Provide a Simple Instruction to the Anthropic Model
This use case demonstrates how to provide a simple question to the specified Anthropic model. The simple prompt focuses on clarity and conciseness, avoiding complex phrasing or unnecessary details that can potentially confuse the model.
- Configure a REST Adapter trigger connection.
- Configure an Anthropic Adapter invoke connection. See Create an Anthropic Adapter Connection.
- Create an application integration.
- Drag the REST Adapter trigger connection into the
integration canvas for configuration. For this example, the REST Adapter is configured as follows:
- A REST Service URL is defined (for
this example,
/anthropicsimple). - A Method of POST is selected.
- A Request Media Type of
JSON is selected and the following sample
JSON structure is
specified:
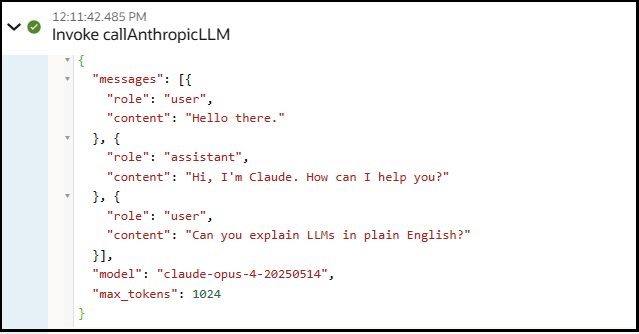
{ "messages" : [ { "role" : "user", "content" : "Hello there." }, { "role" : "assistant", "content" : "Hi, I'm Claude. How can I help you?" }, { "role" : "user", "content" : "Can you explain LLMs in plain English?" } ] } - A Response Media Type of
JSON is selected and the following sample
JSON structure is
specified:
{ "id" : "msg_01QYBJH7FVfL9kGt9a8Adgyj", "type" : "message", "role" : "assistant", "model" : "claude-opus-4-20250514", "content" : [ { "type" : "text", "text" : "I'll help you get the current weather and time in New York." }, { "type" : "tool_use", "id" : "toolu_01XUJFZr22Cy65yQGjC9Abc8", "name" : "get_weather", "input" : "input value" }, { "type" : "tool_use", "id" : "toolu_013sXxnS8VD7Db2oFo1Cxf4k", "name" : "get_time", "input" : "arguments" } ], "stop_reason" : "tool_use", "stop_sequence" : "stop", "usage" : { "input_tokens" : 532, "cache_creation_input_tokens" : 0, "cache_read_input_tokens" : 0, "output_tokens" : 111, "service_tier" : "standard" } }
- A REST Service URL is defined (for
this example,
- Drag the Anthropic
Adapter invoke connection into the
integration canvas and configure it as follows.
- From the Anthropic LLM Models list, select the model to use (for this example, Claude Opus 4 is selected).
- From the Request Type list, select Simple Prompt.
- Open the request mapper automatically created when the Anthropic Adapter invoke connection was added to the integration. The mapper that was automatically created with the REST Adapter trigger connection is not edited and remains empty in this use case.
