







|
This section describes how a BEA AquaLogic Service Bus proxy service can be configured to validate a message passing from a client to a business service. Validation can occur at any stage in the flow, though it usually happens as early as possible to prevent unnecessary processing of the message if an invalid result occurs. Validation can occur in several ways.
AquaLogic Service Bus does not automatically validate the message sent or received against the service interface definition, whether this is a WSDL definition or a messaging interface definition. However, you can configure a Validate action and use XQuery conditional expressions to perform explicit validate checks in the message flow. This reduces the possibility of run time errors as a result of invalid configurations.
This section includes the following topics:
Complete Tutorial 1. Routing a Loan Application and Tutorial 2. Transforming a Loan Application.
The objective of this tutorial is to provide steps to configure and test BEA AquaLogic Service Bus and demonstrate how message validation and error handling is managed using the graphical environment in the AquaLogic Service Bus Console. It includes the following:
This tutorial exposes you to the following features of AquaLogic Service Bus:
A primary mortgage company routes every loan application through a BEA AquaLogic Service Bus proxy service which validates the message. If the application is:
Figure 5-1 summarizes the logical architecture to support this scenario. It illustrates where AquaLogic Service Bus fits in the enterprise to mediate the messaging between the client and the business services.
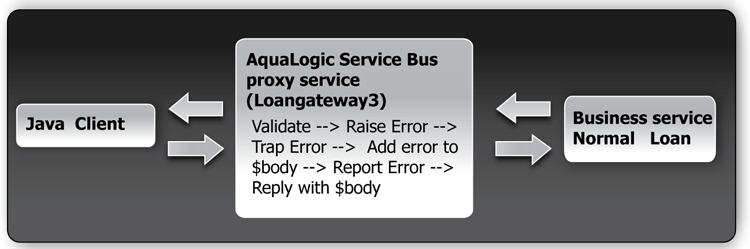
In this scenario, you can configure AquaLogic Service Bus to validate an incoming message in the message flow against a schema definition in a WSDL resource. Every field is checked for valid content. All elements must be populated for the application to be valid. However, in this case, when the value of the loan duration field is not an integer, the validation action raises an error. The context variable, $fault, is populated with the error. The error is trapped by a stage error handler which replaces the body context variable <Notes> field value with the text of the $fault <reason> element. A Report action then saves the error code and, for context, the message body for later viewing and searching in the console. The Reply action returns the body context variable to the client.
In this scenario, the message is:
Use the Project folder, MortgageBroker, and the directory structure that you created in the previous tutorial to hold the project artifacts. The resources required for this scenario are described in Table 5-1.
In this tutorial, BEA AquaLogic Service Bus is used to route a loan application within a Mortgage company to a target Web Service. The loan application has to be completed correctly for the application to be processed. If there is an error in the application, AquaLogic Service Bus raises a validation exception, and returns an error message to the client.
You will create a proxy service, LoanGateway3, and configure it to route a message to the normalLoan business service. You will configure the behavior of the proxy service, which includes:
Complete the following steps to design and configure the proxy service and the associated resources in AquaLogic Service Bus to resolve this user case scenario:
Ensure that AquaLogic Service Bus is running in the domain you created for the tutorial and that you have completed the steps described in Tutorial 1. Routing a Loan Application.
For this tutorial, use the project folder, MortgageBroker, and the directory structure you created in Tutorial 1. Routing a Loan Application to hold the project artifacts.
The Project Explorer pane is opened in the navigation pane and a project page is displayed in the console.
In this step, you will create the proxy service, LoanGateway3. You will use the existing normalLoan service WSDL resource to validate the content of the message. If the loan application is valid, that is, if it meets the expected criteria, and is routed to the existing normalLoan business service. The WSDL resource and business service were created in "Create the normalLoan Service WSDL Resource" section in Tutorial 1. Routing a Loan Application.
In this step, you create a proxy service that is used to route the loan application to the appropriate business service. Follow the steps described in To Create the Proxy Service, but for this instance use the proxy service name and the Endpoint URI described in Table 5-2.
You should also review the configuration settings prior to registering the proxy service.
