4 Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
This chapter is intended to provide the Oracle Database ODBC driver users with information about configuring and using the Oracle Database ODBC driver.
Topics:
4.1 Connecting to Oracle Database Using TLS (Preconfigured for Azure AD)
This example demonstrates how to connect to Oracle Database from Microsoft Excel with the TLS preconfigured to use Azure AD.
- Overview
- Prerequisite Steps to Using Oracle ODBC with Excel
- Installing the ODBC Driver
- Configuring tnsnames.ora, TNS_ADMIN, and PATH
- Getting an OAuth 2 Token
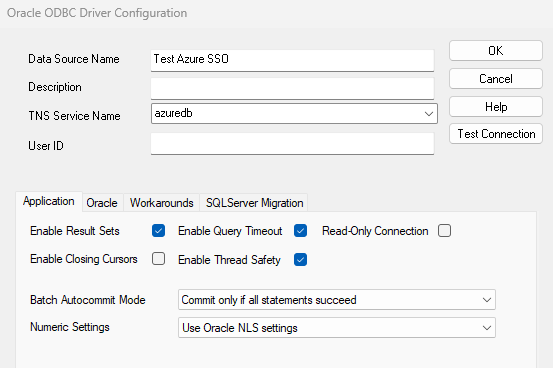
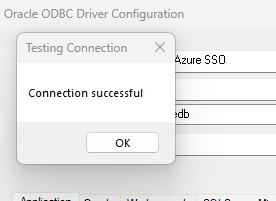
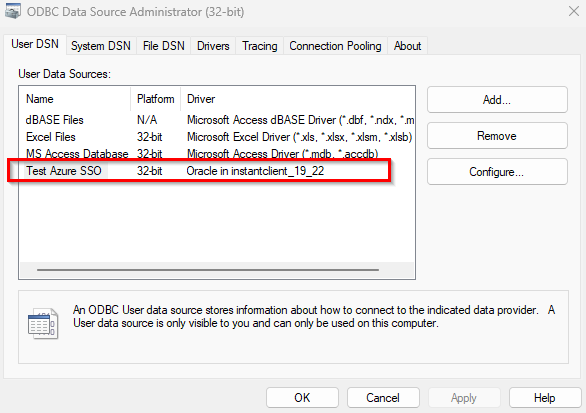
- Configuring DSN
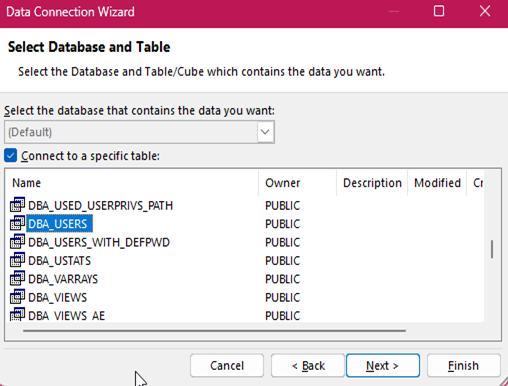
- Configuring Excel
Parent topic: Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
4.1.1 Overview
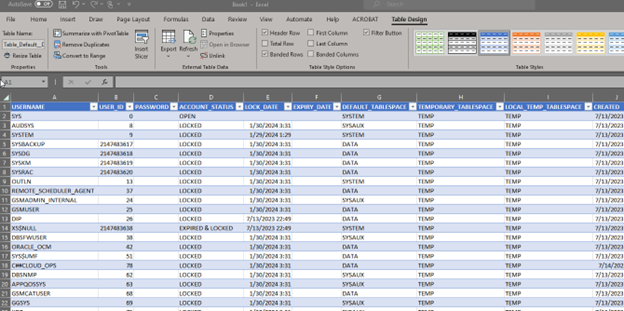
You can use your Microsoft Entra ID (was Azure AD) SSO credentials to access an Oracle Database from Microsoft Excel and other tools, when using the Oracle Database ODBC driver. The following example shows you how you can access an Oracle Database from Microsoft Excel.
4.1.2 Prerequisite Steps to Using Oracle ODBC with Excel
Note:
Only Oracle Database 19.16, and higher, and Oracle Database 23ai (not including Oracle Database 21c) support the Entra ID integration.
-
Configure the database for Entra ID integration.
See Also:
Authenticating and Authorizing Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) Users for Oracle Databases in Oracle Database Security Guide for more information about Entra ID integration with Oracle Database.
-
Get a valid OAuth 2 token for your database before you start your configuration and put the token into the location specified by the
TOKEN_LOCATIONparameter in your connect string.Note:
The token is only valid for about an hour. You may need to request a new token if the time taken to complete the configurations exceeds an hour.
See Also:
Local Naming Parameters in the tnsnames.ora File in Oracle Database Net Services Reference for more information about the
TOKEN_LOCATIONparameter.
