Oracle WebCenter Sites on Kubernetes
The WebLogic Kubernetes Operator supports deployment of Oracle WebCenter Sites. Follow the instructions in this document to set up Oracle WebCenter Sites domains on Kubernetes.
In this release, Oracle WebCenter Sites domains are supported using the “domain on a persistent volume” model only, where the domain home is located in a persistent volume (PV).
The operator has several key features to assist you with deploying and managing Oracle WebCenter Sites domains in a Kubernetes environment. You can:
- Create Oracle WebCenter Sites instances in a Kubernetes persistent volume (PV). This PV can reside in an NFS file system or other Kubernetes volume types.
- Start servers based on declarative startup parameters and desired states.
- Expose the Oracle WebCenter Sites services and composites for external access.
- Scale Oracle WebCenter Sites domains by starting and stopping Managed Servers on demand, or by integrating with a REST API to initiate scaling based on WLDF, Prometheus, Grafana, or other rules.
- Publish operator and WebLogic Server logs to Elasticsearch and interact with them in Kibana.
- Monitor the Oracle WebCenter Sites instance using Prometheus and Grafana.
Current production release
The current supported production release of the Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes Operator, for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment is 4.2.9
Recent changes and known issues
See the Release Notes for recent changes and known issues for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment on Kubernetes.
Limitations in WebCenter Sites Domain
See here for limitations in this release.
About this documentation
This documentation includes sections targeted to different audiences. To help you find what you are looking for more easily, please consult this table of contents:
Quick Start explains how to quickly get an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain instance running, using the defaults, nothing special. Note that this is only for development and test purposes.
Install Guide and Administration Guide provide detailed information about all aspects of using the Kubernetes operator including:
- Installing and configuring the operator.
- Using the operator to create and manage Oracle WebCenter Sites domains.
- Configuring Kubernetes load balancers.
- Configuring Elasticsearch and Kibana to access the operator and WebLogic Server log files.
- Patching an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image.
- Removing/deleting domains.
- And much more!
Additional reading
Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment on Kubernetes leverages the Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes operator framework.
- To develop an understanding of the operator, including design, architecture, domain life cycle management, and configuration overrides, review the operator documentation.
- To learn more about the Oracle WebCenter Sites architecture and components, see Understanding Oracle WebCenter Sites.
- To understand the known issues and common questions for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment on Kubernetes, see the frequently asked questions.
Release Notes
Review the latest changes and known issues for Oracle WebCenter Sites on Kubernetes.
Recent changes
| Date | Version | Introduces backward incompatibilities | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dec 10, 2024 | 24.4.3 | no | Supports Oracle WebCenter Sites 14.1.2.0.0 domains deployment - certified for Oracle WebLogic Kubernetes Operator version 4.2.9. Oracle WebCenter Sites 14.1.2.0.0 container image for this release can be downloaded from container-registry.oracle.com. |
Known issues
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Publishing via LoadBalancer Endpoint | Currenly publishing is only supported via NodePort as described in section For Publishing Setting in WebCenter Sites. |
Install Guide
Install the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator and prepare and deploy Oracle Webcenter Sites domains.
Requirements and Limitations
Understand the system requirements and limitations for deploying and running Oracle WebCenter Sites domains with the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator, including the WebCenter Sites domain cluster sizing recommendations.
Contents
Introduction
This document describes the special considerations for deploying and running a WebCenter Sites domain with the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator. Other than those considerations listed here, WebCenter Sites domains work in the same way as Fusion Middleware Infrastructure domains and WebLogic Server domains.
In this release, WebCenter Sites domains are supported using the domain on a persistent volume model only where a WebCenter Sites domain is located in a persistent volume (PV).
System Requirements
- Container images based on Oracle Linux 8 are now supported. My Oracle Support and the Oracle Container Registry host container images based on both Oracle Linux 8.
- Kubernetes 1.25.0+, 1.26.2+, 1.27.2+, 1.28.2+ and 1.29.1+ (check with
kubectl version). - Review Operator Prerequisites for supported Kubernetes, Docker, Fannel and Calico versions.
- Helm 3.10.2+ (check with
helm version --client --short). - Oracle WebLogic Kubernetes Operator 4.2.9 (see operator releases page).
- Container images based on Oracle Linux 8 and Oracle Linux 9 with JDK 17 and JDK 21 are supported.
- You must have the
cluster-adminrole to install the operator. The operator does not need thecluster-adminrole at runtime. - We do not currently support running WebCenterSites in non-Linux containers.
- These proxy setup are used for pulling the required binaries and source code from the respective repositories:
- export NO_PROXY=“localhost,127.0.0.0/8,$(hostname -i),.your-company.com,/var/run/docker.sock”
- export no_proxy=“localhost,127.0.0.0/8,$(hostname -i),.your-company.com,/var/run/docker.sock”
- export http_proxy=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80
- export https_proxy=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80
- export HTTP_PROXY=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80
- export HTTPS_PROXY=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80
NOTE: Add your host IP by using
hostname -iand alsonslookupIP addresses to the no_proxy, NO_PROXY list above.
Limitations
Compared to running a WebLogic Server domain in Kubernetes using the Operator, the following limitations currently exist for WebCenter Sites domain:
Domain in imagemodel is not supported in this version of the Operator.- Only configured clusters are supported. Dynamic clusters are not supported for WebCenter Sites domains. Note that you can still use all of the scaling features. You just need to define the maximum size of your cluster at domain creation time.
- We do not currently support running WebCenter Sites in non-Linux containers.
- Deploying and running a WebCenter Sites domain is supported only in Operator versions 4.2.9 and later.
- The WebLogic Logging Exporter currently supports WebLogic Server logs only. Other logs will not be sent to Elasticsearch. Note, however, that you can use a sidecar with a log handling tool like Logstash or Fluentd to get logs.
- The WebLogic Monitoring Exporter currently supports the WebLogic MBean trees only. Support for JRF MBeans has not been added yet.
WebCenter Sites Cluster Sizing Recommendations
| WebCenter Sites | Normal Usage | Moderate Usage | High Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Admin Server | No of CPU(s) : 1, Memory : 4GB | No of CPU(s) : 1, Memory : 4GB | No of CPU(s) : 1, Memory : 4GB |
| Managed Server | No of Servers : 2, No of CPU(s) : 2, Memory : 16GB | No of Servers : 2, No of CPU(s) : 4, Memory : 16GB | No of Servers : 3, No of CPU(s) : 6, Memory : 16-32GB |
| PV Storage | Minimum 250GB | Minimum 250GB | Minimum 500GB |
Prepare your environment
Prepare for creating Oracle WebCenter Sites domains, including required secrets creation, persistent volume and volume claim creation, database creation, and database schema creation.
Contents
This document describes the steps to set up the environment that includes setting up of a Kubernetes cluster and setting up the WebLogic Operator including the database.
- Introduction
- Set Up your Kubernetes Cluster
- Build Oracle WebCenter Sites Image
- Pull Other Dependent Images
- Set Up the Code Repository to Deploy Oracle WebCenter Sites Domain
- Grant Roles and Clear Stale Resources
- Install the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
- Configure NFS Server
- Prepare the Environment for the WebCenter Sites Domain
- Configure access to your database
Introduction
Set Up your Kubernetes Cluster
Refer the official Kubernetes set up documentation to set up a production grade Kubernetes cluster.
After creating Kubernetes clusters, you can optionally:
- Create load balancers to direct traffic to backend domains.
- Configure Kibana and Elasticsearch for your operator logs.
Build Oracle WebCenter Sites Image
Build Oracle WebCenter Sites 14.1.2.0.0 Image by following Create or update an Image.
Obtain the Oracle WebCenter Sites Image
The Oracle WebCenter Sites image with the latest bundle patch and required interim patches is prebuilt by Oracle and includes Oracle WebCenter Sites 14.1.2.0.0, the Latest Patch Set Update (PSU), and other fixes released with the Critical Patch Update (CPU) program. This is the only image supported for production deployments. Obtain the Oracle WebCenter Sites image using either of the following methods:
Download from Oracle Container Registry:
Log in to
Oracle Container Registry, navigate to Middleware > webcentersites/webcentersites_cpu and accept the license agreement if not already done.Log in to the Oracle Container Registry (container-registry.oracle.com) from your Podman or Docker client:
$ podman login container-registry.oracle.comPull the image:
For example:
$ podman pull container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/webcentersites:14.1.2.0.0Or pull image with tag:
$ podman pull container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/webcentersites:14.1.2.0.0-<Tag>
Download from My Oracle Support:
Download WebCenter Sites image from My Oracle Support (MOS).
Unzip the downloaded patch zip file.
Load the image archive using the
podman loadcommand.For example:
$ podman load < wcsites-141200.tar.gz Loaded image: oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0
If you want to build and use an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image with any additional patches that are not part of the image obtained from My Oracle Support, then follow the steps in Create or Update an Image topic to create the image.
Note: The default Oracle WebCenter Sites image name used for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment is
oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0. The image obtained must be tagged asoracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0using thepodman tagcommand. If you want to use a different name for the image, make sure to update the new image tag name in thecreate-domain-inputs.yamlfile and also in other instances where theoracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0image name is used.
Pull Other Dependent Images
Dependent images include WebLogic Kubernetes Operator, and Traefik. Pull these images and add them to your local registry:
- Pull these Docker images and re-tag them as shown:
To pull an image from the Oracle Container Registry, in a web browser, navigate to https://container-registry.oracle.com and log in using the Oracle Single Sign-On authentication service. If you do not already have SSO credentials, at the top of the page, click the Sign In link to create them.
Use the web interface to accept the Oracle Standard Terms and Restrictions for the Oracle software images that you intend to deploy. Your acceptance of these terms are stored in a database that links the software images to your Oracle Single Sign-On login credentials.
Then, pull these Docker images and re-tag them:
podman login https://container-registry.oracle.com (enter your Oracle email Id and password)
This step is required once at every node to get access to the Oracle Container Registry.WebLogic Kubernetes Operator image:
$ podman pull container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/weblogic-kubernetes-operator:4.2.9
$ podman tag container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/weblogic-kubernetes-operator:4.2.9 oracle/weblogic-kubernetes-operator:4.2.9- Copy all the above built and pulled images to all the nodes in your cluster or add to a Docker registry that your cluster can access.
NOTE: If you’re not running Kubernetes on your development machine, you’ll need to make the Docker image available to a registry visible to your Kubernetes cluster. Upload your image to a machine running Docker and Kubernetes as follows:
# on your build machine
$ podman save Image_Name:Tag > Image_Name-Tag.tar
$ scp Image_Name-Tag.tar YOUR_USER@YOUR_SERVER:/some/path/Image_Name-Tag.tar
# on the Kubernetes server
$ podman load < /some/path/Image_Name-Tag.tarSet Up the Code Repository to Deploy Oracle WebCenter Sites Domain
Oracle WebCenter Sites domain deployment on Kubernetes leverages the Oracle WebLogic Kubernetes Operator infrastructure. For deploying the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain, you need to set up the deployment scripts as below:
Create a working directory to setup the source code.
$ mkdir $HOME/wcs_1412 $ cd $HOME/wcs_1412Download the WebCenter Sites kubernetes deployment scripts from this repository .
$ git clone https://github.com/oracle/fmw-kubernetes.git
You can now use the deployment scripts from $HOME/wcs_1412/fmw-kubernetes/OracleWebCenterSites/kubernetes to set up the WebCenter Sites domain as further described in this document.
This will be your home directory for runnning all the required scripts.
$ cd $HOME/wcs_1412/fmw-kubernetes/OracleWebCenterSites/kubernetes
$ export WORKDIR=$HOME/wcs_1412/fmw-kubernetes/OracleWebCenterSites/kubernetesClear Stale Resources
To confirm if there is already a WebLogic custom resource definition, execute the following command:
$ kubectl get crd NAME CREATED AT domains.weblogic.oracle 2020-03-14T12:10:21ZIf you find any WebLogic custom resource definition, then delete it by executing the following command:
bash $ kubectl delete crd domains.weblogic.oracle customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io "domains.weblogic.oracle" deleted
Install the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
Create a namespace for the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator:
$ kubectl create namespace operator-ns namespace/operator-ns createdNOTE: For this exercise we are creating a namespace called “operator-ns” (can be any name).
You can also use:
- domainUID/domainname as
wcsitesinfra - Domain namespace as
wcsites-ns - Operator namespace as
operator-ns - traefik namespace as
traefik
- domainUID/domainname as
Create a service account for the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator in the Operator’s namespace:
$ kubectl create serviceaccount -n operator-ns operator-sa serviceaccount/operator-sa createdAdd the Weblogic Kubernetes Operator repo
$ helm repo add weblogic-operator https://oracle.github.io/weblogic-kubernetes-operator/charts --force-updateOptionally, you can follow these steps to send the contents of the operator’s logs to Elasticsearch.
Use helm to install and start the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator from the downloaded repository:
Helm install weblogic-operator
$ helm install weblogic-kubernetes-operator weblogic-operator/weblogic-operator --version 4.2.9 --namespace operator-ns --set serviceAccount=operator-sa --set "javaLoggingLevel=FINE" --wait NAME: weblogic-kubernetes-operator LAST DEPLOYED: Tue May 19 04:04:32 2024 NAMESPACE: operator-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneTo verify that the Operator’s pod is running, list the pods in the Operator’s namespace. You should see one for the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator:
$ kubectl get pods -n operator-ns NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE weblogic-operator-66d44b89fb-d9tqf 2/2 Running 0 5m39s weblogic-operator-webhook-798bbcbfcc-z82rl 2/2 Running 0 5m39sThen, check by viewing the Operator pod’s log as shown in the following sample log snippet:
$ kubectl logs -n operator-ns -c weblogic-operator deployments/weblogic-operator Launching Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes Operator... VM settings: Max. Heap Size (Estimated): 21.59G Using VM: Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:40.520682507Z","thread":1,"fiber":"","namespace":"","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.helpers.HealthCheckHelper","method":"createAndValidateKubernetesVersion","timeInMillis":1728304240520,"message":"Kubernetes version is: v1.27.8","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:40.779242046Z","thread":1,"fiber":"","namespace":"","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.OperatorMain$MainDelegateImpl","method":"logStartup","timeInMillis":1728304240779,"message":"Oracle WebLogic Kubernetes Operator, version: 4.2.9, implementation: 7394a56ef6ac3231a766455d8d199095f6e69fbb.7394a56, build time: 2024-09-11T17:18:22+0000","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:40.78423637Z","thread":1,"fiber":"","namespace":"","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.OperatorMain$MainDelegateImpl","method":"lambda$logStartup$0","timeInMillis":1728304240784,"message":"The following optional operator features are enabled: []","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:40.794745506Z","thread":1,"fiber":"","namespace":"","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.OperatorMain$MainDelegateImpl","method":"logStartup","timeInMillis":1728304240794,"message":"Operator namespace is: operator-ns","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:40.796536215Z","thread":1,"fiber":"","namespace":"","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.OperatorMain$MainDelegateImpl","method":"logStartup","timeInMillis":1728304240796,"message":"Operator service account is: operator-sa","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:42.294724178Z","thread":57,"fiber":"fiber-1-child-2 NOT_COMPLETE","namespace":"wcsites-ns1","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.helpers.EventHelper$CreateEventStep$CreateEventResponseStep","method":"onSuccess","timeInMillis":1728304242294,"message":"Start managing namespace wcsites-ns1","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:42.296199191Z","thread":58,"fiber":"fiber-1-child-1 NOT_COMPLETE","namespace":"wcsites-ns","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.helpers.EventHelper$CreateEventStep$CreateEventResponseStep","method":"onSuccess","timeInMillis":1728304242296,"message":"Start managing namespace wcsites-ns","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""} {"timestamp":"2024-10-07T12:30:44.482491307Z","thread":125,"fiber":"fiber-1 NOT_COMPLETE","namespace":"","domainUID":"","level":"INFO","class":"oracle.kubernetes.operator.OperatorMain","method":"logStartingLivenessMessage","timeInMillis":1728304244482,"message":"Starting operator liveness Thread","exception":"","code":"","headers":{},"body":""}
Configure NFS (Network File System) Server
To configure NFS server, install the nfs-utils package preferably on Master node:
$ sudo yum install nfs-utilsTo start the nfs-server service, and configure the service to start following a system reboot:
$ sudo systemctl start nfs-server
$ sudo systemctl enable nfs-serverCreate the directory you want to export as the NFS share, for example /scratch/K8SVolume:
$ sudo mkdir -p /scratch/K8SVolume
$ sudo chown -R 1000:0 /scratch/K8SVolumehost name or IP address of the NFS Server
Note: Host name or IP address of the NFS Server and NFS Share path which is used when you create PV/PVC in further sections.
Prepare the Environment for the WebCenter Sites Domain
Unless you would like to use the default namespace, create a Kubernetes namespace that can host one or more domains:
$ kubectl create namespace wcsites-ns namespace/wcsites-ns created $ kubectl label namespace wcsites-ns weblogic-operator=enabledCreate Kubernetes secrets:
- Using the create-weblogic-credentials script, create a Kubernetes secret that contains the user name and password for the domain in the same Kubernetes namespace as the domain:
Output: ```bash $ sh kubernetes/create-weblogic-domain-credentials/create-weblogic-credentials.sh
-u weblogic -p Welcome1 -n wcsites-ns
-d wcsitesinfra -s wcsitesinfra-domain-credentialssecret/wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials created secret/wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials labeled The secret wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials has been successfully created in the wcsites-ns namespace. ``` Where:
* weblogic is the weblogic username * Welcome1 is the weblogic password * wcsitesinfra is the domain name * wcsites-ns is the domain namespace * wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials is the secret nameNote: You can inspect the credentials as follows:
bash $ kubectl get secret wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials -o yaml -n wcsites-ns- Create a Kubernetes secret for the Repository Configuration Utility (user name and password) using the
create-rcu-credentials.shscript in the same Kubernetes namespace as the domain:
Output:
$ sh kubernetes/create-rcu-credentials/create-rcu-credentials.sh \ -u WCS1 -p Oradoc_db1 -a sys -q Oradoc_db1 -n wcsites-ns \ -d wcsitesinfra -s wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials secret/wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials created secret/wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials labeled The secret wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials has been successfully created in the wcsites-ns namespace.Where:
* WCS1 is the schema user * Oradoc_db1 is the schema password * Oradoc_db1 is the database SYS users password * wcsitesinfra is the domain name * wcsites-ns is the domain namespace * wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials is the secret nameNote: You can inspect the credentials as follows:
$ kubectl get secret wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials -o yaml -n wcsites-nsCreate a Kubernetes PV and PVC (Persistent Volume and Persistent Volume Claim):
- Update the
kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/create-wcsites-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml.
Replace the token
%NFS_SERVER%with the host name/IP of NFS Server created in Configure NFS Server section.In the NFS Server, create a folder and grant permissions as given below:
$ sudo rm -rf /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites && sudo mkdir -p /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites && sudo chown 1000:0 /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSitesUpdate the
weblogicDomainStoragePathparamter with/scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites.- Execute the
create-pv-pvc.shscript to create the PV and PVC configuration files:
$ sh kubernetes/create-weblogic-domain-pv-pvc/create-pv-pvc.sh \ -i kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/create-wcsites-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml \ -o kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output Input parameters being used export version="create-weblogic-sample-domain-pv-pvc-inputs-v1" export baseName="domain" export domainUID="wcsitesinfra" export namespace="wcsites-ns" export weblogicDomainStorageType="NFS" export weblogicDomainStorageNFSServer="%NFS_SERVER%" export weblogicDomainStoragePath="/scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites" export weblogicDomainStorageReclaimPolicy="Retain" export weblogicDomainStorageSize="10Gi" Generating kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pv.yaml Generating kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc.yaml The following files were generated: kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pv.yaml kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc.yaml Completed- To create the PV and PVC, use
kubectl createwith output configuration files:
Output:
$ kubectl create -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pv.yaml \ -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc.yaml persistentvolume/wcsitesinfra-domain-pv created persistentvolumeclaim/wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc createdNote: You can verify the PV and PV’s details as follows:
$ kubectl describe pv wcsitesinfra-domain-pv -n wcsites-ns$ kubectl describe pvc wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc -n wcsites-ns- Update the
Label the nodes in the Kubernetes cluster for the targeted scheduling of the servers on particular nodes as needed:
kubectl label node <node-name> name=abcNote: Here
<node-name>is the node as displayed in the NAME field ofkubectl get nodescommand. abc is the label that we are defining. Label is a key, value pair and can be anything meaningful. The same should be used for nodeSelector. For scheduling we can select these nodes based on the labels.
Configure access to your database
Oracle WebCenter Sites domains require a database with the necessary schemas installed in them. The Repository Creation Utility (RCU) allows you to create those schemas. You must set up the database before you create your domain. There are no additional requirements added by running Oracle WebCenter Sites in Kubernetes; the same existing requirements apply.
For production deployments, you must set up and use the standalone (non-container) based database running outside of Kubernetes.
Before creating a domain, you will need to set up the necessary schemas in your database.
Create Oracle WebCenter Sites domains
Create an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain home on an existing PV or PVC, and create the domain resource YAML file for deploying the generated Oracle WebCenter Sites domain.
Contents
- Introduction to Scripts
- Prerequisites
- Prepare the WebCenter Sites Domain Creation Input File
- Create the WebCenter Sites Domain
- Initialize the WebCenter Sites Domain
- Verify the WebCenter Sites Domain
- Expose WebCenter Sites Services
- Load Balance With an Ingress Controller or A Web Server
- Configure WebCenter Sites
- Settings in WebCenter Sites Property Management
- For Publishing Setting in WebCenter Sites
- Customization
Introduction to Scripts
This document details on how to use sample scripts to demonstrate the creation of a WebCenter Sites domain home on an existing Kubernetes persistent volume (PV) and persistent volume claim (PVC). The scripts also generate the domain YAML file, which can then be used to start the Kubernetes artifacts of the corresponding domain.
Prerequisites
- Review the Domain resource documentation.
- Review the requirements and limitations.
- Ensure that you have executed all the preliminary steps in Prepare Your Environment.
- Ensure that the database and the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator are running.
Prepare the WebCenter Sites Domain Creation Input File
If required, domain creation inputs can be customized by editing create-domain-inputs.yaml as described below:
Please note that the sample scripts for the WebCenter Sites domain deployment are available from the previously downloaded repository at kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/.
Make a copy of the create-domain-inputs.yaml file before updating the default values.
The default domain created by the script has the following characteristics:
- An Administration Server named
AdminServerlistening on port7001. - A configured cluster named
wcsites-clusterof size5. - Managed Server, named
wcsites_server1, listening on port7103. - Log files that are located in
/shared/logs/<domainUID>.
Configuration parameters
The following parameters can be provided in the inputs file:
| Parameter | Definition | Default |
|---|---|---|
adminPort |
Port number for the Administration Server inside the Kubernetes cluster. | 7001 |
adminServerName |
Name of the Administration Server. | AdminServer |
clusterName |
Name of the WebLogic cluster instance to generate for the domain. By default the cluster name is wcsites-cluster for the WebCenter Sites domain. |
wcsites-cluster |
configuredManagedServerCount |
Number of Managed Server instances for the domain. | 3 |
createDomainFilesDir |
Directory on the host machine to locate all the files that you need to create a WebLogic domain, including the script that is specified in the createDomainScriptName property. By default, this directory is set to the relative path wlst, and the create script will use the built-in WLST offline scripts in the wlst directory to create the WebLogic domain. An absolute path is also supported to point to an arbitrary directory in the file system. The built-in scripts can be replaced by the user-provided scripts or model files as long as those files are in the specified directory. Files in this directory are put into a Kubernetes config map, which in turn is mounted to the createDomainScriptsMountPath, so that the Kubernetes pod can use the scripts and supporting files to create a domain home. |
wlst |
createDomainScriptsMountPath |
Mount path where the create domain scripts are located inside a pod. The create-domain.sh script creates a Kubernetes job to run the script (specified in the createDomainScriptName property) in a Kubernetes pod to create a domain home. Files in the createDomainFilesDir directory are mounted to this location in the pod, so that the Kubernetes pod can use the scripts and supporting files to create a domain home. |
/u01/weblogic |
createDomainScriptName |
Script that the create domain script uses to create a WebLogic domain. The create-domain.sh script creates a Kubernetes job to run this script to create a domain home. The script is located in the in-pod directory that is specified in the createDomainScriptsMountPath property. If you need to provide your own scripts to create the domain home, instead of using the built-it scripts, you must use this property to set the name of the script that you want the create domain job to run. |
create-domain-job.sh |
domainHome |
Home directory of the WebCenter Sites domain. This field cannot be modified. |
/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra |
domainPVMountPath |
Mount path of the domain persistent volume. This field cannot be modified. |
/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains |
domainUID |
Unique ID that will be used to identify this particular domain. Used as the name of the generated WebLogic domain as well as the name of the Kubernetes domain resource. This ID must be unique across all domains in a Kubernetes cluster. This ID cannot contain any character that is not valid in a Kubernetes service name. | wcsitesinfra |
exposeAdminNodePort |
Boolean indicating if the Administration Server is exposed outside of the Kubernetes cluster. | false |
exposeAdminT3Channel |
Boolean indicating if the T3 administrative channel is exposed outside the Kubernetes cluster. | false |
image |
WebCenter Sites Docker image. The Operator requires WebCenter Sites release 14.1.2.0.0. Refer to WebCenter Sites Docker image for details on how to obtain or create the image. | oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0 |
imagePullPolicy |
WebLogic Docker image pull policy. Legal values are IfNotPresent, Always, or Never |
IfNotPresent |
imagePullSecretName |
Name of the Kubernetes secret to access the Docker Store to pull the WebLogic Server Docker image. The presence of the secret will be validated when this parameter is specified. | |
includeServerOutInPodLog |
Boolean indicating whether to include the server.out to the pod’s stdout. | true |
initialManagedServerReplicas |
Number of Managed Server to initially start for the domain. | 1 |
javaOptions |
Java options for starting the Administration Server and Managed Servers. A Java option can include references to one or more of the following pre-defined variables to obtain WebLogic domain information: $(DOMAIN_NAME), $(DOMAIN_HOME), $(ADMIN_NAME), $(ADMIN_PORT), and $(SERVER_NAME). |
-Dweblogic.StdoutDebugEnabled=false |
logHome |
The in-pod location for the domain log, server logs, server out, and Node Manager log files. This field cannot be modified. |
/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/wcsitesinfra |
managedServerNameBase |
Base string used to generate Managed Server names. | wcsites_server |
managedServerPort |
Port number for each Managed Server. | 7103 |
namespace |
Kubernetes namespace in which to create the domain. | wcsites-ns |
persistentVolumeClaimName |
Name of the persistent volume claim created to host the domain home. If not specified, the value is derived from the domainUID as <domainUID>-weblogic-sample-pvc. |
wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc |
productionModeEnabled |
Boolean indicating if production mode is enabled for the domain. | true |
serverStartPolicy |
Determines which WebLogic Server instances will be started. Legal values are Never, IfNeeded, AdminOnly. |
IfNeeded |
t3ChannelPort |
Port for the T3 channel of the NetworkAccessPoint. | 30012 |
t3PublicAddress |
Public address for the T3 channel. This should be set to the public address of the Kubernetes cluster. This would typically be a load balancer address. | If not provided, the script will attempt to set it to the IP address of the Kubernetes cluster. |
weblogicCredentialsSecretName |
Name of the Kubernetes secret for the Administration Server’s user name and password. If not specified, then the value is derived from the domainUID as <domainUID>-weblogic-credentials. |
wcsites-domain-credentials |
weblogicImagePullSecretName |
Name of the Kubernetes secret for the Docker Store, used to pull the WebLogic Server image. | |
serverPodCpuRequest, serverPodMemoryRequest, serverPodCpuCLimit, serverPodMemoryLimit |
The maximum amount of compute resources allowed and minimum amount of compute resources required for each server pod. Please refer to the Kubernetes documentation on Managing Compute Resources for Containers for details. |
Resource requests and resource limits are not specified. Refer to WebCenter Sites Cluster Sizing Recommendations for more details. |
rcuSchemaPrefix |
The schema prefix to use in the database, for example WCS1. You may wish to make this the same as the domainUID in order to simplify matching domains to their RCU schemas. |
WCS1 |
rcuDatabaseURL |
The database URL. | oracle-db.wcsitesdb-ns.svc.cluster.local:1521/devpdb.k8s |
rcuCredentialsSecret |
The loadbalancer hostname to be provided. | wcsites-rcu-credentials |
loadBalancerHostName |
Hostname for the final url accessible outside K8S environment. | abc.def.com |
loadBalancerPortNumber |
Port for the final url accessible outside K8S environment. | 30305 |
loadBalancerProtocol |
Protocol for the final url accessible outside K8S environment. | http |
loadBalancerType |
Loadbalancer name that will be used. Example: Traefik or “” | traefik |
unicastPort |
Starting range of uniciast port that application will use. | 50000 |
sitesSamples |
Sites to be installed without samples sites by default, else true. | false |
adminAdministrationPort |
Administration Port number for admin server. | 9002 |
adminServerSSLPort |
SSL Port number for admin server. | 7002 |
sslEnabled |
Select true to enable SSL. If secureEnabled is set to true, sslEnabled will be set to true by default. | false |
managedServerSSLPort |
SSL Port number for each WCS managed server. | 7104 |
managedServerAdministrationPort |
Administration Port number for managed server. | 9111 |
secureEnabled |
Boolean indicating if secure is enabled for the domain. This value has significance only with 14.1.2.0.0. This value has no significance in dev mode i.e., when productionModeEnabled is false. | false |
You can form the names of the Kubernetes resources in the generated YAML files with the value of these properties specified in the create-domain-inputs.yaml file: adminServerName , clusterName and managedServerNameBase . Characters that are invalid in a Kubernetes service name are converted to valid values in the generated YAML files. For example, an uppercase letter is converted to a lowercase letter and an underscore (“_“) is converted to a hyphen (”-“) .
The sample demonstrates how to create a WebCenter Sites domain home and associated Kubernetes resources for a domain that has one cluster only. In addition, the sample provides the capability for users to supply their own scripts to create the domain home for other use cases. You can modify the generated domain YAML file to include more use cases.
Create the WebCenter Sites Domain
Understanding the syntax of the create-domain.sh script:
$ ./create-domain.sh \ -i create-domain-inputs.yaml \ -o /<path to output-directory>The script performs the following functions:
Creates a directory for the generated Kubernetes YAML files for this domain if it does not already exist. The path name is
/<path to output-directory>/weblogic-domains/<domainUID>. If the directory already exists, remove its content before using this script.Creates a Kubernetes job that will start up a utility WebCenter Sites container and run offline WLST scripts to create the domain on the shared storage.
Runs and waits for the job to finish.
Creates a Kubernetes domain YAML file,
domain.yaml, in the directory that is created above. This YAML file can be used to create the Kubernetes resource using thekubectl create -forkubectl apply -fcommand:$ kubectl apply -f ../<path to output-directory>/weblogic-domains/<domainUID>/domain.yamlCreates a convenient utility script,
delete-domain-job.yaml, to clean up the domain home created by the create script.
