









|
As stated in Event Service, and reiterated here for reference, the EPCIS-related services deal with two types of data: event data and master data.
Event data grows in quantity as more business is transacted, and refers to things that happen at specific moments in time. There is no mechanism to delete or modify an event; events are retracted or corrected via a new event whose business meaning is to rescind or amend the effect of a prior event.
For more information about the event service, and an introductory figure that shows the relationship between event data and master data, see Event Service.
Master data does not grow merely because more business is transacted. It is not typically tied to specific moments in time and provides interpretation for elements of event data.
Master data is business-context information that is associated with event data by the reporting service and by the data exchange service (queries for events can include parameters that filter query results based on master data).
Master data is not present in the captured event data in the WebLogic RFID Enterprise Server 2.0 release; it is created and maintained separately. The relationship between event data and master data is that event data can be used as an index into relevant master data. For example, consider an event that contains following event type and value:
<bizLocation>
<id>urn:epc:id:sgln:0614141.33254.0</id>
</bizLocation>
Unless you already know the answer, the URN representation provides data but not much information. However, when the URN is used as a master data Business Location entry which reference a set of master data attributes, you can associate useful information with the event. This association is shown in Figure 3-2, Event and Master Data, on page 3-5, where urn:epc:id:sgln:0614141.33254.0 references the following master data attributes:
Thus the ability to create master data and associate it with information contained in events provides an efficient mechanism for associating additional business information with tag data.
| Note: | Events and master data have separate XML schemas (XSDs). (The master data schema is used when returning information from a SimpleEventQuery.) The XML types mentioned in this section refer to those used in the master data XSD, not the event data XSD. |
The following sections examine master data relationships:
A master data type is a definition for master data entries of that type.
Each master data type defines a set of attributes and their data types; for example, as shipped, the Business Location type defines an attribute named address1, whose URI is urn:epcglobal:epcis:mda:name, and whose data type is String (Master Data Entries, Attributes, and Children provides tables that list the attributes for master data types.)
Types and the attributes associated with them are extensible: you can use the WebLogic RFID Enterprise Server Master Data Administration Console to create and modify master data types, entries, and attributes.
Table 4-1 shows the master data type name for each event type that has a master data type associated with it.
A master data entry is a concrete instance of a master data type. You can create as many entries as you need of each master data type. Each entry has the same set of attributes defined for its master data type, but where the master data type defines the data type for each attribute, an entry's attributes contain the real business-context information associated with a business's operations.
For example, the master data type Business Location defines an attribute address1 of type String. A master data Business Location entry could define address1 as 123 Elm Street.
In addition to attributes that provide concrete business information, an entry's attribute list can contain zero or more children. A child is the identifier of another master data entry within the same master data type. You can create a hierarchy of entries when it makes business sense to do so. For example, assume three Business Location entries that reference "Acme Corp. Retail Store #3," "Acme Corp. Retail Store #3 Backroom," and "Acme Corp. Retail Store #3 Sales Floor." In this example, there is a natural hierarchical relationship in which the first entry is the parent and the latter two entries are children.
This ability to create a hierarchical parent/child relationship among entries is useful for establishing informative relationships among entries. For example, you have a Business Location entry that represents a building. You create a child entry for each floor in the building. Each floor entry has child entries that represent discrete areas such as "billing office," "store room," "receiving," "storage," etc.
One additional relationship that you can establish between entries is that an entry can be the child of more than one parent. This allows for more than one way of grouping entries; for example, locations could be grouped both by geography and by function.
| Note: | To prevent a circular relationship, an entry cannot become its own descendant via the parent/child relationship. For example, a child entry cannot specify a parent entry as one of its children. |
In Figure 4-2, urn:epc:id:sgln:0614141.33254.1 is a child of the master data entry urn:epc:id:sgln:0614141.33254.0.
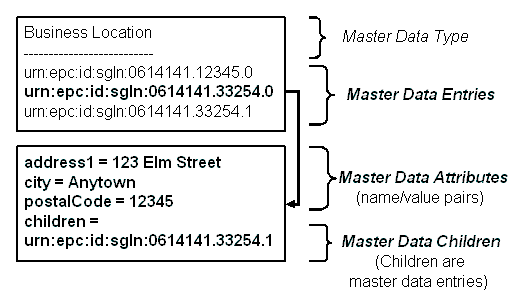
See Master Data XML Example for examples of attributes and children.
WebLogic RFID Enterprise Server 2.0 provides the following pre-defined attributes for each business type:
The data type for all attributes in these tables is String.
In the following example, keep in mind the following mappings:
<attribute> element<children> element<EPCISMasterDataBody>
<VocabularyList>
<Vocabulary type="urn:epcglobal:epcis:vtype:BusinessLocation">
<VocabularyElementList>
<VocabularyElement id="urn:epc:id:sgln:0614141.33254.0">
<attribute id="urn:epcglobal:fmcg:mda:sslt:warehouse"/>
</VocabularyElement>
<VocabularyElement id="urn:epc:id:sgln:0614141.33482.0">
<attribute id="urn:epcglobal:fmcg:mda:sslt:retail"/>
<attribute id="urn:epcglobal:fmcg:mda:address">
<acme:Address
xmlns:acme="http://acme.com/types">
<Street>100 Nowhere Street</Street>
<City>Omaha</City>
<State>NB</State>
<Zip>70475</Zip>
</sample:Address>
</attribute>
<children>
<id>urn:epcglobal:fmcg:ssl:0614141.33482.201</id>
</children>
</VocabularyElement>
<VocabularyElement id="urn:epcglobal:fmcg:ssl:0614141.33482.201">
<attribute id="urn:epcglobal:fmcg:mda:sslt:201"/>
</VocabularyElement>
</VocabularyElementList>
</Vocabulary>
</VocabularyList>
</EPCISMasterDataBody>


|