Implementing Data Sovereignty with Oracle Globally Distributed Database
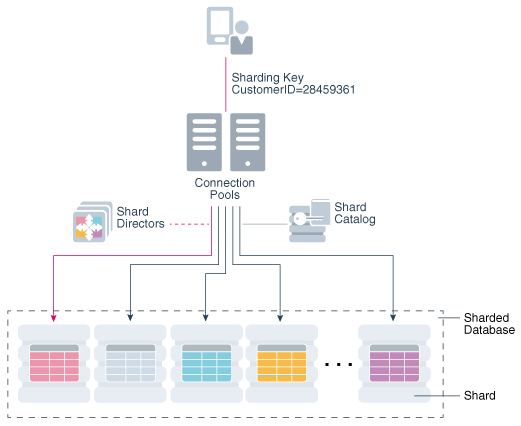
Oracle Globally Distributed Database distributes segments of a data set across many databases (shards) on different computers, on-premises, or in the cloud. These shards can be deployed in multiple regions across the globe. This enables Oracle Globally Distributed Database to create globally distributed databases honoring data residency.
All of the shards in a given database are presented to the application as a single logical database. Applications are seamlessly connected to the right shard based on the queries they run. For example, if an application instance deployed in the US needs data that resides in Europe, the application request is seamlessly routed to an EU data center, without the application having to do anything special.
Figure 16-1 Oracle Globally Distributed Database Architecture
Additionally, Oracle Database security features such as Real Application Security (RAS), Virtual Private Database (VPD), and Oracle Database Vault can be used to limit data access further, even within a region. For example, an administrator in the EU region can further be restricted to see data only from a subset of countries and not all EU countries. Within a Data Sovereignty region, data can be replicated across multiple data centers using Oracle Data Guard.
Oracle Globally Distributed Database management interfaces give you control of the global metadata and provide a view of the physical databases (replicas), data they contain, replication topology, and more. Oracle Globally Distributed Database handles data redistribution when nodes are added or dropped.
You can access worldwide reporting without actually copying the data from the various regions. Sharding can run multi-shard reports without copying any data from any region. Oracle Globally Distributed Database pushes queries to the nodes where the data resides.
Oracle Globally Distributed Database provides comprehensive data sovereignty solutions that focus on the following aspects:
-
Data Residency: Data can be distributed across multiple shards, which can be deployed in different geographical locations.
-
Data Processing: Application requests are automatically routed to the correct shard irrespective of where the application is running.
-
Data Access: Data access within a region can be restricted further using the Virtual Private Database capability of Oracle Database.
-
Derivative Data: Ensuring that the data is stored in an Oracle Database, and using Oracle Database features to contain the proliferation of derivative data.
-
Data Replication: Oracle Globally Distributed Database can be used with Oracle Data Guard to replicate data within the same Data Sovereignty region.