







|
When you move to a production environment, you must configure Autonomy to match the portal environment you use.
This involves editing the configuration files for the search components you are using, deploying the Autonomy Service Dashboard, and configuring Autonomy fetches to search for information according to parameters you set.
| Note: | The Autonomy documentation is included in your WebLogic Portal installation directory at: //WebLogic_Home/cm/thirdparty/autonomy-wlp10/common/docs/*.* |
The tasks covered in this chapter assume a typical Autonomy configuration running in a WebLogic Portal cluster. Consult the Autonomy documentation if you want to create a more complex configuration, such as running HTTPFetch on a separate server.
Figure 4-1 provides an example of a typical production environment.
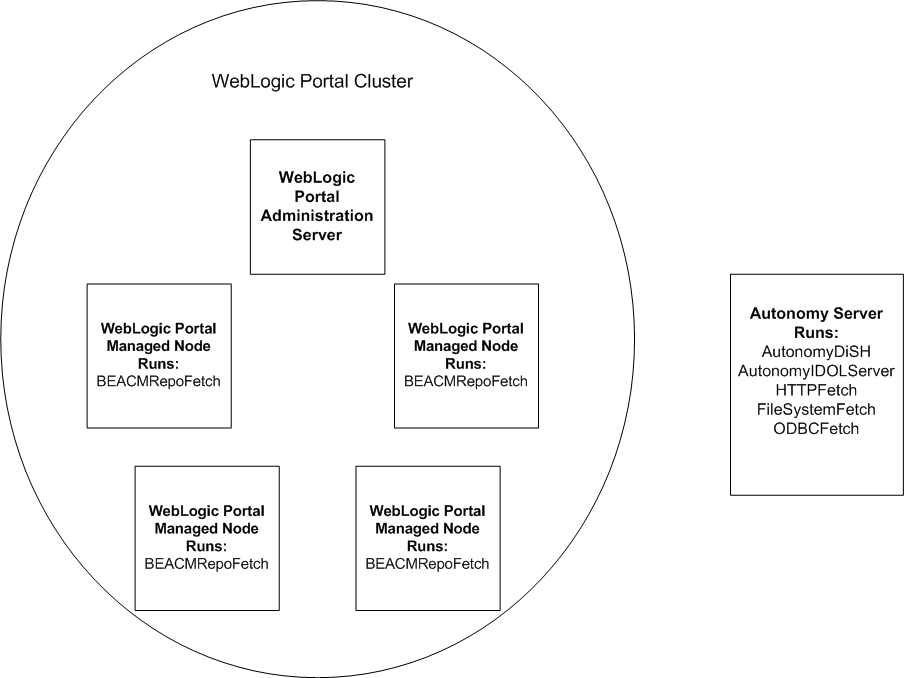
This chapter discusses the following topics:
You need to install the appropriate Autonomy engines for your server’s operating system.
When you installed WebLogic Portal, the Autonomy engine for the target operating system was included. If you need a version of Autonomy for a different operating system than the operating system on which you installed WebLogic Portal, you will need to download and install WebLogic Portal onto the operating system for which you need Autonomy. You can then retrieve the respective operating system files for Autonomy.
| Note: | Remember that due to licensing restrictions, you can only run one Autonomy IDOL Server. |
For example, if you downloaded and installed WebLogic Portal on a Windows server, the Windows version of Autonomy was included in the download. If you want to install Autonomy on a Linux server, you need to download and install the Linux version of WebLogic Portal in order to have the correct version of Autonomy for a Linux machine.
WebLogic Portal makes available versions of Autonomy that are compatible with operating systems that WebLogic Portal also supports. However, you may run Autonomy on separate server that uses an operating system that WebLogic Portal does not support. For more information about the supported configurations for Autonomy, see the Autonomy documentation.
| Note: | To obtain Autonomy files for a non-WebLogic Portal supported operating system, contact your Autonomy representative. For more information about configuring Autonomy on a non-WebLogic supported operating system, see Configuring the BEA Content Management Fetch When Using a Non-WebLogic Portal Supported Operating System. |
WebLogic_Home/cm/thirdparty/autonomy-wlp10/operatingsystem
This section explains how to update the default Autonomy license with a production license. The default license allows 10,000 documents to be indexed, while the production license allows 500,000 documents to be indexed.