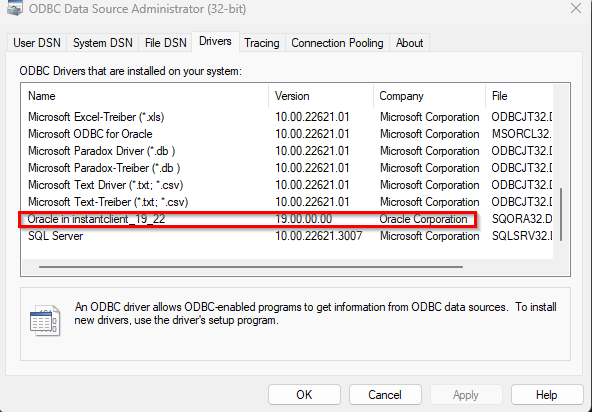
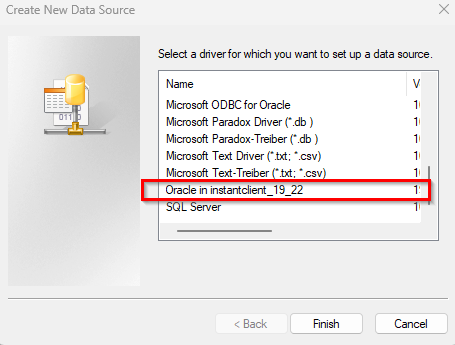
4.1.3 Installing the ODBC Driver
Download and install the appropriate version (19 or 23 ) of the 32 or 64-bit ODBC driver. Follow these steps:
4.1.5 Getting an OAuth 2 Token
- You need to get an OAuth 2 token (if not already done) at this point because you need the token to test the new Data Source Name (DSN) that you will create in the ODBC Data Source Administrator GUI in the next section.
4.2 Creating Oracle Database ODBC Driver TNS Service Names
To create the Oracle Database ODBC driver TNS Service Names with Oracle Net
Services, use the Oracle Net Configuration Assistant (NETCA), which is installed
when you install Oracle Net Services. NETCA creates the Oracle Database ODBC driver
TNS Service Name entries in the tnsnames.ora file.
Parent topic: Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
4.3 SQL Statements
The Oracle Database ODBC Driver is broadly compatible with the SQL-99 Core specification, which is a superset of the SQL-92 Entry Level specification. In addition to Oracle's grammar, the vendor-specific escape sequences outlined in Appendix C of the ODBC specifications are also supported. In accordance with the design of ODBC, the Oracle Database ODBC driver passes the native SQL syntax to Oracle Database.
See Also:
-
Implementation of the ODBC SQL Syntax for programmers
Parent topic: Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
4.4 Data Types
The Oracle Database ODBC driver maps the Oracle Database data types to the ODBC SQL data types.
Note:
All conversions in Appendix D of the Microsoft ODBC 3.52 Software Development Kit and Programmer's Reference are supported for the ODBC SQL data types listed from a call to SQLGetInfo with the appropriate information type.
See Also:
Parent topic: Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
4.5 Implementation of Data Types (Advanced)
Topics:
BOOLEAN Data Types
Starting Oracle Database 23ai, Oracle Database supports the native
BOOLEAN data type in compliance with the ISO SQL standard. The
native boolean type enables you to define a table column as a SQL boolean data type
with the value as true, false, or null.
Using the SQL boolean data type provides clarity, consistency, and speed to coding. With the boolean data type, you can represent a boolean state more clearly, and improve the readability of the code.
Using the native boolean data types support, ODBC-compliant applications can:
-
Fetch or modify
BOOLEANcolumn data -
Fetch metadata about a
BOOLEANcolumn
The boolean data type is represented externally as the
SQLT_BOL data type. The SQLT_BOL data type is
used as the SQL type identifier for BOOLEAN columns. Bind and
define API calls enable the SQLT_BOL data type to be associated
with host variables in ODBC-based applications.
The ODBC interface represents boolean type with
SQL_C_BIT, which is the C data type identifier.
SQL_C_BIT is an unsigned char (UCHAR) that
represents boolean type in applications. SQL_C_BIT only takes a 0
or 1 value, and so, when retrieving boolean data from the database, the data value
is represented as 0 or 1.
To bind and fetch (or modify) boolean type data with
BOOLEAN columns, you can have an application call the bind and
define functions, and specify the C data type: SQL_C_BIT with
the:
-
TargetTypeargument in theSQLBindCol()andSQLGetData()functions. -
ValueTypeargument in theSQLBindParameter()function.
The SQLBindCol() function binds the
BOOLEAN column to an application variable before the fetch and
the SQLGetData() function binds the fetched data to variables after
the fetch. The SQLBindParameter() function binds parameters in an
SQL statement to application variables.
If the TargetType argument is a
SQL_C_BIT data type, the Oracle Database ODBC driver maps
SQLT_BOL to SQL_C_BIT while processing the
bind and define parameters. The driver then performs the necessary conversions when
fetching (or modifying) and retrieving data from the BOOLEAN
columns.