When you complete this step, the MortgageBroker/ProxyService folder contains the proxy services you created in this tutorial and in Tutorial 1. Routing a Loan Application:
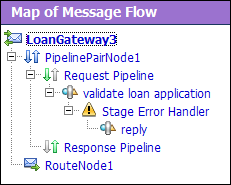
The proxy service is implemented in AquaLogic Service Bus as a message flow, which includes request and response pipelines. AquaLogic Service Bus message flows define the implementation of proxy services. The message flows can include zero or more pipeline pairs:
Pipelines can include one or more stages, which in turn include actions. To configure the behavior of the LoanGateway3 proxy service, for the message flow, you must complete the following:
The Project Explorer pane is opened in the navigation pane.
| Note: | You must be in a session to edit resources. If you have not already done so, begin a session (click Create in the Change Center) so that you can configure the proxy service and edit the message flow. |
The Edit Message Flow page for the proxy service LoanGateway3 is displayed.
The PipelinePairNode1 is created and placed in the message flow. Request and response pipelines are displayed for this node as in Figure 5-2.
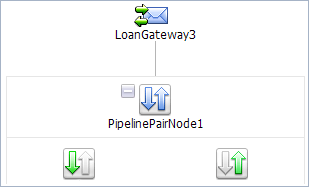
You must now configure the request actions for the proxy service.
The page is displayed as in Figure 5-3.
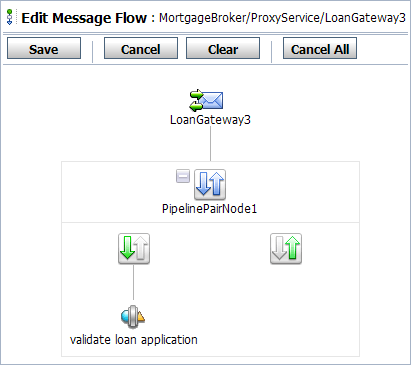
 Stage. The Edit Stage Configuration page is displayed.
Stage. The Edit Stage Configuration page is displayed.  Validate from the drop-down list. The Validate action is added to the stage.
Validate from the drop-down list. The Validate action is added to the stage. link to edit the XPath expression. The XPath Expression Editor page is displayed.A structural representation of the body element is displayed in the Variables Structure pane.
The processLoanApp element is within the $body - processLoanApp (request) element.
A graphical representation of the structure of the loan request document is displayed.
 associated with the loanRequest element, drag and drop it in the XQuery Expression text box. The XQuery expression is written in the text box.
associated with the loanRequest element, drag and drop it in the XQuery Expression text box. The XQuery expression is written in the text box.
./exam:processLoanApp/loanRequest
| Note: | The drag and drop functionality works only in Internet Explorer (IE) browsers. If you are using a browser other than IE, select the loanRequest element in the Variable Structures pane. The expression is displayed in the Property Inspector palette. Place the cursor in the XQuery expression text box and click Copy Property. The expression is copied to the text box. You can also copy the expression in the palette and paste it into the XQuery Expression text box. |
It is good practice to do this before you submit the expression. The expression is validated for syntax. If there are errors in the expression, they are displayed directly above the Validate button. In this case the expression is valid.
The Edit Stage Configuration page displays <XPath> which is replaced by the XQuery expression.
 WSDL from the list. The Select a WSDL browser window is displayed.
WSDL from the list. The Select a WSDL browser window is displayed.You must validate the message against the resource as the proxy service is based on the WSDL resource that you originally created.
The Select WSDL Definitions pane is populated with the content categories of the WSDL.
| Note: | The validation of a message must occur as early as possible in a message flow. This prevents the unnecessary processing of a message in the case where the content of the message is invalid. When an exception is raised, further processing is stopped and a response is immediately returned to the client. |
| Note: | Messages can be validated at the route node or using a separate Validate action (as in this case). When you create a Validation stage, the processing of the message is more modular and logically breaks down the actions in the message flow. If multiple validations are preformed on a message, the validate action is logically expanded. |
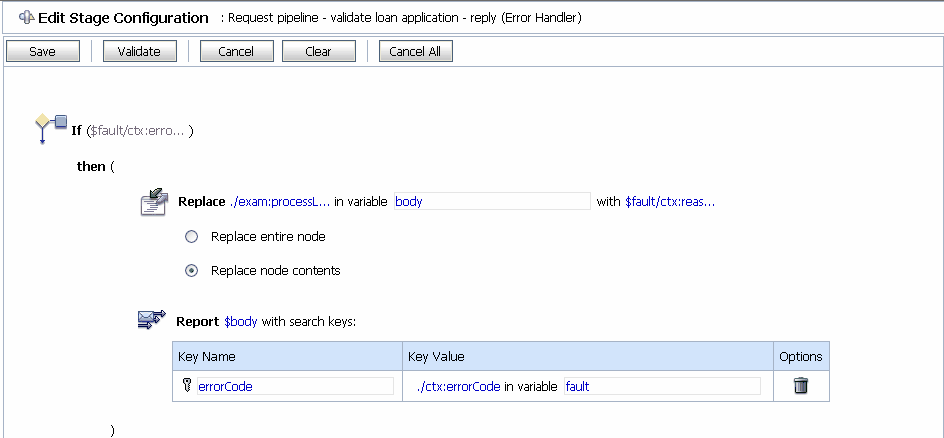
The Stage Error Handler has to be configured as follows:
The steps to add the Stage Handler are as follows:
 Stage Error Handler. The Edit Error Handler page is displayed.
