


|

|
||
|
| |||
You must create source and destination files prior to the conversion process. For converting non-FML to FML buffers or FML buffers to non-FML, you must have the following files:
Creating Files for Conversion
For information about the source file requirements, refer to the Mercator Help file.
For information about creating an FML Field Definition file, refer to the BEA TUXEDO Programmer's Guide and the BEA TUXEDO Reference Manual on the BEA eLink Platform Online Documentation CD-ROM.
For information on the format and definition of the FML Group Format file, refer to the "Creating an FML Group Format File" section.
An FML32 Group Format file ( Listing 5-1 is the syntax for the FML Group Format file.
Creating an FML Group Format File
*.fgf) is used with an FML32 Field Definition Table to apply structure to FML32 fields received by the eLink DIO in an FML input buffer. Data structures applied to input FML32 buffers can range from simple to complex. A simple structure may be an FML Group Format that supplies the order of individual FML32 fields received by a service request. An example of a complex structure could have nested groups of data items with multiple occurrences of some or all of the groups or data items.
Listing 5-1
Syntax for FML Group Format File
GROUP <
groupname> [OCCURS n | s]
field-type FML-field-name [OCCURS n | s]
END
Note: The top GROUP (or root) cannot have an OCCURS clause.
groupname for the top GROUP.
Note: Group names and field names must be unique within an FML Group Format file.
OCCURS n | S
n) denotes the number of times the specific group or data item occurs in an input FML32 buffer.specifying the keyword
S indicates that a group or data item has an indefinite number of occurrences. The number of groups or data items processed may vary from one service call to the next. The eLink DIO product determines how many occurrences of a group or data item exist in the input FML32 buffer and process the data accordingly. Only use the keyword S at the top group level under the outermost group. The OCCURS parameter is optional. The default is 1 occurrence.
Listing 5-2 is a simple FML Group Format file. This sample file supplies the order in which individual FML Fields are formatted for input to the data mapping process. This FML Group Format file specifies the structure to build using the FML32 data items in the input buffer with names that match the FML Group Format field names.
Listing 5-2 Simple FML Group Format File Example
GROUP NAME
string FIRST_NAME
char MIDDLE_INIT
string LAST_NAME
int AGE
END
Listing 5-3 is a sample FML Group Format file with nested groups and occurrences. The GAA_ARRAY is the outermost group and will not support an OCCURS S clause. The valid top level groups in the following example are GAA_UPPER and GAA_SECOND. The OCCURS S definition in GAA_UPPER indicates that this top level group has an indefinite number of occurrences. GAA_UPPER contains another group, GAA_LOWER. Groups nested within groups other than the outermost group must have a fixed number of occurrences. GAA_LOWER occurs five times within each occurrence of GAA_UPPER.
Listing 5-3 Sample FML Group Format File
GROUP GAA_ARRAY OCCURS
GROUP GAA_UPPER OCCURS S
short EMA_S_SHORT
GROUP GAA_LOWER OCCURS 5
string EMA_S_STR OCCURS 2
long EMA_L_LONG OCCURS 4
END
string EMA_S_STR2
END
GROUP GAA_SECOND OCCURS 3
short EMA_S_SHORT
short EMA_S_CHAR
END
END
The BEA eLink DIO Design Client installs the mti2fgf utility. This utility takes a file containing Meta-Type Information and converts it back to FML Group Format language. This utility is helpful if you have the Meta-Type Information file, but no longer have the source FML Group Format file. After using the utility, the resulting *.fgf file is sent to stdout and can be used in the eLink DIO FML Importer.
To use the mti2fgf utility, issue the following command.
Listing 5-4 mti2fgf Utility
$ mti2fgffilename.mti
After you transfer the necessary files to the development environment, you can begin the process for building a Mercator map file. The map file will contain the specific mapping rules used to transform input data to desired output data formats. The following tasks must be done in the development environment prior to the execution of a service request.
Before developing your data maps, you must put the Mercator Open Edition Client in your system path. Select Program>Settings>Control Panel>System Properties to access properties page. Select the Environment tab and enter the path for Mercator Open Edition Client under User Variables. The default installation directory is C:\mercator.
To create an FML type tree file, complete the following tasks.
.fgf). For information on the FML Group
Format file, refer to the "Creating an FML Group Format File" section. For
information on creating FML Field Definitions file, refer to the BEA TUXEDO
Programmer's Guide and the BEA TUXEDO Reference Manual on the eLink
Platform Online Documentation CDROM.
Browse to specify the following files on the FML Group Format File Selection.
FML Group Format File (
Note:
After selecting an FML Group Format file, the eLink DIO FML Importer will default the Type Tree and MTI file names to the same file name as the FML Group Format. The extensions will be unique, FML Field Definition File ( Type Tree File Name is the directory location and name of the FML type tree file to use for creating the Mercator Map file. If you reference only a file name and no directory path, the file will be created in the current directory.
MTI File Name is the directory path and file name for the metadata associated with the FML type tree file. If you reference only a file name and no directory path, the file will be created in the current directory.
Note:
Check the Include /Q header information box when using eLink Data Integration Option with the TUXEDO /Q feature. Do not check the Include /Q header information box when using the BEA eLink Data Integration Option component with eLink for Mainframe.
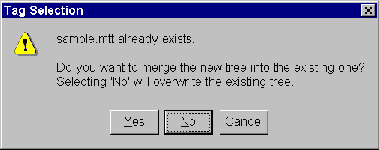
Click OK to validate the If the following screen displays, click No to overwrite the file. No is the default.
