









|

| Note: | The MQSeries control is available in BEA WorkSpace Studio only for licensed users of WebLogic Integration. |
MQSeries is a middleware product from IBM that runs on multiple platforms. It enables message transfer between applications; the sending application PUTs a message on a Queue, and the receiving application GETs the message from the Queue. The sending and receiving applications do not have to be on the same platform, and can execute at different times. MQSeries manages all the storage, logging and communications details required to guarantee delivery of the message to the destination queue.
Use of the MQSeries control and event generator with BEA WebLogic Integration in no manner confers or grants the right to use MQSeries control including "dynamic libraries". In order to use such IBM products, the user of the MQSeries control and event generator must obtain a valid license from IBM.
The MQSeries control enables WebLogic Integration business processes to send and receive messages using MQSeries queues. Using the MQSeries control, you can send and receive Binary, XML, and String messages. You can specify MQSeries control properties while configuring the MQSeries control or dynamically at run time. You can also set the transaction boundaries for the MQSeries business operations.
The MQSeries control complements the other controls provided in WebLogic Integration, and can be used with other WebLogic Integration business processes. For information on how to add control instances to business processes, see Using Controls in Business Processes.
The MQSeries Event Generator can be used for polling specific MQSeries queues for incoming messages. For more information, see Using the MQSeries Event Generator.
Before adding the MQSeries control to the BEA WorkSpace Studio, you must complete the following tasks:
com.ibm.mq.jar file from the MQSeries client installation to the system environment CLASSPATH variable.apacheLog4jCfg.xml file:
<category name=”com.bea.control.MQControl”>
<!-- NOTE: DO NOT CHANGE THIS PRIORITY LEVEL W/O WLI DEV APPROVAL -->
<!-- Debug-level log information is frequently the only tool available to diagnose failures! -->
<priority value="warn"/>
<appender-ref ref="SYSLOGFILE"/>
<appender-ref ref="SYSERRORLOGFILE" />
</category>
The MQSeries control uses the Workshop debugger for logging messages.
| Note: | To change the log level, refer to the control documents. |
com.ibm.mq.jar file from the MQSeries client installation into the Libraries folder of the application where the MQSeries control is used.Now you can add a new MQSeries control to send and receive messages.
You can create and configure a new instance of the MQSeries control and add it to your business process. This topic includes the following sections:
To add a new MQSeries control to WebLogic Integration, perform the following steps:
 on the Data Palette and from the drop-down list choose Integration Controls to display the list of controls used for integrating applications.
on the Data Palette and from the drop-down list choose Integration Controls to display the list of controls used for integrating applications.| Note: | If the Data Palette view is not visible in BEA WorkSpace Studio, click Window > Show View > Data Palette from the menu bar. |
The Insert Control: MQSeries dialog box is displayed (see Figure 9-1).
| Note: | If you are creating the control for the first time, the Locate the MQ Series jar file dialog box will is displayed. Browse for the com.ibm.mq.jar file located in the MQ series installation folder and click Open. |
To specify connection settings for the MQSeries control, perform the following tasks (see Figure 9-2):
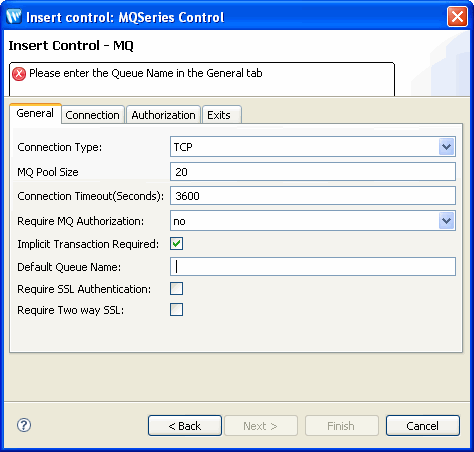
To specify TCP/IP settings for the MQSeries control, perform the following tasks, in the Connection tab (see Figure 9-3):
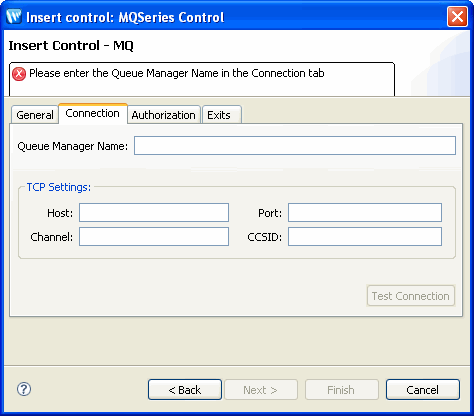
| Note: | Specify TCP/IP settings only if you have set your connection type to TCP. |
| Note: | The TCP Setting of Connection tab is enabled only when the TCP connection mode is selected |
| WARNING: | Do not click the Test Connection button when selecting the SSL option for your control. Clicking this button will cause your connection to fail. |
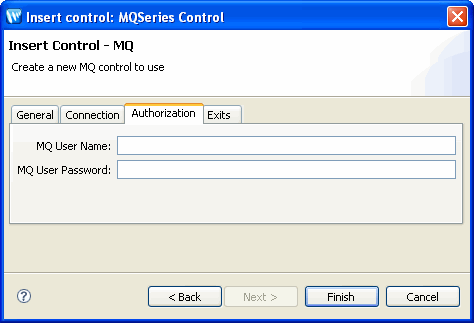
In the Authorization tab (see Figure 9-4), specify user name and password for MQ authorization, perform the following tasks:
In the Exits tab (see Figure 9-5), specify MQSeries control exits, perform the following tasks:
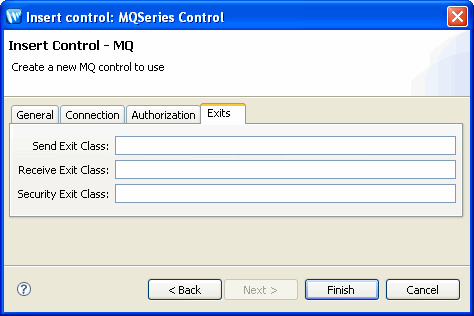
For more information, see Using the MQSeries Control Exit Implementation.