Stage Error Handler. The Edit Error Handler page is displayed. Name and Description as in Figure 5-5.
Name and Description as in Figure 5-5. Stage. The Edit Stage Configuration page is displayed as in Figure 5-6.
Stage. The Edit Stage Configuration page is displayed as in Figure 5-6. If...Then to add an If...Then action to the Reply stage.
If...Then to add an If...Then action to the Reply stage. Replace.
Replace. A structural representation of the body element is displayed in the Variable Structures pane.
The processLoanApp element is within the $body - processLoanApp (request) element.
 associated with the Notes
associated with the Notes element of $body, drag and drop it on the XPath Expression text box. The following XPath expression is written in the text box.
./exam:processLoanApp/loanRequest/java:Notes
| Note: | The drag and drop functionality works only in Internet Explorer (IE) browsers. If you are using a browser other than IE, select the Notes element in the Variable Structures pane. The expression is displayed in the Property Inspector palette. Place the cursor in the XPath expression text box and click Copy Property. The expression is copied to the text box. You can also copy the expression in the palette and paste it into the XPath Expression text box. |
body.<Expression> link to display the XQuery Expression Editor page and accept the default selection of XQuery Text in the page.$fault/ctx:reason/text()The replace action should appear as in Figure 5-7.
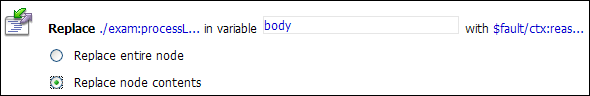
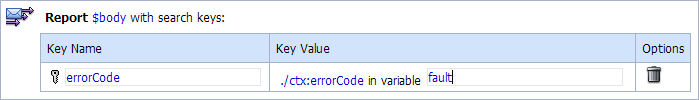
Add a Report action and configure it to report the body context variable as detailed context, and set a key name of errorCode and the key value to the actual error code found in the fault context variable.
 Reporting
Reporting Report. The Report action is added to the page.
Report. The Report action is added to the page. from the Select Structure drop-down list. element and drag and drop it on the XQuery Expression text box.
The $body XQuery expression is written in the text box.
| Note: | The drag and drop functionality works only in Internet Explorer (IE) browsers. If you are using a browser other than IE, select the body element in the Variable Structures pane. The expression is displayed in the Property Inspector palette. Place the cursor in the XQuery expression text box and click Copy Property. The expression is copied to the text box. You can also copy the expression in the palette and paste it into the XQuery Expression text box. |
.  associated with the errorCode
associated with the errorCode and drag and drop it in the XPath Expression text box.
The ./ctx:errorCode expression is written in the text box.
| Note: | The drag and drop functionality works only in Internet Explorer (IE) browsers. If you are using a browser other than IE, select the errorCode element in the Variable Structures pane. The expression is displayed in the Property Inspector palette. Place the cursor in the XPath expression text box and click Copy Property. The expression is copied to the text box. You can also copy the expression in the palette and paste it into the XPath Expression text box. |
This step enables you to index the reporting data by error code. The keys are a convenient way to identify a message. You can use the error code to search for reporting entries in the reporting module.
| Note: | To Add an action on a page, click the Action preceding the placement of the new action and select the Action to be added from there. Actions are added in sequence. |
The report action should appear as in Figure 5-8.
The Edit Stage Configuration page appears as in Figure 5-9.
Click the If...Then icon ![]() and select Add else Condition to add an Else action to the Stage Error Handler.
and select Add else Condition to add an Else action to the Stage Error Handler.
 Replace.
Replace. Log.
