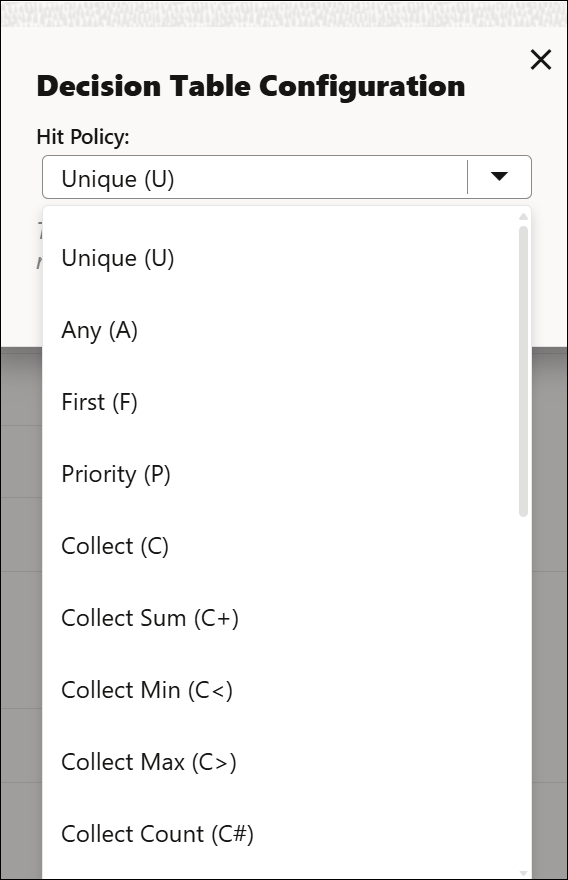
About Hit Policies
The hit policy of a decision table determines the table's output from the output entry cells of matched rules. A rule is matched when the input data to the decision table matches the input entries of a rule.
The hit policy cell displays the selected policy for the table. To locate the hit policy cell, see About Decision Table Elements.
-
Single Hit: A single-hit table returns the output of only one rule. In the single-hit category, Oracle Integration supports the following hit policies:
-
Unique (U): Only one of the rules can match.
-
Any (A): Multiple rules can match, but all matching rules must have the same output.
-
First (F): Multiple rules can match; the output of the first rule that matches is returned.
-
Priority (P): Multiple rules can match; the output value that has the highest priority is returned.
-
-
Multiple Hit: A multiple-hit table returns the output of multiple rules. In this category, Oracle Integration supports the following hit policies:
-
Collect (C): Multiple rules can match; outputs are returned in a list.
-
Collect Sum (C+): Multiple rules can match; the sum of outputs is returned.
-
Collect Min (C<): Multiple rules can match; the smallest output value is returned.
-
Collect Max (C>): Multiple rules can match; the largest output value is returned.
-
Collect Count (C#): Multiple rules can match; the count is returned.
-
When you create a new table, the Unique (U) hit policy is selected by default. To change the policy, click the hit policy cell and choose from the available options in the Hit Policy drop-down list.
Note:
If rules within the table do not conform to the selected hit policy, a warning is displayed in the decision table editor.Hit Policy Examples
- Single Hit Unique
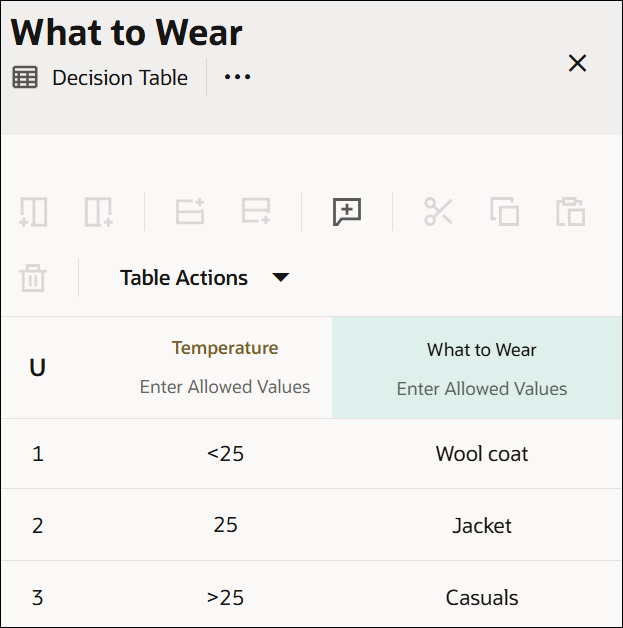
In a decision table with Unique hit policy, only one rule can match. All rules are independent of each other, and no overlap is permitted. The decision table returns the output of the rule that matches.
