4 Using Recovery Manager with Oracle Secure Backup
This chapter explains how to use Recovery Manager (RMAN) with Oracle Secure Backup. It assumes that you are familiar with RMAN concepts and operations.
This chapter contains these sections:
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more information about RMAN
About Recovery Manager and Oracle Secure Backup
Oracle Secure Backup serves as a media management layer for RMAN through the SBT interface. Oracle Secure Backup and third-party backup utilities integrate with RMAN through the SBT interface.
Note:
Information about the Oracle Database and Oracle Enterprise Manager releases with which you can use Oracle Secure Backup is available at the following URL:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/database-technologies/secure-backup/learnmore/index.html
While Oracle Secure Backup supports previous database versions, key functionality has been added beginning with Oracle Database 10g release 2 (10.2). The following integration enhancements are exclusive to Oracle Secure Backup and are not available with other media management products:
-
Oracle Database 10g release 2 (10.2)
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager provides a unified interface for RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup. In addition, managing tape devices, disk pools, and media servers using Oracle Enterprise Manager is exclusive to Oracle Secure Backup.
-
The Oracle Secure Backup SBT library is the only interface that supports RMAN encrypted backups directly to tape. If you attempt an encrypted RMAN backup using another SBT library, then you encounter the following error message:
ORA-19916: encrypted backups to tertiary storage require Oracle Secure Backup
-
Unused block compression directly to tape is available only with Oracle Secure Backup.
If you are backing up to disk or directly to tape using Oracle Secure Backup, then this enables the unused-block optimization. If the backup is directly to tape using a third-party media management product, then this does not have any effect because unused-block optimization directly to tape is available only with Oracle Secure Backup.
-
-
Oracle Database 11g
-
Optimized SBT buffer allocation uses a shared buffer for SBT and tape. This eliminates the copy process from SBT to the tape buffer, which reduces CPU overhead.
-
Enhanced backup of undo tablespace eliminates backup of committed undo, reducing tape consumption and improving performance.
-
This section contains these topics:
RMAN Environment
RMAN is a utility that enables you to back up Oracle Database files. The RMAN environment includes the following basic components:
-
RMAN client
The RMAN client program, which is installed automatically with Oracle Database software, initiates database backup and recovery. The RMAN client can back up and recover any Oracle Database files accessible locally or through Oracle Net so long as it meets compatibility requirements.
-
RMAN target database
The RMAN target database is the database that RMAN backs up or restores. The RMAN metadata used for managing backup and recovery is stored in the control file of the target database and optionally in an RMAN recovery catalog.
-
RMAN recovery catalog
The RMAN recovery catalog is an optional database schema that serves as a secondary repository of RMAN metadata. You can create a centralized recovery catalog in a database to store the metadata for multiple target databases.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more information about RMAN
Database Backups
Oracle Secure Backup supplies an SBT interface that RMAN can use to back up database files to tape. Within the Oracle Secure Backup administrative domain, an SBT backup is initiated through the RMAN command line or Oracle Enterprise Manager, while a file-system backup is initiated through the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool or obtool commands.
Types of Backups
RMAN performs the following types of backups:
- Full backups
-
By default, RMAN performs full backups. A full backup of a data includes every allocated block in the file being backed up.
- Incremental Backups
-
Incremental backups capture block-level changes to a database made after a previous incremental backup. Incremental backups are generally smaller and faster to make than full database backups. An incremental backup at level 0 is identical in content to a full backup.
- Cumulative Incremental Backups
-
These backups include all blocks changed since the most recent level 0 backup.
- Differential Incremental Backups
-
These backups include only blocks changed since the most recent incremental backup.Incremental backups are differential by default.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more detailed backup concepts
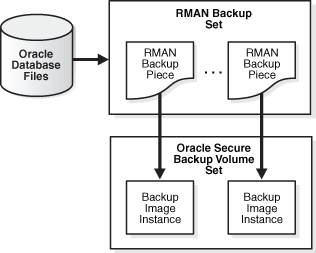
RMAN Backup Sets and Oracle Secure Backup Images
The backup of Oracle Database files performed with RMAN results in a backup set. A backup set is a logical grouping of physical files, each known as a backup piece. For more information about RMAN backup sets and backup pieces, see Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide.