| Note: | The Exits tab is enabled only when TCP connection mode is selected. The fields in this tab are not mandatory. |
When you create a new instance of the MQSeries control, you create a new Control file in your project. The following is a sample control file for an MQSeries control:
package requestquote;
import org.apache.beehive.controls.api.bean.ControlExtension;
/*
* A custom MQ control.
*/
@ControlExtension
@com.bea.control.MQControl.Connection(type = com.bea.control.MQControl.ConnectionType.TCP, QueueManager = "Manager", authorization = false, implicitTransaction = true)
@com.bea.control.MQControl.ConnectionPool(poolSize = 20, timeout = 3600)
@com.bea.control.MQControl.TCPSettings(host = "10.12.45.89", port = "1234", channel = "Host", ccsid = "1234", user = "", password = "", sendExit = "", receiveExit = "", securityExit = "")
@com.bea.control.MQControl.SSLSettings(sslRequired = false, twoSSLRequired = false)
public interface MQSeriesControl extends com.bea.control.MQControl {static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public MQSeriesControl create();
}
The contents of the MQSeries control file depend on the selections made in the Insert MQSeries dialog. The example above was generated based on selecting a TCP connection type.
The MQSeries control allows you to create your own send, receive, and security exits.
To implement an Exit, you must define a new Java class that implements the appropriate interface. Three exit interfaces are defined in the WebSphere MQ package:
The MQSeries MQSendExit interface allows you to examine and change the data sent to the queue manager by the WebSphere MQ Client for Java.
The MQSeries MQReceiveExit interface allows you to examine and change the data received from the queue manager by the WebSphere MQ Client for Java.
The MQSeries MQSecurityExit interface allows you to customize the security settings for connecting to a queue manager.
| Notes: | User Exits are supported for TCP connections only; they are not supported for bindings connections. |
| Note: | User Exits are used to modify the data that is transmitted between the MQSeries queue manager and the MQSeries client application. This data is in the form of MQSeries headers and does not involve the contents of the actual message being put and received from the queue. |
To implement MQSeries Exits, perform the following tasks:
com.ibm.mq.MQSendExit, com.ibm.mq.MQReceiveExit, and com.ibm.mq.MQSecurity interfaces for the send, receive, and security exits, as shown in the following example:
package com.bea.UserExit;
import com.ibm.mq.*;
public class MQUserExit implements MQSendExit, MQReceiveExit, MQSecurityExit {
public MQUserExit()
{
}
public byte[] sendExit(MQChannelExit channelExit,MQChannelDefinition channelDefnition,byte[] agentBuffer)
{
return agentBuffer;
}
public byte[] receiveExit(MQChannelExit channelExit,MQChannelDefinition channelDefnition,byte[] agentBuffer)
{
return agentBuffer;
}
public byte[] securityExit(MQChannelExit channelExit,MQChannelDefinition channelDefnition,byte[] agentBuffer)
{
return agentBuffer;
}
}
You may implement these interfaces in a single class or in separate classes, as required.
For an MQSendExit, the agentBuffer parameter contains the data to be sent. For an MQReceiveExit or an MQSecurityExit, the agentBuffer parameter contains the data just received.
For the MQSendExit and the MQSecurityExit, your exit code should return the byte array that you want to send to the server. For a Receive exit, your exit code must return the modified data that you want WebSphere MQ Client for Java to interpret.
setDomainEnv.cmd file located in the WebLogic domain directory to append the Jar file name to the CLASSPATH. To do this, find the following code in the setDomainEnv.cmd file:and append the following line to it:
Before you append the code containing the Jar file name to the CLASSPATH, you can define the directory in which the Jar file resides, as follows:
Two modes of transaction management are supported by the MQSeries control. They both use the underlying MQSeries syncpoint feature. The two transaction management modes are:
Implicit transaction management is selected by default. When this mode is on, the MQSeries control handles the transaction for each MQSeries Get or Put function. The following diagram describes how an implicit transaction is handled by the MQSeries control.
