4 Setting Up Online Charging for SS7 Networks
This chapter describes the Oracle Communications Service Controller online charging for SS7 networks solution and how to configure Service for this solution.
About the Online Charging for SS7 Networks Solution
You use the online charging for SS7 networks solution to deliver Diameter-based charging for subscriber sessions in the legacy SS7 network. Service Controller delivers SS7 sessions to online charging systems (OCSs) including Oracle Communications Billing and Revenue Management (BRM) and third-party charging systems supporting the Diameter Ro protocol.
Service Controller supports online charging for SS7 networks with a connection to an OCS through the Diameter Ro protocol.
Figure 4-1 shows a basic session charging flow of the online charging for SS7 networks solution. Service Controller supports additional call flow scenarios not shown such as applying charging after answer and internal charging for CAP1, WIN and AIN networks.
Figure 4-1 Basic Call Flow in the Online Charging for SS7 Networks Solution
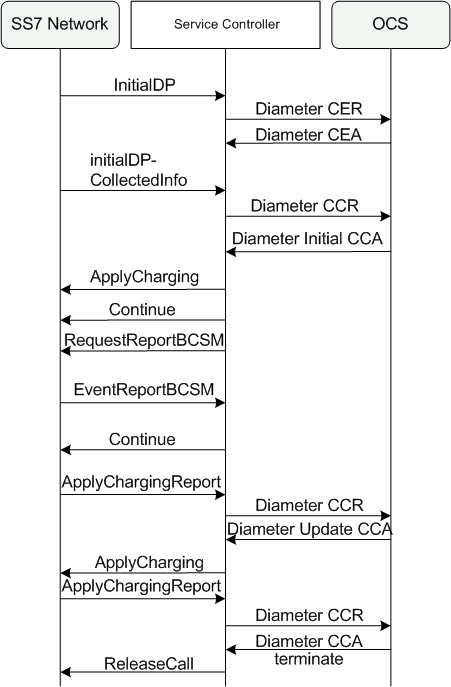
Description of ''Figure 4-1 Basic Call Flow in the Online Charging for SS7 Networks Solution''
Figure 4-2 shows the components in the Service Controller processing tier that you set up to enable SS7 to OCS charging.
The IMSCF Service Controller module translates SS7 messages into an internal format used by the Orchestration Engine. You use different variants of the IMSCF module, depending on the protocol variant used in your network. For example, if your network uses CAP Phase 3, then you use the IMSCF-CAP-Phase 3 module.
To enable Service Controller's SS7 and Ro connectivity to OCS, you also need to configure the appropriate signaling server units (SSU) for your OCS in the signaling tier. The OCS SSUs are not included in the figure. See Service Controller Signaling Server Units Configuration Guide for more information about configuring the SSU(s) for your OCS.
Sessions flow from the SS7 network through the components in the following order:
-
SS7 Network
-
SSU SS7
-
IMSCF
-
Orchestration Engine
-
Ro
-
OCS
Responses from the OCS flow in the reverse direction through the same components
Figure 4-2 Components Required for SS7 Session Charging
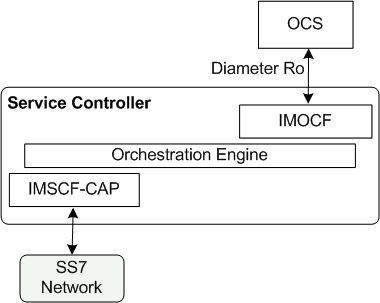
Description of ''Figure 4-2 Components Required for SS7 Session Charging''
Enabling OCS Charging of SS7 Sessions
An end-to-end configuration enabling SS7 charging by a Diameter Ro OCS, requires configuration of SSU SS7, SSU Diameter, IMSCF, IMOCF, and orchestration engine rules.
To set up this configuration:
-
Enable Service Controller to accept traffic of sessions arriving from the legacy SS7 network. See "Setting Up Connectivity to the Legacy SS7 Network" for information about the components that you need to configure and how to configure them.
-
Enable the diameter Ro interface to allow communication between Service Controller and the OCS. See "Setting Up Connectivity to the OCS" for more information.
-
Route sessions that arrive from the legacy SS7 network to the OCS. See "Defining a Service Orchestration Chain" for more information.
Setting Up Connectivity to the Legacy SS7 Network
You can connect Service Controller to a SIGTRAN-based SS7 network. Service Controller does not support TDM-based SS7 networks.
