Configuring Essbase Clusters
This section discusses active-active clustering of Oracle Essbase Server. For information about clustering Oracle Essbase Administration Services Java web application and Oracle Hyperion Provider Services Java web application, see Clustering Java Web Applications Using EPM System Configurator.
Active-passive clustering (Windows): See Configure Essbase Servers in a Failover Cluster.
Active-passive clustering (Linux): See Configure Essbase Servers in a Failover Cluster.
Active-passive clustering:
-
Beginning with EPM Release 11.2.15 and later, Essbase no longer uses OPMN-based Clustering support. Essbase 21c does not support Microsoft Cluster Service integration. See Configure Essbase Servers in a Failover Cluster for more information on setting up an Essbase Active-Passive cluster. Installing and configuring Essbase should only be done on the first node if you are setting up a new Active-passive cluster for Essbase. Essbase should not be configured using the EPM configuration tool; instead, Essbase should be installed using the EPM 11.2.15 installer.
-
Essbase should only be upgraded on the master node when upgrading an existing Active-Passive Essbase cluster. Essbase should be manually uninstalled on the secondary node and then reinstalled using the 11.2.15 EPM installer.
Note:
Essbase should not be configured using the EPM configuration tool on the secondary node. Starting with Release 11.2.15, Essbase can now contain more than two nodes in an Active-passive cluster. See Configure Essbase Servers in a Failover Cluster for more information on adding additional nodes to the cluster.
Active-active clustering: You can configure active-active Essbase clusters using Provider Services. Active-active Essbase clusters support high availability and load balancing. An active-active Essbase cluster supports read-only operations on the databases and should be used only for reporting. Because active-active Essbase clusters do not support data write-back or outline modification, and they do not manage database replication tasks such as synchronizing the changes in one database across all databases in the cluster, they do not support Oracle Hyperion Planning. When Planning is configured to use Essbase in cluster mode as a data source, it does not support the ability to launch business rules with Oracle Hyperion Calculation Manager as the rules engine. See Configure Active-Active (Read-Only) Essbase Clusters.
Table 2-1 Essbase Server Clustering Configurations
| Capability | Active-Passive (Windows) | Active-Passive (Linux) | Active-Active |
|---|---|---|---|
| Write-back | Yes | Yes | No |
| Failover | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Load balancing | No | No | Yes |
| High availability | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Note:
- Beginning with EPM Release 11.2.15, Microsoft Cluster Service is no longer supported.
- See Configure Active-Active (Read-Only) Essbase Clusters for more information.
The following table describes an overview of the process of installing, configuring, and managing Essbase.
Table 2-2 Installing, configuring, and managing Essbase
| Task | Reference |
|---|---|
| Install Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System products,
including Essbase. Install Essbase locally on each node.
Note: Oracle recommends that the Oracle Hyperion Shared Services Registry database be on a different machine than Essbase. |
"Installing EPM System Products" in the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System Installation and Configuration Guide |
|
Configure EPM System products, including Essbase. If you are implementing Essbase clustering (active-passive only), during configuration with EPM System Configurator, do the following:
|
"Configuring EPM System Products" in the Oracle Enterprise Performance Management System Installation and Configuration Guide |
Configuring Active-Active Essbase Clusters
Using Provider Services, you can create active-active cluster of identical databases belonging to one Essbase server, to multiple Essbase servers on the same computer, or to Essbase servers distributed across multiple computers over the network.
Note:
Essbase servers may be subject to licensing restrictions.
Provider Services clients include Oracle Smart View for Office clients, custom Java application programming interface (API) clients, and XML for Analysis (XMLA) clients. Provider Services distributes client requests to database instances belonging to the cluster. An active-active Essbase cluster supports read-only operations on the databases; it does not support data write-back or outline modification. An active-active Essbase cluster does not manage database replication capabilities, such as synchronizing the changes in one database across all databases in the cluster.
Configuring Active-Active Clusters with Provider Services
Adding Servers to Active-Active Essbase Clusters
Active-Active Essbase Clustering Examples
For simplicity, all examples in this section use Smart View.
Essbase Server Clusters
Provider Services enables you to group sets of Essbase servers running applications with identical databases and use them as one resource.
Note:
When adding or deleting an Essbase server in a cluster, restart the server to reflect changes to the group. You can enable or disable components in the group without restarting the server.
