4.2 Quick Start: Creating a SQL Property Graph by Importing Graph Data from Neo4j
Oracle Graph provides PL/SQL scripts that allow you to import Neo4j graph data and create a SQL property graph in either your Oracle Autonomous AI Database instance or an on-premises Oracle AI Database.
The scripts are available at My Oracle Support. Refer to
MOS Note 38578086
for downloading the scripts. Click open the README file and
follow the instructions to migrate Neo4j graph data to an Oracle AI Database (either on Cloud or
on-premises) and create a SQL property graph.
The following outlines the basic steps that you need to perform as
explained in the README file:
- Ensure that you meet the necessary prerequisites.
- Retrieve and export the graph metadata from Neo4j into CSV files.
- Upload the CSV files to Oracle AI Database (that is, through Object Storage for an Autonomous AI Database instance and local directories for an on-premises database).
- Run the migration tool to read the uploaded graph metadata and generate migration scripts in your environment.
- Run the migration scripts to import the Neo4j graph data into Oracle AI Database and finally create a SQL property graph.
The following topics describe the steps to create a SQL property graph by importing Neo4j data:
- Prerequisites for Migrating Neo4j Graph Data into Oracle AI Database
Review the prerequisites for migrating Neo4j Graph Data into an Oracle AI Database, whether on-premises or in Oracle Cloud. - Importing Neo4j Graph Data into an On-Premises Oracle AI Database
This tutorial helps you to import graph data from your Neo4j instance into an on-premises Oracle AI Database and create a SQL property graph. - Importing Neo4j Graph Data into Oracle Autonomous AI Database
This tutorial helps you to import graph data from your Neo4j instance into Oracle Autonomous AI Database and create a SQL property graph. - Gathering Graph Metadata in Neo4j
This section describes how to retrieve the graph metadata in Neo4j. - Mapping Neo4j DataTypes to Oracle AI Database Types
Learn the mapping between Neo4j DataTypes and Oracle AI Database types.
Parent topic: Introduction to SQL Property Graphs
4.2.1 Prerequisites for Migrating Neo4j Graph Data into Oracle AI Database
Review the prerequisites for migrating Neo4j Graph Data into an Oracle AI Database, whether on-premises or in Oracle Cloud.
- Download the Neo4j migration scripts from MOS Note 38578086.
Note that the migration scripts are tested on Neo4j Database Community Edition, versions 5.26.1 and 2025.05.0. The instructions can slightly vary depending on your Neo4j version.
- Install the appropriate APOC library version for your Neo4j installation.
- Enable the APOC library for your Neo4j
version.
apoc.export.file.enabled=trueis configured in<neo4j_home_dir/conf/apoc.conffile. - Note the following for the graph that you plan to migrate from
Neo4j:
- Only vertices with one or more properties can be migrated.
- Vertex and edge label names cannot be repeated. This includes
case sensitive scenarios; Labels
Personandpersonare the same.
- Ensure the graph data coming from Neo4j does not contain new lines.
- Ensure you are using Oracle AI Database 26ai, whether importing the graph data into an on-premises database or Oracle Autonomous AI Database.
Caution:
The migration scripts, when executed, can overwrite or delete existing data in the user schema. Therefore, it is recommended that the user schema used for running the migration remains empty.4.2.2 Importing Neo4j Graph Data into an On-Premises Oracle AI Database
This tutorial helps you to import graph data from your Neo4j instance into an on-premises Oracle AI Database and create a SQL property graph.
Before you begin, ensure that you meet all the prerequisites as described in Prerequisites for Migrating Neo4j Graph Data into Oracle AI Database.
Also, note that the following example uses:
- Neo4j Database Community Edition, Version 2025.05.0.
