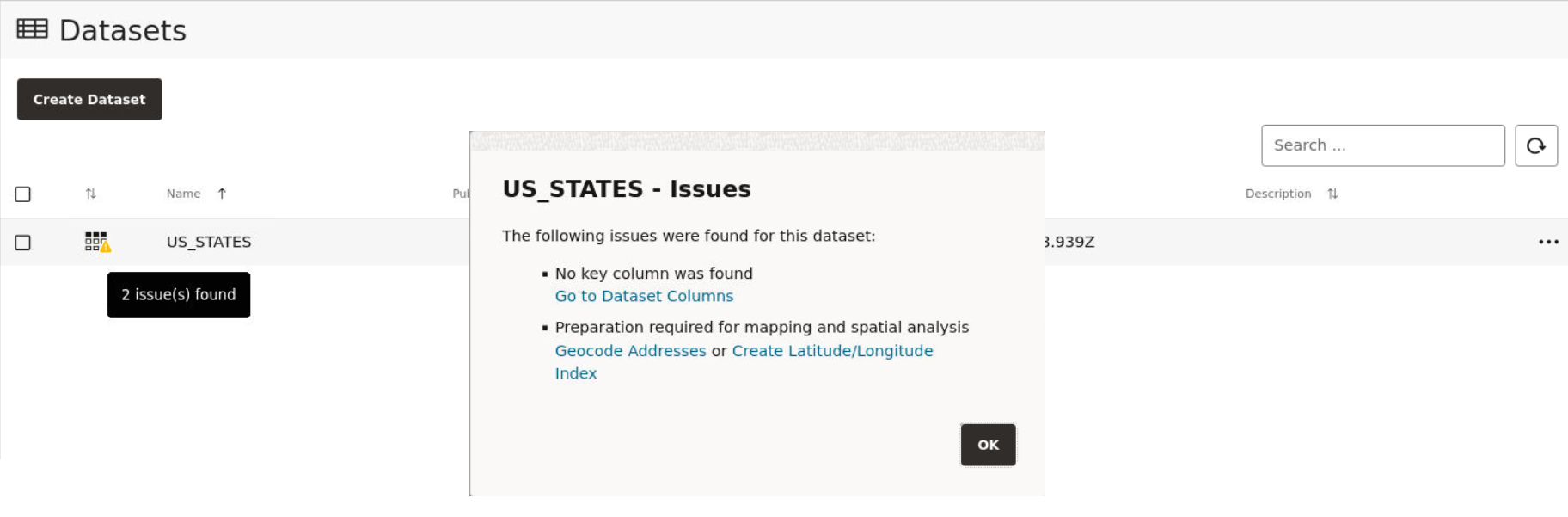
3.4.2 Datasets with Issues
All datasets must meet certain data requirements in order to be used for map visualization and analysis. Otherwise, Spatial Studio highlights these datasets with a warning on the Datasets page.
Table 3-1 Selected List of Dataset Issues
| Issue | Cause | Spatial Studio Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| No key column was found | Primary key is missing on the dataset. |
|
| This dataset needs spatial metadata and index | The geometry column in the dataset does not have the spatial metadata or a spatial index or both. | Click Create Spatial Metadata and Index to create the spatial metadata and index for the geometry column. |
| Preparation Required for mapping and spatial analysis | It can be due to one of the following reasons:
|
Depending on the cause, you may need to perform one of the
following:
|
Parent topic: Spatial Studio Datasets Page
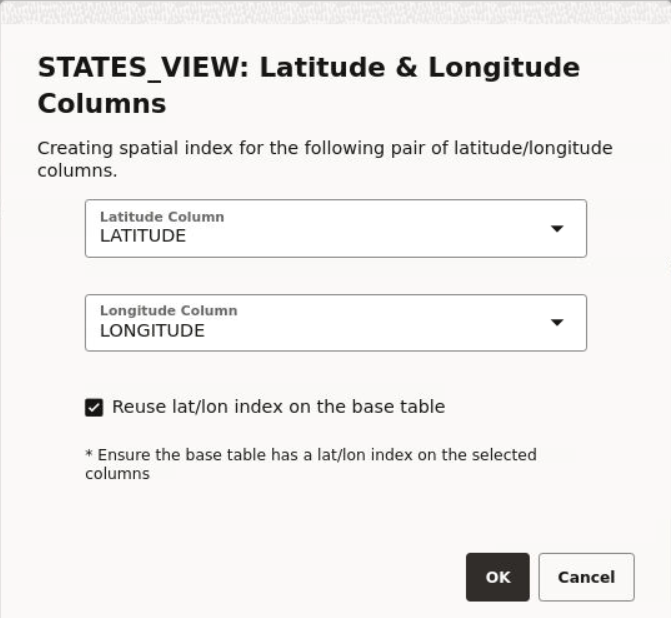
3.4.2.1 Enabling Spatial on a View-Based Dataset with Latitude and Longitude Columns
The instructions assume:
- You have created a dataset from a view having latitude and longitude
columns.
See Creating a Dataset for more information on creating a dataset from a view.
- This view-based dataset is listed on the Datasets page with a warning icon since the dataset is not spatially enabled for visualization.
Parent topic: Datasets with Issues
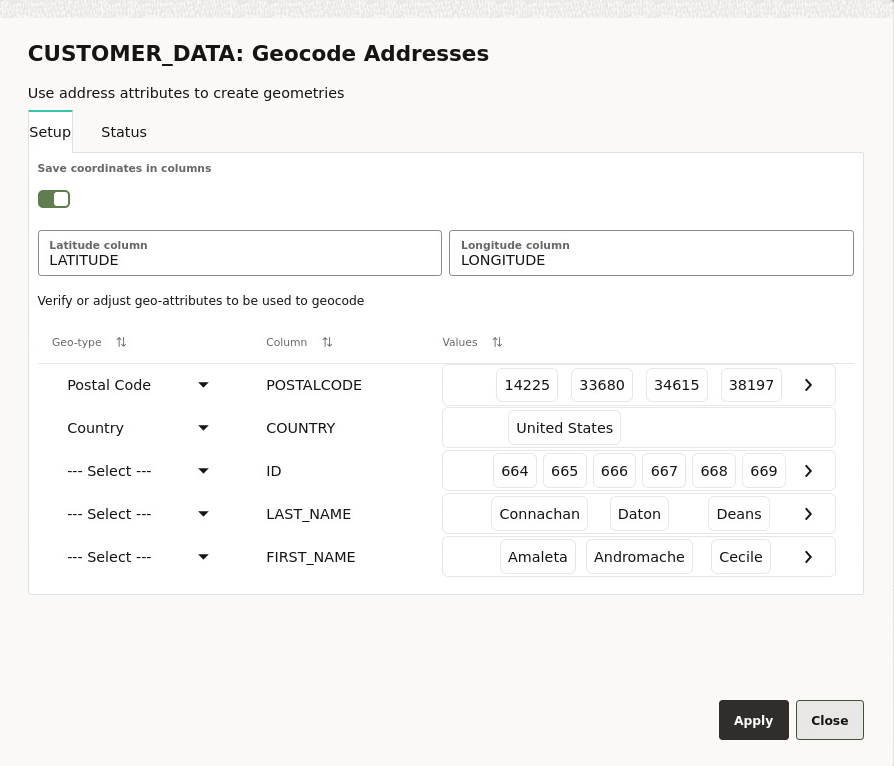
3.4.3 Geocoding a Dataset
You can geocode a
dataset in Spatial Studio to store the
resulting latitude and longitude information as a SDO_GEOMETRY
column. Optionally, you can also store them in a latitude and longitude numeric
columns in the underlying database table referenced by the dataset.
Prior to geocoding a dataset, if the Spatial Studio server is running behind a firewall, then ensure you have the correct Web Proxy information configured in the Administration page. This is because the Spatial Studio application uses an external Oracle hosted geocoding service which is on the public internet.
You can perform the following steps to geocode a dataset.
Parent topic: Spatial Studio Datasets Page
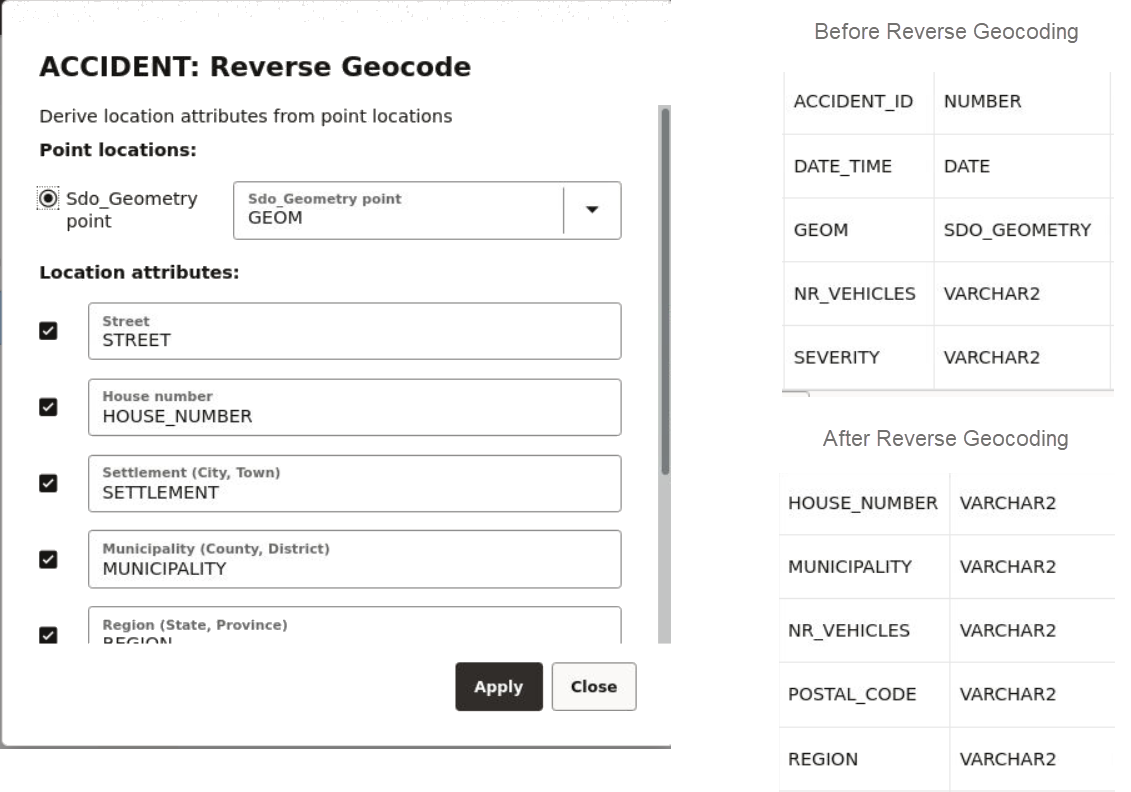
3.4.4 Reverse Geocoding a Dataset
You can reverse geocode a dataset in Spatial Studio to add address information to the dataset's table using the following steps.
