Working with OAuth 2 to Access the REST API
The Oracle Identity Cloud Service REST APIs support SCIM 2.0 compliant endpoints with standard SCIM 2.0 core schemas and Oracle schema extensions to programmatically manage users, groups, applications, and identity functions, such as password management and administrative tasks. To make REST API calls to your Oracle Identity Cloud Service environment, you need an OAuth2 access token to use for authorization. The access token provides a session (with scope and expiration), that your client application can use to perform tasks in Oracle Identity Cloud Service.
The following sequence diagram illustrates a basic example of the OAuth 2.0 authorization flow to access the Oracle Identity Cloud REST API.
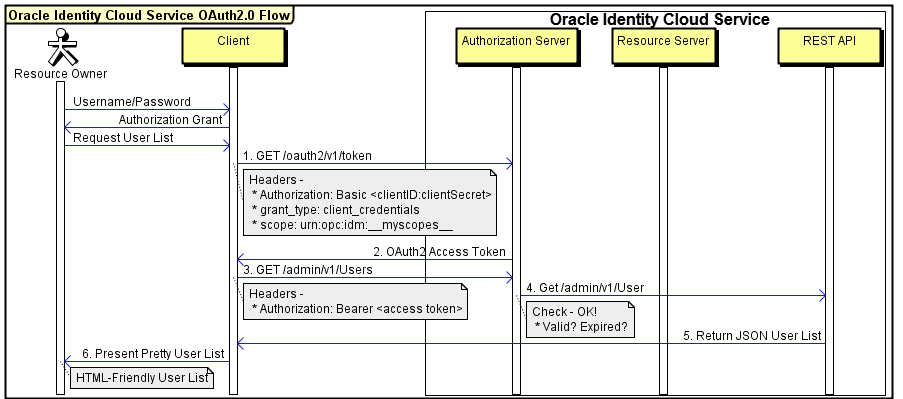
There are specific OAuth 2.0 parameters that you use when working with Oracle Identity Cloud Service. The following table describes the most common parameters.
| Parameter | Value | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Authorization Header |
Basic <base64_clientid_secret> |
Used by the client as a Basic authentication scheme to transmit the access token in a header. The access token value needs to be a base64 UTF-8 encoded value of the Client ID and Client Secret concatenated using a colon as a separator-for example, clientID:clientSecret. |
| Client ID |
<client_id> |
Required. A unique "API Key" that is generated when you register your application in the Oracle Identity Cloud Service administrative console. |
| Client Secret |
<client_secret> |
Required. A private key similar to a password that is generated when you register your application in the Oracle Identity Cloud Service administrative console. Do not share this value. |
| Access Token URL |
/oauth2/v1/token |
An endpoint used to obtain an access token from Oracle Identity Cloud Service. |
| Auth URL |
/oauth2/v1/authorize |
An endpoint used to obtain an authorization code from Oracle Identity Cloud Service, and then used during a 3-legged OAuth flow. |
| Grant Type |
client_credentials |
Required. It means the REST API that is invoked is owned by the client application. |
| Scope (required) |
urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__ |
This scope returns all the grants given to your application, other scopes could be used to get specific grants, if necessary. |
Step 1: Register a Confidential Application in Oracle Identity Cloud Service
When you register a confidential application in the Oracle Identity Cloud Service administrative console, you obtain some of the key parameters that you need to work with OAuth 2.0: Client ID, Client Secret, and Scopes. OAuth 2.0 is a standard for implementing delegated authorization, and authorization is based on the access token required to access a resource. The access token can be issued for a given scope, which defines what the access token can do and what resources it can access. When you register a web application in Oracle Identity Cloud Service, you add scopes. In the following example, the required scopes to request User searches, edits, creates, and deletes are added. But, if you were to do other things-for example, manage Audit Events, that would require other scopes.
To create and register a confidential application:
-
Access your Oracle Identity Cloud Service instance (for example:
https://tenant-base-url/ui/v1/adminconsole)and log in with your Identity Domain Administrator credentials. -
Click Applications, and then Add.
-
Select Confidential Application as the type of application.
-
Enter an application name and a description, and then click Next.
-
On the Authorization page, define the following items:
-
Select the Configure this application as a client now option.
-
Select Client Credentials from the Allowed Grant Type section.
-
At the bottom of the page select the Grant the client access to Identity Cloud Service Admin APIs check box.
-
Click your cursor in the box that appears below the check box, and then select the type of access for the REST APIs. For example, select Identity Domain Administrator. Your credentials and all tasks available to the Identity Domain Administrator will be accessible to you.
-
Click Next, and then Finish.
-
Make note (using your preferred note utility) of the Client ID and the Client Secret that appear in the confirmation window, and then click Close.
-
-
Click Activate in the upper-right section of the page to activate the application.
Step 2: Base64 Encode the Client ID and Client Secret
Note:
Before base64 encoding, individually URL encode the client ID and the client secret. If your client ID and client secret do not contain special characters, you are not required to URL encode them first. However, as a best practice, we highly recommend it.Windows
-
Launch Notepad, and then paste the client ID and client secret into Notepad.
-
Place the client ID and client secret on the same line and insert a colon between them:
clientid:clientsecret -
Save the file to
C:\tempand name the fileappCreds.txt. -
In Windows Explorer, right-click
C:\temp,and then select CMD Prompt Here from the context menu. -
Enter the following command to encode the client ID and client secret:
certutil -encode appCreds.txt appbase64Creds.txt -
In Notepad, open
C:\temp\appbase64Creds.txt,copy its contents, and then close the file.Note:
For security reasons, delete theappCreds.txtand theappbase64Creds.txtfiles after you finish.
