Resolve Conflicts Using the Git Panel
Use the Git panel to review and resolve conflicts that occur when your changes clash with those made by other project members.
Conflicts usually occur when you and your teammate change the same line in different ways, or if one of you deleted a file while the other modified it. In such cases, VB Studio cannot tell which version is correct—it's up to you or your teammate to make that decision and resolve the conflict.
Note:
To help minimize the number of conflicts, the best practice is to make sure your local branch and the remote branch are in sync and up-to-date. Typically, you make changes in a branch private to your workspace, then publish them to a shared branch in your remote repository, so your changes become available to others. To include others' changes in your workspace, you must keep your local branch in sync with the remote branch by merging changes from that remote branch into your workspace.
VB Studio simplifies the task of keeping your workspace up-to-date by periodically checking your repository for updates and notifying you when your workspace needs to be refreshed. Simply click the Refresh Workspace link in the notification to update your workspace with the latest changes and avoid conflicts. See Refresh Your Workspace.
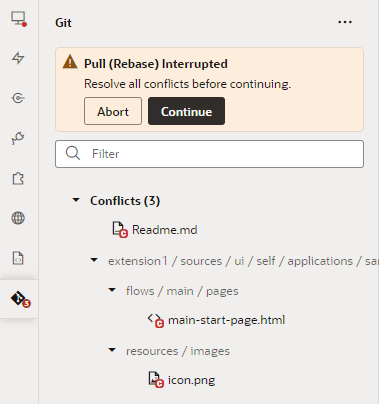
You'll be informed of conflicts when you attempt to merge, pull, or revert commits in your workspace. For example, let's say you've changed lines 2 and 3 in readme.md and committed the changes to a local branch in your Git repo. Now if someone else modified the same lines in readme.md and committed the changes to a remote branch, you'll be warned of conflicts between the file's remote version and your local version when you do a pull request to refresh your workspace, as shown here: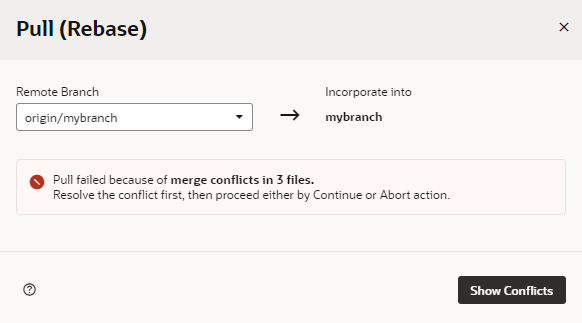
Description of the illustration showconflicts.png
When this happens, here's what to do:
Use the Context Menu to Resolve Conflicts
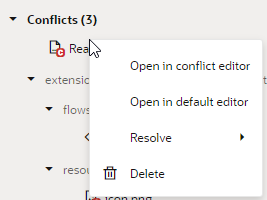
When a file contains conflicts, you can use its context menu in the Git panel to quickly resolve conflicts. You do this when the file has just a few simple conflicts that you can easily resolve by keeping your branch's changes or the other branch's changes.
Tip:
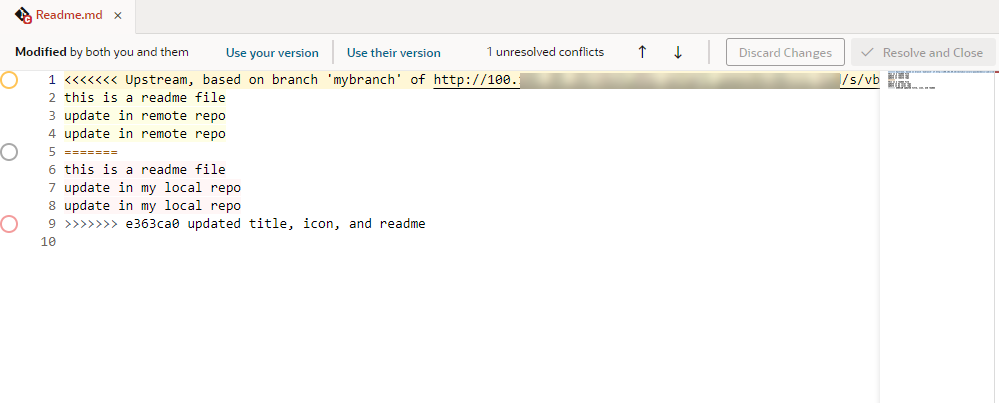
If you want to keep changes from both branches (or a combination of them), or if the file has a large number of conflicts, it's better to open the file in the conflict editor and resolve each conflict separately.The options available to you in the context menu depend on the type of conflict in the file. For example, what you see when a file is deleted in one branch and modified in another (as shown here on the right) is not the same as what you see for a file modified by different people on different branches (shown on the left):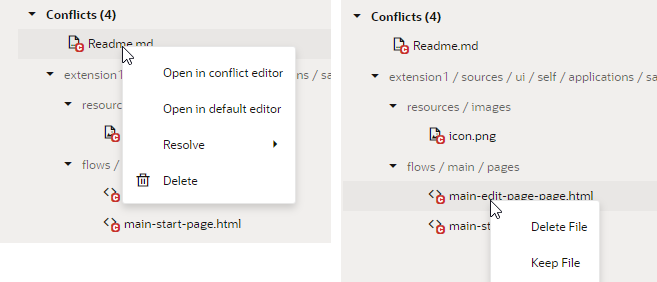
Description of the illustration conflict-types-appui.png
For demo purposes, we'll use the example of a file that's been modified by you and someone else.
- Right-click the file with conflicts in the Git panel and select Resolve.
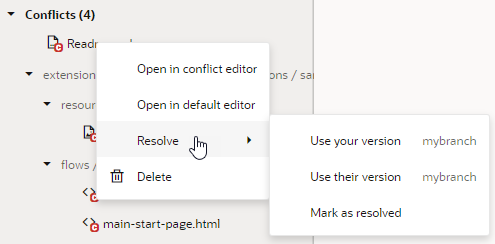
- Select the option you want to use:
- Select Use your version to keep your changes in the local branch.
- Select Use their version to keep changes in the remote branch.
- Select Mark as resolved to mark the file as resolved by staging it in Git.
Note:
When you select a file version (Use your version or Use your version), the file is automatically marked as resolved. Select Mark as resolved only if you manually made changes to a file either in the default editor or the conflict editor and did not mark the file as resolved (using Resolve and Close) in the editor.