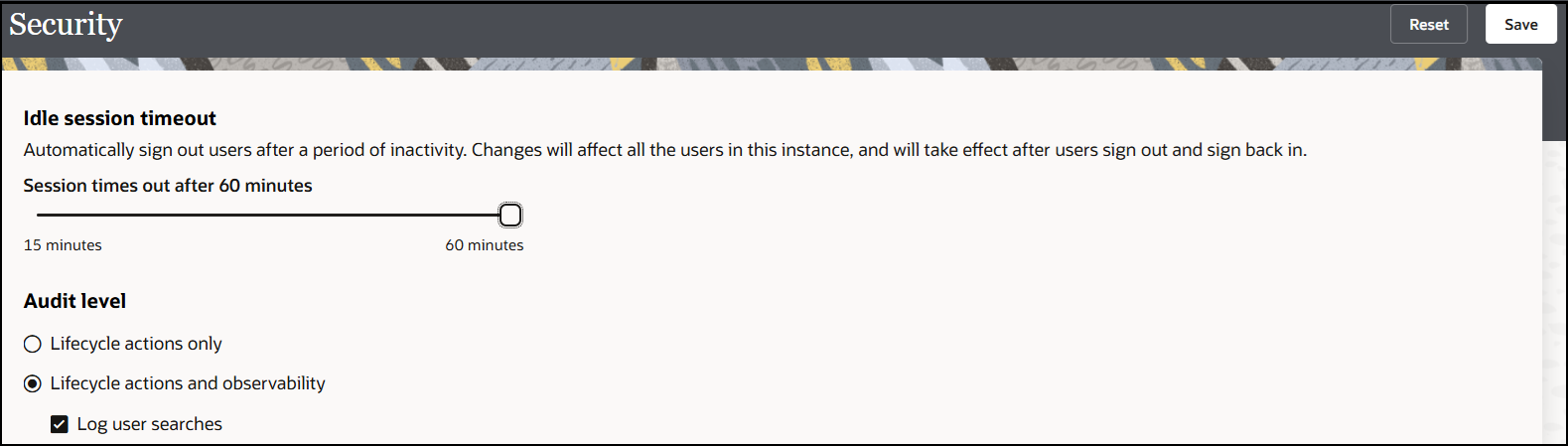
Set the Inactive Session Timeout Limit and Audit Logging Levels
You can set the time limit for inactive sessions in an Oracle Integration instance. This setting automatically signs out a currently authenticated user after a specified period of inactivity. This setting impacts all users of the instance and takes effect after a user signs out and signs back in. You can also select to capture lifestyle and observability actions in the audit logs.
Note the following guidelines for using the options on this page:
| To Set the Timeout for Inactive Sessions | To Set the Audit Levels |
|---|---|
|
|