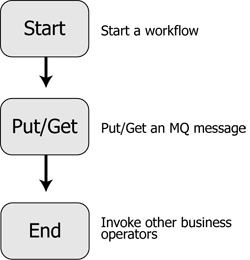
Using implicit transaction management prevents you from grouping several Get and Put functions together as a part of a transactional unit. Each Get and Put are handled individually within a transaction boundary.
Explicit transaction management is enabled when you choose not to use implicit transaction management while configuring the MQSeries control. In the explicit transaction mode, you must set the transaction boundaries explicitly, using the Begin and Commit (or Rollback) MQSeries control functions.
Figure 9-6 describes the process of creating a workflow using explicit transaction management.
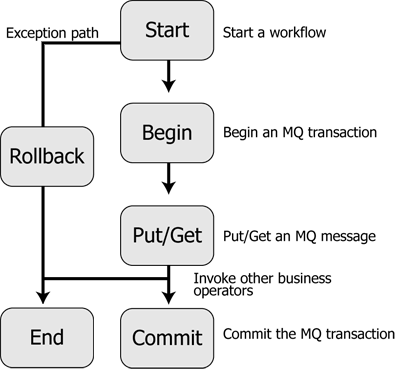
A Message Descriptor is an attribute representing a property of the message that is either being sent or received. Message properties can be the type of message, the message ID, and the message priority. For a detailed list of all the message descriptors supported by the MQSeries control, see Table 9-1, Elements of the MQMDHeaders XML document.
Using the MQSeries control you can set Message Descriptors for each message while sending the message using the putMessage function. You can also get the message descriptors of the messages retrieved from the queue. This facility is supported using the MQMDHeaders document which is provided as an input to the putMessage and getMessage functions. The MQMDHeaders document is represented using an XMLBean that conforms to the MQMDHeaders schema present in the jpdpublic.jar file, located at BEA_Home\wli_10.2\lib.
The following elements of the MQMDHeaders XML document can be set as part of the MQMD parameters:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQMDHeaders"
xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQMDHeaders" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:element name="MQMDHeaders">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="MessageType" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="MessageId" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="CorrelationId" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="GroupMessage" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"> <xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="GroupId" type="xs:string" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="waitForAllMsgs" type="xs:boolean" use="optional"/>
<xs:attribute name="logicalOrder" type="xs:boolean" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Priority" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Format" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="CharacterSet" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Persistence" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Segmentation" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Expiry" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="UserId" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="MessageSequenceNumber" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="GroupOptions" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="IsLastMessage" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ReportOptions" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="COA" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="COD" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Exception" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Expiration" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Feedback" type="xs:int" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/> <xs:element name="ReplyToQueueName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="ReplyToQueueManager" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="WaitInterval" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="ApplicationIdData" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="ApplicationOriginData" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="PutApplType" type="xs:int" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="PutApplName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="PutDateTime" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="AccountingToken" type="xs:base64Binary" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="Version" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="MessageConsumption" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="MQGMO_CONVERT" type="xs:boolean" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
The following is a sample MQMDHeaders document that contains most of the message descriptors you can set using the MQSeries control:
<?xml version="1.0"?><even:MQMDHeaders xmlns:even="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQMDHeaders">
<even:MessageType>8</even:MessageType>
<even:MessageId>1111</even:MessageId> <even:CorrelationId>2222</even:CorrelationId>
<even:GroupMessage>
<even:GroupId>3333</even:GroupId>
</even:GroupMessage>
<even:Priority>9</even:Priority>
<even:Format>MQSTR</even:Format> <even:CharacterSet>819</even:CharacterSet> <even:Persistence>1</even:Persistence> <even:Segmentation>1</even:Segmentation>
<even:Expiry>5000</even:Expiry>
<even:UserId>WebLogic</even:UserId> <even:MessageSequenceNumber>1</even:MessageSequenceNumber> <even:GroupOptions>
<even:IsLastMessage>true</even:IsLastMessage>
</even:GroupOptions>
<even:ReportOptions>
<even:COA>COAWithFullData</even:COA>
<even:COD>CODWithFullData</even:COD>
<even:Exception>ExceptionWithFullData</even:Exception>
<even:Expiration>ExpirationWithFullData</even:Expiration> </even:ReportOptions>
<even:Feedback>1</even:Feedback>
<even:ReplyToQueueName>trial</even:ReplyToQueueName> <even:ReplyToQueueManager>QM_itpl_025051</even:ReplyToQueueManager> <even:ApplicationIdData>App_ID_025051</even:ApplicationIdData> <even:ApplicationOriginData>Windows_app_025051</even:ApplicationOriginData> <even:PutApplType>1</even:PutApplType> <even:PutApplName>MQSeriesClient</even:PutApplName> <even:Version>2</even:Version>
</even:MQMDHeaders>
The MQSeries control MQMDHeaders document element values can be set, and the return values can be retrieved, programmatically, using XML beans. The following is an example of setting the MQMDHeader element values prior to calling the putMessage function:
headers = com.bea.wli.control.mqmdHeaders.MQMDHeadersDocument.Factory.newInstance();com.bea.wli.control.mqmdHeaders.MQMDHeadersDocument.MQMDHeaders header = headers.addNewMQMDHeaders();header.setMessageType(MQC.MQMT_DATAGRAM);
header.setPriority(8);
header.setExpiry(5000);
header.setPersistence(MQC.MQPER_PERSISTENT);
header.getReportOptions().setCOA("COA"); header.setReplyToQueueName("ReportQueue"); header.setApplicationIdData("Testing"); header.setApplicationOriginData("AAAA");
header.setPutApplName("Websphere MQ 2"); header.setPutApplType(MQC.MQAT_JAVA);
You can send and receive messages with the MQSeries control using the Put and Get functions. Messages can be of the form Bytes, String, or XML data.
