









|
The WLS-VE ISO image is the boot image for WLS-VE. It contains the LiquidVM and WLS-VE classes that run on hypervisor software and host your Java applications. To give ESX Server access to these classes, after you install WLS-VE, copy the ISO image to a datastore on each ESX Server that will run WLS-VE. BEA recommends that you copy to a datastore that is on the ESX Server's SAN. (See Figure 4-1.) Copying to a local disk may disable some VMware functionality, such as VMotion. Datastores on NFS will experience degraded performance when booting WLS-VE.
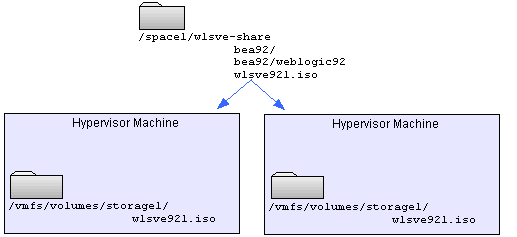
To copy the WLS-VE ISO image to a datastore on local disk or SAN, use the following secure copy (scp) command syntax:scp source-file username@esxhost:/vmfs/volumes/datastore/path/
source-file is the relative or absolute path and file name of the WLS-VE ISO image file.username is the name of a user in your network who has write privileges on the hypervisor host machine.esxhost is the name of an ESX Server host./vmfs/volumes/ is the directory within the VMware file system under which ESX Server stores datastores.datastore is the name of a datastore.path is one or more optional directory levels.| Note: | The Linux operating system includes an scp client. For Windows, you can install (or download for free) third-party utilities that include scp clients. |
Remember the pathname that you specify. When you use the LiquidVM Configuration Wizard to configure virtual machines, you specify this location. Note that the syntax in ESX Server for specifying this path is:[datastore] /path/file
For example, use the following scp command to copy the WLS-VE ISO image from the current directory to the default storage1 datastore (VMware creates the storage1 datastore when you install ESX Server):
scp wlsve921.iso myusername@myESXHost:/vmfs/volumes/storage1/
With the above example, the path name that you specify in the LiquidVM Configuration Wizard is:[ storage1 ] /wlsve921.iso


|