| C H A P T E R 1 |
 CLI
CLI |
This chapter describes the configuration SEFOS using the CLI. Use the CLI to configure SEFOS software from a console attached to the serial port of the switch or from a remote terminal using ssh.
SEFOS is a layer 2 and layer 3 software solution that provides support for Ethernet switching and routing. It comprises the necessary switching, management, and system level features. SEFOS provides the basic bridging functionality and also offers features such as link aggregation, GVRP/GMRP, IGMP snooping, and network access control.
The native SEFOS CLI commands are the main tools for configuring the commonly used layer 2 and layer 3 protocols and switch interface features. In addition to its native CLI commands, SEFOS provides a subset of CLI commands that adhere to the industry-standard CLI syntax. When an industry-standard command is available, the SEFOS native CLI command is shown first, with the industry-standard command shown after a slash (/).
In the following example, the set port gvrp command is the SEFOS native CLI command, and the set port gvrp enable | disable command is the industry-standard CLI command:
Use the industry-standard CLI command whenever it is available.
The SEFOS CLI supports a simple login authentication mechanism. The authentication is based on a user name and password you provide during login. The root user is created by default with password admin123.
Refer to the user’s guide and software configuration guide for details on how to start SEFOS. When SEFOS is started, you must enter the root user name and password at the login prompt to access the CLI shell:
The User EXEC mode is now available. The following section provides a detailed description of the various modes available for SEFOS.
See the table in CLI Command Modes for a quick reference of the command modes used in this document.
When you log into the device, you are in User EXEC mode. In general, User EXEC commands temporarily change terminal settings, perform basic tests, and list system information.
Privileged access is protected with a case sensitive password. The prompt is the device name followed by the hash (#) sign.
Global Configuration commands apply to features that affect the system as a whole, rather than to any specific interface.
Performs interface-specific operations.
Performs port-channel-specific operations.
Performs L3-IPVLAN-specific operations.
Performs tunnel-specific operations.
Specifies a range of interfaces, such as consecutive ports, to certain single interface commands. This mode does not specify a single port at a time.
Performs VLAN specific operations.
Modifies the operations of a terminal line. These commands are used to change terminal parameter settings line by line or a range of lines at a time.
Performs profile-specific operations.
Configures the PIM component. To enter PIM Component mode, use the Global Configuration mode ip pim component componentid command.
Configures the router protocol. To enter Router Configuration mode, use the Global Configuration mode router router-protocol command.
Configure Route Map parameters. To enter Router Map Configuration mode, use the Global Configuration mode route-map 1-20 [{permit | deny}] [1-10] command.
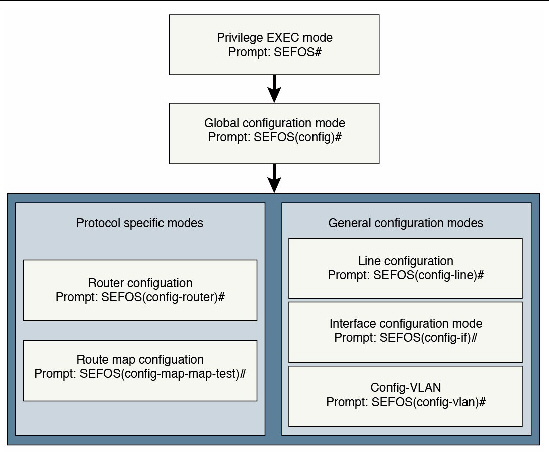
The following is a flowdiagram that shows the hierarchy of accessing command modes.

Copyright © 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.