To send a message, select a putMessage function based on the data type of the message that you want to send:
MQMDHeadersDocument putMessageAsBytes (byte[] message, java.lang.String queue, MQMDHeadersDocument mqmd) throws ResourceException;MQMDHeadersDocument putMessageAsString (String message, java.lang.String queue, MQMDHeadersDocument mqmd) throws ResourceException;MQMDHeadersDocument putMessageAsXml (XmlObject message, java.lang.String queue, MQMDHeadersDocument mqmd) throws ResourceException;The first parameter that is passed to the function is the message to be put into the queue. The possible types for this parameter are byte[], XmlObject and String for sending Binary, XML and plain text messages respectively.
The second parameter that is passed to the function is the queue to which the message is sent. If a value is not provided at runtime, that is, if the value is null, the default queue name mentioned in the control property is used.
The third parameter that is passed to the function is the XML bean representing the MQMDHeadersDocument provided as an XML document during runtime, which conforms to the MQMDHeaders schema. The values provided in this document are used for setting the MQMD attributes of the message being sent. If the MQMDHeadersDocument parameter is not provided, or if the parameter is null, the message is put into the queue with the default values for the message descriptors.
The return value of the function is the MQMDHeadersDocument representing the MQMD attributes of the message sent to the queue.
The following procedure describes how to add any MQSeries control putMessage function to a business process.
putMessage function.putMessage function.putMessage function.putMessageAsString function from the Controls tab in the Data Palette into your business process, just below the Client Request node.putMessageAsString function node. From the Select variables to assign drop-down list, assign the variables that you created in the Receive Data tab of the Client Request node, to the corresponding parameter of the putMessageAsString function listed in the Control Expects column.putMessageAsString function node. From the Select variables to assign drop-down list, create a new variable in which to store the output of the putMessageAsString function, the MQMDHeaders document, which represents the attributes of the message that was sent.
You can use similar steps to send messages using the putMessageAsBytes or the putMessageAsXml functions.
Using the MQSeries control you can add messages to a remote queue managed by a remote queue manager. To do this, you must configure a transmission queue in the queue manager to which the MQSeries control is connected. For more information on how to configure a transmission queue, see the MQSeries documentation on http://www.IBM.com.
To add a message to a remote queue (managed by a remote queue manager) you must drag and drop the following function, before the putMessage call in the workflow:
void setRemoteQueueManager(java.lang.String remoteQueueManager);
The parameter to this function is the name of the remote queue manager. To set the value for this parameter, in the Design view, open the remoteQueueManager node. In the Send Data tab, select or create a string variable, then enter the name of your remote queue manager as the default value.
Once you’ve configured the remote queue manager, the putMessage functions following the setRemoteQueueManager function add messages to the remote queue manager.
To revert to the default (local) queue manager to which your control is connected, in the Design view you must drag and drop the setRemoteQueueManager again in your workflow. On doing this, a default value, null, is passed as the parameter to this function. This null value or empty string reverts control back to the default queue manager. messages are now automatically added to the local queue.
To receive a message, select a get Message function based on the data type of the message that you want to receive:
byte[] getMessageAsBytes(java.lang.String queue, MQMDHeadersDocument mqmd) throws ResourceException;String getMessageAsString(java.lang.String queue, MQMDHeadersDocument mqmd) throws ResourceException;XmlObject getMessageAsXml(java.lang.String queue, MQMDHeadersDocument mqmd) throws ResourceException;
The first parameter of the function, java.lang.String queue, is the name of the queue from which the message is to be received. If a value is not provided at runtime (the value is null) the default queue name mentioned in the control property is used.