Note:
Reverse Geocoding is supported only in point or latitude and longitude datasets.Parent topic: Spatial Studio Datasets Page
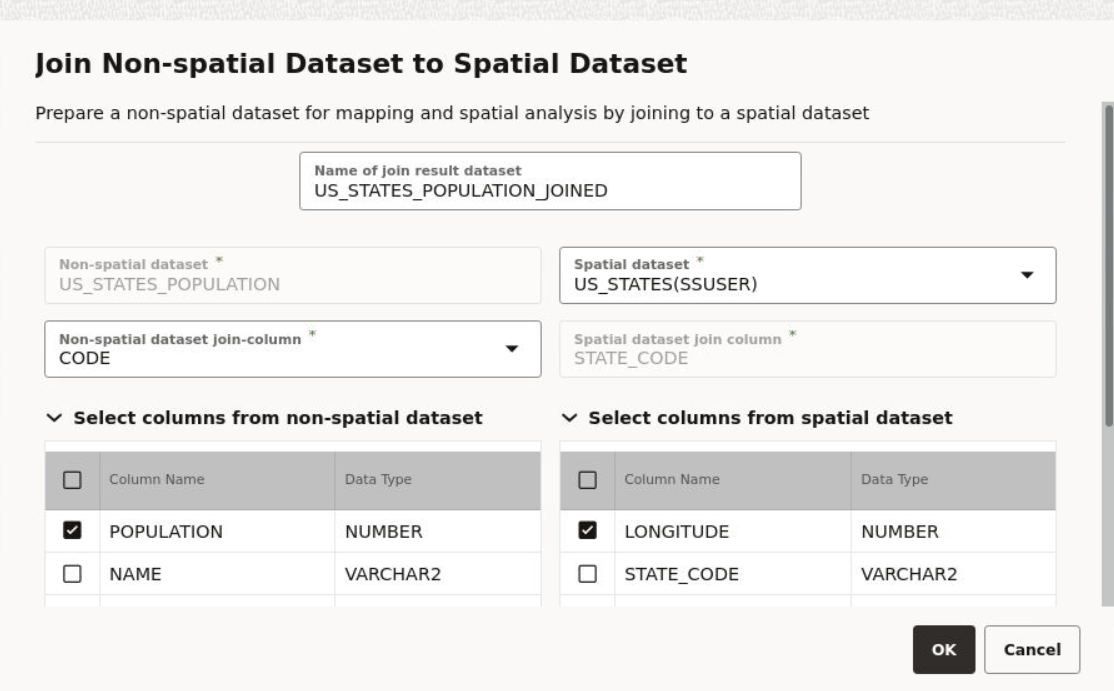
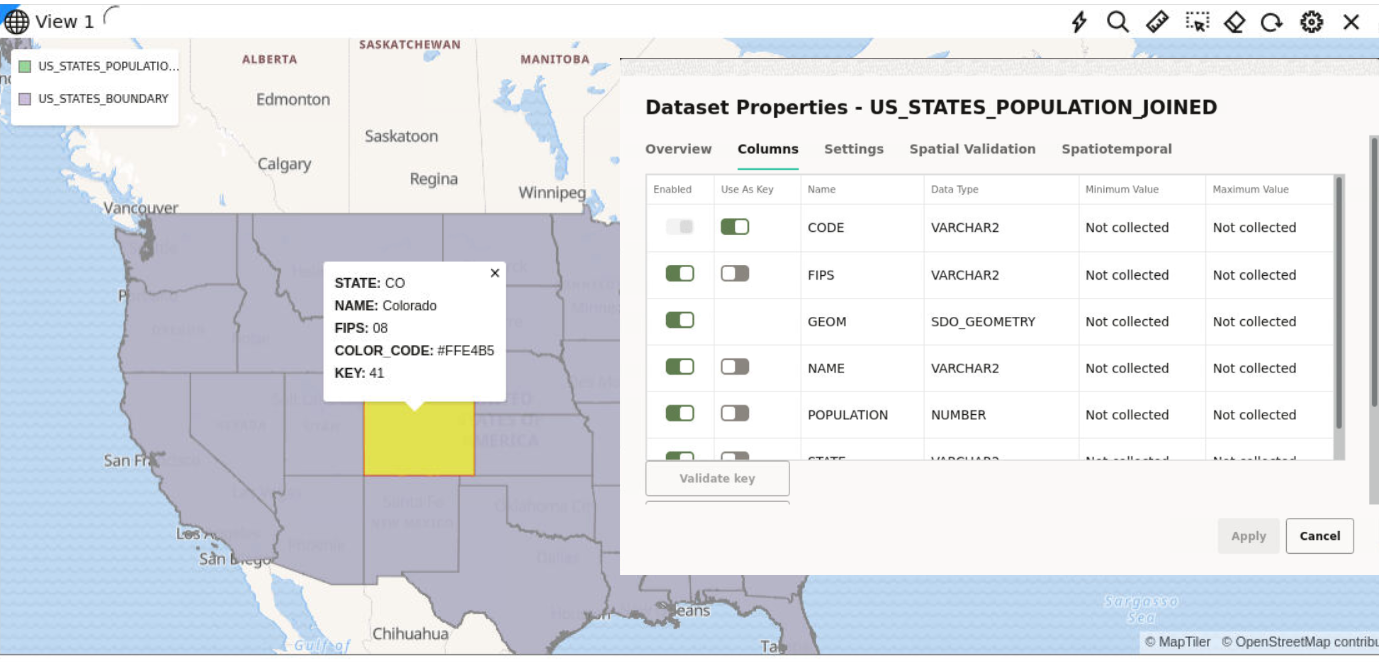
3.4.5 Preparing a Non-Spatial Dataset for Analysis
Also, note the following highlights about joining two datasets:
- You can only join a non-spatial dataset to a spatial dataset and not conversely.
- It is essential that the non-spatial data in one dataset is linked to the spatial data in the other dataset through a common primary key column.
- You can choose the columns for the newly created joined dataset from the attributes of the datasets associated in the join operation.
Parent topic: Spatial Studio Datasets Page
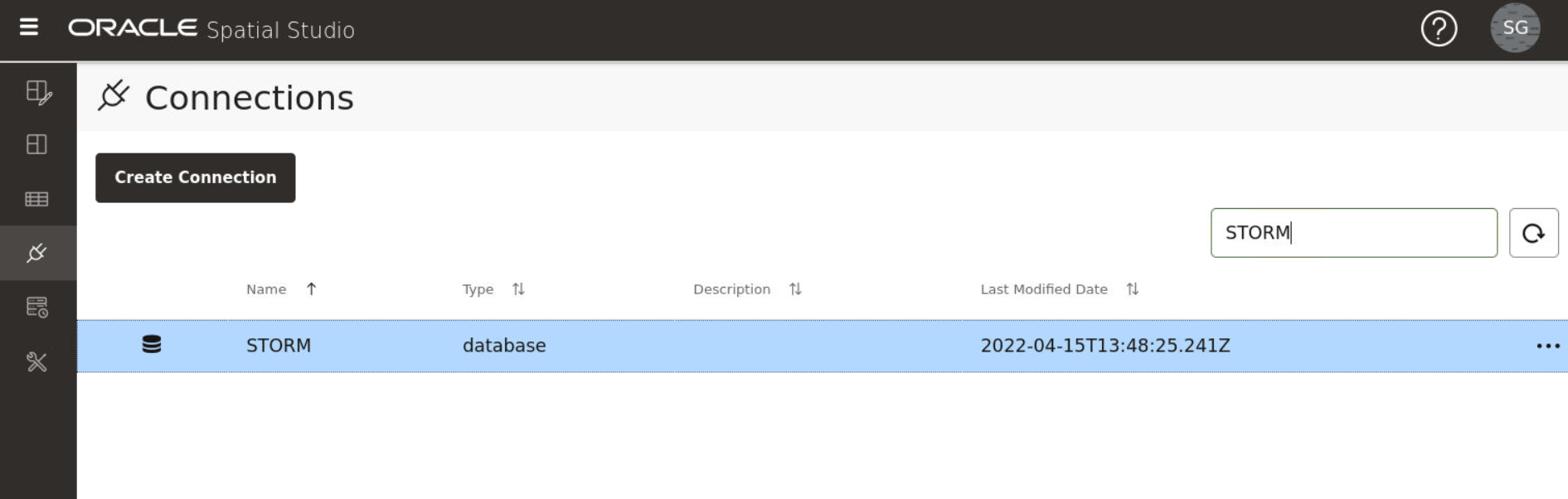
3.5 Spatial Studio Connections Page
The Connections page displays all the existing connections and also allows you to create a new connection.
The following figure shows a layout of the Connections page:
You can perform the following actions on the Connections page:
- You can create a new connection, by clicking Create Connection.
You can create a connection from the following sources:
- Oracle Database: by providing host, port, schema, and other database authentication details
- Oracle Autonomous Database: by providing wallet details
- You can also perform the following actions by clicking the hamburger icon against
any displayed connection or by right-clicking a connection row :
- Properties: View or modify properties of the connection
- Edit: Update the connection details
Note:
You cannot edit the SPATIAL_STUDIO connection on the Connections page. Instead, refer to If the Spatial Studio Repository Schema Password Has Been Changed section. - Test: Validate the connection
- Delete: Delete the connection along with all its datasets
Note:
You cannot delete the SPATIAL_STUDIO connection.
Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
3.6 Spatial Studio Administration Page
You can monitor the status and activity of Spatial Studio in the Administration Page. You can also view server logs, change global system configurations, manage custom basemaps, and configure safe domains.
Note:
You must be logged in as an administrator of Spatial Studio to access this menu option.Settings
- General: This section allows changing the GeoCoding service URL, the web proxy used by the Studio server. It also allows you to customize the frontend branding area of the application.
- Safe Domains: This section allows the administrator to manage the white listing of the domains (host names or IP addresses) that are considered safe for loading various types of the resources from the Studio application. Typically, it is used to add the domain of a custom basemap to the Content Security Policy directives of the Studio. After making the changes to the safe domains list, you must reload or refresh the browser page to reload the new Content Security Policy.
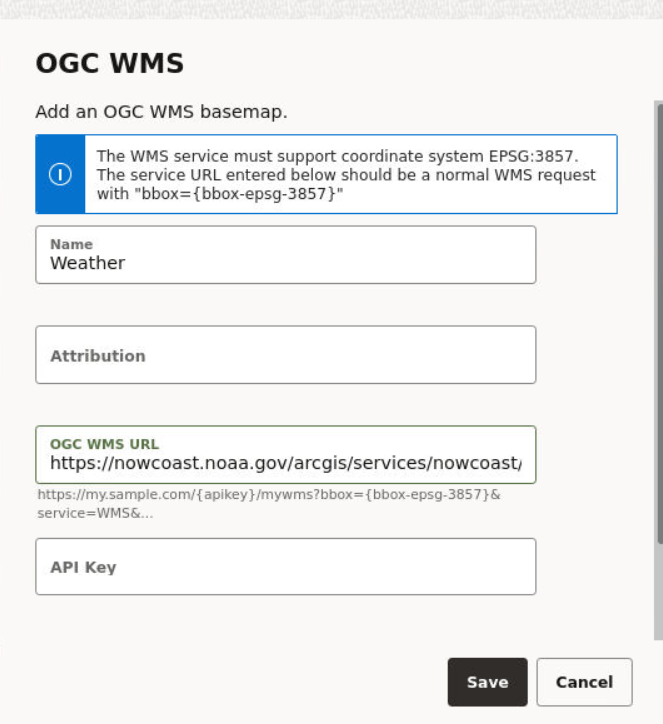
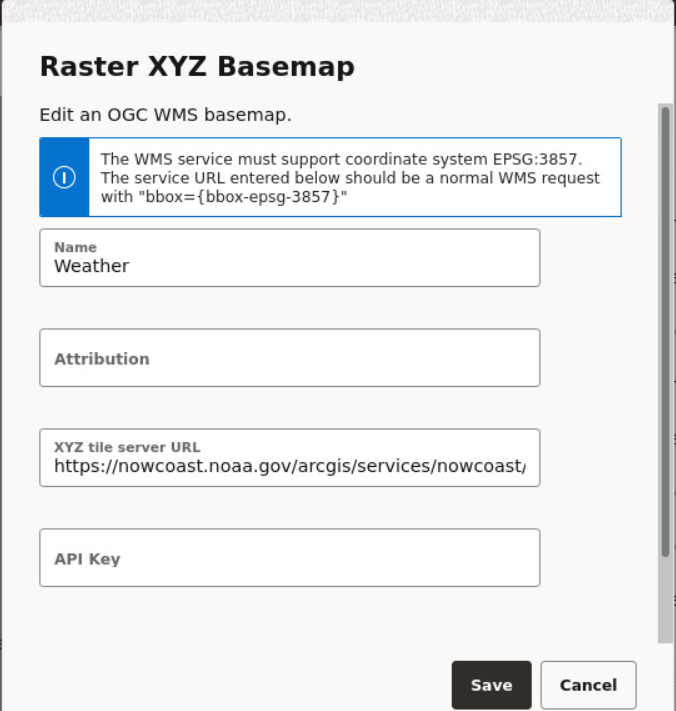
- Basemaps: This section allows a quick view of the existing custom basemaps, and in adding or editing custom basemaps. Custom basemaps can be made of either raster or vector tiles, typically hosted on a third party tile server. Additionally, you can also create a custom basemap using a WMS OGC web service.