When you use Oracle Secure Backup to store database backups on tape, each backup piece is treated as one Oracle Secure Backup backup image instance. Figure 4-1 illustrates the relationship between pieces and instances. A single backup image instance can span multiple tapes. Oracle Secure Backup can write database backup images (RMAN backup pieces) and file-system backup image instances on the same volume.
See Also:
About RMAN Storage Parameters
Defining storage parameters for RMAN backups within Oracle Secure Backup can be accomplished by:
-
Defining parameters in an RMAN script specific to Oracle Secure Backup
-
Defining Oracle Secure Backup database backup storage selectors
It is recommended that you define one or more database backup storage selectors to automate the tape or disk pool storage selection. Use RMAN storage parameter settings only to override the database backup storage selectors in non-recurring backups that require different media selection than included in the backup storage selector.
See Also:
"Database Backup Storage Selectors" for more information about storage selectors
Database Backup Storage Selectors
Oracle Secure Backup uses information encapsulated in a database backup storage selector to interact with RMAN when performing a backup operation. Oracle Secure Backup uses storage selectors to represent backup attributes that identify Oracle Database files.
A database backup storage selector must specify the following
-
The database name or DBID that uniquely identifies the database
-
The name of the database host
-
The name of the media family to use for the RMAN backups
-
The content or type of the backup, for example, whether it is a full backup or an incremental backup (optional)
-
The copy number of duplexed backups (optional)
-
Restrictions on which tape device the backup can use (optional)
When backing up Oracle Database files, RMAN passes the database name, content type, and copy number to Oracle Secure Backup. Using this information, Oracle Secure Backup determines the corresponding database backup storage selector. This storage selector specifies for Oracle Secure Backup what tape devices or disk pools, if any, to restrict this backup to and which media family (if any) to use.
You can create multiple database backup storage selectors. For example, you can create one database storage selector for data file backups of all databases in the administrative domain, and another selector for archived log backups of all databases in the administrative domain. You can specify one tape library destination for the data file backups and a different tape library destination for the archived log backups.
When an RMAN backup job is initiated through its SBT interface, Oracle Secure Backup examines the database backup storage selectors to determine whether a backup storage selector matches the attributes of the backup job. A match occurs when every attribute of a backup storage selector matches the corresponding attribute of the backup job. If multiple storage selectors match the job, then Oracle Secure Backup chooses the selector whose attributes are most specific. For example, a backup storage selector with the database name set to db_1 matches before a backup storage selector with the database name set to all (*).
Oracle Secure Backup maintains storage selectors in the admin/ssel subdirectory of the Oracle Secure Backup home on the administrative server.
Note:
Database storage selectors must be unique. With the exception of a wildcard (*), a more general setting matches a more specific setting. For example, if you create a storage selector with --dbname set to db_1 and db_2, then you cannot create another selector that has --dbname set to db_1 only and has all other attributes identical to those in the first selector. If you create a storage selector that has --dbname set to set to all (*), however, then you can create another selector that has --dbname set to db_1 and has all other attributes identical to those used for the first selector.
See Also:
-
"Creating a Database Backup Storage Selector in Enterprise Manager"
-
"Setting Media Management Parameters in RMAN" explains how media management parameters specified on RMAN channels can override settings in a backup storage selector.
-
Oracle Secure Backup Reference to learn about database backup storage selector commands
Duplexing Backups
You might want to duplex backup operations, each on a separate volume set, keeping one set on-site for convenient access, and storing a second set off-site for disaster recovery. For ease of management, each duplexed backup operation can be defined by its own database storage selectors and written to its own separate Oracle Secure Backup media family.
See Also:
Database backup storage selectors are user-defined Oracle Secure Backup media policies for Oracle Database backups. They define which media family, tape device, and resource wait time should be applied by content and copy number of the backup. One database storage selector can apply to all database backups within the administrative domain or multiple storage selectors can be defined for each database.
In the following example, two database storage selectors named ssel_1 and ssel_2 are created. They both back up all content of all databases on host_name. But ssel_1 uses media family mf_1, while ssel_2 uses media family mf_2:
ob> mkssel --dbid * --host host_name --content * --family mf_1 -- copynum 1 ssel_1 ob> mkssel --dbid * --host host_name --content * --family mf_2 -- copynum 2 ssel_2
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for complete mkssel syntax and semantics
If you use RMAN duplexed backups and PARALLELISM, then the number of available tape drives must accommodate both copies simultaneously. If channel configuration is set to PARALLELISM of 2 for the duplexed backups in the preceding example, then four tape drives are needed for backup operations (two backup copies multiplied by PARALLELISM of 2).