Here is a decision table created with the Unique hit policy. In this example, for any input value of temperature, only one rule can match.
- Single Hit Any
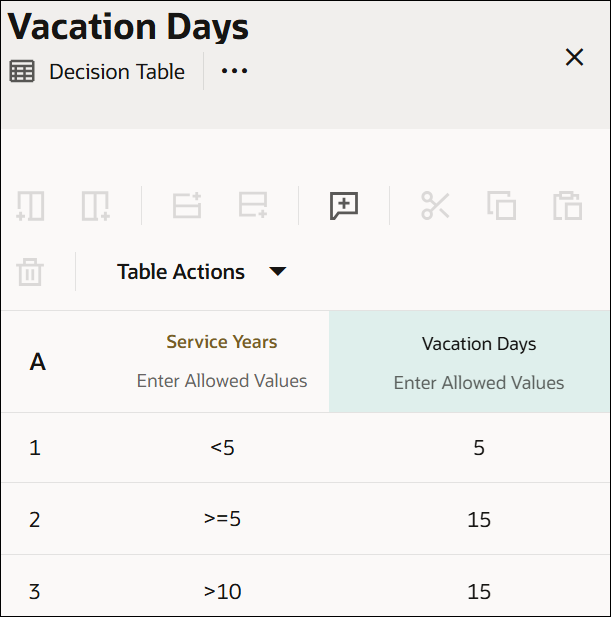
In a decision table with Any hit policy, multiple rules can match. Overlaps are permitted only if the matching rules have the same output. The decision table returns the output of any one of the matching rules. The hit policy is breached if matching rules have different outputs.
Here is a decision table created with the Any hit policy. In this example, for service years of 11, the second and third rules match. This overlap is allowed because these rules have the same output. The decision table returns the output of any one of these rules.
- Single Hit First
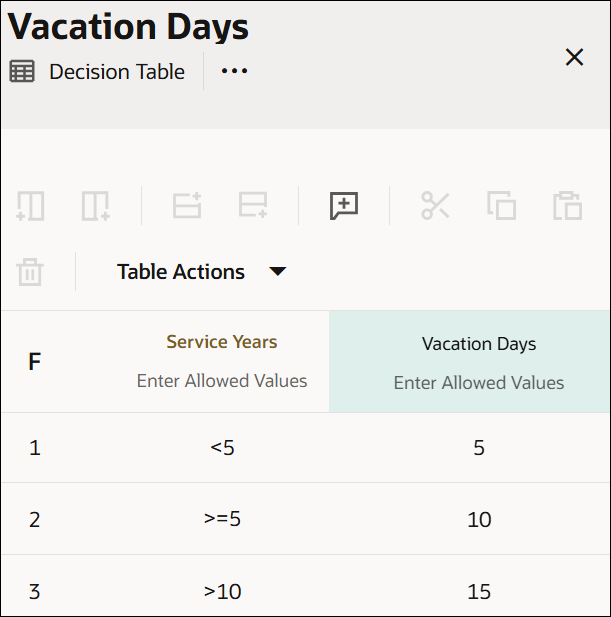
In a decision table with First hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The output of the lowest-numbered matching rule is the result of the table.
Here is a decision table created with the First hit policy. In this example, for service years of 11, the second and third rules match. The decision table returns only the second rule’s output.
- Single Hit Priority
In a decision table with Priority hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The priority of output values (in descending order) is specified as a list in the Allowed Values cell of the output column. The decision table returns the output value that has the highest priority among outputs of all matching rules.