Now, run the
create-domain.shsample script below, pointing it at the create-domain-inputs inputs file and an output directory like below:bash-4.2$ rm -rf kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/weblogic-domains bash-4.2$ sh kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/create-domain.sh \ -i kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/create-domain-inputs.yaml \ -o kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output Input parameters being used export version="create-weblogic-sample-domain-inputs-v1" export sslEnabled="false" export adminPort="7001" export adminServerSSLPort="7002" export adminAdministrationPort="9002" export adminServerName="adminserver" export domainUID="wcsitesinfra" export domainHome="/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/$domainUID" export serverStartPolicy="IfNeeded" export clusterName="wcsites-cluster" export configuredManagedServerCount="3" export initialManagedServerReplicas="1" export managedServerNameBase="wcsites-server" export managedServerPort="7103" export managedServerSSLPort="7104" export managedServerAdministrationPort="9111" export image="oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0" export imagePullPolicy="IfNotPresent" export productionModeEnabled="true" export secureEnabled="false" export weblogicCredentialsSecretName="wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials" export includeServerOutInPodLog="true" export logHome="/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/$domainUID" export t3ChannelPort="30012" export exposeAdminT3Channel="false" export adminNodePort="30701" export exposeAdminNodePort="false" export namespace="wcsites-ns" javaOptions=-Dweblogic.StdoutDebugEnabled=false export persistentVolumeClaimName="wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc" export domainPVMountPath="/u01/oracle/user_projects" export createDomainScriptsMountPath="/u01/weblogic" export createDomainScriptName="create-domain-job.sh" export createDomainFilesDir="wlst" export serverPodMemoryRequest="4G" export serverPodCpuRequest="2000m" export serverPodMemoryLimit="4G" export serverPodCpuLimit="2000m" export rcuSchemaPrefix="wcsk8s1" export rcuDatabaseURL="shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com" export rcuCredentialsSecret="wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials" export loadBalancerHostName="cjuyal-1.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com" export loadBalancerPortNumber="30305" export loadBalancerProtocol="http" export loadBalancerType="traefik" export unicastPort="50000" export sitesSamples="false" validateWlsDomainName called with wcsitesinfra createFiles - valuesInputFile is create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/create-domain-inputs.yaml createDomainScriptName is create-domain-job.sh Generating create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/create-domain-job.yaml Generating create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/delete-domain-job.yaml Generating create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/domain.yaml Checking to see if the secret wcsitesinfra-domain-credentials exists in namespace wcsites-ns configmap "wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-cm" deleted configmap/wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-cm created Checking the configmap wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-cm was created configmap/wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-cm labeled Checking if object type job with name wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job exists No resources found in wcsites-ns namespace. $loadBalancerType is NOT empty Creating the domain by creating the job create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/create-domain-job.yaml job.batch/wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job created Waiting for the job to complete... status on iteration 1 of 20 pod wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg status is Running status on iteration 2 of 20 pod wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg status is Running status on iteration 3 of 20 pod wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg status is Running status on iteration 4 of 20 pod wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg status is Completed Domain wcsitesinfra was created and will be started by the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator The following files were generated: create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/create-domain-inputs.yaml create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/create-domain-job.yaml create-wcsites-domain/output//weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/domain.yaml CompletedTo monitor the above domain creation logs:
$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns |grep wcsitesinfra-create wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg 0/1 Completed 0 6m48s$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns | grep wcsitesinfra-create | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kubectl -n wcsites-ns logs -fSAMPLE OUTPUT:
The domain will be created using the script /u01/weblogic/createSitesDomain.sh Install Automation -> Starting automation script [mkdir] Created dir: /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Work Directory=/u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] DB URL: jdbc:oracle:thin:@ [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Info -> The script.db.connectstring has been set. [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Info.setDBConnectStringPropertey -> setting shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Validation -> Checking if full path to JAVA executable is correctly specified [exec] java version "17.0.12" 2024-07-16 LTS [exec] Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 17.0.12+8-LTS-286) [exec] Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0.12+8-LTS-286, mixed mode, sharing) [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Validation -> Checking database connection [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] dbUrl-----------------: jdbc:oracle:thin:@shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Database Connection --> Success! [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] 1st phase: WebCenter Sites installation started... [copy] Copying 1 file to /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work [copy] Copying /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/rcu.rsp to /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu.rsp [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] 1st phase: WebCenter Sites installation completed [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] 2nd phase: WebCenter Sites RCU configuration started... [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Installation -> Repository Creation Utility - creates schema [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] connectString-----------------: shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com [replace] Replaced 1 occurrences in 1 files. [replace] Replaced 1 occurrences in 1 files. [replace] Replaced 1 occurrences in 1 files. [replace] Replaced 1 occurrences in 1 files. [replace] Replaced 1 occurrences in 1 files. [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] Create schema using command: /u01/oracle/oracle_common/bin/rcu -silent -responseFile /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu.rsp -f < /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcuPasswords10710756107204523639.txt >/u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu_output.log [echo] [10/7/24, 12:48 PM] RCU Create Schema -> Please wait ... may take several minutes [echo] [10/7/24, 12:49 PM] [echo] RCU Logfile: /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/rcu.log [echo] Processing command line .... [echo] Repository Creation Utility - Checking Prerequisites [echo] Checking Global Prerequisites [echo] Repository Creation Utility - Checking Prerequisites [echo] Checking Component Prerequisites [echo] Repository Creation Utility - Creating Tablespaces [echo] Validating and Creating Tablespaces [echo] Create tablespaces in the repository database [echo] Repository Creation Utility - Create [echo] Repository Create in progress. [echo] Percent Complete: 16 [echo] Executing pre create operations [echo] Percent Complete: 33 [echo] Percent Complete: 33 [echo] Percent Complete: 35 [echo] Percent Complete: 37 [echo] Percent Complete: 39 [echo] Percent Complete: 39 [echo] Percent Complete: 39 [echo] Creating Common Infrastructure Services(STB) [echo] Percent Complete: 48 [echo] Percent Complete: 48 [echo] Percent Complete: 58 [echo] Percent Complete: 58 [echo] Percent Complete: 58 [echo] Creating Audit Services Append(IAU_APPEND) [echo] Percent Complete: 66 [echo] Percent Complete: 66 [echo] Percent Complete: 76 [echo] Percent Complete: 76 [echo] Percent Complete: 76 [echo] Creating Audit Services Viewer(IAU_VIEWER) [echo] Percent Complete: 84 [echo] Percent Complete: 84 [echo] Percent Complete: 84 [echo] Percent Complete: 85 [echo] Percent Complete: 85 [echo] Percent Complete: 85 [echo] Percent Complete: 86 [echo] Percent Complete: 86 [echo] Percent Complete: 86 [echo] Percent Complete: 87 [echo] Percent Complete: 88 [echo] Percent Complete: 88 [echo] Percent Complete: 88 [echo] Creating Weblogic Services(WLS) [echo] Percent Complete: 93 [echo] Percent Complete: 93 [echo] Percent Complete: 97 [echo] Percent Complete: 97 [echo] Percent Complete: 100 [echo] Creating Audit Services(IAU) [echo] Creating Oracle Platform Security Services(OPSS) [echo] Creating WebCenter Sites(WCSITES) [echo] Executing post create operations [echo] Repository Creation Utility: Create - Completion Summary [echo] Database details: [echo] ----------------------------- [echo] Host Name : shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com [echo] Port : 1521 [echo] Service Name : ORCL.SUBNET1BOM1.DEVCEC02BOM.ORACLEVCN.COM [echo] Connected As : sys [echo] Prefix for (prefixable) Schema Owners : WCSK8S1 [echo] RCU Logfile : /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/rcu.log [echo] Component schemas created: [echo] ----------------------------- [echo] Component Status Logfile [echo] Common Infrastructure Services Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/stb.log [echo] Oracle Platform Security Services Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/opss.log [echo] WebCenter Sites Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/wcsites.log [echo] Audit Services Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/iau.log [echo] Audit Services Append Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/iau_append.log [echo] Audit Services Viewer Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/iau_viewer.log [echo] WebLogic Services Success /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/work/rcu/RCU2024-10-07_12-48_1569219683/logs/wls.log [echo] Repository Creation Utility - Create : Operation Completed [echo] [10/7/24, 12:49 PM] Successfully created schemas [echo] [10/7/24, 12:49 PM] 2nd phase: WebCenter Sites RCU configuration completed successfully. [echo] [10/7/24, 12:49 PM] Oracle WebCenter Sites Installation complete. You can connect to the WebCenter Sites instance at http://10.244.1.228:7002/sites/ Sites RCU Phase completed successfull!!! Sites Installation completed in 47 seconds. --------------------------------------------------------- The domain will be created using the script /u01/weblogic/create-domain-script.sh wlst.sh -skipWLSModuleScanning /u01/weblogic/createSitesDomain.py -oh /u01/oracle -jh /u01/jdk -parent /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/.. -name wcsitesinfra -user weblogic -password Welcome1 -rcuDb shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com -rcuPrefix wcsk8s1 -rcuSchemaPwd Welcome1 -adminListenPort 7001 -adminName adminserver -managedNameBase wcsites-server -managedServerPort 7103 -prodMode true -secureMode false -managedServerCount 3 -clusterName wcsites-cluster -exposeAdminT3Channel false -t3ChannelPublicAddress 100.69.176.148 -t3ChannelPort 30012 -sslEnabled false -adminServerSSLPort 7002 -managedServerSSLPort 7104 -domainType wcsites -adminAdministrationPort 9002 -managedServerAdministrationPort 9111 -machineName wcsites_machine Initializing WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) ... Welcome to WebLogic Server Administration Scripting Shell Type help() for help on available commands Creating Admin Server... Creating cluster... Creating Node Managers... managed server name is wcsites-server1 managed server name is wcsites-server2 managed server name is wcsites-server3 ['wcsites-server1', 'wcsites-server2', 'wcsites-server3'] Will create Base domain at /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra Writing base domain... Base domain created at /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra Extending domain at /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra Database shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com ExposeAdminT3Channel false with 100.69.176.148:30012 Applying JRF templates... Extension Templates added Applying WCSITES templates... Extension Templates added INFO: deleting wcsites_server1 INFO: deleted wcsites_server1 Configuring the Service Table DataSource... fmwDb...jdbc:oracle:thin:@shivaoke-3.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com:1521/orcl.subnet1bom1.devcec02bom.oraclevcn.com Set user...wcsk8s1_OPSS Set user...wcsk8s1_IAU_APPEND Set user...wcsk8s1_IAU_VIEWER Set user...wcsk8s1_STB Set user...wcsk8s1_WCSITES Getting Database Defaults... Targeting Server Groups... Targeting Server Groups... Set CoherenceClusterSystemResource to defaultCoherenceCluster for server:wcsites-server1 Set CoherenceClusterSystemResource to defaultCoherenceCluster for server:wcsites-server2 Set CoherenceClusterSystemResource to defaultCoherenceCluster for server:wcsites-server3 Targeting Cluster ... Set CoherenceClusterSystemResource to defaultCoherenceCluster for cluster:wcsites-cluster Set WLS clusters as target of defaultCoherenceCluster:[wcsites-cluster] Preparing to update domain... Oct 07, 2024 12:50:27 PM oracle.security.jps.az.internal.runtime.policy.AbstractPolicyImpl initializeReadStore INFO: Property for read store in parallel: oracle.security.jps.az.runtime.readstore.threads = null Domain updated successfully Copying /u01/weblogic/server-config-update.sh to PV /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra Copying /u01/weblogic/unicast.py to PV /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra replacing tokens in /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/server-config-update.sh Successfully Completed
Initialize the WebCenter Sites Domain
To start the domain, apply the above domain.yaml:
```bash
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/domain.yaml
domain.weblogic.oracle/wcsitesinfra created
cluster.weblogic.oracle/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-cluster created
```Verify the WebCenter Sites Domain
Verify that the domain and servers pods and services are created and in the READY state:
Sample run below:
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg 0/1 Completed 0 12m
wcsitesinfra-introspector-s56gz 1/1 Running 0 20s
wcsitesinfra-introspector-s56gz 0/1 Completed 0 51s
wcsitesinfra-introspector-s56gz 0/1 Completed 0 53s
wcsitesinfra-introspector-s56gz 0/1 Terminating 0 54s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 Pending 0 0s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 Pending 0 0s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 Init:0/1 0 0s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 Init:0/1 0 2s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 PodInitializing 0 12s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 Running 0 13s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 0/1 Running 1 (0s ago) 87s
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 1/1 Running 1 (3m4s ago) 4m31s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 Pending 0 0s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 Pending 0 0s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 Init:0/1 0 0s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 Init:0/1 0 1s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 PodInitializing 0 12s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 Running 0 13s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 0/1 Running 1 (1s ago) 87s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 1/1 Running 1 (4m19s ago) 5m45s-bash-4.2$ kubectl get all -n wcsites-ns
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/wcsitesinfra-adminserver 1/1 Running 1 (11m ago) 13m
pod/wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg 0/1 Completed 0 25m
pod/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 1/1 Running 1 (7m10s ago) 8m36s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/wcsitesinfra-adminserver ClusterIP None <none> 7001/TCP 13m
service/wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster ClusterIP 10.96.46.39 <none> 7103/TCP 8m36s
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 ClusterIP None <none> 7103/TCP 8m36s
NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE
job.batch/wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job 1/1 2m2s 25m
NAME AGE
domain.weblogic.oracle/wcsitesinfra 14m
NAME AGE
cluster.weblogic.oracle/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-cluster 14mTo see the Admin and Managed Servers logs, you can check the pod logs:
$ kubectl logs -f wcsitesinfra-adminserver -n wcsites-ns$ kubectl exec -it wcsitesinfra-adminserver -n wcsites-ns -- /bin/bash$ kubectl logs -f wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 -n wcsites-ns$ kubectl exec -it wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 -n wcsites-ns -- /bin/bashVerify the Pods
Use the following command to see the pods running the servers:
$ kubectl get pods -n NAMESPACEHere is an example of the output of this command:
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 1/1 Running 1 (12m ago) 13m
wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg 0/1 Completed 0 26m
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 1/1 Running 1 (7m50s ago) 9m16sVerify the Services
Use the following command to see the services for the domain:
$ kubectl get services -n NAMESPACEHere is an example of the output of this command:
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get services -n wcsites-ns
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
wcsitesinfra-adminserver 1/1 Running 0 7m38s
wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6l7zh 0/1 Completed 0 23m
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 1/1 Running 0 5m50sExpose WebCenter Sites Services
Below are the default values for exposing services required for all the WebCenter Sites Managed Servers. Reset them if any values are modified.
Details on kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/wcs-services.yaml:
- name: wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np
- namespace: wcsites-ns
- weblogic.domainUID: wcsitesinfra
- weblogic.serverName: wcsites_server1
- NodePort port: Default value is 7103 for NONSSL. Update to 7104 for SSL/E2ESSL.
Execute the below command for exposing the services: (If domain is configured for more than 3 Managed Servers then add the service yaml for additional servers.)
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/wcs-services.yaml
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np created
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-svc created
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server2-svc created
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server3-svc createdTo verify the services created, here is an example of the output of this command:
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get services -n wcsites-ns
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
wcsitesinfra-adminserver ClusterIP None <none> 7001/TCP 14m
wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster ClusterIP 10.96.46.39 <none> 7103/TCP 10m
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 ClusterIP None <none> 7103/TCP 10m
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np NodePort 10.96.201.245 <none> 7103:30966/TCP 18s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-svc ClusterIP None <none> 50000/TCP,50001/TCP,50002/TCP,50003/TCP,50004/TCP,50005/TCP,50006/TCP,50007/TCP,50008/TCP,50009/TCP 18s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server2-svc ClusterIP None <none> 50000/TCP,50001/TCP,50002/TCP,50003/TCP,50004/TCP,50005/TCP,50006/TCP,50007/TCP,50008/TCP,50009/TCP 18s
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server3-svc ClusterIP None <none> 50000/TCP,50001/TCP,50002/TCP,50003/TCP,50004/TCP,50005/TCP,50006/TCP,50007/TCP,50008/TCP,50009/TCP 18sLoad Balance With an Ingress Controller or A Web Server
You can choose a load balancer provider for your WebLogic domains running in a Kubernetes cluster. Please refer to the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator Load Balancer Samples for information about the current capabilities and setup instructions for each of the supported load balancers.
For information on how to set up Loadbalancer for setting up WebCenter Sites domain on K8S:
For Traefik, see Setting Up Loadbalancer Traefik for the WebCenter Sites Domain on K8S
For Nginx, see Setting Up Loadbalancer Nginx for the WebCenter Sites Domain on K8S
For Apache webtier, see Setting Up Loadbalancer Apache Webtier for the WebCenter Sites Domain on K8S
Configure WebCenter Sites
Configure WebCenter Sites by hitting url
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-PORT}/sites/sitesconfigsetupWhen installing, select sample sites to be installed and enter the required passwords. Do not change the sites-config location. If you change the location, installation will fail.
After the configuration is complete, edit the domain, and restart the Managed Server.
To stop Managed Servers:
$ kubectl patch cluster wcsitesinfra-wcsites-cluster -n wcsites-ns --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"replicas":0}}'To start all configured Managed Servers:
$ kubectl patch cluster wcsitesinfra-wcsites-cluster -n wcsites-ns --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"replicas":3}}'Wait till the Managed Server pod is killed and then restart it. Monitor with below command:
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns -w NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE wcsitesinfra-adminserver 1/1 Running 0 111m wcsitesinfra-create-fmw-infra-sample-domain-job-6x8cg 0/1 Completed 0 126m wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1 1/1 Running 0 3m7s wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server2 1/1 Running 0 3m7s wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server3 1/1 Running 0 3m7s
Settings in WebCenter Sites Property Management
Incase of Traefik Load Balancer: Use Property Management Tool and update cookieserver.validnames property with value JSESSIONID,sticky.
Incase of Nginx Load Balancer: Use Property Management Tool and update cookieserver.validnames property with value JSESSIONID,stickyid.
For Publishing Setting in WebCenter Sites
While configuring publishing destination use NodePort port of target cluster which can be found by executing below command:
(In this example for publishihng the port 30155 has to be used.)
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np -n wcsites-ns
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np NodePort 10.96.201.245 <none> 7103:30966/TCP 18mCustomization
A customer specific customizations (extend.sites.webapp-lib.war) has to be placed in sites-home directory inside your domain mount path.
Administration Guide
Describes how to use some of the common utility tools and configurations to administer Oracle WebCenter Sites domains.
Set up a load balancer
The Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes operator supports ingress-based load balancers such as Traefik and NGINX (kubernetes/ingress-nginx). It also supports Apache Webtier load balancer.
Traefik
This section provides information about how to install and configure the ingress-based Traefik load balancer (version 2.2.1 or later for production deployments) to load balance Oracle WebCenter Sites domain clusters. You can configure Traefik for non-SSL, SSL termination, and end-to-end SSL access of the application URL.
Follow these steps to set up Traefik as a load balancer for an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain in a Kubernetes cluster:
- Install the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer
- Create an Ingress for the domain
- Verify application URL access
- Uninstall the Traefik ingress
- Uninstall Traefik
Install the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer
Use Helm to install the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer. Use the
values.yamlfile in the sample but setkubernetes.namespacesspecifically.$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ kubectl create namespace traefik $ helm repo add traefik https://helm.traefik.io/traefik --force-updateSample output:
"traefik" has been added to your repositoriesInstall Traefik:
$ helm install traefik traefik/traefik \ --namespace traefik \ --values charts/traefik/values.yaml \ --set "kubernetes.namespaces={traefik}" \ --set "service.type=NodePort" --wait{{%expand “Click here to see the sample output.” %}}
LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Sep 13 21:32:00 2024 NAMESPACE: traefik STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneA sample
values.yamlfor deployment of Traefik:image: name: traefik pullPolicy: IfNotPresent ingressRoute: dashboard: enabled: true # Additional ingressRoute annotations (e.g. for kubernetes.io/ingress.class) annotations: {} # Additional ingressRoute labels (e.g. for filtering IngressRoute by custom labels) labels: {} providers: kubernetesCRD: enabled: true kubernetesIngress: enabled: true # IP used for Kubernetes Ingress endpoints ports: traefik: port: 9000 expose: true # The exposed port for this service exposedPort: 9000 # The port protocol (TCP/UDP) protocol: TCP web: port: 8000 # hostPort: 8000 expose: true exposedPort: 30305 nodePort: 30305 # The port protocol (TCP/UDP) protocol: TCP # Use nodeport if set. This is useful if you have configured Traefik in a # LoadBalancer # nodePort: 32080 # Port Redirections # Added in 2.2, you can make permanent redirects via entrypoints. # https://docs.traefik.io/routing/entrypoints/#redirection # redirectTo: websecure websecure: port: 8443 # # hostPort: 8443 expose: true exposedPort: 30443 # The port protocol (TCP/UDP) protocol: TCP nodePort: 30443Verify the Traefik status and find the port number of the SSL and non-SSL services:
$ kubectl get all -n traefik NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/traefik-5fc4947cf9-fbl9r 1/1 Running 5 7d17h NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE service/traefik NodePort 10.100.195.70 <pending> 80:30305/TCP,443:30443/TCP 7d17h NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE deployment.apps/traefik 1/1 1 1 7d17h NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE replicaset.apps/traefik-5fc4947cf9 1 1 1 7d17hAccess the Traefik dashboard through the URL
http://<MASTERNODE-HOSTNAME>:30305, with the HTTP hosttraefik.example.com:$ curl -H "host: <MASTERNODE-HOSTNAME>" http://<MASTERNODE-HOSTNAME>:30305/dashboard/Note: Make sure that you specify a fully qualified node name for
<MASTERNODE-HOSTNAME>Configure Traefik to manage ingresses created in this namespace, where
traefikis the Traefik namespace andwcsites-nsis the namespace of the domain:
$ helm upgrade traefik traefik/traefik --namespace traefik --reuse-values \
--set "kubernetes.namespaces={traefik,wcsites-ns}"
Release "traefik" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: traefik
LAST DEPLOYED: Sun Sep 13 21:32:12 2020
NAMESPACE: traefik
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: NoneCreate an ingress for the domain
Create an ingress for the domain in the domain namespace by using the sample Helm chart. Here path-based routing is used for ingress. Sample values for default configuration are shown in the file ${WORKDIR}/charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml. By default, type is TRAEFIK, sslType is NONSSL, and domainType is wcs. These values can be overridden by passing values through the command line or can be edited in the sample file values.yaml based on the type of configuration (NONSSL, SSL, and E2ESSL).
If needed, you can update the ingress YAML file to define more path rules (in section spec.rules.host.http.paths) based on the domain application URLs that need to be accessed. The template YAML file for the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer is located at ${WORKDIR}/charts/ingress-per-domain/templates/traefik-ingress.yaml.
Choose an appropriate
LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAMEfor accessing the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain application URLs.$ export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=<LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME>For example, if you are executing the commands from a master node terminal, where the master hostname is
LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME:$ export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=$(hostname -f)Install
ingress-per-domainusing Helm forNONSSLconfiguration:$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress \ charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set "traefik.hostname=${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}"Sample output:
NAME: wcsitesinfra-ingress LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Jul 20 11:44:13 2024 NAMESPACE: wcsites-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneFor secured access (
SSLtermination andE2ESSL) to the Oracle WebCenter Sites application, create a certificate, and generate a Kubernetes secret:$ openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /tmp/tls1.key -out /tmp/tls1.crt -subj "/CN=*" $ kubectl -n wcsites-ns create secret tls wcs-tls-cert --key /tmp/tls1.key --cert /tmp/tls1.crtCreate the Traefik TLSStore custom resource.
In case of SSL termination, Traefik should be configured to use the user-defined SSL certificate. If the user-defined SSL certificate is not configured, Traefik will create a default SSL certificate. To configure a user-defined SSL certificate for Traefik, use the TLSStore custom resource. The Kubernetes secret created with the SSL certificate should be referenced in the TLSStore object. Run the following command to create the TLSStore:
$ cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f - apiVersion: traefik.containo.us/v1alpha1 kind: TLSStore metadata: name: default namespace: wcsites-ns spec: defaultCertificate: secretName: wcs-tls-cert EOFInstall
ingress-per-domainusing Helm forSSLconfiguration.$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress \ charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set "traefik.hostname=${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}" \ --set sslType=SSLSample output:
NAME: wcsitesinfra-ingress LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Jul 20 11:44:13 2020 NAMESPACE: wcsites-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneInstall
ingress-per-domainusing Helm forE2ESSLconfiguration.Note: To use the
E2ESSLconfiguration, you must have created the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain withsslEnabledset totrue. See Create Oracle WebCenter Sites domains for details.$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress \ charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set sslType=E2ESSLSample output:
NAME: wcsitesinfra-ingress LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Apr 9 09:47:27 2021 NAMESPACE: wcsites-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneFor NONSSL access to the Oracle WebCenter Sites application, get the details of the services by the ingress:
$ kubectl describe ingress wcsitesinfra-traefik -n wcsites-ns Name: wcsitesinfra-traefik Labels: app.kubernetes.io/managed-by=Helm weblogic.resourceVersion=domain-v2 Namespace: wcsites-ns Address: Ingress Class: <none> Default backend: <default> Rules: Host Path Backends ---- ---- -------- www.example.com /console wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /em wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /wls-exporter wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /weblogic wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /sbconsole wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /management wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /testconsole wcsitesinfra-adminserver:7001 (10.244.3.138:7001) /sites wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster:7103 (10.244.1.230:7103) /cas wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster:7103 (10.244.1.230:7103) /wls-exporter wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster:7103 (10.244.1.230:7103) Annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik meta.helm.sh/release-name: wcsitesinfra-ingress meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: wcsites-ns traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/router.middlewares: wcsites-ns-custom-header@kubernetescrd Events: <none>For SSL access to the Oracle WebCenter Sites application, get the details of the services by the above deployed ingress:
$ kubectl describe ingress wcsitesinfra-traefik -n wcsites-nsFor E2ESSL access to the Oracle WebCenter Sites application, get the details of the services by the above deployed ingress:
$ kubectl describe IngressRouteTCP wcsitesinfra-traefik -n wcsites-nsTo confirm that the load balancer noticed the new ingress and is successfully routing to the domain server pods, you can send a request to the URL for the “WebLogic ReadyApp framework”, which should return an HTTP 200 status code, as follows:
bash $ curl -v http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_PORT}/weblogic/ready * Trying 149.87.129.203... > GET http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_PORT}/weblogic/ready HTTP/1.1 > User-Agent: curl/7.29.0 > Accept: */* > Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive > host: ${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME} > < HTTP/1.1 200 OK < Date: Sat, 14 Mar 2020 08:35:03 GMT < Vary: Accept-Encoding < Content-Length: 0 < Proxy-Connection: Keep-Alive < * Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
Verify application URL access
For NONSSL configuration
After setting up the Traefik loadbalancer, verify that the domain applications are accessible through the loadbalancer port 30305. Through load balancer (Traefik port 30305), the following URLs are available for setting up domains of WebCenter Sites domain types:
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-PORT}/weblogic/ready
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-PORT}/console
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-PORT}/em
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-PORT}/sites/version.jspFor SSL configuration
After setting up the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer, verify that the domain applications are accessible through the SSL load balancer port 30443 for HTTPS access. The sample URLs for Oracle WebCenter Sites domain of type wcs are:
https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready
https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/console
https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/em
https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/sites/version.jspFor E2ESSL configuration
After setting up the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer, verify that the domain applications are accessible through the SSL load balancer port 30443 for HTTPS access.
To access the application URLs from the browser, update
/etc/hostson the browser host (in Windows,C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts) with the entries belowX.X.X.X admin.domain.org X.X.X.X wcsites.domain.orgNote: The value of X.X.X.X is the host ipaddress on which this ingress is deployed.
Note: If you are behind any corporate proxy, make sure to update the browser proxy settings appropriately to access the host names updated
/etc/hostsfile.
The sample URLs for Oracle WebCenter Sites domain of type wcs are:
https://admin.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready
https://admin.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/console
https://admin.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/em
https://wcsites.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/sites/version.jspUninstall the Traefik ingress
Uninstall and delete the ingress deployment:
$ helm delete wcsitesinfra-ingress -n wcsites-nsUninstall Traefik
$ helm delete traefik -n traefikNGINX
This section provides information about how to install and configure the ingress-based NGINX load balancer to load balance Oracle WebCenter Sites domain clusters. You can configure NGINX for for non-SSL, SSL termination, and end-to-end SSL access of the application URL.
Follow these steps to set up NGINX as a load balancer for an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain in a Kubernetes cluster:
See the official installation document for prerequisites.
- Install the NGINX load balancer for non-SSL and SSL termination configuration
- Generate secret for SSL access
- Install NGINX load balancer for end-to-end SSL configuration
- Configure NGINX to manage ingresses
- Verify domain application URL access
- Uninstall NGINX ingress
- Uninstall NGINX
To get repository information, enter the following Helm commands:
$ helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
$ helm repo updateInstall the NGINX load balancer for non-SSL and SSL termination configuration
Deploy the
ingress-nginxcontroller by using Helm on the domain namespace:$ helm install nginx-ingress -n wcsites-ns \ --set controller.service.type=NodePort \ --set controller.admissionWebhooks.enabled=false \ --set controller.service.nodePorts.http=30305 \ ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx
Generate secret for SSL access
For secured access (SSL and E2ESSL) to the Oracle WebCenter Sites application, create a certificate and generate secrets:
$ openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /tmp/tls1.key -out /tmp/tls1.crt -subj "/CN=domain1.org" $ kubectl -n wcsites-ns create secret tls wcs-tls-cert --key /tmp/tls1.key --cert /tmp/tls1.crtNote: The value of
CNis the host on which this ingress is to be deployed and secret name should be <domainUID>-tls-cert.
Install NGINX load balancer for end-to-end SSL configuration
Deploy the ingress-nginx controller by using Helm on the domain namespace:
$ helm install nginx-ingress -n wcsites-ns \ --set controller.extraArgs.default-ssl-certificate=wcsites-ns/wcs-tls-cert \ --set controller.service.type=NodePort \ --set controller.admissionWebhooks.enabled=false \ --set controller.extraArgs.enable-ssl-passthrough=true \ ingress-nginx/ingress-nginxCheck the status of the deployed ingress controller:
$ kubectl --namespace wcsites-ns get services | grep ingress-nginx-controllerSample output:
nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller NodePort 10.106.186.235 <none> 80:30305/TCP,443:30443/TCP 19m
Configure NGINX to manage ingresses
Choose an appropriate
LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAMEfor accessing the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain application URLs.$ export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=<LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME>For example, if you are executing the commands from a master node terminal, where the master hostname is
LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME:$ export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=$(hostname -f)Create an ingress for the domain in the domain namespace by using the sample Helm chart. Here path-based routing is used for ingress. Sample values for default configuration are shown in the file
${WORKDIR}/charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml. By default,typeisTRAEFIK,sslTypeisNONSSL, anddomainTypeiswcs. These values can be overridden by passing values through the command line or can be edited in the sample filevalues.yaml.
If needed, you can update the ingress YAML file to define more path rules (in sectionspec.rules.host.http.paths) based on the domain application URLs that need to be accessed. Update the template YAML file for the NGINX load balancer located at${WORKDIR}/charts/ingress-per-domain/templates/nginx-ingress.yaml.$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set "nginx.hostname=${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}" \ --set type=NGINXSample output:
NAME: wcsitesinfra-ingress LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 24 09:34:03 2020 NAMESPACE: wcsites-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneInstall
ingress-per-domainusing Helm for SSL termination configuration:$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set "nginx.hostname=${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}" \ --set type=NGINX --set sslType=SSLSample output:
NAME: wcsitesinfra-ingress LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 24 09:34:03 2020 NAMESPACE: wcsites-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: NoneInstall
ingress-per-domainusing Helm forE2ESSLconfiguration.Note: To use the
E2ESSLconfiguration, you must have created the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain withsslEnabledset totrue. See Create Oracle WebCenter Sites domains.$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set type=NGINX --set sslType=E2ESSLSample output:
NAME: wcsitesinfra-ingress LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 24 09:34:03 2020 NAMESPACE: wcsites-ns STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: None
Verify domain application URL access
NONSSL configuration
Get the
LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORTNodePort of NGINX using the command:$ LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT=$(kubectl --namespace wcsites-ns get services -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller) $ echo ${LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT}Verify that the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain application URLs are accessible through the
LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT:http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT}/console http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT}/em http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_NON_SSLPORT}/sites/version.jsp
SSL configuration
Get the
LOADBALANCER_SSLPORTNodePort of NGINX using the command:$ LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT=$(kubectl --namespace wcsites-ns get services -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[1].nodePort}" nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller) $ echo ${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}Verify that the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain application URLs are accessible through the
LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT:https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/console https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/em https://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/sites/version.jsp
E2ESSL configuration
To access the WebCenter Sites domain application URLs from a remote browser, update the browser host config file
/etc/hosts(In Windows,C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts) with the IP address of the host on which the ingress is deployed with below entries:X.X.X.X admin.domain.org X.X.X.X wcsites.domain.orgNote:
- The value of X.X.X.X is the host IP address on which this ingress is deployed.