Note:
If a tape drive is not available for one copy, then the other copy cannot proceed. In addition, if a backup stream fails for one copy, then it fails for the other copy as well.
Restore operations require only two tape drives in this situation, because restore operations are not duplexed.
RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup Encryption
Oracle Database backup encryption can be performed in one of two ways using Oracle Secure Backup:
-
Use RMAN backup encryption, which encrypts data within the database.
This option is available with Oracle Database 10g release 2 (10.2) forward. Please refer to Oracle Database licensing documentation for any restrictions.
-
Use Oracle Secure Backup encryption, which encrypts data after RMAN has passed the data through the SBT to Oracle Secure Backup.
This option is available with Oracle9i forward. While encryption occurs outside the database, the data is encrypted on the server before transport over the network or written to a locally attached tape device.
Note:
Oracle Secure Backup encryption is available for both RMAN and file-system backup operations.
See Also:
Managing Backup Encryption for more information about Oracle Secure Backup encryption and an example on encrypting a database backup
RMAN Backup and Restore Policies
To control the length of queue time before the onset of a backup job, modify the following policy settings:
-
Operations policy
rmanresourcewaittimeThis policy is set to
foreverby default. Any configuration in a backup storage selector or RMAN parameter overrides this policy. -
Specifying the
--waittimeoption in anmksselorchsselcommand inobtool -
RMAN parameter
OB_RESOURCE_WAIT_TIME
For RMAN restore operations, the start time depends on the setting of the rmanrestorestartdelay policy in the operations policy class.
See Also:
-
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for more information about the
mksselandchsselcommands -
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for information on defaults and policies
Database Restore and Recovery
A restore operation that you initiate through RMAN is called an Oracle Database restore operation. RMAN first performs a full backup to restore data files, and only then moves on to performing incremental backups. The RMAN restore operation retrieves data files from backups for a recovery operation in case of loss or damage of these files.
Interfaces for Managing Database Backup and Recovery
When performing RMAN backup and restore operations with the Oracle Secure Backup SBT interface, you can use the following interfaces:
RMAN Command-Line Client
The rman executable is located in the ORACLE_HOME/bin directory of a database installation. The RMAN client can run from any Oracle home, regardless of whether the computer containing this home is a member of the Oracle Secure Backup administrative domain. The target database host must be a member of the Oracle Secure Backup administrative domain. The target database uses the Oracle Secure Backup SBT on the target host to communicate with the Oracle Secure Backup administrative domain.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
You can manage multiple databases with Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, which is the graphical user interface for database administration. The Cloud Control console can run on any database host in the administrative domain.
You can manage SBT backups of all databases in the Oracle Secure Backup administrative domain through Cloud Control. You can create a centralized RMAN recovery catalog in the same database that contains the Cloud Control repository.
When you use Cloud Control, you can use Oracle Secure Backup on a host that runs an Oracle Database 10g release 1 (10.1) or earlier database if the repository for Enterprise Manager is in an Oracle Database 10g release 2 (10.2) database.
RMAN and the Oracle Secure Backup Administrative Domain
This section describes RMAN operations in the following situations:
Single-Host Administrative Domain
In a single-host administrative domain, one host plays the role of administrative server, media server, and client. An Oracle database is installed on this host. Figure 4-2 illustrates a typical single-host scenario.
Figure 4-2 Single-Host Administrative Domain with Database Backups
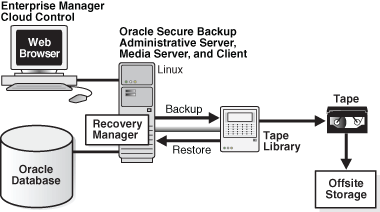
Description of "Figure 4-2 Single-Host Administrative Domain with Database Backups"
Note:
This chapter is written from the perspective of the administrator of a single-host administrative domain that is configured like the one in Figure 4-2.
Multiple-Host Administrative Domain with Database Backups
In a multiple-host administrative domain, the administrative server, media server, and client hosts might all be separate, or each database server might also be a media server. The latter arrangement has the advantage of minimizing network-based backup operations. A single administrative domain can include only one administrative server but can include multiple media servers and clients.