Before you start, make sure that you have a detailed plan of how Service Controller connects to your SS7 network, including point codes that you assign to Service Controller. To connect Service Controller to the legacy SS7 network:
-
Configure a SIGTRAN-based SS7 SSU for your SIGTRAN-based SS7 network. See Service Controller Signaling Server Units Configuration Guide for more information.
-
Deploy and configure the proper IMSCF module variant, as described in Service Controller Modules Configuration Guide.
-
Configure routing rules in the SS7 SSU to route sessions arriving from the SS7 network to the IMSCF module that you deployed in the step 1.
In the Administration Console:
-
In the navigation tree, expand OCSB node, and then the Signaling Tier node.
-
Select SSU SS7 SIGTRAN.
-
In the Routing tab, in the left pane, click the Add button. The New dialog box appears.
-
In the Name field, enter a name for the routing rule. Click Apply. The newly created rule now appears in the rules tree in the left pane.
-
Select the newly created rule node, and then select the Incoming Routing Rules tab.
-
In the Module Instance field enter module.type@domain where module is the name of the IMSCF module that you deployed in step 2, type is the type of the IMSCF module that you deployed, and domain is the name of the domain where you deployed the module. For example, for an instance of IMSCFCAP3, imscf.IMSCFCAP3@ocsb.
-
Optionally, you can define criteria for the rule, so that the SSU SS7 route to the IMSCF application only sessions that meet the criteria. You define criteria for the rule in the Incoming Routing Rule Criteria tab.
-
-
Configure the IMSCF parameters under the Charging Service tab in the Administration Console. See the charging service configuration section for the IMSCF module you are using in Service Controller Modules Configuration Guide, for more information on setting these parameters.
Setting Up Connectivity to the OCS
Before you start, make sure that you have a detailed plan of how Service Controller connects to your OCS, including information such as connection credentials and IP addresses or host names. Ask your OCS administrator for the required information
You can connect Service Controller to the OCS through Diameter Ro.
To connect Service Controller to the IMS network:
-
Define Service Controller as a Diameter node and configure how other Diameter entities access it, as described in the discussion about creating Diameter nodes in the chapter about the Diameter SSU in Service Controller Signaling Server Units Configuration Guide.
In the Administration Console:
-
In the navigation tree, expand the OCSB node, and then the Signaling Tier node.
-
Select the SSU Diameter node.
-
In the DIAMETER tab, select the Diameter Configuration tab.
-
You can either use the default node or create a new node by clicking the Add button on the bottom of the list of existing Diameter nodes.
-
In the General tab, in the Name field, enter a unique name for the Diameter node.
-
In the Realm field, enter the realm name that other Diameter nodes use to access Service Controller.
-
In the Port field, enter the port number that signaling servers use to listen to Diameter traffic.
-
Leave the Address, Host and Target fields blank to apply the configuration to all signaling servers in the Signaling Domain and have them all provide a Diameter network channel on the same port.
-
Click Apply.
Note:
If you run multiple signaling servers on the same physical machine, you have to define each signaling server as a different Diameter node which listens on a different port. Otherwise, the Diameter SSU running on all signaling servers using the same port will result in network traffic collisions.
-
-
Deploy the IMOCF-Ro module as described in the discussion on setting up IMOCF-Ro in Service Controller Modules Configuration Guide.
In the Administration Console:
-
In the navigation tree, expand the OCSB node.
-
Expand the Processing Tier node, and then the Interworking Modules node.
-
Click IM Management.
-
In the IM Management tab, click the New button. The New dialog box appears.
-
From the Type list, select IMOCF.
-
In the Name field, enter a module instance name. For example, rimocfro_instance.
-
Click the OK button.
-
-
Configure the IMOCF-Ro module as described in the discussion on setting up IMOCF-Ro in Service Controller Modules Configuration Guide.
-
Activate the IMOCF-Ro module that you deployed and configured in steps 2 and 3.
In the Administration Console:
-
In the navigation tree, expand the OCSB node.
-
Expand the Processing Tier node and then the Interworking Modules node.
-
Click on IM Management.
-
In the IM Management tab, select the IMOCF-Ro module in the table.
-
Click the Activate button.
-
Defining a Service Orchestration Chain
To route sessions to the OCS, you have to choose the method (LSS, HSS, or static service orchestration) that you want to use for service orchestration, and then, based on your choice, define a service orchestration chain with the OCS in it.
See "Configuring Service Orchestration" for information about the different options for service orchestration, and how to configure them.