Intercompany Elimination Example
This example involves intercompany transactions for a global organization with multiple subsidiaries and currencies. The organization has four subsidiaries in a three-level hierarchy that roll up to the consolidated parent subsidiary.
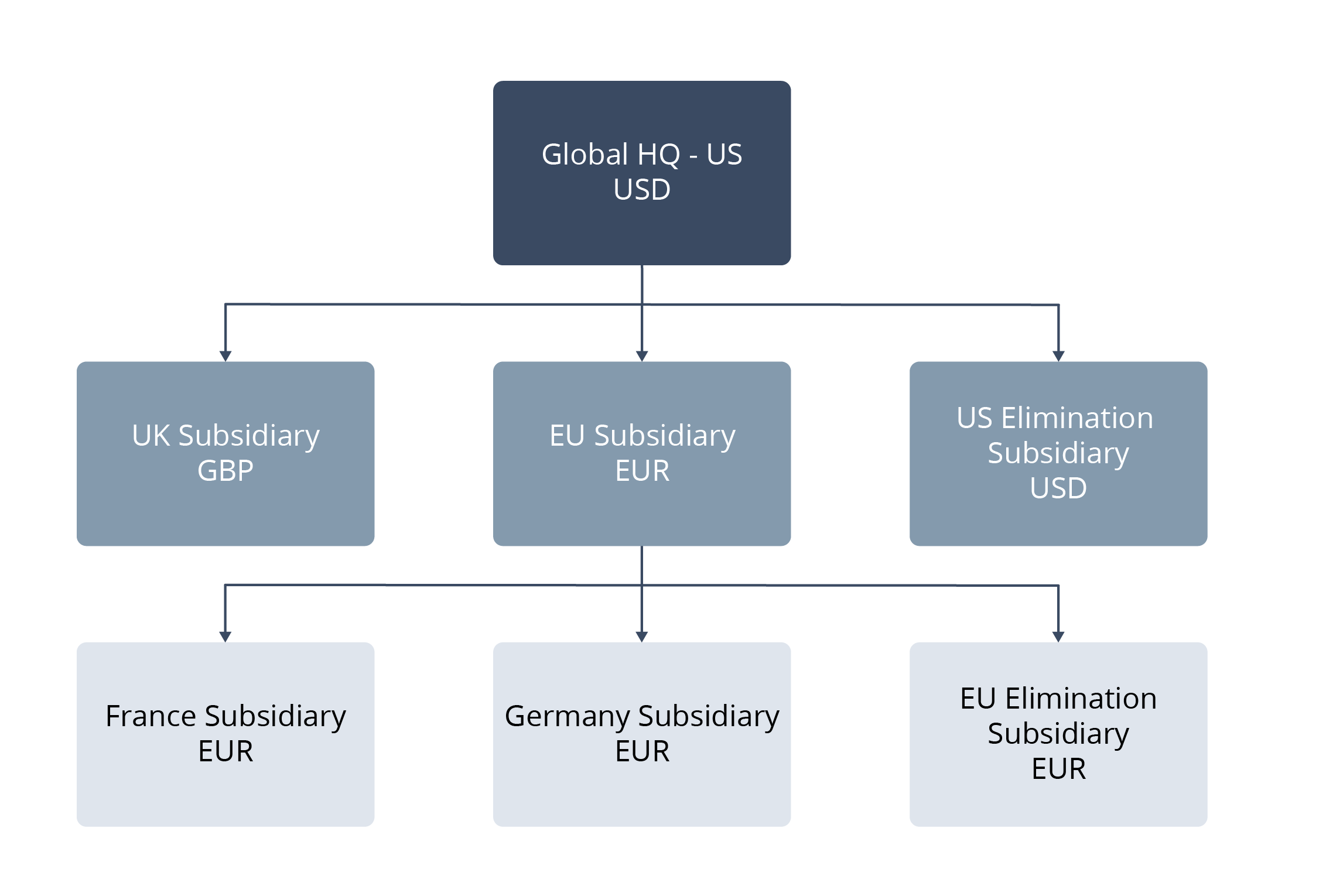
The hierarchy is based on geography and represents the following organizational relationships:
-
U.S. Subsidiary (HQ), currency USD
-
U.K. Subsidiary, currency GBP
-
EU Subsidiary, currency EUR
-
France Subsidiary, currency EUR
-
Germany Subsidiary, currency EUR
-
EU Elimination Subsidiary, currency EUR (the same currency as its parent, EU Subsidiary)
-
-
U.S. Elimination Subsidiary, currency USD (the same currency as its parent, Global HQ-US)
-
In this example, the U.K. subsidiary transfers funds to the EU subsidiary using the following parameters:
-
U.K. subsidiary transacting with EU subsidiary.