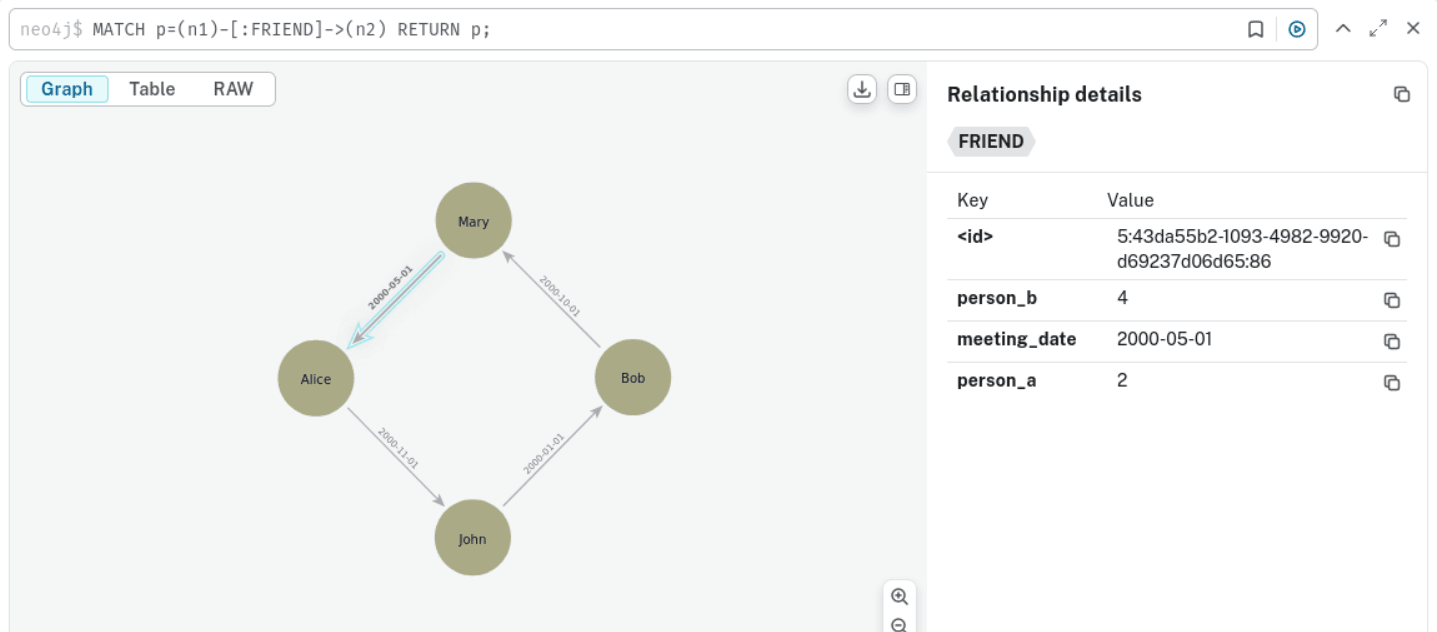
- The Neo4j graph to be migrated comprises
Personvertices andFriendedges as shown:Figure 4-3 Example Graph in Neo4j for Migration
4.2.3 Importing Neo4j Graph Data into Oracle Autonomous AI Database
This tutorial helps you to import graph data from your Neo4j instance into Oracle Autonomous AI Database and create a SQL property graph.
Before you begin, ensure that you meet all the prerequisites as described in Prerequisites for Migrating Neo4j Graph Data into Oracle AI Database.
Also, note that the following example uses:
- Neo4j Database Community Edition, Version 2025.05.0.
- The Neo4j graph comprises
Personvertices andFriendedges as shown:Figure 4-4 Example Graph in Neo4j for Migration
4.2.4 Gathering Graph Metadata in Neo4j
This section describes how to retrieve the graph metadata in Neo4j.
4.2.5 Mapping Neo4j DataTypes to Oracle AI Database Types
Learn the mapping between Neo4j DataTypes and Oracle AI Database types.
Table 4-1 Mapping Neo4j Data Types to Oracle AI Database Types
| Neo4j Data Type | Oracle AI Database Data Type | Maximum Length/ Precision (if applicable) |
|---|---|---|
BOOLEAN |
BOOLEAN |
N/A |
TIME, ZONED TIME |
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE |
N/A |
LOCAL TIME, LOCAL_TIME,
LOCALTIME |
TIMESTAMP |
N/A |
ZONED DATETIME, DATE-TIME,
DATETIME, DATE_TIME |
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE |
N/A |
LOCAL DATETIME, LOCAL DATE
TIME, LOCALDATETIME,
LOCAL_DATE_TIME |
TIMESTAMP |
N/A |
DATE |
DATE |
N/A |
POINT |
JSON |
N/A |
| Other unspecified types | CLOB |
N/A |
STRING (if MAX_STRING_SIZE
initialization parameter is set to
EXTENDED)
|
VARCHAR2 |
32767 |
STRING, VARCHAR |
VARCHAR2 |
4000 |
LIST, MAP,
ARRAY |
VARCHAR2 |
4000 |
FLOAT |
FLOAT |
53 |
DURATION |
VARCHAR2 |
50 |
INT, INTEGER, SIGNED
INTEGER |
NUMBER |
10 |