To update your Autonomy license:
autonomy.cmd script with the stop parameter. See Starting the Autonomy Services. IDOLserver/DiSH directory, do the following: IDOLserver/IDOL directory, do the following: IDOLserver/DiSH/licensekey.dat file to prevent overwriting it. licensekey.dat) into IDOLserver/DiSH. license.log files in the above directories and verify that the license now allows 500,000 documents, rather than the evaluation license limit of 10,000 documents. To do this, search in IDOLserver\IDOL\logs\content_application.log for the string “This license allows 500000 documents to be indexed”.
You need to modify your Autonomy configuration to match your production environment and the parameters of your cluster. This includes modifying the respective configurations of the search tools you are using to account for security concerns and their network location.
You also need to configure the types of information you want to include in your searches.
Table 4-1 lists the location of the configuration files you need to modify.
This section includes the following topics:
The Intelligent Data Operating Layer (IDOL) server is responsible for indexing content as well as processing queries. For more information about the IDOL server, see the Autonomy IDOL Server documentation.
To configure the IDOL server for your production environment modify the AutonomyIDOLServer.cfg file. The file is located //autonomy/IDOLserver/IDOL/AutonomyIDOLServer.cfg.
To configure the Autonomy IDOL server:
AutonomyIDOLServer.cfg file in a text editor.[License] section, edit the LicenseServerACIPort to match the port on which DiSH is running, if you changed this port.[Service] section, edit the ServicePort if needed. This setting must match the corresponding setting in the autonomyDiSH.cfg.[Server] section, [Paths] section, edit the Modules and TemplateDirectory to point to the location of these directories on the target system. These must be absolute paths. [NT_V4] Library). These must be absolute paths. [Database] section, create and remove Autonomy databases as required for your needs. Consult the Autonomy documentation for managing databases. The Distributed Services Handler (DiSH) is used to manage Autonomy components. You can access DiSH functions through the Autonomy Service Dashboard or use Autonomy’s ACI interface. For more information about the Autonomy DiSH, see the Autonomy DiSH documentation.
To configure DiSH, you can use a text editor to modify the autonomyDiSH.cfg file. The autonomyDiSH.cfg file is located in the //autonomy/IDOLserver/IDOL/AutonomyIDOLDiSH.cfg directory.
autonomyDiSH.cfg file in a text editor.[Service] section, edit the ServicePort setting if needed to avoid port conflicts. [Server] section, edit the following:[Email] section, make modifications as defined by your company’s SMTP setup. [ChildServices] section, remove the setting for the BEACMRepoFetch service. [BEACMRepoFetch] section. [IDOLServer], [HTTPFetch] and [FileSystemFetch] sections, modify each path to ensure the executable files use the location on the target server. These paths must be absolute. Service Port or ACI port (or plan on doing so in the agentstore.cfg file), you need to adjust these settings to match. Agents provide the facilities to find and monitor information from a configurable list of internet and intranet sites, news feeds, chat streams and internal repositories that you want to enable your portal users to search.
For more information about using agents, see the Autonomy IDOL Server Guide.
To configure the Agentstore for your cluster, edit the agentstore.cfg file. The file is located //IDOLserver/IDOL/agentstore/agentstore.cfg.
HTTP Fetch is responsible for crawling specified websites and passes the content to the IDOLServer for indexing.You need configure this fetch and create HTTP fetch jobs that you need.