- If you are behind any corporate proxy, make sure to update the browser proxy settings appropriately to access the host names updated
/etc/hostsfile.
Get the
LOADBALANCER_SSLPORTNodePort of NGINX using the command:$ LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT=$(kubectl --namespace wcsites-ns get services -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[1].nodePort}" nginx-ingress-ingress-nginx-controller) $ echo ${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}Verify that the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain application URLs are accessible through
LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT:https://admin.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready https://admin.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/console https://admin.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/em https://wcsites.domain.org:${LOADBALANCER_SSLPORT}/sites/version.jspNote: This is the default host name. If you have updated the host name in
values.yaml, then use the updated values.
Uninstall NGINX ingress
Uninstall and delete the wcsitesinfra-ingress deployment:
$ helm uninstall wcsitesinfra-ingress -n wcsites-nsUninstall NGINX
$ helm uninstall nginx-ingress -n wcsites-nsApache webtier
This section provides information about how to install and configure the Apache webtier to load balance Oracle WebCenter Sites domain clusters. You can configure Apache webtier for non-SSL and SSL termination access of the application URL.
Follow these steps to set up the Apache webtier as a load balancer for an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain in a Kubernetes cluster:
- Build the Apache webtier image
- Create the Apache plugin configuration file
- Prepare the certificate and private key
- Install the Apache webtier Helm chart
- Verify domain application URL access
- Uninstall Apache webtier
Build the Apache webtier image
Refer to the sample, to build the Apache webtier Docker image.
Create the Apache plugin configuration file
The configuration file named
custom_mod_wl_apache.confshould have all the URL routing rules for the Oracle WebCenter Sites applications deployed in the domain that needs to be accessible externally. Update this file with values based on your environment. The file content is similar to below.The sample content of the configuration file custom_mod_wl_apache.conf for wcs domain
# Copyright (c) 2018, 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates. # Licensed under the Universal Permissive License v 1.0 as shown at https://oss.oracle.com/licenses/upl. <IfModule mod_weblogic.c> WebLogicHost ${WEBLOGIC_HOST} WebLogicPort 7001 </IfModule> # Directive for weblogic admin Console deployed on Weblogic Admin Server <Location /console> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicHost wcsitesinfra-adminserver WebLogicPort 7001 </Location> <Location /em> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicHost wcsitesinfra-adminserver WebLogicPort 7001 </Location> <Location /wls-exporter> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicHost wcsitesinfra-adminserver WebLogicPort 7001 </Location> <Location /weblogic> SetHandler weblogic-handler WebLogicHost wcsitesinfra-adminserver WebLogicPort 7001 </Location> # Directive for all application deployed on weblogic cluster with a prepath defined by LOCATION variable # For example, if the LOCAITON is set to '/weblogic', all applications deployed on the cluster can be accessed via # http://myhost:myport/weblogic/application_end_url # where 'myhost' is the IP of the machine that runs the Apache webtier, and # 'myport' is the port that the Apache webtier is publicly exposed to. # Note that LOCATION cannot be set to '/' unless this is the only Location module configured. <Location /sites> WLSRequest On WebLogicCluster wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster:7103 PathTrim /weblogic1 </Location> <Location /cas> WLSRequest On WebLogicCluster wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster:7103 PathTrim /weblogic1 </Location> <Location /wls-exporter> WLSRequest On WebLogicCluster wcsitesinfra-cluster-wcsites-cluster:7103 PathTrim /weblogic1 </Location>Create a PV and PVC (pv-claim-name) that can be used to store the custom_mod_wl_apache.conf. Refer to the Sample for creating a PV or PVC.
Prepare the certificate and private key
(For the SSL termination configuration only) Run the following commands to generate your own certificate and private key using
openssl.$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ cd charts/apache-samples/custom-sample $ export VIRTUAL_HOST_NAME=WEBLOGIC_HOST $ export SSL_CERT_FILE=WEBLOGIC_HOST.crt $ export SSL_CERT_KEY_FILE=WEBLOGIC_HOST.key $ sh certgen.shNOTE: Replace WEBLOGIC_HOST with the host name on which Apache webtier is to be installed.
Output of the certifcate generation
$ls certgen.sh custom_mod_wl_apache.conf custom_mod_wl_apache.conf_orig input.yaml README.md $ sh certgen.sh Generating certs for WEBLOGIC_HOST Generating a 2048 bit RSA private key ........................+++ .......................................................................+++ unable to write 'random state' writing new private key to 'apache-sample.key' ----- $ ls certgen.sh custom_mod_wl_apache.conf_orig WEBLOGIC_HOST.info config.txt input.yaml WEBLOGIC_HOST.key custom_mod_wl_apache.conf WEBLOGIC_HOST.crt README.mdPrepare input values for the Apache webtier Helm chart.
Run the following commands to prepare the input value file for the Apache webtier Helm chart.
$ base64 -i ${SSL_CERT_FILE} | tr -d '\n' $ base64 -i ${SSL_CERT_KEY_FILE} | tr -d '\n' $ touch input.yamlUpdate the input parameters file,
charts/apache-samples/custom-sample/input.yaml.Snapshot of the sample input.yaml file
$ cat apache-samples/custom-sample/input.yaml # Use this to provide your own Apache webtier configuration as needed; simply define this # Persistence Volume which contains your own custom_mod_wl_apache.conf file. persistentVolumeClaimName: <pv-claim-name> # The VirtualHostName of the Apache HTTP server. It is used to enable custom SSL configuration. virtualHostName: <WEBLOGIC_HOST> # The customer-supplied certificate to use for Apache webtier SSL configuration. # The value must be a string containing a base64 encoded certificate. Run following command to get it. # base64 -i ${SSL_CERT_FILE} | tr -d '\n' customCert: <cert_data> # The customer-supplied private key to use for Apache webtier SSL configuration. # The value must be a string containing a base64 encoded key. Run following command to get it. # base64 -i ${SSL_KEY_FILE} | tr -d '\n' customKey: <key_data>
Install the Apache webtier Helm chart
Install the Apache webtier Helm chart to the domain namespace (for example
wcsites-ns) with the specified input parameters:$ cd ${WORKDIR}/charts $ helm install apache-webtier --values apache-samples/custom-sample/input.yaml --namespace wcsites-ns apache-webtier --set image=oracle/apache:12.2.1.3Check the status of the Apache webtier:
$ kubectl get all -n wcsites-ns | grep apacheSample output of the status of the Apache webtier:
pod/apache-webtier-apache-webtier-65f69dc6bc-zg5pj 1/1 Running 0 22h service/apache-webtier-apache-webtier NodePort 10.108.29.98 <none> 80:30305/TCP,4433:30443/TCP 22h deployment.apps/apache-webtier-apache-webtier 1/1 1 1 22h replicaset.apps/apache-webtier-apache-webtier-65f69dc6bc 1 1 1 22h
Verify domain application URL access
After the Apache webtier load balancer is running, verify that the domain applications are accessible through the load balancer port 30305/30443. The application URLs for domain of type wcs are:
Note: Port
30305is the LOADBALANCER-Non-SSLPORT and port30443is LOADBALANCER-SSLPORT.
NONSSL configuration
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-Non-SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-Non-SSLPORT}/console
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-Non-SSLPORT}/em
http://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-Non-SSLPORT}/sites/version.jspSSL configuration
https://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-SSLPORT}/weblogic/ready
https://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-SSLPORT}/console
https://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-SSLPORT}/em
https://${LOADBALANCER-HOSTNAME}:${LOADBALANCER-SSLPORT}/sites/version.jspUninstall Apache webtier
$ helm delete apache-webtier -n wcsites-nsMonitor a domain and publish logs
Monitor an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain and publish the WebLogic Server logs to Elasticsearch.
After the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain is set up, you can:
- Monitor the Oracle WebCenter Sites instance using Prometheus and Grafana
- Set Up the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter
Monitor the Oracle WebCenter Sites instance using Prometheus and Grafana
Using the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter you can scrape runtime information from a running Oracle WebCenter Sites instance and monitor them using Prometheus and Grafana.
Prerequisites
This document assumes that the Prometheus Operator is deployed on the Kubernetes cluster. If it is not already deployed, follow the steps below for deploying the Prometheus Operator.
Clone the kube-prometheus project
$ git clone https://github.com/coreos/kube-prometheus.gitLabel the nodes
Kube-Prometheus requires all the exporter nodes to be labelled with kubernetes.io/os=linux. If a node is not labelled, then you must label it using the following command:
$ kubectl label nodes --all kubernetes.io/os=linuxCreate Prometheus and Grafana resources
Change to the kube-prometheus directory and execute the following commands to create the namespace and CRDs:
NOTE: Wait for a minute for each command to process.
$ cd kube-prometheus
$ kubectl create -f manifests/setup
$ until kubectl get servicemonitors --all-namespaces ; do date; sleep 1; echo ""; done
$ kubectl create -f manifests/Provide external access
To provide external access for Grafana, Prometheus, and Alertmanager, execute the commands below:
$ kubectl patch svc grafana -n monitoring --type=json -p '[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/type", "value": "NodePort" },{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/ports/0/nodePort", "value": 32100 }]'
$ kubectl patch svc prometheus-k8s -n monitoring --type=json -p '[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/type", "value": "NodePort" },{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/ports/0/nodePort", "value": 32101 }]'
$ kubectl patch svc alertmanager-main -n monitoring --type=json -p '[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/type", "value": "NodePort" },{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/ports/0/nodePort", "value": 32102 }]'NOTE:
32100is the external port for Grafana32101is the external port for Prometheus32102is the external port for Alertmanager
Set Up the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter
Set up the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter that will collect WebLogic Server metrics and monitor your WebCenter Sites domain.
Generate the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter Deployment Package
Two packages are required as the listening ports are different for the Administration Server and Managed Servers. One binary required for the Admin Server (wls-exporter-as.war) and one for Managed Cluster (wls-exporter-ms.war). Set the required proxies and then run the script getX.X.X.sh to generate two binaries:
$ cd kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-monitoring-exporter
$ sh get1.1.0.shOutput:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 607 0 607 0 0 357 0 --:--:-- 0:00:01 --:--:-- 357
100 2016k 100 2016k 0 0 398k 0 0:00:05 0:00:05 --:--:-- 797k
-------------------wls-exporter-ms start-------------------
created /tmp/ci-GNysQzP1kv
Copying completed
/tmp/ci-GNysQzP1kv /kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-monitoring-exporter
in temp dir
adding: WEB-INF/weblogic.xml (deflated 66%)
adding: config.yml (deflated 63%)
wls-exporter-ms.war is ready
-------------------wls-exporter-ms end-------------------
-------------------wls-exporter-as start-------------------
Copying completed
in temp dir
adding: WEB-INF/weblogic.xml (deflated 66%)
adding: config.yml (deflated 52%)
wls-exporter-as.war is ready
-------------------wls-exporter-as end-------------------
zip completed
kubernetes/3.3.0/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-monitoring-exporterCopy the WAR Files to the WebLogic Domain Home
Copy the wls-exporter-as.war and wls-exporter-ms.war files to the domain home directory in the Administration Server pod.
$ kubectl cp wls-exporter-as.war wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/
$ kubectl cp wls-exporter-ms.war wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/Deploy the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter
Follow these steps to deploy the package in the WebLogic Server instances:
In the Administration Server and Managed Servers, deploy the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter (
wls-exporter-ms.war) separately using the Oracle Enterprise Manager.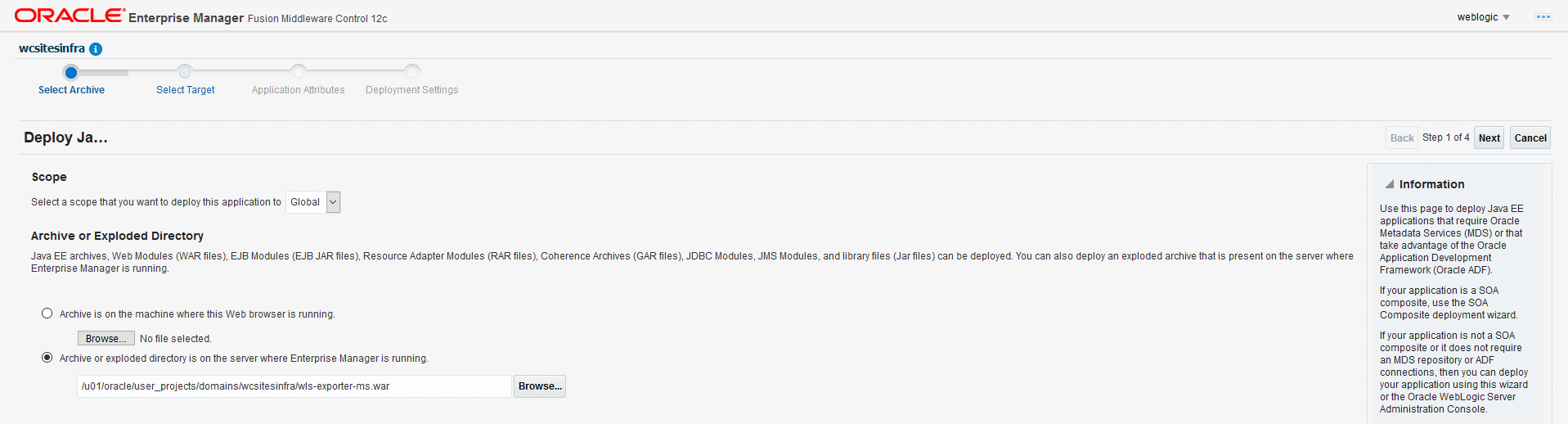
Select the servers to which the Exporter WAR should be deployed:
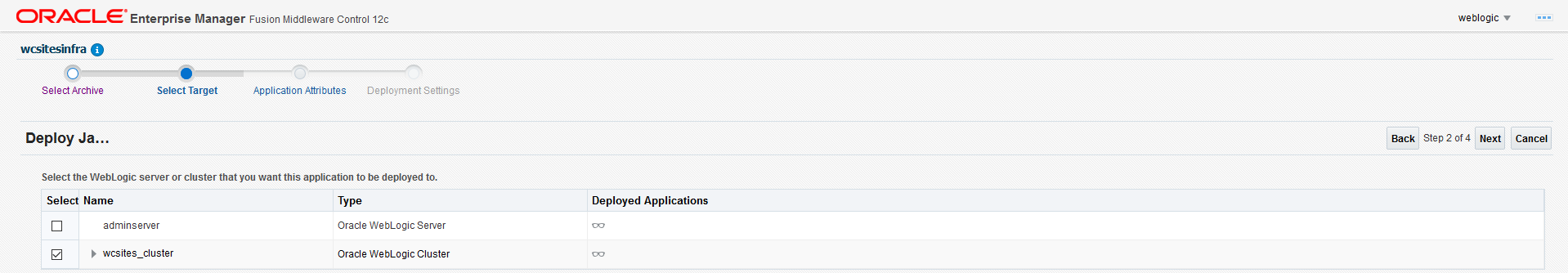
Set the application name. The application name must be different if it is deployed separately in the Administration Server and Managed Servers. Make sure the context-root for both the deployments is
wls-exporter:
Click Install and start application.
Then deploy the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter application (
wls-exporter-ms.war).Activate the changes to start the application. If the application is started and the port is exposed, then you can access the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter console using this URL:
http://<server:port>/wls-exporter.
Repeat same steps for
wls-exporter-as.war.
Configure Prometheus Operator
Prometheus enables you to collect metrics from the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter. The Prometheus Operator identifies the targets using service discovery. To get the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter end point discovered as a target, you must create a service monitor pointing to the service.
See the following sample service monitor deployment YAML configuration file located at
kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-monitoring-exporter/wls-exporter.yaml.
ServiceMonitor for wls-exporter:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: basic-auth
namespace: monitoring
data:
password: V2VsY29tZTE= # Welcome1 i.e.'WebLogic password'
user: d2VibG9naWM= # weblogic i.e. 'WebLogic username'
type: Opaque
---
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: wls-exporter-wcsitesinfra
namespace: monitoring
labels:
k8s-app: wls-exporter
spec:
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- wcsites-ns
selector:
matchLabels:
weblogic.domainName: wcsitesinfra
endpoints:
- basicAuth:
password:
name: basic-auth
key: password
username:
name: basic-auth
key: user
port: default
relabelings:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
interval: 10s
honorLabels: true
path: /wls-exporter/metricsThe exporting of metrics from wls-exporter requires basicAuth so a Kubernetes Secret is created with the user name and password that are base64 encoded. This Secret will be used in the ServiceMonitor deployment.
When generating the base64 encoded strings for the user name and password, observe if a new line character is appended in the encoded string. This line character causes an authentication failure. To avoid a new line string, use the following example:
$ echo -n "Welcome1" | base64
V2VsY29tZTE=In the deployment YAML configuration for wls-exporter shown above, weblogic.domainName: wcsitesinfra is used as a label under spec.selector.matchLabels, so all the services will be selected for the service monitor. If you don’t use this label, you should create separate service monitors for each server–if the server name is used as matching labels in spec.selector.matchLabels. Doing so will require you to relabel the configuration because Prometheus, by default, ignores the labels provided in the wls-exporter.
By default, Prometheus does not store all the labels provided by the target. In the service monitor deployment YAML configuration, you must mention the relabeling configuration (spec.endpoints.relabelings) so that certain labels provided by weblogic-monitoring-exporter (required for the Grafana dashboard) are stored in Prometheus. Do not delete the following section from the configuration YAML file:
relabelings:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)Add RoleBinding and Role for the WebLogic Domain Namespace
The RoleBinding is required for Prometheus to access the endpoints provided by the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter. You need to add RoleBinding for the namespace under which the WebLogic Servers pods are running in the Kubernetes cluster. Edit the kube-prometheus/manifests/prometheus-roleBindingSpecificNamespaces.yaml file in the Prometheus Operator deployment manifests and add the RoleBinding for the namespace (wcsites-ns) similar to the following example:
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: prometheus-k8s
namespace: wcsites-ns
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: prometheus-k8s
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: prometheus-k8s
namespace: monitoringSimilarly, add the Role for the namespace under which the WebLogic Servers pods are running in the Kubernetes cluster. Edit kube-prometheus/manifests/prometheus-roleSpecificNamespaces.yaml in the Prometheus Operator deployment manifests and add the Role for the namespace (wcsites-ns) similar to the following example:
- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: prometheus-k8s
namespace: wcsites-ns
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
- endpoints
- pods
verbs:
- get
- list
- watchThen apply prometheus-roleBindingSpecificNamespaces.yaml and prometheus-roleSpecificNamespaces.yaml for the RoleBinding and Role to take effect in the cluster.
$ kubectl apply -f kube-prometheus/manifests/prometheus-roleBindingSpecificNamespaces.yaml
$ kubectl apply -f kube-prometheus/manifests/prometheus-roleSpecificNamespaces.yamlDeploy the Service Monitor
To deploy the service monitor, use the above wls-exporter.yaml deployment YAML and run the following command:
$ kubectl create -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-monitoring-exporter/wls-exporter.yamlEnable Prometheus to Discover the Service
After the deployment of the service monitor, Prometheus should be able to discover wls-exporter and export metrics.
You can access the Prometheus dashboard at http://mycompany.com:32101/.
Deploy Grafana Dashboard
To view the domain metrics, deploy the Grafana dashboard provided in the WebLogic Monitoring Exporter.
You can access the Grafana dashboard at http://mycompany.com:32100/.
Log in to Grafana dashboard with
admin/admin.Go to Settings, then select DataSources, and then Add Data Source.
HTTP URL: Prometheus URL
http://mycompany.com:32101/Auth: Enable Basic Auth
Basic Auth Details: WebLogic credentials provided in step Configure Prometheus Operator
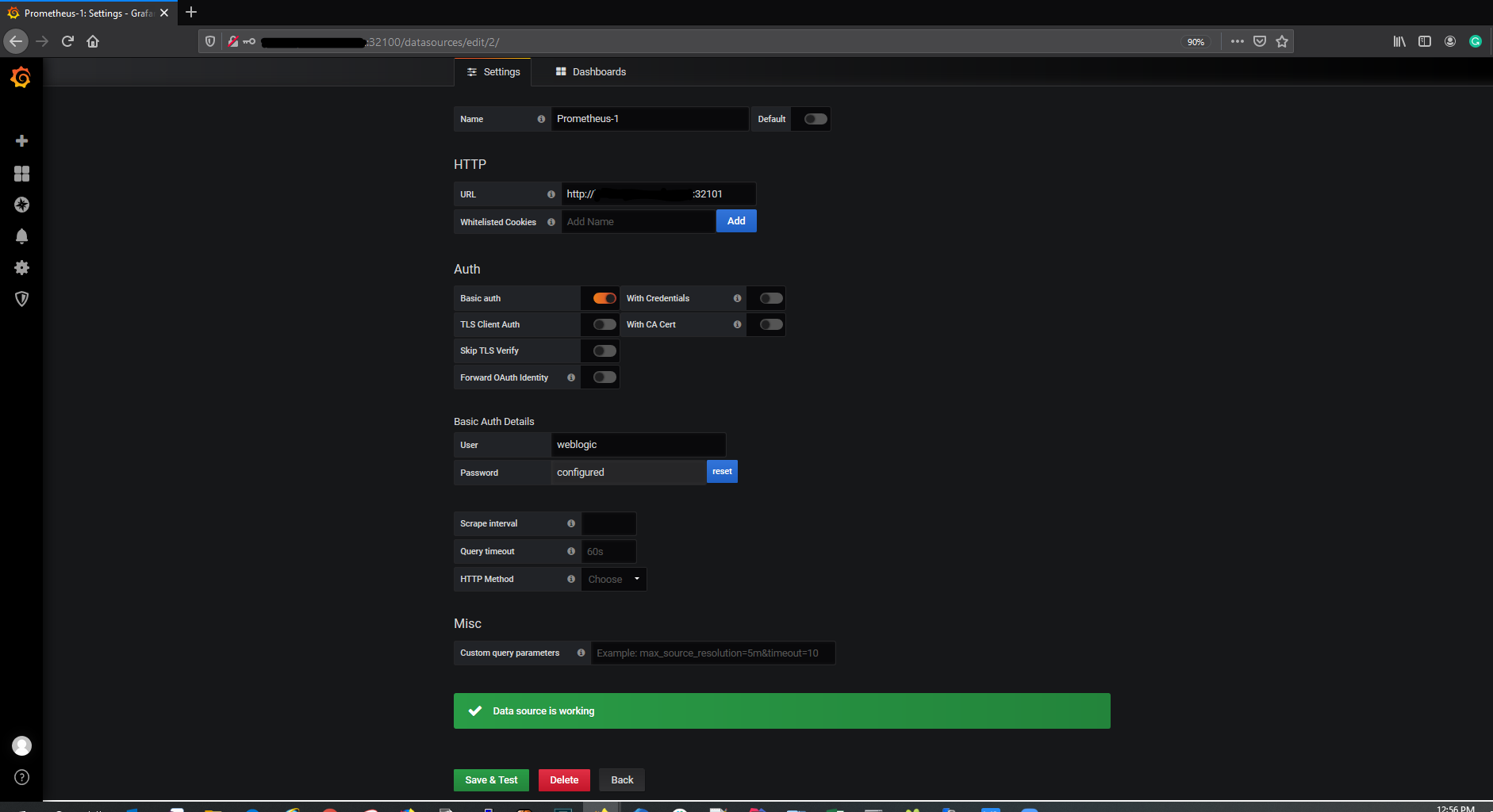
Download the
weblogic_dashboard.jsonfile from here.Click Add and then Import. Paste the modified JSON in the Paste JSON block, and then load it.
This displays the WebLogic Server Dashboard.
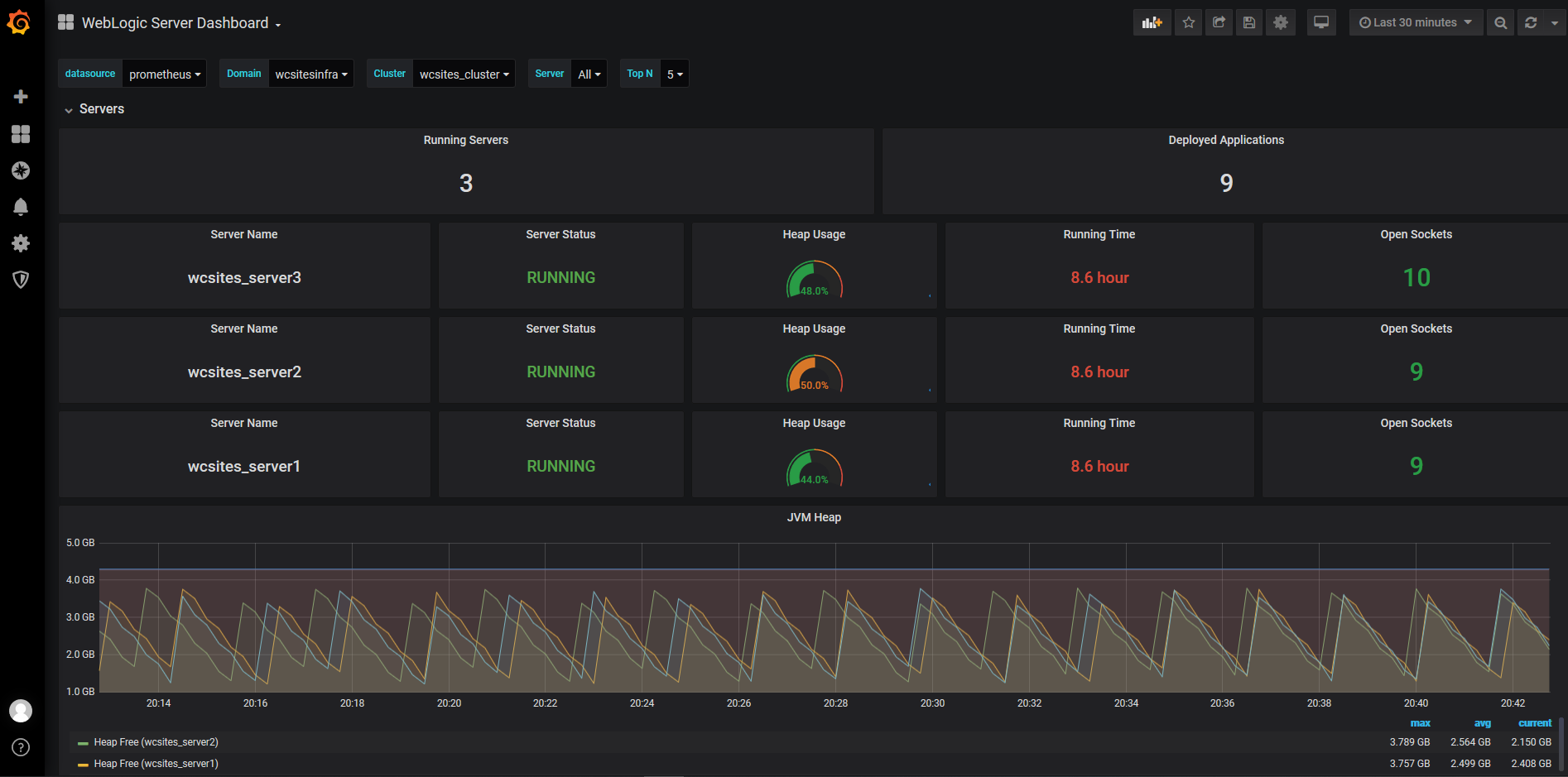
Elasticsearch integration for logs
Monitor an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain and publish the WebLogic Server logs to Elasticsearch.
1. Integrate Elasticsearch to WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
For reference information, see Elasticsearch integration for the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator.
To enable elasticsearch integration, you must edit file kubernetes/charts/weblogic-operator/values.yaml before deploying the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator.
# elkIntegrationEnabled specifies whether or not ELK integration is enabled.
elkIntegrationEnabled: true
# logStashImage specifies the Docker image containing logstash.
# This parameter is ignored if 'elkIntegrationEnabled' is false.
logStashImage: "logstash:6.6.0"
# elasticSearchHost specifies the hostname of where Elasticsearch is running.
# This parameter is ignored if 'elkIntegrationEnabled' is false.
elasticSearchHost: "elasticsearch.default.svc.cluster.local"
# elasticSearchPort specifies the port number of where Elasticsearch is running.
# This parameter is ignored if 'elkIntegrationEnabled' is false.
elasticSearchPort: 9200After you’ve deployed WebLogic Kubernetes Operator and made the above changes, the weblogic-operator pod will have additional Logstash container. The Logstash container will push the weblogic-operator logs to the configured Elasticsearch server.
2. Publish WebLogic Server and WebCenter Sites Logs using Logstash Pod
You can publish the WebLogic Server logs to Elasticsearch Server using Logstash pod. This Logstash pod must have access to the shared domain home. For the WebCenter Sites wcsitesinfra, you can use the persistent volume of the domain home in the Logstash pod. The steps to create the Logstash pod are as follows:
Sample Logstash configuration file is located at kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/logstash/logstash.conf
$ vi kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/logstash/logstash.confinput {
file {
path => "/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/wcsitesinfra/adminserver.log"
start_position => beginning
}
file {
path => "/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/wcsitesinfra/wcsites-server*.log"
start_position => beginning
}
file {
path => "/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/wcsitesinfra/adminserver.out"
start_position => beginning
}
file {
path => "/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/wcsitesinfra/wcsites-server*.out"
start_position => beginning
}
file {
path => "/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/servers/**/logs/sites.log"
start_position => beginning
}
file {
path => "/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/servers/**/logs/cas.log"
start_position => beginning
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => [ "message", "<%{DATA:log_timestamp}> <%{WORD:log_level}> <%{WORD:thread}> <%{HOSTNAME:hostname}> <%{HOSTNAME:servername}> <%{DATA:timer}> <<%{DATA:kernel}>> <> <%{DATA:uuid}> <%{NUMBER:timestamp}> <%{DATA:misc}> <%{DATA:log_number}> <%{DATA:log_message}>" ]
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["elasticsearch.default.svc.cluster.local:9200"]
}
}Here ** means that all sites.log and cas.log from any servers under wcsitesinfra will be pushed to Logstash.
