









|
TIBCO® Rendezvous™ (a product from TIBCO: www.tibco.com) enables exchange of data across applications running on distributed platforms. TIBCO Rendezvous (TIBCO RV) Control in WebLogic Integration™ enables seamless connection to, and transfer of data using the Rendezvous daemon. It enables communication via many of the features provided by the TIBCO Rendezvous product, including Certified Message Delivery, Distributed Queue and so on. The sending and receiving applications can be on multiple platforms, as long as the Rendezvous daemon is running on the host machine, or is remotely accessible to the host.
| Note: | The TIBCO RV control is available in BEA Workshop for WebLogic Platform only for licensed users of WebLogic Integration. |
Use of the TIBCO RV control and event generator with BEA WebLogic Integration in no manner confers or grants the right to use TIBCO Rendezvous including "dynamic libraries". In order to use such TIBCO products, the user of the TIBCO RV control and event generator must obtain a valid license from TIBCO. See http://www.tibco.com for information on how to obtain a licensed copy of Rendezvous.
The TIBCO RV control enables WebLogic Integration business processes to send and receive messages in the Rendezvous environment. In this environment, the messages are conveyed using Rendezvous daemon (rvd) and Rendezvous agent (rva) transports.
Using the TIBCO RV control, you can send and receive messages in XML, String and TIBCO proprietary Rendezvous Message (TibrvMsg) formats. You can specify TIBCO RV control properties while configuring Rendezvous control or dynamically at run time. Following are some of the other features of TIBCO RV control:
The TIBCO RV control complements the other controls provided in WebLogic Integration, and can be used with other WebLogic Integration business processes. To learn more, see Using Controls in Business Processes in Using Integration Controls.
The TIBCO RV event generator listens on a subject, and publishes the received messages to the WebLogic Integration message broker channels. For more information, see the TIBCO Rendezvous Event Generator.
You can create and configure a new instance of the TIBCO RV control and add it to your business process. This topic includes the following sections:
To add a new TIBCO RV control to WebLogic Integration, perform the following steps:
| Note: | If the Data Palette view is not visible in BEA Workshop for WebLogic Platform, click Window Show View Show View Data Palette from the menu bar. Data Palette from the menu bar. |
The Insert control: Tibco dialog box appears.
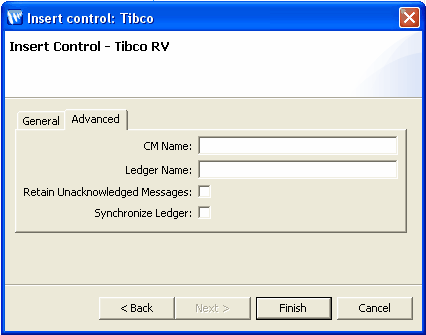
beaserv1:1589 where beaserv1 is the remote host name and 1589 is the port id. To specify certified messaging settings for the TIBCO RV control, perform the following tasks in Step 3 of the Insert Control - TIBCO RV dialog; the Advanced Settings tab, (see Figure 14-1) below:
When you create a new instance of the TIBCO RV control, you create a new Java file in your project. The contents of the TIBCO RV control's file depends on the selections made in the Insert Control - TIBCO RV dialog.
The two examples in this section depict control files created for a certified message and a non-certified message.
package processes;
import com.bea.control.*;
import com.bea.xml.XmlCursor;
import com.bea.control.tibrv.*;
import javax.resource.ResourceException;
import com.bea.xml.XmlObject;
/*
* A custom Tibrv control.
*/
/**
* @jc:Transport service="7500" //<service name used by the TIBCO daemon for conveying messages>
network="beaserv1" //<network with which the TIBCO daemon will communicate>
deamon="beasever1:7500 " //<location where the TIBCO daemon is running>
* @jc:UseCM usecm="true" //<indicates certified messaging enabled>
* @jc:CMTransport cmname="cmname.new" //<the certified message name>
ledgername="C:\TIBCO\TIBRV\Ledger.txt" //<name and location of the ledger file>
requestold="true" //<indicates any unacknowledged messages will be stored>
syncledger="true"//<performs synchronized update of the ledger file>
*/
public interface sendReq extends TibcoRV, com.bea.control.ControlExtension
{
/*
* A version number for this control. This will be incremented in new versions of
* this control to ensure that conversations for instances of earlier
* versions were invalid.