The second parameter of the function, MQMDHeadersDocument, is an XML bean. This represents the MQMDHeadersDocument provided as an XML document at runtime, which conforms to the MQMDHeaders schema. The values provided in this document are used to retrieve the message corresponding to the MQMD attributes specified in the document. If the MQMDHeadersDocument parameter is not provided, or if the parameter is null, the first message present in the queue is retrieved. If the MQMDHeadersDocument parameter is not null, the MQMD attributes of the message obtained from the queue are updated in this XML bean object itself.
| Note: | If the MQMDHeadersDocument parameter to the getMessage function is null, you must use the getMQMDHeaders function after the getMessage function in the workflow, to get the MQMD attributes of the message retrieved from the queue. Also, if the MQMDHeadersDocument parameter to the getMessage function is null, Delete is used as the default MessageConsumption option. |
The return value of the function is the message obtained from the queue. The data type of the message depends on the getMessage function added. The values may be byte[], XmlObject, or String, depending on whether the message obtained is to be processed as a Binary, XML, or plain text message.
The following procedure describes how to add a MQSeries control getMessage function to a business process.
getMessage function.getMessage function.getMessageAsString function from the Controls tab in the Data Palette into your business process, just below the Client Request node.getMessageAsString function node. From the Select variables to assign drop-down list, assign the variables that you created (in the Receive Data tab of the Client Request node) to the corresponding parameter of the getMessageAsString function listed in the Control Expects column.getMessageAsString function node. From the Select variables to assign drop-down list, create a new variable in which to store the output of the getMessageAsString function. The output is a string representing the message that was retrieved from the queue.
The Message Descriptor attributes of the message retrieved from the queue are updated in the MQMDHeaders document. This document was provided as input to the getMessageAsString function.
You can use a similar procedure to retrieve messages using the getMessageAsBytes or the getMessageAsXml functions.
You can send group messages using the MQSeries control putMessage function within a loop. The loop can be created using one of the following process nodes: While Do, Do while, and For Each.
Provide the GroupOptions element in the MQMDHeadersDocument. You only provide this element in the input MQMDHeaders XML document if a group message is to be sent.
In the MQMDHeaders document, set the IsLastMessage element within GroupOptions to False, for all messages except the last message. For the last message, the IsLastMessage element must be set to True.
If you specify a GroupID for the first message, then the MQSeries control assigns this ID to the group message. If you do not specify a GroupID for the first message, the MQSeries queue manager assigns a group ID to the first message. This ID is returned in the output MQMDHeaders document of the putMessage function.
The Group Id assigned to the first message must be used for all the subsequent messages of the group. The MessageSequenceNumber of the first message of the group should be 1; the MessageSequenceNumber of the second message should be 2, and so on.
You can retrieve group Messages using the MQSeries control getMessage function within a loop. The loop can be created using one of the following process nodes: While Do, Do while, and For Each.
You can retrieve group messages using the MQSeries control in a logical order. To configure the MQSeries control to retrieve group messages in a logical order, set the logicalOrder attribute of the GroupMessage element to True.
You can retrieve messages in a logical order only when you use explicit transaction mode. The Figure 9-7 depicts a sample workflow for retrieving group messages in logical order:
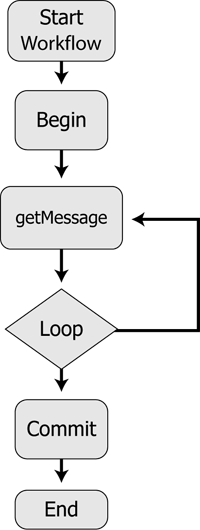
The loop executes until the IsLastMessage element within the GroupOptions element is set to True in the response MQMDHeaders document of the getMessage function.
| Note: | The GroupOptions element does not appear in the Get Response MQMDHeaders document if the retrieved message is not a part of a group. |
The logicalOrder attribute must be set to True in each call of the Get service, to retrieve the messages of the group in their logical order (by message sequence number, beginning at one for the first message).
Changing the logicalOrder attribute from True to False while getting group messages, when its value was True in the previous Get service call, changes the logical ordering.
Setting the logicalOrder attribute to False or not providing this attribute in the Get request document means that the control gets the first message of the group as it appears on the queue irrespective of its message sequence number.
The following is an example of a Get Request MQMDHeaders document for retrieving group messages in logical order, and also waits for all messages in the group:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<even:MQMDHeaders xmlns:even="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQMDHeaders"> <even:GroupMessage waitForAllMsgs="true" logicalOrder="true"> <even:GroupId></even:GroupId>
</even:GroupMessage>
<even:MessageConsumption>Delete</even:MessageConsumption>
</even:MQMDHeaders>
You can configure the MQSeries control to wait for all messages of the group to be present in the queue before retrieving any message within the group. To configure the MQSeries control to wait for all messages, set the waitForAllMsgs attribute of the GroupMessage element to True.
| Note: | The waitForAllMsgs and the logicalOrder attribute are optional and can be set to either True or False. |
You can set the waitForAllMsgs to True while retrieving the first message of the group. After you retrieve the first message in the group, you can set this attribute to True again, for retrieving the other messages of the group, provided that you have also set the logicalOrder attribute to True.