$ kubectl cp kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/logstash/logstash.conf wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/logstash.confGet the persistent volume details of the domain home of the WebLogic Server(s). The following command will list the persistent volume details in the namespace - “wcsites-ns”:
$ kubectl get pv -n wcsites-ns
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
wcsitesinfra-domain-pv 10Gi RWX Retain Bound wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc wcsitesinfra-domain-storage-class 5d21hSample Logstash deployment is located at kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/logstash/logstash.yaml for Logstash pod. The mounted persistent volume of the domain home will provide access to the WebLogic Server logs to Logstash pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: logstash-wls
namespace: wcsites-ns
spec:
template: # create pods using pod definition in this template
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: logstash-wls
spec:
volumes:
- name: weblogic-domain-storage-volume
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc
- name: shared-logs
emptyDir: {}
containers:
- name: logstash
image: logstash:6.6.0
command: ["/bin/sh"]
args: ["/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash", "-f", "/u01/oracle/user_projects/logs/logstash.conf"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /u01/oracle/user_projects
name: weblogic-domain-storage-volume
- name: shared-logs
mountPath: /shared-logs
ports:
- containerPort: 5044
name: logstashAfter you have created the Logstash deployment yaml and Logstash configuration file, deploy Logstash using following command:
$ kubectl create -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/logstash/logstash.yaml3. Test the Deployment of Elasticsearch and Kibana
The WebLogic Operator also provides a sample deployment of Elasticsearch and Kibana for testing purpose. You can deploy Elasticsearch and Kibana on the Kubernetes cluster as shown below:
$ kubectl create -f kubernetes/elasticsearch-and-kibana/elasticsearch_and_kibana.yamlGet the Kibana dashboard port information as shown below:
Wait for pods to start:
-bash-4.2$ kubectl get pods -w
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
elasticsearch-8bdb7cf54-mjs6s 1/1 Running 0 4m3s
kibana-dbf8964b6-n8rcj 1/1 Running 0 4m3s-bash-4.2$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
elasticsearch ClusterIP 10.100.11.154 <none> 9200/TCP,9300/TCP 4m32s
kibana NodePort 10.97.205.0 <none> 5601:31884/TCP 4m32s
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 71dYou can access the Kibana dashboard at http://mycompany.com:kibana-nodeport/. In our example, the node port would be 31884.
Create an Index Pattern in Kibana
Create an index pattern logstash* in Kibana > Management. After the servers are started, you will see the log data in the Kibana dashboard:
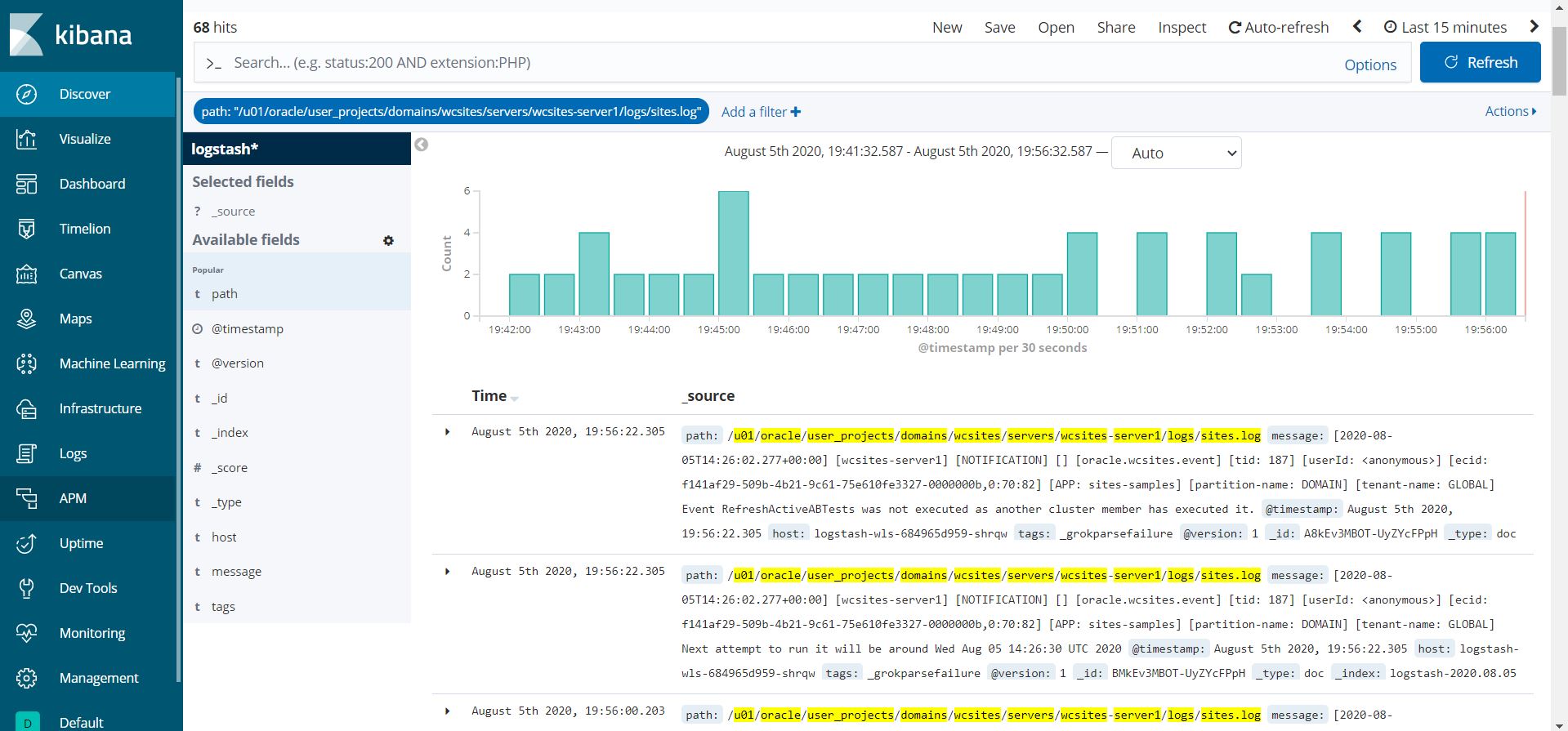
Publish logs to Elasticsearch
Monitor an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain and publish the WebLogic Server logs to Elasticsearch.
The WebLogic Logging Exporter adds a log event handler to WebLogic Server. WebLogic Server logs can be pushed to Elasticsearch in Kubernetes directly by using the Elasticsearch REST API. For more details, see to the WebLogic Logging Exporter project.
This sample shows you how to publish WebLogic Server logs to Elasticsearch and view them in Kibana. For publishing operator logs, see this sample.
Prerequisites
This document assumes that you have already set up Elasticsearch and Kibana for logs collection. If you have not, please see this document.
Download the WebLogic Logging Exporter binaries
The pre-built binaries are available on the WebLogic Logging Exporter Releases page.
Download:
- weblogic-logging-exporter-1.0.0.jar from the Releases page.
- snakeyaml-1.25.jar from Maven Central.
These identifiers are used in the sample commands in this document.
* `wcsites-ns`: WebCenter Sites domain namespace
* `wcsitesinfra`: `domainUID`
* `wcsitesinfra-adminserver`: Administration Server pod nameCopy the JAR Files to the WebLogic Domain Home
Copy the weblogic-logging-exporter-1.0.0.jar and snakeyaml-1.25.jar files to the domain home directory in the Administration Server pod.
$ kubectl cp <file-to-copy> <namespace>/<Administration-Server-pod>:<domainhome>
$ kubectl cp snakeyaml-1.25.jar wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/
$ kubectl cp weblogic-logging-exporter-1.0.0.jar wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/Add a Startup Class to the Domain Configuration
Login to WebLogic Remote Console, in the left navigation pane, click on Edit Tree, expand Environment, and then click on Startup Classes.
Click on New to add a new startup class. You may choose any descriptive name, however, the class name must be
weblogic.logging.exporter.Startup.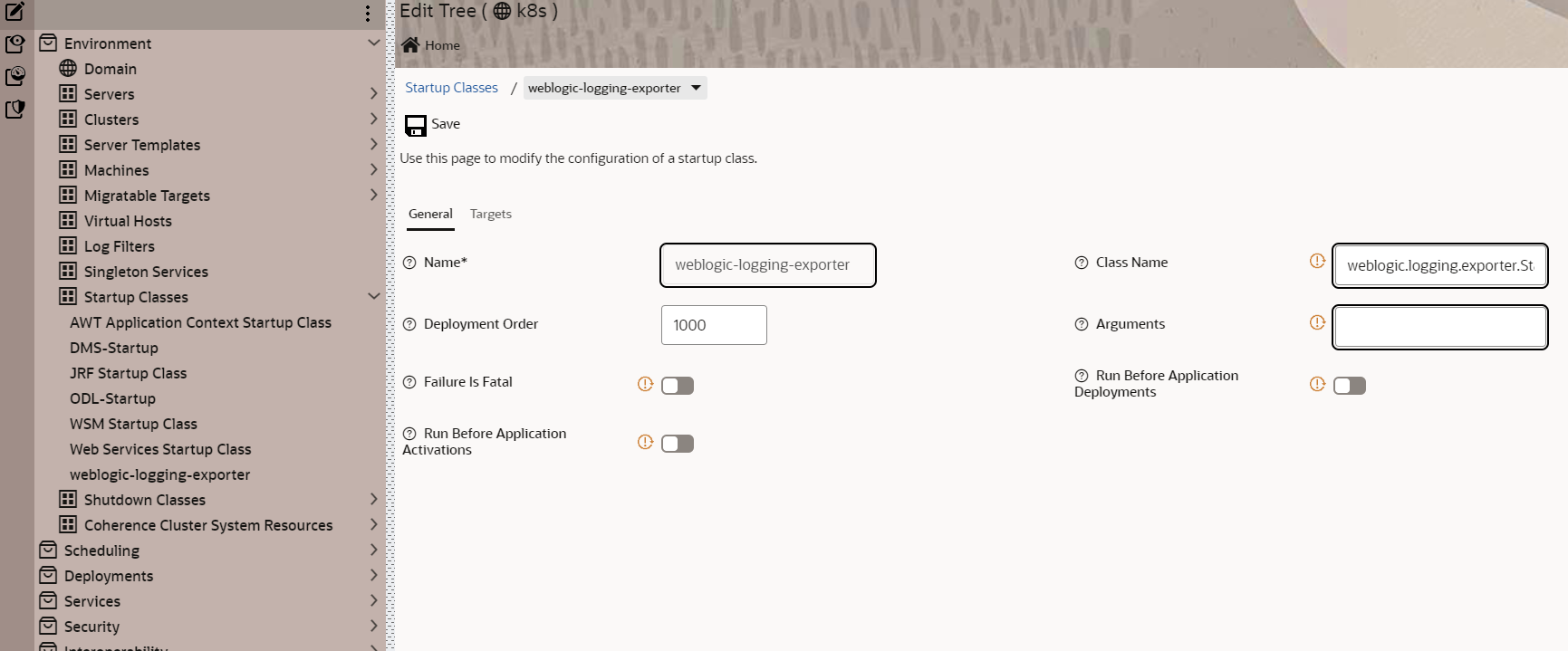
Target the startup class to each server from which you want to export logs.
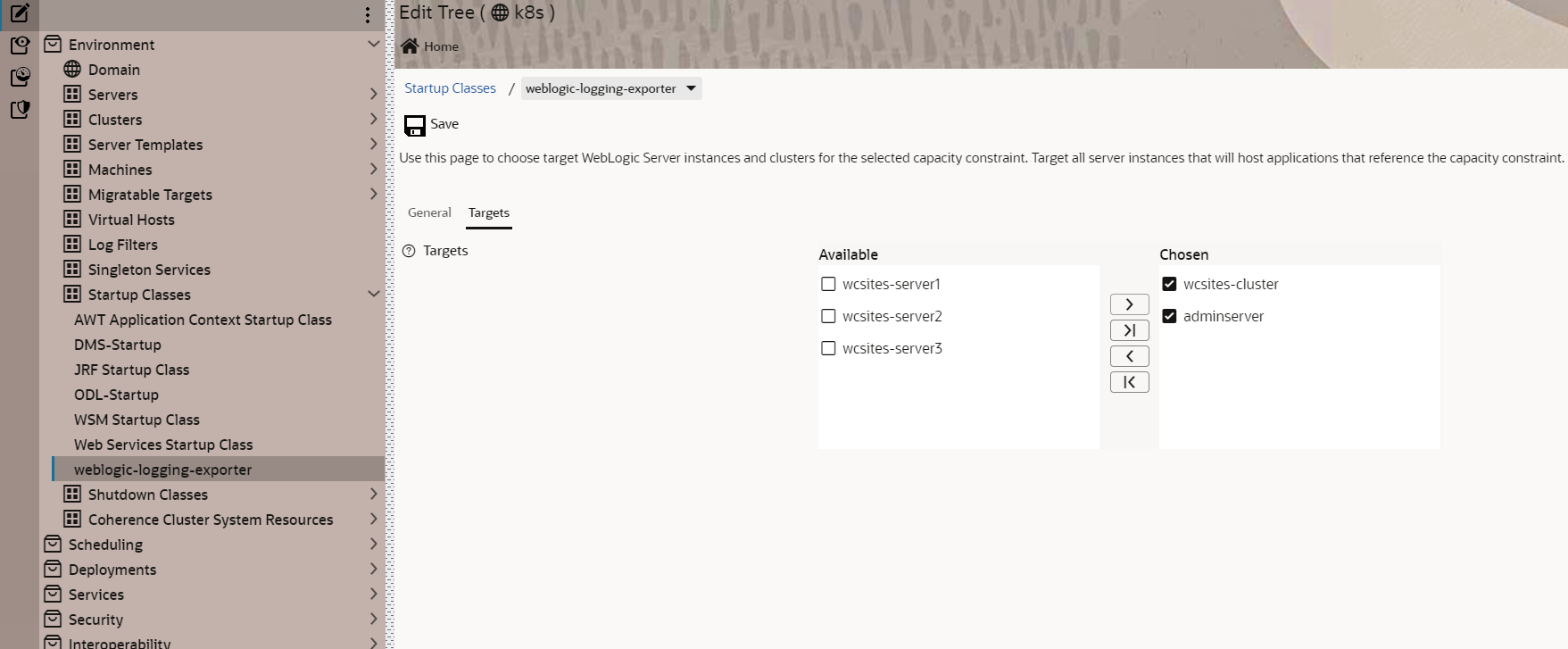
In your
/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/config/config.xmlfile, this update should look similar to the following example:$ kubectl exec -it wcsitesinfra-adminserver -n wcsites-ns cat /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/config/config.xml<startup-class> <name>weblogic-logging-exporter</name> <target>AdminServer,wcsites_cluster</target> <class-name>weblogic.logging.exporter.Startup</class-name> </startup-class>
Update the WebLogic Server CLASSPATH
Copy the
setDomainEnv.shfile from the pod to a local folder:$ kubectl cp wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/bin/setDomainEnv.sh $PWD/setDomainEnv.sh tar: Removing leading `/' from member namesIgnore exception:
tar: Removing leading '/' from member namesUpdate the server class path in
setDomainEnv.sh:CLASSPATH=/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/weblogic-logging-exporter-1.0.0.jar:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/snakeyaml-1.25.jar:${CLASSPATH} export CLASSPATHCopy back the modified
setDomainEnv.shfile to the pod:$ kubectl cp setDomainEnv.sh wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/bin/setDomainEnv.sh
Create a Configuration File for the WebLogic Logging Exporter
Specify the Elasticsearch server host and port number in file
kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-logging-exporter/WebLogicLoggingExporter.yaml:Example:
weblogicLoggingIndexName: wls publishHost: elasticsearch.default.svc.cluster.local publishPort: 9200 domainUID: wcsitesinfra weblogicLoggingExporterEnabled: true weblogicLoggingExporterSeverity: TRACE weblogicLoggingExporterBulkSize: 1Copy the
WebLogicLoggingExporter.yamlfile to the domain home directory in the WebLogic Administration Server pod:$ kubectl cp kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/weblogic-logging-exporter/WebLogicLoggingExporter.yaml wcsites-ns/wcsitesinfra-adminserver:/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/config/
Restart All the Servers in the Domain
To restart the servers, stop and then start them using the following commands:
To stop the servers:
$ kubectl patch domain wcsitesinfra -n wcsites-ns --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/serverStartPolicy", "value": "Never" }]'To start the servers:
$ kubectl patch domain wcsitesinfra -n wcsites-ns --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/serverStartPolicy", "value": "IfNeeded" }]'After all the servers are restarted, see their server logs to check that the weblogic-logging-exporter class is called, as shown below:
======================= WebLogic Logging Exporter Startup class called
Reading configuration from file name: /u01/oracle/user_projects/domains/wcsitesinfra/config/WebLogicLoggingExporter.yaml
Config{weblogicLoggingIndexName='wls', publishHost='domain.host.com', publishPort=9200, weblogicLoggingExporterSeverity='Notice', weblogicLoggingExporterBulkSize='2', enabled=true, weblogicLoggingExporterFilters=FilterConfig{expression='NOT(MSGID = 'BEA-000449')', servers=[]}], domainUID='wcsitesinfra'}Create an Index Pattern in Kibana
Create an index pattern wls* in Kibana > Management. After the servers are started, you will see the log data in the Kibana dashboard:
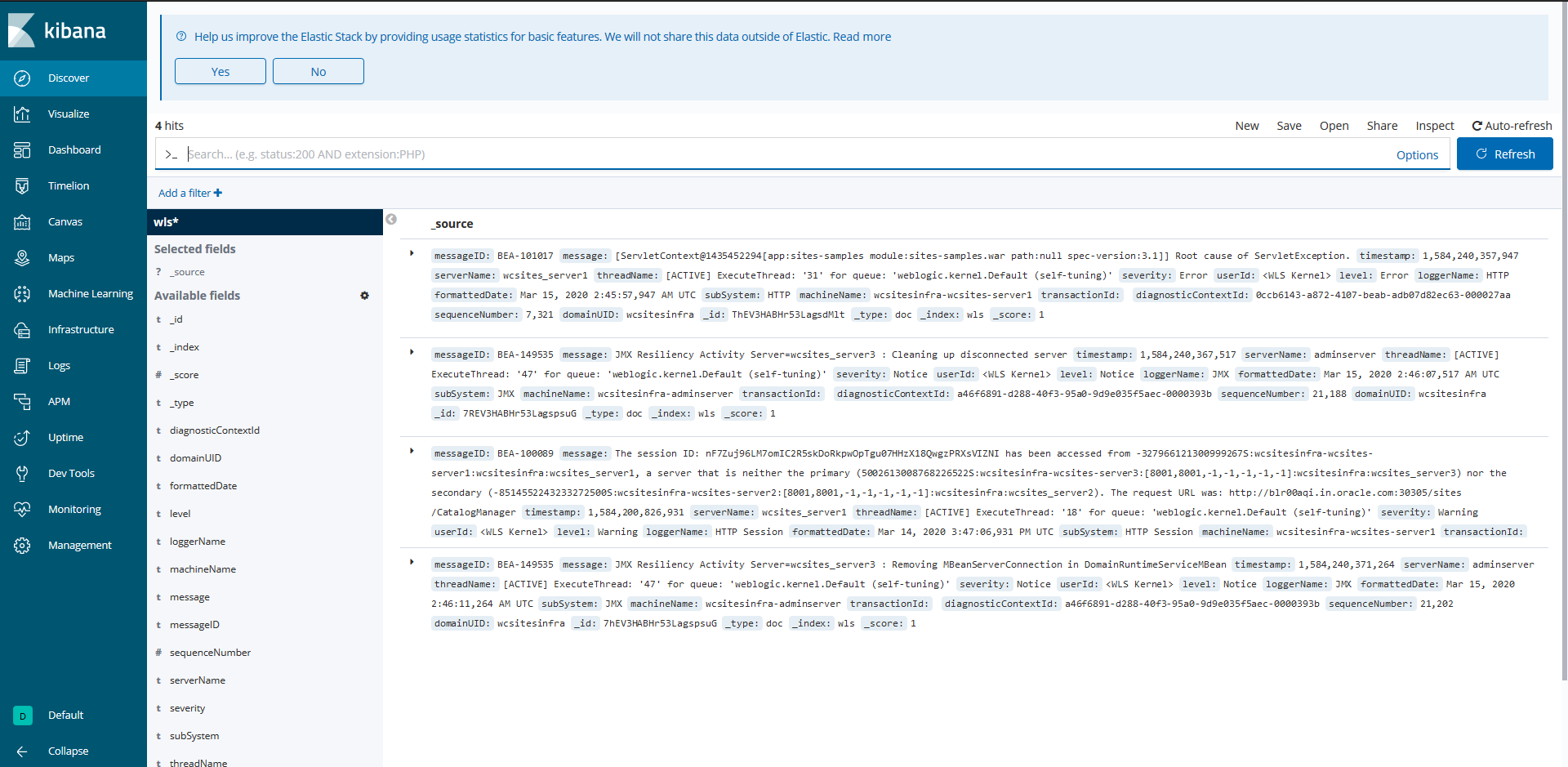
Upgrade and Patch
Patch an existing Oracle WebCenter Sites image or upgrade the infrastructure, such as upgrading the underlying Kubernetes cluster to a new release and upgrading the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator release.
Patch a Oracle WebCenter Sites product Docker image
Upgrade the underlying Oracle WebCenter Sites product image in a running Oracle WebCenter Sites Kubernetes environment.
These instructions describe how to upgrade a new release of Oracle WebCenter Sites product Docker image in a running Oracle WebCenter Sites Kubernetes environment. A rolling upgrade approach is used to upgrade managed server pods of the domain.
Note : It is expecting a Zero down time as a rolling upgrade approach is used.
Prerequisites
- Make sure Oracle WebCenter Sites domain is created and all the admin and managed pods are up and running.
- Make sure the database used for the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain deployment is up and running during the upgrade process.
Prepare the upgrade-domain-inputs.yaml
Modify the kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/upgrade/upgrade-domain-inputs.yaml. Below are given default values.
# Name of the Admin Server
adminServerName: adminserver
# Unique ID identifying a domain.
# This ID must not contain an underscope ("_"), and must be lowercase and unique across all domains in a Kubernetes cluster.
domainUID: wcsitesinfra
# Number of managed servers to generate for the domain
configuredManagedServerCount: 3
#Number of managed servers running at the time of upgrade
managedServerRunning: 3
# Base string used to generate managed server names
managedServerNameBase: wcsites-server
# Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image.
# Refer to build Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image https://github.com/oracle/docker-images/tree/master/OracleWebCenterSites
# for details on how to obtain or create the image.
# tag image to a new tag for example: oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-XXXXXX
image: oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-XXXXXX
# Image pull policy
# Legal values are "IfNotPresent", "Always", or "Never"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# Name of the domain namespace
namespace: wcsites-nsRun the upgrade script
Run the upgrade script with the modified upgrade-domain-inputs.yaml file and wait for the script to be finished.
$ sh kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/upgrade/upgrade.sh -i upgrade-domain-inputs.yamlMonitor the pods rolling out incrementaly.
$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns -wConfigure WebCenter Sites patch
Configure WebCenter Sites patch by hitting url http://LOADBALANCER − HOSTNAME:{LOADBALANCER-PORT}/sites/sitespatchsetup
Upgrade an operator release
Upgrade the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator release to a newer version.
These instructions apply to upgrading operators within the 4.x release family as additional versions are released.
To upgrade the Kubernetes operator, use the helm upgrade command. When upgrading the operator, the helm upgrade command requires that you supply a new Helm chart and image. For example:
helm repo add weblogic-operator https://oracle.github.io/weblogic-kubernetes-operator/charts
--force-update
helm upgrade \
--reuse-values \
--set version=4.2.9 \
--namespace operator-ns \
--wait \
weblogic-kubernetes-operator \
charts/weblogic-operatorUpgrade a Kubernetes cluster
Upgrade the underlying Kubernetes cluster version in a running Oracle WebCenter Sites Kubernetes environment.
These instructions describe how to upgrade a Kubernetes cluster created using kubeadm on which an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain is deployed. A rolling upgrade approach is used to upgrade nodes (master and worker) of the Kubernetes cluster.
Warning : It is expected that there will be a down time during the upgrade of the Kubernetes cluster as the nodes need to be drained as part of the upgrade process.
Prerequisites
- Review Prerequisites and ensure that your Kubernetes cluster is ready for upgrade. Make sure your environment meets all prerequisites.
- Make sure the database used for the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain deployment is up and running during the upgrade process.
Upgrade the Kubernetes version
An upgrade of Kubernetes is supported from one MINOR version to the next MINOR version, or between PATCH versions of the same MINOR. For example, you can upgrade from 1.x to 1.x+1, but not from 1.x to 1.x+2. To upgrade a Kubernetes version, first all the master nodes of the Kubernetes cluster must be upgraded sequentially, followed by the sequential upgrade of each worker node.
- See here for Kubernetes official documentation to upgrade from 1.29 to 1.30
- See here for Kubernetes official documentation to upgrade from 1.28 to 1.29
- See here for Kubernetes official documentation to upgrade from 1.27 to 1.28
- See here for Kubernetes official documentation to upgrade from 1.26 to 1.27
- See here for Kubernetes official documentation to upgrade from 1.25 to 1.26
Create or update an image
Create or update an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image used for deploying Oracle WebCenter Sites domains. An Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image can be created using the WebLogic Image Tool or using the Dockerfile approach.
If you have access to the My Oracle Support (MOS), and there is a need to build a new image with a patch (bundle or interim), it is recommended to use the WebLogic Image Tool to build an Oracle WebCenter Sites image for production deployments.
- Create or update an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image using the WebLogic Image Tool
- Create an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image using Dockerfile
Create or update an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image using the WebLogic Image Tool
Using the WebLogic Image Tool, you can create a new Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image (can include patches as well) or update an existing image with one or more patches (bundle patch and interim patches).
Recommendations:
- Use create for creating a new Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image either:
- without any patches
- or, containing the Oracle WebCenter Sites binaries, bundle patch and interim patches. This is the recommended approach if you have access to the Oracle WebCenter Sites patches because it optimizes the size of the image.
- Use update for patching an existing Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image with a single interim patch. Note that the patched image size may increase considerably due to additional image layers introduced by the patch application tool.
Set up the WebLogic Image Tool
- Prerequisites for WebLogic Image Tool
- Setting up the WebLogic Image Tool
- Validate setup
- WebLogic Image Tool build directory
- WebLogic Image Tool cache
- Set up additional build scripts
Prerequisites for WebLogic Image Tool
Verify that your environment meets the following prerequisites:
- Docker client and daemon on the build machine, with minimum Docker version 19.03.1.ce.
- Bash version 4.0 or later, to enable the
command complete feature. - JAVA_HOME environment variable set to the appropriate JDK location.
Setting up the WebLogic Image Tool
To set up the WebLogic Image Tool:
Create a working directory and change to it. In these steps, this directory is
imagetool-setup.bash $ mkdir imagetool-setup $ cd imagetool-setupDownload the latest version of the WebLogic Image Tool from the releases page.
Unzip the release ZIP file to the
imagetool-setupdirectory.Execute the following commands to set up the WebLogic Image Tool on a Linux environment:
$ cd imagetool-setup/imagetool/bin $ source setup.sh
Validate setup
To validate the setup of the WebLogic Image Tool:
Enter the following command to retrieve the version of the WebLogic Image Tool:
$ imagetool --versionEnter
imagetoolthen press the Tab key to display the availableimagetoolcommands:$ imagetool <TAB> cache create help rebase update
WebLogic Image Tool build directory
The WebLogic Image Tool creates a temporary Docker context directory, prefixed by wlsimgbuilder_temp, every time the tool runs. Under normal circumstances, this context directory will be deleted. However, if the process is aborted or the tool is unable to remove the directory, it is safe for you to delete it manually. By default, the WebLogic Image Tool creates the Docker context directory under the user’s home directory. If you prefer to use a different directory for the temporary context, set the environment variable WLSIMG_BLDDIR:
$ export WLSIMG_BLDDIR="/path/to/buid/dir"WebLogic Image Tool cache
The WebLogic Image Tool maintains a local file cache store. This store is used to look up where the Java, WebLogic Server installers, and WebLogic Server patches reside in the local file system. By default, the cache store is located in the user’s $HOME/cache directory. Under this directory, the lookup information is stored in the .metadata file. All automatically downloaded patches also reside in this directory. You can change the default cache store location by setting the environment variable WLSIMG_CACHEDIR:
$ export WLSIMG_CACHEDIR="/path/to/cachedir"Set up additional build scripts
Creating an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image using the WebLogic Image Tool requires additional container scripts for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains.
Clone the docker-images repository to set up those scripts. In these steps, this directory is
DOCKER_REPO:$ cd imagetool-setup $ git clone https://github.com/oracle/docker-images.gitCopy the additional WebLogic Image Tool build files from the operator source repository to the
imagetool-setuplocation:$ mkdir -p imagetool-setup/docker-images/OracleWebCenterSites/imagetool/14.1.2.0.0 $ cd imagetool-setup/docker-images/OracleWebCenterSites/imagetool/14.1.2.0.0 $ cp -rf ${WORKDIR}/imagetool-scripts/* .
Create an image
After set up the WebLogic Image Tool and required build scripts, follow these steps to use the WebLogic Image Tool to create a new Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image.
Download the Oracle WebCenter Sites installation binaries and patches
You must download the required Oracle WebCenter Sites installation binaries and patches as listed below from the Oracle Software Delivery Cloud and save them in a directory of your choice. In these steps, this directory is download location.
The sample list of installation binaries and patches: * JDK:
* jdk-21.0.3_linux-x64.tar.gz or jdk-17.0.12_linux-x64.tar.gz
- Fusion MiddleWare Infrastructure installer:
- fmw_14.1.2.0.0_infrastructure_generic.jar
- Fusion MiddleWare Infrastructure patches:
- if any
- WCS installers:
- fmw_14.1.2.0.0_wcsites_generic.jar
- WCS patches:
- if any
Note: This is a sample list of patches. You must get the appropriate list of patches for your Oracle WebCenter Sites image.
Update required build files
The following files available in the code repository location ${WORKDIR}/imagetool-scripts are used for creating the image.
additionalBuildCmds.txtbuildArgs
In the
buildArgsfile, update all the occurrences of%DOCKER_REPO%with thedocker-imagesrepository location, which is the complete path ofimagetool-setup/docker-images.For example, update:
%DOCKER_REPO%/OracleWebCenterSites/imagetool/14.1.2.0.0/to:
<imagetool-setup-location>/docker-images/OracleWebCenterSites/imagetool/14.1.2.0.0/Similarly, update the placeholders
%JDK_VERSION%and%BUILDTAG%with appropriate values.
Create the image
Add a JDK package to the WebLogic Image Tool cache:
$ imagetool cache addInstaller --type jdk --version 17.0.12 --path <download location>/jdk-17.0.12_linux-x64_bin.tar.gzAdd the downloaded installation binaries to the WebLogic Image Tool cache:
$ imagetool cache addInstaller --type fmw --version 14.1.2.0.0 --path <download location>/fmw_14.1.2.0.0_infrastructure_generic.jar $ imagetool cache addInstaller --type wcs --version 14.1.2.0.0 --path <download location>/fmw_14.1.2.0.0_wcsites_generic.jarAdd the downloaded patches to the WebLogic Image Tool cache:
The commands to add patches in to the cache:
$ imagetool cache addEntry --key <KEY-VALUE> --value <download location>/<PATCH-FILE-NAME>Update the patches list to
buildArgs.To the
createcommand in thebuildArgsfile, append the Oracle WebCenter Sites patches list using the--patchesflag and Opatch patch using the--opatchBugNumberflag. Sample options for the list of patches above are:Example
buildArgsfile after appending product’s list of patches and Opatch patch:imagetool create --jdkVersion=17.0.12 --type WCS --version=14.1.2.0.0 --tag=oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0 --chown oracle:root --installerResponseFile <imagetool-setup-location>/OracleFMWInfrastructure/dockerfiles/14.1.2.0.0/install.file,<imagetool-setup-location>/OracleWebCenterSites/dockerfiles/14.1.2.0.0/wcs.file --additionalBuildCommands <imagetool-setup-location>/OracleWebCenterSites/imagetool/14.1.2.0.0/additionalBuildCmds.txt --additionalBuildFiles <imagetool-setup-location>/OracleWebCenterSites/dockerfiles/14.1.2.0.0/sites-container-scripts,<imagetool-setup-location>/OracleWebCenterSites/dockerfiles/14.1.2.0.0/wcs-wls-docker-installRefer to this page for the complete list of options available with the WebLogic Image Tool
createcommand.Create a wcs-wls-docker-install installer jar
cd <imagetool-setup-location>/OracleWebCenterSites/dockerfiles/14.1.2.0.0/wcs-wls-docker-install docker run --rm -u root -v ${PWD}:/wcs-wls-docker-install groovy:4.0.4-jdk17 /wcs-wls-docker-install/packagejar.shEnter the following command to create the Oracle WebCenter Sites image:
$ imagetool @<absolute path to `buildargs` file>"The sample Dockerfile generated with the imagetool command.