Figure 4-3 illustrates a typical multiple-host domain in which each client host runs an Oracle database. In this example, the administrative server and media server do not run databases. The Windows database includes a centralized recovery catalog to store metadata for backups of all databases in the administrative domain.
Figure 4-3 Multiple-Host Administrative Domain
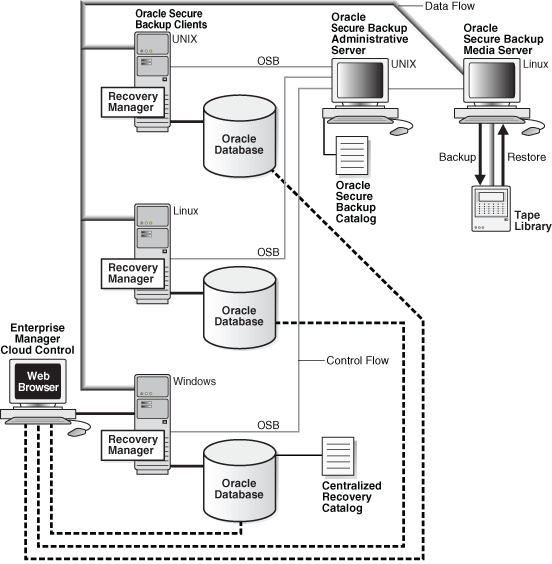
Description of "Figure 4-3 Multiple-Host Administrative Domain"
You can use Cloud Control on a client to initiate SBT operations involving all databases in the administrative domain.
How RMAN Accesses Oracle Secure Backup
Regardless of the administrative domain configuration and the front-end interface that you use to manage backup and recovery, the process by which RMAN communicates with the Oracle Secure Backup SBT library is the same. Figure 4-4 displays the basic components of RMAN backup and restore operations that use the Oracle Secure Backup SBT.
Figure 4-4 RMAN and the Oracle Secure Backup SBT Interface
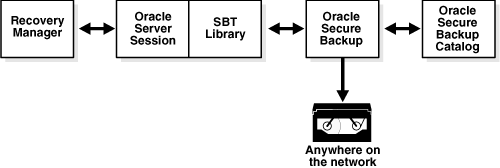
Description of "Figure 4-4 RMAN and the Oracle Secure Backup SBT Interface"
The basic process for RMAN backup and restore operations with Oracle Secure Backup is as follows:
-
An Oracle Secure Backup user starts the RMAN client, either through the command line or the Oracle Enterprise Manager console.
-
The Oracle Secure Backup user allocates an SBT channel and runs an RMAN
BACKUPorRESTOREcommand.When the channel is allocated, a server session starts on the Oracle database.
-
The server session on the database host makes the backup or restore job request through the Oracle Secure Backup SBT library.
-
Oracle Secure Backup creates the backup or restore job and assigns it a unique identifier such as
sbt/15.See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for a description of job identifiers
-
For an RMAN backup operation, Oracle Secure Backup immediately tries to reserve and start the appropriate resources. If the resources are unavailable, then Oracle Secure Backup queues the job while it waits for the resources to become available.
See Also:
"RMAN Backup and Restore Policies" for information on settings related to RMAN backup and restore operations
-
RMAN creates or restores the backup pieces.
-
For backups, Oracle Secure Backup stores metadata about RMAN backup pieces in the Oracle Secure Backup catalog.
The Oracle Secure Backup catalog is stored and managed completely separately from the RMAN recovery catalog. Oracle Secure Backup stores each backup piece and corresponding metadata about the piece.
Oracle Secure Backup Support for Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA)
Starting with Oracle Secure Backup 10.4.0.1, Oracle Secure Backup supports NUMA architecture. In a NUMA system, the processors are grouped into smaller systems called nodes or regions. Each node has its own processors and a common memory. All processors within a node share the common memory. Access to this local memory area is faster thus resulting in improved scalability and performance.
During a database backup or restore operation, the Oracle shadow process manages the interaction between Oracle Secure Backup and the Oracle Database. The shadow process loads the SBT library and starts the Oracle Secure Backup data service (obndmpd process), which performs the network I/O required for the operation, on the client. The Oracle shadow process and the Oracle Secure Backup data service use a common memory area to exchange data.
On NUMA machines, Oracle Secure Backup ensures that the Oracle shadow process and the Oracle Secure Backup data service run on the same node and therefore access the same common memory. This results in improved performance when the Oracle shadow process and the Oracle Secure Backup data service are not on the same node.