Setting the waitForAllMsgs attribute to False, or not providing this attribute in the Get Request document means that the control can still get group messages from the queue even when not all of the messages of the group are present in the queue.
GroupId is an optional element within the GroupMessage element. Its value may not be provided if the hexadecimal group ID of the group message is not known. When there are multiple group messages present in the queue, the first group message in the queue is retrieved. The GroupId value may be specified, if known. If specified and there are multiple group messages in the queue, the group message matching the group ID is retrieved.
Group Messages can also be retrieved by specifying the MessageSequenceNumber element and the GroupId. Messages can be retrieved in this way only if the logicalOrder attribute value is False or is not provided. When the MessageSequenceNumber and the GroupId are provided, the message of the group matching the MessageSequenceNumber is retrieved. The group messages can still be retrieved in a loop by providing the GroupId and incrementing the MessageSequenceNumber by one in each Get function call in the loop, the MessageSequenceNumber of the first message being one.
Format is a message descriptor attribute. Messages of a particular Format conform to a specific structure which depends on the Format type. For example, CICS, IMS, MQRFH2, and so on. The structure for each built-in MQSeries Format is different and is defined by MQSeries. For more information on MQSeries Formats, see the online MQSeries documentation at the following URL:
Using the MQSeries control you can send messages that correspond to built-in MQSeries formats and user-defined formats. This can only be done using the putMessageAsBytes function.
To send a message that conforms to an MQSeries Format, you must add Java code to the business process file. This is shown in the following examples.
putin, in your business process file, as follows:public com.bea.wli.control.mqmdHeaders.MQMDHeadersDocument putin;
This variable represents the input MQMDHeaders document XMLBean variable for the putMessage function.
public void perform() throws Exception
{
putin.getMQMDHeaders().setFormat(MQC.MQFMT_CICS);
bytmsg = getCICSHeader();
}
public byte[] getCICSHeader() throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bstream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream ostream = new DataOutputStream (bstream); ostream.writeChars("CIH "); // Struct id
ostream.writeInt(1); // Version
ostream.writeInt(164); // StrucLength
ostream.writeInt(273); // Encoding
ostream.writeInt(819); // CodedCharSetId
ostream.writeChars(" "); // Format
ostream.writeInt(0); //Flags
ostream.writeInt(0); //ReturnCode
ostream.writeInt(0); //CompCode
ostream.writeInt(0); //Reason
ostream.writeInt(273); //UOWControl
ostream.writeInt(-2); //GetWaitInterval
ostream.writeInt(1); //LinkType
ostream.writeInt(-1); //OutputDataLength
ostream.writeInt(0); //FacilityKeepTime
ostream.writeInt(0); //ADSDescriptor
ostream.writeInt(0); //ConversationalTask
ostream.writeInt(0); //TaskEndStatus
ostream.writeBytes("\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0"); //Facility
ostream.writeChars(" "); //Function
ostream.writeChars(" "); //AbendCode
ostream.writeChars(" "); //Authenticator
ostream.writeChars(" "); //Reserved1
ostream.writeChars(" "); //ReplyToFormat
ostream.writeChars(" "); //RemoteSysId
ostream.writeChars(" "); //RemoteTransId
ostream.writeChars(" "); //TransactionId
ostream.writeChars(" "); //FacilityLike
ostream.writeChars(" "); //AttentionId
ostream.writeChars(" "); //StartCode
ostream.writeChars(" "); //CancelCode
ostream.writeChars(" "); //NextTransactionId
ostream.writeChars(" "); //Reserved2
ostream.writeChars(" "); //Reserved3
ostream.writeChars("HelloWorld");
ostream.flush();
byte[] bArr = bstream.toByteArray();
return bArr;
}
This code sets the Format element in the input MQMD Headers document of the putMessage function to MQC.MQFMT_CICS, represented by the String "MQCICS".
The getCICSHeader function writes the fields present in the CICS header to a byte array output stream and returns an array of bytes. The field values given in this example can be modified as required. The actual message can be appended to the end of this byte array and can be Put into the MQSeries queue. The byte array can be provided as the first parameter to the putMessageAsBytes function, which is added to the process.java file after the Perform node. For more information on the putMessage function, see Sending and Receiving Messages.
putin, in the business process file, as follows:public com.bea.wli.control.mqmdHeaders.MQMDHeadersDocument putin;
This variable represents the input MQMDHeaders document XMLBean variable for the putMessage function.
