
![BEA BEA Tuxedo Release [Release Number]](../images/top.gif)

|
![BEA BEA Tuxedo Release [Release Number]](../images/top.gif)
|
|
|
|
Connectivity Between a BEA Tuxedo CORBA Client and an EJB in WebLogic Server
This topic includes the following sections:
Overview of the WLStrader Value Type Sample Application
The WLStrader Value Type sample application demonstrates connectivity between an RMI over IIOP client and an EJB. More specifically, this sample application illustrates how a CORBA C++ client application developed in BEA Tuxedo can interact with an EJB in WebLogic Server. The application makes use of the Trader EJB included in the WebLogic Server examples. The WLStrader Value Type sample builds on components of the Trader sample application, while providing its own build and run procedures.
Figure 2-1 illustrates the connectivity provided in the WLStrader Value Type sample application.
Figure 2-1 CORBA C++ Client to WebLogic Server EJB
In the WLStrader Value Type example, a BEA Tuxedo CORBA C++ client employs a value type, passing an object-by-value. This supports an RMI over IIOP invocation of an IDL interface, and provides connectivity to the WebLogic Server TraderBean Enterprise JavaBean (EJB). A value type represents a class whose values can be moved between systems. Value types can be passed as arguments or results of remote methods, or as fields within other objects that are passed remotely. For information on support for value types in BEA Tuxedo CORBA, see Chapter 13, "Mapping of OMG IDL Statements to C++," in the CORBA Programming Reference in the BEA Tuxedo online documentation. The CORBA client obtains the WebLogic Server Inter-operable Object Reference (IOR) by invoking the COSNaming Service layer provided in the WebLogic Server JNDI implementation. For information on the CORBA Name Service and the COSNaming data structures, see Using the CORBA Name Service in the BEA Tuxedo online documentation.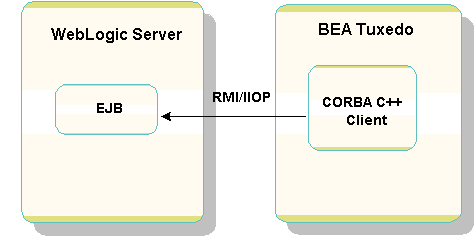
Components of the WLStrader Value Type Sample Application
This topic describes the components and operations in the WLStrader Value Type sample application. It includes the following sections:
WebLogic Server Trader Sample Application
The WLStrader Value Type sample builds on components of the WebLogic Server Trader sample application, employing its XML deployment files and Trader EJB. To derive the optimum benefit from this example, read through the source code files to understand the design and the steps involved. Review the deployment files to understand the general structure of the Trader EJB.
The WebLogic Server code sample files for the Trader sample are in the wlserver6\samples\examples\rmi_iiop\ejb\rmi_iiop directory.
Mapping from a WebLogic Server to a CORBA Client
When deriving the mapping from a WebLogic Server application to a CORBA client, the sources of the mapping information are the EJB classes as defined in the Java source files. WebLogic Server provides the weblogic.ejbc utility for generating required CORBA IDL files. These files represent the CORBA view into the state and behavior of the target EJB.
The weblogic.ejbc utility performs the following:
The weblogic.ejbc utility supports a number of command qualifiers. In the WLStrader Value Type example, the ejbc step invokes these qualifiers on the command line:
Directs the utility to create CORBA Interface Definition Language (IDL) files for all appropriate classes.
Directs the utility to create a directory tree named idlSources, and to store IDL files in this location. The directory tree structure corresponds to the Java package hierarchy.
Directs the utility to overwrite any existing IDL files in the idlSources output directory.
Resulting files are processed using the BEA Tuxedo IDL compiler, reading source files from the idlSources directory and generating CORBA C++ stub and skeleton files. These generated files are sufficient for all CORBA data types with the exception of value types. Value types need to be implemented on each platform on which they are defined or referenced. Specifying the -i qualifier directs the IDL compiler to create implementation files named FileName_i.h and FileName_i.cpp. For example, this syntax creates the TradeResult_i.h and TradeResult_i.cpp implementation files:
idl -IidlSources -i idlSources\examples\rmi_iiop\ejb\rmi_iiop\TradeResult.idl
The resulting source files provide implementations for application-defined operation on a value type. Implementation files are included in a CORBA client application.
BEA Tuxedo CORBA C++ Client
The CORBA C++ client program tuxclient performs the exercises against the Trader. The results from a Trader transaction are returned to the client through the TradeResult value type. The tuxclient application performs these operations:
Listing 2-1 tuxclient.cpp—Register Value Factories
. . .
// Need to register value factories for all value types we
// might receive.
//
examples_rmi_iiop_ejb_rmi_iiop_TradeResult_factory* TRf = new
examples_rmi_iiop_ejb_rmi_iiop_TradeResult_factory();
orb->register_value_factory((char*const)
examples::rmi_iiop::ejb::rmi_iiop::_tc_TradeResult->id(), TRf);
//
. . .
The code extract from tuxclient.cpp in Listing 2-2 contains the steps for creating a Trader instance and buying some shares of BEAS.
Listing 2-2 tuxclient.cpp—Create a Trader; Buy Some Shares
. . .
// Create a Trader instance
::examples::rmi_iiop::ejb::rmi_iiop::Trader_ptr trader =
home->create();
// Buy some shares
CORBA::WStringValue_ptr BEASsym = new
CORBA::WStringValue(CORBA::wstring_dup((wchar_t *)L"BEAS"));
::examples::rmi_iiop::ejb::rmi_iiop::TradeResult_ptr result;
cout << "Buying 3000 shares of BEAS" << endl;
result = trader->buy(BEASsym, 3000);
. . .
