9 Enabling and Configuring the Oracle Database API for MongoDB
This section describes how to enable and configure the Oracle Database API for MongoDB.
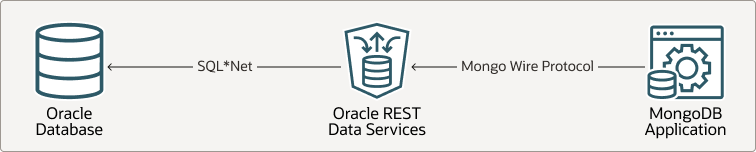
Starting with ORDS release 22.3, Oracle REST Data Services supports the Oracle Database API for MongoDB when running in a standalone mode. This enables the use of MongoDB drivers, frameworks, and tools to develop your JSON document-store applications against the Oracle Database. The Oracle Database API for MongoDB, translates the MongoDB wire protocol into SQL statements that are executed using the ORDS connection pools.
Figure 9-1 Architecture Diagram for Oracle Database API for MongoDB
- The MongoDB concept of a database is mapped to the concept of a
schema in Oracle Database. Specifically, an ORDS-enabled schema. For example,
when you insert a JSON document into a collection in the database
foo, the API for MongoDB inserts the document into a collection in the ORDS-enabled schemafoo. - Authentication and authorization when using the API for MongoDB
depends on the Oracle Database users and access controls and not the MongoDB
users. When you are connecting a MongoDB client, you must specify the Oracle
Database credentials using the LDAP authentication mechanism of MongoDB using
the connection options
authMechanism=PLAINandauthSource=$external. The protocol passes the username and password as a plain text and so, TLS/SSL must be enabled using the connection optiontls=true. - The Oracle API for MongoDB maps the MongoDB commands to the
corresponding SQL statements on the table backing the collection.
For example, a MongoDB command such as
emp.find({"name":"John"})is executed against the database using a SQL select statement similar toselect data from emp e where e.data."name" = 'John'. - When required, SQL can be executed directly over JSON collections. With this model, you get the speed, flexibility, and ease-of-use of a NoSQL document store while still having the ability to use SQL for analytics and reporting directly over your natively stored JSON data.
- Getting Started
- Requirements
This section lists the client and database requirements. - Configurable Settings for MongoDB
This section lists the editable configuration settings to support the MongoDB API stored in the global configuration, located atglobal/settings.xml. - Examples
This section lists some examples that use theords config setcommand to store the MongoDB settings in the current working directory (CWD)global/settings.xmland also provides an example for MongoDB listener settings inglobal/settings.xmlfile. - Accessing the Connection Pools
- Logging MongoDB API Access
This section describes how to enable logging of requests to the MongoDB API. - Achieving High Peformance
This section describes the settings that are useful in achieving high performance.
9.1 Getting Started
- Install and configure ORDS:
From a command prompt, install and configure ORDS using the following commands:
Note:
- If you are installing ORDS against the Autonomous Database, then use
the command
ords install adb. - Oracle API for MongoDB is only supported for installations in a non-CDB database or PDB.
See Also:
- Install ORDS in a standalone mode in a non-CDB Database or in a
PDB.
Note:
Oracle API for MongoDB is only supported for installations in a non-CDB database or PDB.ords install - By default, the Oracle API for MongoDB is not enabled. To enable the API, in your
configuration, include the
following:
ords config set mongo.enabled true - Start ORDS
ords serve
When the MongoDB API is enabled, you will get a notification and you get the connect string when ORDS is started.
Log showing that the Oracle API for MongoDB is enabled:After starting ORDS using theords servecommand, the log shows a message similar to the following to verify if the Oracle API for MongoDB is enabled:Disabling document root because the specified folder does not exist: ./config/global/doc_root 2022-08-17T15:23:04.043Z INFO Oracle API for MongoDB listening on port: 27017 2022-08-17T15:23:04.050Z INFO The Oracle API for MongoDB connection string is: mongodb://[{user}:{password}@]localhost:27017/{user}?authMechanism=PLAIN&authSource=$external&ssl=true&retryWrites=false&loadBalanced=true - If you are installing ORDS against the Autonomous Database, then use
the command
- Create an ORDS-enabled user:
Leave the server running and from SQLcl, create an ORDS-enabled user.
create user foo identified by "<Password>"; grant soda_app, create session, create table, create view, create sequence, create procedure, create job, unlimited tablespace to foo; connect foo/<Password> exec ords.enable_schema; - Connect to ORDS using the MongoDB shell:
By default, ORDS uses a self-signed certificate for secure communication. The Mongo API does not allow self-signed certificates, so you cannot directly connect with any Mongo tool or driver to the Mongo API.
