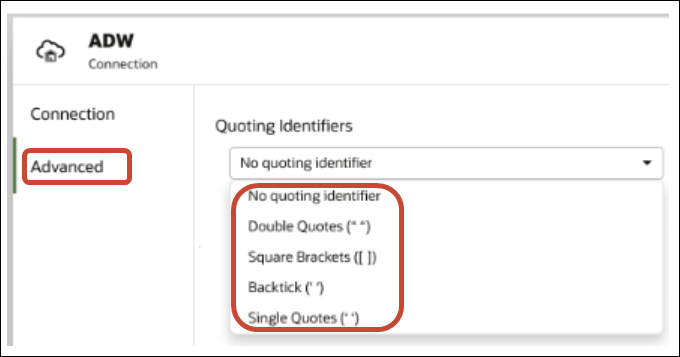
Connect to Data with Upper, Lower, or Mixed-case Characters
If you're connecting to an Oracle database, Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse, Oracle Autonomous AI Transaction Processing, Snowflake, SQL Server, or My SQL, you can change the default quoting identifier so that you can read data with upper, lower, or mixed-case characters in table or column names.
For example, you might choose double quotes as the quoting identifier. Oracle Analytics then adds double quotes to the underlying SQL statement
select "EfG_Field" from "AbCd"; instead of issuing select EfG_Field from AbCd;, (which would fail).