- Cesium Basemaps: This section gives you a quick view of the existing custom basemaps used exclusively for the 3D Cesium Map visualization. It also allows you to add new basemaps to be used by the 3D Map visualizations.
Note:
Each listed host entry for Basemaps and Cesium Basemaps must be present as one of the entries in the Safe Domains list. If the host basemap comes from a domain that is not present in the Safe Domains list, then the basemap may not render correctly when visualizing the map.Maintenance
- Rebuild WKText Index: Use this only when needed to rebuild the text index of the repository database schema’s supported Spatial Reference Well Known text definitions. For the shapefile upload, this well known text index is used to automatically match the best SRID.
- Refresh Metadata Cache: Spatial Studio typically caches all of the frequently used metadata such as the definitions of Datasets, Connections, and Projects. Sometimes it is required to refresh the whole cache in case some cached metadata becomes stale or out of sync in rare events.
Monitoring
- System Status: This section provides read-only information about the general health and system status of the Spatial Studio server.
- Service Logs: This section allows loading and viewing a desired number of server-side logs. To reduce the clutter, you can filter the result using the desired logging level .
In a cluster deployment, both the preceding options display only the information of the particular Spatial Studio instance to which the current session is connected.
3.6.1 Adding a Custom Basemap
The following steps enable you to add a custom basemap.
Parent topic: Spatial Studio Administration Page
3.6.2 Editing a Custom Basemap
The following steps enable you to edit a custom basemap.
Parent topic: Spatial Studio Administration Page
3.7 Spatial Studio Jobs Page
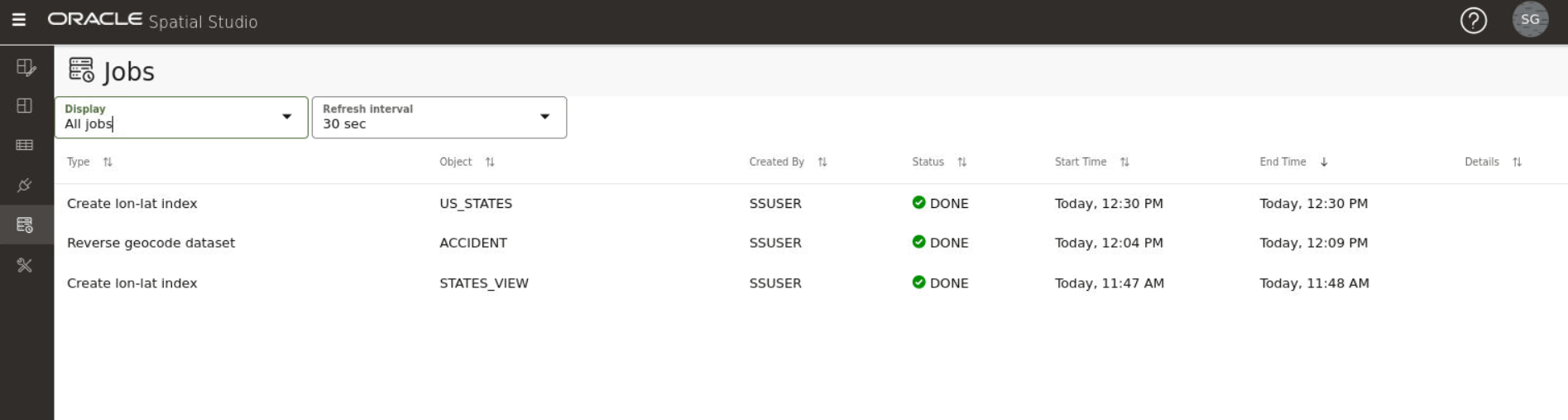
The Jobs page displays details of all the background jobs that run in Spatial Studio.
The following figure shows a layout of the Jobs page:
You can perform the following actions on the Jobs page:
- Select a job to be displayed in the grid: Active, Past or All.
- Select a refresh interval for the jobs grid.
The grid table displays the following properties for each job entry row:
- Type: The job type, such as Geocode dataset, Create lon-lat index and so on.
- Object: The entity being altered by the job, which can be a Dataset, Table, Index or other.
- Created by: The user that submitted the job.
Note:
System maintenance jobs are created by “$system” account - Status: Indicates the state or progress of a job, which can be:
- PENDING
- RUNNING
- DONE
- FAILED
- ABORTED
- Start Time: The scheduled next run time for jobs with PENDING status, or the actual job start time for the other status.
- End Time: The time at which a job completed.
- Details: Provides extra feedback on which step a RUNNING job is currently executing, or error details for FAILED or ABORTED jobs.
Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
3.8 Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
You can visualize your spatial data in Oracle Spatial Studio using different modes of visualization.
Spatial Studio supports the following visualization methods:
- Table
- Map
- Cesium-Map
You can save your visualization as a Project in Spatial Studio. You can rework on a project or publish a project to share the results with other users.
The following sections explain in detail how you can use the various visualization techniques:
- Using a Table Visualization
- Using a Map Visualization
- Using a Cesium Map Visualization
- Styling a Map Layer
- Visualizing Map Data Over Time
Parent topic: Using Oracle Spatial Studio
3.8.1 Using a Table Visualization
Parent topic: Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
3.8.2 Using a Map Visualization
Spatial Studio supports the following types of map visualizations:
- Geometry Data Visualization:
- Point type
- Line type
- Polygon / Area type
- GeoRaster Data Visualization
- Hexagonal Data Visualization using H3 Aggregations
The following sections describe how to get started on these visualizations:
- Visualizing a Point Map
- About GeoRaster Data Visualization
- About Hexagonal Data Visualization Using H3 Aggregations
- About Custom Map Regions Visualization
- Visualizing a Moving Object
Starting from Oracle Spatial Studio Release 22.1.0, you can visualize moving objects using a spatiotemporal dataset.
Parent topic: Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
3.8.2.1 Visualizing a Point Map
Parent topic: Using a Map Visualization
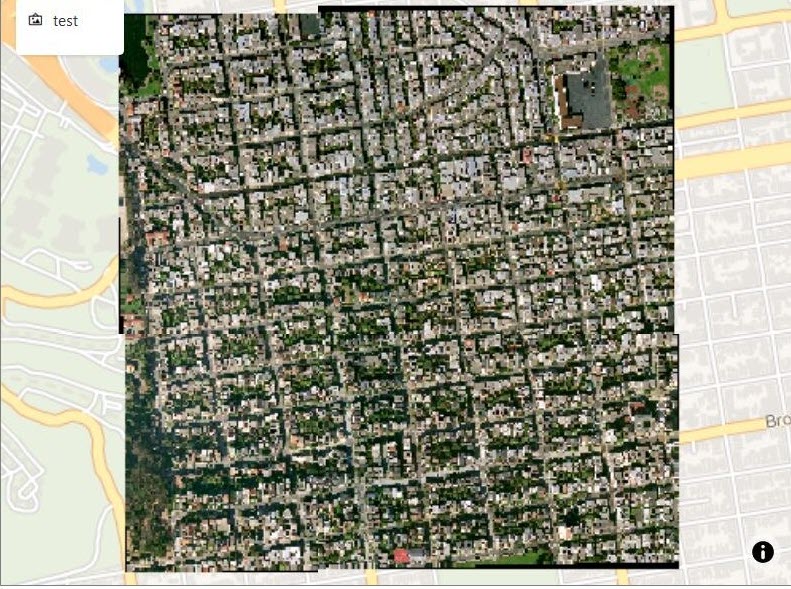
3.8.2.2 About GeoRaster Data Visualization
Oracle Spatial Studio allows you to visualize GeoRaster data stored in spatial GeoRaster type in Oracle Database.
Geo-referenced raster data, including satellite imagery, aerial photos from drones, and gridded data, is very useful for mapping applications. It can be directly analyzed, or layered with vector data as a background map for additional context. See Spatial GeoRaster Developer's Guide for more information on GeoRaster data.
The following sections describe how you can create and visualize GeoRaster data in Spatial Studio.
Parent topic: Using a Map Visualization
3.8.2.2.1 Creating a GeoRaster Dataset
Parent topic: About GeoRaster Data Visualization
3.8.2.2.2 Visualizing GeoRaster Data on a Map
Parent topic: About GeoRaster Data Visualization
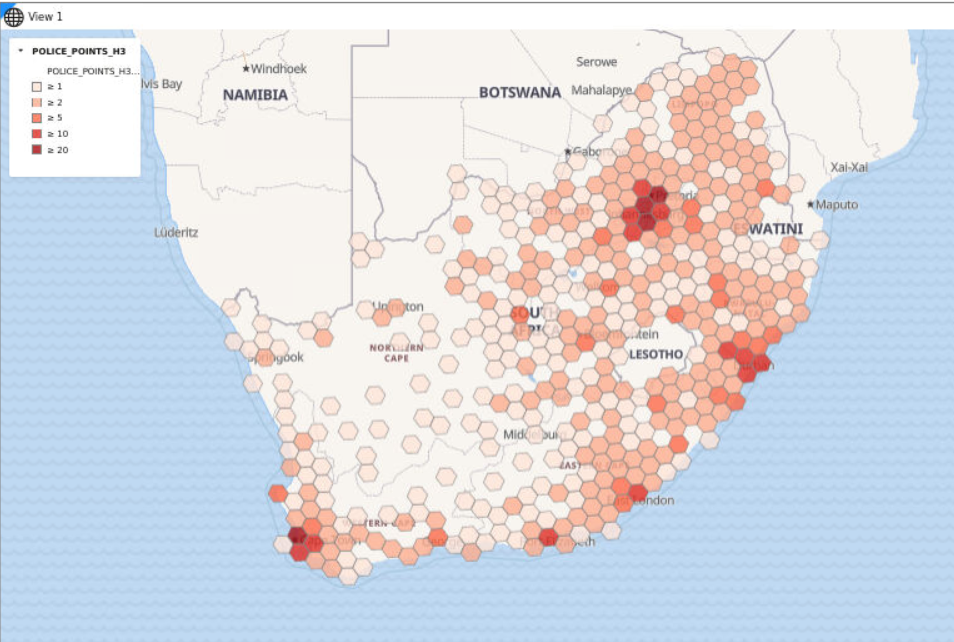
3.8.2.3 About Hexagonal Data Visualization Using H3 Aggregations
Oracle Spatial Studio allows you to visualize point-type map data using hexagons with H3 (Hexagonal Hierarchical Spatial Index) aggregations.
