


|

|
|
|
|
Overview of Personalization Development
WebLogic Personalization Server provides developers with the ability to create personalized applications for e-commerce Web sites. This topic provides a broad overview of personalization development for Java and JSP developers.
This topic includes the following sections:
Personalization Server Run-Time Architecture
The WebLogic Personalization Server run-time architecture is designed to support a variety of personalized applications. These applications can be built on the portal/portlet infrastructure, on the tags and EJBs supplied by the Advisor, and on select tags and EJBs supplied by other personalization server components.
The following high-level architecture picture may be used to visualize the relationships between the components.
Figure 1-1 WebLogic Personalization Server High Level Architecture
The personalized application is one built by the developer to use the personalization components. It may consist of a set of traditional JSP pages or servlets and/or code that accesses EJB objects directly. Advisor The Advisor component is the primary interface to the most common operations that personalized applications will use. It provides access through tags or a single EJB session bean. Specific functionality provided by the Advisor includes classifying users, selecting content based on user properties, and querying content management directly. The Advisor uses the Foundation, User Management, Rules Service, and Content Management components. User Management The User Management component supports the run-time access of users, groups, and the relationships between them. The notion of property sets is used by the user and group property access scheme. This component is set up using the User Management Administration tools and supports access via JSP tags or direct access to EJB objects. A Unified User Profile may be built by the developer, extending the base user profile, to provide custom data source access to user property values. Content Management The Content Management component provides the run-time API by which content is queried and retrieved. The functionality of this component is accessible via tags. The content retrieval functionality is provided using either the provided reference implementation or third-party content retrieval products. Rules Management The Rules Management component is the run-time service that runs the rules that are built in the E-Business Control Center. Foundation Classes and Utilities The Foundation is a set of miscellaneous utilities to aid JSP and Java developers in the development of personalized applications using the WebLogic Personalization Server. Its utilities include JSP files and Java classes that can be used by JSP developers to gain access to functions provided by the server and helpers for gaining access to Advisor services.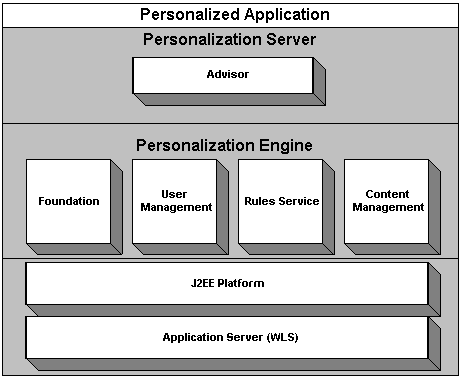
JSP Tags
The JSP tags included with WebLogic Personalization Server (Table 1-1) allow developers to create personalized applications without having to program using Java.
Integration of External Components
A range of external components either come already integrated into the WebLogic Personalization Server, or can be integrated easily by a developer as extensions to the core components. A specific set of components that are known to be widely useful are described in Table 1-2. Other custom component integrations are possible given the JSP and EJB basis for the WebLogic Personalization Server, but the entire range of possibilities is not addressed here.
Support for Native Types
WebLogic Personalization Server supports the native types shown in Table 1-3.
Any property can be a multi-value of a specific single native type as well. This is implemented as a java.util.Collection. Comparators for multi-values are contains and containsall, although the rules development tool will only allow the use of contains. The values possible as part of a multi-value may be restricted to a valid set, using the Property Set management tools.

|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2001 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|