-
Elimination subsidiary is the U.S. Elimination Subsidiary.
-
Parent subsidiary is Global HQ-US.
-
Original and elimination journal entries roll up to the Global HQ-US subsidiary using the consolidated exchange rate.
-
Revenue and expense balances roll up using the average rate.
The journal entry for the intercompany transfer of funds is as follows:
|
Subsidiary |
Account |
Transaction Currency GL Impact |
Subsidiary Base Currency GL Impact |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Debit |
Credit |
Debit |
Credit |
|
U.K. |
Intercompany Expense |
100 GBP |
|
100 GBP |
|
|
U.K. |
Cash U.K. |
|
100 GBP |
|
100 GBP |
|
EU |
Cash EU |
100 GBP |
|
150 EUR |
|
|
EU |
Intercompany Revenue |
|
100 GBP |
|
150 EUR |
When the funds transfer occurred, the currency exchange rate was 1.5 EUR to 1.0 GBP. The base currency of the U.S. Elimination subsidiary is USD. At the end of the month, the currency rate is 2 USD to 1 GBP.
Because the foreign currency exchange rate fluctuated during the period, the resulting gain or loss posts to the cumulative translation adjustment - elimination (CTA-E) account. When you run the intercompany elimination process at period close, NetSuite eliminates the revenue and expense directly to the CTA-E account. The consolidated exchange rates used by the income statement accounts are different from the consolidated exchange rates used by the balance sheet accounts:
-
Income statement accounts -average rates
-
2 USD to 1 EUR
-
2.5 USD to 1 GBP
-
1.25 EUR to 1.0 GBP
-
-
Balance sheet accounts - current rates
-
1.2 USD to 1.0 EUR
-
2.0 USD to 1.0 GBP
-
1.67 EUR to 1.0 GBP
Note:Not all balance sheet accounts use current rates. Most asset and liability accounts use current rates.
Equity accounts use historical rates.
-
Running intercompany elimination produces two results.
-
The elimination journal entries post to the U.S. Elimination subsidiary to eliminate revenue and expense from the consolidated financials.
-
The original and elimination journal entries roll up to the Global HQ-US subsidiary. Any unbalanced currency adjustment gain and loss amounts accumulate in the CTA-E account.
|
Subsidiary |
Account |
Elimination JE in Original Offsetting Currency |
HQ Consolidation Currency GL Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
|
U.S. Elimination |
Intercompany Revenue |
Dr 150 EUR |
Dr 300 USD (Eliminate revenue at HQ) |
|
U.S. Elimination |
CTA-E |
Cr 150 EUR |
Cr 300 USD |
|
U.S. Elimination |
CTA-E |
Dr 100 GBP |
Dr 250 USD |
|
U.S. Elimination |
Intercompany Expense |
Cr 100 GBP |
Cr 250 USD (Eliminate expense at HQ) |
After running intercompany elimination, the CTA-E account has a translation adjustment balance of 50 USD.
Setting different exchange rate types for different accounts can result in balance sheet discrepancies, particularly discrepancies in consolidated reports.