Note:
Do not click Yes. It will merge the existing tree with the new tree.
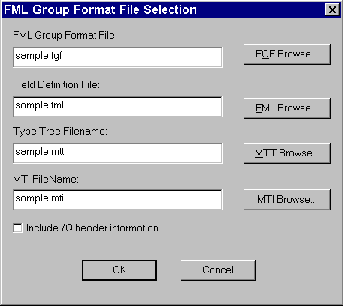
.fgf) specifies the FML Group Format file to use in the data mapping conversion. This file is used in conjunction with an FML Field Definition file for the conversion.
*.mtt and *.mti respectively.
.fml) specifies the FML buffer to use in the data mapping conversion.
.fgf and .fml files and create the .mtt and .mti files.
The FML type tree specifies the type definitions of the input and output files. There are four branches for the type tree file; Control, Field, Message, and SET. The SET line is not used.
From your source file, create a type tree file ( Create a non-FML Type Tree File Using Importers
*.mtt).
.mmc).
Note:
If you are using the TUXEDO /Q feature, refer to the "Control Information for TUXEDO /Q" section.
Listing 5-5
Sample COBOL Type Tree Header Information
CONTROL
FIELD
FieldName
Format
Service
The control information consists of the following elements.
An input card and an output card must be created prior to compiling a Mercator map file ( Create a Mercator Map File
*.mmc). Input cards contain a type tree and an adapter. Use both type tree files for the buffer types (for example FML and COBOL copybook) that are being mapped. For information on how to build a Mercator map file, refer to the Mercator Map Editor Reference Guide and the Mercator Functions & Expressions Reference Guide.
Enter a unique name for the new input card in the Card Name field.
In the Type section, click File to browse and select the input card type tree file ( In the Name field of the Type section, click the Browse button to display the contents of the type tree file ( Leave the default value, File, in the Data Source field.
In the File section, you can use the Name field as a comment box. Enter a description of the input card as your comment. Text must be entered in this field.
Note:
The value in this field is ignored and has no effect on the data mapping process; therefore, you can use this field as a comment field.
Click OK to create the input card.
*.mtt) for the File field.
.mtt). From the display, select the input record.
Enter a unique name for the new output card in the Card Name field.
In the Type section, click File to browse and select the output card type tree file ( In the Name field of the Type section, click the Browse button to display the contents of the type tree file ( Leave the default value, File, in the Data Source field.
In the File section, you can use the Name field as a comment box. Enter a description of the output card as your comment. Text must be entered in this field.
Note:
The value in this field is ignored and has no effect on the data mapping process; therefore, you can use this field as a comment field.
Click OK to create the output card.
*.mtt) for the File field.
.mtt). From the display, select the output record.
="C" as the rule in the Format field. If the output
record is an FML buffer, enter ="FML" as the rule in the Format field.
Map the remaining fields. For information on mapping rules and defining functional maps, refer to the Mercator Functions & Expressions Reference Guide.
*.mmc) by selecting the Build option from the Map
menu. If errors occur during the build process, access the building results for an
explanation of the error. Resolve the errors in the mappings and execute the build
process again until no errors occur.
To set up the execution environment, complete the following tasks:
The client program requests the mainframe service advertised by the eLink for Mainframe gateway.
After completing the development process, the following files must exist and be transferred to the execution environment.
*.fml - ASCII file)
Transfer this file to the execution environment. Define the FLDTBLDIR32 to point to the file's directory structure. Also, define the FML Field Definition file with other FML32 tables in the FIELDTBL32 environment variable.
filename.mti - ASCII files)
Transfer the Meta-Type Information file to the directory listed as MTI_DIR in the SERVER section of the eLink DIO configuration file. If the eLink DIO configuration does not specify an MTI_DIR, then load these files to APPDIR.
filename.mmc - Binary file)
Note:
If you are executing on HP-UX, AIX, or SUN Solaris, the map files will have a platform-specific extension after the porting function. For example, after porting the Transfer the Mercator map files to the directory listed as MAP_DIR in the SERVER section of the eLink DIO configuration file. If the eLink DIO configuration does not specify a MAP_DIR, then load these files to APPDIR.
filename.mmc file to Sun Solaris, the file is named filename.sun.
Be sure to set the following environment variables.
Set Environment Variables
After transferring the necessary files to the execution environment, be sure that the BEA TUXEDO and other products such as BEA eLink for Mainframe are running. For information on how to start these products, refer to the related BEA TUXEDO documentation and the BEA eLink for Mainframe online documentation CD.
The client program should be a standard TUXEDO program. This program should create and populate an FML32, STRING, or CARRAY buffer. The client calls a service advertised by the eLink DIO Server using this buffer as input. The eLink DIO Server performs data mapping and returns any required output to the client program.
Execute client programs previously created to perform service calls to services supported by the eLink DIO Server.
After starting these products, you can issue a service request for data mapping. For information on setting up TUXEDO service requests, refer to the BEA TUXEDO documentation.
Note:
Leave logging on during execution of your map files to assist in diagnostics if errors occur. Logging will produce a large amount of output. The log file (.log) can be accessed directly in the directory where the compiled map file (*.mmc) is located.
Start BEA TUXEDO and Other Remote Applications
Write a Client Program to Call eLink DIO Services
Issue a Service Request for Data Mapping