Log.<Expression> link to display the XQuery Expression Editor page. Enter $fault/ctx:reason/text() in the XQuery Text window. Other than validation error, in the With Annotation window.Now, the completed Else condition appears as in Figure 5-10.

 Flow Control
Flow Control Reply. The Reply action is added to the page.
Reply. The Reply action is added to the page.Add a Route Node to the Pipeline pair, then configure the Route Node to route to the normalLoan business service.
 Route Node. The Edit Stage Configuration page is displayed.
Route Node. The Edit Stage Configuration page is displayed.  Routing.
Routing. The Route action is displayed in the page.
processLoanApp.
This is the operation on the NormalLoan business service that is invoked at run time.
You have now defined the case for routing the loan application to the NormalLoan business service.
The Edit Message Flow screen appears as in Figure 5-12.
You can view the map of the message flow of the proxy service as in Figure 5-13.
Now that you have configured BEA AquaLogic Service Bus to work with the client and the target business services, you can test the configuration. Testing is performed at the command prompt by changing the value of the Loan duration (in years) field in the build.xml file and then running ant. The behavior for the proxy service in this scenario depends on the correct value being entered for the loan duration. If the value is entered for the loan is a non integer, a fault is triggered and an error message results in the Notes field of the message. If the value is entered for the loan is an integer, the message is routed to the NormalLoanApprovalService business service.
This section describes how you can test the proxy service for both cases. The message returned in the command window after running a test indicates whether a validation exception results or whether the message was routed to the appropriate business service.
| Note: | Run the tests in this section multiple times (at least five times) to generate data to enable you to explore the reporting and monitoring features described in Step 7: Using Reporting and Monitoring. |
This section includes the following test scenarios:
To run this test correctly, ensure that WebLogic Server is started in the BEA AquaLogic Service Bus 2.5 (ServiceBusTutorial) domain.
setEnv.cmd to set up your environment, you must do so now. BEA_HOME\weblogic92\samples\servicebus\examples\src\examples\webservices\jws_basic\normal
build.xml file run target:build.xml. build.xml file looking for the string:<arg line="http://$... :<arg line="http://${wls.hostname}:${wls.port}/loan/gateway3 steve 555 2500 20.5 4.9 notes" />
This changes the URI to that of the proxy service running in the tutorial domain, and specifies a value of 20.5 (a non-integer value) for the loan duration.
The remainder of the input parameters specified on the arg line are described in Table 5-3.
antrun
This tests the routing logic of the proxy service. A response message from the Web Service is displayed at the command line.
[java] Loan Application Response: ALSB Validate action failed validation
[java] Rate: 4.9 Duration: 20.5
BUILD SUCCESSFUL
The response message indicates that a validation exception occurred because the loan duration is not an integer.
build.xml file in the following directory:BEA_HOME\weblogic92\samples\servicebus\examples\src\examples\webservices\jws_basic\normal
| Note: | In this case (to test the NormalLoanApprovalService business service), enter a value of 20 for the loan duration in the build.xml file (see Table 5-3), then save the changes. |
ant runA response message from the Web Service is displayed at the command prompt:
[java] Loan Application Response: APPROVED BY THE <i><b>NORMAL</b></i> LOAN APPLICATION PROCESSING SERVICE[java] Rate: 4.9BUILD SUCCESSFUL
The response message indicates that the NormalLoan business service processed the request because the loan duration requested is an integer.
Now that you have tested the proxy service you can explore the reporting and monitoring features of the AquaLogic Service Bus Console.
| Note: | You must have run the tests in Step 6: Test the Loan Application Routing Configuration multiple times (at least five times) to generate data to enable you to explore the reporting and monitoring features. |
AquaLogic Service Bus includes a JMS Reporting Provider for message reporting. The Reporting module in the AquaLogic Service Bus Console displays the information captured from this reporting provider. You can create your own reporting provider using the Reporting Service Provider Interface (SPI) if you do not wish to use the out-of-the-box reporting provider.
The dashboard of AquaLogic Service Bus Console contains reporting features that are presented in a drill-down format. When you explore the links presented, the information is made available to you.
BEA AquaLogic Service Bus can monitor and collect run time information for both systems operations and business auditing purposes. AquaLogic Service Bus aggregates run time statistics that you can view on a customizable Dashboard. The Dashboard allows you to monitor the health of the system and alerts you to problems in your messaging services. With this information, you can quickly and easily isolate and diagnose problems as they occur.


|