To determine if a data source supports boolean data type, you can have an
application call the SQLGetTypeInfo function.
To retrieve metadata for table columns that are externally defined with
the SQLT_BOL data type, you can have an application call the
SQLDescribeCol() function.
For backward compatibility, Oracle Database releases prior to 23ai use internal data type conversions to support boolean values in the Oracle Database ODBC driver.
See Also:
-
Boolean Data Type in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about boolean data types
-
Microsoft ODBC API specifications for more information about the ODBC bind and define functions and supported data types
DATE and TIMESTAMP
The semantics of Oracle DATE and TIMESTAMP data
types do not correspond exactly with the ODBC data types with the same names. The
Oracle DATE data type contains both date and time information while
the SQL_DATE data type contains only date information. The Oracle
TIMESTAMP data type also contains date and time information,
but it has greater precision in fractional seconds. The ODBC driver reports the data
types of both Oracle DATE and TIMESTAMP columns as
SQL_TIMESTAMP to prevent information loss. Similarly, the ODBC
driver binds SQL_TIMESTAMP parameters as Oracle
TIMESTAMP values.
Floating Point Data Types
When connected to a 10.1 or later Oracle server, the ODBC driver maps the Oracle
floating point data types BINARY_FLOAT and
BINARY_DOUBLE to the ODBC data types SQL_REAL
and SQL_DOUBLE, respectively. In previous releases,
SQL_REAL and SQL_DOUBLE are mapped to the
generic Oracle numeric data type.
See Also:
VECTOR Data Type
Starting Oracle Database 23ai, the Oracle Database ODBC driver supports
VECTOR data type. The driver uses SQL_CHAR to
map to the VECTOR data type.
See Also:
Vector Data Type in Oracle Database SQL Language Reference for more information about vector data types
Parent topic: Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
4.6 Error Messages
When an error occurs, the Oracle Database ODBC driver returns the native error
number, the SQLSTATE (an ODBC error code), and an error message. The
driver derives this information both from errors detected by the driver and errors
returned by the Oracle server.
Native Error
For errors that occur in the data source, the Oracle Database ODBC driver returns the native error returned to it by the Oracle server. When the Oracle Database ODBC driver or the Driver Manager detects an error, the Oracle Database ODBC driver returns a native error of zero.
SQLSTATE
For errors that occur in the data source, the Oracle Database ODBC driver maps the
returned native error to the appropriate SQLSTATE. When the Oracle
Database ODBC driver detects an error, it generates the appropriate
SQLSTATE. When the Driver Manager detects an error, it
generates the appropriate SQLSTATE.
Error Message
For errors that occur in the data source, the Oracle Database ODBC driver returns an
error message based on the message returned by the Oracle server. For errors that
occur in the Oracle Database ODBC driver or the Driver Manager, the Oracle Database
ODBC driver returns an error message based on the text associated with the
SQLSTATE.
Error messages have the following format:
[vendor] [ODBC-component] [data-source] error-message
The prefixes in brackets ( [ ] ) identify the source of the error. The following table shows the values of these prefixes returned by the Oracle Database ODBC driver. When the error occurs in the data source, the [vendor] and [ODBC-component] prefixes identify the vendor and name of the ODBC component that received the error from the data source.
Table 4-1 Error Message Values of Prefixes Returned by the Oracle Database ODBC Driver
| Error Source | Prefix | Value |
|---|---|---|
|
Driver Manager |
[vendor][ODBC-component][data-source] |
[Microsoft/unixODBC][ODBC Driver Manager]N/A |
|
Oracle ODBC Driver |
[vendor][ODBC-component][data-source] |
[ORACLE][ODBC Driver]N/A |
|
Oracle server |
[vendor][ODBC-component][data-source] |
[ORACLE][ODBC Driver]N/A |
For example, if the error message does not contain the [Ora] prefix shown in the following format, the error is an Oracle ODBC Driver error and should be self-explanatory.
[Oracle][ODBC]Error message text here
If the error message contains the [Ora] prefix shown in the following format, it is not an Oracle ODBC Driver error.
Note:
Although the error message contains the [Ora] prefix, the actual error may be originating from one of several sources.
[Oracle][ODBC][Ora]Error message text here
If the error message text starts with the following prefix, you can obtain more information about the error in the Oracle server documentation.
ORA-
Oracle Net Services errors and Trace logging are located under the
ORACLE_HOME\NETWORK directory on
Windows systems or the ORACLE_HOME/NETWORK
directory on UNIX systems where the OCI software is installed and specifically in
the log and trace directories respectively. Database logging is located under the
ORACLE_HOME\RDBMS directory on
Windows systems or the ORACLE_HOME/rdbms
directory on UNIX systems where the Oracle server software is installed.
See the Oracle server documentation for more information about server error messages.
Parent topic: Using the Oracle Database ODBC Driver