public void perform() throws Exception
{
putin.getMQMDHeaders().setFormat(MQC.MQFMT_IMS);
bytmsg = getIMSHeader();
}
public byte[] getIMSHeader() throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream bstream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
DataOutputStream ostream = new DataOutputStream (bstream);
ostream.writeBytes("IIH "); // Struct id
ostream.writeInt(1); // Version
ostream.writeInt(84); // Length
ostream.writeInt(0); // Encoding
ostream.writeInt(0); // CodedCharacterSet
ostream.writeBytes(" "); // Format (8 characters)
ostream.writeInt(0); // Flags
ostream.writeBytes(" "); // LTermOverride
ostream.writeBytes(" "); // MFSMapName
ostream.writeBytes(" "); // ReplyToFormat
ostream.writeBytes(" "); // Authenticator
ostream.writeBytes("\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0"); // TransInstanceId
ostream.writeBytes(" "); //Transtate
ostream.writeBytes("1"); // CommitMode
ostream.writeBytes("F"); // Security Scope
ostream.writeBytes(" "); // Resrved
ostream.writeChars("HelloWorld");
ostream.flush();
byte[] bArr = bstream.toByteArray();
return bArr;
}
The previous lines of code set the Format element in the input MQMD Headers document of the putMessage function to MQC.MQFMT_IMS, represented by the String "MQIMS ".
The getIMSHeader function writes the fields present in the IMS header structure to a byte array output stream and returns an array of bytes. The values of the fields given in this example can be modified as required. The actual message can be appended to the end of the byte array and can be Put into the MQSeries queue. The byte array can be provided as the first parameter to the putMessageAsBytes function, which is added to the business process file after the Perform node. For more information on the putMessage function, see Sending and Receiving Messages.
putin, in the business process file of your process project in the application, as follows:public com.bea.wli.control.mqmdHeaders.MQMDHeadersDocument putin;
This variable represents the input MQMDHeaders document XMLBean variable for the putMessage function.
public void perform() throws Exception
{
putin.getMQMDHeaders().setFormat(MQC.MQFMT_RF_HEADER_2);
bytmsg = getMQRFH2Header();
}
public byte[] getMQRFH2Header() throws Exception { ByteArrayOutputStream bstream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); DataOutputStream ostream = new DataOutputStream (bstream);
String strVariableData = "<mcd><Msd>jms_text</Msd></mcd><jms><Dst>someplace</Dst></jms>";
int iStrucLength = MQC.MQRFH_STRUC_LENGTH_FIXED_2 + strVariableData.getBytes().length;
while(iStrucLength % 4 != 0)
{
strVariableData = strVariableData + " ";
iStrucLength = MQC.MQRFH_STRUC_LENGTH_FIXED_2 + strVariableData.getBytes().length;
}
ostream.writeChars(MQC.MQRFH_STRUC_ID);//StrucID ostream.writeInt(MQC.MQRFH_VERSION_2);//Version ostream.writeInt(iStrucLength );//StrucLength ostream.writeInt(273);//Encoding ostream.writeInt(1208);//CodedCharSetID ostream.writeChars(MQSTR);//Format ostream.writeInt(MQC.MQRFH_NO_FLAGS);//Flags ostream.writeInt(1208);//NameValueCCSID ostream.writeInt(strVariableData.getBytes().length);//NameValueLength ostream.writeChars(strVariableData ); //NameValueData ostream.writeChars(“HelloWorld“);
ostream.flush();
byte[] bArr = bstream.toByteArray();
return bArr;
}
The previous code sets the Format element in the input MQMD Headers document of the putMessage function to MQC.MQFMT_RF_HEADER_2,represented by the String "MQHRF2 ".
The getMQRFH2Header function writes the fields present in the MQRFH2 header structure to a byte array output stream and returns an array of bytes. The values of the fields given in this example can be modified as required. The actual message can be appended to the end of the byte array and can be Put into the MQSeries queue. The byte array can be provided as the first parameter to the putMessageAsBytes function, which is added to the business process file after the Perform node. For more information on the putMessage function, see Sending and Receiving Messages.
You can change the MQSeries control properties dynamically at runtime. The MQSeries control properties that you can modify are specified in the MQDynamicProperties document. This document conforms to the MQDynamicProperties schema which is available in the jpdpublic.jar file, located at BEA_Home\wli_10.2\lib.