Configuring Oracle Secure Backup for Use with RMAN
To configure Oracle Secure Backup for use with RMAN, perform the following steps in Oracle Secure Backup:
Configuring RMAN Access to the Oracle Secure Backup SBT Library
You can use Enterprise Manager Cloud Control to configure RMAN access to Oracle Secure Backup. You need only specify the Oracle Secure Backup home directory. RMAN locates the SBT library automatically.
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Installation and Configuration Guide for information on registering an administrative server in Enterprise Manager
By default, RMAN looks in a platform-specific default location for the SBT library. On Linux and UNIX the default library filename is /lib/libobk.so, with the extension name varying according to platform: .so, .sl, .a, and so on. On Windows the default library location is %WINDIR%\System32\orasbt.dll.
When you install Oracle Secure Backup on Linux and UNIX, the installer automatically copies the SBT library to the lib subdirectory of the Oracle Secure Backup home and creates a symbolic link to the library in the /lib or /usr/lib directory.
By default, RMAN searches the standard path and loads the Oracle Secure Backup SBT library when an SBT channel is allocated.
Creating a Preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup User
Oracle Secure Backup honors SBT requests only if the Oracle Secure Backup user making the request has been preauthorized for RMAN backup on that host. This preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user must meet two sets of requirements:
-
The preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user must be mapped to operating system privileges to access the files to be backed up or restored. the preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user can perform RMAN operations only on the host where it has access to files.
-
The preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user must also be assigned to an Oracle Secure Backup class possessing the following rights:
-
access Oracle backups(set toowner,class, orall) -
perform Oracle backups and restores
-
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for more information about Oracle Secure Backup rights
Only one Oracle Secure Backup user can be preauthorized for RMAN backup and restore operations on a particular host. A database can have multiple RMAN users that can start backup or restore operations, but Oracle Secure Backup has only one preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user for that database server.
You can also preauthorize an Oracle Secure Backup user for command-line (obtool) operations. This is useful if you use backup and restore scripts.
See Also:
How Oracle Secure Backup Preauthorizes SBT Backups
The following figure illustrates the basic process by which an Oracle Secure Backup user preauthorized for RMAN operations on a particular host submits a backup or restore request to Oracle Secure Backup.
Figure 4-5 Preauthorization for Database Backup and Restore Operations
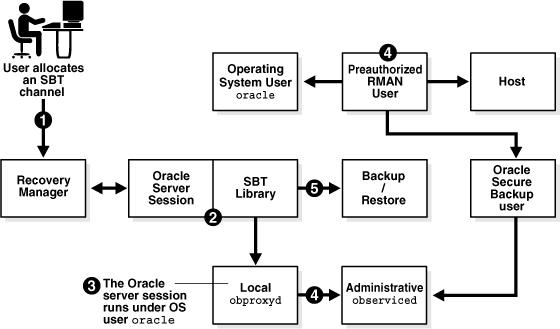
Description of "Figure 4-5 Preauthorization for Database Backup and Restore Operations"
The process works as follows:
-
When you start RMAN and allocate an SBT channel, Oracle Database starts a server session.
-
The server session uses the SBT library to communicate with the
obproxyddaemon running locally on its host. -
The local
obproxyddaemon determines which operating system user the server session runs under. Assume in this example that the operating system user is namedoracleand runs on Linux host brhost2. -
The local
obproxyddaemon checks the operating system user information with the administrative serverobserviceddaemon. If the operating system user on this host and operating system is preauthenticated as an Oracle Secure Backup user, then the login to Oracle Secure Backup is successful.For example, assume that the
oracleoperating system user on hostbrhost2is preauthorized to run as Oracle Secure Backup userobuser. Assume also thatobuseris a member of theoracleclass, which is assigned theperformOraclebackupsandrestoresright by default.See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for more information about Oracle Secure Backup rights
-
The server session uses the Oracle Secure Backup user to back up or restore files.
The Oracle Secure Backup operations submitted through the SBT use the operating system user defined by the Oracle Secure Backup user to access the host. In this figure, the backup and restore operations run under the
oracleoperating system account onbrhost2.
Configuring an RMAN Preauthorization
You can configure a preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user with required rights to perform backups of Oracle Database files to tape with Oracle Secure Backup during installation of the Oracle Secure Backup software or after installation using either the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool or the mkuser command in obtool.