########## BEGIN DOCKERFILE ########## # # Copyright (c) 2021, Oracle and/or its affiliates. # # Licensed under the Universal Permissive License v 1.0 as shown at # https://oss.oracle.com/licenses/upl # # FROM oraclelinux:7-slim as OS_UPDATE LABEL com.oracle.weblogic.imagetool.buildid="3b37c045-11c6-4eb8-b69c-f42256c1e082" USER root RUN yum -y --downloaddir= install gzip tar unzip libaio \ && yum -y --downloaddir= clean all \ && rm -rf /var/cache/yum/* \ && rm -rf ## Create user and group RUN if [ -z "$(getent group oracle)" ]; then hash groupadd &> /dev/null && groupadd oracle || exit -1 ; fi \ && if [ -z "$(getent passwd oracle)" ]; then hash useradd &> /dev/null && useradd -g oracle oracle || exit -1; fi \ && mkdir /u01 \ && chown oracle:root /u01 # Install Java FROM OS_UPDATE as JDK_BUILD LABEL com.oracle.weblogic.imagetool.buildid="3b37c045-11c6-4eb8-b69c-f42256c1e082" ENV JAVA_HOME=/u01/jdk COPY --chown=oracle:root jdk-8u291-linux-x64.tar.gz /tmp/imagetool/ USER oracle RUN tar xzf /tmp/imagetool/jdk-8u291-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /u01 \ && mv /u01/jdk* /u01/jdk \ && rm -rf /tmp/imagetool # Install Middleware FROM OS_UPDATE as WLS_BUILD LABEL com.oracle.weblogic.imagetool.buildid="3b37c045-11c6-4eb8-b69c-f42256c1e082" ENV JAVA_HOME=/u01/jdk \ ORACLE_HOME=/u01/oracle \ OPATCH_NO_FUSER=true RUN mkdir -p /u01/oracle \ && mkdir -p /u01/oracle/oraInventory \ && chown oracle:root /u01/oracle/oraInventory \ && chown oracle:root /u01/oracle COPY --from=JDK_BUILD --chown=oracle:root /u01/jdk /u01/jdk/ COPY --chown=oracle:root fmw_14.1.2.0.0_infrastructure.jar install.file /tmp/imagetool/ COPY --chown=oracle:root fmw_14.1.2.0.0_wcsites.jar wcs.file /tmp/imagetool/ COPY --chown=oracle:root oraInst.loc /u01/oracle/ COPY --chown=oracle:root p28186730_139428_Generic.zip /tmp/imagetool/opatch/ COPY --chown=oracle:root patches/* /tmp/imagetool/patches/ USER oracle RUN \ /u01/jdk/bin/java -Xmx1024m -jar /tmp/imagetool/fmw_14.1.2.0.0_infrastructure.jar -silent ORACLE_HOME=/u01/oracle \ -responseFile /tmp/imagetool/install.file -invPtrLoc /u01/oracle/oraInst.loc -ignoreSysPrereqs -force -novalidation RUN \ /u01/jdk/bin/java -Xmx1024m -jar /tmp/imagetool/fmw_14.1.2.0.0_wcsites.jar -silent ORACLE_HOME=/u01/oracle \ -responseFile /tmp/imagetool/wcs.file -invPtrLoc /u01/oracle/oraInst.loc -ignoreSysPrereqs -force -novalidation RUN cd /tmp/imagetool/opatch \ && /u01/jdk/bin/jar -xf /tmp/imagetool/opatch/p28186730_139428_Generic.zip \ && /u01/jdk/bin/java -jar /tmp/imagetool/opatch/6880880/opatch_generic.jar -silent -ignoreSysPrereqs -force -novalidation oracle_home=/u01/oracle RUN /u01/oracle/OPatch/opatch napply -silent -oh /u01/oracle -phBaseDir /tmp/imagetool/patches \ && /u01/oracle/OPatch/opatch util cleanup -silent -oh /u01/oracle FROM OS_UPDATE as FINAL_BUILD ARG ADMIN_NAME ARG ADMIN_HOST ARG ADMIN_PORT ARG MANAGED_SERVER_PORT ENV ORACLE_HOME=/u01/oracle \ JAVA_HOME=/u01/jdk \ LC_ALL=${DEFAULT_LOCALE:-en_US.UTF-8} \ PATH=${PATH}:/u01/jdk/bin:/u01/oracle/oracle_common/common/bin:/u01/oracle/wlserver/common/bin:/u01/oracle LABEL com.oracle.weblogic.imagetool.buildid="3b37c045-11c6-4eb8-b69c-f42256c1e082" COPY --from=JDK_BUILD --chown=oracle:root /u01/jdk /u01/jdk/ COPY --from=WLS_BUILD --chown=oracle:root /u01/oracle /u01/oracle/ USER oracle WORKDIR /u01/oracle #ENTRYPOINT /bin/bash USER root COPY --chown=oracle:root files/sites-container-scripts/overrides/oui/ /u01/oracle/wcsites/common/templates/wls/ USER oracle RUN cd /u01/oracle/wcsites/common/templates/wls && \ $JAVA_HOME/bin/jar uvf oracle.wcsites.base.template.jar startup-plan.xml file-definition.xml && \ rm /u01/oracle/wcsites/common/templates/wls/startup-plan.xml && \ rm /u01/oracle/wcsites/common/templates/wls/file-definition.xml # # Install the required packages # ----------------------------- USER root ENV SITES_CONTAINER_SCRIPTS=/u01/oracle/sites-container-scripts \ SITES_INSTALLER_PKG=wcs-wls-docker-install \ DOMAIN_ROOT="${DOMAIN_ROOT:-/u01/oracle/user_projects/domains}" \ ADMIN_PORT=7001 \ WCSITES_PORT=7002 \ ADMIN_SSL_PORT=9001 \ WCSITES_SSL_PORT=9002 \ PATH=$PATH:/u01/oracle/sites-container-scripts RUN yum install -y hostname && \ rm -rf /var/cache/yum RUN mkdir -p ${SITES_CONTAINER_SCRIPTS} && \ mkdir -p /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install COPY --chown=oracle:root files/sites-container-scripts/ ${SITES_CONTAINER_SCRIPTS}/ COPY --chown=oracle:root files/wcs-wls-docker-install/ /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/ RUN chown oracle:root -R /u01/oracle/sites-container-scripts && \ chown oracle:root -R /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install && \ chmod a+xr /u01/oracle/sites-container-scripts/* && \ chmod a+xr /u01/wcs-wls-docker-install/*.sh # Expose all Ports # ------------------------------------------------------------- EXPOSE $ADMIN_PORT $ADMIN_SSL_PORT $WCSITES_PORT $WCSITES_SSL_PORT USER oracle WORKDIR ${ORACLE_HOME} # Define default command to start. # ------------------------------------------------------------- CMD ["/u01/oracle/sites-container-scripts/createOrStartSitesDomain.sh"] ########## END DOCKERFILE ##########Check the created image using the
Docker imagescommand:$ Docker images | grep wcsites
Update an image
After set up the WebLogic Image Tool and required build scripts, use the WebLogic Image Tool to update an existing Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image:
Enter the following command for each patch to add the required patch(es) to the WebLogic Image Tool cache:
$ cd <imagetool-setup> $ imagetool cache addEntry --key 35188131_14.1.2.0.0 --value < %path-to-downloaded-pathes%/patches/p35188131_141200_Generic.zip [INFO] Added entry 35188131_14.1.2.0.0=< %path-to-downloaded-pathes%/patches/p35188131_122140_Generic.zipProvide the following arguments to the WebLogic Image Tool
updatecommand:–-fromImage- Identify the image that needs to be updated. In the example below, the image to be updated isoracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0.–-patches- Multiple patches can be specified as a comma-separated list.--tag- Specify the new tag to be applied for the image being built.
Refer here for the complete list of options available with the WebLogic Image Tool
updatecommand.Note: The WebLogic Image Tool cache should have the latest OPatch zip. The WebLogic Image Tool will update the OPatch if it is not already updated in the image.
Examples
The example
updatecommand:$ imagetool update --fromImage oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0 --chown oracle:root --tag=oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-35188131 --patches=35188131_14.1.2.0.0 --opatchBugNumber=28186730_13.9.4.2.12 [INFO ] Image Tool build ID: 7c268a9a-723f-424e-a06e-cb615c783e6d [INFO ] Temporary directory used for docker build context: %path-to-temp-directory%/tmpBuild/wlsimgbuilder_temp8555048225669509 [INFO ] Using patch 28186730_13.9.4.2.8 from cache: %path-to-downloaded-pathes%/patches/p28186730_139428_Generic.zip [INFO ] OPatch will not be updated, fromImage has version 13.9.4.2.4, available version is 13.9.4.2.4 [WARNING] skipping patch conflict check, no support credentials provided [WARNING] No credentials provided, skipping validation of patches [INFO ] Using patch 31548912_14.1.2.0.0 from cache: %path-to-downloaded-pathes%/patches/p31548912_122140_Generic.zip [INFO ] docker cmd = docker build --no-cache --force-rm --tag oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-21.1.1 --build-arg http_proxy=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80 --build-arg https_proxy=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80 --build-arg no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,/var/run/docker.sock %path-to-temp-directory%/tmpBuild/wlsimgbuilder_temp8555048225669509 Sending build context to Docker daemon 212.7MB Step 1/7 : FROM oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-21.1.1 as FINAL_BUILD ---> 480f1a31c02b Step 2/7 : USER root ---> Running in 9d5a81ad5bde Removing intermediate container 9d5a81ad5bde ---> 71b50b0b34dc Step 3/7 : ENV OPATCH_NO_FUSER=true ---> Running in c361884e8a71 Removing intermediate container c361884e8a71 ---> 2951de256951 Step 4/7 : LABEL com.oracle.weblogic.imagetool.buildid="7c268a9a-723f-424e-a06e-cb615c783e6d" ---> Running in e2f485ac9039 Removing intermediate container e2f485ac9039 ---> 970f6552ef9a Step 5/7 : USER oracle ---> Running in e3c85228af4b Removing intermediate container e3c85228af4b ---> 4401fdb4ebbe Step 6/7 : COPY --chown=oracle:root patches/* /tmp/imagetool/patches/ ---> 978a48e1cc95 Step 7/7 : RUN /u01/oracle/OPatch/opatch napply -silent -oh /u01/oracle -phBaseDir /tmp/imagetool/patches && /u01/oracle/OPatch/opatch util cleanup -silent -oh /u01/oracle && rm -rf /tmp/imagetool ---> Running in 5039320b2f10 Oracle Interim Patch Installer version 13.9.4.2.4 Copyright (c) 2020, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved. Oracle Home : /u01/oracle Central Inventory : /u01/oracle/oraInventory from : /u01/oracle/oraInst.loc OPatch version : 13.9.4.2.4 OUI version : 13.9.4.0.0 Log file location : /u01/oracle/cfgtoollogs/opatch/opatch2020-08-04_05-15-38AM_1.log OPatch detects the Middleware Home as "/u01/oracle" Verifying environment and performing prerequisite checks... OPatch continues with these patches: 31548912 Do you want to proceed? [y|n] Y (auto-answered by -silent) User Responded with: Y All checks passed. Please shutdown Oracle instances running out of this ORACLE_HOME on the local system. (Oracle Home = '/u01/oracle') Is the local system ready for patching? [y|n] Y (auto-answered by -silent) User Responded with: Y Backing up files... Applying interim patch '31548912' to OH '/u01/oracle' ApplySession: Optional component(s) [ oracle.wcsites.wccintegration, 14.1.2.0.0 ] , [ oracle.wcsites.wccintegration, 14.1.2.0.0 ] not present in the Oracle Home or a higher version is found. Patching component oracle.wcsites, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.visitorservices, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.visitorservices, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.examples, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.examples, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.developer.tools, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.developer.tools, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.satelliteserver, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.satelliteserver, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.sitecapture, 14.1.2.0.0... Patching component oracle.wcsites.sitecapture, 14.1.2.0.0... Patch 31548912 successfully applied. Log file location: /u01/oracle/cfgtoollogs/opatch/opatch2020-08-04_05-15-38AM_1.log OPatch succeeded. Oracle Interim Patch Installer version 13.9.4.2.4 Copyright (c) 2020, Oracle Corporation. All rights reserved. Oracle Home : /u01/oracle Central Inventory : /u01/oracle/oraInventory from : /u01/oracle/oraInst.loc OPatch version : 13.9.4.2.4 OUI version : 13.9.4.0.0 Log file location : /u01/oracle/cfgtoollogs/opatch/opatch2020-08-04_05-16-11AM_1.log OPatch detects the Middleware Home as "/u01/oracle" Invoking utility "cleanup" OPatch will clean up 'restore.sh,make.txt' files and 'scratch,backup' directories. You will be still able to rollback patches after this cleanup. Do you want to proceed? [y|n] Y (auto-answered by -silent) User Responded with: Y Backup area for restore has been cleaned up. For a complete list of files/directories deleted, Please refer log file. OPatch succeeded. Removing intermediate container 5039320b2f10 ---> 1be958e1e859 Successfully built 1be958e1e859 Successfully tagged oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-21.1.1-29710661 [INFO ] Build successful. Build time=73s. Image tag=oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-21.1.1-29710661 The example Dockerfile generated by the WebLogic Image Tool with the `–-dryRun` option: $ imagetool update --fromImage oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0 --chown oracle:root --tag=oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0-35188131 --patches=35188131_14.1.2.0.0 --opatchBugNumber=28186730_13.9.4.2.12 --dryRun [INFO ] Image Tool build ID: a2fca032-7807-4bfb-b5a4-0ed90a710a56 [INFO ] Temporary directory used for docker build context: %path-to-temp-directory%/tmpBuild/wlsimgbuilder_temp4743247141639108603 [INFO ] Using patch 28186730_13.9.4.2.8 from cache: %path-to-downloaded-pathes%/patches /p28186730_139428_Generic.zip [INFO ] OPatch will not be updated, fromImage has version 13.9.4.2.8, available version is 13.9.4.2.8 [WARNING] skipping patch conflict check, no support credentials provided [WARNING] No credentials provided, skipping validation of patches [INFO ] Using patch 29710661_14.1.2.0.0 from cache: %path-to-downloaded-pathes%/patches /p29710661_122140_Generic.zip [INFO ] docker cmd = docker build --no-cache --force-rm --tag oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0 --build-arg http_proxy=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80 --build-arg https_proxy=http://www-proxy-your-company.com:80 --build-arg no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,/var/run/docker.sock %path-to-temp-directory%/tmpBuild/wlsimgbuilder_temp4743247141639108603 ########## BEGIN DOCKERFILE ########## # # Copyright (c) 2019, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. # # Licensed under the Universal Permissive License v 1.0 as shown at https://oss.oracle.com/licenses/upl. # # FROM oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0 as FINAL_BUILD USER root ENV OPATCH_NO_FUSER=true LABEL com.oracle.weblogic.imagetool.buildid="a2fca032-7807-4bfb-b5a4-0ed90a710a56" USER oracle COPY --chown=oracle:root patches/* /tmp/imagetool/patches/ RUN /u01/oracle/OPatch/opatch napply -silent -oh /u01/oracle -phBaseDir /tmp/imagetool/patches \ && /u01/oracle/OPatch/opatch util cleanup -silent -oh /u01/oracle \ && rm -rf /tmp/imagetool ########## END DOCKERFILE ########## [INFO ] Dry run complete. No image created.Check the built image using the
Docker imagescommand:$ Docker images | grep wcsites oracle/wcsites 14.1.2.0.0-35188131 2ef2a67a685b About a minute ago 3.74GB
Create an Oracle WebCenter Sites Docker image using Dockerfile
For test and development purposes, you can create an Oracle WebCenter Sites image using the Dockerfile. Consult the README file for important prerequisite steps, such as building or pulling the Server JRE Docker image, Oracle FMW Infrastructure Docker image, and downloading the Oracle WebCenter Sites installer and bundle patch binaries.
A prebuilt Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure image, container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/fmw-infrastructure:14.1.2.0.0, is available at container-registry.oracle.com. We recommend that you pull and rename this image to build the Oracle WebCenter Sites image.
$ docker pull <path-to-container-registry>/fmw-infrastructure:14.1.2.0.0
$ docker tag <path-to-container-registry>/fmw-infrastructure:14.1.2.0.0 oracle/fmw-infrastructure:14.1.2.0.0Follow these steps to build an Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure image, and then the Oracle WebCenter Sites image as a layer on top of that:
Make a local clone of the sample repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/oracle/docker-imagesBuild the
oracle/fmw-infrastructure:14.1.2.0.0image:$ cd docker-images/OracleFMWInfrastructure/dockerfiles $ sh buildDockerImage.sh -v 14.1.2.0.0 -sThis will produce an image named
oracle/fmw-infrastructure:14.1.2.0.0.Download the Oracle WebCenter Sites installer from the Oracle Technology Network or e-delivery.
Note: Copy the installer binaries to the same location as the Dockerfile.
To build the Oracle WebCenter Sites image with patches, you must download and drop the patch zip files (for example,
p35188131_141200_Generic.zip) into thepatches/folder under the version that is required. For example, for14.1.2.0.0the folder is14.1.2.0.0/patches.Create the Oracle WebCenter Sites image by running the provided script:
$ cd docker-images/OracleWebCenterSites/dockerfiles $ ./buildDockerImage.sh -v 14.1.2.0.0 -sThe image produced will be named
oracle/wcsites:14.1.2.0.0. The samples and instructions assume the Oracle WebCenter Sites image is namedwcsites:14.1.2.0.0. You must rename your image to match this name, or update the samples to refer to the image you created.
Uninstall
Clean up the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain setup.
Learn how to clean up the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain setup.
Stop Administration and Managed server pods
Stop all server pods in a domain. This can be done by patching domain “serverStartPolicy” to “Never”. Here is the sample command for the same.
$ kubectl patch domain wcsites-domain-name -n wcsites-namespace --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/serverStartPolicy", "value": "Never" }]'For example:
$ kubectl patch domain wcsitesinfra -n wcsites-ns --type='json' -p='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/serverStartPolicy", "value": "Never" }]'Delete exposed services
```bash
$ kubectl delete -f create-wcsites-domain/utils/wcs-services.yaml
```Remove the domain
Remove the domain’s ingress (for example, Traefik ingress) using Helm:
$ helm uninstall wcsites-domain-ingress -n wcsites-namespaceFor example:
$ helm uninstall wcsitesinfra-ingress -n wsites-nsDelete Domain Job (This will Drop the RCU schemas)
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/output/weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/delete-domain-job.yamlCheck if the job has finished.
Remove the domain resources by using the sample
delete-weblogic-domain-resources.shscript present at${WORKDIR}/delete-domain:$ cd ${WORKDIR}/delete-domain $ ./delete-weblogic-domain-resources.sh -d sample-domain1For example:
$ cd ${WORKDIR}/delete-domain $ ./delete-weblogic-domain-resources.sh -d wcsites-nsUse
kubectlto confirm that the server pods and domain resource are deleted:$ kubectl get pods -n sample-domain1-ns $ kubectl get domains -n sample-domain1-ns $ kubectl get clusters -n sample-domain1-nsFor example:
$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns $ kubectl get domains -n wcsites-ns $ kubectl get clusters -n wcsites-ns
Remove the domain namespace
Configure the installed ingress load balancer (for example, Traefik) to stop managing the ingresses in the domain namespace:
$ helm upgrade traefik traefik/traefik \ --namespace traefik \ --reuse-values \ --set "kubernetes.namespaces={traefik}" \ --waitDelete the domain namespace:
$ kubectl delete namespace sample-domain1-nsFor example:
$ kubectl delete namespace wcsites-ns
Remove the operator
Remove the operator:
$ helm uninstall sample-weblogic-operator -n sample-weblogic-operator-nsFor example:
$ helm uninstall weblogic-kubernetes-operator -n operator-nsRemove the operator’s namespace:
$ kubectl delete namespace sample-weblogic-operator-nsFor example:
$ kubectl delete namespace operator-ns
Remove the load balancer
Remove the installed ingress based load balancer (for example, Traefik):
$ helm uninstall traefik-operator -n traefikRemove the Traefik namespace:
$ kubectl delete namespace traefik
Delete the domain home
To remove the domain home that is generated using the create-domain.sh script, with appropriate privileges manually delete the contents of the storage attached to the domain home persistent volume (PV).
For example, for the domain’s persistent volume of type host_path:
$ rm -rf /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites/*Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Setting up WebCenter Sites domains with WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
This is a guide to run WebLogic Kubernetes Operator managed WebcenterSites domains on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure.
Preparing an OKE environment
Running WebLogic Kubernetes Operator managed WebCenter Sites domains on OKE
Overview
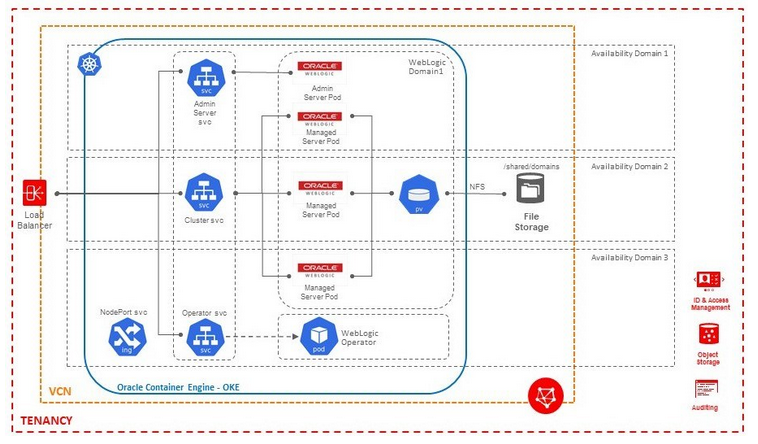
Create Public SSH Key to access all the Bastion/Worker nodes
- Create SSH key using ssh-keygen on linux terminal.
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Your identification has been saved in <path>/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in <path>/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:xCi1gf1QFafbRwOM3WjUTgqEInwi6UklbuxbBeMzA6M demokey
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| +++oo..++*++ |
| ++==+==. oo=.+ |
|Eo+o*+++o .o +o |
| oo * .. o.... |
| . . S . . . |
| o . |
| . |
| |
| |
+----[SHA256]-----+- This will generate id_rsa and id_rsa.pub in
- You will be using id_rsa.pub while creating the instance and id_rsa which is a private key, will be used during login to the instance later.
Create a compartment for OKE
Within your tenancy, there must be a compartment to contain the necessary network resources (VCN, subnets, internet gateway, route table, security lists). 1. Go to OCI console, and use the top-left Menu to select the Identity > Compartments option. 2. Click the Create Compartment button. 3. Enter the compartment name(WCSCDev) and description(OKE compartment), the click the Create Compartment button.
Create Virtual Cloud Network
- From OCI console, use navigation menu. Under Solutions, Platform and Edge, go to Networking and click Virtual Cloud Networks (VCN)
- Choose a WCSCDev Compartment and then click Create Virtual Cloud Network
- Choose a WCSCDev Compartment and then click Networking QuickStart ? VCN with Internet Connectivity ? Start Workflow
- Add Name (ex. WCNVCN)
- Click Next ? Review and Create.
Create Container Clusters (OKE)
- From OCI console, use navigation menu. Under Solutions, Platform and Edge, go to Developer Services and click Container Clusters (OKE)
- Choose a WCSCDev Compartment and then click Create Cluster
 *In the Cluster Creation dialog, change the placeholder value in the Name field and enter WCSOKECluster instead.
*In the Cluster Creation dialog, change the placeholder value in the Name field and enter WCSOKECluster instead. 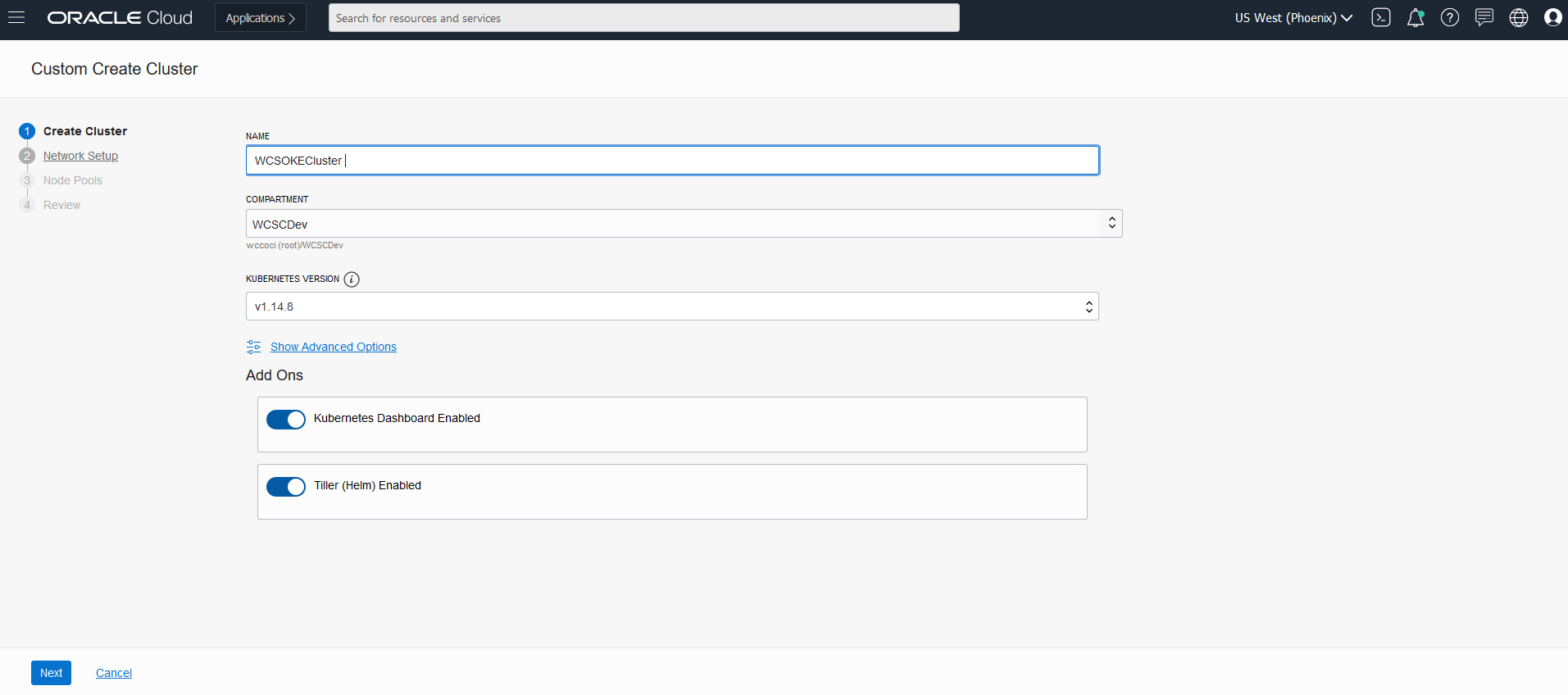
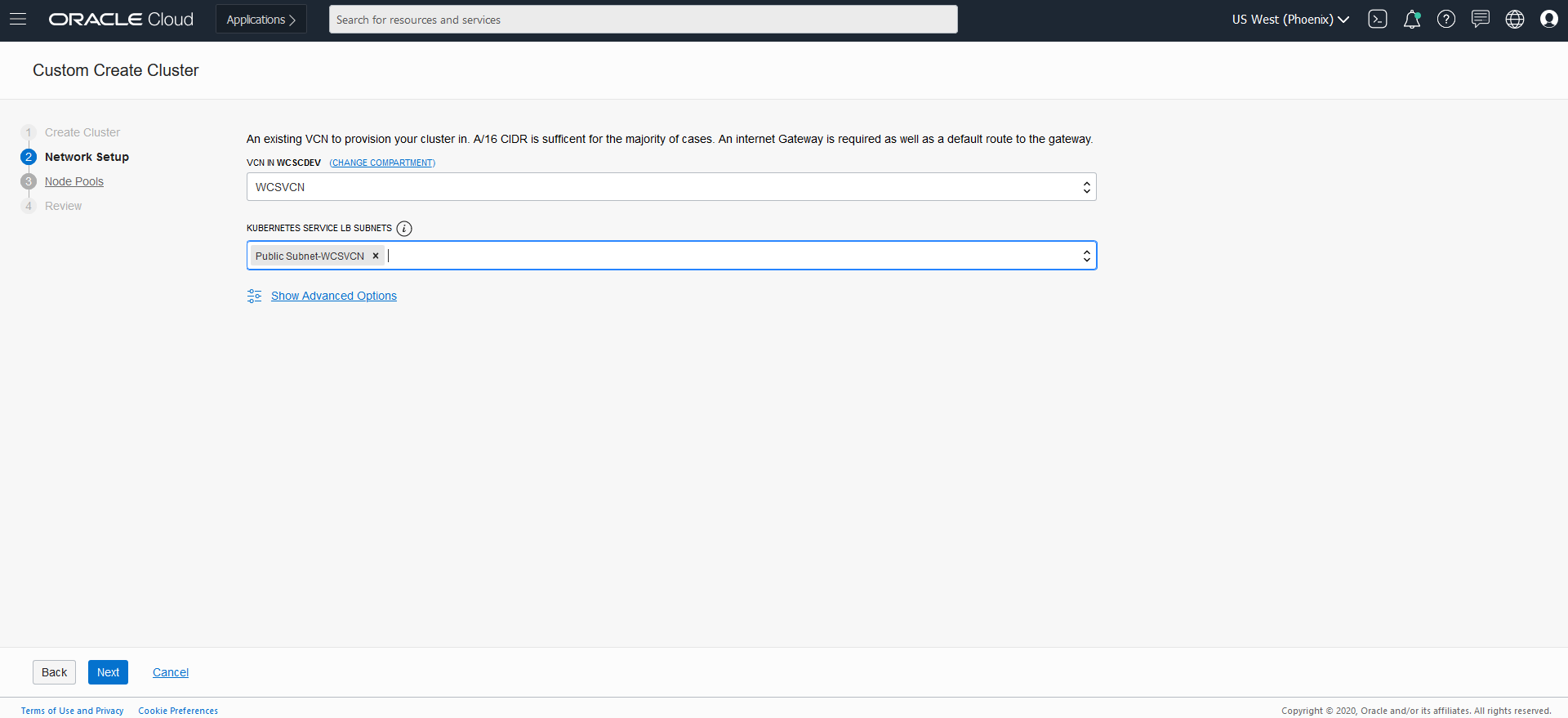
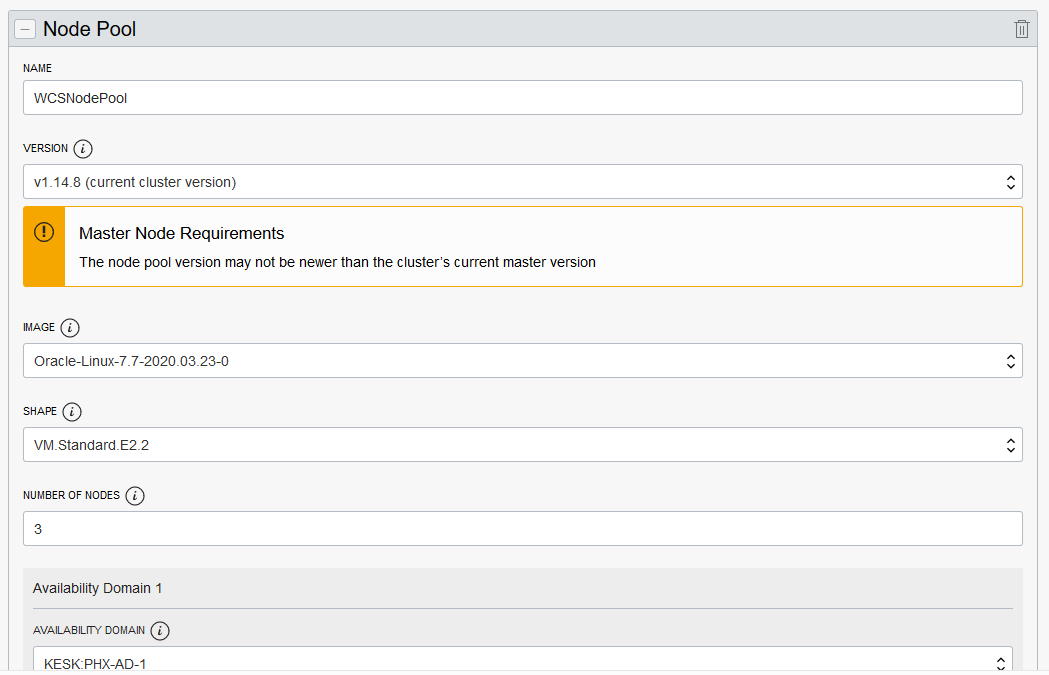
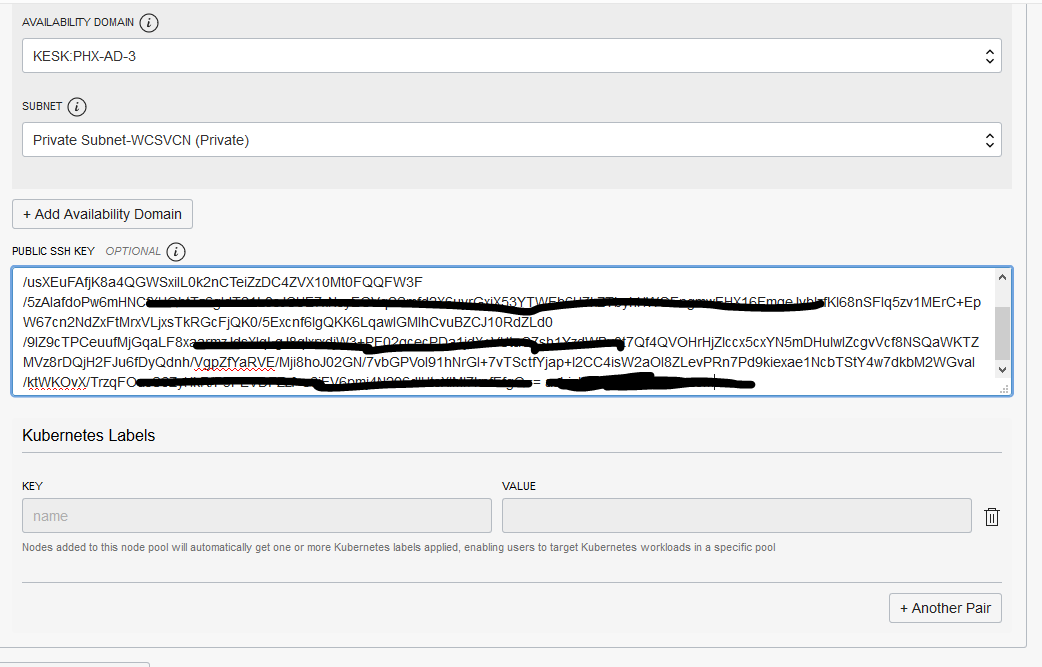
- Initially, the Cluster is in “Creating” state and no buttons are accessible. Once its state is “Active”, then all the button gets are enabled.