Essbase Database Clusters
Clustering Essbase databases enables load balancing and failover support. Provider Services provides parallel clustering, in which a series of active, duplicate databases respond to user requests. Which database is accessed is transparent to users, who connect to and retrieve data from one data source. Provider Services facilitates the routing of connections between databases in a cluster, based on availability and precedence rules.
Figure 2-1 Essbase Database Clustering with Provider Services
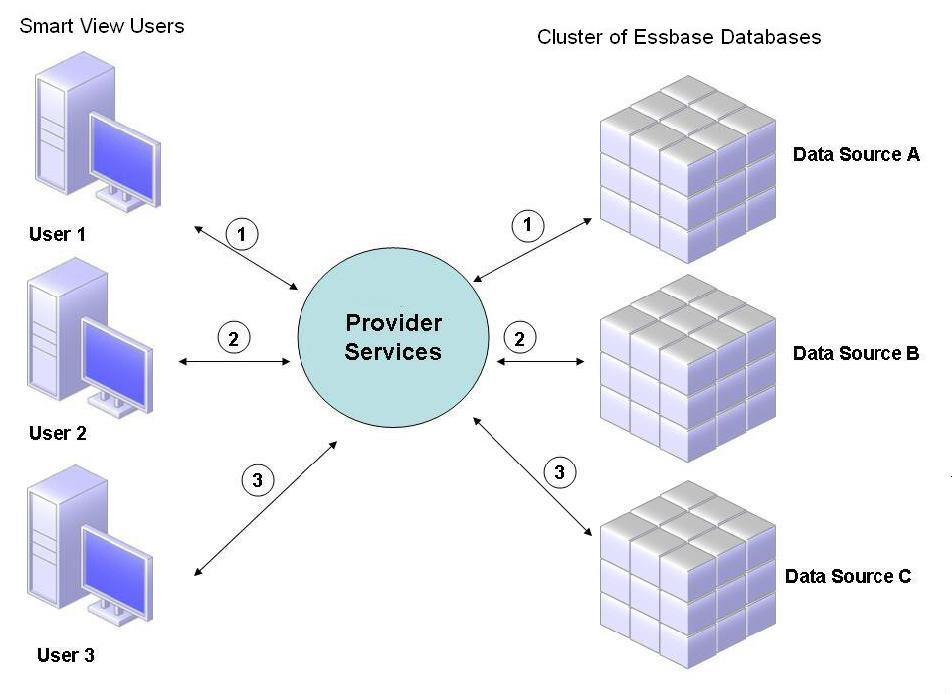
In Figure 2-1, Smart View users connect to Essbase through Provider Services.
Each user connection is assigned to a server during the Essbase session. Provider Services uses session-level load balancing. For example, in Figure 2-1, User 1’s connection is mapped to Data Source A. User 2’s connection is mapped to Data Source B. User 3’s connection is mapped to data source C. All requests from User 1 are handled by Data Source A for the duration of the connection.
If data source A fails:
-
User 1 times out at Data Source A.
-
User 1 is rerouted to the next available data source, which is Data Source C in Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 illustrates what happens when Data Source A goes offline.
Figure 2-2 Database Cluster with One Data Source Offline
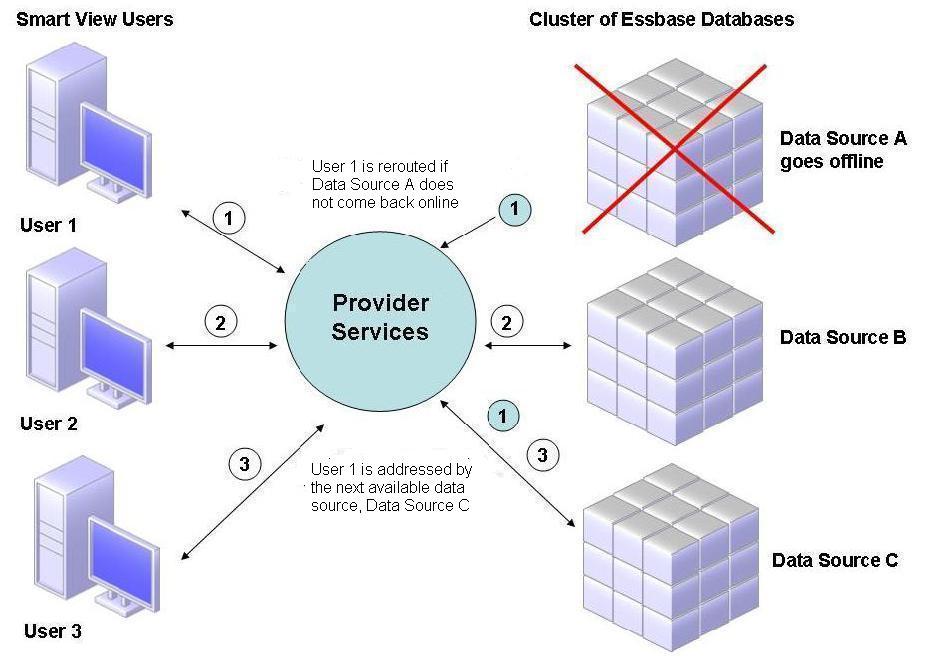
In Figure 2-2, the state of query 1 is maintained at the middle tier and rerouted. Provider Services also provides load balancing across servers.