Here is a decision table created with the Priority hit policy. In this example, the last two rules match for an input age of 61. The decision table returns the output value that has the highest priority among these rules, that is, 15. The priority order is defined in the Allowed Values cell.
![The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Priority hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as 5,15,10 for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15. The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Priority hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as 5,15,10 for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15.](img/dm-dt-priority.png)
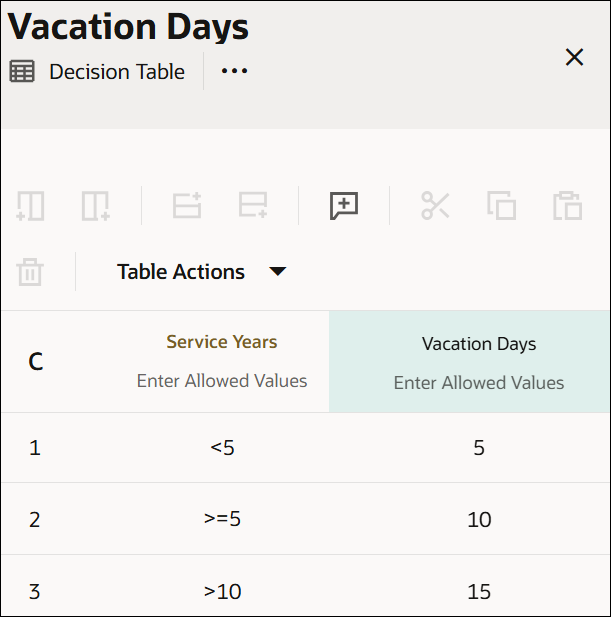
- Multiple Hit Collect
In a decision table with Collect hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The decision table returns outputs of all matching rules in a list.
Here is a decision table created with the Collect hit policy. In this example, two rules match for service years of 11. The decision table returns output values of these rules in a list, that is, 10 and 15.
- Multiple Hit Collect (Sum)
In a decision table with Collect (Sum) hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The decision table returns the sum of outputs of all matching rules.
Here is a decision table created with the Collect (Sum) hit policy. In this example, the last two rules match for an input age of 61. The decision table returns the sum of output values of these rules, that is, 25.
![The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Sum) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15. The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Sum) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15.](img/dm-dt-c1.png)
- Multiple Hit Collect (Min)
In a decision table with Collect (Min) hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The decision table returns the smallest output value among all matching rules.
Here is a decision table created with the Collect (Min) hit policy. In this example, the last two rules match for an input age of 61. The decision table returns the smallest output value among these rules, that is, 10.
![The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Min) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15. The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Min) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15.](img/dm-dt-cmin.png)
- Multiple Hit Collect (Max)
In a decision table with Collect (Max) hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The decision table returns the largest output value among all matching rules.
Here is a decision table created with the Collect (Max) hit policy. In this example, the last two rules match for an input age of 61. The decision table returns the largest output value among these rules, that is, 15.
![The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Max) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15. The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Max) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15.](img/dm-dt-cmax.png)
- Multiple Hit Collect (Count)
In a decision table with Collect (Count) hit policy, multiple rules with different output entries can match. The decision table returns the count of matching rules.
Here is a decision table created with the Collect (Count) hit policy. In this example, the last two rules match for an input age of 61. The decision table returns the count of matching rules, that is, 2.
![The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Count) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15. The image shows a decision table called Discount Percentage. The first row of the table contains the hit policy cell with the Collect (Count) hit policy selected, an input header cell that has the input variable Age entered, and an output header cell named Discount Percentage. There is an Allowed Values cell within each header cell, with values set as Auto for the input and as Any for the output. There are four subsequent rows that constitute rules of the decision table. Each row consists of the following: a cell indicating the rule number, an input entry cell, and an output entry cell. Values entered for each rule are: First rule: <18 and 15; Second rule: [18..45] and 5; Third rule: >45 and 10; Fourth rule: >60 and 15.](img/dm-dt-count.png)