You do this by editing the HTTPFetch.cfg file. It is located //autonomy/HTTPFetch/HTTPFetch.cfg
HTTPFetch.cfg in a text editor.[Service] section determines which machines are permitted to use and control the HTTPFetch service via the service port. Modify the port and client security control as required.| Note: | If you modify the port settings in this file, you need to update the HTTPFetch port settings in the AutonomyDiSH.cfg file. |
[Default] section contains the default settings that apply to all the jobs that you define in [Spider]section. If you changed the IndexPort in the AutonomyIDOLserver.cfg file, you need to modify the IndexPort setting to match. File System Fetch polls specified areas of a filesystem and, when content changes are found, imports the content and passes the content to the IDOLServer for indexing.
To control how files are imported from an internal location (for example, from a computer on your network), you need to configure File System Fetch and then create the fetch jobs you need.
The File System Fetch configuration file is located: //autonomy/FileSystemFetch/FileSystemFetch.cfg
Use a text editor to edit the FileSystemFetch.cfg file to match your production environment.
To configure File System Fetch:
[Server] and [Service] sections to change ports, if needed, and to control security. If you modify the port information in this file, you need to also update the settings related to File System Fetch in the AutonomyDiSH.cfg file. [Default] section, modify the IndexPort to match the IndexPort set in AutonomyIDOLserver.cfg, if necessary.If deploying WebLogic Portal in a cluster environment, you need to ensure that each machine in your cluster can access the content indexed by File System Fetch, see Staging File System Fetch within a WebLogic Cluster.
To set up full-text search for your BEA repositories, you must configure the BEA Content Management fetch and then enable your BEA repositories for full-text search.
This section includes the following topics:
The BEA content management fetch enables full-text search for BEA repositories. For each managed server in your WebLogic Portal cluster, you need to configure the BEA content management fetch.
To configure the content management fetch:
CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION and assign it a value of minimal. BEACMRepoFetch.cfg file located in //operating_system_directory/internal/BEACMRepoFetch/BEACMRepoFetch.cfg. This file configures the settings for the full-text search of BEA repositories.[Server] and [Default] settings to change port numbers and client security as required. [Default] DreHost settings to point to the hostname or IP address of the server which is running the IDOLServer.[Default] IndexPort to match the IndexPort setting in the AutonomyIDOLServer.cfg file on the remote server. | WARNING: | Do not modify any other settings within this file. |
After you have configured the BEA Content Management Fetch, you need to enable your BEA repositories to take advantage of full-text search. This ensures your BEA repositories can locate the Autonomy IDOL server.
This section includes the following topics:
You need to define Autonomy properties for your BEA repositories within the Virtual Content Repository using the Portal Administration Console. These properties ensure that your BEA repositories can locate the Autonomy services.
Table 4-2 lists the Autonomy properties you need to add.
You need to set this property ONLY if you are using using a shared drive to index content. For more information, see Configuring the BEA Content Management Fetch When Using a Non-WebLogic Portal Supported Operating System.
When setting this property, you must use the system default file delimiter or the data will not be properly indexed, as shown in the following examples:
|
|||
|
This value needs to match the
[Server]IndexPort setting in the AutonomyIDOLServer.cfg file. See Configuring the Autonomy IDOL Server for information about this file.
|
|||
|
This value needs to match the
[Server]Port setting in the AutonomyIDOLServer.cfg file. See Configuring the Autonomy IDOL Server for information about this file.
|
|||
| Note: | After you make any changes to repository properties, Portal Administration Console users must log out and log back in to view the changes. |
To add a property to a repository:
A summary of the new repository information is displayed in the Summary tab.
You need to ensure that all full-text functions are enabled for each BEA repository you want to enable to use full-text search.
Table 4-3 lists the advanced full-text search repository properties and how they are used.
To edit full-text search repository properties:
Your modifications display in the Advanced section of the Summary page.
| Note: | After you disconnect a repository or make any changes to repository properties, Portal Administration Console users must log out and log back in to view the changes. |
If you run Autonomy on an operating system that is not also supported by WebLogic Portal, you must configure BEA content management search differently. You must create a shared filesystem that can be written to by WebLogic Portal and also accessed by Autonomy’s server.
Figure 4-2 provides an example of a remote Autonomy installation using a shared file system.