The "buy" request from the CORBA client is for 3000 shares of BEA stock with symbol BEAS. The actual number of shares traded is 500, imposed by the tradeLimit threshold defined in the ejb-jar.xml deployment file for the WebLogic Server examples.
Listing 2-3 tradeLimit Defined in ejb-jar.xml
. . .
<env-entry-name>tradeLimit</env-entry-name>
<env-entry-type>java.lang.Integer</env-entry-type>
<env-entry-value>500</env-entry-value>
. . .
To achieve different results when you run the WLStrader Value Type sample application, you can vary definitions in the ejb-jar.xml file, or constants in the tuxclient.cpp source file.
Building and Running the WLStrader Value Type Sample Application
This section leads you through the process of building and running the WLStrader Value Type sample application.
Before running the example, described later in the sequence of steps, you must obtain the WebLogic Server Inter-operable Object Reference (IOR) by running the host2ior utility. Complete this step once for any WebLogic Server installation. You can obtain this file any time after installing WebLogic Server, and before running an application requiring the file.
To build and run the wlstrader sample application, complete the following steps. Each step is described in detail in subsequent sections. The steps detailed here supplement the information in the WebLogic Server installation location:wlserver6\samples\examples\rmi_iiop\ejb\rmi_iiop\package-summary.html
.Set the Development Environment
When developing in Java, make sure you have a controlled development environment.
For example:
Windows
> set TUXDIR=D:\TUXDIR
UNIX
ksh prompt> export TUXDIR=/usr/local/TUXDIR
Copy the BEA Tuxedo WLStrader Value Type Files
Rename the build command script, and copy the BEA Tuxedo WLStrader Value Type files from the BEA Tuxedo CORBA samples directory to your WebLogic Server examples build area.
For example:
Windows
rename %TUXDIR%\samples\corba\wlstrader\build.cmd tuxbuild.cmd
UNIX
mv $TUXDIR/samples/corba/wlstrader/build.sh tuxbuild.sh
For example:
Windows
copy %TUXDIR%\samples\corba\wlstrader\*.*
D:\bea\wlserver6\samples\examples\rmi_iiop\ejb\rmi_iiop\*.*
UNIX
cp $TUXDIR/samples/corba/wlstrader/*.*
/usr/local/wlserver6/samples/examples/rmi_iiop/ejb/rmi_iiop/*.*
The sample files listed in Table 2-3 should now be in your WebLogic Server examples build area.
Build the Example
Execute the renamed build script for this example. This is the file you renamed before copying from the BEA Tuxedo samples\corba\wlstrader directory into the samples\examples\rmi_iiop\ejb\rmi_iiop directory of your WebLogic Server installation. The script performs the following steps presented here for a Windows environment:
> mkdir build build\META-INF build\images
> copy *.xml build\META-INF
> copy *.gif build\images
> javac -d build Trader.java TraderHome.java
TraderResult.java TraderBean.java
> cd build
> jar cv0f std_ejb_over_iiop.jar META-INF examples images
> cd ..
> java weblogic.ejbc -compiler javac -keepgenerated
-idl -idlDirectory idlSources
-iiop build\std_ejb_over_iiop.jar
%APPLICATIONS%\ejb_over_iiop.jar
> javac -d %CLIENT_CLASSES% Trader.java TraderHome.java
TradeResult.java Client.java
>%IDL2CPP% idlSources\examples\rmi_iiop\ejb\rmi_iiop\Trader.idl
. . .
>%IDL2CPP% idlSources\javax\ejb\RemoveException.idl
Configure the Server
Start the WebLogic Server by reviewing and implementing the steps defined in the WebLogic Server Examples documentation. See Starting WebLogic Server with the Examples Configuration. Review the configuration file containing the configuration attributes for all of the examples, located in config\examples\config.xml in the WebLogic Server installation location. To run a start server script:
Windows
prompt> startExampleServer
Alternatively, on Windows platforms you can start the WebLogic Server with the examples configuration from the Windows Start Menu.
UNIX
$ sh startExamplesServer.sh
Run the Example
Run the WLStrader Value Type sample program by setting up the environment and starting the tuxclient.exe executable program. The following steps are for a Windows environment:
prompt> set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%WL_HOME%\config\
examples\applications\ejb_over_iiop.jar
prompt> java utils.host2ior hostname port
prompt> tuxclient.exe
Creating a trader
Buying 3000 shares of BEAS
500 shares bought
Buying 100 shares of PSFT
100 shares bought
End statelessSession.Client
Additional Sources of Information
The process of developing a BEA Tuxedo CORBA client application to interact with a WebLogic Server application begins with an EJB. If you are creating a new WebLogic Server application, the first step is to design and implement the server.
The following sections list sources of information about the steps required to implement connectivity between an RMI over IIOP CORBA Client and an EJB in WebLogic Server.
WebLogic Server
These topics are included in the WebLogic Server online documentation:
Object Management Group (OMG)
Information about CORBA objects and value types, which are objects passable by value, is available from the OMG Web site: http://www.omg.org.
BEA Tuxedo CORBA
The BEA Tuxedo online documentation provides complete documentation on CORBA topics in the BEA Tuxedo product. The references listed here contain information on creating CORBA clients, the COSNaming Service, the IDL command, and BEA Tuxedo support for value types:

|
|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2001 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|