Figure 2-3 depicts clustered databases deployed on one server.
Figure 2-3 Essbase Database Cluster on One Server
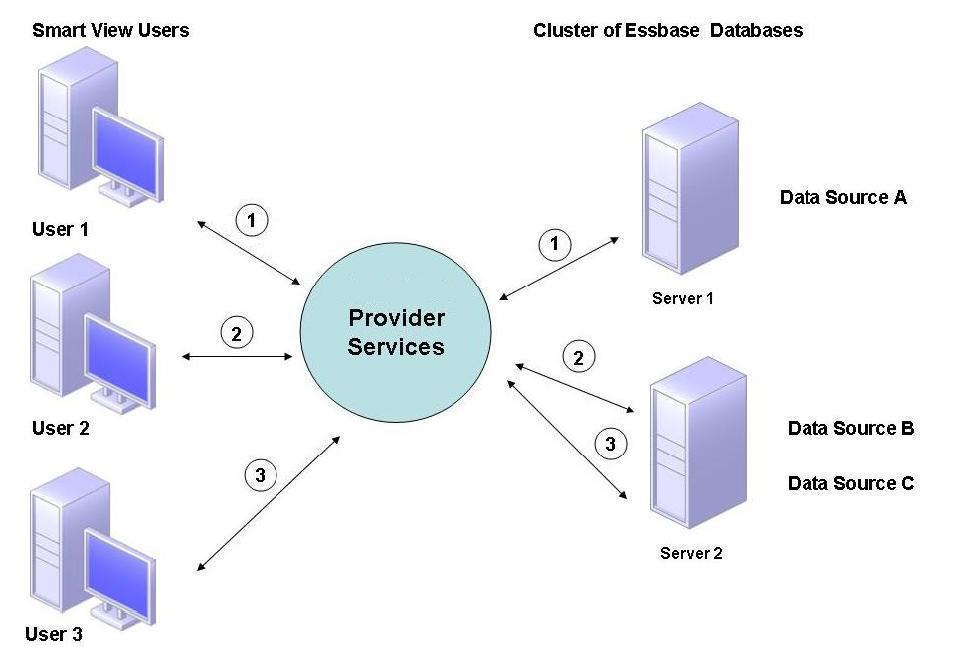
In Figure 2-3, two servers contain Essbase databases. Server 1 has four processors and 8 GB of RAM. Server 2 has eight processors and 16 GB of RAM. Because Server 2 has more resources, it contains Data Sources B and C. Therefore, Server 2 can handle both connections.
Failover support also applies for database clusters on one server. In Figure 2-4, Server 2 goes offline. User 2 and User 3 are then rerouted to the next available server, Server 1.
Figure 2-4 Failover for Database Cluster on One Server

Connections to Essbase Clusters
Essbase clients and servers can connect to an Essbase cluster by way of a URL in this format:
http(s)://host:port/essbase/agent?ClusterName=clusterName
You can also connect to an Essbase cluster using only the cluster name, but you must first enable this by modifying a configuration file to specify the Provider Services server that resolves the cluster name in the URL.
Restart Essbase after updating these files.
To connect to a Provider Services active-active Essbase cluster using Oracle Hyperion Financial Reporting, you must configure Financial Reporting for three-tier mode.
To configure Financial Reporting for three-tier mode:
-
Start MIDDLEWARE_HOME
/EPMSystem11R1/products/financialreporting/bin/FRConfig.cmd. -
Select the MBeans tab and browse to com.hyperion/Financial Reporting/Attributes/EssbaseJAPIServer.
-
Confirm that EssbaseJAPIServer is set as the Provider Services server.
-
Enter the Provider Services cluster name as the Server Name in the Attribute value Value box and then click Refresh.
-
Exit and restart Financial Reporting.