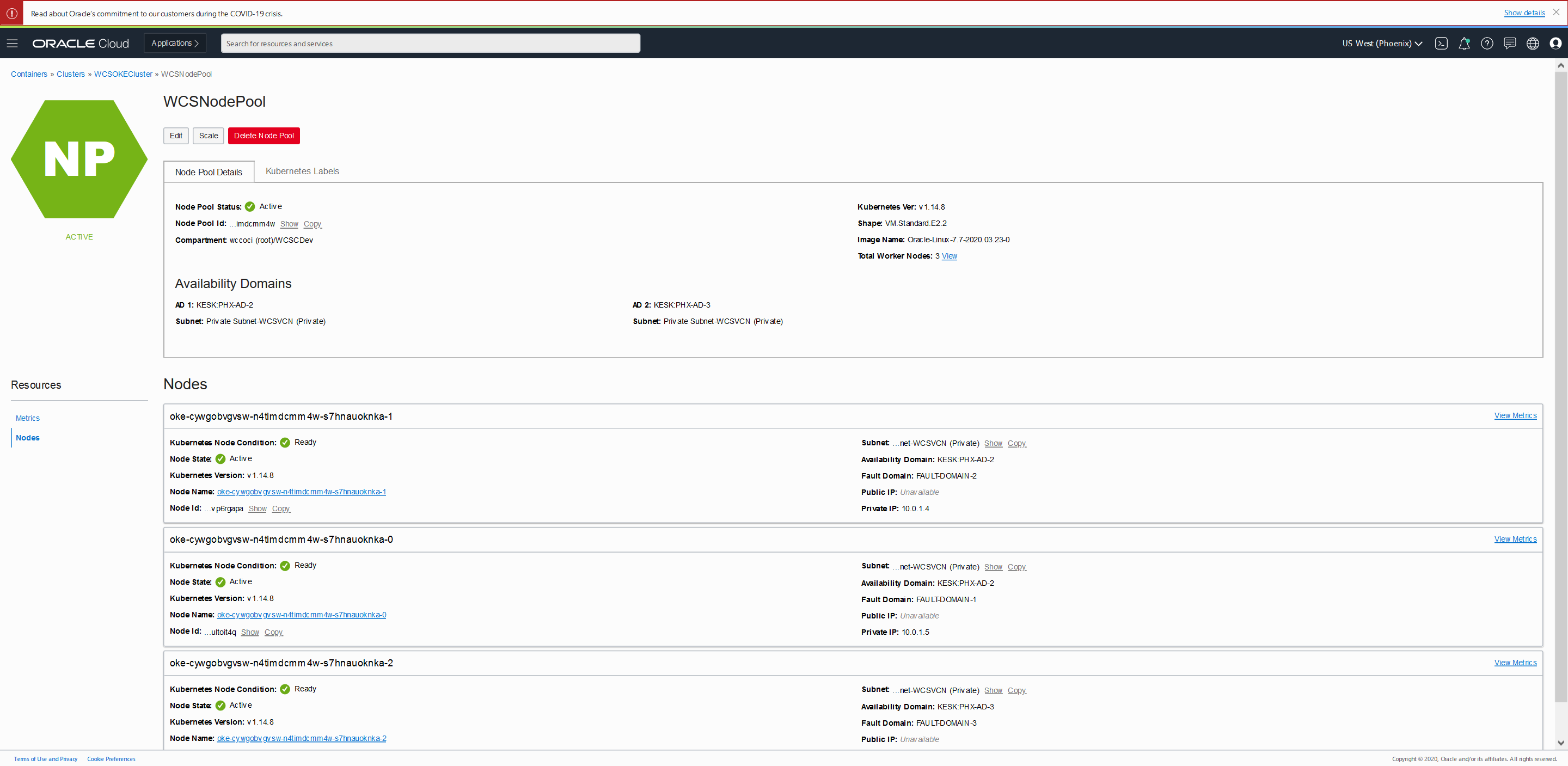
Create Bastion Node
Setup a bastion node for accessing internal resources.
Setup OCI CLI to download kubeconfig and access OKE Cluster
- Login to Bastion Node
- Install OCI CLI
$ bash -c "$(curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/oracle/oci-cli/master/scripts/install/install.sh)"- Respond to the Installation Script Prompts.
- To download the kubeconfig later after setup, we need to setup the oci config file. Follow the below command and enter the details when prompted.
$ oci setup config
This command provides a walkthrough of creating a valid CLI config file.
The following links explain where to find the information required by this
script:
User OCID and Tenancy OCID:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/Content/API/Concepts/apisigningkey.htm#Other
Region:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/Content/General/Concepts/regions.htm
General config documentation:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/Content/API/Concepts/sdkconfig.htm
Enter a location for your config [/home/opc/.oci/config]:
Enter a user OCID: ocid1.user.xxxxx5n3a
Enter a tenancy OCID: ocid1.tenancy.xxxxxxmffq
Enter a region (e.g. ap-mumbai-1, ap-seoul-1, ap-sydney-1, ap-tokyo-1, ca-toronto-1, eu-frankfurt-1, eu-zurich-1, sa-saopaulo-1, uk-london-1, us-ashburn-1, us-gov-ashburn-1, us-gov-chicago-1, us-gov-phoenix-1, us-langley-1, us-luke-1, us-phoenix-1): us-phoenix-1
Do you want to generate a new RSA key pair? (If you decline you will be asked to supply the path to an existing key.) [Y/n]: Y
Enter a directory for your keys to be created [/home/opc/.oci]:
Enter a name for your key [oci_api_key]:
Public key written to: /home/opc/.oci/oci_api_key_public.pem
Enter a passphrase for your private key (empty for no passphrase):
Private key written to: /home/opc/.oci/oci_api_key.pem
Fingerprint: 30:b9:a6:80:6e:b7:bb:7d:f9:79:6b:84:48:30:03:16
Config written to /home/opc/.oci/config
If you haven't already uploaded your public key through the console,
follow the instructions on the page linked below in the section 'How to
upload the public key':
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/Content/API/Concepts/apisigningkey.htm#How2- Now you need to upload the created public key in $HOME/.oci (oci_api_key_public.pem) to OCI console. Login to Console and navigate to User Settings, which is in the drop down under your OCI username in the top nav
 On User Details page, select “Api Keys” in the left nav and then Click the “Add Public Key” button and then copy the content of “oci_api_key_public.pem”. Click “Add”.
On User Details page, select “Api Keys” in the left nav and then Click the “Add Public Key” button and then copy the content of “oci_api_key_public.pem”. Click “Add”.  Now you can use the oci cli to access the OCI resources.
Now you can use the oci cli to access the OCI resources.
Setup Access Kubeconfig (OKE Cluster)
Install docker
- Login to Bastion Node
- Login to instance and install the latest docker-engine and start docker service
#install docker-engine
sudo yum -y install docker-engine
#Enable and start docker service
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
#Add opc to docker group
sudo /sbin/usermod -a -G docker opc- Logout and log back into the host - to ensure user is added to group correctly
- Check your Docker Version.
$ docker version
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.1-ol
API version: 1.40
Go version: go1.12.5
Git commit: ead9442
Built: Wed Sep 11 06:40:28 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.1-ol
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.12.5
Git commit: ead9442
Built: Wed Sep 11 06:38:43 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Default Registry: docker.io
containerd:
Version: v1.2.0-rc.0-108-gc444666
GitCommit: c4446665cb9c30056f4998ed953e6d4ff22c7c39
runc:
Version: spec: 1.0.1-dev
GitCommit:
docker-init:
Version: 0.18.0
GitCommit: fec3683- If your instances are on corporate network then Configuring Proxy Requirements (run as root)
### Create the drop-in file /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf that contains proxy details:
cat <<EOF > /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf
[Service]
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http://<your-company-domain>:80"
Environment="HTTPS_PROXY=http://<your-company-domain>:80"
Environment="NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,.<no-proxy-domain>,/var/run/docker.sock"
EOF- Restart docker daemon to load latest changes
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl restart docker- Verify if the proxy is configured with docker
$ docker info|grep -i proxyInstall Kubernetes Packages
- Login to Bastion Node
- Add the external kubernetes repository (run as root)
cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
exclude=kube*
EOF- Set SELinux in permissive mode (effectively disabling it)
export PATH=/sbin:$PATH
setenforce 0
sudo sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/config- Export proxy (if your instances are on corporate network) and install latest kubeadm, kubelet and kubectl
VERSION=1.27.6-0
sudo yum install -y kubelet-$VERSION kubeadm-$VERSION kubectl-$VERSION --disableexcludes=kubernetes
### enable kubelet service so that it auto-restart on reboot
sudo systemctl enable --now kubelet- Ensure net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables is set to 1 in your sysctl to avoid traffic routing issues ( run as root user)
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl --system- Update the kubelet with –fail-swap-on flag to false and restart kubelet (starting in 1.8, kubelet fails to start with swap enabled)
### run as a root user
### Update --fail-swap-on=false into /etc/sysconfig/kubelet
sed -i 's/KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=/KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="--fail-swap-on=false"/' /etc/sysconfig/kubelet
cat /etc/sysconfig/kubelet
### Reload and restart kubelet
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart kubelet Setup bastion Node to Access Kubeconfig
- From OCI console, use navigation menu. Under Solutions, Platform and Edge, go to Developer Services and click Container Clusters (OKE), click on ‘WCSOKECluster’
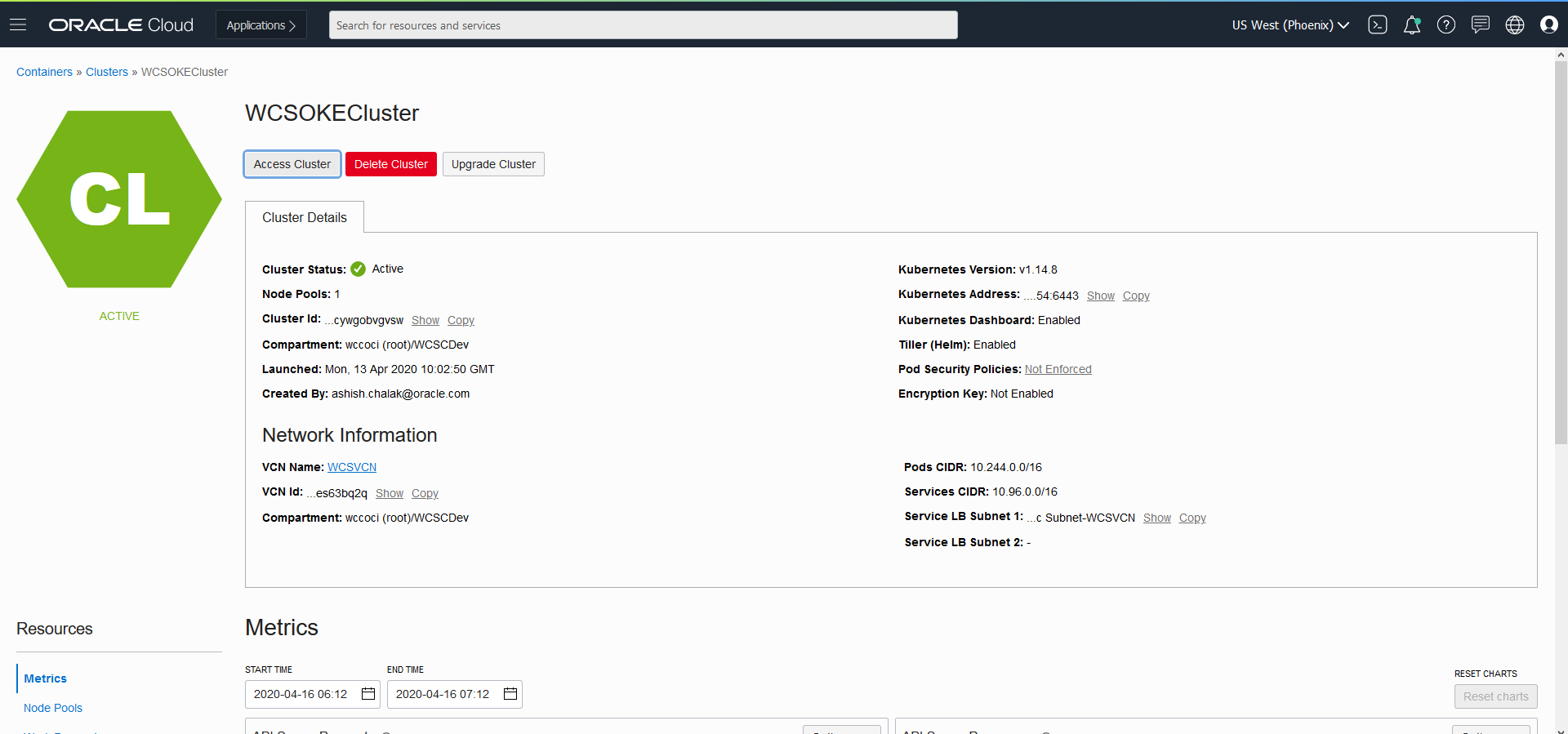
- Now click on “Access Cluster” then click on “Local Access”, gives details on how to download the kubeconfig to access the cluster.
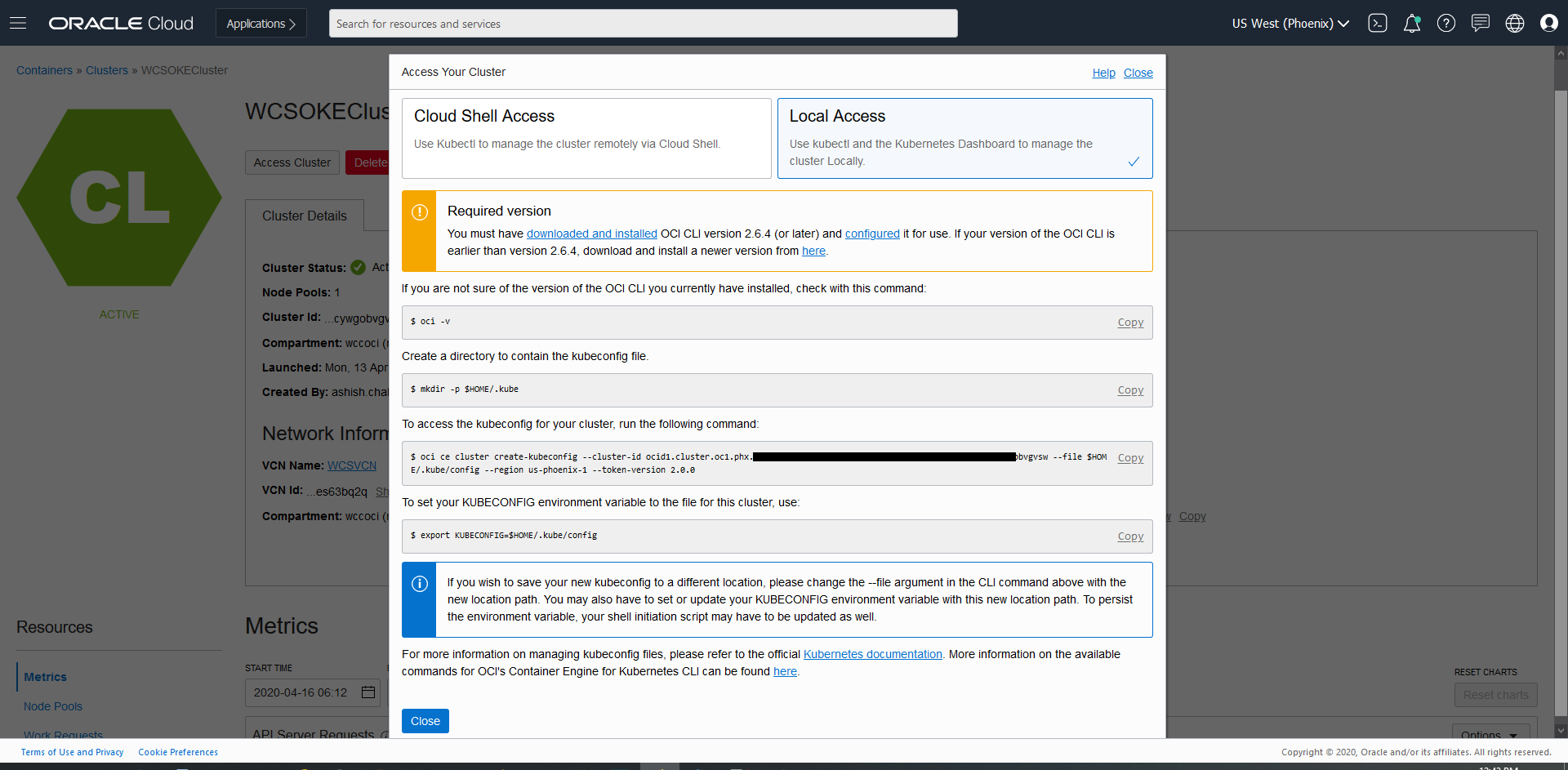
$ oci -v
$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
$ oci ce cluster create-kubeconfig --cluster-id ocid1.cluster.oc1.phx.xxxxxx --file $HOME/.kube/config --region us-phoenix-1 --token-version 2.0.0
$ export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/config- Once the kubeconfig is setup, you can access the Cluster with kubectl commands from any host or laptop.
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
10.0.10.2 Ready node 111m v1.27.6
10.0.10.3 Ready node 111m v1.27.6
10.0.10.4 Ready node 111m v1.27.6Create Filesystem and security list for FSS
Setup Filesystem
Creation of OCIR
Setup the OCIR for managing Docker images.
Preparing the Bastion host
Running WebLogic Kubernetes Operator managed Oracle WebCenter Sites domains on OKE
STEP 1 : Create Public Security List
Create Public Security List (bastion_public_sec_list) in same VCN as that of OKE Cluster for Bastion Node * Ingress Rules as: (where 10.0.22.0/24 is the CIDR planned to be used for bastion subnet)  * Egress as:
* Egress as: 
STEP 2 : Create Private Security List
Create Private Security List (bastion_private_sec_list) in same VCN as that of OKE Cluster which will be added into Worker Node subnet. * Ingress Rules as: (where 10.0.22.0/24 is the CIDR planned to be used for bastion subnet) 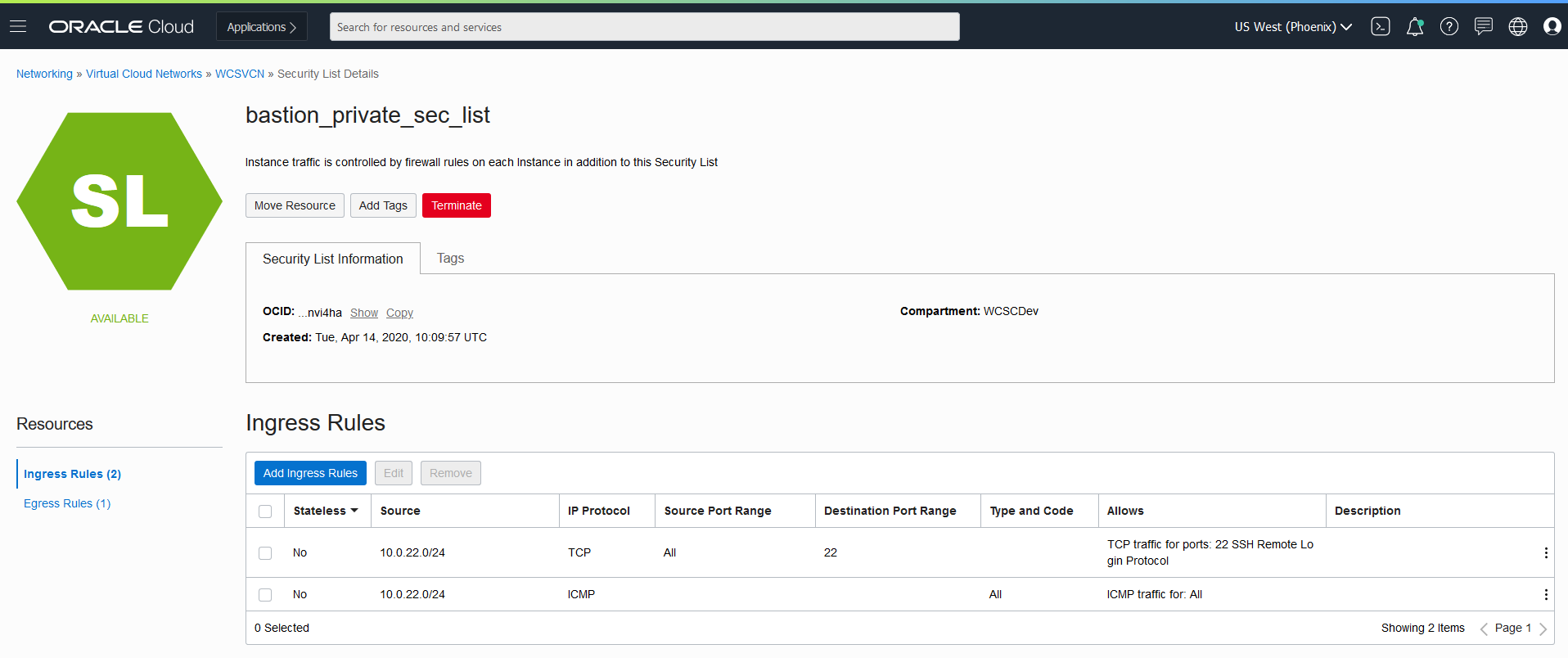 * Egress Rules as:
* Egress Rules as: 
STEP 3 : Create Route Table
Create Route Table (oke-bastion-routetables) with below details which will be used for bastion subnet 
STEP 4 : Create Bastion Subnet
Create Bastion Subnet with CIDR Block : 10.0.22.0/24 , RouteTable: oke-bastion-routetables (created in step 3) , Security List: bastion_public_sec_list ( created in Step 1) and DHCP Options : Default available 
STEP 5 : Add Private Security to Worker Subnet for bastion access
Add the private security list (bastion_private_sec_list), created at Step 2 to Worker Subnet, so that bastion node can ssh to Worker Nodes 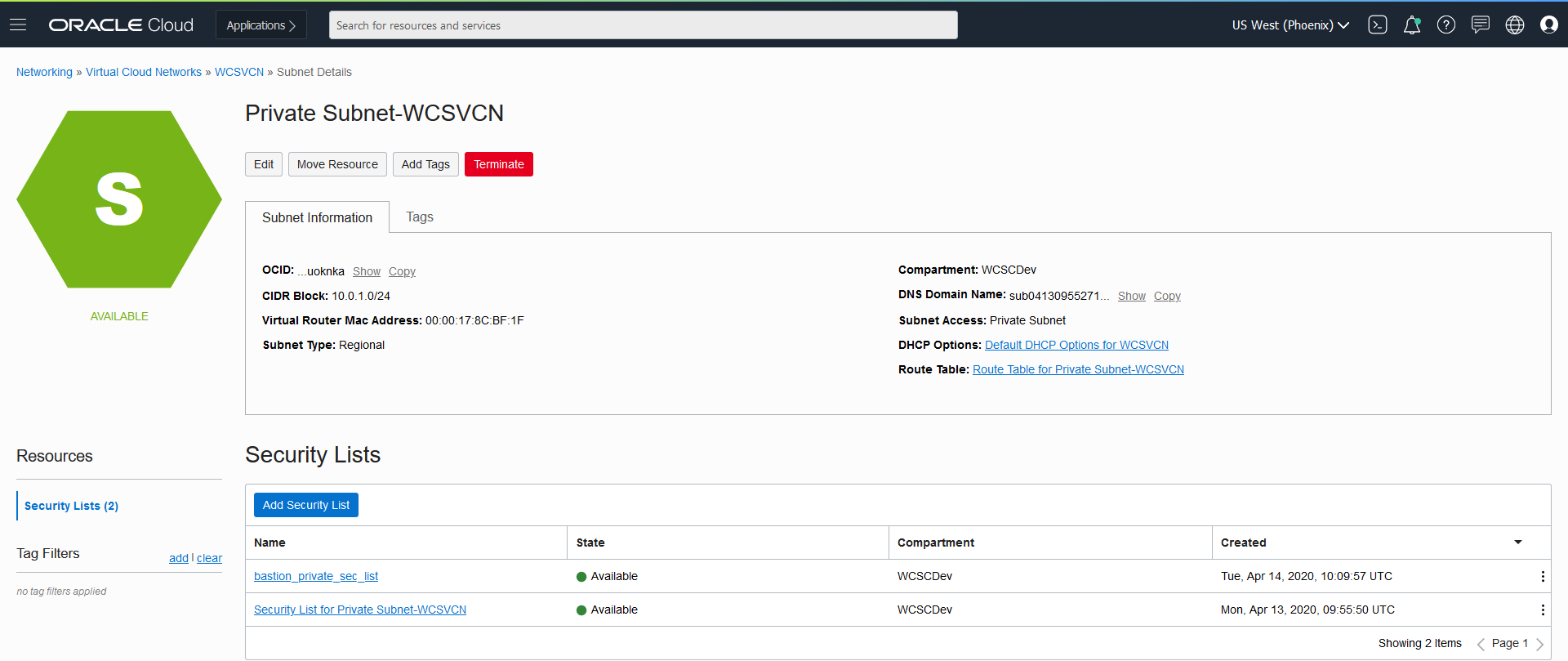
STEP 6 : Create Bastion Node
Create Bastion Node with Subnet as “bastion-subnet”, created at Step 4, Add the private security list (bastion_private_sec_list), created at Step 2 to Worker Subnet, so that bastion node can ssh to Worker Nodes * Update Name for the instance, Chose the Operating System Image, Availability Domain and Instance Type  * Select the Compartment, VCN and Subnet Compartment where Cluster is created. Select the regional bastion-subnet created at Step4. Make sure to click on “Assign a public IP address”.
* Select the Compartment, VCN and Subnet Compartment where Cluster is created. Select the regional bastion-subnet created at Step4. Make sure to click on “Assign a public IP address”.  * Once the bastion is created as shown below
* Once the bastion is created as shown below 
STEP 7 : Access Worker Node from bastion host
- Login to bastion host
scp -i id_rsa id_rsa opc@<bastion-host-address>:/home/opc
ssh -i id_rsa opc@<bastion-host-address>- Place a copy of id_rsa in bastion node to access worker node
ssh -i id_rsa opc@10.0.1.5More details refer: https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Resources/Assets/whitepapers/bastion-hosts.pdf
Preparing a file system
Running WebLogic Kubernetes Operator managed Oracle WebCenter Sites domains on OKE
Create Filesystem and security list for FSS
Note: Make sure you create the filesystem and security list in the OKE created VCN * Login to OCI Console and go to File Storage and Click “File System”  * Click “Create File System”
* Click “Create File System”  * You can create File System and Mount Targets with the default values. But in case you want to rename the file System and mount targets, follow below steps.