*/
static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public void addListenerForCM(String cmName, String subject);
}
package processes;
import com.bea.control.*;
import com.bea.xml.XmlCursor;
import com.bea.control.tibrv.*;
import javax.resource.ResourceException;
import com.bea.xml.XmlObject;
/*
* A custom Tibrv control.
*/
/**
* @jc:Transport service="7500" //<service name used by the TIBCO daemon for conveying messages>
network="beaserv1" //<network with which the TIBCO daemon will communicate>
deamon="beasever1:7500 " //<location where the TIBCO daemon is running>
* @jc:UseCM usecm="false" //<indicates certified messaging disabled>
* @jc:CMTransport cmname=""
ledgername=""
requestold="false"
syncledger="false"
*/
public interface sendReq extends TibcoRV, com.bea.control.ControlExtension
{
/*
* A version number for this control. This will be incremented in new versions of
* this control to ensure that conversations for instances of earlier
* versions were invalid.
*/
static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
}
This section provides details on construction of a subject name. Each message in the TIBCO Rendezvous environment contains a subject name. An application creates a message and sends it with a subject through the Rendezvous environment. Applications at the other end accept the message by listening on the subject.
Subject name definitions have basic restrictions, for example, its length, structure and usage of special characters. System designers and developers can set the conventions for subject names keeping in mind the following:
| Caution: | The restrictions and conventions are implemented by TIBCO Rendezvous and information in this section is indicative only. Refer TIBCO Rendezvous product documentation for more up-to-date information on restrictions, guidelines and examples. |
| Caution: | http://www.tibco.com |
You can send and receive messages with TIBCO RV control using any one of sendMessage, sendReply or sendRequest functions, and the TIBCO Event Generator, respectively. Messages can be in the form of Rendezvous proprietary data format, string and XML.
This section provides information on the various functions available for sending messages. To send a message, select a function based on the data type of the message that you want to send. All these functions can send reliable and certified messages, as defined while creating the control. Certified message functions will return sequence numbers while reliable message functions will return zero.
The sendRequest function creates a listener that keeps listening for messages to the reply subject and hence, it does not require explicit creation of listeners. The function returns an instance of the TibrvMsg, which can be used for sending replies.
The sendRequest and sendReply functions are often used together as pairs. An example of such an implementation is:
replymsg = sendRequest(msg, "send.Subject","reply.Subject",5.0);
sendReply( replyMsg, newMsg);
Used to send a message via RVDTransport, or a labelled message via CMTransport.
public long sendMessage(TibrvMsg msg , String subject, double timeout)
msg: the message that needs to be sent
subject: subject of the message
timeout: time limit for delivery of the message
Used to send a string message via RVDTransport, or a labelled string message via CMTransport.
public long sendMessageAsString(String msg , String fieldName ,String subject, double timeout)
msg: the string message that needs to be sent
fieldName: name of the TibRV field used to send the payload
subject: subject of the message
timeout: time limit for delivery of the message
Used to send an XML message via RVDTransport, or a labelled XML message via CMTransport.
public long sendMessageAsXML(XmlObject msg ,String fieldName ,String subject, double timeout)
msg: the XML message that needs to be sent
fieldName: name of the TibRV field used to send the payload
subject: subject of the message
timeout: time limit for delivery of the message
Used to send a request message via RVDTransport, or a labelled request message via CMTransport and wait for a reply.
public TibrvMsg sendRequest(TibrvMsg msg, String sendSubject, double timeout)
msg: the request message that needs to be sent
sendSubject: the send subject of the message
timeout: amount of time to wait for the reply
Used to send a request string message via RVDTransport, or a labelled request string message via CMTransport and wait for a reply.
public TibrvMsg sendRequestAsString(String msg, String fieldName, String sendSubject, double timeout)
msg: the request string message that needs to be sent
fieldName: name of the TibRV field used to send the payload
sendSubject: subject of the message
timeout: amount of time to wait for the reply
Used to send a request XML message via RVDTransport, or a labelled request message via CMTransport and wait for a reply.
public TibrvMsg sendRequestAsXML(XmlObject msg, String fieldName,String sendSubject, double timeout)
msg: the request XML message that needs to be sent
fieldName: name of the TibRV field used to send the payload
sendSubject: subject of the message
timeout: amount of time to wait for the reply
Used to send a reply via RVDTransport, or a labelled reply via CMTransport.