To create a preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user during an Oracle Secure Backup installation on Linux or UNIX, you must set the obparameters parameter create preauthorized oracle user.
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Installation and Configuration Guide for information on configuring obparameters for creating a preauthorized oracle user
To create a preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user during an Oracle Secure Backup installation on Windows, you must enable the action for Create "oracle" user when selecting features for the administrative server.
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Installation and Configuration Guide for information on administrative server features
To configure a preauthorized Oracle Secure Backup user after installation, use the Web tool or the mkuser command in obtool. Example 4-1 uses mkuser to create an Oracle Secure Backup user named preauth_user and assign this user to the oracle class. The example uses --preauth to map preauth_user to the Linux or UNIX user oracle on host brhost2. The mapping to an operating system user with access to the files to be backed up or restored is required.
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Reference to learn about the mkuser command
Example 4-1 Preauthorizing an Operating System User to Make RMAN Backups
mkuser preauth_user --class oracle --preauth brhost2:oracle+rman
Creating Media Families for RMAN Backups
It is recommended that you create dedicated media families for use in RMAN operations. If you do not create dedicated RMAN media families, then Oracle Secure Backup uses a default media family.
The default media family for use by RMAN is named RMAN-DEFAULT. You cannot delete or rename the RMAN-DEFAULT media family, although you can modify some of its attributes through the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool or obtool.
It is useful to create different media families for archived redo log and data file backup sets. You can create media families with Enterprise Manager, the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool, or the mkmf command in obtool.
See Also:
-
"Adding a Media Family" for information on adding a media family
-
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for complete syntax and semantics for the
obtoolmkmfcommand
When you create a media family, you specify a volume expiration policy that determines when a volume in that media family is eligible to be overwritten and recycled. Volumes in a media family use either a content-managed expiration policy or time-managed expiration policy.
Content-managed volumes can only be used for RMAN operations. You can use time-managed volumes for both RMAN and file-system backup and restore operations. It is possible, therefore, that time-managed volumes could contain a mixture of file-system backups and RMAN backup pieces.
Note:
If you make RMAN backups to time-managed volumes, then it is possible for a volume to expire and be recycled while the RMAN repository reports a backup piece that was on that volume as available. In this case, you must use the CROSSCHECK command in RMAN to resolve the discrepancy.
Setting Media Management Parameters in RMAN
If you use Oracle Secure Backup database storage selectors, then you are not required to set media management parameters in RMAN. In some circumstances, however, you might want to override the database storage selectors by setting RMAN parameters.
See Also:
Oracle Secure Backup Reference to learn about the RMAN media management parameters and their relationship with database backup storage selectors
To set media management parameters in an RMAN database backup:
-
Follow Step 1 through Step 9 in "Performing Backups with RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup".
-
Click Edit RMAN Script.
The Schedule Customized Backup: Review: Edit RMAN Script page appears.
-
In the main window, modify the script to use media management parameters. For example, assume the backup script is as follows:
backup device type sbt database include current controlfile; backup device type sbt archivelog all not backed up;
To configure the backup to use the
my_mfmedia family, you could modify the script as follows:run { allocate channel c1 device type sbt parms 'ENV=(OB_MEDIA_FAMILY=my_mf)'; backup database include current controlfile; backup archivelog all not backed up; } -
Click Submit Job.
The Status page appears.
Performing Backups with RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup
After you have configured RMAN to use the Oracle Secure Backup SBT, the procedure for making RMAN backups is identical to the procedure described in Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide.
To backup a database file using RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup:
Performing Recovery with RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup
After you have configured RMAN to use the Oracle Secure Backup SBT, the procedure for restoring database files is identical to the procedure described in Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide.
To restore database files using RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup:
RMAN Backup Metadata in Oracle Secure Backup
Oracle Secure Backup maintains backup metadata for all RMAN and file-system backup operations. This section explains how to access RMAN metadata within the Oracle Secure Backup catalog.
This section contains these topics:
About RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup Metadata
Oracle Secure Backup maintains a catalog of metadata for Oracle Secure Backup jobs on the administrative server. You can use the Web tool to display catalog metadata about each backup piece, referred to as a backup image in the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool. You can also use the lsjob, catxcr, and lspiece commands in obtool.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for more information about accessing RMAN metadata
Expiration of RMAN Backups on Tape
You can make RMAN backups on a volume that use a content-managed or time-managed expiration policy. If the RMAN backup is on a content-managed volume, then you should use the DELETE OBSOLETE command in RMAN to mark backup pieces as deleted in the RMAN repository. In response, Oracle Secure Backup updates its catalog to indicate that the backup pieces are deleted, so both the RMAN repository and Oracle Secure Backup catalog show the pieces as deleted.