- It helps you to identify patterns or clusters in a larger point dataset
- Easier interpretation of data, as in a hexagonal cell, all the points are equidistant from the hexagon center-point
- Hexagonal cells are color coded based on the number of datapoints they hold, which enables you to easily understand data patterns
The following sections describe how you can use H3 aggregations in Spatial Studio:
Parent topic: Using a Map Visualization
3.8.2.3.1 Preparing an H3 Aggregation Dataset
Parent topic: About Hexagonal Data Visualization Using H3 Aggregations
3.8.2.3.2 Visualizing Data With H3 Aggregations
To prepare a dataset for H3 aggregation, see Preparing an H3 Aggregation Dataset for more information.
Parent topic: About Hexagonal Data Visualization Using H3 Aggregations
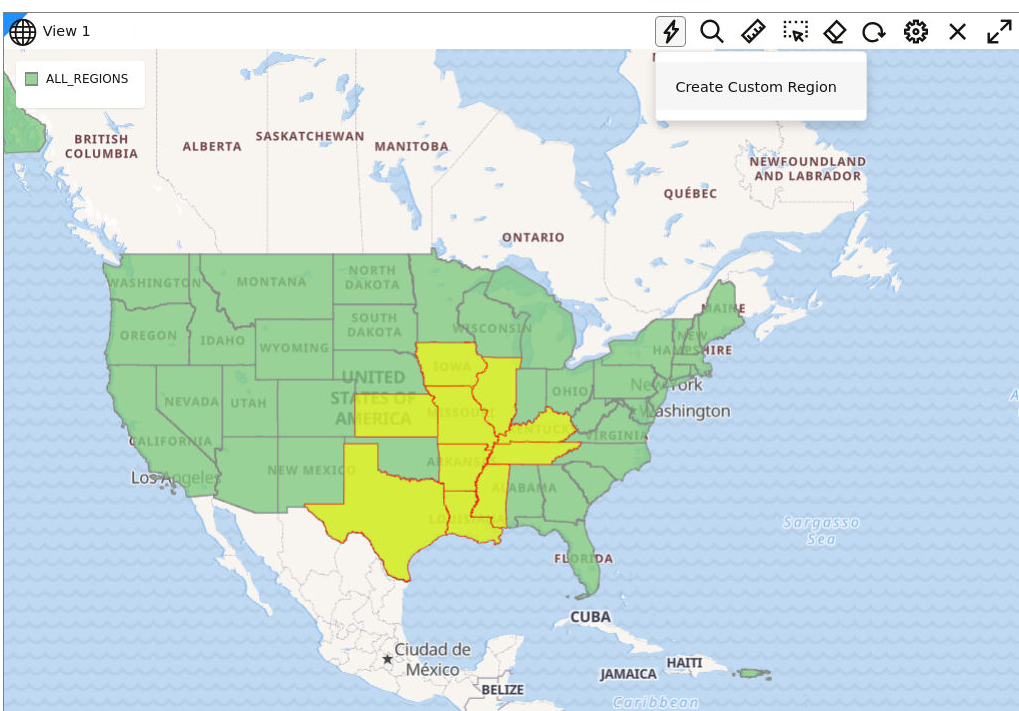
3.8.2.4 About Custom Map Regions Visualization
Oracle Spatial Studio allows you to create custom map regions on map layers that support polygon type geometry.
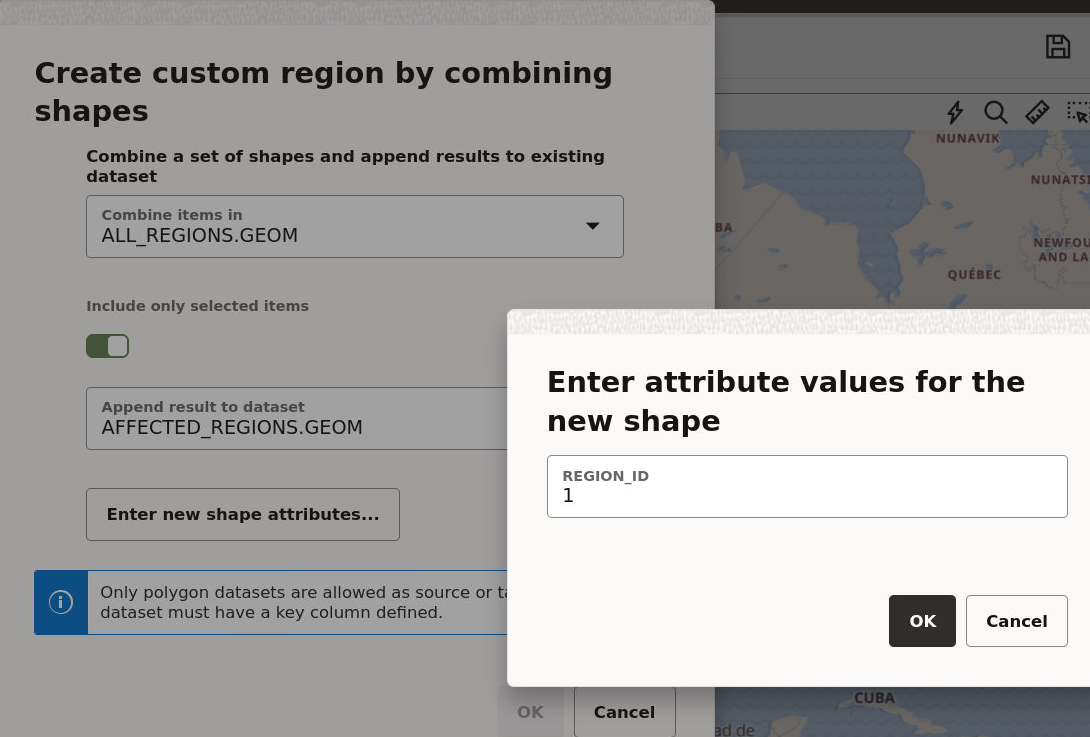
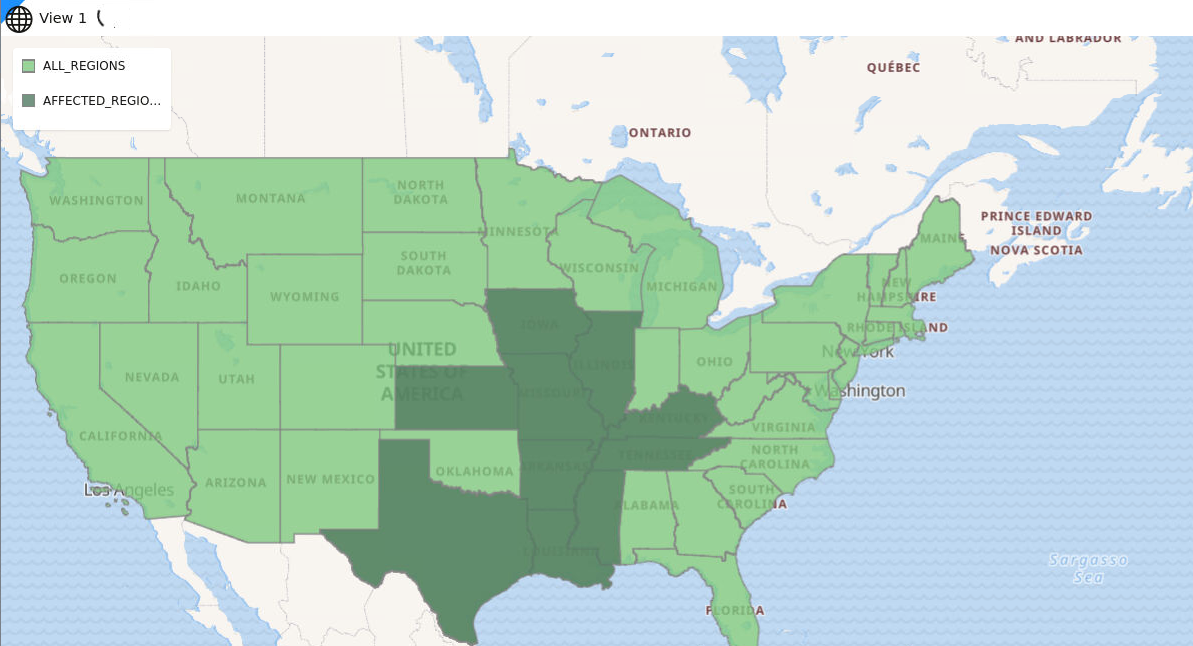
You can create a new map region by selecting multiple polygon shapes and combining them with a new key-value. You can then append or insert this new map region with the new key-value into a target dataset containing all of your other custom map regions.
These newly created custom shapes are persisted on the underlying database table of the target dataset, and therefore can be used for data visualization or reporting just like any other dataset.
- The source dataset, that is the dataset whose polygon shapes you
will be selecting and then combining into a custom map region, must always be
based on an Oracle Database table.
Datasets from Oracle views and Studio's Analyses are not currently supported.
- The new regions may or may not be contiguous.
- The target dataset, that is the dataset on which you want to store the newly created custom map regions, will store them in its geo-reference system.
- Only the key value and new geometry value are inserted into the target table.
- The target dataset must meet the following requirements:
- The geometry metadata information for the target dataset must be available in the SDO_GEOM_METADATA view.
- A spatial index must exist on the geometry column.
Note:
If a spatial index is not created on the geometry column, then the target data layer cannot be dragged on to the map visualization canvas. See Creating a Target Dataset for more information.