Mac and Linux
-
Launch your preferred note utility (for example, Mac Notes, LINUX gedit, or Vi), and then paste the client ID and client secret into the note utility.
-
Place the client ID and client secret on the same line and insert a colon between them:
clientid:clientsecret. -
Copy the
clientid:clientsecretline. -
Launch a terminal and enter the following command, replacing
clientid:clientsecretwith the value that you just copied to the clipboard.echo -n "clientid:clientsecret" | base64 -w 0Note:
For Linux, add-w 0to the command to remove line breaks. -
Copy the value that is returned.
Note:
If the value that is returned is broken into more than one line, return to your text editor and make sure the entire results are on a single line with no text wrapping.
Step 3: Obtain an Access Token
The next step in this process is to request the access token.
-
Launch a command prompt.
-
Enter the cURL command below, replacing the text in brackets ( < > ) with the appropriate values:
curl -i -H "Authorization: Basic <base64encoded clientid:secret>" -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8" --request POST https://tenant-base-url/oauth2/v1/token -d "grant_type=client_credentials&scope=urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__"Note:
If you are using a UNIX OS, you can append| awk -F"\"" '{print $4}'to the end of the cURL command to parse out just the Bearer token. Just remember the default expiration of the token is 3600 seconds from the time of the request.Note:
Optionally, execute the following cURL command to have the access token value accessible through a UNIX variable calledAccessTokenValuein your environment:
You can then executeexport AccessTokenValue=`curl -i -H "Authorization: Basic <base64encoded clientid:secret>" -H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded;charset=UTF-8" --request POST https://tenant-base-url/oauth2/v1/token -d "grant_type=client_credentials&scope=urn:opc:idm:__myscopes__" | awk -F"\"" '{print $4}' | tail -n +16`echo $AccessTokenValuecommand to get the access token value.Text in Brackets Value base64encoded clientid:secret Replace with the encoded credentials that you generated in the Base64 Encode the client ID and client secret section. IDCS_Service_Instance Replace with your Oracle Identity Cloud Service URL (for example, https://tenant-base-url).Note:
Theurn:opc:idm:__myscopes__scope in the command is used as a tag by Oracle Identity Cloud Service clients requesting access tokens from the OAuth authorization server. Access tokens are returned that contain all applicable Oracle Identity Cloud Service scopes based on the privileges represented by the Oracle Identity Cloud Service administrator roles granted to the requesting client and the user being specified by the client's request (if present). This scope is not granted directly to any Oracle Identity Cloud Service administrator role. -
Copy the
access_tokenvalue from the response. Make sure to copy only the actual token, which is theaccess_tokenvalue between the quotation marks:Status: 200 "access_token":"eyJ4NXQiOiI4Wk. . ." "token":"Bearer", "expires_in":3600Note:
The response includes theexpires_in: 3600parameter. This means that your token is no longer valid after one hour from the time that you generate it. After one hour, you must refresh the token or get a new access token.
Step 4: Make a REST Request to the Environment
After you obtain the OAuth 2.0 access token, you can use the token in a cURL command to send a REST request to the Oracle Identity Cloud Service REST API. The following command returns a list of users in your Oracle Identity Cloud Service instance.
curl
-X GET
-H "Content-Type:application/scim+json"
-H "Authorization: Bearer <access_token>"
https://tenant-base-url/admin/v1/Users| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Method | -X GET |
| Content Type Header | -H "Content-Type:application/scim-json" |
| Authorization Header | -H "Authorization: Bearer <access_token>" |
| HTTP Protocol | HTTP or HTTPS (HTTP is recommended) |
| IDCS-Service-Instance | Your Oracle Identity Cloud Service URL (for example, https://tenant-base-url). |
| Oracle Identity Cloud Service REST Endpoint | /admin/v1/Users |
Example - Example JSON Output from the Oracle Identity Cloud Service REST API
In the previous step, the REST request sent using cURL returned a response in JSON format. JSON is an open standard that can be formatted or parsed per your needs like getting specific attributes required by your application.
{
"schemas": [
"urn:scim:api:messages:2.0:ListResponse"
],
"totalResults": 1,
"Resources": [
{
"displayName": "admin opc",
"name": {
"givenName": "admin",
"formatted": "admin opc",
"familyName": "opc"
},
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:oracle:idcs:extension:userState:User": {
"locked": {
"on": false
}
},
"userName": "admin@example.com",
"id": "d252a54d83c344eb8f59f7053a0562ce",
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:oracle:idcs:extension:user:User": {
"isFederatedUser": false
},
"active": true,
"nickName": "TAS_TENANT_ADMIN_USER",
"emails": [
{
"verified": false,
"value": "admin@example.com",
"type": "work",
"primary": true
},
{
"verified": false,
"value": "admin@example.com",
"primary": false,
"type": "recovery"
}
],
"schemas": [
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:oracle:idcs:extension:user:User",
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:oracle:idcs:extension:userState:User",
"urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:core:2.0:User"
],
"meta": {
"resourceType": "User",
"created": "2016-07-22T18:11:08Z",
"lastModified": "2016-07-25T21:19:28Z",
"location": "https://tenant-base-url/admin/v1/Users/d252a54d83c344eb8f59f7053a0562ce"
},
"idcsLastModifiedBy": {
"value": "idcssso",
"$ref": "https://tenant-base-url/admin/v1/Apps/idcssso",
"type": "App",
"display": "idcssso"
}
}
],
"startIndex": 1,
"itemsPerPage": 50
}