







|
The Java Security Service Module is a java-based product that allows an application developer to access sets of interfaces to define and implement security related information and requirements specific to a Java application. These interfaces support the most commonly required security functions and are organized into services that are logically grouped by functionality.
After you use the Java Security Service Module interfaces to implement security functions in your Java application, you can deploy and run your application on any instance of a Java Security Service Module runtime that supports the configuration requirements of your application.
The Java Security Service Module offers five security services: Authentication Service, Authorization Service, Auditing Service, Role Service, and Credential Mapping Service. The name of each service indicates the type of function it is used to implement within a Java application. Each of these services is discussed in more detail later.
Because most major functions required by Java applications developed using the Java Security Service Module are performed within the security framework, this architecture has several benefits, including:
The following topics provide more information on the Java Security Service Module:
Figure 2-1 shows the major components that make up the Security Service Module environment.
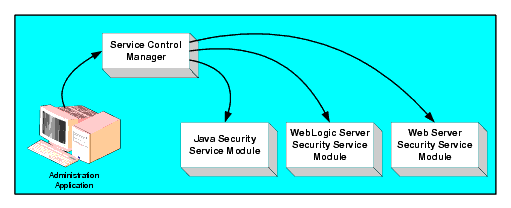
The Administration Application allows you to manage and configure multiple Security Service Modules. While Security Service Modules specify and consume configuration data and then services security requests accordingly, the Administration Application allows you to display the security providers that are plugged into the security framework and to display and modify the configuration data for those providers.
The Service Control Manager (SCM) is an essential component of the BEA AquaLogic Enterprise Security configuration provisioning mechanism and of a fully-distributed security enforcement architecture.
| Note: | AquaLogic Enterprise Security version 2.5 removed the requirement that a Service Control Module (SCM) be installed on each system where one or more Security Service Modules (SSMs) are installed. |
An Service Control Manager is a machine agent that exposes a provisioning interface to the Administration Application to facilitate the management of a potentially large number of distributed Security Service Modules. A Service Control Manager can receive and store metadata updates, both full and incremental, initiated by the Administration Application.
The Administration Application uses the provisioning mechanism of the Service Control Manager to distribute configuration and policy data to each Security Service Module where it is consumed locally (see Figure 2-2). Security Service Modules (which can be distributed throughout an enterprise) can be embedded in Java applications, application servers, and web servers. After you use the Administration Application to configure an instance of an Security Service Module with configuration and policy data, the Security Service Module does not require any additional communication with the Service Control Manager to perform security functions. However, the Service Control Manager maintains communication with the Security Service Module to distribute full and incremental updates.
Figure 2-3 shows the major components of the Java Security Service Module. The Java Security Service Module comprises the security service APIs, the security framework, and the security providers that you configure in any given instance of a Java Security Service Module runtime.
The following topics describe these components:
The Java Security Service Module supports the following security service APIs:
The Authentication Service provides functions to an application related to establishing, verifying, and transferring a person or a process. Thus, the Authentication Service provides two main functions: authentication and identity assertion.
The Authorization Service is a service that allows an application to determine if a specific identity is permitted to access a specific resource. This decision may then be enforced in the application directly at the policy enforcement point.
The Auditing Service allows an application to log events based upon activity related to enterprise security. The Java Security Service Module runtime uses these mechanisms to log appropriate data when events occur.
The Role Service allows an application to extract role information about specific identities and resources within the context of the application. These roles may then be used to customize interfaces.
| Note: | Roles themselves should not be used for authorization, as many policies allowing or disallowing access to a resource may be written against a role. It is best that you use the Authorization Service to determine actual rights. |
The Credential Mapping Service allows an application to fetch credentials of certain types that are associated with a specific identity for a specific resource. These credentials may then be used on behalf of that identity to provide some privileged function, such as logging into a database or sending e-mail.
The primary function of the Security Framework is to provide an application programming interface (API) that security and application developers use to implement security functions in Java applications. Within that context, the Security Framework also acts as an intermediary between security functions that you implement in Java applications using the Java security service APIs and security providers configured into the Java Security Service Module. For more information on the Security Framework, see Introduction to BEA AquaLogic Enterprise Security.
When you install the Java Security Service Module, a JAR file is deployed that contains all the default security providers that ship with the product. However, before any of the security providers can be used, you must use the Administration Application to configure them in the Java Security Service Module. You have the option of configuring either the default security providers that ship with the product or custom security providers, which you develop or purchase from third-party security vendors. The Java Security Service Module supports the following types of security providers:
For more information on the security providers, see Introduction to BEA AquaLogic Enterprise Security. For information on developing custom security providers, see Developing Security Providers for BEA AquaLogic Enterprise Security.


|