Parent topic: Using a Map Visualization
3.8.2.4.1 Creating Custom Regions for Visualization
Parent topic: About Custom Map Regions Visualization
3.8.2.4.2 Creating a Target Dataset
Parent topic: About Custom Map Regions Visualization
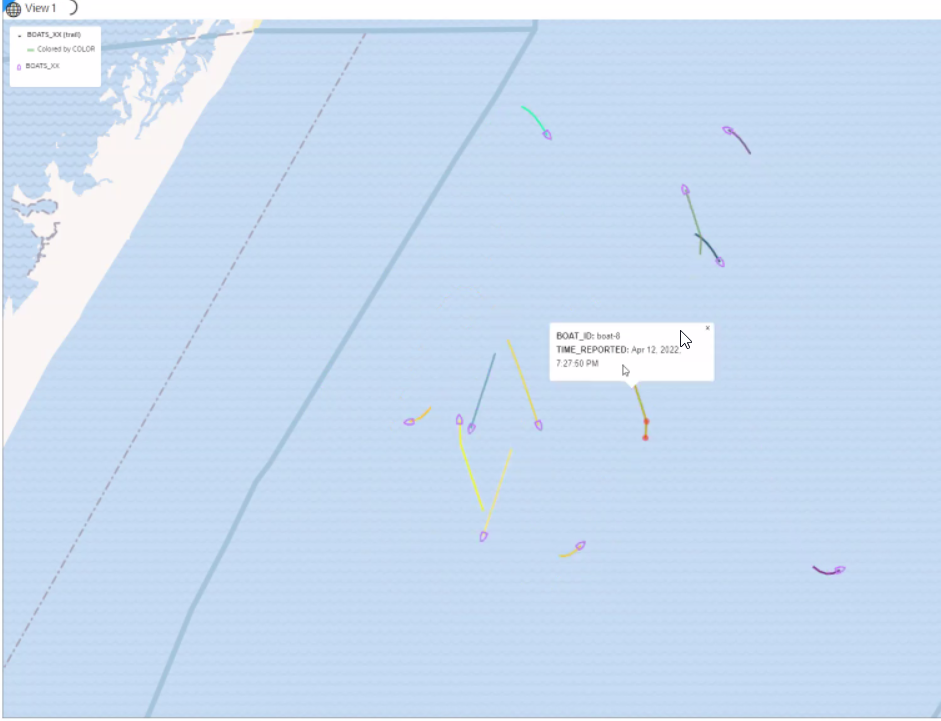
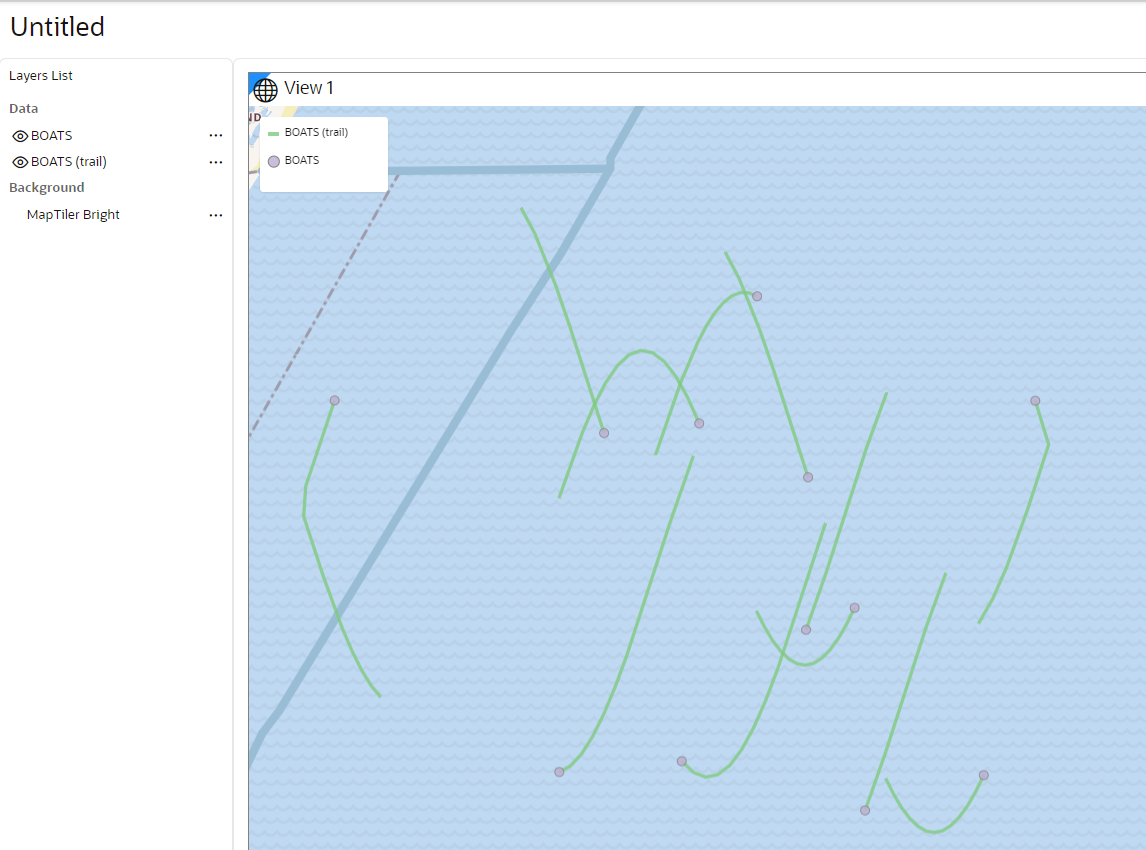
3.8.2.5 Visualizing a Moving Object
Starting from Oracle Spatial Studio Release 22.1.0, you can visualize moving objects using a spatiotemporal dataset.
To get started on visualizing moving objects in Spatial Studio, you must:
- Enable a dataset as a spatiotemporal dataset by defining the essential space, time and entity information.
- Configure animation settings after adding the spatiotemporal dataset to a map for visualization.
The following sections describe in detail how you can perform the preceding two steps:
- Enabling Spatiotemporal for a Dataset
In order to visualize and animate moving objects, you must enable Spatiotemporal for the dataset containing spatiotemporal data on the Datasets page. - Configuring Animation for a Moving Object
To visualize moving objects on a map in Spatial Studio, you must configure the animation settings on the map layer. - Characteristics of Spatiotemporal Map Layers
This section describes the distinct characteristics of the spatiotemporal map layers when visualizing a spatiotemporal dataset.
Parent topic: Using a Map Visualization
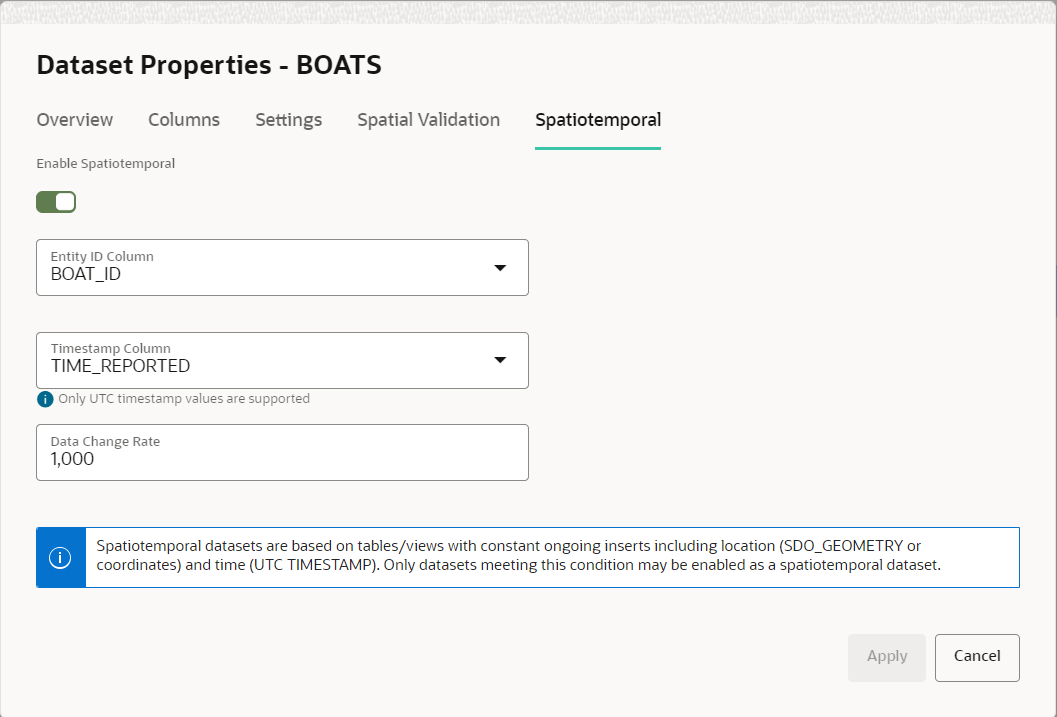
3.8.2.5.1 Enabling Spatiotemporal for a Dataset
In order to visualize and animate moving objects, you must enable Spatiotemporal for the dataset containing spatiotemporal data on the Datasets page.
- It must be based on a geometry table or view with a geometry column or pair of latitude/longitude columns.
- There must be one or more “moving objects” or entities uniquely identified by one of the columns.
- There must be a column of the type
TIMESTAMP, that stores the UTC datetime of the entities as they are being observed and recorded. - The dataset's underlying table or view must have ongoing inserts with recently obtained location data of entities being observed or monitored.
You can perform the following steps to enable spatiotemporal for a dataset. The instructions assume that the dataset containing spatiotemporal data is already existing in your database schema.
Parent topic: Visualizing a Moving Object
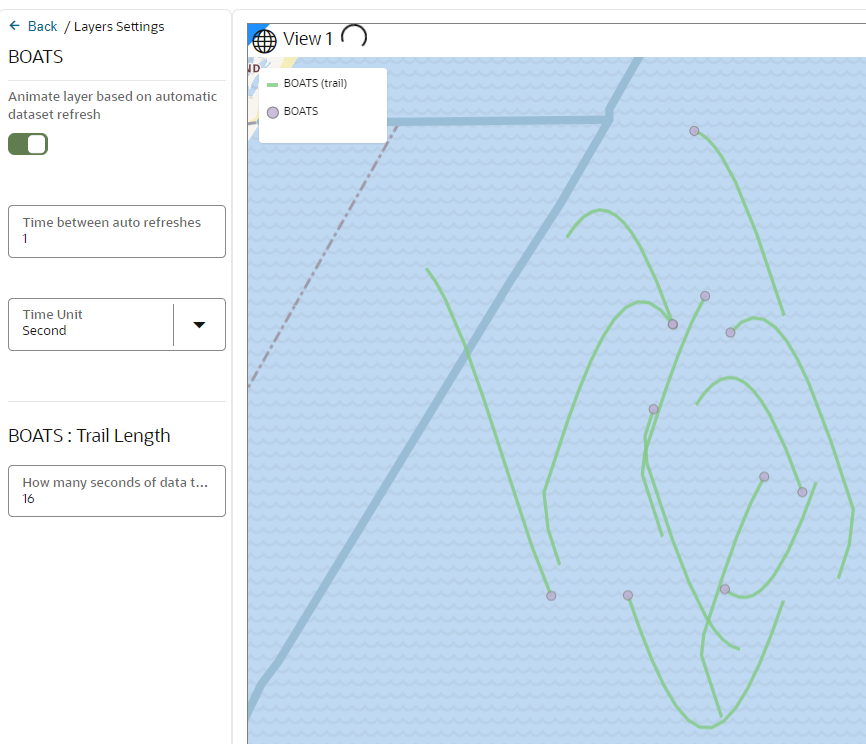
3.8.2.5.2 Configuring Animation for a Moving Object
To visualize moving objects on a map in Spatial Studio, you must configure the animation settings on the map layer.
Parent topic: Visualizing a Moving Object
3.8.2.5.3 Characteristics of Spatiotemporal Map Layers
This section describes the distinct characteristics of the spatiotemporal map layers when visualizing a spatiotemporal dataset.
- The trails map layer is considered the secondary layer to the main layer. If you delete the main layer from the map, then the trails map layer is automatically deleted as well.
- The main layer which shares the same name as the dataset is always a
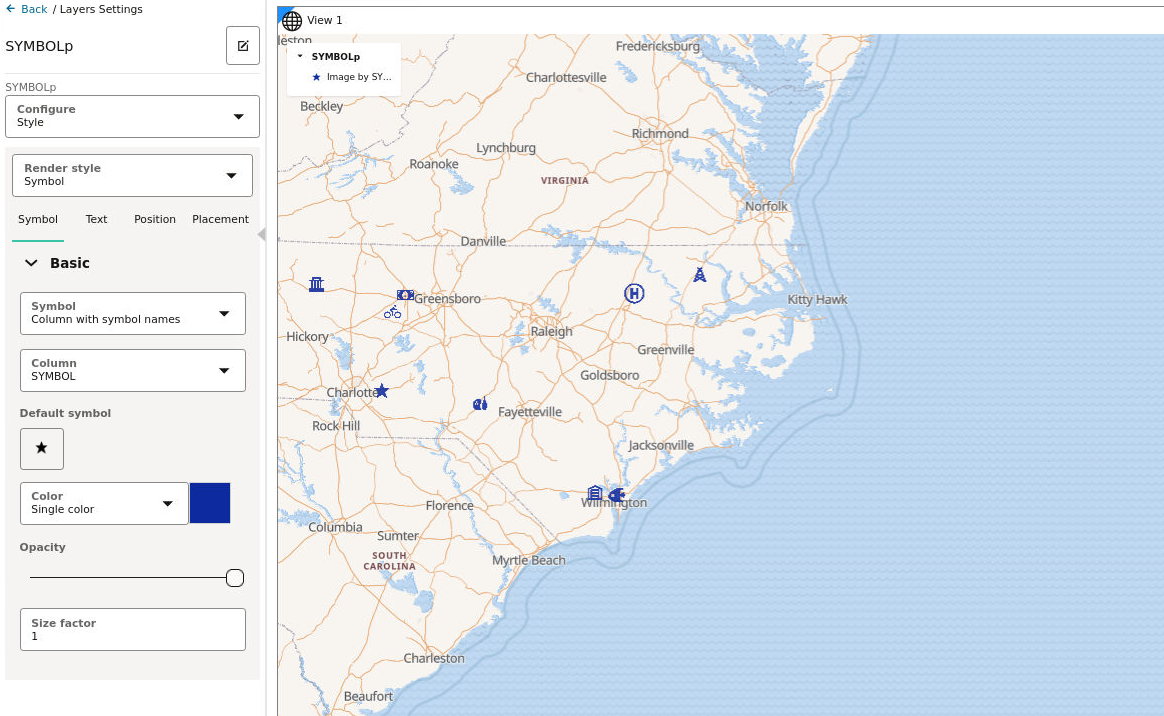
Point-type layer, that you can visualize using either as circle or using symbols or
icons. When you use symbols, Spatial Studio
will also automatically rotate the symbol based on the direction your object is
moving.
