Create a Custom Backend
You can create your own backend to map to a custom server other than the built-in Oracle Cloud Applications backend.
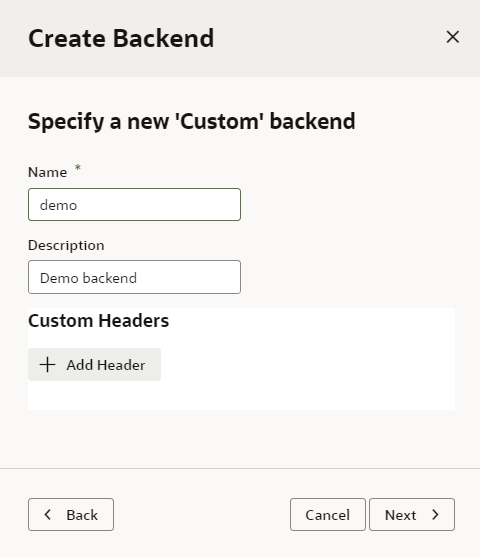
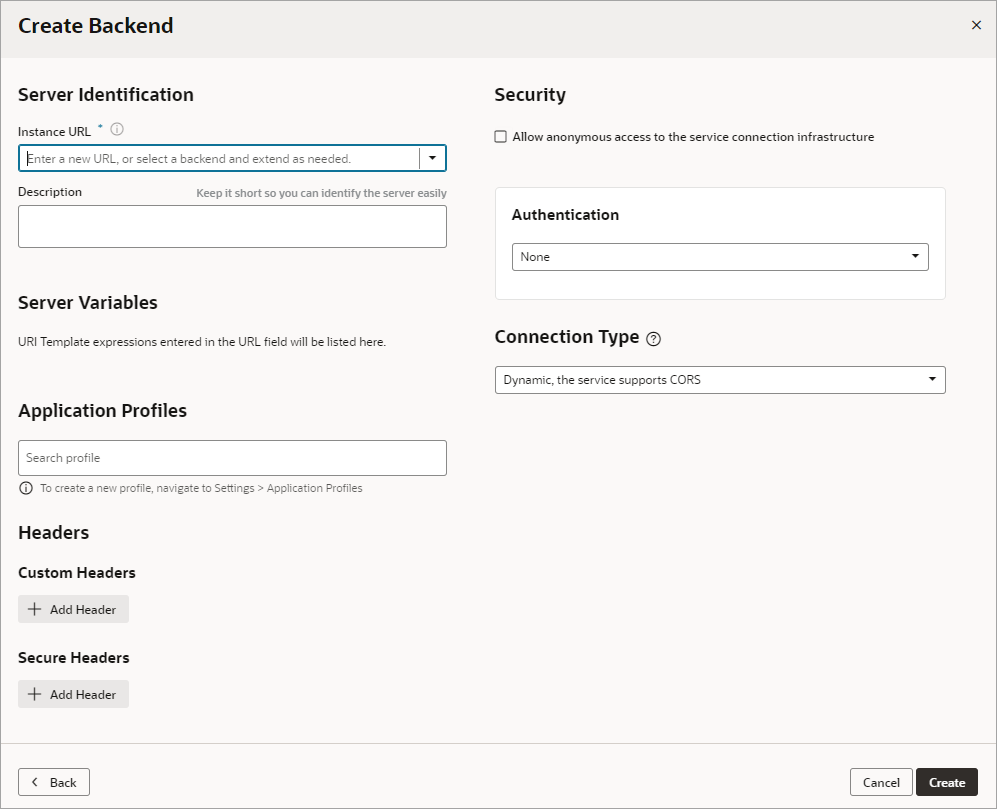
A custom backend lets you access a service when you know its URL. You can create a custom backend with a free-form URL, or create a custom ADF backend when you know the Describe URL that points to an ADF Describe service.
To create a custom backend:
A new custom backend displays in the Backends tab on the Services pane. Click the newly created custom backend to view and edit its details. See Edit a Backend.
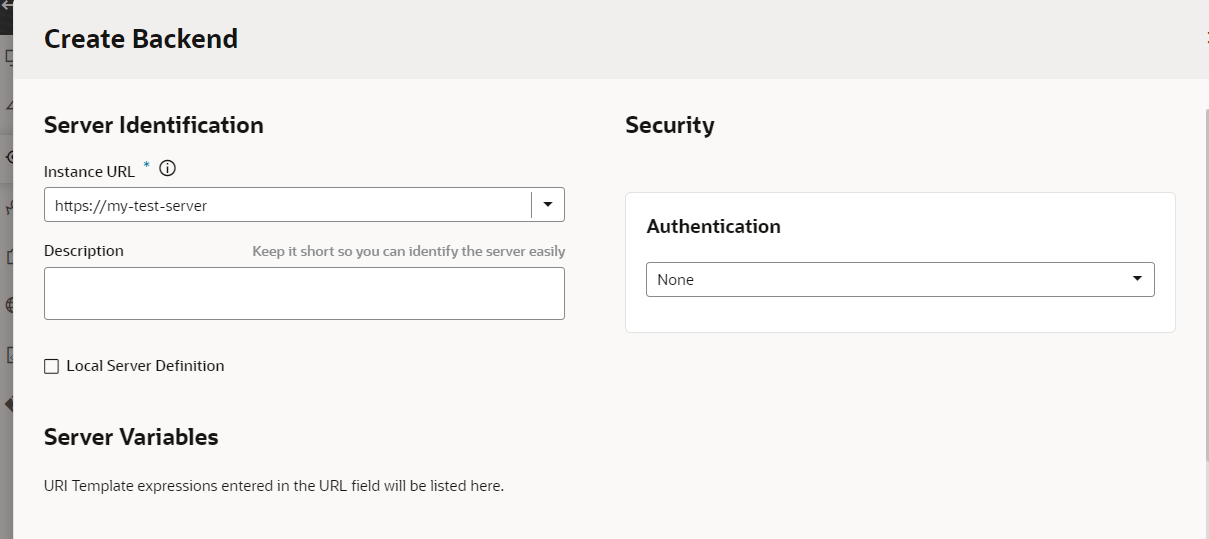
If this backend was created with a local server, you'll need to provide the corresponding runtime server details in Oracle Cloud Applications so that the backend will work for the Preview action. See Provide a Backend's Runtime Server Details.
Now that your custom backend is registered, you can click + Service Connection to create a service connection to your backend, either by providing a service specification document or by pointing to the URL of a service endpoint. See Create a Service Connection from a Service Specification or Create a Service Connection from an Endpoint.