The alternatives are as follows:- Disabling TLS option is specifically for local environments that are not dealing
with sensitive data. To disable TLS, you must invoke the following command before
starting
ORDS:
ords config set mongo.tls false ords serveNote:
Mongo API connect string changes to reflect thatmongo.tlsis not enabled. For example:...ssl=false.... -
Use the mongo tools and drivers to explicitly disable the requirement for TLS to require a valid signed certificate.
The settings change depending on the tools and the APIs. For example, themongoshhas a ar--tlsAllowInvalidCertificatescommand line argument, whereasmongoimporthas--tlsInsecurecommand line argument. -
Configure the properties
standalone.https.certandstandalone.https.cert.keyto aquire a valid signed cerfificate.
Example using
mongoshwithout a valid signed certificate:mongosh --tlsAllowInvalidCertificates 'mongodb://foo:<Password>@localhost:27017/foo?authMechanism=PLAIN&authSource=$external&tls= true&retryWrites=false&loadBalanced=true'foo> db.createCollection('emp'); { ok: 1 } foo> db.emp.insertOne({"name":"Blake","job": "Intern","salary":30000}); ... foo> db.emp.insertOne({"name":"Smith","job": "Programmer","salary": 60000,"email" : "smith@oracle.com"}); ... foo> db.emp.insertOne({"name":"Miller","job": "Programmer","salary": 70000}); ... foo> db.emp.find({"name":"Miller"}); [ { _id: ObjectId("6320bfc40dd73b60ef5641b9"), name: 'Miller', job: 'Programmer', salary: 70000 } ] foo> db.emp.updateOne({"name":"Miller"}, {$set: {"email":"miller@oracle.com"}}) { acknowledged: true, insertedId: null, matchedCount: 1, modifiedCount: 1, upsertedCount: 0 } - Disabling TLS option is specifically for local environments that are not dealing
with sensitive data. To disable TLS, you must invoke the following command before
starting
ORDS:
- The data inserted from the MongoDB client can be accessed from
SQL:
SQL> select json_serialize(e.data) from emp e; JSON_SERIALIZE(E.DATA) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- {"_id":"6320bfa30dd73b60ef5641b7","name":"Blake","job":"Intern","salary":30000} {"_id":"6320bfb30dd73b60ef5641b8","name":"Smith","job":"Programmer","salary":60000,"email":"smith@oracle.com"} {"_id":"6320bfc40dd73b60ef5641b9","name":"Miller","job":"Programmer","salary":70000,"email":"miller@oracle.com"} SQL> select e.data."name".string() n, e.data."job".string() j from emp e where e.data."email".string() = 'miller@oracle.com'; N J -------------------- ----------------------- Miller Programmer
9.2 Requirements
This section lists the client and database requirements.
The MongoDB API supports Oracle Database version 21c or later and the Autonomous Oracle Database 19c or later (serverless, dedicated, and cloud@customer). In general, Oracle API for MongoDB supports MongoDB tools and drivers that support the loadBalanced connection option.
9.3 Configurable Settings for MongoDB
This section lists the editable configuration settings to support the
MongoDB API stored in the global configuration, located at
global/settings.xml.
Note:
Oracle recommends users to use the Oracle REST Data Services command-line interface to edit the configuration files.Table 9-1 Configuration Settings to Support the Mongo API
| Key | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
mongo.enabled(Mandatory property) |
boolean | Specifies to enable the API for MongoDB. Default value
is false.
Specifies to enable the API
for MongoDB, set the value to |
mongo.tls |
boolean | Specifies whether the API requires TLS for secure
encrypted communication. The default value is
true.
|
mongo.access.log |
path | Specifies the path to the folder where you want to store the API for MongoDB access logs. If the path is not specified, then no access is generated. |
mongo.host |
string | Specifies a comma separated list of host names or IP
addresses to identify a specific network interface on which to listen.