Also note, the current release of Spatial Studio supports only those symbols that naturally point North (or point up) or those that do not represent an inherent direction or angle, such as any rounded symbols.
- The main layer will keep its animation even when you toggle the secondary layer invisible. However, if you toggle the main layer invisible, the trail layer will remain static as no new data is fetched from the backend.
- You cannot switch the main layer to Heatmap or Cluster type.
- You cannot use sticky Tooltip or popup as they cannot stick to the moving object when it moves to new locations.
- Spatial Studio drives the animation of moving
objects and their trails by constantly refreshing the main layer’s data from the
backend. This implies that the base table is queried and the last
Nseconds of data is fetched by filtering the records based on theTIMESTAMPcolumn. - If you are working in a multi-user or multi-visualization environment or both, you must take care to avoid overloading the database with many animating layer's data refresh queries. For instance, ensure a layer is not refreshing its data too frequently, or fetching too many seconds of data on each refresh, or both.
Parent topic: Visualizing a Moving Object
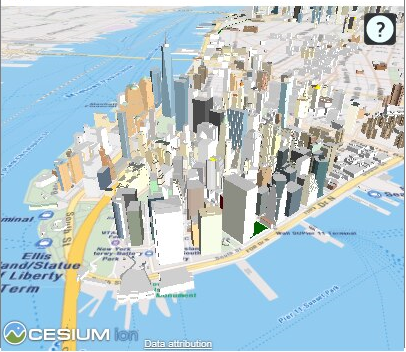
3.8.3 Using a Cesium Map Visualization
Spatial Studio uses a CesiumJS plugin to enable you to view 3D visualizations using 3D Tiles or CZML data on a Cesium map.
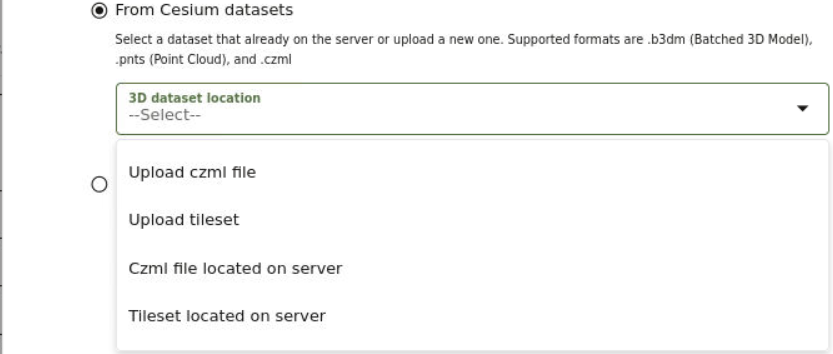
Cesium map allows you to display your real-world geospatial 3D data in a 3D environment. In order to build interactive 3D visualizations using Cesium maps, you can upload one of the following files to Spatial Studio:
- 3D Tileset: Supports formats are:
- Point Cloud (
.pnts) - Batched 3D Model
(
.b3dm)
- Point Cloud (
- CZML file: CZML formatted data in
.czmlfiles
It is important to note the following when using a Cesium map visualization:
- Generating 3D Tiles or CZML formatted data file for your geospatial 3D data must be carried out using any third party software outside of Oracle Spatial Studio.
- 3D Tiles and CZML files are stored in the file system on Spatial Studio's server, not in Oracle Database.
- Currently this feature supports only displaying 3D Tiles and CZML data on maps. It does not support 3D analysis.
Parent topic: Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
3.8.3.1 Visualizing a 3D Tileset Using a Cesium Map
Parent topic: Using a Cesium Map Visualization
3.8.3.2 Visualizing CZML Data Using a Cesium Map
.czml file, see Creating a Dataset for more information.
Parent topic: Using a Cesium Map Visualization
3.8.4 Styling a Map Layer
Spatial Studio allows you to explore different styling options for your map layers, in order to enhance visualization and analysis.
The styling options provided to you may vary depending on the type of data you are mapping.
The following sections describe a few styling techniques for the different data types:
- Applying a Render Style For a Point Layer
- Applying Style for a GeoRaster Layer
- Applying Data-Driven Style to a Map with H3 Aggregations
- Applying Predefined Colors to a Map Layer
- Applying Predefined Symbols to a Map Layer
- Setting Selection Tolerance on a Map Layer
- Adding a Pin on a Map
- Applying Map Backgrounds
Parent topic: Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
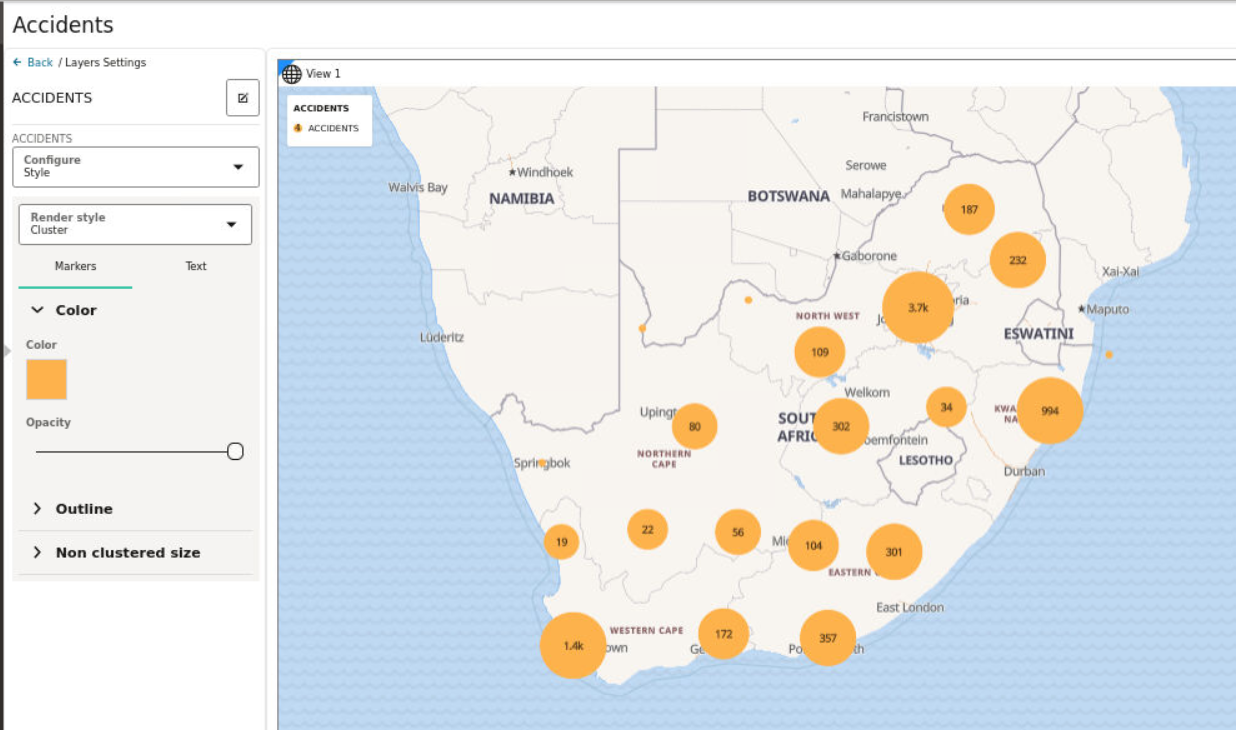
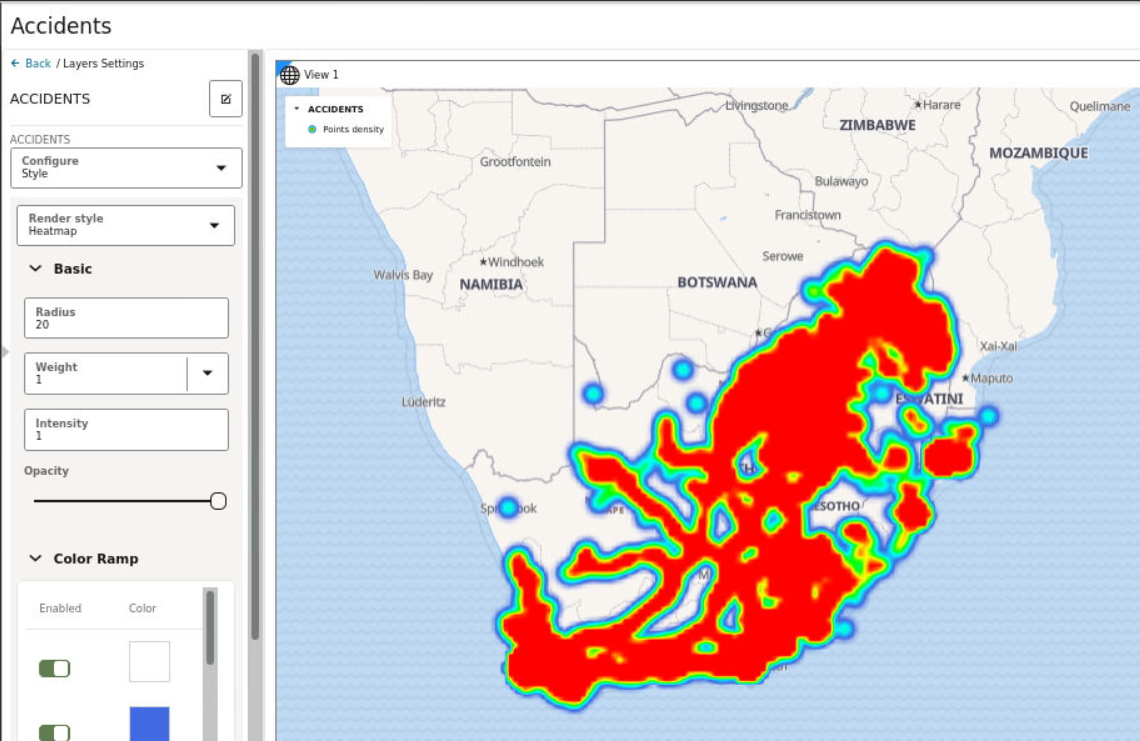
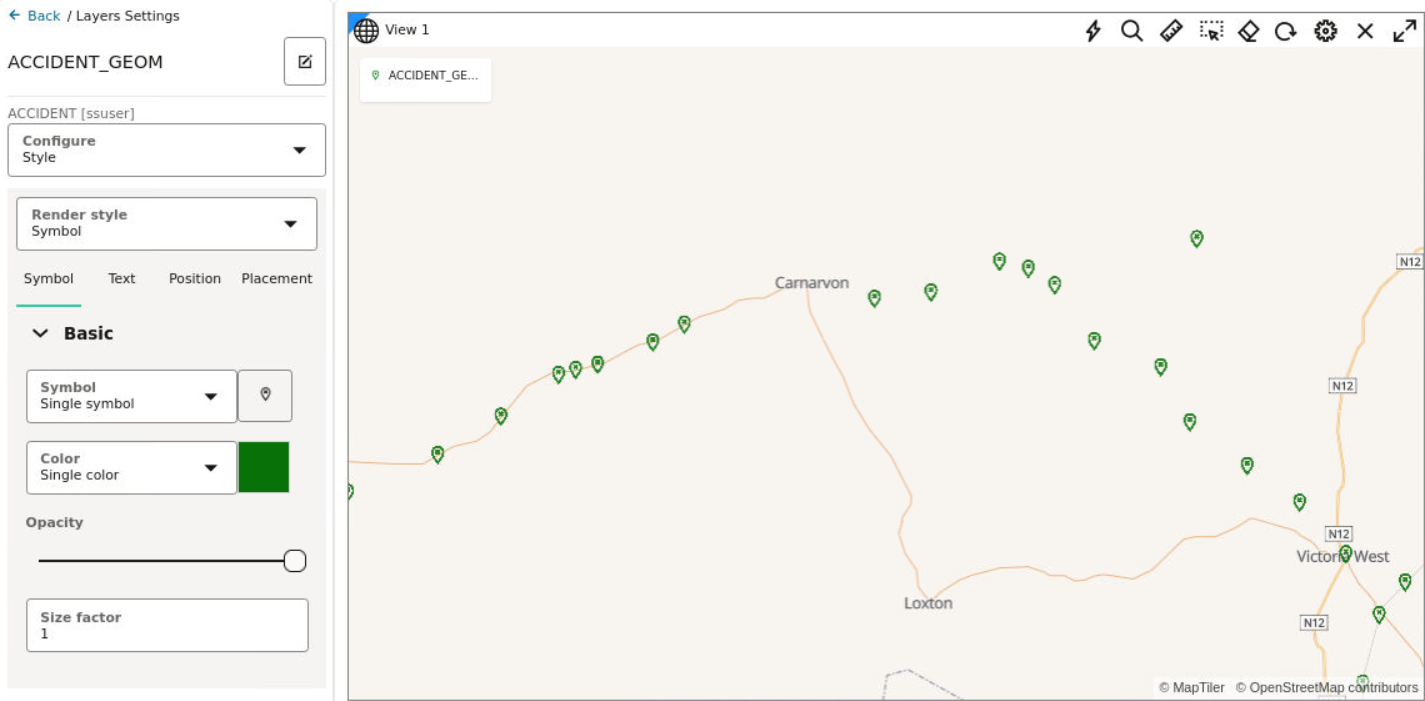
3.8.4.1 Applying a Render Style For a Point Layer
- Circle (default)
- Symbol
- Heatmap
- Cluster
The following steps enable you to apply your preferred render style option.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
3.8.4.2 Applying Style for a GeoRaster Layer
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
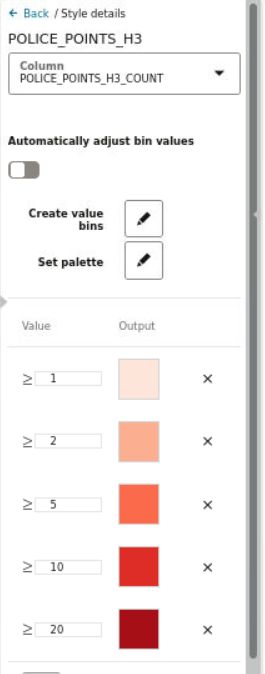
3.8.4.3 Applying Data-Driven Style to a Map with H3 Aggregations