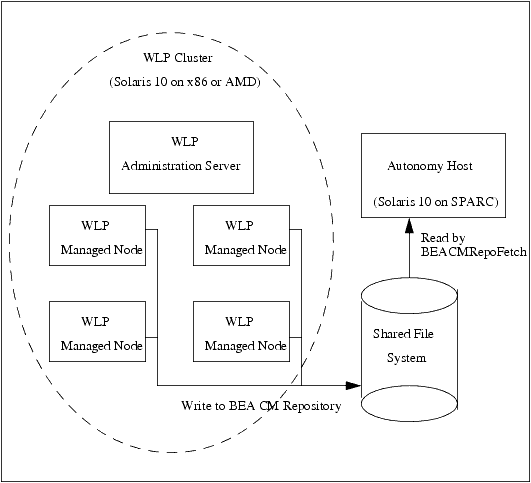
To configure BEA Content Management search:
shared_drive is the name of your shared drive.shared_drive. shared_drive.| Note: | Mount shared_drive with the same exact mapping on each managed server. |
CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION environment variable to none. This prevents Autonomy from starting the content management search.search.staging.area with a value of shared_drive. For more information on setting other Autonomy properties, see
Staging File System Fetch within a WebLogic Cluster
.WebLogic_Home/cm/thirdparty/autonomy-wlp10/<operating_system_directory>/internal/BEACMRepoFetch/BEACMRepoFetch.cfg file to point to the shared_drive you have created. This will ensure that BEA content gets indexed.autonomy.sh or autonomy.cmd file in WebLogic_Home/cm/thirdparty/autonomy-wlp10 for a sample start script.
When you deploy WebLogic Portal in a cluster environment, each machine in the cluster must be able to access information and content that is indexed by Autonomy fetches. For example, both BEA repositories and Autonomy’s File System Fetch use filesystems to store indexed content. You should configure each machine in your cluster to be able to access these filesystems.
| Note: | The BEA Content Management Fetch does not require these steps, see Setting up BEA Content Management Search |
File System Fetch is used to index content that resides in a filesystem. When indexing, unless otherwise configured, the DREREFERENCE property is set to the complete path of the file. Therefore, with default queries, the link to return the actual content (file) will be the path to the file. Within a server cluster, each node in the cluster must have access to the filesystem on which the document resides.
| Note: | When returning query results to the browser and displaying a link to access/download the file, pass the DREREFERENCE property (which will contain the fully qualified path/file name) through a servlet which will stream the file to the browser. For more information about indexing and queries, see the Autonomy IDOL Server Guide and the Autonomy JavaDoc. |
You must configure the start script that is used to start Autonomy services on your server. You can either copy these to your target server and modify as required, based on your target directory or you can create similar scripts to meet your needs.
The Autonomy start script depends on two environment variables that should be set on your portal domain server: WL_ and CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION.
You call this script with either start or stop as a parameter.
autonomy.cmd/sh files that reside in the //WebLogic_Home/cm/thirdparty/autonomy-wlp10 directory. Listing 4-1 shows an example script.AutonomyDiSH.exe is started.setlocal
if "%WL_%" == "" goto :NO_WL_
if "%1" == "" goto :USAGE
cd %WL_%\cm\thirdparty\autonomy-wlp10\win32
if "%1" == "start" (
echo Cleaning up license and uid files
rmdir /s /q HTTPFetch\license >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\DiSH\license >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\content\license >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\agentstore\license >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\category\license >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\community\license >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q HTTPFetch\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q internal\BEACMRepoFetch\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\DiSH\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\content\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\agentstore\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\category\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q IDOLserver\IDOL\community\uid >nul 2>&1
rmdir /s /q FileSystemFetch\uid >nul 2>&1
echo Starting Autonomy with CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION = %CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION%
if "%CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION%" == "full" (
if not exist IDOLserver\DiSH\AutonomyDiSH.exe (
@echo Unable to locate the Autonomy DiSH executable. Cannot start the search engine.
goto :_the_end
)
cd IDOLserver\DiSH
%WL_%\server\bin\beaexecg.exe -hidewindow -command:"AutonomyDiSH.exe"
@echo Autonomy Distributed Search Handler engine started.