public long sendReply(TibrvMsg replyMsg, TibrvMsg sendMsg, double timeout)
replyMsg: the reply message
sendMsg: the request message
timeout: time limit for delivery of the message
Used to send a string type reply via RVDTransport, or a labelled string type reply via CMTransport.
public long sendReplyAsString(TibrvMsg replyMsg, String sendMsg, String fieldName, double timeout)
replyMsg: the reply string message
sendMsg: the request string message
fieldName: the name of the TibRV field used to send the payload
timeout: time limit for delivery of the message
Used to send an XML type reply via RVDTransport, or a labelled XML type reply via CMTransport.
public long sendReplyAsXML(TibrvMsg replyMsg, XmlObject sendMsg, String fieldName, double timeout)
replyMsg: the reply XML message
sendMsg: the request XML message
fieldName: the name of the TibRV field used to send the payload
timeout: time limit for delivery of the message
Used to set the character encoding for converting between Java Unicode strings and wire format strings.
void setStringEncoding(java.lang.String encoding) throws java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
You can include the following two functions when using the CMTransport.
Used to define a callback method to receive confirmation for message sent. It can only be used with sendMessage or sendReply functions. TIBCO RV control subscribes to two confirmation advisories: _RV.INFO.RVCM.DELIVERY.COMPLETE.> and _RV.ERROR.RVCM.DELIVERY.FAILED.>.
| Note: | A TIBCO RV control with certified messaging enabled must have an onCMReceipt() method implemented in the process definition. Without this, a runtime exception will be thrown. |
public void onCMMessageReceipt(byte[] data);
Used to pre-register an anticipated listener. When a sending application pre-registers listeners, Rendezvous will store all outbound messages in the sender's ledger. So, when the listener requests certified delivery, it receives the backlogged messages. This function is the same as the addListener method in Rendezvous. Refer TIBCO Rendezvous product documentation for more details.
void addListenerForCM(String cmName, String subject);
The following procedure in an example that describes how to add any TIBCO RV control sendMessage function to a business process.
sendMessage function. sendMessage function. TibrvMsg format. See sample code below: // Generating a Tibrv message from the string data format
public void perform() throws Exception
{
com.tibco.tibrv.TibrvMsg tibrvMsg = new com.tibco.tibrv.TibrvMsg();
tibrvMsg.update(TibcoField,TibcoMessage);
}
sendMessage function from the Controls tab in the Data Palette into your business process, just below the Client Request node. sendMessage function node. From the Select variables to assign drop-down list, assign the variables that you created in the Receive Data tab of the Client Request node, to the corresponding parameter of the sendMessage function listed in the Control Expects column. sendMessage function note. From the Select variables to assign drop-down list, create a new variable in which to store the sequence number provided by the sendMessage function.
You can use similar steps to send messages using the sendMessageAsString or the sendMessageAsXML functions. Ignore step 9 above as these functions do not require conversion to TibrvMsg format.
To receive messages, use the TIBCO RV Event Generator utility. For details, refer to TIBCO Rendezvous Event Generator.
You can change the TIBCO RV control properties dynamically at runtime. The TIBCO RV control properties that you can modify are specified in the TibRVDynamicPropertiesDocument type document. This document conforms to the TIBCO RV Control Dynamic Properties schema, which is available in the TibRVSchemas.jar file.
The following is an example on how to change properties dynamically.
TibRVDynamicPropertiesDocument.setXMLProperties function in the business process) using the properties you specified in the TibRVControlDynamicPropertiesDocument.TibRVControlDynamicPropertiesDocument as input. <?xml version="1.0"?>
<xs:schema
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/TibRVControlDynamicProperties.xsd"
targetNamespace="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/TibRVControlDynamicProperties.xsd"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="TibRVDynamicProperties">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="service" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="network" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="daemon" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="useCM" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="cmName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="ledgerName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="requestOld" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="syncLedger" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
The following is a sample TIBCO RV Control document. You must provide this document at runtime when you execute your business process:
<tib:TibRVDynamicProperties>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:service>7500</tib:service>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:network>beaserv1</tib:network>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:daemon>beaserv1:7500</tib:daemon>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:useCM>true</tib:useCM>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:cmName>cmname.runtime</tib:cmName>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:ledgerName>c:/file.txt</tib:ledgerName>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:requestOld>false</tib:requestOld>
<!--Optional:-->
<tib:syncLedger>false</tib:syncLedger>
</tib:TibRVDynamicProperties>


|