Note:
If you use content-managed volumes for RMAN backups, then the RMAN retention configuration determines when the tape expires. If you use a control file for the RMAN repository, then the record keep time must be at least equal to the period you want backups retained.
Oracle does not recommend using the rmpiece command in Oracle Secure Backup to delete backup pieces from tape, because the RMAN metadata then fails to reflect the tape contents. This discrepancy can also occur when RMAN backup pieces exist on volumes that are expired by a time-managed expiration policy, or when you forcibly overwrite a volume containing RMAN backup pieces. Use the CROSSCHECK command in RMAN to resolve discrepancies between the Oracle Secure Backup catalog and the RMAN repository.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide to learn about crosschecking backups and deleting RMAN backups
Displaying RMAN Job Information in Oracle Secure Backup
RMAN backups made with the Oracle Secure Backup SBT are subject to all Oracle Secure Backup job management commands.
See Also:
When you use RMAN to backup or restore a database, the job contains the name of the database. Example 4-2 shows sample output for backup and restore jobs relating to a database named orcl. The Job IDs in this example include oracle because the jobs were run by the oracle user.
Example 4-2 Database Backup and Restore Jobs
ob> lsjob --all Job ID Sched time Contents State ---------------- ----------- ------------------------------ --------------------------------------- oracle/1 none database orcl (dbid=1091504057) completed successfully at 2013/11/21.15:24 oracle/1.1 none datafile backup completed successfully at 2013/11/21.15:28 oracle/2 none database orcl (dbid=1091504057) completed successfully at 2013/11/21.15:53 oracle/2.1 none datafile backup completed successfully at 2013/11/21.15:54 oracle/3 none database orcl (dbid=1091504057) completed successfully at 2013/11/21.15:57 oracle/3.1 none restore piece '06grqejs_1_1' completed successfully at 2013/11/21.15:59
Displaying Job Transcripts
Job transcripts contain detailed information about Oracle Secure Backup jobs. Example 4-3 shows part of the transcript for an archived log backup. This backup uses the RMAN-DEFAULT media family.
See Also:
-
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for complete syntax and semantics for the
catxcrcommand inobtool -
"Displaying Job Transcripts" for instructions on using the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool to display job transcripts
Example 4-3 Transcript of an Archived Log Backup Job
ob> catxcr --head 22 sbt/6.1
2008/06/28.13:01:04 ______________________________________________________________________
2008/06/28.13:01:04
2008/06/28.13:01:04 Transcript for job sbt/6.1 running on brhost1
2008/06/28.13:01:04
Volume label:
Volume tag: ADE202
Volume ID: RMAN-DEFAULT-000002
Volume sequence: 1
Volume set owner: root
Volume set created: Tue Jun 28 13:01:30 2008
Media family: RMAN-DEFAULT
Volume set expires: never; content manages reuse
Archive label:
File number: 1
File section: 1
Owner: root
Client host: brhost1
Backup level: 0
S/w compression: no
Archive created: Tue Jun 28 13:01:30 2008Displaying SBT Errors
If an error occurs during an SBT session, then Oracle Secure Backup attempts to send the error description to the administrative server to be saved in the job transcript. The database writes SBT errors to the sbtio.log trace file, unless the user has configured the file to be named otherwise. Typically, sbtio.log is located in the rdbms/log subdirectory of the Oracle home.
See Also:
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide to learn how to troubleshoot RMAN backup and restore operations
Displaying Backup Piece Information
Oracle Secure Backup maintains information about RMAN backups at the backup piece level. This information can be browsed in the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool under backup image or by using obtool commands. While information regarding backup pieces is available with Oracle Secure Backup, backup sets are logical groupings that only RMAN has knowledge of.
An RMAN backup piece is represented in Oracle Secure Backup as a backup image. You can use the lspiece command in obtool to display information about backup pieces recorded in the Oracle Secure Backup catalog. Example 4-4 shows sample output for lspiece.