You can apply different resolutions to your H3 map layer to enhance your visualization.
In case of an H3 aggregation dataset, the hexagonal cells and the distribution of points in these hexagons automatically change at each resolution level, as you zoom in and out of the map. This implies that the color bins for one level might not be the same as for another level.
Spatial Studio provides an option to automatically calculate color bins as you alter your resolutions. You can also turn this option off if you want to test against a set of specific thresholds.
The following steps enable you to apply a data-driven styling option for your H3 map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
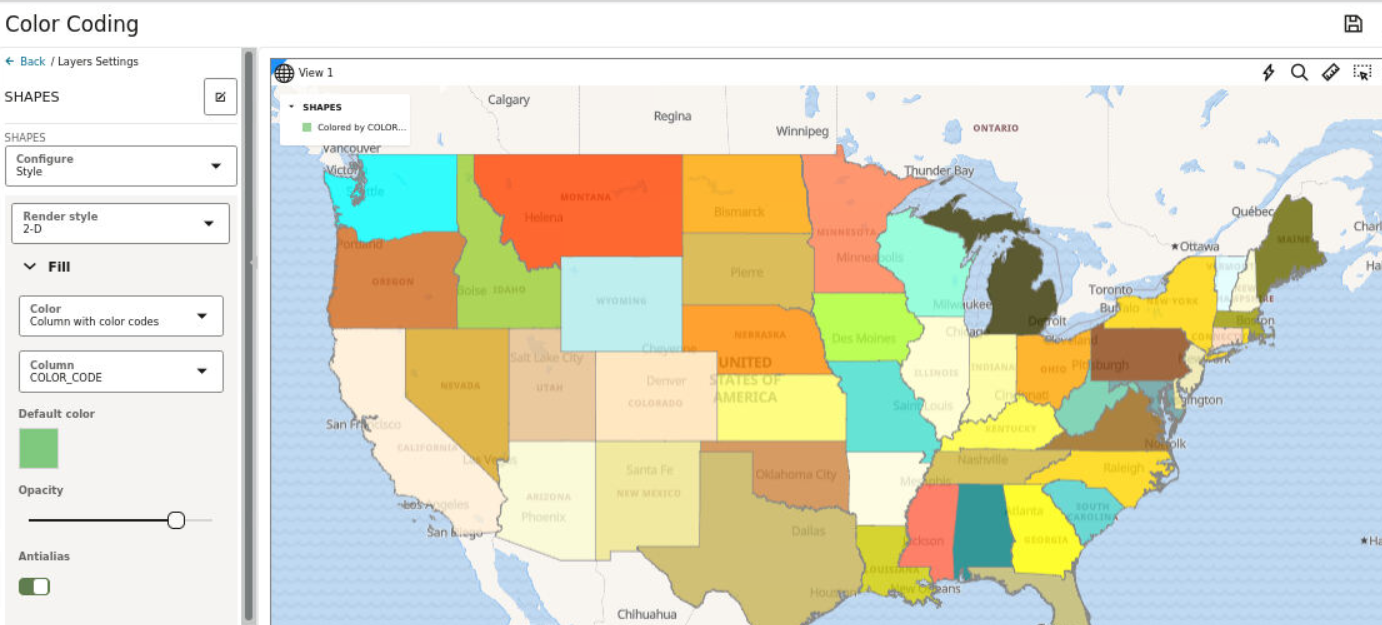
3.8.4.4 Applying Predefined Colors to a Map Layer
Using a column with predefined color codes or values, you can create accurate and consistent choropleth map layers.
You can store a color-coded value in a column of your dataset and then use this column property to color code your map.
The following steps enable you to color code your map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
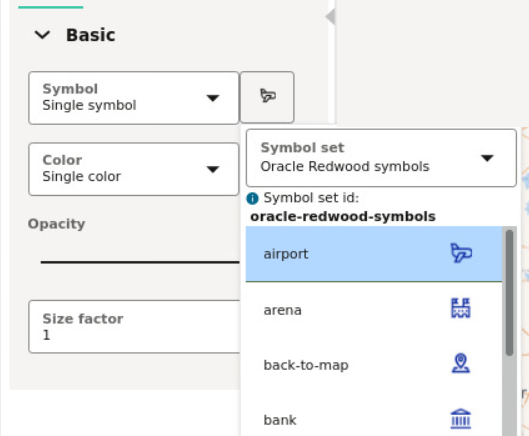
3.8.4.5 Applying Predefined Symbols to a Map Layer
Using a column with predefined symbol values, you can apply data-driven symbol styling to your map layer.
Symbol set id as
described in the following table:
Table 3-2 Symbol Set
| Symbol Set | Symbol set id |
|---|---|
| Spatial Studio default | studio |
| Oracle Redwood symbols | oracle-redwood-symbols |
| Airfields | airfields |
You can store a symbol name and the symbol set to which it belongs in a column of your dataset and then use this column property to assign symbols to your map.
airport icon as
shown in the following figure:
You must then use oracle-redwood-symbols/airport as the
symbol name in your dataset column. In this case:
oracle-redwood-symbols: is the symbol set idairport: is the name for the icon to be used on the map layer
The following steps enable you to apply data driven symbol styling for your map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
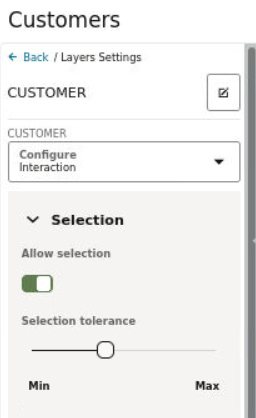
3.8.4.6 Setting Selection Tolerance on a Map Layer
Spatial Studio allows you to increase or decrease the selection tolerance on a map layer, so that selecting small and linear geometry features is easier.
The following steps enable you to adjust and set the selection tolerance on a map.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
3.8.4.7 Adding a Pin on a Map
The following steps enable you to inspect the current mouse pointer's latitude and longitude coordinates and pin a location on the map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
3.8.4.8 Applying Map Backgrounds
Spatial Studio provides ready-to-use map backgrounds to enhance your visualization.
You can select one of the following map backgrounds for your project visualization:
- MapTiler Vector Basemaps
- Oracle Raster Basemaps
- Blank Basemaps
- User-defined Basemaps
As an administrator, you can also register custom basemaps and use them in map visualizations. They may be raster or vector tiles that are typically hosted on third party servers, or they be created using a WMS OGC web service. See Spatial Studio Administration Page for more information on adding basemaps.
The following section describes how to apply a specific map background for your project:
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
3.8.4.8.1 Changing Map Backgrounds
The following steps enable you to apply different map backgrounds in your project visualization.
Parent topic: Applying Map Backgrounds
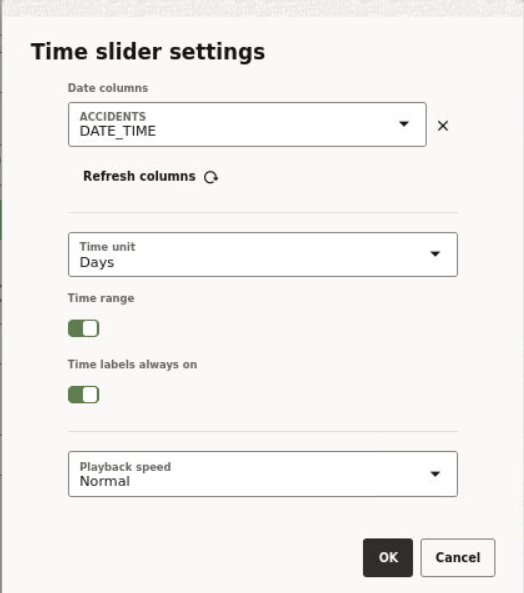
3.8.5 Visualizing Map Data Over Time
In order to visualize map data over time, your dataset must contain a date column or a time column or both. You can then use the time slider feature to interact with the map.