* You can create File System and Mount Targets with the default values. But in case you want to rename the file System and mount targets, follow below steps. 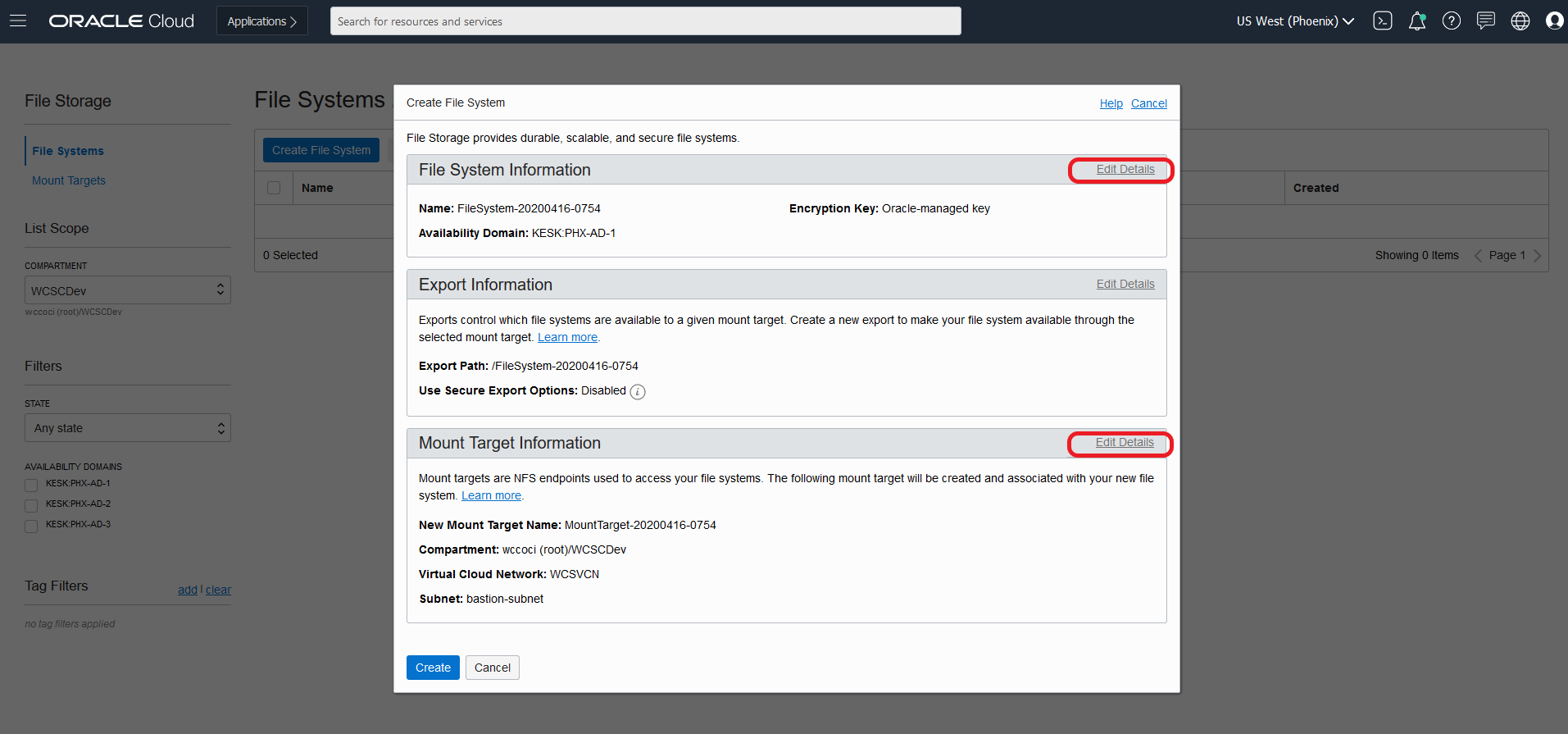 Note: Make Sure the Virtual Cloud Network in Mount Target refers to the one where your instances are created and you will be accessing this file system. * Edit and change the File System name to say “WCSFileSystem”
Note: Make Sure the Virtual Cloud Network in Mount Target refers to the one where your instances are created and you will be accessing this file system. * Edit and change the File System name to say “WCSFileSystem” 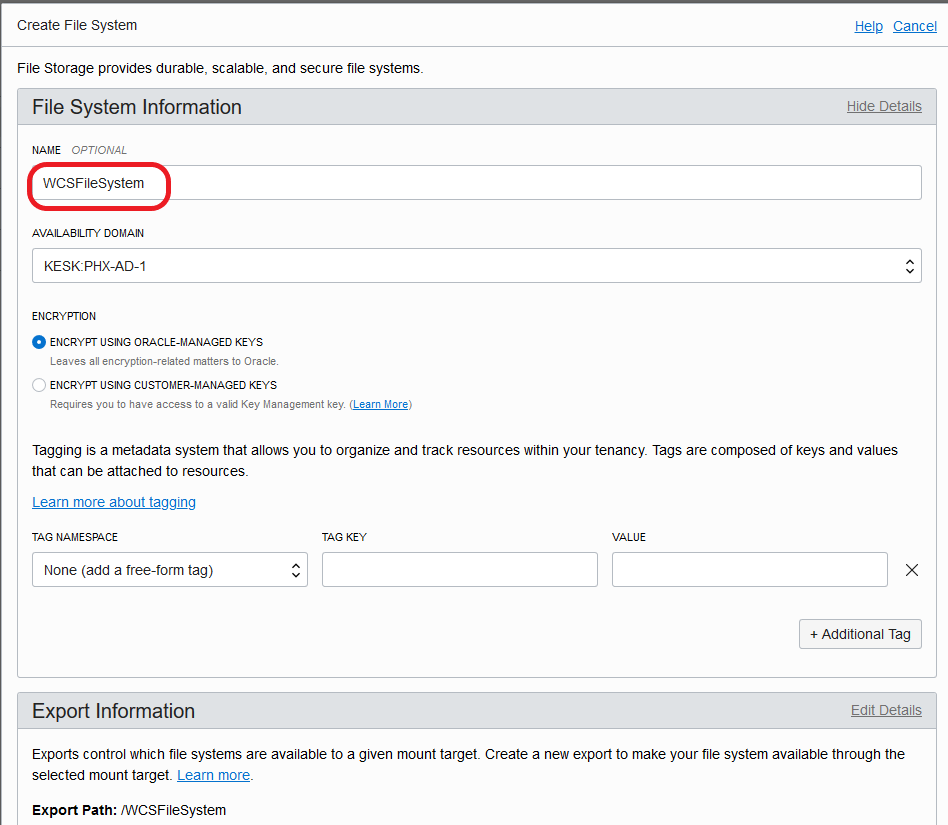 * Edit and change the Mount Target name to WCSMountTarget and make sure the Virtual Cloud Network selected is “WCSVCN” the one where all the instances are created. Select Public Subnet. Click “Create”
* Edit and change the Mount Target name to WCSMountTarget and make sure the Virtual Cloud Network selected is “WCSVCN” the one where all the instances are created. Select Public Subnet. Click “Create” 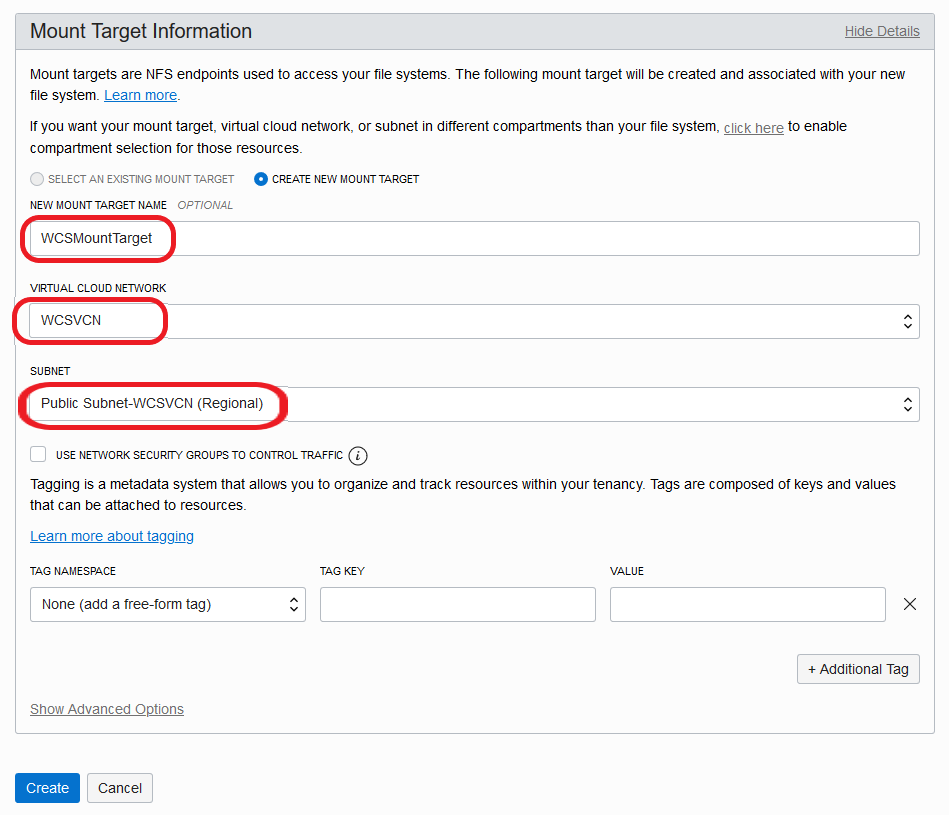 * Once the File System is created, it lands at below page. Click on “WCSFileSystem” link.
* Once the File System is created, it lands at below page. Click on “WCSFileSystem” link. 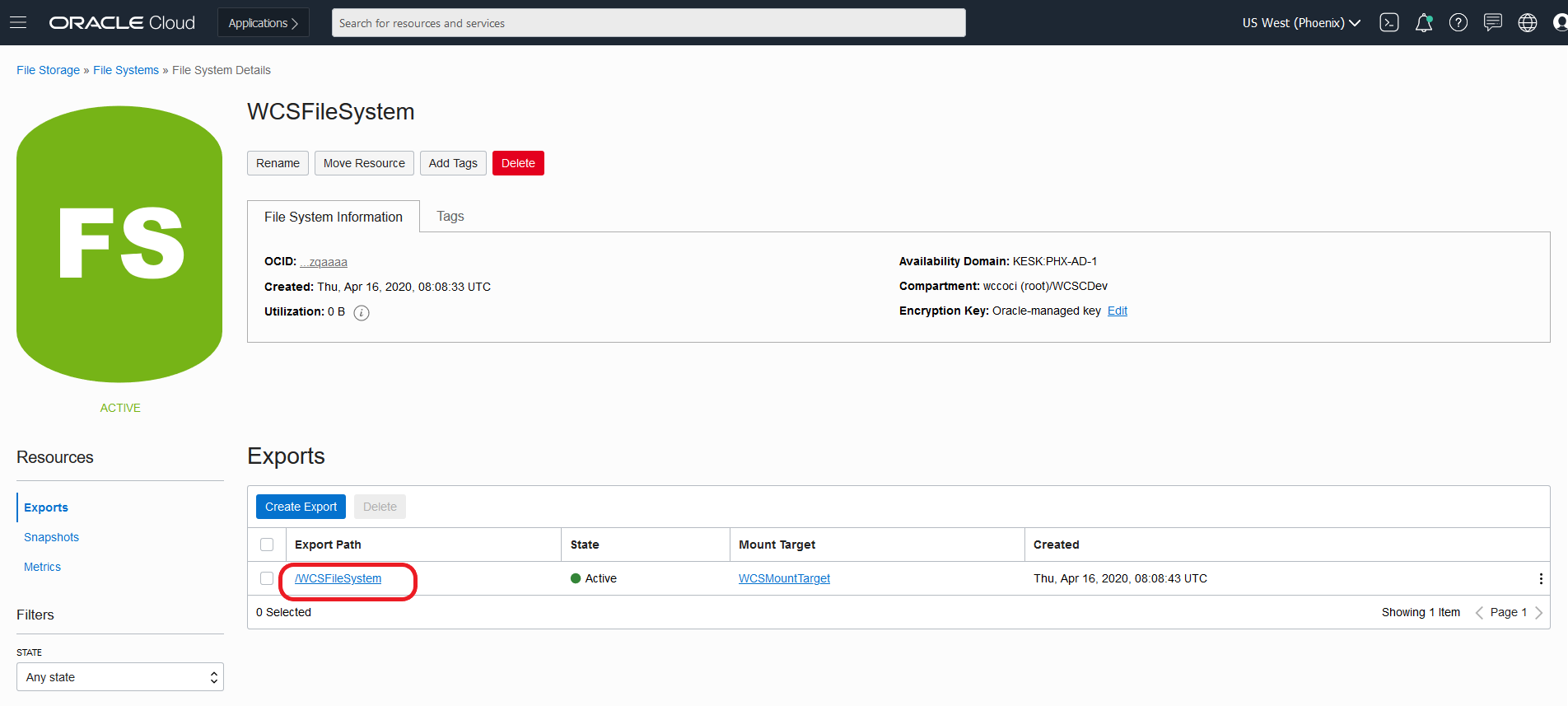 * Click on Mount Commands which gives details on how to mount this file system on your instances.
* Click on Mount Commands which gives details on how to mount this file system on your instances. 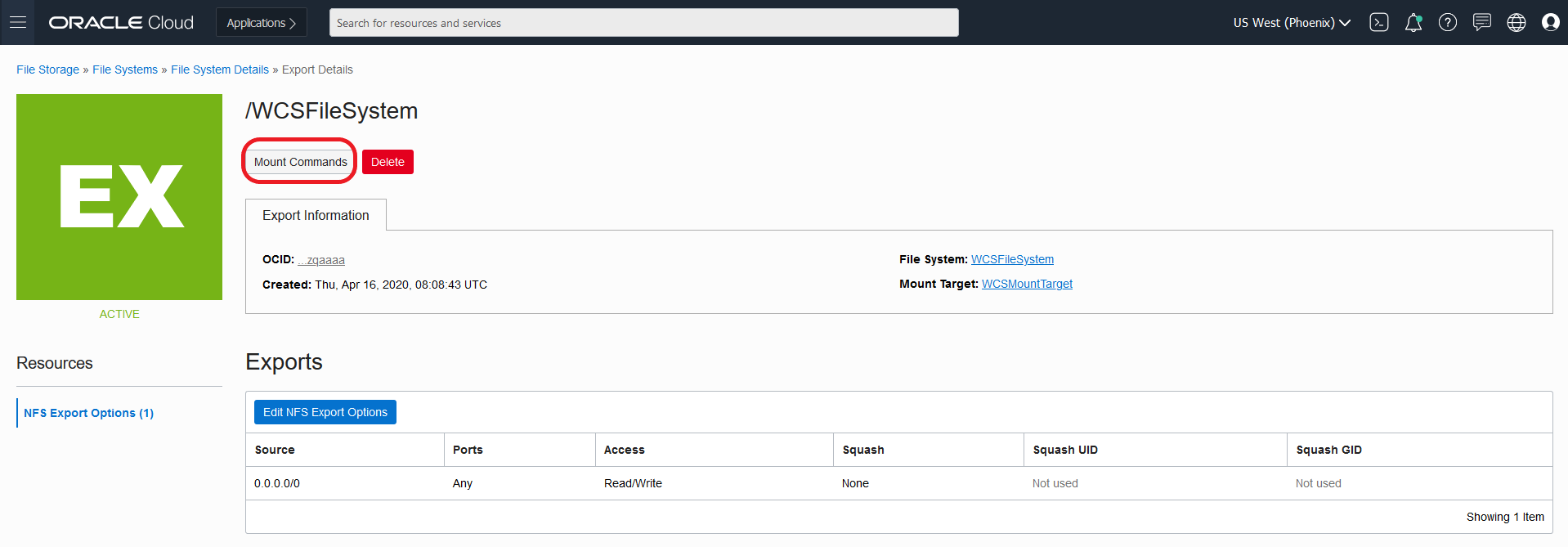 * Mount Command pop up gives details on what must be configured on security list to access the mount targets from instances. Note down the mount command which need to be executed on the instance
* Mount Command pop up gives details on what must be configured on security list to access the mount targets from instances. Note down the mount command which need to be executed on the instance 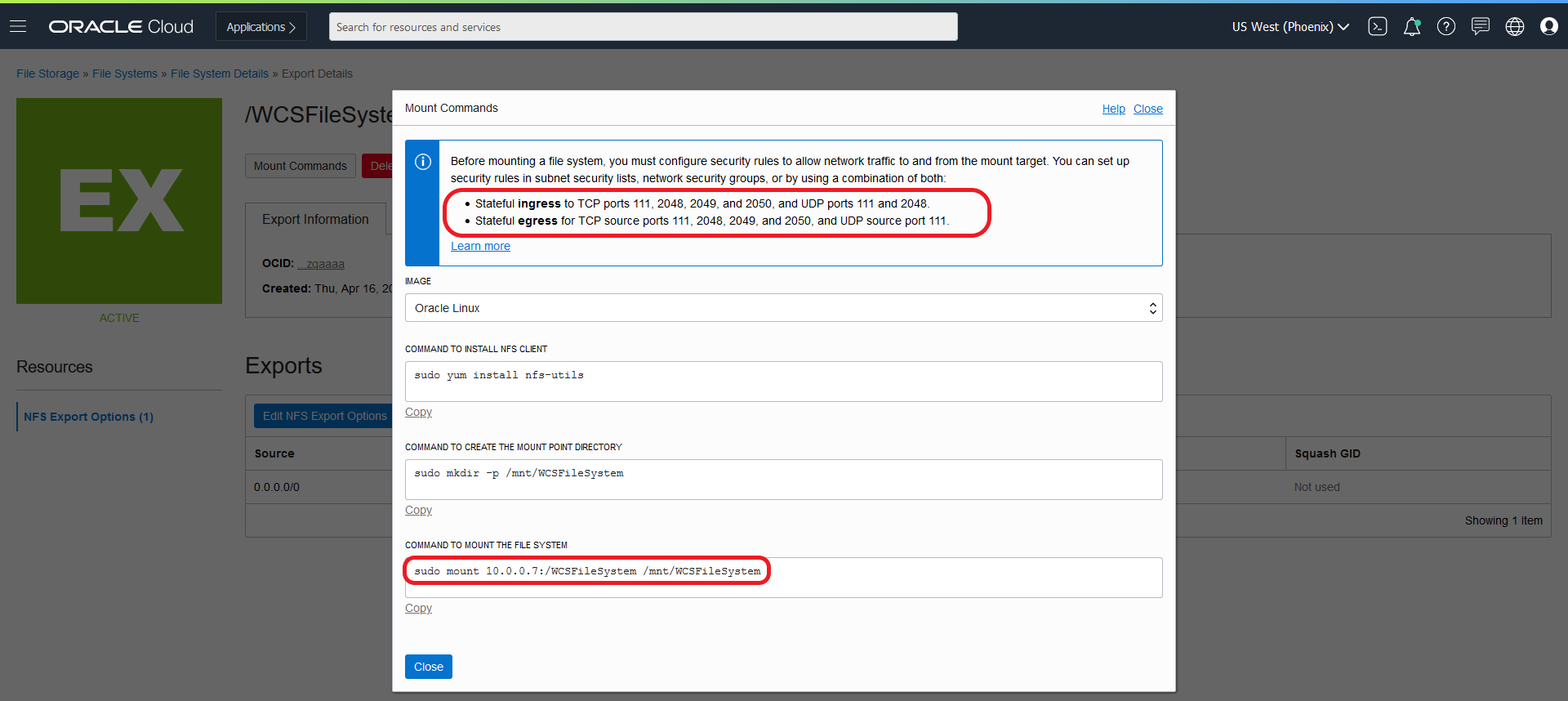 * Create the security list “fss_security list” with below Ingress Rules as given in the Mount commands pop up.
* Create the security list “fss_security list” with below Ingress Rules as given in the Mount commands pop up. 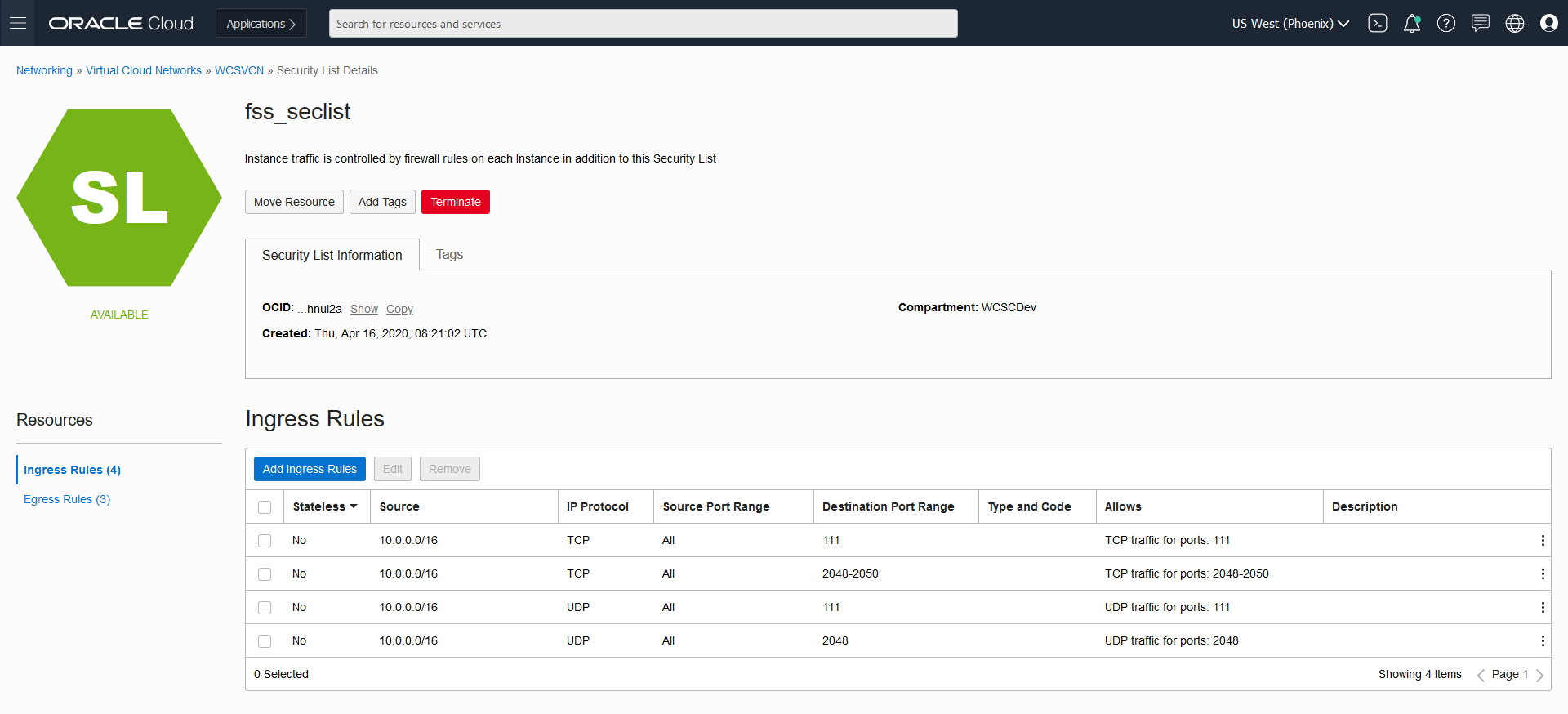 * Create the Egress rules as below as given in the Mount commands pop up.
* Create the Egress rules as below as given in the Mount commands pop up. 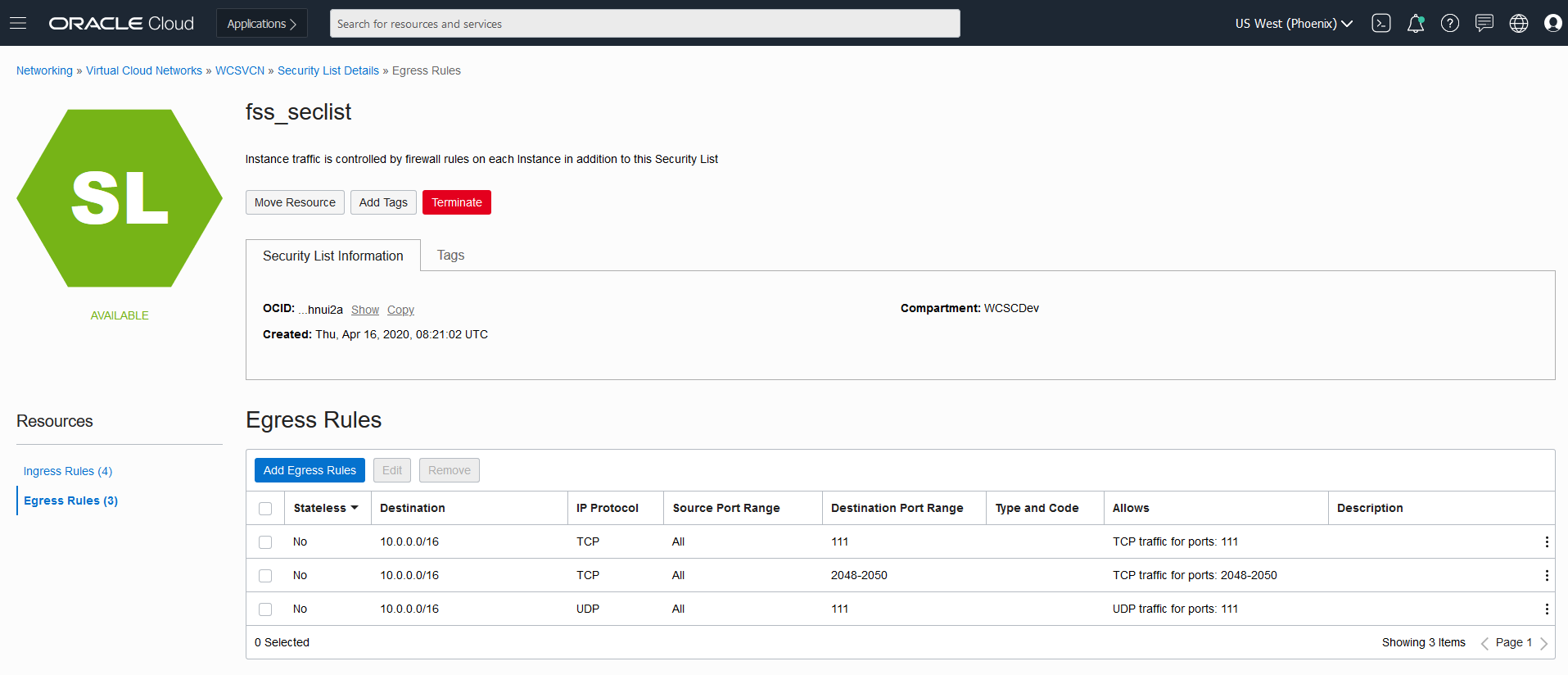 * Make sure to add the created security list “fss_security list” to each subnets as shown below: Otherwise the created security list rules will not apply to the instances.
* Make sure to add the created security list “fss_security list” to each subnets as shown below: Otherwise the created security list rules will not apply to the instances. 
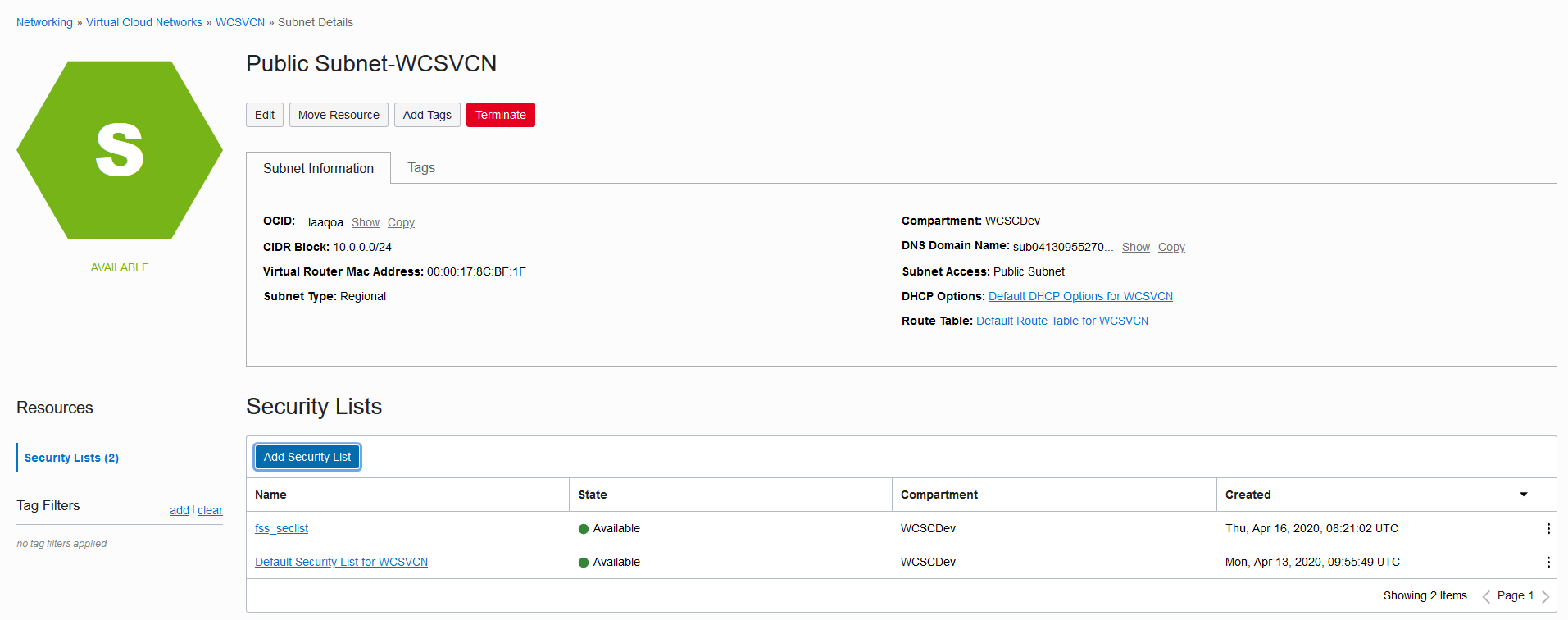 * Once the created security list “fss_security list” is added into the subnet, login to the instances and mount the file systems on to Bastion Node
* Once the created security list “fss_security list” is added into the subnet, login to the instances and mount the file systems on to Bastion Node
#login as root
sudo su
#Install NFS Utils
yum install nfs-utils
#Create directory where you want the mount the file system
mkdir -p /mnt/WCSFileSystem
#Give proper permissions so that all users can access the share volume
chmod 777 /mnt/WCSFileSystem
# Alternatively you can use: "mount 10.0.0.7:/WCSFileSystem /mnt/WCSFileSystem". To persist on reboot add into /etc/fstab
echo "10.0.0.7:/WCSFileSystem /mnt/WCSFileSystem nfs nfsvers=3 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
mount -a
cd /mnt/WCSFileSystem- Confirm that /WCSFileSystem is now pointing to created File System
[root@wcsbastioninstance WCSFileSystem]# df -h .