)
if "%CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION%" == "minimal" (
if not exist internal\BEACMRepoFetch\BEACMRepoFetch.exe (
@echo Unable to locate the BEACMRepoFetch executable. Cannot start the search engine.
goto :_the_end
)
cd internal\BEACMRepoFetch
%WL_%\server\bin\beaexecg.exe -hidewindow -command:"BEACMRepoFetch.exe"
@echo Autonomy BEACMRepoFetch engine started.
)
goto :_the_end
)
if "%1" == "stop" (
@REM taskkill depends on the path to WBem. Adding it here
@REM just to ensure that it exists on the system path.
set PATH=%SystemRoot%\System32\Wbem;%PATH%
if "%CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION%" == "minimal" (
taskkill /F /T /IM BEACMRepoFetch* >nul
@echo Autonomy BEACMRepoFetch engine stopped.
)
if "%CONTENT_SEARCH_OPTION%" == "full" (
taskkill /F /T /IM AutonomyDiSH* >nul
@echo Autonomy processes stopped.
)
goto :_the_end
)
goto :USAGE
:NO_WL_
@echo The environment variable WL_ is not set. Cannot start Autonomy DiSH.
goto _the_end
:USAGE
@echo Usage: "autonomy.cmd [start|stop]"
pause
goto _the_end
:_the_end
endlocal
ps command to view a list of services that are currently running. The following services should be running:
The Autonomy Service Dashboard is an stand-alone front-end web application that allows administrators to manage all Autonomy modules and child services running locally or remotely.
The Dashboard communicates with one or more Autonomy Distributed Service Handler (DiSH) modules that provide the back-end process for monitoring and controlling all the Autonomy child services, such as fetches.
You deploy the Autonomy Service Dashboard as a portal application within your enterprise application using the WebLogic Server Console. Before deploying the dashboard, you must modify the configuration to match your production environment.
For complete documentation on how to use the Autonomy Service Dashboard, see the Autonomy DiSH documentation.
This section includes the following topics:
Before you deploy the Autonomy Service Dashboard, you need to edit the location configuration to match the new deployment location. The default location that is used is: \\WebLogic_Home\cm\thirdparty\autonomy-wlp10\common\lib\.
To prepare the Autonomy Service Dashboard for installation:
autonomyservicedashboard.cfg to its new location.web.xml file for the Autonomy Service Dashboard.c:/temp/working autonomyservicedashboard.war to your working directory.autonomyservicedashboard.war.WEB-INF/web.xml file by editing the <context-param> value to match the new location of the autonomyservicedashboard.cfg file. The default location is //WebLogic_Home/cm/thirdparty/autonomy-wlp10/common/lib.C:/working/META-INF/web.xml file.C:/temp/working directory, re-zip or re-compress the autonomyservicedashboard.war file. Overwrite the existing autonomyservicedashboard.war file with the new file of the same name that contains your modified web.xml file. Be sure to keep the files in their original directory structure, including the META-INF directory. autonomyservicedashboard.war file you just created back to the location where you want to locate the Autonomy Service Dashboard. For example, \\WebLogic_Home\portal\thirdparty\autonomy-wlp10\common\lib\You should deploy the Autonomy Service Dashboard in the same domain as is used by your portal cluster. However it needs to be deployed as a stand-alone application rather than part of your portal application.
| Note: | You can also deploy the Autonomy Service Dashboard into another web application container, such as Tomcat. |
After you deploy the Autonomy Service Dashboard, you can use the default username of admin and the default password of admin to log in.
To deploy the Autonomy Service Dashboard:
autonomyservicedashboard.war file and select it.http://localhost:7001/autonomyservicedashboard. admin) and password (admin), log in to the Autonomy Service Dashboard.autonomyDiSH.cfg file in Configuring the Autonomy DiSH.For complete documentation on how to use the Autonomy Service Dashboard, see the Autonomy DiSH documentation.


|