The following steps allow you to configure and use a time slider for your map visualization.
Parent topic: Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
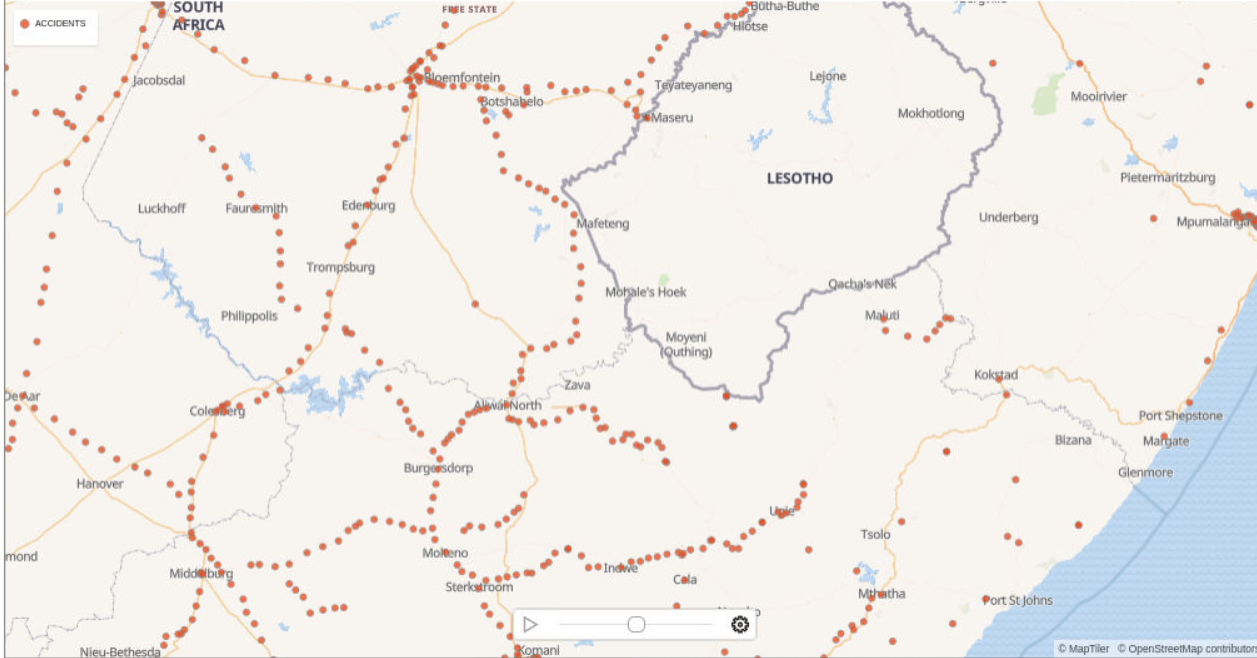
3.9 Performing Analyses in Spatial Studio
You can perform various spatial analyses (such as filtering by proximity, nearest neighbor analysis and so on) and visualize the results in Spatial Studio.
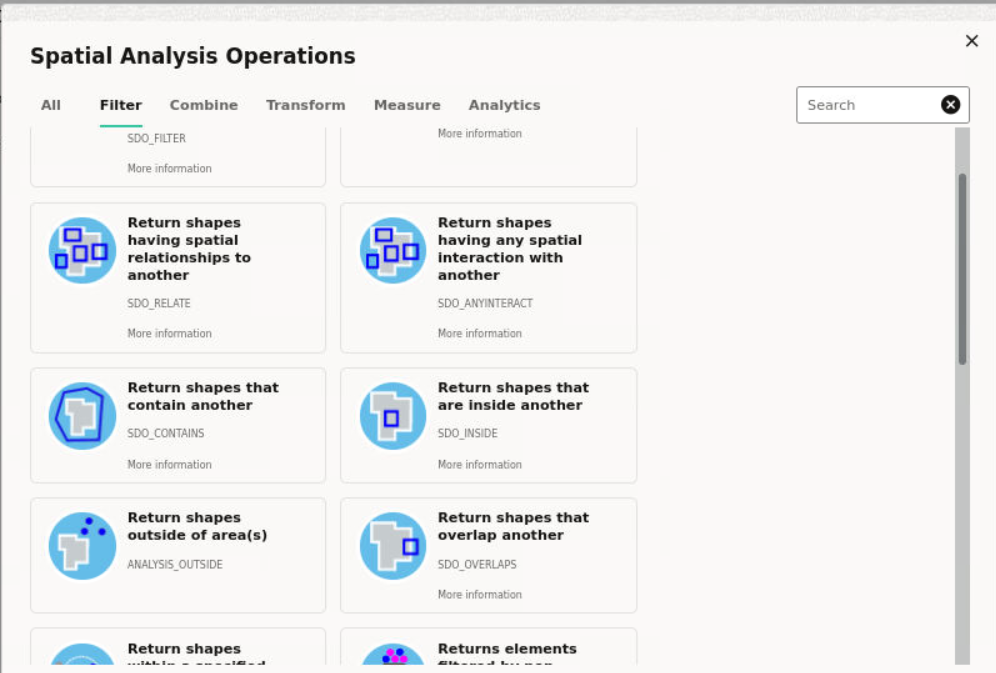
These spatial analyses are grouped under the following categories in Spatial Studio :
- Filter
- Combine
- Transform
- Measure
- Analytics
The following topics describe the use of
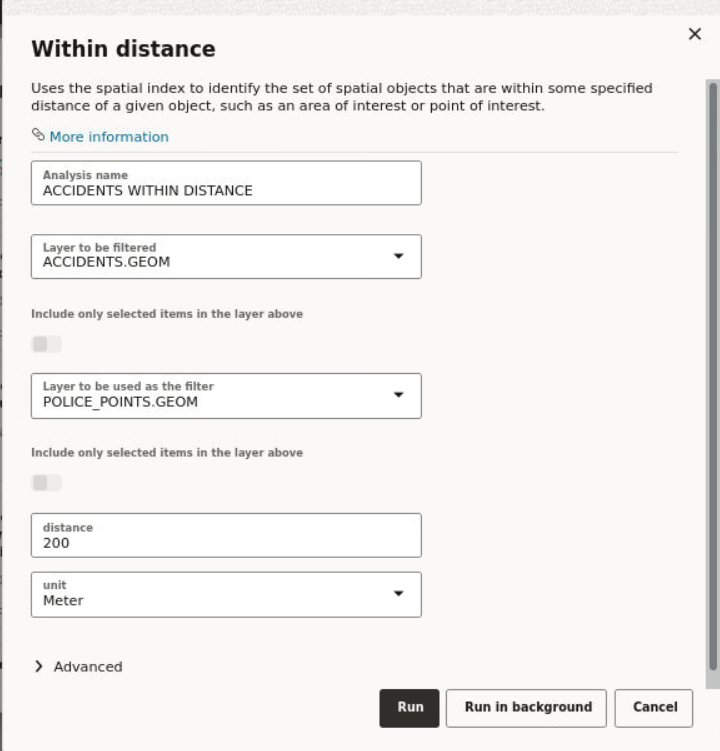
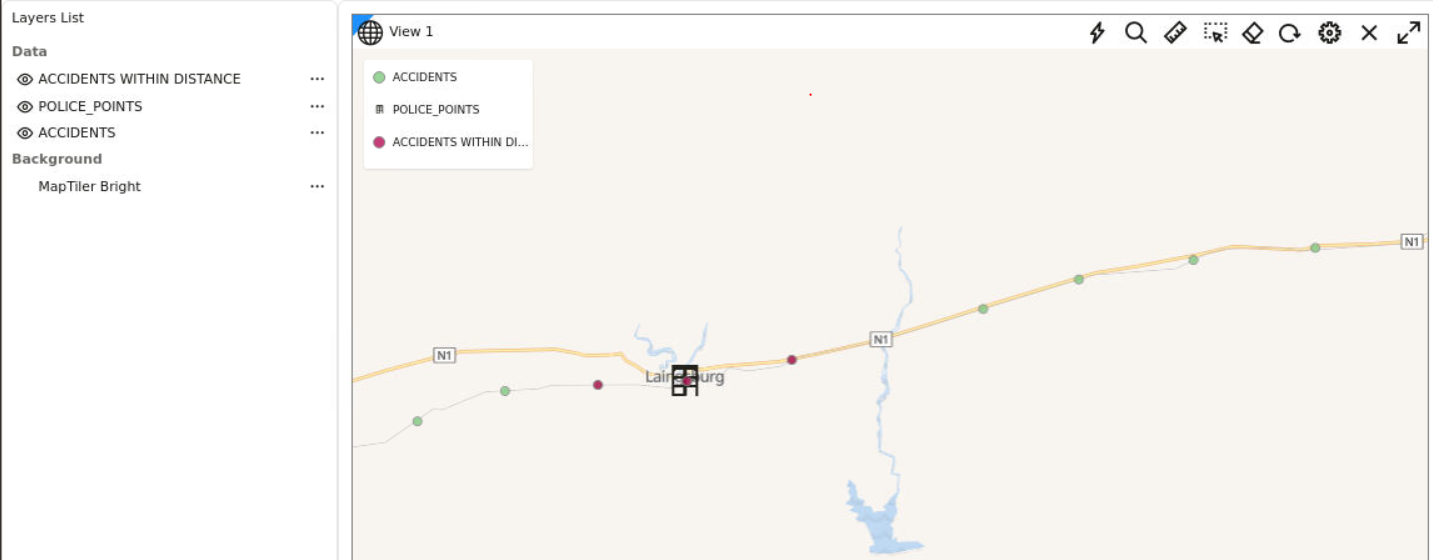
SDO_WITHIN_DISTANCE operation as an example.
3.9.1 Exploring a Proximity Filter
Parent topic: Performing Analyses in Spatial Studio
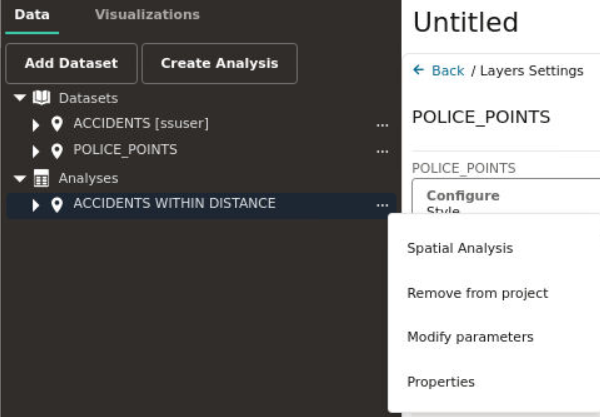
3.9.2 Editing a Spatial Analysis
However, only the following list of spatial analysis operations allow their parameters to be modified after creation:
Filter
SDO_FILTERSDO_NNSDO_RELATESDO_WITHIN_DISTANCE
Combine
- Spatial Join
Transform
SDO_BUFFERSDO_MBCSDO_UTIL.AT_BEARINGSDO_UTIL.SIMPLIFYSDO_SAM.SIMPLIFY_GEOMETRY
Measure
SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREASDO_GEOM.SDO_DIAMETERSDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTHSDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCESDO_GEOM.SDO_MAXDISTANCESDO_GEOM.SDO_MAX_MBR_ORDINATESDO_GEOM.SDO_MBC_RADIUSSDO_GEOM.SDO_MIN_MBR_ORDINATE
Analytics
- Summarize within distance
- Summarize by region
To modify the parameters in a spatial analysis, you must perform the following steps.
Parent topic: Performing Analyses in Spatial Studio