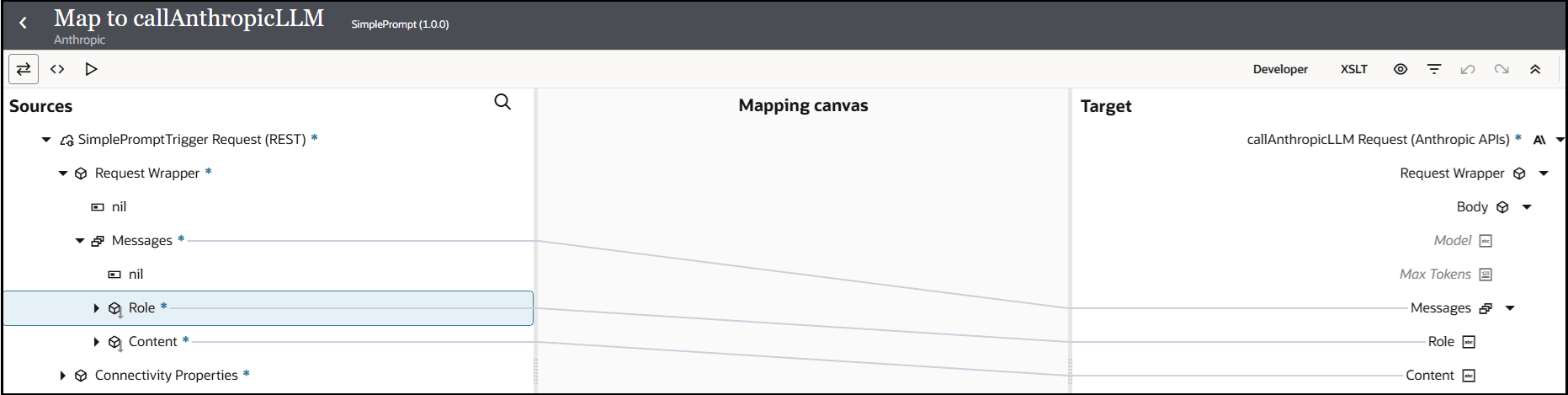
- In the request mapper, map the source Messages elements
to the target Messages elements.
- Add a response mapper.
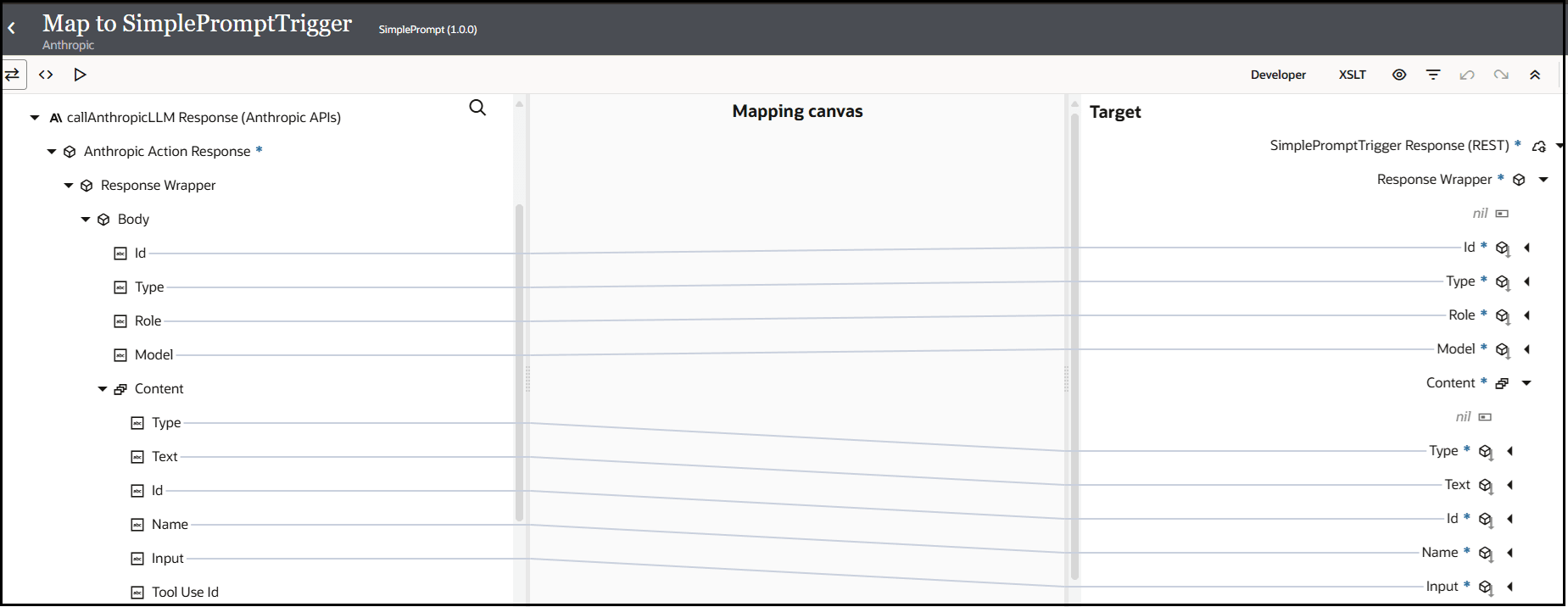
- In the response mapper, expand the source Response
Wrapper element and target Response
Wrapper element and perform the following source-to-target
mappings..