Note:
Each piece name must be unique across all databases in the Oracle Secure Backup administrative domain. You can make piece names unique either by using the RMAN catalog option, so that the backup catalog for all databases in the domain is centralized, or by using RMAN format string to create unique piece names.
See Also:
-
"Displaying Backup Sections" for instructions on using the Oracle Secure Backup Web tool to display information about backup pieces
-
Oracle Database Backup and Recovery User's Guide for detailed information on backup piece names
-
Oracle Secure Backup Reference for complete syntax and semantics for the
lspiececommand
Example 4-4 Displaying Backup Pieces
ob> lspiece --long
Backup piece OID: 104
Database: ob
Database ID: 1566254457
Content: archivelog
Copy number: 0
Created: 2008/06/28.13:01
Host: brhost1
Piece name: 05go3tgd_1_1
Backup piece OID: 105
Database: ob
Database ID: 1566254457
Content: archivelog
Copy number: 0
Created: 2008/06/28.13:02
Host: brhost1
Piece name: 06go3ti5_1_1Using RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup in an Oracle RAC Environment
Installing Oracle Secure Backup in an Oracle RAC Environment
It is recommended that you install Oracle Secure Backup on each node in the cluster, configuring the node as a client, media server, or both. By including all nodes in the administrative domain, local files on the node can be protected. Oracle Secure Backup handles file-system backup operations for an Oracle RAC client no differently from any other client host.
Figure 4-6 shows a sample administrative domain that includes a three-node Oracle RAC system, with each node configured as an Oracle Secure Backup client. In Oracle RAC environments, RMAN can restore a backup piece to any node within a cluster that has the Oracle Secure Backup software installed, regardless of which node created the backup piece.
Figure 4-6 Using RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup in a Real Application Clusters Environment
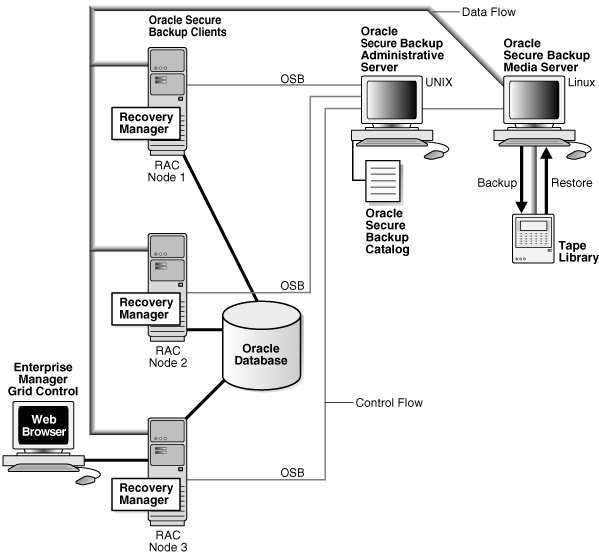
Description of "Figure 4-6 Using RMAN and Oracle Secure Backup in a Real Application Clusters Environment"
Network Versus Local Backups
For performance reasons, it is important to configure the Oracle RAC environment differently for networked or local backups. RMAN backups can be dynamically allocated in the Oracle RAC environment based on the work load distribution. This technique works well if the Oracle RAC database is backed up over the network using Oracle Secure Backup because it does not matter to Oracle Secure Backup which of the nodes performs a client backup.
If a node in the Oracle RAC environment is a media server, then it is more efficient for this node to create backups on a locally accessed tape device. This technique avoids allocating network bandwidth for backups, as would happen if an Oracle RAC node configured as a client were to perform the backup.
You can configure RMAN backups to be performed from specific nodes. It is recommended that RMAN be configured persistently so it must be configured only once and affects all backup and restore operations from that database.
In the following example, there are three tape drives attached to hostA and another three tape drives attached to hostB. The configuration steps are as follows:
-
Connect to any node in the Oracle RAC environment to configure RMAN parameters.
-
Set parallelism.
-
Configure channel (3 channels) /connect / sid hostA.
-
Configure channel (3 channels) /connect / sid hostB.
In the preceding example, you are establishing that six total channels are necessary, three from each host. This configuration applies to every backup and restore operation unless you override this setting. You can start an RMAN operation by connecting to any node within the Oracle RAC environment. The operation is performed only on the two configured hosts.
Note:
If you do not configure persistent settings, then you can accomplish the same goal in RMAN scripts by allocating channels by host.