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
10.0.0.7:/WCSFileSystem 8.0E 0 8.0E 0% /mnt/WCSFileSystem
[root@wcsbastioninstance WCSFileSystem]#Creating an OCIR
Running WebLogic Kubernetes Operator managed Oracle WebCenter Sites domains on OKE
Push all the required images to OCIR and use from OCIR. Follow the below steps before pushing the images to OCIR
Create an “Auth token”
Create an “Auth token” which will be used as docker password to push/pull images from OCIR Login to Console and navigate to User Settings, which is in the drop down under your OCI username in the top nav  * On User Details page, select “Auth Tokens” in the left nav and then Click the “Generate Token” button: Enter a Name and Click “Generate Token”
* On User Details page, select “Auth Tokens” in the left nav and then Click the “Generate Token” button: Enter a Name and Click “Generate Token” 
 * Token will get generated
* Token will get generated 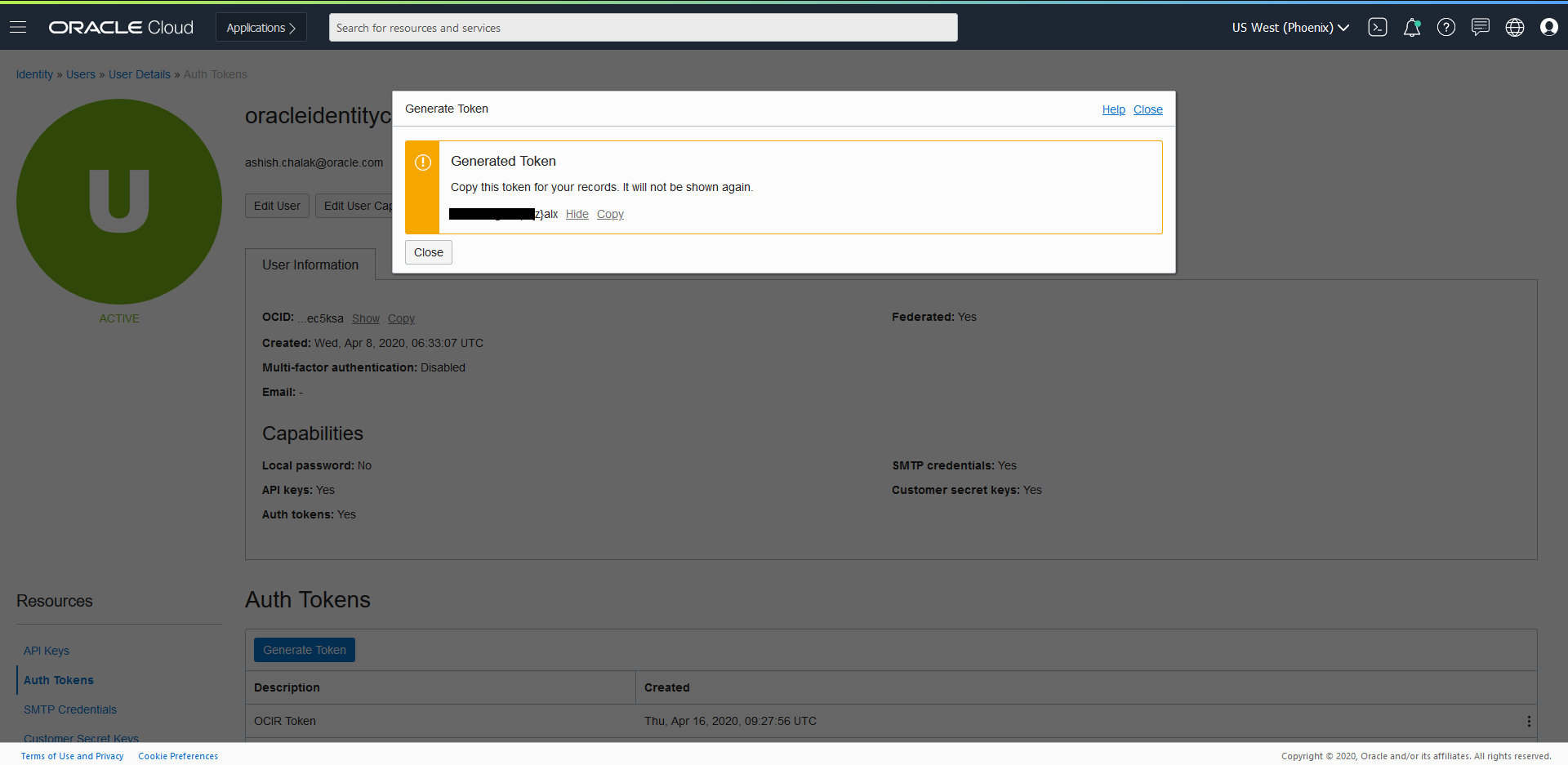 * Copy the generated token. NOTE: It will only be displayed this one time, and you will need to copy it to a secure place for further use. NOTE: It will only be displayed this one time, and you will need to copy it to a secure place for further use.
* Copy the generated token. NOTE: It will only be displayed this one time, and you will need to copy it to a secure place for further use. NOTE: It will only be displayed this one time, and you will need to copy it to a secure place for further use.
Get the OCIR name
Get the OCIR Repo Name by Log in to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console. In he OCI Console, open the Navigation menu. Under Solutions and Platform, go to Developer Services and click Registry (OCIR). 
Using the OCIR
Using the Docker CLI to login to OCIR ( for phoenix : phx.ocir.io , ashburn: iad.ocir.io etc) a. docker login phx.ocir.io b. When promoted for username enter docker username as OCIR RepoName/oci username ( eg., axcmmdmzqtqb/oracleidentitycloudservice/myemailid@oracle.com) c. When prompted for your password, enter the generated Auth Token i.e p[3k;pYePDSTD:-(LlAS
Now you can tag the images and push to OCIR.
$ docker login phx.ocir.io
$ username - axcmmdmzqtqb/oracleidentitycloudservice/myemailid@oracle.com
$ password - p[3k;pYePDSTD:-(LlAS (Token Generated for OCIR using user setting)This has to be done on Bastion Node for all the images.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section describes known issues for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment on Kubernetes. Also, provides answers to frequently asked questions.
Configure the external URL access for Oracle WebCenter Sites composite applications
For Oracle WebCenter Sites composite applications to access the external URLs over the internet (if your cluster is behind a http proxy server), you must configure the following proxy parameters for Administration Server and Managed Server pods.
-Dhttp.proxyHost=www-your-proxy.com
-Dhttp.proxyPort=proxy-port
-Dhttps.proxyHost=www-your-proxy.com
-Dhttps.proxyPort=proxy-port
-Dhttp.nonProxyHosts="localhost|wcsitesinfra-adminserver|wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1|*.svc.cluster.local|*.your.domain.com|/var/run/docker.sock" To do this, edit the domain.yaml configuration file and append the proxy parameters to the spec.serverPod.env.JAVA_OPTIONS environment variable value.
For example:
serverPod:
env:
- name: JAVA_OPTIONS
value: -Dweblogic.StdoutDebugEnabled=false -Dweblogic.ssl.Enabled=true -Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification=true -Dhttp.proxyHost=www-your-proxy.com -Dhttp.proxyPort=proxy-port -Dhttps.proxyHost=www-your-proxy.com -Dhttps.proxyPort=proxy-port -Dhttp.nonProxyHosts="localhost|wcsitesinfra-adminserver|wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1|*.svc.cluster.local|*.your.domain.com|/var/run/docker.sock"
- name: USER_MEM_ARGS
value: '-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -Xms256m -Xmx1024m '
volumeMounts:Note: The
-Dhttp.nonProxyHostsparameter must have the pod names of the Administration Server and each Managed Server. For example:wcsitesinfra-adminserver,wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1, and so on.
Apply the updated domain.yaml file:
$ kubectl apply -f domain.yamlNote: The server pod(s) will be automatically restarted (rolling restart).
Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes Operator FAQs
See the general frequently asked questions for using the Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes operator.
Appendix
This section provides information on miscellaneous tasks related to Oracle WebCenter Sites domains deployment on Kubernetes.
Domain resource sizing
Describes the resourse sizing information for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains setup on Kubernetes cluster.
Oracle WebCenter Sites cluster sizing recommendations
| Oracle WebCenter Sites | Normal Usage | Moderate Usage | High Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Administration Server | No of CPU core(s) : 1, Memory : 4GB | No of CPU core(s) : 1, Memory : 4GB | No of CPU core(s) : 1, Memory : 4GB |
| Managed Server | No of Servers : 2, No of CPU core(s) : 2, Memory : 16GB | No of Servers : 2, No of CPU core(s) : 4, Memory : 16GB | No of Servers : 3, No of CPU core(s) : 6, Memory : 16-32GB |
| PV Storage | Minimum 250GB | Minimum 250GB | Minimum 500GB |
Security hardening
Review resources for the Docker and Kubernetes cluster hardening.
Securing a Kubernetes cluster involves hardening on multiple fronts - securing the API servers, etcd, nodes, container images, container run-time, and the cluster network. Apply principles of defense in depth, principle of least privilege, and minimize the attack surface. Use security tools such as Kube-Bench to verify the cluster’s security posture. Since Kubernetes is evolving rapidly refer to Kubernetes Security Overview for the latest information on securing a Kubernetes cluster. Also ensure the deployed Docker containers follow the Docker Security guidance.
This section provides references on how to securely configure Docker and Kubernetes.
References
- Docker hardening
- Kubernetes hardening
- Security best practices for Oracle WebLogic Server Running in Docker and Kubernetes
Quick start deployment on-premise
Use this Quick Start to create an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain deployment in a Kubernetes cluster (on-premise environments) with the Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes operator. Note that this walkthrough is for demonstration purposes only, not for use in production. These instructions assume that you are already familiar with Kubernetes. If you need more detailed instructions, refer to the Install Guide.
Hardware requirements
Supported Linux kernel for deploying and running Oracle WebCenter Sites domains with the operator is Oracle Linux 8 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. Refer to the prerequisites for more details.
For this exercise the minimum hardware requirement to create a single node Kubernetes cluster and then deploy wcsitesinfra domain type with one managed server for Oracle WebCenter Sites and Oracle Database running as a container
| Hardware | Size |
|---|---|
| RAM | 32GB |
| Disk Space | 250GB+ |
| CPU core(s) | 6 |
See here for resourse sizing information for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains setup on Kubernetes cluster.
Set up Oracle WebCenter Sites in an on-premise environment
Perform the steps in this topic to create a single instance on-premise Kubernetes cluster and then create an Oracle WebCenter Sites wcsitesinfra domain type.
- Step 1 - Prepare a virtual machine for the Kubernetes cluster
- Step 2 - Set up a single instance Kubernetes cluster
- Step 3 - Get scripts and images
- Step 4 - Install the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
- Step 5 - Install the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer
- Step 6 - Create and configure an Oracle WebCenter Sites Domain
1. Prepare a virtual machine for the Kubernetes cluster
For illustration purposes, these instructions are for Oracle Linux 8. If you are using a different flavor of Linux, you will need to adjust the steps accordingly.
Note : These steps must be run with the
rootuser, unless specified otherwise. Any time you seeYOUR_USERIDin a command, you should replace it with your actualuserid.
1.1 Prerequisites
Choose the directories where your Docker and Kubernetes files will be stored. The Docker directory should be on a disk with a lot of free space (more than 100GB) because it will be used for the Docker file system, which contains all of your images and containers. The Kubernetes directory is used for the
/var/lib/kubeletfile system and persistent volume storage.$ export kubelet_dir=/u01/kubelet $ mkdir -p $docker_dir $kubelet_dir $ ln -s $kubelet_dir /var/lib/kubeletVerify that IPv4 forwarding is enabled on your host.
Note: Replace eth0 with the ethernet interface name of your compute resource if it is different.
$ /sbin/sysctl -a 2>&1|grep -s 'net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding' $ /sbin/sysctl -a 2>&1|grep -s 'net.ipv4.conf.lo.forwarding' $ /sbin/sysctl -a 2>&1|grep -s 'net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind'For example: Verify that all are set to 1
$ net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding = 1 $ net.ipv4.conf.lo.forwarding = 1 $ net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind = 1Solution: Set all values to 1 immediately with the following commands:
$ /sbin/sysctl net.ipv4.conf.eth0.forwarding=1 $ /sbin/sysctl net.ipv4.conf.lo.forwarding=1 $ /sbin/sysctl net.ipv4.ip_nonlocal_bind=1To preserve the settings post-reboot: Update the above values to 1 in files in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/, /run/sysctl.d/ and /etc/sysctl.d/
Verify the iptables rule for forwarding.
Kubernetes uses iptables to handle many networking and port forwarding rules. A standard Docker installation may create a firewall rule that prevents forwarding.
Verify if the iptables rule to accept forwarding traffic is set:
$ /sbin/iptables -L -n | awk '/Chain FORWARD / {print $4}' | tr -d ")"If the output is “DROP”, then run the following command:
$ /sbin/iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPTVerify if the iptables rule is set properly to “ACCEPT”:
$ /sbin/iptables -L -n | awk '/Chain FORWARD / {print $4}' | tr -d ")"Disable and stop firewalld:
$ systemctl disable firewalld $ systemctl stop firewalld
1.2 Install CRI-O and Podman
Note : If you have already configured CRI-O and Podman, continue to Install and configure Kubernetes
Make sure that you have the right operating system version:
$ uname -a $ more /etc/oracle-releaseFor example:
Linux xxxxxx 5.15.0-100.96.32.el8uek.x86_64 #2 SMP Tue Feb 27 18:08:15 PDT 2024 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux Oracle Linux Server release 8.6Installing CRI-O:
Add OLCNE( Oracle Cloud Native Environment ) Repository to dnf config-manager. This allows dnf to install the additional packages required for CRI-O installation.
On Oracle Linux 8:
$ dnf config-manager --add-repo https://yum.oracle.com/repo/OracleLinux/OL8/olcne18/x86_64On Oracle Linux 9:
$ dnf config-manager --add-repo https://yum.oracle.com/repo/OracleLinux/OL9/olcne18/x86_64Install the cri-o:
$ dnf install -y cri-oNote : To install a different version of CRI-O or on a different operating system, see CRI-O Installation Instructions.
Start the CRI-O service:
Set up Kernel Modules and Proxies
### Enable kernel modules overlay and br_netfilter which are required for Kubernetes Container Network Interface (CNI) plugins $ modprobe overlay $ modprobe br_netfilter ### To automatically load these modules at system start up create config as below $ cat <<EOF > /etc/modules-load.d/crio.conf overlay br_netfilter EOF $ sysctl --system ### Set the environmental variable CONTAINER_RUNTIME_ENDPOINT to crio.sock to use crio as the container runtime $ export CONTAINER_RUNTIME_ENDPOINT=unix:///var/run/crio/crio.sock ### Setup Proxy for CRIO service $ cat <<EOF > /etc/sysconfig/crio http_proxy=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT https_proxy=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT HTTPS_PROXY=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT HTTP_PROXY=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LIST,/var/run/crio/crio.sock NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LIST,/var/run/crio/crio.sock EOFSet the runtime for CRI-O
### Setting the runtime for crio ## Update crio.conf $ vi /etc/crio/crio.conf ## Append following under [crio.runtime] conmon_cgroup = "kubepods.slice" cgroup_manager = "systemd" ## Uncomment following under [crio.network] network_dir="/etc/cni/net.d" plugin_dirs=[ "/opt/cni/bin", "/usr/libexec/cni", ]Start the CRI-O Service
## Restart crio service $ systemctl restart crio.service $ systemctl enable --now crioInstalling Podman:
On Oracle Linux 8, if podman is not available, then install Podman and related tools with following command syntax:
$ sudo dnf module install container-tools:ol8On Oracle Linux 9, if podman is not available, then install Podman and related tools with following command syntax:
$ sudo dnf install container-toolsSince the setup uses “docker” CLI commands, on Oracle Linux 8/9, install the podman-docker package if not available, that effectively aliases the docker command to podman,with following command syntax:
$ sudo dnf install podman-dockerConfigure Podman rootless:
For using podman with your User ID (Rootless environment), Podman requires the user running it to have a range of UIDs listed in the files /etc/subuid and /etc/subgid. Rather than updating the files directly, the usermod program can be used to assign UIDs and GIDs to a user with the following commands:
$ sudo /sbin/usermod --add-subuids 100000-165535 --add-subgids 100000-165535 <REPLACE_USER_ID> $ podman system migrateNote : The above “podman system migrate” need to be executed with your User ID and not root.
Verify the user-id addition
$ cat /etc/subuid $ cat /etc/subgidExpected similar output
opc:100000:65536 <user-id>:100000:65536
1.3 Install and configure Kubernetes
Add the external Kubernetes repository:
$ cat <<EOF | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/rpm/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.28/rpm/repodata/repomd.xml.key exclude=kubelet kubeadm kubectl cri-tools kubernetes-cni EOFSet SELinux in permissive mode (effectively disabling it):
$ export PATH=/sbin:$PATH $ setenforce 0 $ sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing$/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/configExport proxy and install
kubeadm,kubelet, andkubectl:### Get the nslookup IP address of the master node to use with apiserver-advertise-address during setting up Kubernetes master ### as the host may have different internal ip (hostname -i) and nslookup $HOSTNAME $ ip_addr=`nslookup $(hostname -f) | grep -m2 Address | tail -n1| awk -F: '{print $2}'| tr -d " "` $ echo $ip_addr ### Set the proxies $ export NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LIST,/var/run/crio/crio.sock,$ip_addr,.svc $ export no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LIST,/var/run/crio/crio.sock,$ip_addr,.svc $ export http_proxy=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT $ export https_proxy=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT $ export HTTPS_PROXY=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT $ export HTTP_PROXY=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT ### Install the kubernetes components and enable the kubelet service so that it automatically restarts on reboot $ dnf install -y kubeadm kubelet kubectl $ systemctl enable --now kubeletEnsure
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptablesis set to 1 in yoursysctlto avoid traffic routing issues:$ cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 EOF $ sysctl --systemDisable swap check:
$ sed -i 's/KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=/KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS="--fail-swap-on=false"/' /etc/sysconfig/kubelet $ cat /etc/sysconfig/kubelet ### Reload and restart kubelet $ systemctl daemon-reload $ systemctl restart kubeletPull the images using crio:
$ kubeadm config images pull --cri-socket unix:///var/run/crio/crio.sock
1.4 Set up Helm
Install Helm v3.10.3+.
Download Helm from https://github.com/helm/helm/releases. Example to download Helm v3.10.3:
$ wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.10.3-linux-amd64.tar.gzUnpack
tar.gz:$ tar -zxvf helm-v3.10.3-linux-amd64.tar.gzFind the Helm binary in the unpacked directory, and move it to its desired destination:
$ mv linux-amd64/helm /usr/bin/helm
Run
helm versionto verify its installation:$ helm version version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.10.3", GitCommit:"835b7334cfe2e5e27870ab3ed4135f136eecc704", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.18.9"}
2. Set up a single instance Kubernetes cluster
Notes :
- These steps must be run with the
rootuser, unless specified otherwise! - If you choose to use a different cidr block (that is, other than
10.244.0.0/16for the--pod-network-cidr=in thekubeadm initcommand), then also updateNO_PROXYandno_proxywith the appropriate value.- Also make sure to update
kube-flannel.yamlwith the new value before deploying.
- Also make sure to update
- Replace the following with appropriate values:
ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LISTREPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT
2.1 Set up the master node
Create a shell script that sets up the necessary environment variables. You can append this to the user’s
.bashrcso that it will run at login. You must also configure your proxy settings here if you are behind an HTTP proxy:## grab my IP address to pass into kubeadm init, and to add to no_proxy vars ip_addr=`nslookup $(hostname -f) | grep -m2 Address | tail -n1| awk -F: '{print $2}'| tr -d " "` export pod_network_cidr="10.244.0.0/16" export service_cidr="10.96.0.0/12" export PATH=$PATH:/sbin:/usr/sbin ### Set the proxies export NO_PROXY=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LIST,/var/run/docker.sock,$ip_addr,$pod_network_cidr,$service_cidr export no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.0/8,ADD-YOUR-INTERNAL-NO-PROXY-LIST,/var/run/docker.sock,$ip_addr,$pod_network_cidr,$service_cidr export http_proxy=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT export https_proxy=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT export HTTPS_PROXY=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORT export HTTP_PROXY=http://REPLACE-WITH-YOUR-COMPANY-PROXY-HOST:PORTSource the script to set up your environment variables:
$ . ~/.bashrcTo implement command completion, add the following to the script:
$ [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ] && . /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion $ source <(kubectl completion bash)Run
kubeadm initto create the master node:$ kubeadm init \ --pod-network-cidr=$pod_network_cidr \ --apiserver-advertise-address=$ip_addr \ --ignore-preflight-errors=Swap > /tmp/kubeadm-init.out 2>&1Log in to the terminal with
YOUR_USERID:YOUR_GROUP. Then set up the~/.bashrcsimilar to steps 1 to 3 withYOUR_USERID:YOUR_GROUP.Note : that from now on we will be using
YOUR_USERID:YOUR_GROUPto execute anykubectlcommands and notroot.Set up
YOUR_USERID:YOUR_GROUPto access the Kubernetes cluster:$ mkdir -p $HOME/.kube $ sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config $ sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configVerify that
YOUR_USERID:YOUR_GROUPis set up to access the Kubernetes cluster using thekubectlcommand:$ kubectl get nodesNote : At this step, the node is not in ready state as we have not yet installed the pod network add-on. After the next step, the node will show status as Ready.
Install a pod network add-on (
flannel) so that your pods can communicate with each other.Note : If you are using a different cidr block than
10.244.0.0/16, then download and updatekube-flannel.ymlwith the correct cidr address before deploying into the cluster:$ wget https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/download/v0.25.1/kube-flannel.yml ### Update the CIDR address if you are using a CIDR block other than the default 10.244.0.0/16 $ kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.ymlVerify that the master node is in Ready status:
$ kubectl get nodesFor example:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION mymasternode Ready master 8m26s v1.27.2or:
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-systemFor example:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/coredns-86c58d9df4-58p9f 1/1 Running 0 3m59s pod/coredns-86c58d9df4-mzrr5 1/1 Running 0 3m59s pod/etcd-mymasternode 1/1 Running 0 3m4s pod/kube-apiserver-node 1/1 Running 0 3m21s pod/kube-controller-manager-mymasternode 1/1 Running 0 3m25s pod/kube-flannel-ds-amd64-6npx4 1/1 Running 0 49s pod/kube-proxy-4vsgm 1/1 Running 0 3m59s pod/kube-scheduler-mymasternode 1/1 Running 0 2m58sTo schedule pods on the master node,
taintthe node:$ kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/master-
Congratulations! Your Kubernetes cluster environment is ready to deploy your Oracle WebCenter Sites domain.
Refer to the official documentation to set up a Kubernetes cluster.
3. Get scripts and images
3.1 Set up the code repository to deploy Oracle WebCenter Sites domains
Follow these steps to set up the source code repository required to deploy Oracle WebCenter Sites domains.
3.2 Get required Docker images and add them to your local registry
Obtain the Oracle WebLogic Operator image from the Oracle Container Registry:
- For first time users, to pull an image from the Oracle Container Registry, navigate to https://container-registry.oracle.com and log in using the Oracle Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication service. If you do not already have SSO credentials, click the Sign In link at the top of the page to create them.
Use the web interface to accept the Oracle Standard Terms and Restrictions for the Oracle software images that you intend to deploy. Your acceptance of these terms are stored in a database that links the software images to your Oracle Single Sign-On login credentials.
To obtain the image, log in to the Oracle Container Registry:
$ podman login container-registry.oracle.com- Pull the operator image:
$ podman pull container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/weblogic-kubernetes-operator:4.2.9 $ podman tag container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/weblogic-kubernetes-operator:4.2.9 oracle/weblogic-kubernetes-operator:4.2.9Pull WebCenter Sites image from the Oracle Container Registry or Build Oracle WebCenter Sites 14.1.2.0.0 Image by following Create or update an Image. pull the prebuilt Oracle WebCenter Sites image 14.1.2.0.0 install image:
$ podman pull container-registry.oracle.com/middleware/webcentersites:14.1.2.0.0Copy all the above built and pulled images to all the nodes in your cluster or add to a Docker registry that your cluster can access.
3.3 Set Up the Code Repository to Deploy Oracle WebCenter Sites Domain
Oracle WebCenter Sites domain deployment on Kubernetes leverages the Oracle WebLogic Kubernetes Operator infrastructure. For deploying the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain, you need to set up the deployment scripts as below:
Create a working directory to set up the source code.
$ mkdir $HOME/wcs_1412 $ cd $HOME/wcs_1412Download the WebCenter Sites kubernetes deployment scripts from this repository and copy them in to WebLogic operator samples location.
$ git clone https://github.com/oracle/fmw-kubernetes.git $ export WORKDIR=$HOME/wcs_1412/fmw-kubernetes/OracleWebCenterSites/kubernetesYou can now use the deployment scripts from
$HOME/wcs_1412/fmw-kubernetes/OracleWebCenterSites/kubernetesto set up the WebCenter Sites domain as further described in this document.
4. Install the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
4.1 Prepare for the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator.
Create a namespace
operator-nsfor the operatorWORKDIRfor the Oracle WebCenter Sites operator code:$ kubectl create namespace operator-nsCreate a service account
operator-safor the operator in the operator’s namespace:$ kubectl create serviceaccount -n operator-ns operator-sa
4.2 Install the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
Use Helm to install and start the operator from the directory you just cloned:
$ cd ${WORKDIR}
$ helm repo add weblogic-operator https://oracle.github.io/weblogic-kubernetes-operator/charts --force-update
$ helm install weblogic-kubernetes-operator weblogic-operator/weblogic-operator --version 4.2.9 --namespace operator-ns --set serviceAccount=operator-sa --set "javaLoggingLevel=FINE" --wait
NAME: weblogic-kubernetes-operator
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue May 19 04:04:32 2024
NAMESPACE: operator-ns
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None4.3 Verify the WebLogic Kubernetes Operator
Verify that the operator’s pod is running by listing the pods in the operator’s namespace. You should see one for the operator:
$ kubectl get pods -n operator-nsVerify that the operator is up and running by viewing the operator pod’s logs:
$ kubectl logs -n operator-ns -c weblogic-operator deployments/weblogic-operator
The WebLogic Kubernetes Operator v4.2.9 has been installed. Continue with the load balancer and Oracle WebCenter Sites domain setup.
5. Install the Traefik (ingress-based) load balancer
The Oracle WebLogic Server Kubernetes operator supports three load balancers: Traefik, Nginx, Apache webtier. Samples are provided in the documentation.
This Quick Start demonstrates how to install the Traefik ingress controller to provide load balancing for an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain.
Create a namespace for Traefik:
$ kubectl create namespace traefikSet up Helm for 3rd party services:
$ helm repo add traefik https://helm.traefik.io/traefik --force-updateInstall the Traefik operator in the
traefiknamespace with the provided sample values:$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install traefik traefik/traefik \ --namespace traefik \ --values charts/traefik/values.yaml \ --set "kubernetes.namespaces={traefik}" \ --set "service.type=NodePort" \ --wait
6. Create and configure an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain
6.1 Prepare for an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain
Create a namespace that can host Oracle WebCenter Sites domains:
$ kubectl create namespace wcsites-ns $ kubectl label namespace wcsites-ns weblogic-operator=enabledCreate Kubernetes secrets.
Create a Kubernetes secret for the domain in the same Kubernetes namespace as the domain. In this example, the username is
weblogic, the password inWelcome1, and the namespace iswcsites-ns:$ cd ${WORKDIR}/create-weblogic-domain-credentials $ ./create-weblogic-credentials.sh \ -u weblogic \ -p Welcome1 \ -n wcsites-ns \ -d wcsitesinfra \ -s wcsitesinfra-domain-credentialsCreate a Kubernetes secret for the RCU in the same Kubernetes namespace as the domain:
- Schema user : WCS1
- Schema password : Oradoc_db1
- DB sys user password : Oradoc_db1
- Domain name : wcsitesinfra
- Domain Namespace : wcsites-ns
- Secret name : wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentials
$ cd ${WORKDIR}/create-rcu-credentials $ ./create-rcu-credentials.sh \ -u WCS1 \ -p Oradoc_db1 \ -a sys \ -q Oradoc_db1 \ -d wcsitesinfra \ -n wcsites-ns \ -s wcsitesinfra-rcu-credentialsCreate the Kubernetes persistence volume and persistence volume claim.
Create the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain home directory. Determine if a user already exists on your host system with
uid:gidof1000:0:$ sudo getent passwd 1000If this command returns a username (which is the first field), you can skip the following
useraddcommand. If not, create the oracle user withuseradd:$ sudo useradd -u 1000 -g 0 oracleCreate the directory that will be used for the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain home:
$ sudo mkdir /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites $ sudo chown -R 1000:0 /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSitesUpdate
create-wcsites-domain/utils/create-wcsites-pv-pvc-inputs.yamlwith the following values:
- baseName: domain
- domainUID: wcsitesinfra
- namespace: wcsites-ns
- weblogicDomainStoragePath: /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites
$ cd ${WORKDIR}/ $ cp create-wcsites-domain/utils/create-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml create-wcsites-domain/utils/create-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml.orig $ sed -i -e "s:baseName\: weblogic-sample:baseName\: domain:g" create-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml $ sed -i -e "s:domainUID\::domainUID\: wcsitesinfra:g" create-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml $ sed -i -e "s:namespace\: default:namespace\: wcsites-ns:g" create-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml $ sed -i -e "s:#weblogicDomainStoragePath\: /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites:weblogicDomainStoragePath\: /scratch/K8SVolume/WCSites:g" create-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml- Run the
create-pv-pvc.shscript to create the PV and PVC configuration files:
$ sh create-weblogic-domain-pv-pvc/create-pv-pvc.sh \ -i create-wcsites-domain/utils/create-wcsites-pv-pvc-inputs.yaml \ -o create-wcsites-domain/output- Create the PV and PVC using the configuration files created in the previous step:
$ kubectl create -f create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pv.yaml $ kubectl create -f create-wcsites-domain/output/pv-pvcs/wcsitesinfra-domain-pvc.yamlInstall and configure the database for the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain.
This step is required only when a standalone database is not already set up and you want to use the database in a container.
Note : The Oracle Database Docker images are supported only for non-production use. For more details, see My Oracle Support note: Oracle Support for Database Running on Docker (Doc ID 2216342.1). For production, it is suggested to use a standalone database. This example provides steps to create the database in a container.
Now the environment is ready to start the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain creation.
6.2 Create an Oracle WebCenter Sites domain
The sample scripts for Oracle WebCenter Sites domain deployment are available at
<weblogic-kubernetes-operator-project>/kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain. You must editcreate-domain-inputs.yaml(or a copy of it) to provide the details for your domain.Run the
create-domain.shscript to create a domain:$ cd ${WORKDIR}/ $ sh create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/create-domain.sh \ -i create-wcsites-domain/domain-home-on-pv/create-domain-inputs.yaml \ -o create-wcsites-domain/outputCreate a Kubernetes domain object:
Once the create-domain.sh is successful, it generates the
output/weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/domain.yamlthat you can use to create the Kubernetes resource domain, which starts the domain and servers:$ cd ${WORKDIR}/ $ kubectl create -f create-wcsites-domain/output/weblogic-domains/wcsitesinfra/domain.yamlVerify that the Kubernetes domain object named
wcsitesinfrais created:$ kubectl get domain -n wcsites-ns NAME AGE wcsitesinfra 3m18sOnce you create the domain, introspect pod is created. This inspects the domain home and then starts the
wcsitesinfra-adminserverpod. Once thewcsitesinfra-adminserverpod starts successfully, then the Managed Server pods are started in parallel. Watch thewcsites-nsnamespace for the status of domain creation:$ kubectl get pods -n wcsites-ns -wVerify that the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain server pods and services are created and in Ready state:
$ kubectl get all -n wcsites-ns
6.3 Create WebCenter Sites Expose Services
Details on kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/wcs-services.yaml:
- name: wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np
- namespace: wcsites-ns
- weblogic.domainUID: wcsitesinfra
- weblogic.serverName: wcsites_server1
- NodePort port: Default value is 7103 for NONSSL. Update to 7104 for SSL/E2ESSL.
Execute the below command for exposing the services: (If domain is configured for more than 3 Managed Servers then add the service yaml for additional servers.)
$ kubectl apply -f kubernetes/create-wcsites-domain/utils/wcs-services.yaml
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-np created
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server1-svc created
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server2-svc created
service/wcsitesinfra-wcsites-server3-svc created6.4 Configure Traefik to access in Oracle WebCenter Sites domain services
Configure Traefik to manage ingresses created in the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain namespace (
wcsites-ns):$ helm upgrade traefik traefik/traefik \ --reuse-values \ --namespace traefik \ --set "kubernetes.namespaces={traefik,wcsites-ns}" \ --waitCreate an ingress for the domain in the domain namespace by using the sample Helm chart:
$ cd ${WORKDIR} $ helm install wcsitesinfra-ingress charts/ingress-per-domain \ --namespace wcsites-ns \ --values charts/ingress-per-domain/values.yaml \ --set "traefik.hostname=$(hostname -f)" \Verify the created ingress per domain details:
$ kubectl describe ingress wcsitesinfra-ingress -n wcsites-ns
6.5 Verify that you can access the Oracle WebCenter Sites domain URL
Get the
LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAMEfor your environment:export LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME=$(hostname -f)The following URLs are available for Oracle WebCenter Sites domains of domain type
wcsitesinfra:Credentials: username:
weblogicpassword:Welcome1http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:30305/console http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:30305/em http://${LOADBALANCER_HOSTNAME}:30305/sites
Deploying and Managing Oracle WebCenter Sites on Kubernetes
G16992-01
Last updated: December 2024
Copyright © 2024, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Primary Author: Oracle Corporation