To change properties dynamically, perform the following tasks
setDynamicProperties function in the business process use the properties that you specify in the MQDynamicProperties document.| Caution: | When you use Explicit Transaction mode, always call the setDynamicProperties function before the Begin function or after the Commit or the Rollback functions. If this sequence is not followed, the business process will throw an exception at runtime. |
<?xml version="1.0"?><xs:schema xmlns="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQDynamicProperties" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQDynamicProperties" elementFormDefault="qualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified"> <xs:element name="MQDynamicProperties">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="connectionType" type="connType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="queueManager" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="requireAuthorization" type="authType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="host" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="port" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="channel" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="ccsid" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="user" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="password" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="sendExit" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="receiveExit" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="securityExit" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="defaultQueueName" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="implicitTransactionRequired" type="transType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:simpleType name="connType">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="Bindings"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="TCP"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="authType">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="Yes"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="No"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="transType">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="true"></xs:enumeration>
<xs:enumeration value="false"></xs:enumeration>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
The following is a sample MQDynamicProperties document. You must provide this document at runtime when you execute your business process:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<even:MQDynamicProperties
xmlns:even="http://www.bea.com/wli/control/MQDynamicProperties">
<even:connectionType>TCP</even:connectionType>
<even:queueManager>newqm</even:queueManager>
<even:requireAuthorization>Yes</even:requireAuthorization>
<even:host>localhost</even:host>
<even:port>1869</even:port>
<even:channel>chn</even:channel>
<even:ccsid>437</even:ccsid>
<even:user>WebLogic</even:user>
<even:password>WebLogic</even:password>
<even:defaultQueueName>errqueue</even:defaultQueueName>
</even:MQDynamicProperties>
SSL functionality is available only if you selected TCP Connection mode while configuring an MQSeries control. For more information on configuration options for the MQSeries control, see Creating and Configuring a New Instance of the MQSeries Control.
This topic includes the following sections:
Setting Server-side SSL Properties
Setting Client-side SSL Properties
Example: Configuring SSL Within a Workflow
The cipher suite algorithm is used to encrypt and decrypt message communication between the MQSeries server and the MQSeries client. If you selected either of the two SSL options while creating a new MQSeries control, you must set the SSL cipher suite before you put or get messages from the queue. This can be done using the following function:
void setSSLCipherSuite(java.lang.String cipherSuite);
The parameter to this function is the string representing the selected SSL cipher suite. You can get the different values for the cipher suites from the final static variables of the MQControlConstants class.
After enabling either of the SSL options for your MQSeries control, you must set server-side SSL properties before you put or get messages from the queue. You can do this using the following function:
void setServerSideSSL(java.lang.String trustStoreLocation, java.lang.String trustStoreType, java.lang.String trustStorePassword) throws com.bea.control.ControlException;
The parameters to this function are:
trustStoreLocationThe path representing the location of the trust store. This parameter is optional, and if not provided, takes the default trust store of the Weblogic JDK.
trustStoreTypeThe type of trust store, for example, JavaKeyStore (JKS). This parameter is optional, and if not provided, takes the default trust store type.
trustStorePassword
The password for the trust store. This parameter is mandatory if the trustStoreLocation parameter is provided.
After enabling two-way SSL for your MQSeries control, you must set server-side and client-side SSL properties before you put or get messages from the queue. To set the client-side SSL properties, use the following function:
void setClientSideSSL(java.lang.String keyStoreLocation, java.lang.String keyStoreType, java.lang.String keyStorePassword, java.lang.String keyPassword);
The parameters to this function are:
keyStoreLocationThe path representing the location of the key store. This parameter is mandatory.
keyStoreTypeThe type of key store, for example, JKS. This parameter is optional, and if not provided takes the default key store type.
keyStorePasswordThe password for the key store. This parameter is mandatory.
keyPassword
The password for the key. This parameter is optional, and if not provided, considers the keyStorePassword as the keyPassword.
After selecting either of the two SSL options while creating a new MQSeries control, your workflow must adhere to the order of MQSeries control function calls represented in Figure 9-8.
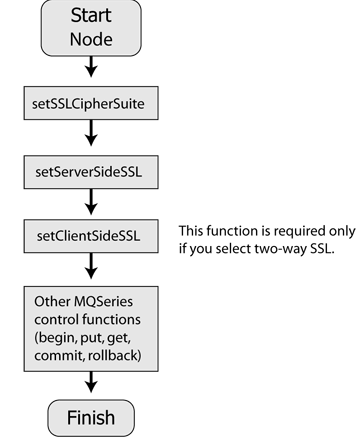
| WARNING: | If the sequence represented in Figure 9-8 is not followed in the workflow when SSL authentication is required, the MQSeries Control will throw an exception at runtime. |
For information on how to set up the Queue Manager for SSL connections, refer to the MQSeries Product documentation at http://www.IBM.com. SSL support is available only from WebSphere MQ version 5.3 onwards.
The MQSeries event generator polls the MQSeries queue for messages and publishes them to WebLogic Message Broker channels. The MQSeries event generator supports three different data types — Bytes, String, and XML.
You can configure event generator channels for different data types using a Message Broker channel name, which instructs that any message coming into the specified MQSeries queue will be published to that message broker channel.
Similar to the MQSeries control, the MQSeries event generator also provides two modes of connections — TCP-IP and Bindings. You can also implement content-filters to filter messages based on the specific content that you want. By doing this, you can ensure that you generate events only for the messages that you require.
The MQSeries event generator can also spawn multiple threads of events. Each thread can separately poll the MQSeries queue. You can configure the number of messages to be picked by the event generator thread in each poll.
To learn more, see Event Generators.


|