Default value is 0.0.0.0.
|
mongo.port |
integer | Specifies the API for MongoDB listen port. Default value
is 27017.
|
mongo.idle.timeout |
duration | Specifies the maximum idle time for a connection in
milliseconds. Default value is 30m |
mongo.op.timeout |
duration | Specifies the maximum time for a database operation in
milliseconds. Default value is 10m.
|
9.4 Examples
This section lists some examples that use the ords config
set command to store the MongoDB settings in the current working directory
(CWD) global/settings.xml and also provides an example for MongoDB listener
settings in global/settings.xml file.
Examples of using the ords config set command
ords config set mongo.enabled trueords config set mongo.host example.comords config set mongo.port 27017ords config set mongo.idle.timeout 40mords config set mongo.op.timeout 15m
Example of Mongo Listener settings in global/settings.xml
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>Saved on Wed Jun 15 01:33:58 UTC 2022</comment>
<entry key="debug.printDebugToScreen">true</entry>
. . .
<entry key="mongo.host">example.com</entry>
<entry key="mongo.idle.timeout">40m</entry>
<entry key="mongo.enabled">true</entry>
<entry key="mongo.op.timeout">15m</entry>
<entry key="mongo.port">27016</entry>
. . .
</properties>Examples of using the ords config get command
ords config get mongo.enabledtrueords config get mongo.port27016
Using the ords serve Command
Use the ords serve command to run in standalone
mode.
Note:
To enable the Oracle API for MongoDB, prior to running theserve command, you must set
mongo.enabled property to true
9.5 Accessing the Connection Pools
Oracle REST Data Services supports the ability to connect to more than one database.
Multiple named pools can be defined using the install command. Adding a pool creates a
corresponding directory under ./databases within the ORDS configuration
directory. An initial install of Oracle REST Data Services typically adds a default
database connection pool named default.
mydb1 has a configuration directory at
ords_config/databases/mydb1.
Note:
You cannot use multiple pools whenmongo.tls key is disabled, only default pool is
supported.
If you create the hostname file
ords_config/databases/mydb1/hostnames containing two hostnames as
follows:
www.example.com
example.commydb1
conection pool instead of the default connection
pool:"mongodb://www.example.com:27017/scott?authMechanism=PLAIN&authSource=$external&ssl=true&retryWrites=false&loadBalanced=true"
"mongodb://example.com:27017/scott?authMechanism=PLAIN&authSource=$external&ssl=true&retryWrites=false&loadBalanced=true"
See Also:
9.6 Logging MongoDB API Access
This section describes how to enable logging of requests to the MongoDB API.
By default, requests to the MongoDB API are not logged. To enable logging access to
MongoDB API, you must set the configuration property mongo.access.log
to a directory path. If the directory path is not absolute, it is resolved relative to
the the ORDS configuration directory (<ords config>). If the
directory does not exist, then ORDS creates the directory on startup. ORDS then adds an
access log file entry within this directory each time the MongoDB API is accessed.
Example:
ords config set mongo.access.log mongologs
This command writes access log files under <ords
config>/mongologs/ folder.
9.7 Achieving High Peformance
This section describes the settings that are useful in achieving high performance.
In environments where higher performance or throughput is desired, some ORDS connection pool parameters are required to be configured and tuned.
To achieve higher throughput, the following settings and the values are useful. The optimal tuning of these parameters depend on the requirements of an application:
ords config set jdbc.MaxConnectionReuseCount 5000
ords config set jdbc.MaxConnectionReuseTime 900
ords config set jdbc.SecondsToTrustIdleConnection 1
ords config set jdbc.InitialLimit 100
ords config set jdbc.MaxLimit 100Where:
MaxConnectionReuseTime: Enables connections to be gracefully closed and removed from the connection pool after a connection is borrowed a specific number of times.SecondsToTrustIdleConnection: Sets the time in seconds to trust a recently used or recently tested database connection and skip the validation test during connection checkout.InitialLimitandMaxLimits: Sets the connection pool size in the UCP for the specified connection pool.