- Specify a business identifier and activate the integration. For this example,
the Debug tracing level is selected.
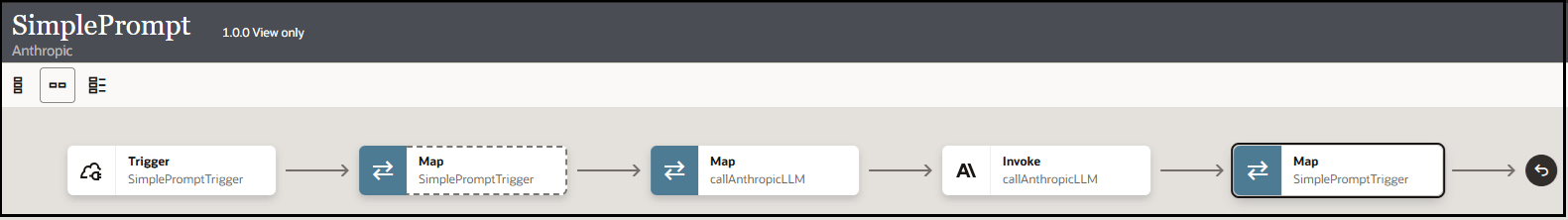
The completed integration looks as follows:
- From the Actions
 menu, select Run.The Configure and run page appears.
menu, select Run.The Configure and run page appears. - In the Body field of the Request
section, enter the following content, then click
Run.
role: The roles for the user that is commenting/questioning and the assistant that is responding.content: The message contents.
{ "messages": [{ "role": "user", "content": "Hello there." }, { "role": "assistant", "content": "Hi, I'm Claude. How can I help you?" }, { "role": "user", "content": "Can you explain LLMs in plain English?" }] }The Body field of the Response section returns the following output.{ "id" : "msg_013HeB3TaTKmLPSimSbctotz", "type" : "message", "role" : "assistant", "model" : "claude-opus-4-20250514", "content" : [ { "type" : "text", "text" : "Sure! LLMs (Large Language Models) are computer programs that have learned to understand and generate human-like text by studying massive amounts of writing from the internet, books, and other sources.\n\nThink of them like very advanced autocomplete systems. Just as your phone can predict the next word you might type, LLMs can predict and generate entire sentences, paragraphs, or even essays that make sense.\n\nHere's how they work in simple terms:\n\n1. **Training**: They read billions of pages of text and learn patterns - like how words typically go together, grammar rules, and facts about the world\n\n2. **Size**: \"Large\" means they have billions of connections (parameters) that help them remember and use what they've learned\n\n3. **Capabilities**: They can answer questions, write stories, translate languages, summarize text, and have conversations - basically anything involving understanding or creating text\n\n4. **Limitations**: They don't truly \"understand\" like humans do - they're pattern-matching machines. They can make mistakes, generate false information, or produce biased content based on their training data\n\nPopular examples include ChatGPT, Claude (that's me!), and Google's Bard. They're useful tools, but it's important to remember they're not human and should be used thoughtfully." } ] } - Expand the activity stream to view the flow of the message sent by the invoke
connection to the Anthropic model: