1 Introduction to Container Runtimes
This chapter introduces the container runtimes available in Oracle Cloud Native Environment. The available container runtimes are compliant with the Open Container Initiative (OCI) Runtime Specification.
This chapter provides introductory information about runC and Kata Containers.
This document doesn't try to explain how to use images to create containers in any detail, nor does it try to explain how to create and use Kubernetes pods or deployments.
For more detailed information on creating and managing containers using Kubernetes, see Kubernetes Module.
Introduction to runC
runC is a container runtime based on the Linux Foundation's
Runtime Specification (runtime-spec). runC is
developed by the Open Container Initiative.
runC is a component of Oracle Cloud Native Environment. runC is a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) compliant environment to deploy microservices, and to orchestrate containers.
runC is based on a stable release of the upstream runC project. Differences between Oracle versions of the software and upstream releases are limited to Oracle specific fixes and patches for specific bugs.
For upstream runC documentation, see:
https://github.com/opencontainers/runc/blob/main/man/runc.8.md
For more information about runC, see:
Introduction to Kata Containers
You can provide extra security and isolation of workloads using Kata Containers. Kata Containers is based on the upstream Kata Containers OpenStack Foundation project. Kata Containers delivers the framework for creating lightweight virtual machines, that can easily plug into a container ecosystem. Kata Containers offers extra levels of security, while maintaining the development and deployment speed of traditional containers.
Kata Containers is a component of Oracle Cloud Native Environment. Kata Containers is a Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) compliant environment to deploy microservices, and to orchestrate containers.
Kata Containers is based on a stable release of the upstream Kata Containers project. Differences between Oracle versions of the software and upstream releases are limited to Oracle specific fixes and patches for specific bugs.
For upstream Kata Containers documentation, see:
https://github.com/kata-containers/documentation
For more information about Kata Containers, see:
Setting Runtime Classes
CRI-O uses a Kubernetes annotation or Runtime class set in the pod
configuration file to decide whether to run a pod using
runc or kata-runtime.
Figure 1-1 Kubernetes Runtimes
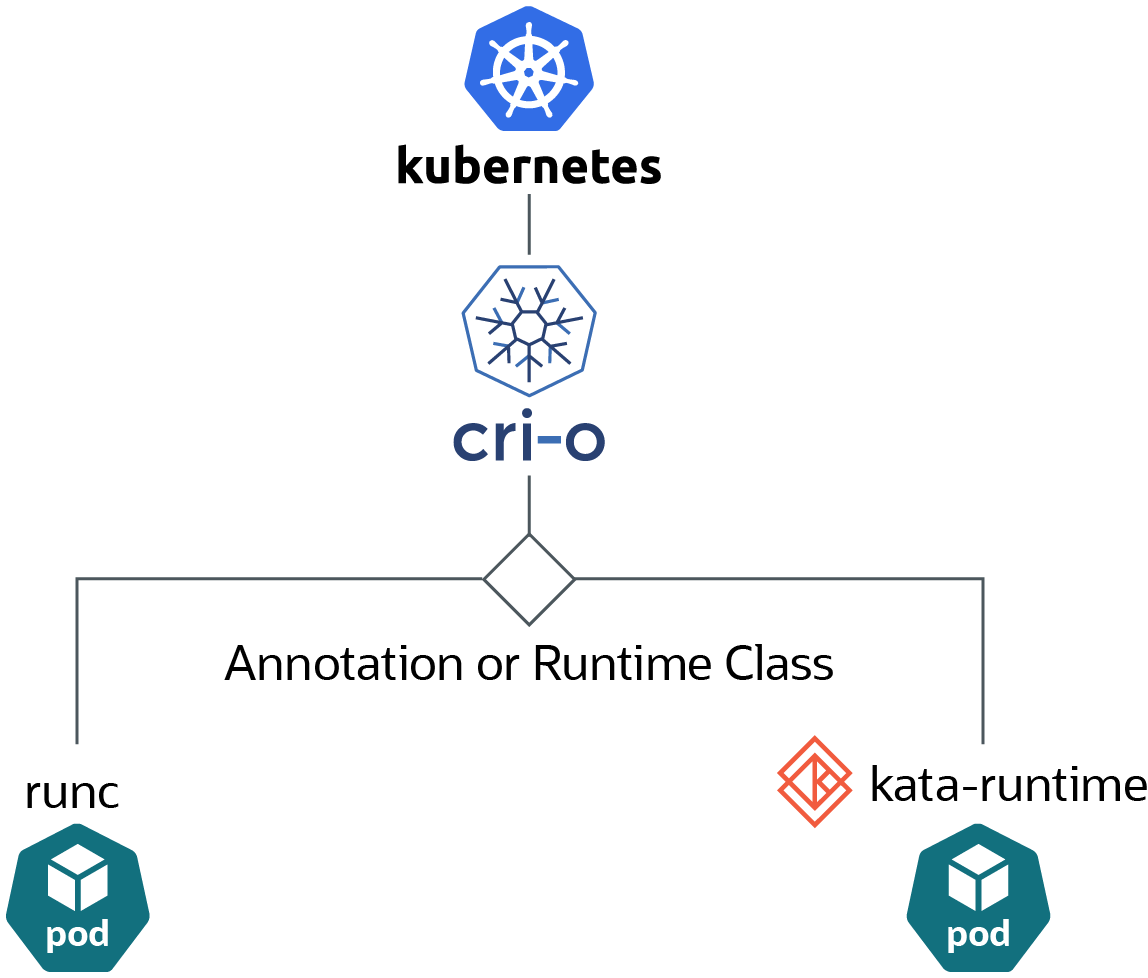
You can create Kubernetes runtime classes to specify whether containers are run as the
default runtime, runc, or using kata-runtime. The examples
in this book use the name native to specify the use of runc,
and the name kata-containers to specify the use of
kata-runtime. You can use any name you like.
To create a runtime class:
-
Create a file for a runtime class for Kata Containers named
kata-runtime.yamlwith the following contents:kind: RuntimeClass apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: kata-containers handler: kataLoad the runtime class to the Kubernetes deployment:
kubectl apply -f kata-runtime.yamlThe runtime class
kata-containerscan now be used in pod configuration files to specify a container is to be run as a Kata container, using thekata-containersruntime. For examples of creating pods using this runtime class, see Creating Kata Containers. -
(Optional) To specify a runtime for
runc, you can do this in a similar way. This is an optional configuration step. Asruncis the default runtime, pods automatically run usingruncunless you specify otherwise. This file is namedrunc-runtime.yaml:kind: RuntimeClass apiVersion: node.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: native handler: runcLoad the runtime class to the Kubernetes deployment:
kubectl apply -f runc-runtime.yamlThe runtime class
nativecan be used in pod configuration files to specify a container is to be run as a runC container, using theruncruntime. -
You can see a list of the available runtime classes for a Kubernetes cluster using the
kubectl get runtimeclass. For example:kubectl get runtimeclassThe output looks similar to:
NAME HANDLER AGE kata-containers kata 7m29s native runc 7m7s